What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.

Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Topic Sentence + Examples
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
- What Is a Topic Sentence?
- 5 Steps to Writing a Good Topic Sentence
Elements of a Good Topic Sentence
Common pitfalls to avoid.
- Where To Get Your Essay Edited For Free
Crafting the perfect essay takes time and dedication. There are so many elements you have to worry about, such as tone, purpose, and correct spelling and grammar. Writing a strong topic sentences is another critical part in writing a cohesive essay.
Without a strong topic sentence, you risk losing your reader and perhaps part of your grade. If it’s a college admissions essay, then you need it to be as strong as possible to back up your application. Learn about what steps you should take to write a strong topic sentence.
What Is a Topic Sentence?
People often confuse a topic sentence with a thesis statement. A thesis statement is typically at the end of your opening paragraph, that dictates the main argument you’ll be making in your essay.
Throughout your essay, you’ll have multiple topic sentences, as each paragraph should start off with one. This beginning sentence is used to direct the topic of the paragraph and outline the flow of the following sentences. It’s used to help guide your reader and to continue to keep them hooked on your overall essay. Without topic sentences, your essay will be unorganized, lack transitions, and sound very choppy. To write a good topic sentence, there are several steps to take.
Writing a Good Topic Sentence: 5 Steps
Step 1: decide what you’re going to write about..
When you see the essay prompt, you’ll have some time to think through what you want to say and why. You have to decide if it’s a persuasive essay, informative, narrative, or descriptive. Determine your purpose for writing the essay after reading through the prompt. Whether it’s an assignment for school or if it’s to get into college, you need to make sure you have that purpose clearly outlined.
Step 2: Create a thesis statement.
One of the first things you need to do is create a thesis statement. This is typically a sentence with three points that you’ll back up throughout your essay.
For example: The Office became a cultural phenomenon because it spurred the careers of many of today’s successful movie stars, it talked about situations that most American workers can relate to, and even 15 years later, offers funny, relevant content that helps to break down prejudices.
You then use that thesis statement to create an essay around the points you want to make.
Step 3: Make your essay outline.
Once you have the points you want to make within your thesis statement hammered out, make an outline for your essay. This is where you’ll start to create your topic sentence for each paragraph. You want to clearly state the main idea of that paragraph in the very first sentence. From there, you back up that main idea with facts and reputable sources. Make sure your topic sentence is clear, but does not just announce your topic.
For example, do not write something like: “In this paragraph, I will discuss why it’s bad that poachers are killing giraffes.”
Instead, write something that clearly states your idea with a reasonable opinion and that gives direction to the paragraph: “Giraffes are a key part of the African ecosystem, so it’s important to enforce regulations against the poachers who are killing them for their body parts.”
You’d then follow that up with reasons why giraffes are a key part of the African ecosystem and how poachers are destroying their population.
Step 4: Begin writing your essay.
Once you have your thesis statement and you’ve created an outline with supporting paragraphs and their topic sentences, you can begin writing your essay. It’s important to make that outline before just jumping in–a disorganized essay can spell disaster for you as you continue to write, and could result in a poor grade. Many times, teachers will even require you to turn in your outline as part of your overall essay grade.
Step 5: Proofread and check your resources.
After you’ve written the essay, go back through it with a fine tooth comb. Read through each topic sentence and the paragraphs that follow to ensure that you’ve written clear, solid topic sentences throughout and that the paragraphs with them make sense. During the proofreading phase, you also need to recheck the sources you’re using. Make sure each source is reputable. In other words, do not use sites like Wikipedia where anyone can go in and edit an article to add misinformation. Use sites that:
- Are actual reputable news sources, such as the New York Times , CNN, CBS News
- Have domain names that end in .edu or .gov
- Come from an encyclopedia, such as Encyclopedia Britannica
Using sites that are not reputable could jeopardize the validity of your argument.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
Now that you know the steps to set yourself up for success when writing a topic sentence, there are certain elements that go into a quality first sentence. Always make sure that your topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph. You don’t want to make your reader hunt for the point you’re trying to make. Check out some key elements of a good topic sentence:
Make sure your topic sentence isn’t too vague.
You need a topic sentence that has some specifics to it. It also needs to hook in your reader in some way with an opinion. A vague sentence makes it harder to write a paragraph that can clearly backs up your thoughts. For example:
DON’T: “In Pride and Prejudice, Mr. Bingley seems like a nice guy.”
DO: “When Mr. Bingley is first introduced, he comes across as a kind person because he speaks to everyone and doesn’t immediately pass judgment.”
Choose a reasonable opinion.
Your topic sentence should clearly outline whatever point you’re trying to make in the paragraph, but you want to pick a reasonable opinion that you can easily reinforce with facts and statistics. Here’s an example of what you should and should not do:
DON’T: “It’s obvious that Mr. Bingley was a total loser with no backbone.”
DO: “Mr. Bingley could have shown more confidence in his choices and stood up to Mr. Darcy when he found himself in love with Jane Bennet.”
You can then back that up with facts, saying that he was a wealthy Englishman and thus one of the key players in society at the time, which should have given him more confidence. If he’d been more confident, perhaps he would not have left and devastated Jane.
Use your topic sentence as a transition.
Along with telling the reader the point of your next paragraph, your topic sentence should also serve as a transition from the previous paragraph. Without a transition, the essay can feel like it’s choppy and disjointed. For example:
DON’T: “Mr. Bingley is a good man and here’s why.”
DO: “Although Mr. Bingley did break Jane’s heart by leaving, he ended up redeeming himself by returning to Netherfield Hall.”
Keep your topic sentence short.
A long, drawn-out topic sentence can risk losing your reader. Many times, it’s hard to determine the point of a sentence when it goes on for too long. You want a clear, concise sentence that draws in the reader but also leaves some room for you to expand on it in the following paragraph.
DON’T: “Throughout the novel of Pride and Prejudice, Mr. Bingley was often quite different from Mr. Darcy as he would treat all people in a friendly manner, considering them all his friends and acquaintances, even agreeing to throw a ball after Elizabeth’s sisters rudely demanded he do so and was gracious to Mr. and Mrs. Bennet as well despite their manners.”
DO: “Overall, Mr. Bingley served as a foil to Mr. Darcy throughout the story by treating everyone around him equally with dignity and grace.”
Writing an essay can be overwhelming at times, but so long as you avoid some of these common pitfalls, it can be easier to get it done on time.
Don’t wait until the last minute.
If your teacher assigns you an essay or tells you that you have an essay test coming up, don’t wait until the day before to do anything about it. You have to plan or study and you need to give yourself time to do that. If you know it takes you a while to write something, then start planning it as soon as you get the assignment.
Don’t forget to write an outline.
Along with planning, make sure you have that outline written up and planned out well. It will serve as your guideline for writing the essay. Without it, you’ll face the risk of a disorganized essay that does not clearly illustrate your point.
Ask for help if you need it.
This may be the most important pitfall to avoid. If you get in over your head while writing, don’t be afraid to ask for help. Ask a friend to review the essay or ask your teacher for guidance.
Where to Get Your Essay Edited for Free
Once you’ve finished your essay, you may want additional input. There are tools out there to help, but CollegeVine’s free peer essay review tool can provide you with actionable feedback from students just like you. CollegeVine’s tool has helped many students and may be able to help you, too! Asking for peer feedback can help to refine your essay and it never hurts to have an extra set of eyes read through what you’ve written. Check out the free tool today!

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


How to Write a Topic Sentence (30+ Tips & Examples)
Writing the perfect topic sentence took me years to master.
After endless drafts, feedback sessions, and seeing what resonates with readers, I’ve distilled the ultimate guide to craft attention-grabbing, informative, and concise topic sentences.
Let’s dive into the essential tips for how to write a topic sentence.
What Is a Topic Sentence and Why Is It Important?

