Literary Theory and Criticism
Home › Journal › Top Scopus Indexed Journals in English Literature

Top Scopus Indexed Journals in English Literature
By NASRULLAH MAMBROL on June 15, 2020 • ( 0 )
1. English Historical Review -(OXFORD) (https://academic.oup.com/ehr/pages/About)
2. ASIATIC: IITUM Journal of English Language & Literature ( https://journals.iium.edu.my/asiatic/index.php/AJELL )
3. English for Specific Purposes ( https://www.journals.elsevier.com/english-for-specific-purposes )
4. The Australian Association for the Teaching of English (AATE) ( https://www.aate.org.au/journals/english-in-australia )
5. English in Education (Wiley) ( https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/17548845 )
6. English World-Wide | A Journal of Varieties of English ( https://benjamins.com/catalog/eww )
7. European Journal of English Studies– Taylor & Francis Online ( https://www.tandfonline.com/toc/neje20/current )
8. Journal of English for Academic Purposes – Elsevier B.V. ( https://www.journals.elsevier.com/journal-of-english-for-academic-purposes )
9. Journal of English Linguistics- SAGE Journals ( https://journals.sagepub.com/home/eng )
10. Research in the Teaching of English-NCTE ( https://www2.ncte.org/resources/journals/research-in-the-teaching-of-english/ /)
11. The English Classroom – Regional Institute of English ( http://www.riesielt.org/english-classroom-journal )
12. World Englishes (Wiley Blackwell) ( https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/1467971x )
13. English Language & Linguistics – Cambridge Core ( https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/english-language-and-linguistics )
14. English Today-The International Review of the English Language-Cambridge Core ( https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/english-today )
Share this:
Categories: Journal
Tags: Best Scopus Indexed Journals in English Literature , Free Scopus Indexed Journals in English Literature , Gnuine Scopus Indexed Journals in English Literature , Journals in English Literature , Literary Theory , Scopus Indexed Journals , Top Scopus Indexed Journals in English , Top Scopus Indexed Journals in English Literature , UGC Approved Journals , UGC Approved Journals in English
Related Articles

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- All subject areas
- Agricultural and Biological Sciences
- Arts and Humanities
- Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology
- Business, Management and Accounting
- Chemical Engineering
- Computer Science
- Decision Sciences
- Earth and Planetary Sciences
- Economics, Econometrics and Finance
- Engineering
- Environmental Science
- Health Professions
- Immunology and Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics
- Multidisciplinary
- Neuroscience
- Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics
- Physics and Astronomy
- Social Sciences
- All subject categories
- Acoustics and Ultrasonics
- Advanced and Specialized Nursing
- Aerospace Engineering
- Agricultural and Biological Sciences (miscellaneous)
- Agronomy and Crop Science
- Algebra and Number Theory
- Analytical Chemistry
- Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine
- Animal Science and Zoology
- Anthropology
- Applied Mathematics
- Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology
- Applied Psychology
- Aquatic Science
- Archeology (arts and humanities)
- Architecture
- Artificial Intelligence
- Arts and Humanities (miscellaneous)
- Assessment and Diagnosis
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atmospheric Science
- Atomic and Molecular Physics, and Optics
- Automotive Engineering
- Behavioral Neuroscience
- Biochemistry
- Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology (miscellaneous)
- Biochemistry (medical)
- Bioengineering
- Biological Psychiatry
- Biomaterials
- Biomedical Engineering
- Biotechnology
- Building and Construction
- Business and International Management
- Business, Management and Accounting (miscellaneous)
- Cancer Research
- Cardiology and Cardiovascular Medicine
- Care Planning
- Cell Biology
- Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience
- Ceramics and Composites
- Chemical Engineering (miscellaneous)
- Chemical Health and Safety
- Chemistry (miscellaneous)
- Chiropractics
- Civil and Structural Engineering
- Clinical Biochemistry
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Colloid and Surface Chemistry
- Communication
- Community and Home Care
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Complementary and Manual Therapy
- Computational Mathematics
- Computational Mechanics
- Computational Theory and Mathematics
- Computer Graphics and Computer-Aided Design
- Computer Networks and Communications
- Computer Science Applications
- Computer Science (miscellaneous)
- Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
- Computers in Earth Sciences
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Conservation
- Control and Optimization
- Control and Systems Engineering
- Critical Care and Intensive Care Medicine
- Critical Care Nursing
- Cultural Studies
- Decision Sciences (miscellaneous)
- Dental Assisting
- Dental Hygiene
- Dentistry (miscellaneous)
- Dermatology
- Development
- Developmental and Educational Psychology
- Developmental Biology
- Developmental Neuroscience
- Discrete Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Drug Discovery
- Drug Guides
- Earth and Planetary Sciences (miscellaneous)
- Earth-Surface Processes
- Ecological Modeling
- Ecology, Evolution, Behavior and Systematics
- Economic Geology
- Economics and Econometrics
- Economics, Econometrics and Finance (miscellaneous)
- Electrical and Electronic Engineering
- Electrochemistry
- Electronic, Optical and Magnetic Materials
- Emergency Medical Services
- Emergency Medicine
- Emergency Nursing
- Endocrine and Autonomic Systems
- Endocrinology
- Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism
- Energy Engineering and Power Technology
- Energy (miscellaneous)
- Engineering (miscellaneous)
- Environmental Chemistry
- Environmental Engineering
- Environmental Science (miscellaneous)
- Epidemiology
- Experimental and Cognitive Psychology
- Family Practice
- Filtration and Separation
- Fluid Flow and Transfer Processes
- Food Animals
- Food Science
- Fuel Technology
- Fundamentals and Skills
- Gastroenterology
- Gender Studies
- Genetics (clinical)
- Geochemistry and Petrology
- Geography, Planning and Development
- Geometry and Topology
- Geotechnical Engineering and Engineering Geology
- Geriatrics and Gerontology
- Gerontology
- Global and Planetary Change
- Hardware and Architecture
- Health Informatics
- Health Information Management
- Health Policy
- Health Professions (miscellaneous)
- Health (social science)
- Health, Toxicology and Mutagenesis
- History and Philosophy of Science
- Horticulture
- Human Factors and Ergonomics
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Immunology and Allergy
- Immunology and Microbiology (miscellaneous)
- Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering
- Industrial Relations
- Infectious Diseases
- Information Systems
- Information Systems and Management
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Insect Science
- Instrumentation
- Internal Medicine
- Issues, Ethics and Legal Aspects
- Leadership and Management
- Library and Information Sciences
- Life-span and Life-course Studies
- Linguistics and Language
- Literature and Literary Theory
- LPN and LVN
- Management Information Systems
- Management, Monitoring, Policy and Law
- Management of Technology and Innovation
- Management Science and Operations Research
- Materials Chemistry
- Materials Science (miscellaneous)
- Maternity and Midwifery
- Mathematical Physics
- Mathematics (miscellaneous)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Mechanics of Materials
- Media Technology
- Medical and Surgical Nursing
- Medical Assisting and Transcription
- Medical Laboratory Technology
- Medical Terminology
- Medicine (miscellaneous)
- Metals and Alloys
- Microbiology
- Microbiology (medical)
- Modeling and Simulation
- Molecular Biology
- Molecular Medicine
- Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
- Nature and Landscape Conservation
- Neurology (clinical)
- Neuropsychology and Physiological Psychology
- Neuroscience (miscellaneous)
- Nuclear and High Energy Physics
- Nuclear Energy and Engineering
- Numerical Analysis
- Nurse Assisting
- Nursing (miscellaneous)
- Nutrition and Dietetics
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Therapy
- Ocean Engineering
- Oceanography
- Oncology (nursing)
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Surgery
- Organic Chemistry
- Organizational Behavior and Human Resource Management
- Orthodontics
- Orthopedics and Sports Medicine
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Paleontology
- Parasitology
- Pathology and Forensic Medicine
- Pathophysiology
- Pediatrics, Perinatology and Child Health
- Periodontics
- Pharmaceutical Science
- Pharmacology
- Pharmacology (medical)
- Pharmacology (nursing)
- Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics (miscellaneous)
- Physical and Theoretical Chemistry
- Physical Therapy, Sports Therapy and Rehabilitation
- Physics and Astronomy (miscellaneous)
- Physiology (medical)
- Plant Science