Table of Contents
A topic sentence introduces the main idea, usually appearing at the start of a paragraph.
It sets the tone for the entire paragraph by giving a glimpse of what’s coming. Think of it as a headline for each paragraph that keeps your writing clear and focused.
A strong topic sentence is important because:
- Grabs Attention: Captures the reader’s interest, encouraging them to keep reading.
- Guides Structure: Helps organize thoughts in a logical way.
- Provides Focus: Prevents rambling by clarifying the main point.
Types of Topic Sentences
Different types of topic sentences can fit various writing styles and purposes.
Understanding these types will help you select the best approach for your specific content.
- Declarative Statements: These are straightforward sentences that make a clear assertion. They introduce the main idea without any fluff or ambiguity. Example: “Water conservation is critical in regions prone to drought.”
- Interrogative Sentences: These topic sentences pose a question, encouraging readers to think critically and seek answers within the paragraph. Example: “How can sustainable practices help reduce waste in the fashion industry?”
- Complex Sentences: By combining independent and dependent clauses, these topic sentences present a nuanced main idea that prepares readers for a more detailed discussion. Example: “Although renewable energy sources are gaining popularity, fossil fuels still dominate the global energy sector.”
- Bridge Sentences: These link the preceding paragraph to the next, providing continuity and coherence in the overall structure. Example: “While electric vehicles offer a greener alternative to traditional cars, the infrastructure for widespread adoption remains lacking.”
- Contrasting Statements: These topic sentences highlight opposing viewpoints or circumstances, building intrigue and depth into the following paragraph. Example: “Despite the technological advancements in healthcare, access remains limited for underserved communities.”
My 30 Best Tips for Writing a Topic Sentence
Now let’s get into the main section of this guide — where you will learn all the best tips for writing a compelling topic sentence on any subject.
Tip #1: State the Main Idea Clearly
Make sure your topic sentence introduces the primary idea succinctly.
Avoid vague language or cluttered wording. Your reader should immediately understand the topic.
- Clear: “Recycling programs reduce landfill waste by promoting reusable packaging.”
- Unclear: “Programs for recycling can be a good thing because it’s important.”
Tip #2: Keep It Simple and Direct
A topic sentence should be straightforward. Avoid complex structures and over-complicated phrasing.
Shorter sentences work best.
- Simple: “Exercise improves mental health through endorphin production.”
- Complicated: “One can expect to experience benefits in their mental state with exercise due to the generation of endorphins.”
Tip #3: Link to the Previous Paragraph
Create a smooth flow by connecting ideas to the paragraph before.
Transition words like “similarly,” “however,” or “in contrast” help show relationships.
- Linked: “Similarly, the agricultural industry is also impacted by climate change.”
- Disjointed: “Farmers are struggling with erratic weather patterns.”
Tip #4: Avoid Announcing Your Intentions
Steer clear of sentences like “In this paragraph, I will discuss…” They sound amateurish and reduce reader engagement.
- Natural: “Effective communication skills are crucial for career advancement.”
- Announcing: “This paragraph will explain why communication skills are important.”
Tip #5: Vary Sentence Structure
Using the same structure repeatedly can bore readers.
Mix up your approach by experimenting with different forms like questions, facts, and lists.
- Varied: “How does cultural background influence consumer behavior?”
- Repetitive: “Consumer behavior is influenced by cultural background.”
Tip #6: Be Specific, Not General
A vague topic sentence leaves the reader confused. Instead, provide specific information to establish clarity and interest.
- Specific: “Remote work improves productivity by reducing commute times.”
- General: “Remote work is beneficial for many reasons.”
Tip #7: Reflect Your Argument’s Tone
Match your topic sentence with the tone of your argument. For serious discussions, avoid informal language.
- Formal: “The socioeconomic impact of urbanization requires comprehensive policy solutions.”
- Informal: “The effects of city living need some fixing.”
Tip #8: Include a Controlling Idea
The controlling idea limits the scope of the paragraph, ensuring the reader knows what to expect next.
- With Control: “Social media marketing increases brand visibility through targeted campaigns.”
- Without Control: “Social media is important.”
Tip #9: Use Active Voice
Active voice is more engaging and dynamic. It also provides clarity.
- Active: “New policies will reshape healthcare accessibility.”
- Passive: “Healthcare accessibility will be reshaped by new policies.”
Tip #10: Make It Unique
Avoid using overused phrases or predictable statements. Offer a fresh perspective to captivate your reader.
- Unique: “Biodegradable packaging is transforming the fast-food industry.”
- Cliché: “The fast-food industry is changing with new trends.”
Tip #11: Create Curiosity
Tease your reader by leaving questions unanswered. Encourage them to keep reading for more.
- Curious: “What are the unexpected benefits of rising inflation rates?”
- Blunt: “Rising inflation rates have some positive effects.”
Tip #12: Support Your Thesis
Your topic sentence should align with your overall thesis. It will give your argument more coherence.
- Aligned: “Reducing plastic waste aligns with our sustainability goals.”
- Unaligned: “Plastic recycling is controversial.”
Tip #13: Focus on One Point
Don’t overwhelm readers with multiple ideas in one topic sentence. Stick to one clear concept.
- One Point: “Artificial intelligence streamlines data analysis.”
- Too Broad: “Artificial intelligence changes marketing, finance, and data analysis.”
Tip #14: Use Key Terms From the Prompt (if applicable)
If you are responding to an assignment or specific topic prompt, make sure your topic sentence directly incorporates relevant keywords.
- Key Terms Included: “Global warming solutions must involve international cooperation.”
- Lacks Terms: “Solutions for the environment require cooperation.”
Tip #15: Offer Context
Provide some context in the topic sentence to frame the discussion, giving the reader essential background information.
With Context: “As urbanization accelerates, city infrastructure struggles to keep up.” Without Context: “City infrastructure is lagging.”
Tip #16: Incorporate Comparisons
Comparisons can clarify complex concepts and give readers a familiar reference.
- Comparison: “Just as the printing press revolutionized communication, the internet has transformed modern commerce.”
- No Comparison: “The internet has transformed modern commerce.”
Tip #17: Present Solutions
Offering a solution at the start engages readers who are seeking actionable advice.
- Solution: “Installing solar panels reduces energy bills while cutting carbon emissions.”
- Problem-Only: “High energy bills are a widespread issue.”
Tip #18: Address Common Misconceptions
Challenge preconceived notions to spark curiosity and highlight the importance of your argument.
- Challenging: “Despite common belief, vitamin supplements aren’t always beneficial.”
- Reinforcing: “Vitamin supplements have benefits.”
Tip #19: Use Emotional Appeals
Appeal to the reader’s emotions to deepen their connection to your writing.
- Emotional: “Volunteering at shelters uplifts communities and transforms lives.”
- Neutral: “Volunteering at shelters is helpful.”
Tip #20: Avoid Redundancy
Ensure your topic sentence adds new value. Avoid repeating points covered elsewhere.
- New Value: “Stronger copyright laws are crucial for protecting intellectual property.”
- Redundant: “Intellectual property needs stronger protection.”
Tip #21: Ask a Thought-Provoking Question
Pose a question that makes the reader stop and think. This engages them immediately.
- Provocative: “How will automation reshape the global workforce?”
- Plain: “Automation is changing the global workforce.”
Tip #22: Include an Action Verb
Action verbs add momentum and urgency to your topic sentence. They make your point more dynamic.
- Active Verb: “Investing in renewable energy fosters long-term economic growth.”
- Lacks Action: “Renewable energy investments are beneficial.”
Tip #23: Paint a Picture
Use descriptive language to help readers visualize your point.
- Descriptive: “Increased droughts have turned fertile farmlands into arid deserts.”
- Bland: “Droughts are affecting farmlands.”
Tip #24: Use Parallel Structure
Parallel structure involves repeating similar grammatical forms.
It makes your writing rhythmic and easy to follow.
- Parallel: “Tackling pollution requires reducing emissions, cleaning waterways, and limiting waste.”
- Non-Parallel: “Tackling pollution requires emission reductions, waterways cleaning, and limiting waste.”
Tip #25: Emphasize Urgency
Highlight the time-sensitive nature of your argument to create urgency.
- Urgent: “Immediate action is needed to prevent further deforestation.”
- Calm: “Deforestation is a concern.”
Tip #26: Highlight Contrasts
Contrasting different ideas helps to emphasize your point and draw clear distinctions.
- Contrast: “While technology creates new jobs, it also disrupts traditional industries.”
- No Contrast: “Technology affects the job market.”
Tip #27: Lead with a Statistic
Start with a compelling number to catch the reader’s attention and back up your argument.
- Statistic: “80% of small businesses struggle to comply with data privacy regulations.”
- General Statement: “Small businesses struggle with data privacy.”
Tip #28: Build on Existing Knowledge
Assume the reader has some background knowledge and expand on it.
- Builds On Knowledge: “With the rise of remote work, companies are rethinking their office spaces.”
- Basic Information: “Remote work is changing office spaces.”
Tip #29: Start with an Anecdote
A brief anecdote adds a human touch, creating an immediate connection with the reader.
- Anecdotal: “After years of burnout, Sarah switched to a part-time schedule to improve her work-life balance.”
- Abstract: “Work-life balance is important.”
Tip #30: Use an Engaging Metaphor
A metaphor can illuminate your argument in an unexpected way.
- Metaphor: “Effective teamwork is the glue that holds successful organizations together.”
- Literal: “Effective teamwork is important for organizations.”
Check out this video about how to write a topic sentence:
Final Thoughts: How to Write a Topic Sentence
Writing compelling topic sentences takes practice, but mastering this skill can transform your writing.
I hope this guides empowers you in your topic-sentence writing journey.
Beyond the topic sentence, there are other techniques and terms you really need to know to improve your writing.
Read This Next:
- 30 Narrative Writing Examples to Elevate Your Writing
- What Is a Summary In Writing? (Explained + 40 Examples)
- What Is A Warrant In Writing? (Explained + 20 Examples)
- What Is A Universal Statement In Writing? (Explained)
- How to Describe Tone in Writing: 300 Examples You Can Use
Topic sentences and signposts make an essay's claims clear to a reader. Good essays contain both. Topic sentences reveal the main point of a paragraph. They show the relationship of each paragraph to the essay's thesis, telegraph the point of a paragraph, and tell your reader what to expect in the paragraph that follows. Topic sentences also establish their relevance right away, making clear why the points they're making are important to the essay's main ideas. They argue rather than report. Signposts , as their name suggests, prepare the reader for a change in the argument's direction. They show how far the essay's argument has progressed vis-ˆ-vis the claims of the thesis.
Topic sentences and signposts occupy a middle ground in the writing process. They are neither the first thing a writer needs to address (thesis and the broad strokes of an essay's structure are); nor are they the last (that's when you attend to sentence-level editing and polishing). Topic sentences and signposts deliver an essay's structure and meaning to a reader, so they are useful diagnostic tools to the writer—they let you know if your thesis is arguable—and essential guides to the reader
Forms of Topic Sentences
Sometimes topic sentences are actually two or even three sentences long. If the first makes a claim, the second might reflect on that claim, explaining it further. Think of these sentences as asking and answering two critical questions: How does the phenomenon you're discussing operate? Why does it operate as it does?
There's no set formula for writing a topic sentence. Rather, you should work to vary the form your topic sentences take. Repeated too often, any method grows wearisome. Here are a few approaches.
Complex sentences. Topic sentences at the beginning of a paragraph frequently combine with a transition from the previous paragraph. This might be done by writing a sentence that contains both subordinate and independent clauses, as in the example below.
Although Young Woman with a Water Pitcher depicts an unknown, middle-class woman at an ordinary task, the image is more than "realistic"; the painter [Vermeer] has imposed his own order upon it to strengthen it.
This sentence employs a useful principle of transitions: always move from old to new information. The subordinate clause (from "although" to "task") recaps information from previous paragraphs; the independent clauses (starting with "the image" and "the painter") introduce the new information—a claim about how the image works ("more than Ôrealistic'") and why it works as it does (Vermeer "strengthens" the image by "imposing order").
Questions. Questions, sometimes in pairs, also make good topic sentences (and signposts). Consider the following: "Does the promise of stability justify this unchanging hierarchy?" We may fairly assume that the paragraph or section that follows will answer the question. Questions are by definition a form of inquiry, and thus demand an answer. Good essays strive for this forward momentum.
Bridge sentences. Like questions, "bridge sentences" (the term is John Trimble's) make an excellent substitute for more formal topic sentences. Bridge sentences indicate both what came before and what comes next (they "bridge" paragraphs) without the formal trappings of multiple clauses: "But there is a clue to this puzzle."
Pivots. Topic sentences don't always appear at the beginning of a paragraph. When they come in the middle, they indicate that the paragraph will change direction, or "pivot." This strategy is particularly useful for dealing with counter-evidence: a paragraph starts out conceding a point or stating a fact ("Psychologist Sharon Hymer uses the term Ônarcissistic friendship' to describe the early stage of a friendship like the one between Celie and Shug"); after following up on this initial statement with evidence, it then reverses direction and establishes a claim ("Yet ... this narcissistic stage of Celie and Shug's relationship is merely a transitory one. Hymer herself concedes . . . "). The pivot always needs a signal, a word like "but," "yet," or "however," or a longer phrase or sentence that indicates an about-face. It often needs more than one sentence to make its point.
Signposts operate as topic sentences for whole sections in an essay. (In longer essays, sections often contain more than a single paragraph.) They inform a reader that the essay is taking a turn in its argument: delving into a related topic such as a counter-argument, stepping up its claims with a complication, or pausing to give essential historical or scholarly background. Because they reveal the architecture of the essay itself, signposts remind readers of what the essay's stakes are: what it's about, and why it's being written.
Signposting can be accomplished in a sentence or two at the beginning of a paragraph or in whole paragraphs that serve as transitions between one part of the argument and the next. The following example comes from an essay examining how a painting by Monet, The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train, challenges Zola's declarations about Impressionist art. The student writer wonders whether Monet's Impressionism is really as devoted to avoiding "ideas" in favor of direct sense impressions as Zola's claims would seem to suggest. This is the start of the essay's third section:
It is evident in this painting that Monet found his Gare Saint-Lazare motif fascinating at the most fundamental level of the play of light as well as the loftiest level of social relevance. Arrival of a Train explores both extremes of expression. At the fundamental extreme, Monet satisfies the Impressionist objective of capturing the full-spectrum effects of light on a scene.
The writer signposts this section in the first sentence, reminding readers of the stakes of the essay itself with the simultaneous references to sense impression ("play of light") and intellectual content ("social relevance"). The second sentence follows up on this idea, while the third serves as a topic sentence for the paragraph. The paragraph after that starts off with a topic sentence about the "cultural message" of the painting, something that the signposting sentence predicts by not only reminding readers of the essay's stakes but also, and quite clearly, indicating what the section itself will contain.
Copyright 2000, Elizabeth Abrams, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
Writing Topic Sentences — Purpose, Structure, and Examples
What is a topic sentence.
A topic sentence in academic writing identifies how a body paragraph relates to the overall purpose of an essay stated in the thesis statement . Topic sentences are usually at the beginning of a paragraph and identify the paragraph’s controlling idea.
While an essay’s thesis statement identifies the point of the essay in its entirety, the topic sentence has a much narrower focus, as it relates only to the paragraph in which it is located.

What is the purpose of a topic sentence?
The purpose of a topic sentence is to inform the reader of the main idea of the paragraph and how it connects to the overall objective of the essay. An effective topic sentence accomplishes one or more of the following:
Makes a claim
Supports other claims made in the paper
Identifies the purpose of the rest of the paragraph
Relates the paragraph to the purpose of the paper
Precedes information that defends a claim

How to write a topic sentence
To write a topic sentence, incorporate the following guidelines:
Determine the thesis of the essay.
Identify the main supports that help prove the thesis.
Use each main support to structure a topic sentence for each paragraph.
Compose a sentence that answers the following questions:
What will the paragraph prove?
How does the paragraph connect to the thesis?

Where is the topic sentence in a paragraph?
Topic sentences can be placed at the beginning or end of a paragraph.
Although it does not need to be the first sentence, the topic sentence should be placed at the beginning of the paragraph so the reader can quickly identify the purpose of the paragraph.
While not a common placement for a topic sentence, some writers use topic sentences at the end of a paragraph. Writers who choose this method want the reader to deduce the main point of the paragraph by presenting the evidence first.
Topic sentence examples
The following list identifies topic sentences based on the provided thesis statements for five-paragraph essays:
Thesis Statement: Capital punishment should be banned because it is inhumane, unconstitutional, and ineffective at deterring crime.
Support Paragraph 1 Topic Sentence: The inhumane nature of the death penalty proves it should be abolished.
Support Paragraph 2 Topic Sentence: Capital punishment should be outlawed because it violates the Constitution.
Support Paragraph 3 Topic Sentence: Because the death penalty does not effectively deter criminal behavior, states should not continue to use it.
Thesis Statement: College athletes should be financially compensated because they sacrifice their minds and bodies, cannot hold an outside job, and increase the school’s revenue.
Support Paragraph 1 Topic Sentence: Student athletes should be paid for their performance because of sports’ impact on their minds and bodies.
Support Paragraph 2 Topic Sentence: Because most college athletes cannot play their sport and hold a job, colleges should give them a living wage.
Support Paragraph 3 Topic Sentence: Student-athletes’ ability to increase their college’s revenue proves they should be awarded financial compensation.

Thesis Statement: Using alternative energy sources can help lessen the impact of global climate change.
Support Paragraph 1 Topic Sentence: Through the widespread use of solar power, countries can limit the environmental impact of other energy sources.
Support Paragraph 2 Topic Sentence: Utilizing more wind turbines as a power source can help mitigate the effects of climate change.
Support Paragraph 3 Topic Sentence: Using geothermal power will effectively decrease the world's reliance on fossil fuels.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- English Grammar
How to Write a Good Topic Sentence
Last Updated: June 26, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 2,252,279 times.
Perfecting the skill of writing topic sentences is essential to successful writing. A topic sentence usually comes at the beginning of a paragraph and lets your reader know what to expect from each paragraph. Think of it as the preview for a movie or a headline in a newspaper, highlighting the “main point” that’s to come in that paragraph. [1] X Research source Make sure your topic sentences are up to par, and the rest of your writing will feel like a breeze.
Writing a Successful Topic Sentence

- Keep in mind that this is not an invitation to simply announce your topic. “Today I’m going to discuss the benefits of gardening” is not an effective topic sentence. You should be able to make your intentions clear without stating them explicitly.
- The topic sentence in this example states a clear direction (“health benefits of gardening”) that you can then elaborate on in your paragraph.

- Don’t write too vague or general an idea or you will never be able to discuss it in a single paragraph. This is too general: “The United States suffered a lot during the Civil War.”
- Don’t write too narrow of a statement. There’s nothing much to talk about then, because it’s probably a fact. This is too narrow: “Christmas trees are either cedars or firs."
- Instead, aim for a good balance: “Sherman’s destruction in the South during the Civil War also caused incredible suffering.” This is big enough to relate to the broader idea of an essay, but not so narrow that there’s nothing left to discuss.

- Describe a character. This can be a physical or emotional description.
- Use dialogue. If there is a relevant conversation that will attract your reader’s attention, consider using part of it to start your paragraph.
- Portray an emotion. Use the opening sentence to portray an emotion to your reader.
- Use detail. While you don’t want to write a run on sentence by creating too much detail, it’s a good idea to create interest using sensory language in your topic sentence.
- Avoid rhetorical questions. While you want your reader to formulate questions in his or her mind, you do not want to formulate the questions yourself.

- Avoid presenting only facts in your topic sentence. While facts may be interesting, they do not introduce the reader to your paragraph nor do they draw the reader in. If you wish to include a fact, also include your own input. For example, instead of writing “All dogs need food,” try “All dogs need regular care, including healthy food, and children are the best ones to do it.” Alternatively, save your facts to use as evidence in the body of your paragraph.

- Using transitional elements, such as “In addition” or “In contrast,” is a good way to show the relationship between your ideas.
- For example: “Although gardening has many health benefits, people still need to exercise caution when outside.” This topic sentence establishes a connection to the main idea of the previous paragraph (“health benefits of gardening”) and points to the direction of the new paragraph (“things to be cautious of”).
Planning Your Topic Sentences

- You don’t have to write a formal outline using Roman numerals and the like. Even a loose, idea-based outline can help you know what you want to discuss.

- A topic sentence, unlike a thesis statement, doesn’t have to present an argument. It can present a “preview” of what the paragraph will argue or discuss.

- For example, a topic sentence could look like this: “In addition, increasing funding for public roads in Jackson County will improve local residents’ quality of life.” The rest of the sentences in this paragraph would relate to the main idea of public roads and how they will help benefit local residents.
- This is not as successful a topic sentence: “Increased funding for public roads in Jackson County has decreased traffic by 20%.” While this is probably an interesting fact for your argument, it’s too narrow for a topic sentence. The topic sentence has to direct the whole paragraph.
Avoiding Common Problems

- Unless it is an opinion piece, avoid using ‘I’ in your topic sentences.

- Rather than stating something like “In the story, Amelia did many good things such as help out her friends, talk to her parents, and support her team at school” say something like “As a result of the many activities Amelia participated in, she was recognized for her positive influence on the community.”