- Political Science and International Relations
- Polymers and Plastics
- Process Chemistry and Technology
- Psychiatry and Mental Health
- Psychology (miscellaneous)
- Public Administration
- Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health
- Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine
- Radiological and Ultrasound Technology
- Radiology, Nuclear Medicine and Imaging
- Rehabilitation
- Religious Studies
- Renewable Energy, Sustainability and the Environment
- Reproductive Medicine
- Research and Theory
- Respiratory Care
- Review and Exam Preparation
- Reviews and References (medical)
- Rheumatology
- Safety Research
- Safety, Risk, Reliability and Quality
- Sensory Systems
- Signal Processing
- Small Animals
- Social Psychology
- Social Sciences (miscellaneous)
- Social Work
- Sociology and Political Science
- Soil Science
- Space and Planetary Science
- Spectroscopy
- Speech and Hearing
- Sports Science
- Statistical and Nonlinear Physics
- Statistics and Probability
- Statistics, Probability and Uncertainty
- Strategy and Management
- Stratigraphy
- Structural Biology
- Surfaces and Interfaces
- Surfaces, Coatings and Films
- Theoretical Computer Science
- Tourism, Leisure and Hospitality Management
- Transplantation
- Transportation
- Urban Studies
- Veterinary (miscellaneous)
- Visual Arts and Performing Arts
- Waste Management and Disposal
- Water Science and Technology
- All regions / countries
- Asiatic Region
- Eastern Europe
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Northern America
- Pacific Region
- Western Europe
- ARAB COUNTRIES
- IBEROAMERICA
- NORDIC COUNTRIES
- Afghanistan
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brunei Darussalam
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- Russian Federation
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Switzerland
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Trinidad and Tobago
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Vatican City State
- Book Series
- Conferences and Proceedings
- Trade Journals

- Citable Docs. (3years)
- Total Cites (3years)

| Title | Type | --> | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | journal | 1.607 Q1 | 17 | 15 | 45 | 822 | 163 | 43 | 1.67 | 54.80 | 57.14 | ||
| 2 | journal | 1.445 Q1 | 46 | 40 | 123 | 3097 | 619 | 119 | 4.22 | 77.43 | 40.87 | ||
| 3 | journal | 1.222 Q1 | 6 | 23 | 58 | 767 | 32 | 57 | 0.82 | 33.35 | 26.09 | ||
| 4 | journal | 1.214 Q1 | 31 | 17 | 45 | 993 | 200 | 45 | 2.42 | 58.41 | 69.64 | ||
| 5 | journal | 1.130 Q1 | 73 | 44 | 130 | 2054 | 466 | 128 | 3.84 | 46.68 | 50.00 | ||
| 6 | journal | 0.929 Q1 | 34 | 116 | 191 | 5181 | 375 | 179 | 1.80 | 44.66 | 56.02 | ||
| 7 | journal | 0.858 Q1 | 76 | 40 | 189 | 2813 | 454 | 185 | 2.31 | 70.33 | 38.36 | ||
| 8 | journal | 0.752 Q1 | 63 | 36 | 58 | 2530 | 167 | 58 | 2.05 | 70.28 | 61.19 | ||
| 9 | journal | 0.629 Q1 | 48 | 57 | 179 | 1678 | 327 | 172 | 1.76 | 29.44 | 45.16 | ||
| 10 | journal | 0.586 Q1 | 10 | 12 | 72 | 507 | 120 | 71 | 0.90 | 42.25 | 33.33 | ||
| 11 | journal | 0.501 Q1 | 18 | 23 | 72 | 1178 | 91 | 69 | 1.15 | 51.22 | 62.96 | ||
| 12 | journal | 0.488 Q1 | 7 | 12 | 39 | 559 | 45 | 39 | 1.14 | 46.58 | 45.00 | ||
| 13 | journal | 0.477 Q1 | 10 | 53 | 114 | 2500 | 244 | 114 | 2.38 | 47.17 | 45.16 | ||
| 14 | journal | 0.463 Q1 | 20 | 24 | 52 | 1152 | 53 | 52 | 1.09 | 48.00 | 60.38 | ||
| 15 | journal | 0.454 Q1 | 21 | 44 | 49 | 2419 | 85 | 46 | 2.54 | 54.98 | 41.35 | ||
| 16 | journal | 0.446 Q1 | 7 | 23 | 67 | 1207 | 82 | 67 | 1.49 | 52.48 | 50.00 | ||
| 17 | journal | 0.429 Q1 | 3 | 27 | 72 | 1339 | 27 | 70 | 0.36 | 49.59 | 52.17 | ||
| 18 | journal | 0.422 Q1 | 20 | 94 | 115 | 830 | 88 | 87 | 0.49 | 8.83 | 58.70 | ||
| 19 | journal | 0.409 Q1 | 16 | 20 | 69 | 799 | 88 | 69 | 1.21 | 39.95 | 62.50 | ||
| 20 | journal | 0.405 Q1 | 20 | 37 | 135 | 1267 | 109 | 93 | 0.87 | 34.24 | 67.74 | ||
| 21 | journal | 0.402 Q1 | 24 | 33 | 96 | 1077 | 101 | 75 | 0.97 | 32.64 | 68.18 | ||
| 22 | journal | 0.390 Q1 | 18 | 21 | 88 | 1243 | 101 | 87 | 1.07 | 59.19 | 55.81 | ||
| 23 | journal | 0.387 Q1 | 36 | 20 | 71 | 1012 | 75 | 68 | 0.98 | 50.60 | 51.85 | ||
| 24 | journal | 0.386 Q1 | 54 | 61 | 157 | 3135 | 126 | 148 | 0.61 | 51.39 | 33.71 | ||
| 25 | journal | 0.385 Q1 | 5 | 45 | 155 | 1072 | 49 | 155 | 0.41 | 23.82 | 40.35 | ||
| 26 | journal | 0.382 Q1 | 5 | 21 | 46 | 806 | 46 | 46 | 1.46 | 38.38 | 83.33 | ||
| 27 | journal | 0.366 Q1 | 19 | 57 | 178 | 2707 | 220 | 178 | 0.94 | 47.49 | 50.00 | ||
| 28 | journal | 0.364 Q1 | 11 | 90 | 193 | 4414 | 310 | 193 | 1.48 | 49.04 | 47.11 | ||
| 29 | journal | 0.363 Q1 | 19 | 52 | 142 | 1674 | 101 | 129 | 0.57 | 32.19 | 71.25 | ||
| 30 | journal | 0.360 Q1 | 4 | 49 | 75 | 1990 | 23 | 75 | 0.28 | 40.61 | 42.86 | ||
| 31 | journal | 0.360 Q1 | 11 | 43 | 127 | 1301 | 58 | 123 | 0.36 | 30.26 | 52.94 | ||
| 32 | journal | 0.349 Q1 | 14 | 29 | 81 | 1111 | 72 | 68 | 1.16 | 38.31 | 70.83 | ||
| 33 | journal | 0.349 Q1 | 5 | 127 | 412 | 2342 | 89 | 412 | 0.19 | 18.44 | 47.15 | ||
| 34 | journal | 0.344 Q1 | 13 | 17 | 71 | 717 | 33 | 64 | 0.46 | 42.18 | 57.14 | ||
| 35 | journal | 0.337 Q1 | 43 | 47 | 97 | 2432 | 65 | 95 | 0.70 | 51.74 | 45.10 | ||
| 36 | journal | 0.335 Q1 | 5 | 29 | 94 | 698 | 44 | 94 | 0.55 | 24.07 | 72.73 | ||
| 37 | journal | 0.333 Q1 | 28 | 37 | 131 | 2578 | 68 | 125 | 0.57 | 69.68 | 32.43 | ||
| 38 | journal | 0.328 Q1 | 5 | 61 | 193 | 1240 | 49 | 192 | 0.25 | 20.33 | 77.42 | ||
| 39 | journal | 0.327 Q1 | 4 | 22 | 94 | 866 | 29 | 90 | 0.25 | 39.36 | 42.86 | ||
| 40 | journal | 0.323 Q1 | 19 | 71 | 170 | 2647 | 172 | 169 | 0.76 | 37.28 | 55.96 | ||
| 41 | journal | 0.323 Q1 | 26 | 13 | 28 | 544 | 49 | 28 | 1.35 | 41.85 | 50.00 | ||
| 42 | journal | 0.322 Q1 | 7 | 118 | 330 | 3583 | 71 | 320 | 0.23 | 30.36 | 42.99 | ||
| 43 | journal | 0.320 Q1 | 10 | 15 | 52 | 1693 | 27 | 52 | 0.46 | 112.87 | 18.75 | ||
| 44 | journal | 0.313 Q1 | 22 | 22 | 68 | 959 | 72 | 66 | 1.06 | 43.59 | 71.43 | ||
| 45 | journal | 0.313 Q1 | 14 | 9 | 25 | 828 | 22 | 25 | 0.40 | 92.00 | 10.00 | ||
| 46 | journal | 0.307 Q1 | 4 | 33 | 101 | 664 | 39 | 99 | 0.52 | 20.12 | 22.22 | ||
| 47 | journal | 0.306 Q1 | 22 | 16 | 62 | 698 | 55 | 61 | 0.66 | 43.63 | 62.50 | ||
| 48 | journal | 0.305 Q1 | 3 | 11 | 31 | 374 | 6 | 31 | 0.20 | 34.00 | 27.27 | ||
| 49 | journal | 0.305 Q1 | 5 | 17 | 71 | 672 | 33 | 67 | 0.55 | 39.53 | 52.38 | ||
| 50 | journal | 0.302 Q1 | 8 | 21 | 83 | 1574 | 22 | 83 | 0.18 | 74.95 | 28.57 |

Follow us on @ScimagoJR Scimago Lab , Copyright 2007-2024. Data Source: Scopus®

Cookie settings
Cookie Policy
Legal Notice
Privacy Policy
Current Issue

https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10448030
c o n t e n t s.
01 | Reddygari Yamini | Deconstructing Boundaries: Githa Hariharan’s Application of Critical Literary Theories in ‘The Thousand Faces of Night’
| 01-10 |
|
02 | Ela Kaushikee & Prof. Sumitra Kukreti | Examining Resistance and Rebellion: Unveiling Sujata’s Journey in
| 11-21 |
|
03 | Dr. Pankaj B. Vaishnav | Naipaul’s Distorted Understanding of Indian Socio-Political and Cultural Aspects in
| 22-33 |
|
04 | Dr Diksha Shukla | Security Implications of Climate Change in
| 34-43 |
|
05 | Harshaurya Kaur & Dr. Diksha Sharma | Transcending Illusions: Siddhartha’s Path to Self-Realization through Shankaracharya’s Advaita Vedanta
| 44-55 |
|
06 | Dr. J. Sareen | : A Cruise on the Waves of Curses?
| 56-67 |
|
07 | Dr. Dev Kant Sharma | Unearthing the Feministic Perspective: A Study of Amitav Ghosh’s
| 68-77 |
|
08 | Sandhani Dutta | Dissolving Boundaries: A Study of Nitoo Das’s Poem
| 78-85 |
|
09 | Poulami Malakar & Dr. Prajna Paramita Panigrahi | Cultural and Personal Isolation in Jhumpa Lahiri’s Novels
| 86-93 |
|
10 | Nirbachita Giri | Spiritual Quest for Self-understanding: Metamorphosis of Raju in R.K. Narayan’s
| 94-100 |
|
11 | Sushmitha B P | Unveiling the Saga of a Women during the Pre-Partition Period: A Feminist Analysis of Amrita Pritam’s
| 101-109 |
|
12 | Dr Mohd Faiez | The Making of a Woman: Manju Kapur’s as a Novel of Stereotypical Gender Roles
| 110-117 |
|
13 | Soumyadeb Roy | Re-searching “A House for Mr. Biswas”: An Interdisciplinary Analysis
| 118-133 |
|
14 | Dr. Phani Kiran & Brindha B | Unearthing Harmony: Tagore’s through an Ecofeminist Light
| 134-144 |
|
15 | Mudita Choudhary & Dr. Veerendra Mishra | Deconstructing the Absurd: Violence, Ideology and Othering in Badal Sircar’s
| 145-157 |
|
16 | Adithi M J | Unveiling R K Narayan’s : A Treasure of Wit and Wisdom
| 158-168 |
|
17 | Deepika R Nair, Sreya R Nair & Dr. Indu B | Humanitarian Quandary: Mourning, Violence and Precarity in Easterine Kire’s
| 169-183 |
|
18 | Prakhar Medhavi & Dr. Vikash Mohan Sahay | Tracing Feminist Waves in Arundhati Roy’s Novels Through Beauvoirian and Cixousian Approaches
| 184-194 |
|
19 | Dr. Garima Jain | From the Sundarbans to Venice: Environmental Crisis and Postcolonial Contexts in Amitav Ghosh’s
| 195-203 |
|
20 | Dr. Geeta | The Unheard Story of a Banjara Warrior: With Special Reference to a Play (2018)
| 204-212 |
|
21 | Sampurna Chatterjee | A Study of by Perumal Murugan: Evaluating Social Conventions, Natural Laws, and Human Choices to Find Purpose in a Changing World
| 213-221 |
|
22 | Prachi Sharma | Blurring the Boundary between Fact and Fiction in by Chitra Banerjee Divakaruni: A Study