Sample Topic Sentences

Community Q&A
- Avoid using words like you or we because it implies you know the reader, which you don’t. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- In formal writing, avoid contractions such as “don’t,” “can’t,” and “isn’t.” Also avoid other common contractions like “would’ve” and “could’ve” which are commonly used. Instead type them out to look like “do not,” “can not”, “is not”, “would have”, and “could have.” Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Type out all numbers under a ten. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/planning-and-organizing/topic-sentences
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/paragraphs-and-topic-sentences.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/paragraphs_and_paragraphing/index.html
- ↑ https://stlcc.edu/student-support/academic-success-and-tutoring/writing-center/writing-resources/topic-sentence-paragraph.aspx
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/paragraphs/topicsentences
- ↑ https://www.rit.edu/ntid/sea/processes/paragraph/process/sentence
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/writingprocess/outlining
- ↑ https://www.touro.edu/departments/writing-center/tutorials/topic-sentence/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/engagement/2/2/57/
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/paragraphs/
About This Article

If you’re trying to write a good topic sentence, start by clearly stating your main idea, which should include the topic and the position you’re taking on it. Aim to write a sentence that’s broad enough for discussion but narrow enough to be covered in a single paragraph. If you can, start with a hook, like a detail, character, or emotion that would draw in your readers. For more advice from our reviewer on writing a good topic sentence, like how to make it effective while keeping it short and sweet, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Besamim Shemesh
Apr 27, 2020
Did this article help you?

Feb 28, 2017
Richard Lefevre
May 1, 2017
Halie Burke
Apr 19, 2017
Anne Korzyniowski
Oct 5, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Writing Home
- Writing Advice Home
Using Topic Sentences
- Printable PDF Version
- Fair-Use Policy
What is a topic sentence?
A topic sentence states the main point of a paragraph: it serves as a mini-thesis for the paragraph. You might think of it as a signpost for your readers—or a headline—something that alerts them to the most important, interpretive points in your essay. When read in sequence, your essay’s topic sentences will provide a sketch of the essay’s argument. Thus topics sentences help protect your readers from confusion by guiding them through the argument. But topic sentences can also help you to improve your essay by making it easier for you to recognize gaps or weaknesses in your argument.
Where do topic sentences go?
Topic sentences usually appear at the very beginning of paragraphs. In the following example from Anatomy of Criticism , Northrop Frye establishes the figure of the tragic hero as someone more than human, but less than divine. He backs up his claim with examples of characters from literature, religion and mythology whose tragic stature is a function of their ability to mediate between their fellow human beings and a power that transcends the merely human:
The tragic hero is typically on top of the wheel of fortune, half-way between human society on the ground and the something greater in the sky. Prometheus, Adam, and Christ hang between heaven and earth, between a world of paradisal freedom and a world of bondage. Tragic heroes are so much the highest points in their human landscape that they seem the inevitable conductors of the power about them, great trees more likely to be struck by lightning than a clump of grass. Conductors may of course be instruments as well as victims of the divine lightning: Milton’s Samson destroys the Philistine temple with himself, and Hamlet nearly exterminates the Danish court in his own fall.
The structure of Frye’s paragraph is simple yet powerful: the topic sentence makes an abstract point, and the rest of the paragraph elaborates on that point using concrete examples as evidence.
Does a topic sentence have to be at the beginning of a paragraph?
No, though this is usually the most logical place for it. Sometimes a transitional sentence or two will come before a topic sentence:
We found in comedy that the term bomolochos or buffoon need not be restricted to farce, but could be extended to cover comic characters who are primarily entertainers, with the function of increasing or focusing the comic mood. The corresponding contrasting type is the suppliant, the character, often female, who presents a picture of unmitigated helplessness and destitution. Such a figure is pathetic, and pathos, though it seems a gentler and more relaxed mood than tragedy, is even more terrifying. Its basis is the exclusion of an individual from the group; hence it attacks the deepest fear in ourselves that we possess—a fear much deeper than the relatively cosy and sociable bogey of hell. In the suppliant pity and terror are brought to the highest possible pitch of intensity, and the awful consequences of rejecting the suppliant for all concerned is a central theme of Greek tragedy.
The context for this passage is an extended discussion of the characteristics of tragedy. In this paragraph, Frye begins by drawing a parallel between the figure of the buffoon in comedy and that of the suppliant in tragedy. His discussion of the buffoon occurred in a earlier section of the chapter, a section devoted to comedy. The first sentence of the current paragraph is transitional: it prepares the way for the topic sentence. The delayed topic sentence contributes to the coherence of Frye’s discussion by drawing an explicit connection between key ideas in the book. In essays, the connection is usually between the last paragraph and the current one.
Sometimes writers save a topic sentence for the end of a paragraph. You may, for example, occasionally find that giving away your point at the beginning of a paragraph does not allow you to build your argument toward an effective climax.
How do I come up with a topic sentence? And what makes a good one?
Ask yourself what’s going on in your paragraph. Why have you chosen to include the information you have? Why is the paragraph important in the context of your argument? What point are you trying to make?
Relating your topic sentences to your thesis can help strengthen the coherence of your essay. If you include a thesis statement in your introduction, then think of incorporating a keyword from that statement into the topic sentence. But you need not be overly explicit when you echo the thesis statement. Better to be subtle rather than heavy-handed. Do not forget that your topic sentence should do more than just establish a connection between your paragraph and your thesis. Use a topic sentence to show how your paragraph contributes to the development of your argument by moving it that one extra step forward. If your topic sentence merely restates your thesis, then either your paragraph is redundant or your topic sentence needs to be reformulated. If several of your topic sentences restate your thesis, even if they do so in different words, then your essay is probably repetitive.
Does every paragraph need one?
No, but most do. Sometimes a paragraph helps to develop the same point as in the previous paragraph, and so a new topic sentence would be redundant. And sometimes the evidence in your paragraph makes your point so effectively that your topic sentence can remain implicit. But if you are in doubt, it’s best to use one.
Essay Writing Guide
What Is A Topic Sentence
Last updated on: Jun 28, 2024
What is a Topic Sentence - An Easy Guide with Writing Steps & Examples
By: Nova A.
11 min read
Reviewed By: Melisa C.
Published on: Mar 12, 2019

A topic sentence is the opening sentence at the beginning of each paragraph. These sentences tell the readers about the main idea that will be discussed in that paragraph.
It is the most important part of a body paragraph, and knowing how to write a good topic sentence is essential for writing an essay . However, writing an effective topic sentence could be tough.
If you find it difficult to write clear and engaging topic sentences, you are not alone. But don’t worry!
This blog will help you understand topic sentences better with examples. Also, you’ll get step-by-step guide and tips for writing more effective topic sentences.
So let’s dive in!

On this Page
What is a Topic Sentence in a Paragraph?
A topic sentence is the opening sentence of the body paragraphs of your essay. It introduces the main idea of that paragraph.
So what is the purpose of a topic sentence?
It serves as a guidepost, indicating the main purpose and point of the paragraph. Essentially, it is a concise and direct statement that captures the essence of what you want to convey.
A topic sentence is defined by the following characteristics:
- It is the first sentence of a paragraph
- It indicates the main idea of the paragraph
- Acts as a signpost and transition sentence, ensuring clarity and cohesiveness of an essay.
Why are Topic Sentences Important?
Topic sentences are an essential component of body paragraphs , especially in academic writing which is more formal. Here’s why good these sentences are necessary for an essay:
- They help maintain the organization and coherence of the essay.
Topic sentences act as a roadmap for your essay, providing a clear path for your readers to follow. They establish the main ideas or arguments of each paragraph, allowing your essay to flow logically and coherently.
By presenting a central focus in each paragraph, they help you maintain a strong sense of organization. Also, they prevent your essay from becoming a jumbled collection of random thoughts.
- They enhance clarity and readability.
Well-crafted topic sentences promote clarity and conciseness in your writing by summarizing the main idea in a concise manner.
Moreover, they serve as signposts that signal the beginning of a particular discussion. This creates a smooth reading experience and reduces the chances of confusion.
- They help the reader skim through the essay.
These sentences provide readers with a preview of what each paragraph will discuss. This helps them grasp the main point before delving into the rest of the paragraph.
They also enable the readers to quickly grasp the content of a paragraph. This makes it easier for them to skim through the main ideas of the essay without reading it word-by-word.
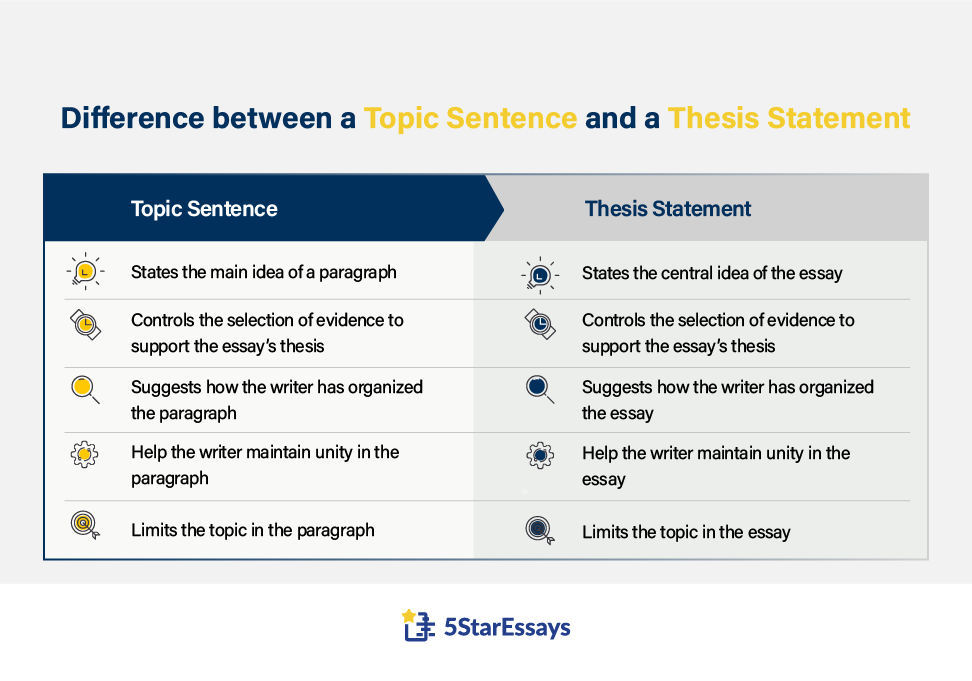
Topic Sentence vs Thesis Statement: Main Differences
Topic sentences are similar to thesis statements as they fulfill a similar purpose: they show the reader what the paragraph or essay is about.
However, a thesis statement is written at the end of the essay introduction, and it presents the main idea of the entire paper or essay. Whereas, a topic sentence presents the main idea of a specific paragraph, and is the first sentence of that paragraph.
Here are the major differences between topic sentences and thesis statements:
How to Write a Topic Sentence? Here are 4 Simple Steps
If you think about it, writing such a sentence seems like a simple task. All you have to do is write one line about the idea you’ll discuss, and you’re done.
Well, it’s not as easy as it sounds. You need to follow some conditions to write good opening lines for your body paragraphs.
Here are the steps to write engaging topic sentences:
1. Develop your Thesis Statement
Writing a specific and self-defining thesis statement is the first step in writing an essay. A thesis statement is necessary as it lays out the main points or structure of your entire essay.
Having a thesis statement helps you figure out what your body paragraphs will be about. This, in turn, helps you identify each paragraphs controlling idea and craft a topic sentence.
2. Identify the Controlling Ideas of Your Body Paragraphs
Once you have a thesis statement for your essay, identify the main idea or central theme of the paragraphs.
Ask yourself, "What is the key point I want to convey in this paragraph?" This will serve as the focus and topic of your paragraph. Moreover, identifying your main points will also help you make an essay outline.
Here’s an example of how you can identify the main ideas of your body paragraphs:
Topic of the Essay:
Body Paragraph 1: The impact of greenhouse gas emissions on rising global temperatures. Body Paragraph 2: The consequences of climate change on ecosystems and biodiversity. Body Paragraph 3: Strategies for mitigating climate change through sustainable practices. |
3. Write your Topic Sentence
Now that you know the main idea of each paragraph, you should attempt to write your topic sentences. It is not necessary that you get the sentences right the first time. Try different variations and see which of the sentences explains the paragraph idea in a better way.
Ensure that your topic sentence relates directly to your thesis statement or the main argument of your essay. The topic sentence should support and reinforce the overall message you want to convey in your writing.
The example below shows topic sentences based on the main ideas identified in step 2:
Topic Sentence for Body Paragraph 1:
Topic Sentence for Body Paragraph 2:
Topic Sentence for Body Paragraph 3:
|
4. Revise and Make your Topic Sentences Better
A strong topic sentence should be clear, concise, and directly related to your thesis statement. They should also be logically connected to the previous paragraph. It is important that you revise, make them better, and rewrite the sentences as you progress with the paper.
Make sure that they reflect the main theme of the paragraph and are according to the paragraph’s content. Use appropriate transition words for essays when transitioning from one paragraph to another.
Read on to learn about different types of topic sentences. They will help you to write, rewrite, and revise your opening sentences in the best ways.
What are the Different Types of Topic Sentences?
Here are some common types of topic sentences you can incorporate in your essay.
[Infographic]
- Statement of Fact or Information
This type of topic sentence presents a straightforward statement of fact or information that sets the stage for the paragraph. It provides essential background knowledge or introduces a key concept.
For example: · The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on global economic systems. · Renewable energy sources offer a sustainable solution to reducing carbon emissions. |
- Hook or Shocker
This kind of sentence presents a shocking statement of fact about the paragraph’s key idea. This type of topic sentence aims to grab the reader’s attention and make them want to read more.
Here’s an example: · Do you know that the first ever Thanksgiving was celebrated almost four thousand years ago? |
- Illustration or Example
An illustration or example topic sentence provides a specific instance or anecdote to support the main idea of the paragraph. It helps to clarify and reinforce your argument by providing concrete evidence or a real-life scenario.
For instance: |
- Question or Thought-Provoking Statement
A topic sentence in the form of a question or thought-provoking statement engages readers by encouraging them to seek an answer. It stimulates curiosity and anticipation for what follows in the paragraph.
For example: |
You can also watch this video that explains topic sentences in a simple way:
Topic Sentence Examples
‘What is a topic sentence example?’
Check out some helpful and effective topic sentence examples to help you get started.
- Professional baking is a lot more than mixing some flour, eggs, and sugar into a bowl and putting it into the oven; it requires precision, attention to detail, and dedication to the craft.
- Writing is a thorough and time-consuming process, but with some dedicated practice, you can become a better writer.
- Learning a foreign language opens doors to several new opportunities that are not only available when a person is familiar with his mother tongue.
- Home remodeling is an exciting project, but without proper designer skills and taste, it could turn into a disaster.
- Several human activities are the main reasons behind global environmental pollution, and excess usage of plastic is one such cause.
Helpful Tips for Writing Better Topic Sentences
You’ve read some great examples, but how can you write similarly effective topic sentences yourself? Here are some amazing tips to help you out.
- Be Clear and Concise: Focus on expressing the main idea of the paragraph in a concise and direct manner. Avoid unnecessary details or convoluted language that may confuse your readers.
- Consider the Paragraph's Focus: Avoid including multiple ideas or concepts within a single topic sentence. Instead, focus on one central point for each paragraph.
- Vary Your Sentence Structure: To maintain reader interest and engagement, vary the structure of your topic sentences. Experiment with different types, such as simple sentences, rhetorical questions, or even shocking facts.
- Use Strong and Descriptive Language: Choose powerful and descriptive words that accurately capture the essence of your main idea. Avoid vague or generic language that lacks impact. Instead, opt for words that evoke emotions or create vivid imagery.
- Seek Feedback: Consider sharing your writing with others and seeking feedback on your paragraphs. Ask for input on clarity, coherence, transitions, and overall effectiveness.
A great topic sentence directs the reader about the main content of the paragraph. It is brief and engages the reader.
Remember, mastering the art of writing effective topic sentences takes practice and refinement. As you develop your writing skills, focus on crafting clear and engaging topic sentences that align with your thesis statement.
However, we understand that writing essays can still be challenging, especially when faced with tight deadlines or complex assignments.
That's where 5staressays.com comes in!
If you’re short on time or lack good writing skills, you can team up with a professional essay writer. Our ‘ write my essay ’ service works with professional and subject-expert writers that help you write engaging and A-worthy essays.
So contact us and get quality papers at the most pocket-friendly rates!
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the topic sentence located in your essay.
Topic sentences come at the beginning of body paragraphs. They are the first sentence of a paragraph and introduces the main idea of that paragraph.
Can a topic sentence be a question?
Yes, a topic sentence could be a question. You can use a rhetorical question or an interrogative sentence to engage your reader and encourage them to read on.
How long is a topic sentence?
It depends on the depth of the idea. Usually, it is just one sentence, but in some cases, it could be composed of two sentences. However, the first few lines of the paragraph should be able to present its main idea effectively.