| 222-230 |
|
23 | Dr Neelam Mulchandani | Analyzing the Traditional Gender Roles in Anita Nair’s
| 231-240 |
|
01 | Ahinasha N.S. | The Poetic Wisdom of Romantic Love: An Exploration of Gabriel Garcia Marquez’s
| 241-250 |
|
02 | Riya | Spectator to Spect-actor: Audience Engagement in Augusto Boal’s Theatre of the Oppressed
| 251-258 |
|
03 | Aparajita Hazra | Of Memory, Trauma and the Gothic: Reading Keith Thomas’s
| 259-269 |
|
04 | Dhanapati Sharma | Aligning Spirituality and Development: The Role of Buddhism in Bhutan’s Gross National Happiness
| 270-277 |
|
05 | Ann Mary Manuel Chemparathy | The Magic of Nature and the Realism of Social Alienation: A Reading of Marquez’s
| 278-286 |
|
06 | Anjali Parmar & Dr Saurabh Kumar | Magical Realism: An Aide in Exploring the Self in ‘The Pilgrimage’ and ‘The Alchemist’
| 287-294 |
|
07 | Poorva Gulati & Shubhangi | Food and Clothing as Cultural Metaphors in Select Diasporic Fictions
| 295-308 |
|
01 | Dr. Ajaz Ahmad | Reconciling Existential and Mystical Elements in T. S. Eliot’s Poetry
| 309-323 |
|
02 | Dr. Vinaya Bhaskaran | Speaking for the Silenced: Medical Exploitation and Power Dynamics in Rebecca Skloot’s
| 324-334 |
|
03 | D. Mohanapriya & Dr. S. Geetha | Anthropocentric Infliction of War Over Water Reflected in Paolo Bacigalupi’s
| 335-342 |
|
04 | Shubhi Sharma | Resilience and Survival in the Face of Adversity: A Study of James Ragan’s Poetic Themes
| 343-351 |
|
05 | Jonitha Joyson | Fragmented Voices: Analysing Trauma and Neglect in Kimberly Brubaker Bradley’s
| 352-362 |
|
01 | Dr. Pinki Negi Bora | Endorsement of Destruction and Damnation of Unconventional Women in Thomas Hardy’s
| 363-376 |
|
02 | Dr. Tanvi Garg | Hysteria Beyond Gender: Analyzing Male and Female Perspectives in
| 377-386 |
|
03 | Ali Oublal | Wittgenstein’s Seeing-as Approach to Literary Propositions The novel by Daisy Johnson as a Case Study
| 387-401 |
|
04 | Dr. Arati Sinha | George Orwell’s Vision of Life
| 402-408 |
|
01 | Chisti Das & Soumya Sangita Sahoo | Men and Masculinity in Contemporary Fiction
| 409-418 |
|
02 | Qudsia Ahmad & Dr. Sahar Rahman | Popular but not Prized: A Cultural Perspective on Popular Fiction
| 419-425 |
|
03 | Dr. Reema Chaudhary | Writing to Heal: Exploring Narrative Therapy in Autobiographical Writings
| 426-435 |
|
04 | Devendra Kumar Katroliya | Posthumanism in Contemporary Literature: A Critical Analysis of Theory, Themes, and Texts
| 436-447 |
|
01 | Aswathy A | Exploring “fat-positive” Mainstream Indian Cinema: An Analysis of their Structural Similarities
| 448-455 |
|
02 | Shefin. S | Intercultural Adaptations of Shakespeare’s in Kerala: Assimilation and Juxtapositioning of Lady Macbeth in Jayaraj’s and Ettumanoor Kannan’s
| 456-466 |
|
03 | Dharmendra Kumar | Hermeneutics of Pyasa: The Elusive Identity of Vijay
| 467-481 |
|
01 | Ashish Awasthi & Dr. Ram Prakash Gupt | Race and Gender Intersectionality in Nadine Gordimer’s
| 482-491 |
|
01 | Karobi Dutta & Dr. Swati Kiran | Multicultural Education in Assam: A Content Analysis of Assamese Textbooks in the 21st Century
| 492-502 |
|
01 | Dr. Aswathy Balachandran | Sthayibhava | 503 |
|
02 | Jasiya Manzoor | Undefeated Warriors | 504-505 |
|
03 | Mariyumma VK | Passage to the North | 506-507 |
|
04 | Masum Ahmed | The Rain-bathed Road | 508-509 |
|
05 | Sahil Mudasir | Womanhood | 510-512 |
|
06 | Dr. R. Prabhakar | The Pain of Ageing | 513-514 |
|
07 | Pramod Rastogi | A Piece of Shroud | 515-516 |
|
08 | Dr. Damuluri Venkateswar Rao | Lighting The Lamp: Invocation of a Muse! | 517 |
|
09 | Riyaz Ahmad Dantoo | Hollow Promises | 518-519 |
|
10 | Vivek Vilas Salve | All are Authors | 520 |
|
01 | P R Gopalakrishnan | Bastard | 521-529 |
|
02 | Yash Mali | Stationed in Suspense: Three Nights at the Railway Station | 530-534 |
|
01 | Dr Jan Mudasir Gul | Akh Dour (Once Upon a Time) Translated by: Qaisar Bashir | 535-537 |
|
02 | Dr. Julia Devardhi | by Katamneni Gopichand | 538-541 |
|
03 | Renu Dhotre | by P. V. Laxmiprasad | 542-549 |
|
04 | Saira Tak | by Rattan Lal Shant | 550-554 |
|
*****************************************************************************************************************************
Indexed/Abstracted/Included in
Indexing and Abstracting: The journal has been included in the following prestigious directories and the contents are indexed/abstracted/ included/ Cataloged there for wider dissemination and access:
WhatsApp us
- Author Guidelines
- Current Issue
- ISSN :2395-2636(P) : 2321 – 310 8(E)
Submission open for the Vol.12 Issue 3: 2024; July-Sept Issue
Subscribe rjelal journal to your library with low cost just 4000rs for one year.