Law, Marketing
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- How to Write an Essay - A Complete Guide with Examples

- The Art of Effective Writing: Thesis Statements Examples and Tips

- Writing a 500 Word Essay - Easy Guide

- A Complete Essay Outline - Guidelines and Format

- 220 Best Transition Words for Essays

- Essay Format: Detailed Writing Tips & Examples

- How to Write a Conclusion - Examples & Tips

- Essay Topics: 100+ Best Essay Topics for your Guidance

- How to Title an Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide for Effective Titles

- How to Write a Perfect 1000 Word Essay

- How To Make An Essay Longer - Easy Guide For Beginners

- Learn How to Start an Essay Effectively with Easy Guidelines

- Types of Sentences With Examples

- Hook Examples: How to Start Your Essay Effectively

- Essay Writing Tips - Essential Do’s and Don’ts to Craft Better Essays

- How To Write A Thesis Statement - A Step by Step Guide

- Art Topics - 200+ Brilliant Ideas to Begin With

- Writing Conventions and Tips for College Students

People Also Read
- classification essay outline
- what is a topic sentence
- mla format paper
- evaluation essay
- rhetorical analysis essay writing
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved

Topic Sentence: Definition, Examples and Useful Tips for Writing A Topic Sentence
When writing, there are many aspects which we need to take into consideration. One such aspect is the topic sentence, but how do we use this? In this article, we are looking at what the topic sentence is and how it is used within a piece of writing . We are also going to be looking at a variety of examples to give us a better understanding of its function.
Topic Sentence
What is a topic sentence.
Some might say that the topic sentence is one of the most important aspects and definitely the most vital sentence within a paragraph . In some cases, you might hear the topic sentence is referred to as the focus sentence but these are essentially the same thing.
A topic sentence is used to summarise all of the information within a paragraph. When writing in a more formal style, the topic sentence will usually feature at the beginning of the paragraph, although this is not a set rule.
What Is A Topic Sentence Used For?
A writer will use a topic sentence as a way of explaining to the audience what the paragraph is going to be about. Any sentences which appear after the topic sentence should give further information about the topic sentence or should give facts about it in order to prove the claim that it has made. The following sentences might also serve as a way to further describe the topic sentence by giving more details about it. For example, if the topic sentence is about animals kept as domestic pets, the following sentences should relate back to that subject.
On top of this, the topic sentence should always refer back to the thesis statement which was made at the beginning of the essay . You can imagine the thesis statement as being a map which directs the reader as to where you are going with the information and how it is being treated.
Controlling Ideas
When writing a topic sentence, each one should feature a controlling idea. This will serve as an indicator as to where the rest of the paragraph will go and what will be discussed.
Topic Sentences Examples
Now that we are clear on what a topic sentence is, we are going to take a look at some examples to further grow our understanding of them.
- ‘There are a lot of reasons why (name of a city) is the most polluted in the world.’
The controlling topic here is that there are ‘a lot of reasons’ and the topic is that a certain town is the most polluted.
- ‘In order to be an effective manager, one must have certain qualities.’
The topic of this sentence is being an effective manager and it has a controlling idea of ‘certain qualities.’
- ‘There are a lot of factors which contribute to global warming .’
This sentence has a topic of global warming whilst the controlling idea is related to ‘factors which contribute.’
- ‘We can improve teen pregnancy rates by improving education.’
The topic of this sentence in that teen pregnancy can be improved and the controlling idea is ‘improving education.’
How To Write A Topic Sentence
When it comes to writing a good topic sentence, there are many things that you should take into consideration before you put pen to paper. We are now going to look at the various steps you should take in order to write an effective and strong topic sentence.
Write Your Thesis Statement
Before you can write a topic sentence, you must have a thesis statement. This should be strong and be effective in summing up the purpose of the essay as well as the main argument.
Outline Your Essay And Draft Out The Topic Sentences
The next step is to create your essay outline, this will give your essay structure and will allow you to detail what is going to be discussed in each paragraph. You will also make note of what data and evidence will be included in each of the paragraphs.
This is the point where you can play with words and draft up some topic sentences for each of your paragraphs. A topic sentence needs to be much more specific than your thesis statement but it should relate clearly to it.
Expand With Some Evidence
The remaining sentences within your paragraph should logically flow from the original topic sentence. They should be used to expand on what has been said in the topic sentence. This will not only make your workflow but will also ensure that each paragraph remains focused and relevant to the topic sentence. You should give some evidence to support your topic sentence.
Revise The Topic Sentences
What your topic sentence looks like to begin with may not be how it ends up in the final draft and that is OK. It is very important that you look over and edit each topic sentence within the essay as you go along. This will ensure that they remain relevant to the content of your paragraphs.
When making the final edits for your topic sentences, you should ensure that they are clear enough to allow the reader to know what the paragraph is going to be about but also not so clear that they detail everything you wish to talk about within that paragraph.
Transitions
Your topic sentence will sometimes serve as a transition between your paragraphs and in this case, they may do one of the following things:
- Compare and contrast
- Emphasise or expand
A topic sentence is one which appears, usually (but not always) at the beginning of each paragraph of an essay. The topic sentence is used to layout the ideas and arguments that will be covered within the paragraph and should be carefully planned out to ensure that they are clear enough to give the reader an idea of what will be discussed but not to give away too much about the content of the paragraph. Your topic sentence may serve one of many purposes including summarising and comparing.
Topic Sentence Infographic

- Latest Posts
- Color vs. Colour: Regional Spelling Differences - January 8, 2024
- Christian vs. Catholic: Understanding the Differences - January 8, 2024
- Graduate vs. Undergraduate: Understanding the Distinction - January 6, 2024
Improve your writing with the help of AI writing assistants!

Topic Sentence in an Essay: Pillar of Your Writing
Table of contents
- 1 What Is a Topic Sentence
- 2 Characteristics of an Effective Topic Sentence
- 3.1 Interrogative
- 3.2 Reinforcement
- 3.3 Transitional
- 4.1 Understanding the Paragraph’s Main Idea
- 4.2 Keeping it Concise
- 4.3 Positioning the Topic Sentence
- 4.4 Make it Interesting but not Over-complicating
- 4.5 Better to Use Active Voice
- 4.6 Enhance with Evidence
- 4.7 Bind the Paragraph Together by Repeating Words or Phrases
- 4.8 Use Transition Words
- 5 Examples of Topic Sentences
- 6 Topic Sentences as an Integral Part of Every Paragraph
- 7.1 How to find a topic sentence?
- 7.2 How long should a topic sentence be?
- 7.3 Is the topic sentence always the first sentence?
- 7.4 Can topic sentences be questions?
- 7.5 What is the difference between a topic sentence and a thesis statement?
The structure of academic writing requires several standards to be followed to ensure the coherence of your essay. One of the techniques you should use in your writing is essay topic sentences. However, why is it necessary, and how to write a topic sentence? We will answer this and many further questions in this article. Keep reading if you want to know:
- The essence of the topic sentence and its use;
- The crucial aspects of composing a topic sentence;
- Types of topic sentences and their implementation in the text;
- How to write your topic sentence and see the examples of it.
A strong topic sentence is a guarantee to be heard by the readers! Let’s start by looking at the meaning of this term and the main purpose of topic sentence.

What Is a Topic Sentence

A topic sentence is a generalized main idea of a paragraph summarized in one phrase. This statement provides a smooth transition from one central point to the next. But do not confuse it with the thesis statement. So, let’s review the topic sentence vs thesis statement and see if there is any difference.
A thesis statement sums up the idea of your essay or thesis, but it is usually found in the introduction, presenting the main point of the whole piece. Our service is ready to help you with writing a thesis statement correctly to ensure the highest results. An effective topic sentence includes two parts: the topic and the controlling idea. Use a topic sentence to organize your formal writing. Thus, you will delimit the main ideas within the boundaries of your essay paragraphs and ensure your text is coherent. This technique also aims to interest the reader by revealing the concept of your written work.
Characteristics of an Effective Topic Sentence
Using a topic sentence is an efficient strategy that will inform a reader about the topic of its paragraph briefly. To achieve this result of idea explanation and its evolution through the following parts of the text, learn the main characteristics of effective topic sentences. Below, we listed particular features that create a perfect topic sentence formula.
A good topic sentence requires clarity and unambiguity. The reader must understand exactly what work he is about to read. Therefore, your task is to introduce the main idea of each paragraph clearly.
Always remember about the idea of your paper, and don’t add anything extraordinary. You should only include information in your topic sentences that will be presented in the supporting sentences of the body part of an essay . Thus, your text will be easy and exciting to read, regardless of the topic.
- Completeness
You are faced with the difficult task of condensing a complete main idea into just one topic sentence. It must be comprehensive, express a complete thought, contain the controlling idea, and convey the topic you presented in a particular paragraph.
The topic sentences should motivate further reading. Therefore, you should present the information in a captivating way, ensuring the reader’s interest.
Types of Topic Sentences

There are three main types of topic sentences that cover a wide range of functions. Each type is suitable for a different purpose, but they all aim to include the key information in the current paragraph and emphasize the reader’s attention to it.
Interrogative
The topic sentence is presented as a question, and the following paragraph provides the answer. Such a topic sentence will effectively attract attention, increasing interest in reading. However, be careful to give an unambiguous answer to the question posed in your topic sentence.
Topic: Fast fashion
Topic sentence: What changes are required in the organization of the fashion industry to overcome total environmental pollution?
Reinforcement
Topic sentences and supporting details can serve as a reinforcement, supporting the central idea expressed in the essay’s thesis statement. This keeps the story flowing, showing that you’re not jumping between ideas inconstantly.
Thesis statement: AI development will provide the labor market with dozens of new positions.
Topic sentence: A lot of new job opportunities will be discovered with the development of AI.
Transitional
The topic sentences can also play the role of a link, logically and smoothly connecting several paragraphs into one whole. In this way, a clear structure of academic writing is maintained, and the author can relate one central point to another.
Last sentence of the previous paragraph: The issue of the need for school uniforms has been actively discussed for many years.
Topic sentence: School uniform is necessary for the development of discipline in children.
How to Write a Good Topic Sentence
First, remember that the focus sentence is the most important sentence in a paragraph. It should not only state the paragraph’s main idea, but it should be intriguingly interesting, concise, and include a controlling idea. Experts of our writing service have prepared for you some tips on how to make a topic sentence. It’s important to consider many different factors before writing a topic sentence for an essay. Keep reading to see the most essential ones.
Understanding the Paragraph’s Main Idea
The key to writing the topic sentence is to determine the main point of the paragraph. Think about the purpose for which you wrote this fragment. What would you like the reader to remember most? In other words, if you extract all the topic sentences from your essay and compose a text from them, you will get a complete digest of all the main ideas of the thesis.
Keeping it Concise
Sometimes, it can be difficult to fit everything you want to convey to the reader into one concluding sentence. After all, everything you wrote is valuable information worthy of attention. Still, be brief when writing your topic sentence to entice the audience to continue reading the rest of the paragraph.
Positioning the Topic Sentence
The topic sentence can be written in any part of the paragraph. Most commonly, placing it in the beginning, thus you ensure a smooth transition from the previous paragraph and give readers a hint about what the upcoming piece will be about. If it’s in the middle of the text, it can describe the main idea after having revealed some crucial background details of the main idea. When you write the topic sentence at the end of the paragraph, it concludes and highlights the essential concepts of the piece.
Make it Interesting but not Over-complicating
To start with, brainstorm to point out the most creative and interesting idea for your topic sentences. For example, if you use statistics in later paragraphs, include them in the hook sentence as well, this will intrigue readers. At the same time, do not forget that due to the topic sentence structure, the size of the topic sentence is very limited, so do not try to overcomplicate it.
Better to Use Active Voice
From a grammatical and lexical point of view, it is believed that the passive voice complicates the construction of sentences. You may consider the previous sentence as an example of a topic sentence that is difficult for a reader. Your topic sentences should be brief and comprehensive yet simple to understand. Prefer active voice to make the body paragraph easier to read.
Enhance with Evidence
First of all, any essay, likewise scientific work, requires accuracy. That is why using verified statistical data and citing reliable sources makes your topic sentence and controlling idea credible and respected. Pay attention to the plausibility of data when you write academic essay papers to avoid misleading information. Topic sentences for essays should also contain precise facts, which you subsequently describe in the new paragraph.
Bind the Paragraph Together by Repeating Words or Phrases
In poetry, there is a technique called anaphora, when each line or sentence of a verse begins the same. This is often used to influence the reader’s emotions, strengthening his awareness of a certain concept of the subject. So, to reinforce your main idea and relate your paragraphs, you can also use this device in your essay writing.
Use Transition Words
Of course, without connecting words, argumentative essays will turn into a collection of words and incoherent sentences. Build a clear essay structure by combining topic sentences with the rest of the paragraph with linking words. Therefore, to make your narrative coherent and logical, you should soften the transitions. Introduce these words at the beginning: first of all, to start with, therefore, based on this, moreover, and many others to enrich your writing.
Examples of Topic Sentences
Modern technologies have helped to significantly simplify working conditions for people. For centuries, people have had to work hard to provide basic means of living. In the absence of mechanization, unfathomable amounts of effort were required to complete basic tasks. For this reason, people worked day and night for six days a week and, in some cases, without days off at all. However, our generation was much luckier. The development of artificial intelligence and the automation of most production processes at this point allow people to work more efficiently while spending less time and effort.
What we know about recycling is a drop, what we don’t know is the ocean. In recent years, there have been many environmental campaigns to explain the importance of recycling. Most developed countries invest a large share of their budget in developing environmental solutions for the most optimal recycling of waste. However, at the same time, ordinary users still know very little about the rules for sorting waste. In reality, only a very small percentage of plastic can be recycled. Few people know that only the cap of a plastic bottle is recycled.
Society is moving online, and the changes it brings to the future are difficult to ignore. Of course, we don’t know exactly what the future of our society will be, but now we can trace some trends that will lead to steady changes. The children from the youngest age know how to use gadgets and independently find information on the Internet. Friendship, relationships, study, work, and all this already exist in the electronic dimension. Sociologists are interested in the question of what the society of the future will look like and whether there will be a place for offline communication in it.
The eternal question of style: to follow or not to follow the fashion trends. There probably is no single correct answer to this question. Social media influencers are actively sharing the hottest trends in the fashion world. The main fashionistas immediately run to the store to buy the latest new items. However, one thing is obvious – trends are certainly not for everyone. Starting from different body types to color types. We are all different, and this is our uniqueness. Trends certainly cannot look complimentary to everyone.
Our inner confidence provides external attractiveness. I have seen more than once that confident people often receive more positive attention. This is due to certain biological factors since a person with leadership qualities can lead a community, and therefore, people are drawn to him/her. And yet the advantage is not only respect from others. People with high self-esteem are perceived as more physically attractive.
Topic Sentences as an Integral Part of Every Paragraph
Your creative ideas that bring scientific novelty are the key element of your academic essays. At the same time, an idea without form is just a set of concepts. Using topic sentences will help you navigate and organize your ideas in a logical flow. Furthermore, it not only provides direction and focus for a paragraph, ensuring coherence and unity, but it also guides the reader’s journey through a text.
How to find a topic sentence?
How long should a topic sentence be, is the topic sentence always the first sentence, can topic sentences be questions, what is the difference between a topic sentence and a thesis statement, readers also enjoyed.

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
How To Write An Essay
Topic Sentence

Learn How to Write a Topic Sentence that Stands Out
Published on: Jan 13, 2021
Last updated on: Jul 23, 2024

People also read
How To Write An Essay - "The Secret To Craft an A+ Essay"
Learn How to Title an Essay Like a Professional Writer
How to Write an Essay Outline Like a Pro
Essay Format - An Easy Guide & Examples
What is a Thesis Statement, and How is it Written? - Know Here
Arguable and Strong Thesis Statement Examples for Your Essay
200+ Creative Hook Examples: Ready, Set, Hook
A Guide to Writing a 1000 Word Essay for School or College
All You Need to Know About a 500-word Essay
Different Types of Essay: Definition With Best Examples
Writing an Essay Introduction - Step by Step Guide
Transition Words for Essays - An Ultimate List
Jumpstart Your Writing with These Proven Strategies on How to Start an Essay
A Guide to Crafting an Impactful Conclusion for Your Essay
Amazing Essay Topics & Ideas for Your Next Project (2024)
Explore the Different Types of Sentences with Examples
Share this article
As a student, you have probably heard the term "topic sentence" thrown around a lot in your English or writing classes. But do you really understand what it means and how important it is for effective writing?
Well, many students struggle with crafting strong topic sentences that effectively convey their ideas. They may find themselves unsure of how to make their topic sentence stand out in a sea of other ideas.
In this blog, we will explore the art of writing a great topic sentence, with examples and tips to help you enhance your skills. By the end of this blog, you will have a better understanding of how to craft a topic sentence that will make your writing clear, concise, and engaging.
So let’s get started!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Topic Sentence?
A topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph in an essay that introduces the main idea or topic of that paragraph. It serves as a roadmap for the reader, letting them know what to expect in the upcoming paragraph.
Purpose of Topic Sentence
The purpose of a topic sentence is to clearly and concisely convey the main point of the paragraph to the reader.
It helps to guide the reader through the essay, making it easier for them to follow the overall argument or narrative.
Features of a Good Topic Sentence
A good topic sentence has a few key features. Letâs take a look:
- Expresses the main idea of the paragraph or essay clearly and concisely.
- Is specific and focused , avoiding vague or overly general statements.
- Introduces the main point and is typically located at the beginning of the paragraph or essay.
- Presents a claim or position that is arguable or debatable, which the rest of the paragraph or essay will support.
- Can be a complete sentence or a concise phrase that effectively conveys the main idea.
- Is relevant to the thesis statement and overall topic of the essay.
- Engages the reader by creating interest and highlighting the significance of the topic.
- Is well-written and avoids grammar and spelling errors.
- Provides a roadmap for the rest of the paragraph or essay by indicating what will be covered.
- Encourages coherence and unity in the writing by linking the paragraph or essay to the broader topic.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Types of Topic Sentences
There are several different types of topic sentences that can be used in writing to introduce the reader through a paragraph or essay.
Simple Statement Topic Sentence This is the most common type of topic sentence, which straightforwardly states the main point or idea of the paragraph or essay.
Example: The rise of social media has revolutionized the way people communicate with each other.
Complex Topic Sentence This type of topic sentence is more nuanced and may require some explanation or elaboration to fully understand.
Example: While the rise of social media has had many positive effects on communication, it has also led to concerns about privacy and online harassment.
Pivot Topic Sentence A pivot topic sentence begins by connecting the current paragraph or idea to the previous one, before pivoting to introduce a new point or idea.
Example: Building on the idea of social media's impact on communication, it is important to consider how it has also affected business and marketing strategies.
Question Topic Sentence A question topic sentence poses a question that the rest of the paragraph or essay will answer or explore.
Example: How has social media changed the way businesses interact with customers and advertise their products?
Command Topic Sentence This type of topic sentence gives a directive or instruction, often used in persuasive or argumentative essays.
Example: Support local businesses by shopping at independently owned stores instead of large chains.
How to Write a Topic Sentence?
Here are a few instructions to help you write a good topic sentence.
Step#1 Clearly State The Main Idea
A topic sentence is the first paragraph of the paragraph. It must clearly explain the particular subject that would be discussed in the paragraph. This should be stated in very clear language so that the reader can easily understand the idea.
Also, it should include a bit of your personal opinion and also the main idea.
Step#2 Hook Your Reader
Grab your reader's attention with an intriguing topic sentence. It would excite and make the reader curious about the content and convince them to read the particular part.
Look out for some amazing hook examples and see what fits your essay type.
Use a meaningful and relevant question or a fact as a topic sentence of the paragraph. Make sure that you have identified your audience and are developing everything accordingly.
Step#3 Keep It Short and Precise
The paragraph topic sentence must be expressive enough that a reader understands your point of view effortlessly. This is only possible if you keep everything to the point, short, and meaningful.
Choose the words in such a way that they help you express your idea in an ideal way. Avoid using complex sentences and use independent clauses.
A topic sentence acts as a link between a paragraph and the main thesis statement. It should be specific and connected to the overall essay. Keeping it short and precise helps maintain the paragraph's flow and its relevance to the rest of the writing.
Step#4 Give A Reasonable Opinion
The body paragraph explains a topic sentence. This is why it is important that you should write this sentence in such a way that it can be explained in the paragraph. If you are mentioning a fact in the topic statement, make sure that you have authentic evidence to support it.
While the topic sentence is an integral part of the paragraph, it should stand out and possess a distinctiveness that sets it apart from the other sentences. This can be achieved by employing transition words and establishing connections between sentences.
Step#5 Use The Topic Sentence As A Transition
The topic sentences that serve as transition sentences can be considered a guide for the readers. This way, they can help the reader to move through the essay in a flow.
Write this sentence in such a way that it creates a gateway between the previous paragraph and the rest of the essay. Moreover, it will also help keep the essay organized, and the reader understands the point of a paragraph.
Step#6 Look For Some Good Examples
Examples can help you learn a thing in a better way. If you are new to writing topic sentences, it can help to look at some examples. Find some great examples of topic sentences relevant to your essay topic.
Difference Between Topic Sentence and Thesis Sentence
Here's a table outlining the differences between a topic sentence and a thesis statement:
|
| |
| A sentence that introduces the main idea or topic of a paragraph | A statement that presents the main argument or claim of an essay or research paper |
| | Typically found at the beginning of a paragraph | Typically found at the end of an introduction |
| | Limited to one paragraph | Spans the entire essay or research paper |
| | Introduces the main idea of a paragraph and connects it to the thesis statement | Presents the main argument or claim of an essay and provides a roadmap for the reader |
| | Helps to organize the content of the paragraph and keeps the writer focused on the main point | Helps to organize the content of the entire essay or research paper and guides the reader through the argument |
| |
Good Topic Sentence Examples
Here are ten examples of good topic sentences:
- "Despite the advancements in technology, traditional forms of communication are still essential in today's society."
- "The theme of power is prevalent throughout Shakespeare's play, Macbeth."
- "In recent years, there has been a growing concern over the impact of climate change on our planet."
- "The legalization of marijuana has been a topic of debate for many years." "Education is the key to success in life."
- "The rise of social media has greatly impacted the way we communicate with one another."
- "The effects of childhood trauma can have a lasting impact on mental health."
- "The concept of justice is explored in depth in Harper Lee's To Kill a Mockingbird."
- "Eating a balanced diet is crucial for maintaining good health."
- "The Industrial Revolution had a profound effect on the world as we know it today."
The Bottom Line!
An opening sentence is crucial to grab your reader's attention and set the tone for your piece of writing. The topic sentence introduces the controlling idea and acts as an important sentence in the essay outline.
Effective topic sentences are necessary for a well-structured and organized essay. It's an integral part of the writing process that should not be overlooked.
Make sure to spend time crafting a compelling topic sentence that clearly conveys your main point and guides your readers throughout your essay. You can even take ideas from an AI essay generator to get started.
However, if you find yourself struggling to write a good opening sentence, don't worry! CollegeEssay.org is here to help you with all your writing needs. We have the best online essay writing service providing top-quality essays that are sure to impress your professors.
So, why wait? Contact our essay writing service now and take the first step toward academic success!
Frequently Asked Questions
How long is a topic sentence.
A topic sentence can be multiple sentences long. The first sets the context for your ideas, while the second provides more depth on what you are saying beyond just stating it outright.
Barbara P (Literature, Marketing)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Literary Terms
Topic Sentence
I. what is a topic sentence.
A topic sentence in a paragraph is like the GPS in a car. It shows you (and others) where you are going and explains the point of the paragraph. Everything else is used as supporting details. The topic sentence contains two parts: the topic and a controlling idea. The topic is WHAT the paragraph is going to be about, and the controlling idea explains WHY the paragraph is being written. The topic sentence helps your reader understand the purpose of your paragraph.
II. Examples of a Topic Sentence
The purpose of your paragraph will be made clear in your topic sentence. The most common reasons for writing are to persuade, to inform, and to entertain. It is also possible that a sentence could do more than one of these.
You will often use a persuasive topic sentence when writing for school, such as in literary essays .
The character Pip in the novel Great Expectations learns the importance of loyalty through his interactions with the convict Abel Magwitch.
An informative topic sentence is often found in scientific articles.
White blood cells help fight infections by attacking bacteria, viruses and germs that invade the body.
Topic sentences that entertain are sometimes found in magazines or other less formal writing.
It’s not hard to raise a bad child if you follow these simple instructions.
III. Parts of a Topic Sentence
There are just two parts in a topic sentence, the topic and the controlling idea. The topic is WHAT the paragraph is about, and the controlling idea explains WHY you are writing the paragraph. In the examples below, the topic is in orange and the controlling idea is in green .
Joseph loves to spend time with his friends .
What/who is this paragraph about? Joseph. Why is this paragraph being written? To explain something that Joseph loves to do.
Disneyland is the happiest place on Earth .
What/who is this paragraph about? Disneyland. Why is it being written? To show why Disneyland is the happiest place on Earth.
IV. Placement of Topic Sentences
A. initial placement.
The most common place for a topic sentence is at the beginning of the paragraph because it explains what the paragraph is going to discuss. The initial placement helps the writer organize the paragraph and tells the reader what to expect right in the beginning.
The best things in life are free . Although most people work hard to buy a good home or a nice car, those are not the things that they care about the most. At the end of their lives, they don’t want to hug their cars, or the walls of their fine houses. They want to be surrounded by the people they care about and who care about them. Kindness is free. Love is free. Friendship is free (or at least it should be!). Of course it is important to make money to survive, but love is important to live happily.
b. Final Placement
Sometimes the topic sentence is at the end of the paragraph, especially when the paragraph is a narrative or a mysterious story. Placing it at the end creates suspense or sometimes works to tell the point of the story.
The wealthy man was dying. He called for his friends and family to be near him and placed a hand on each one’s shoulder. They cried because they would miss him, and he cried because he had no more time to share with them. The beautiful things that he’d purchased over the years held no meaning. He didn’t care about his diamonds or his yacht or his large home. He cared for his children and the love they shared. They were here with him now and held his hands. He was glad he’d learned the most important lesson in life: the best things in life are free .
c. Medial Placement
The last place, the least common place for a topic sentence, is in the middle of the paragraph. The medial topic sentence usually functions as a transition between two ideas or details. This works when you want to show that there are two (sometimes opposite) points to an issue, but the one you are arguing, the second point, is stronger, more specific, or more important. This topic sentence is generally introduced with a transition signal.
You can’t survive on love alone. People need money for basic necessities: food, shelter and clothing. Without money, life would be uncomfortable and difficult. However, time and energy should not be completely spent on making money because the best things in life are free . Having fun with friends and family is more important and more satisfying than buying a new car or nice clothes. People provide warmth, affection, understanding, and most of all, love. Money can’t love you back, and it does not guarantee happiness. Some of the richest people in the world are miserable, while some of the poorest people in the world are happy because they have the simple joy of loving people in their lives.
V. How to Write a Topic Sentence
A. the best way to write your topic sentence is to consider why you are writing the paragraph.
- Decide on your reason for writing the paragraph
- After you have figured that out, write down the important details you want to include and see what they all have in common.
- Summarize the details into one sentence.
For example, if you want to write about your favorite movie, think about all the reasons that you like it. Is it funny? Exciting? Dramatic? Romantic? Be sure not to include too many things or else you will end up with an essay instead of a simple sentence. Once you have decided on your details, you are ready to write the topic sentence.
Here’s an example, the topic will be in orange and the controlling idea will be in green :
The best movie ever made was “Star Wars: the Force Awakens” because it was exciting and surprising .
An important point to remember is that the topic sentence should contain all relevant information that’s going to be in the paragraph. There should be no information about romance or comedy. It should only talk about what made the movie exciting.
b. Mistakes to Avoid
One of the biggest problems students face is keeping a paragraph or essay on topic. Sometimes they will write a good topic sentence but halfway through the paragraph, they think of another good idea and follow that. Without revision and editing, the topic sentence will not serve its purpose in the paragraph.
The best vacation I ever had was in Hawaii. The beaches were so beautiful and clean that swimming in them was like a dream . I especially loved the Waikiki beach. At night, there were free shows with dancers and live music. The music was so good that it made me want to dance. Dancing is my favorite thing to do in the world. When I was young, I studied ballet and tap dance. I’m thinking about taking it back up again. I might even study hip-hop!
The paragraph started out with Hawaii and end up with hip-hop dancing. You can see how the writer’s train of thought began to wander in the seventh sentence. With a different topic sentence, it would be possible to save this paragraph. Consider how different the direction would be with the following topic sentence.
The best vacation I ever had was in Hawaii. I especially loved the Waikiki beach. At night, there were free shows with dancers and live music. The music was so good that it made me want to dance and reminded me that dancing is my favorite activity in the world. In fact, when I was young, I studied ballet and tap dance. The dancing that I saw in Hawaii inspired me to get back into dancing . I might even study hip-hop!
With this new topic sentence, the second sentence would have to be eliminated or changed a bit. You can see how easy it is to get off-topic, but with a good topic sentence, and constant reference back to it, you are less likely to have that problem.
VI. So remember
- A topic sentence needs to contain the topic of your paragraph and a controlling idea.
- Everything in the paragraph should be connected to the topic sentence.
- The placement of the topic sentence depends on the type of paragraph.
VII. Exercises
Each of the paragraphs in this exercise has three possible topic sentences following it. Choose the best one and make sure that it includes the main idea of the paragraph.
1. _____________________________________________. In fact, he usually shows up five minutes early everywhere he goes. Because he’s so considerate, he hates to keep people waiting. He also believes that being early creates a better expereince. One time, when we were going to a movie together, John arrived thirty minutes earlier just so he could get the best seats in the theatre. I’m glad to have such a punctual friend.
a. John loves going to the movies.
b. John is always on time.
c. John hates to be kept waiting.
2. _________________________________________. The place is never crowded, but the service is still terrible. It seems like the staff has better things to do than wait on customers. Once I waited ten minutes just to buy a slice of pizza, and I was the only person in the whole store! I recommend staying away from Billy Bob’s Pizzeria.
a. Billy Bob’s Pizzeria has the worst pizza.
b. Billy Bob’s Pizzeria is an unpopular place to eat.
c. Billy Bob’s Pizzeria has terrible customer service.
3. I walked slowly down the dark path, afraid of my own shadow. But the tug on the leash propelled me forward. Buck, my golden retriever, was determined to take the most deserted trails through the forest. I could hear unfamiliar noises on all sides and urged Buck to do his business quickly. Oh, why couldn’t he be toilet trained? That would be better for everyone! _____________________________________.
a. Buck is an inconsiderate dog.
b. I hate walking my dog at night.
c. The forest is a dangerous place to walk at night.
4. Generally speaking, zoos these days are losing popularity. Many people feel that it’s unfair to lock up wild animals to entertain humans. ________________________________ . Some zoos go to great lengths to build a good environment for its animals. The good zoos treat their animals well and provide opportunities for the public to learn about the natural world. The best zoos protect endangered species and raise awareness about animals and their habitats.
a. Zoos perform a valuable service to society and should be part of every person’s childhood memory.
b. Zoos are horrible places that should be shut down because it’s not humane to lock up wild animals.
c. Zoos that do their best to make a pleasant habitat for the animals can be a pleasant place to visit.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
Frequently asked questions
What is a topic sentence.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
Frequently asked questions: Writing an essay
For a stronger conclusion paragraph, avoid including:
- Important evidence or analysis that wasn’t mentioned in the main body
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
Your essay’s conclusion should contain:
- A rephrased version of your overall thesis
- A brief review of the key points you made in the main body
- An indication of why your argument matters
The conclusion may also reflect on the broader implications of your argument, showing how your ideas could applied to other contexts or debates.
The conclusion paragraph of an essay is usually shorter than the introduction . As a rule, it shouldn’t take up more than 10–15% of the text.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
Let’s say you’re writing a five-paragraph essay about the environmental impacts of dietary choices. Here are three examples of topic sentences you could use for each of the three body paragraphs :
- Research has shown that the meat industry has severe environmental impacts.
- However, many plant-based foods are also produced in environmentally damaging ways.
- It’s important to consider not only what type of diet we eat, but where our food comes from and how it is produced.
Each of these sentences expresses one main idea – by listing them in order, we can see the overall structure of the essay at a glance. Each paragraph will expand on the topic sentence with relevant detail, evidence, and arguments.
The topic sentence usually comes at the very start of the paragraph .
However, sometimes you might start with a transition sentence to summarize what was discussed in previous paragraphs, followed by the topic sentence that expresses the focus of the current paragraph.
Topic sentences help keep your writing focused and guide the reader through your argument.
In an essay or paper , each paragraph should focus on a single idea. By stating the main idea in the topic sentence, you clarify what the paragraph is about for both yourself and your reader.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
In rhetorical analysis , a claim is something the author wants the audience to believe. A support is the evidence or appeal they use to convince the reader to believe the claim. A warrant is the (often implicit) assumption that links the support with the claim.
Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, building up logical arguments . Ethos appeals to the speaker’s status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example.
Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical triangle . They are central to rhetorical analysis , though a piece of rhetoric might not necessarily use all of them.
The term “text” in a rhetorical analysis essay refers to whatever object you’re analyzing. It’s frequently a piece of writing or a speech, but it doesn’t have to be. For example, you could also treat an advertisement or political cartoon as a text.
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain the effect a piece of writing or oratory has on its audience, how successful it is, and the devices and appeals it uses to achieve its goals.
Unlike a standard argumentative essay , it’s less about taking a position on the arguments presented, and more about exploring how they are constructed.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
If you have to hand in your essay outline , you may be given specific guidelines stating whether you have to use full sentences. If you’re not sure, ask your supervisor.
When writing an essay outline for yourself, the choice is yours. Some students find it helpful to write out their ideas in full sentences, while others prefer to summarize them in short phrases.
You will sometimes be asked to hand in an essay outline before you start writing your essay . Your supervisor wants to see that you have a clear idea of your structure so that writing will go smoothly.
Even when you do not have to hand it in, writing an essay outline is an important part of the writing process . It’s a good idea to write one (as informally as you like) to clarify your structure for yourself whenever you are working on an essay.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison.
You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response.
Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework .
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
If you’re not given a specific prompt for your descriptive essay , think about places and objects you know well, that you can think of interesting ways to describe, or that have strong personal significance for you.
The best kind of object for a descriptive essay is one specific enough that you can describe its particular features in detail—don’t choose something too vague or general.
If you’re not given much guidance on what your narrative essay should be about, consider the context and scope of the assignment. What kind of story is relevant, interesting, and possible to tell within the word count?
The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to reflect on a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
Don’t worry too much if your topic seems unoriginal. The point of a narrative essay is how you tell the story and the point you make with it, not the subject of the story itself.
Narrative essays are usually assigned as writing exercises at high school or in university composition classes. They may also form part of a university application.
When you are prompted to tell a story about your own life or experiences, a narrative essay is usually the right response.
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
An expository essay is a common assignment in high-school and university composition classes. It might be assigned as coursework, in class, or as part of an exam.
Sometimes you might not be told explicitly to write an expository essay. Look out for prompts containing keywords like “explain” and “define.” An expository essay is usually the right response to these prompts.
An expository essay is a broad form that varies in length according to the scope of the assignment.
Expository essays are often assigned as a writing exercise or as part of an exam, in which case a five-paragraph essay of around 800 words may be appropriate.
You’ll usually be given guidelines regarding length; if you’re not sure, ask.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
5 Steps to Write a Topic Sentence for Argumentative Essay
by Antony W
June 9, 2024