Research Journal of English Language and Literature (RJELAL) an International Journal open access print and online, indexed, peer reviewed and refereed journal that provides rapid publication (quarterly) of articles in all areas Related to English Language and Literature, Linguistics of the subject. Philosophy of RJELAL guides it to map new frontiers in emerging and developing areas in research, Teaching, industry and governance as well as to link with centers of excellence worldwide to stimulate young minds for creating knowledge based community
NOTE: The submission must not have been previously published, nor should it be under consideration for publication elsewhere. We also have a strict policy against plagiarism. The plagiarism is checked through two methods: reviewer check and plagiarism prevention tool. All submissions will be checked by online software before being sent to reviewers. Editor in Chief having the right to publish or reject the article in pre or post publication updated on 01-08-2015
Journal Keywords: English Literature Journal, Print Journal, Linguistics Journal, ELT Journal, International Journal of English Literature, Indian Journal, English Literature Journal, Online English Journal, Indexed journal, English Language Journal, English Journal With Impact Factor
Submission: Article in MS Word format submit to [email protected]
Please check your article format before submission to RJELAL: Title, Author and Affiliation with email address, Abstract, Key words (4-5), Introduction, Discussion, Acknowledgement (if any) References (not less less than 4-5) Annexure (if any)
The Research Journal of English Language and Literature (RJELAL) is seeking volunteer full and junior members to join its National/International Editorial Board who support our mission, values, and commitment to provide a high-quality experience for our authors. Positions will begin January 1, 2023
| 1,2,3School of Humanities and Social Sciences, Department of Linguistics: Pwani University; Kilifi, Kenya Email: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected] | ||
| 1Research Scholar, C.C.S University, Meerut 2Assistant Professor, K.M.G.G.P.G. College, Badalpur (G.B. Nagar) | ||
| 1Research Scholar, CSJM University (PPN PG College Campus), Pin-208001 (UP) E-mail: [email protected] 2Dept. of English, PPN PG College Campus), Pin-208001 (UP) E-mail: [email protected]. | ||
| Assistant Professor, Department of English, Jhanji Hemnath Sarma College, Sivasagar (District), Assam, India Email: [email protected]. | ||
| Lecturer in English, Hindu College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India. | ||
| Associate Professor of English Hindu College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, | ||
| Assistant Professor, Department of English, Haringhata Mahavidyalaya | ||
| M.A. in English, Rabindra Bharati University, Kolkata Email: [email protected] | ||
| 1Teacher in English, Shree Vivekanand High School, Manekpur Email:[email protected] 2Assistant Professor of English, Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam Govt. College, Silvassa. Email:[email protected]. | ||
| Lecturer in English, KRK Govt. Degree College, Addanki -523201, Bapatla District, Andhra Pradesh. | ||
| Please note that this journal issue is still being developed and that the contents listed here are tentative. |
Types of papers accepting
Original Research Articles
Super Express Papers : Research Article Needs to Publish within short period (2-3 working days after submissions)
Review Articles ; Short Communications
Letters to the editors and book reviewers
Papers presented in national and International Seminars .
Scope of the Journal
Research Journal of English Language and Literature ( RJELAL ) is an open access journal that provides rapid publication (quarterly) of articles in all areas Related to English Language and Literature of the subject.
The scopes of the journal include, but are not limited to, the following topics:
Literatures written in the English language, English linguistics, English sociolinguistics, translation studies and related areas, African literatures, literature appreciation, cultural studies, literary styles, Asian English’s as well as Asian literatures in English, including Asian diasporic literature and Asian literatures in translation, the connection between stylistics, critical theory, linguistics and literary criticism, and their applications in teaching to native and non-native speaking students, CALL; CLT and TBLT ;Computational Linguistics ;Corpus linguistics; Discourse and Inter language Pragmatics ; Discourse and Organization; ELT Materials Development and Evaluation; English Globalization English Language Teacher Education.... .More
Publication Fee
Open access publishing is not without costs. RJELAL therefore charges (See Below) as Article Processing Charge for each article accepted for publication after double-blind review. We routinely waive charges for authors from low-income countries. For other countries, article-processing charge waivers or discounts are granted on a case-by-case basis to authors with insufficient funds. Authors can apply for a waiver or discount during the submission process
___Research Article, Review & Short Communications: For Authors Affiliated to Indian Institutions 2000Rs/For Others 100US$ (online only),
_____Express mode: 3000Rs for Indian Authors,150$ for Others (Publish within 72 hours) online only*
_____For Printed copy :1000Rs (Indian Address)
______For Others: one printed copy 55US$ + Shipping charge depending upon origin country * contact editor for more details & Conditions Apply
Submission open for
Vol.12.issue 3:2024, impact factor: 6.8992.