In this guide, we’ll look at how to write a topic sentence for an argumentative essay. And don’t worry, it’s an incredibly simple thing to do, so you don’t necessary have to overthink anything here.
Key Takeaways
- A topic sentence begins every paragraph of your argumentative essay.
- The purpose of the topic sentence is to communicate the main idea you intend to cover in the paragraph, so it should be clear, sensible, and coherent.
- If possible, include new information in your topic sentence to make your writing stand out.
- You can use transition words such as “another” and “even though” to start a topic sentence in your argumentative essay.
- Use compound and complex sentences to strengthen your paragraphs.
- You can use reasonable options, but make sure you can support them so that they’re convincing.
What Is a Topic Sentence in an Argumentative Essay?
A topic sentence is the opening statement in every paragraph of an argumentative essay. It provides an idea of what you’ll cover in the paragraph.
A topic sentence should be vast so that it can support many subtopics in the rest of its paragraphs.
It’s important to note that a topic sentence in an argumentative essay is completely different from the thesis statement.
A thesis statement states the repeated focus in an entire writing. A thesis makes a major point that you will discuss in the rest of the argument.
A topic sentence on the other hand will introduce the topics of every supporting paragraphs to back up the thesis.
What is the Purpose of a Topic Sentence in an Argumentative Essay?
You need a topic sentence because it makes the idea of the main paragraph more clear and sensible for coherence.
The topic sentence joins sentences of a given paragraph, backs up what the paper claims, explains what a paragraph says, and claims mini thesis statements.
Tips for Writing a Topic Sentence for an Argumentative Essay
Here are 4 useful tips that will help you write a good topic sentence for an argumentative essay:
1. Use New Information
You should write a topic sentence that’s interesting to read so that it immerses your readers deeply into your essay.
Try as much as you can to make the information you provide look new. By doing so, way it will be far from being another fact statement.
2. Use a Topic Sentence Later in the Opening Paragraph
Many students often choose to write their topic sentence as the first thing in every paragraph. While that’s the standard approach, you can be a bit flexible.
In other words, instead of having your topic sentence in every first sentence of a paragraph, you can write it after the hook in an opening paragraph to grab the reader’s attention and that makes him or her want to read more.
3. Try Transition Words
Transitional words can be used on opening topic sentences or on sentence that begin with supporting paragraphs.
You can use transitional words like “another”, “although” or “even though” to start your new paragraph
4. Make your Topic Sentence Compound and Complex
To make your topic sentence high level with a stronger feels, consider the use of compound and complex sentences.
For compound sentences, use independent clauses – preferably two – and then connect them using a comma and conjunction.
For complex sentences, use independent and subordinate clauses and link them with a comma and subordinating conjunction.
Here are examples of compound and complex sentences:
- Complex sentence : When planes fly, they follow paths used by other planes for centuries. “When” at this point is the subordinate conjunction.
- Compound sentences : The colonial period was a period of intrusion, but it was monitored by strict social nods. In this case, “but” is the coordinating conjunction.
Argumentative Essay Writing Help
If you have multiple assignments to complete and your argumentative essay is running late, we can help.
You can order an argumentative essay online here and one of our best writers will help you get the work done.
How to Write a Topic Sentence for an Argumentative Essay
1. clearly state your major idea.
Since a topic sentence is the first statement in every paragraph, it is important to make it more clear, straight to the point and easy to digest.
Avoid using extra, unnecessary words as it makes understanding more difficult.
Make sure you include controlling ideas and topics because the sentences that follow thereafter should relate to the topic sentence.
Avoid using an opening statement like “Today we are going to discuss the benefits of afforestation”.
After all, a topic sentence is not an invitation, which allows announcement of topics at hand.
2. Use the Topic Sentence as a Transition
Topic sentences that work as transitions guide readers through arguments on essays.
This makes sure they are not only on track but also don’t get lost in words.
3. Keep it Short and Concise
Don’t have your readers figure out your intentions in your argumentative essay are; just use the topic statements to show them the aim of your essay.
So make your topic sentence more specific than your thesis.
When you use short sentence on your essay you make your paragraph retain its flow.
The shorter you keep the sentences the more you clearly bring out your intentions.
4. Balance the Topic Sentence between Specifics and General Ideas
Topic sentences ought to relate to the thesis statement on your essay. Importantly, ensure the topic sentence is broad and balanced.
Avoid the use of general ideas because they will be a bit challenging to discuss. Avoid the use of narrow statements instead aim for a balance that is good.
Also, hook your readers more by describing characters, portray emotions, use dialogues, details but avoid rhetorical questions.
5. Make Use of Reasonable Opinions
The topic sentence is supposed to outline things that can be supported by concrete evidence. That’s why we need topic sentences in paragraphs.
You are allowed to highlight an opinion on your topic sentence but only make the move when you are certain of backing it up with the paragraph that follows.
Facts are good but avoid them because they won’t introduce the reader to your main idea.
If you find it necessary, consider an input of your own. For example, instead of writing, “All patients need treatment”, you can say, “All patients need regular care, like food, water and nurses are the best for it”.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
11 Rules for Essay Paragraph Structure (with Examples)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
How do you structure a paragraph in an essay?
If you’re like the majority of my students, you might be getting your basic essay paragraph structure wrong and getting lower grades than you could!
In this article, I outline the 11 key steps to writing a perfect paragraph. But, this isn’t your normal ‘how to write an essay’ article. Rather, I’ll try to give you some insight into exactly what teachers look out for when they’re grading essays and figuring out what grade to give them.
You can navigate each issue below, or scroll down to read them all:
1. Paragraphs must be at least four sentences long 2. But, at most seven sentences long 3. Your paragraph must be Left-Aligned 4. You need a topic sentence 5 . Next, you need an explanation sentence 6. You need to include an example 7. You need to include citations 8. All paragraphs need to be relevant to the marking criteria 9. Only include one key idea per paragraph 10. Keep sentences short 11. Keep quotes short
Paragraph structure is one of the most important elements of getting essay writing right .
As I cover in my Ultimate Guide to Writing an Essay Plan , paragraphs are the heart and soul of your essay.
However, I find most of my students have either:
- forgotten how to write paragraphs properly,
- gotten lazy, or
- never learned it in the first place!
Paragraphs in essay writing are different from paragraphs in other written genres .
In fact, the paragraphs that you are reading now would not help your grades in an essay.
That’s because I’m writing in journalistic style, where paragraph conventions are vastly different.
For those of you coming from journalism or creative writing, you might find you need to re-learn paragraph writing if you want to write well-structured essay paragraphs to get top grades.
Below are eleven reasons your paragraphs are losing marks, and what to do about it!

Essay Paragraph Structure Rules
1. your paragraphs must be at least 4 sentences long.
In journalism and blog writing, a one-sentence paragraph is great. It’s short, to-the-point, and helps guide your reader. For essay paragraph structure, one-sentence paragraphs suck.
A one-sentence essay paragraph sends an instant signal to your teacher that you don’t have much to say on an issue.
A short paragraph signifies that you know something – but not much about it. A one-sentence paragraph lacks detail, depth and insight.
Many students come to me and ask, “what does ‘add depth’ mean?” It’s one of the most common pieces of feedback you’ll see written on the margins of your essay.
Personally, I think ‘add depth’ is bad feedback because it’s a short and vague comment. But, here’s what it means: You’ve not explained your point enough!
If you’re writing one-, two- or three-sentence essay paragraphs, you’re costing yourself marks.
Always aim for at least four sentences per paragraph in your essays.
This doesn’t mean that you should add ‘fluff’ or ‘padding’ sentences.
Make sure you don’t:
a) repeat what you said in different words, or b) write something just because you need another sentence in there.
But, you need to do some research and find something insightful to add to that two-sentence paragraph if you want to ace your essay.
Check out Points 5 and 6 for some advice on what to add to that short paragraph to add ‘depth’ to your paragraph and start moving to the top of the class.
- How to Make an Essay Longer
- How to Make an Essay Shorter
2. Your Paragraphs must not be more than 7 Sentences Long
Okay, so I just told you to aim for at least four sentences per paragraph. So, what’s the longest your paragraph should be?
Seven sentences. That’s a maximum.
So, here’s the rule:
Between four and seven sentences is the sweet spot that you need to aim for in every single paragraph.
Here’s why your paragraphs shouldn’t be longer than seven sentences:
1. It shows you can organize your thoughts. You need to show your teacher that you’ve broken up your key ideas into manageable segments of text (see point 10)
2. It makes your work easier to read. You need your writing to be easily readable to make it easy for your teacher to give you good grades. Make your essay easy to read and you’ll get higher marks every time.
One of the most important ways you can make your work easier to read is by writing paragraphs that are less than six sentences long.
3. It prevents teacher frustration. Teachers are just like you. When they see a big block of text their eyes glaze over. They get frustrated, lost, their mind wanders … and you lose marks.
To prevent teacher frustration, you need to ensure there’s plenty of white space in your essay. It’s about showing them that the piece is clearly structured into one key idea per ‘chunk’ of text.
Often, you might find that your writing contains tautologies and other turns of phrase that can be shortened for clarity.
3. Your Paragraph must be Left-Aligned
Turn off ‘Justified’ text and: Never. Turn. It. On. Again.
Justified text is where the words are stretched out to make the paragraph look like a square. It turns the writing into a block. Don’t do it. You will lose marks, I promise you! Win the psychological game with your teacher: left-align your text.
A good essay paragraph is never ‘justified’.
I’m going to repeat this, because it’s important: to prevent your essay from looking like a big block of muddy, hard-to-read text align your text to the left margin only.
You want white space on your page – and lots of it. White space helps your reader scan through your work. It also prevents it from looking like big blocks of text.
You want your reader reading vertically as much as possible: scanning, browsing, and quickly looking through for evidence you’ve engaged with the big ideas.
The justified text doesn’t help you do that. Justified text makes your writing look like a big, lumpy block of text that your reader doesn’t want to read.
What’s wrong with Center-Aligned Text?
While I’m at it, never, ever, center-align your text either. Center-aligned text is impossible to skim-read. Your teacher wants to be able to quickly scan down the left margin to get the headline information in your paragraph.
Not many people center-align text, but it’s worth repeating: never, ever center-align your essays.

Don’t annoy your reader. Left align your text.
4. Your paragraphs must have a Topic Sentence
The first sentence of an essay paragraph is called the topic sentence. This is one of the most important sentences in the correct essay paragraph structure style.
The topic sentence should convey exactly what key idea you’re going to cover in your paragraph.
Too often, students don’t let their reader know what the key idea of the paragraph is until several sentences in.
You must show what the paragraph is about in the first sentence.
You never, ever want to keep your reader in suspense. Essays are not like creative writing. Tell them straight away what the paragraph is about. In fact, if you can, do it in the first half of the first sentence .
I’ll remind you again: make it easy to grade your work. Your teacher is reading through your work trying to determine what grade to give you. They’re probably going to mark 20 assignments in one sitting. They have no interest in storytelling or creativity. They just want to know how much you know! State what the paragraph is about immediately and move on.
Suggested: Best Words to Start a Paragraph
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: Writing a Topic Sentence If your paragraph is about how climate change is endangering polar bears, say it immediately : “Climate change is endangering polar bears.” should be your first sentence in your paragraph. Take a look at first sentence of each of the four paragraphs above this one. You can see from the first sentence of each paragraph that the paragraphs discuss:
When editing your work, read each paragraph and try to distil what the one key idea is in your paragraph. Ensure that this key idea is mentioned in the first sentence .
(Note: if there’s more than one key idea in the paragraph, you may have a problem. See Point 9 below .)
The topic sentence is the most important sentence for getting your essay paragraph structure right. So, get your topic sentences right and you’re on the right track to a good essay paragraph.
5. You need an Explanation Sentence
All topic sentences need a follow-up explanation. The very first point on this page was that too often students write paragraphs that are too short. To add what is called ‘depth’ to a paragraph, you can come up with two types of follow-up sentences: explanations and examples.
Let’s take explanation sentences first.
Explanation sentences give additional detail. They often provide one of the following services:
Let’s go back to our example of a paragraph on Climate change endangering polar bears. If your topic sentence is “Climate change is endangering polar bears.”, then your follow-up explanation sentence is likely to explain how, why, where, or when. You could say:
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: Writing Explanation Sentences 1. How: “The warming atmosphere is melting the polar ice caps.” 2. Why: “The polar bears’ habitats are shrinking every single year.” 3. Where: “This is happening in the Antarctic ice caps near Greenland.” 4. When: “Scientists first noticed the ice caps were shrinking in 1978.”
You don’t have to provide all four of these options each time.
But, if you’re struggling to think of what to add to your paragraph to add depth, consider one of these four options for a good quality explanation sentence.
>>>RELATED ARTICLE: SHOULD YOU USE RHETORICAL QUESTIONS IN ESSAYS ?
6. Your need to Include an Example
Examples matter! They add detail. They also help to show that you genuinely understand the issue. They show that you don’t just understand a concept in the abstract; you also understand how things work in real life.
Example sentences have the added benefit of personalising an issue. For example, after saying “Polar bears’ habitats are shrinking”, you could note specific habitats, facts and figures, or even a specific story about a bear who was impacted.
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: Writing an ‘Example’ Sentence “For example, 770,000 square miles of Arctic Sea Ice has melted in the past four decades, leading Polar Bear populations to dwindle ( National Geographic, 2018 )
In fact, one of the most effective politicians of our times – Barrack Obama – was an expert at this technique. He would often provide examples of people who got sick because they didn’t have healthcare to sell Obamacare.
What effect did this have? It showed the real-world impact of his ideas. It humanised him, and got him elected president – twice!
Be like Obama. Provide examples. Often.
7. All Paragraphs need Citations
Provide a reference to an academic source in every single body paragraph in the essay. The only two paragraphs where you don’t need a reference is the introduction and conclusion .
Let me repeat: Paragraphs need at least one reference to a quality scholarly source .
Let me go even further:
Students who get the best marks provide two references to two different academic sources in every paragraph.
Two references in a paragraph show you’ve read widely, cross-checked your sources, and given the paragraph real thought.
It’s really important that these references link to academic sources, not random websites, blogs or YouTube videos. Check out our Seven Best types of Sources to Cite in Essays post to get advice on what sources to cite. Number 6 w ill surprise you!
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: In-Text Referencing in Paragraphs Usually, in-text referencing takes the format: (Author, YEAR), but check your school’s referencing formatting requirements carefully. The ‘Author’ section is the author’s last name only. Not their initials. Not their first name. Just their last name . My name is Chris Drew. First name Chris, last name Drew. If you were going to reference an academic article I wrote in 2019, you would reference it like this: (Drew, 2019).
Where do you place those two references?
Place the first reference at the end of the first half of the paragraph. Place the second reference at the end of the second half of the paragraph.
This spreads the references out and makes it look like all the points throughout the paragraph are backed up by your sources. The goal is to make it look like you’ve reference regularly when your teacher scans through your work.
Remember, teachers can look out for signposts that indicate you’ve followed academic conventions and mentioned the right key ideas.
Spreading your referencing through the paragraph helps to make it look like you’ve followed the academic convention of referencing sources regularly.
Here are some examples of how to reference twice in a paragraph:
- If your paragraph was six sentences long, you would place your first reference at the end of the third sentence and your second reference at the end of the sixth sentence.
- If your paragraph was five sentences long, I would recommend placing one at the end of the second sentence and one at the end of the fifth sentence.
You’ve just read one of the key secrets to winning top marks.
8. Every Paragraph must be relevant to the Marking Criteria
Every paragraph must win you marks. When you’re editing your work, check through the piece to see if every paragraph is relevant to the marking criteria.
For the British: In the British university system (I’m including Australia and New Zealand here – I’ve taught at universities in all three countries), you’ll usually have a ‘marking criteria’. It’s usually a list of between two and six key learning outcomes your teacher needs to use to come up with your score. Sometimes it’s called a:
- Marking criteria
- Marking rubric
- (Key) learning outcome
- Indicative content
Check your assignment guidance to see if this is present. If so, use this list of learning outcomes to guide what you write. If your paragraphs are irrelevant to these key points, delete the paragraph .
Paragraphs that don’t link to the marking criteria are pointless. They won’t win you marks.
For the Americans: If you don’t have a marking criteria / rubric / outcomes list, you’ll need to stick closely to the essay question or topic. This goes out to those of you in the North American system. North America (including USA and Canada here) is often less structured and the professor might just give you a topic to base your essay on.
If all you’ve got is the essay question / topic, go through each paragraph and make sure each paragraph is relevant to the topic.
For example, if your essay question / topic is on “The Effects of Climate Change on Polar Bears”,
- Don’t talk about anything that doesn’t have some connection to climate change and polar bears;
- Don’t talk about the environmental impact of oil spills in the Gulf of Carpentaria;
- Don’t talk about black bear habitats in British Columbia.
- Do talk about the effects of climate change on polar bears (and relevant related topics) in every single paragraph .
You may think ‘stay relevant’ is obvious advice, but at least 20% of all essays I mark go off on tangents and waste words.
Stay on topic in Every. Single. Paragraph. If you want to learn more about how to stay on topic, check out our essay planning guide .
9. Only have one Key Idea per Paragraph
One key idea for each paragraph. One key idea for each paragraph. One key idea for each paragraph.
Don’t forget!
Too often, a student starts a paragraph talking about one thing and ends it talking about something totally different. Don’t be that student.
To ensure you’re focussing on one key idea in your paragraph, make sure you know what that key idea is. It should be mentioned in your topic sentence (see Point 3 ). Every other sentence in the paragraph adds depth to that one key idea.
If you’ve got sentences in your paragraph that are not relevant to the key idea in the paragraph, they don’t fit. They belong in another paragraph.
Go through all your paragraphs when editing your work and check to see if you’ve veered away from your paragraph’s key idea. If so, you might have two or even three key ideas in the one paragraph.
You’re going to have to get those additional key ideas, rip them out, and give them paragraphs of their own.
If you have more than one key idea in a paragraph you will lose marks. I promise you that.
The paragraphs will be too hard to read, your reader will get bogged down reading rather than scanning, and you’ll have lost grades.
10. Keep Sentences Short
If a sentence is too long it gets confusing. When the sentence is confusing, your reader will stop reading your work. They will stop reading the paragraph and move to the next one. They’ll have given up on your paragraph.
Short, snappy sentences are best.
Shorter sentences are easier to read and they make more sense. Too often, students think they have to use big, long, academic words to get the best marks. Wrong. Aim for clarity in every sentence in the paragraph. Your teacher will thank you for it.
The students who get the best marks write clear, short sentences.
When editing your draft, go through your essay and see if you can shorten your longest five sentences.
(To learn more about how to write the best quality sentences, see our page on Seven ways to Write Amazing Sentences .)
11. Keep Quotes Short
Eighty percent of university teachers hate quotes. That’s not an official figure. It’s my guestimate based on my many interactions in faculty lounges. Twenty percent don’t mind them, but chances are your teacher is one of the eight out of ten who hate quotes.
Teachers tend to be turned off by quotes because it makes it look like you don’t know how to say something on your own words.
Now that I’ve warned you, here’s how to use quotes properly:
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: How To Use Quotes in University-Level Essay Paragraphs 1. Your quote should be less than one sentence long. 2. Your quote should be less than one sentence long. 3. You should never start a sentence with a quote. 4. You should never end a paragraph with a quote. 5 . You should never use more than five quotes per essay. 6. Your quote should never be longer than one line in a paragraph.
The minute your teacher sees that your quote takes up a large chunk of your paragraph, you’ll have lost marks.
Your teacher will circle the quote, write a snarky comment in the margin, and not even bother to give you points for the key idea in the paragraph.
Avoid quotes, but if you really want to use them, follow those five rules above.
I’ve also provided additional pages outlining Seven tips on how to use Quotes if you want to delve deeper into how, when and where to use quotes in essays. Be warned: quoting in essays is harder than you thought.