https://doi.org/10.33329 /rjelal
RJELAL Started in 2013-till to date
KY PUBLICATIONS JOURNALS
| Payment via Paypal Use the Following link |
| RJELAL-google Scholar Citations (as on 13-04-2024)
|
| RJELAL is in UGC list (Valid Up to 2018) for more information |
| |
Journal Issues
| Author Agreement form in RJELAL Publication Fee | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
 Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more. Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars. English and American Literature
Using BobCat to Find Literature JournalsOne of the best methods of staying current with your field is by browsing the journal literature. Literature journals help you keep up with the latest scholarship and provide potential venues for publishing your own research. The numerous online databases available to you through the library allow you to search through the contents of these journals (and many others), but browsing through an individual journal will allow you the opportunity for more specific topic research. You can use the advanced search options in BobCat , the NYU Libraries' catalog, to limit the material type to "Journal" while searching for a subject or keyword of your choice. Here are some sample subject searches, limited to journals:
Try adding in additional terms to narrow your search down, or use the "Tweak my results" options on the left side of the page if you're getting too many results. If this method doesn't work for you, you may want to look at a more specialized list of journals (see "Using the MLA Directory of Periodicals" below). Using the MLA Directory of Periodicals to Find Literature JournalsIf you want to look at a list of journals for any topic within literary studies, try the MLA Directory of Periodicals (DOP). Each entry in the DOP provides information about the journal's scope, subject matter, publication schedule, editors, submission guidelines, peer review status, and more. You can access the DoP from within the MLA International Bibliography database, or directly through its own link (below and in the library's Articles & Databases portal). The video below, from the Modern Language Association, explains the basics of using the DoP.
What Is the MLA Directory of Periodicals? (on EBSCO) from Modern Language Association on Vimeo . Closed captioning is available through the Vimeo platform. No transcript is available. This video is one of many MLA International Bibliography tutorials available on the MLA's own website. A Sampling of Literature JournalsHere is a small sampling of the literature journals available to you through the library:
Need to find out if a journal is peer-reviewed? Use Ulrichs

English Language and Literature: Journals
A journal is a regular publication (monthly, yearly, etc.) in which you will find academic and research articles. The articles present current research and are critiqued by experts before publication, so you can be confident of their quality. The majority of journals held by the Bodleian Libraries in both physical and electronic formats can be searched via SOLO , as can the individual articles within ejournals. On this page you will find relevant journals and periodicals, and guidance on how to search for and access print and ejournals. DefinitionsTerms you may encounter in your research. Journal: A regular publication of academic and research articles. Serial: A broad term that refers to items published in a series but the items are separate and standalone. Examples include indexes, yearbooks and some journals. Periodical: A regular publication that includes articles, stories and other text. Magazines and newspapers are examples of these. Conference proceedings: The published record of a conference. Full-text: This means you can read the item in full from beginning to end, not just the abstract or summary. Platform: This refers to the site on which you can find and access the journal. Finding journal articlesYou can search for journal articles via SOLO , if you use the 'Articles' option. You can refine a regular search to articles only via the 'resource type' filter. If you're interested in searching for articles on a particular topic, it's best to use a bibliographic database like the MLA International Bibliography or ABELL - see the Bibliographic Databases page of this guide for more information. Electronic journals (e-journals)
Ejournals are digital versions of select types of regular publications. Broadly speaking they come in two forms: they are either 'born digital' or are digital reproductions of physical works. The tab at the top of this box lists key ejournals relevant to the study of English Language and Literature. Members of Oxford University can use ejournals that the Bodleian Libraries have purchased for free. Search for them on SOLO . They can be read on a desktop computer, laptop, tablet, e-reader or mobile phone; you just need your Oxford Single Sign On to access them. Individually purchased ejournals are all searchable on SOLO. Note, some ejournals have restrictive access and usage terms, for example they can only be read by one person at a time. Some ejournals are acquired via 'electronic Legal Deposit'. These must be read on a library desktop computer in one of the Bodleian Libraries. Further information on how to identify and access electronic Legal Deposit items on SOLO is at the link below.
Help with ejournalsThe links below are provided for those wishing to learn more about ejournals.
The Bodleian Libraries subscribe to over 118,000 ejournal titles, across all subjects. To browse or search for English Language and Literature ejournals, use the Journal Search below, or BrowZine. Below is a selection of ejournals for English Language and Literature, but many more can be found via SOLO.
Physical journals
The tabs at the top of this box list Oxford University libraries with print journals of interest to those studying English Language and Literature. A lot of journals are available online but some are still in print, especially those published before the introduction of computers and online journals, and they have not all been digitised. Help with print journalsFor those wishing to learn more about searching for journals in Oxford, we recommend the following guide:
The Bodleian library's extensive collections include many print journals relevant to English Language and Literature. All journal titles can be found via SOLO (using Advanced Search and choosing 'Journals' in the 'Resource Type' menu will refine your search). Most of the Bodleian Library journals are kept off-site in the storage facility. Journal issues or volumes can be called over to a library reading room via SOLO (there are daily deliveries to most Bodleian Libraries reading rooms). A scan of an individual article can requested via the Libraries Scan & Deliver service. The Bodleian's Upper Reading Room accommodates a display of current issues of major English Language and Literature journals. The Gladstone Link also has runs of selected Humanities print journals.
There are hard copy runs of selected key periodicals for English on the lower floor of the EFL, including ELH: English Literary History, English Studies, English Literary Renaissance, Modernism/Modernity, Shakespeare Survey, Studies in the Age of Chaucer, and more. The EFL also has a collection of nineteenth- and early twentieth-century periodicals, such as All the Year Round, the Edinburgh Review, the Cornhill Magazine, the Quarterly Review, Bentley's Miscellany, and more. Many of the EFL's nineteenth-century periodicals are digitised and can be accessed via SOLO. Physical volumes are held on closed access and can be requested for viewing in the reading room.