Follow the advice above and you’ll be well on your way to getting top marks at university.
Writing essay paragraphs that are well structured takes time and practice. Don’t be too hard on yourself and keep on trying!
Below is a summary of our 11 key mistakes for structuring essay paragraphs and tips on how to avoid them.
I’ve also provided an easy-to-share infographic below that you can share on your favorite social networking site. Please share it if this article has helped you out!
11 Biggest Essay Paragraph Structure Mistakes you’re probably Making
1. Your paragraphs are too short 2. Your paragraphs are too long 3. Your paragraph alignment is ‘Justified’ 4. Your paragraphs are missing a topic sentence 5 . Your paragraphs are missing an explanation sentence 6. Your paragraphs are missing an example 7. Your paragraphs are missing references 8. Your paragraphs are not relevant to the marking criteria 9. You’re trying to fit too many ideas into the one paragraph 10. Your sentences are too long 11. Your quotes are too long

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Number Games for Kids (Free and Easy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Word Games for Kids (Free and Easy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Outdoor Games for Kids
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 50 Incentives to Give to Students
4 thoughts on “11 Rules for Essay Paragraph Structure (with Examples)”
Hello there. I noticed that throughout this article on Essay Writing, you keep on saying that the teacher won’t have time to go through the entire essay. Don’t you think this is a bit discouraging that with all the hard work and time put into your writing, to know that the teacher will not read through the entire paper?

Hi Clarence,
Thanks so much for your comment! I love to hear from readers on their thoughts.
Yes, I agree that it’s incredibly disheartening.
But, I also think students would appreciate hearing the truth.
Behind closed doors many / most university teachers are very open about the fact they ‘only have time to skim-read papers’. They regularly bring this up during heated faculty meetings about contract negotiations! I.e. in one university I worked at, we were allocated 45 minutes per 10,000 words – that’s just over 4 minutes per 1,000 word essay, and that’d include writing the feedback, too!
If students know the truth, they can better write their essays in a way that will get across the key points even from a ‘skim-read’.
I hope to write candidly on this website – i.e. some of this info will never be written on university blogs because universities want to hide these unfortunate truths from students.
Thanks so much for stopping by!
Regards, Chris
This is wonderful and helpful, all I say is thank you very much. Because I learned a lot from this site, own by chris thank you Sir.
Thank you. This helped a lot.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Conferences
- Editorial Process
- Recent Advances
- Sustainability
- Academic Resources

Author Services Guide To Sentence Structure
Correct sentence structure is essential for communicating effectively in English. Knowing how to order words, phrases, and clauses accurately lends clarity and cohesion to your work. This is especially true in academic papers, where quality of expression is paramount.
Here, we delve into how to structure your sentences correctly to present your research accurately and write engagingly.
What is a sentence?
A sentence, at its most basic level, is a series of words that express a complete thought. They can be constructed in many different ways to add variety and engage a reader more effectively. But, fundamentally, every sentence shares crucial components—subjects and verbs, and most also contain objects.
Sentence components
What are subjects, verbs, objects, and complements? These are the smallest components of sentences that are ordered to express the author’s thoughts and findings effectively.
What are subjects?
The term subject is used to described what the sentence is about—the idea, person, place, or thing that is performing an action or being described. Take the following:
Paris is my favourite city.
Earth orbits the Sun.
In the first sentence, the subject ( Paris ) is being described by the author to express an opinion. In the second, it ( Earth ) is directly performing an action that is related to the end component of the sentence.
The subjects of both are placed at the beginning of the sentence, and thus are clearly the main topics.
What are verbs?
The verb is the action that the subject is performing. Or, it is used to link a subject to a description. For example:
The team were tired.
Plants absorb sunlight.
In the first example, the subject ( The team ) is being linked to a state ( tired ) by the verb. These are called linking verbs, which are used to link the subject to additional information that describes a state of being, appearance, etc.
In the second, the subject ( Plants ) are performing an action. These are called action verbs , and can be divided into transitive and intransitive : the former is used to describe verbs that are followed by an object; the latter is used to describe verbs that are not followed by an object, which are the simplest constructions in the English language.
What are objects?
The object of a sentence is the component that is influenced by the subject performing its action. For example:
The man gave them a stern look .
The researcher analysed the data .
Here, both objects add clarity to the sentence, by describing what the subject is concerned with. There are two types of objects: direct and indirect. A direct object is what the subject influences; an indirect object usually comes before the direct object and informs us of who the verb is being performed for. Thus, an indirect object can’t exist without a direct object.
In the first example, the object ( a stern look ) is preceded by an indirect object ( them ), giving us detail of who his action was direct at. In the second, there is only a direct object ( the data ), as the subject is directly influencing this component.
What are complements?
Complements are similar to objects but are used to describe the subject instead of what the subject is influencing. For example:
The new model was a significant improvement .
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas .
In these two examples, the subject is not influencing the end components of the sentence. Instead, these components—the complements—are used to describe the properties of the subjects.
Clauses are made up of the components described above, the use and order of which determine the type of clause used. They can be divided into two categories— independent and dependent clauses.
What are independent clauses?
An independent clause , sometimes referred to as a main clause , is the focal point of the sentence. Such clauses can stand up as sentences in their own right, as they express a complete thought, or be used with other phrases and clauses that provide more detail.
Usually, they follow the order Subject–Verb–Object . For example:
The experiment [ subject ] used [ verb ] the new software [ object ].
But, as suggested before, they can also follow the structures:
- Subject–Verb
- Subject–Verb–Complement
- Subject–Verb–Indirect Object–Direct Object
They can also be used with other clauses to create more complicated constructions.
What are dependent clauses?
A dependent clause , sometimes called a subordinate clause , is used to add more detail to the independent clause . As such, they cannot be used in isolation and must be used in conjunction with a main clause to be grammatically correct. For example:
Because the conditions were too severe , the expedition was delayed.
Here, the clause after the comma is the independent clause—it contains a subject ( the expedition ), verb ( was ), and complement ( delayed ). Thus, the preceding information is not necessary for it to make sense. The independent clause (underlined), however, adds more context to the sentence.
They can be used to provide explanations and detail, such as time or place, as well as add complexity and nuance to the sentence. By using a mixture of clauses, different types of sentences can be created, keeping a reader interested and adding depth to the author’s work.
Sentence types
Much like how the order of words determines the clause type, the number and order of clauses determines the type of sentence used. They can be divided into Simple, Compound, Complex, and Compound–Complex.
What is a simple sentence?
As the name suggests, a simple sentence is the most basic sentence class, made up of just an independent clause. They express a complete thought, with no other detail provided by adjoining clauses.
What is a compound sentence?
A compound sentence is composed of two independent clauses that are joined by a conjunction— e.g., and, for, but, or, etc. For example:
The students collected the samples and then they analysed them in class .
Both underlined parts of the above sentence could be used as single sentences in their own right, as they both contain a subject, verb, and object.
What is a complex sentence?
Complex sentences are made up of one independent clause and at least one dependent clause. For example:
As they had finished their work , they went home for the day.
Underlined is the dependent clause, which couldn’t function on its own as a full sentence—it needs the context provided by the independent clause to make sense. Additionally, it should be noted that multiple dependent clauses can be used with a main clause.
What is a compound–complex sentence?
A compound–complex sentence is a mixture of the last two sentence types—they have at least one dependent clause, as well as two independents. For example:
The researcher conducted the experiment to test their theory and the results were analysed, although the initial findings were inconclusive .
Underlined is the dependent clause, which adds more detail to the two independent clauses that precede it. Again, any number of either clause types can be used in these constructions, but authors should be wary of making their sentences too long-winded and hard to follow.
Varying sentence structure
To conclude, mixing up sentence structure by using different combinations of sentence components, clauses, and types is the key to writing engaging and coherent articles. By applying the principles of sentence construction, researchers can convey meaning effectively and potentially improve the impact of their papers.
If you want to further your knowledge of grammar and punctuation, read our Guide To Word Classes and Guide To Prepositions .

If you want to prepare your research for publication, MDPI Author Services offers high-quality academic editing by PhD specialists in your field. This service offers a detailed report compiled by the Academic Editor, reviewing each section in detail as well as structure, terminology, and more.
Our team of highly skilled English editors have edited over 60,000 papers, with a 97% author satisfaction rate. Our services are available to both MDPI authors and those publishing with other journals. Visit the link above to get a free quote today.
Related posts

Open Science
Using Wastewater as a Fertiliser to Increase Crop Production

MDPI Papers Cited in the News: July 2024

Open Science , Open Access
Clean Energy Research Must Be Open

Spotlight on International Journal of Neonatal Screening
Academic Resources , Open Access , Open Science
Open Access in Switzerland

New Genetic Test to Prevent Inherited Blindness in Dogs
Academic Resources , English Resources , Open Science
Will Artificial Intelligence Replace Academic Editors?
World Hepatitis Day 2024: Test, Treat, Vaccinate.

Monitoring the Impact of Sea Level Rise on Hawaiian Loko’ia

Monitoring the Impact of Hurricanes on Coral Reefs in the Carribbean
Add comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Preference Center
Privacy preferences.
From sharing the latest MDPI blog news, to showcasing our most popular articles, the newsletters will keep you in the loop with everything good going on in the science world.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Learn how to write topic sentences for your research paper paragraphs with this guide from Scribbr. Find out what a topic sentence is, how to write one, and see examples of different types of topic sentences.
Learn the steps and elements of writing a good topic sentence for an essay, with examples and tips. A topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph that states the main idea and directs the flow of the following sentences.
Learn the definition, importance, and types of topic sentences, and get 30+ tips and examples for writing them effectively. A topic sentence introduces the main idea of a paragraph and guides the structure, focus, and tone of your writing.
Learn the purpose, structure and tips for writing effective topic sentences for your introductory and supporting paragraphs. See examples of topic sentences for different types of essays and non-fiction writing.
Topic sentences and signposts make an essay's claims clear to a reader. Good essays contain both. Topic sentences reveal the main point of a paragraph.They show the relationship of each paragraph to the essay's thesis, telegraph the point of a paragraph, and tell your reader what to expect in the paragraph that follows.
How to write a topic sentence. To write a topic sentence, incorporate the following guidelines: Determine the thesis of the essay. Identify the main supports that help prove the thesis. Use each main support to structure a topic sentence for each paragraph. Compose a sentence that answers the following questions: What will the paragraph prove?
1. Avoid introducing yourself. Although topic sentences vary in structure and content from person to person, at least two things can be assumed about your paper: 1) that you have a title and entire paper to introduce a topic, and 2) your personal information is present somewhere on your essay.
How to Write a Topic Sentence: 3 Topic Sentence Examples. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Sep 28, 2022 • 3 min read. Learn how to write topic sentences to support the main thesis of any piece of writing. Explore.
When read in sequence, your essay's topic sentences will provide a sketch of the essay's argument. Thus topics sentences help protect your readers from confusion by guiding them through the argument. But topic sentences can also help you to improve your essay by making it easier for you to recognize gaps or weaknesses in your argument.
The first step is to write the thesis statement. The next step is to outline the paper. A clear outline will help to organize the ideas, research, and evidence into paragraphs. Once the thesis statement and an outline for the paper are created, the topic sentences should be drafted. Be sure your topic sentence reviews what you wrote in the ...
Essentially, it is a concise and direct statement that captures the essence of what you want to convey. A topic sentence is defined by the following characteristics: It is the first sentence of a paragraph. It indicates the main idea of the paragraph. Acts as a signpost and transition sentence, ensuring clarity and cohesiveness of an essay.
Topic Sentence vs. Thesis. A thesis statement could be called the topic sentence of your whole essay. Usually, you will want to write your thesis statement before writing your topic sentences. When you've written both, you have the outline. So after doing all nine steps, you should find writing the paper easy.
Conclusion. A topic sentence is one which appears, usually (but not always) at the beginning of each paragraph of an essay. The topic sentence is used to layout the ideas and arguments that will be covered within the paragraph and should be carefully planned out to ensure that they are clear enough to give the reader an idea of what will be ...
Typically, the topic sentence is at the beginning or end and presents a general idea, while supporting sentences provide details or examples. Ensure every sentence in the paragraph relates to the topic sentence. If writing, after drafting, discern the main theme and craft a topic sentence based on it.
A bad example of a topic sentence would be: Dogs are good. While most people agree with that statement, it is too broad to make a good topic sentence. Yes, it lets the readers know that you will be writing about dogs and that it will be positive, but they have no idea where that topic will go. Your topic sentence needs to do more than tell the ...
It's simple enough. A topic sentence is the one sentence in a paragraph—usually the first—that informs readers of what's to come. Your topic sentence is like a mini-thesis statement. It provides important context and lets the reader anticipate what's ahead. It introduces the main idea of a paragraph and supports the details that follow.
Step#1 Clearly State The Main Idea. A topic sentence is the first paragraph of the paragraph. It must clearly explain the particular subject that would be discussed in the paragraph. This should be stated in very clear language so that the reader can easily understand the idea.
The topic sentence contains two parts: the topic and a controlling idea. The topic is WHAT the paragraph is going to be about, and the controlling idea explains WHY the paragraph is being written. The topic sentence helps your reader understand the purpose of your paragraph. II. Examples of a Topic Sentence.
How To Write A Topic Sentence | Essay Writing Part 3. Struggling to write a sustained argument? Read this post to learn how to write a topic sentence that connect to your thesis statement.
Elementary students often write simple topic sentences that focus solely on the main idea of the paragraph. Some examples of topic sentences for this age group include: When we had a snow day, I made snow angels, drank hot cocoa, and went sledding. Students should not have to do homework because it takes a lot of time.
Topic sentences help keep your writing focused and guide the reader through your argument. In an essay or paper, each paragraph should focus on a single idea. By stating the main idea in the topic sentence, you clarify what the paragraph is about for both yourself and your reader. ... When writing an essay outline for yourself, the choice is ...
The topic sentence joins sentences of a given paragraph, backs up what the paper claims, explains what a paragraph says, and claims mini thesis statements. Tips for Writing a Topic Sentence for an Argumentative Essay. Here are 4 useful tips that will help you write a good topic sentence for an argumentative essay: 1. Use New Information
4. Your paragraphs must have a Topic Sentence. The first sentence of an essay paragraph is called the topic sentence. This is one of the most important sentences in the correct essay paragraph structure style. The topic sentence should convey exactly what key idea you're going to cover in your paragraph.
To conclude, mixing up sentence structure by using different combinations of sentence components, clauses, and types is the key to writing engaging and coherent articles. By applying the principles of sentence construction, researchers can convey meaning effectively and potentially improve the impact of their papers.