The Taylor is the is the University's centre for the study of Modern European languages and literatures (other than English), and also includes collections in Linguistics and Film Studies. It holds approximately 850–900 periodical titles. These include original literary journals dating from the 18th century onwards, and many current subscriptions covering literary criticism and original writing. Historical periodicals and newspapersSee below for collections of historic newspapers and periodicals. Individual titles can also be found via SOLO. For more newspapers, see the Newspapers category of Databases A-Z , or search SOLO for individual titles This database provides access to over 1,270 newsbooks, newspapers, pamphlets and a variety of other news materials published in England, Ireland and Scotland, plus papers from British colonies in Asia and the Americas. The collection is particularly rich in 18th century London newspapers. All the major titles are included, such as the Daily Courant from 1702 to 1735, the first daily newspaper published in London, and the London Gazette from 1665. Periodicals, such as Tatler (1709-1711) and Spectator (1711-1712), are also included. Also represented are English provincial titles from 1712, Irish newspapers (the earliest being the Dublin Intelligence of 1691), Scottish ones from 1708 onwards, and many 18th century American ones too, including the New England Courant (1721-1723). Features the newspapers, periodicals, pamphlets and broadsheets that form the Nichols newspaper collection held at the Bodleian Library. All 296 volumes of bound material, covering the period 1672-1737 have been digitized. This collection charts the history of the development of the press in England and provides invaluable insight into 17th and 18th century England. The nineteenth century was a time of revolutionary change and expansion. Britain was one of the world’s first industrial, urban superpowers and developed a press to feed the demands of its increasingly literate population. The Nineteenth Century UK Periodicals series covers the events, lives, values, and themes that shaped the nineteenth century world. It provides an invaluable, fully-searchable facsimile resource for the study of British life in the nineteenth century—from art to business, and from children to politics. Few of the materials in this extensive collection have ever been reissued, in any format since original publication. Titles included have been identified and selected by leading scholars in nineteenth century studies; their choices reflect the broad scope and thrust of research and teaching in the twenty-first century. Part I: Women's, Children's, Humour, and Leisure covers the advent of commercial lifestyle publishing in Britain, drawn from the remarkable collections of the British Library, National Library of Scotland, National Library of Australia, and National Library of South Africa. The series acts as a barometer of literacy and social mobility in the 1800s, with a particular focus on the rarely documented aspects of women, children, humour, and leisure activity in the Victorian age. The rise of magazine publishing is reflected in the selection of publications, spanning publications aimed at and tailored to various audiences, including women and children. 19th Century U.S. Newspapers provides access to approximately 1.7 million pages of primary source newspaper content from the 19th century, featuring full-text content and images from numerous newspapers from a range of urban and rural regions throughout the U.S. The collection encompasses the entire 19th century, with an emphasis on such topics as the American Civil War, African-American culture and history, Western migration and Antebellum-era life among other subjects. Date coverage: 1800-1900
The collection provides digital access to the full text of thousands of American periodicals published between 1684 and 1912, digitised from the collections of the American Antiquarian Society. Titles cover a broad range of subjects and interests related to every aspect of American life and culture, from politics to religion, science, law, literature and the arts. Over 1,100 periodicals that first began publishing between 1740 and 1900, including special interest and general magazines, literary and professional journals, children's and women's magazines, and many other historically-significant periodicals. The Chicago Defender (1905-1975) offers full page and article images with searchable full text back to the first issue. The collection includes digital reproductions providing access to every page from every available issue. The New York Times (1851-2004) offers full page and article images with searchable full text back to the first issue. The collection includes digital reproductions providing access to every page from every available issue. The Washington Post (1877-1991) offers full page and article images with searchable full text back to the first issue. The collection includes digital reproductions providing access to every page from every available issue. Online access to millions of fully searchable pages in over 150 national and regional titles chosen by leading experts and academics from the holdings of the British Library. From the Glasgow Herald to the Graphic, from the Illustrated Police News to the Preston Chronicle, the collection greatly enhances research into the history, society and culture of the UK. The website also offers contextual essays regarding the role of newspapers in the Victorian age, bibliographic head-notes and a chronological overview. This resource provides access to British Newspaper Archive (BNA) content (except for very small numbers of newspapers).
British Periodicals traces the development and growth of the periodical press in Britain from its origins in the seventeenth century through to the Victorian 'age of periodicals' and beyond. On completion this unique digital archive will consist of almost 500 periodical runs published from the 1680s to the 1930s, comprising six million keyword-searchable pages and forming an unrivalled record of more than two centuries of British history and culture. Provides access to the full-text of nearly 460 British popular and literary periodicals published from the 17th century to the early 20th century. Includes amongst others the Anti-Slavery Reporter, London Review, Royal Magazine or Gentleman’s Monthly Companion, some religious titles such as The Wesleyan-Methodist Magazine. Topics covered include literature, philosophy, history, science, music, architecture, drama, the fine arts and the social sciences. This is a digital collection of 18th century journals published between 1693 and 1799, including many rare or ephemeral titles drawn from the Hope Collection at the Bodleian Library and the Harry Ransom Humanities Research Centre, University of Texas at Austin. The journals are invaluable to the study of all aspects of the eighteenth century, including crime, sport, advertising, the theatre; fashion; politics, revolution; agriculture; social issues and society life. There are also polemics, poetry, letters to the press, reviews of drama and novels, contemporary adverts and essays on almost every conceivable topic. This resource provides online access to 57 women’s magazine and journal publications covering the late eighteenth century to the 1930s. The material allows researchers to explore the role of women in society and the development of the public lives of women as the push for women's rights (woman suffrage, fair pay, better working conditions, etc.) grew in the United States and England. Some of the titles in this collection were conceived and published by men, for women; others, conceived and published by male editors with strong input from female assistant editors or managers; others were conceived and published by women, for women. It is therefore also useful for the study of the history of women’s publishing. The strongest suffrage and anti-suffrage writing was done by women for women's periodicals. Suffrage and anti-suffrage writing, domesticity columns, and literary genres from poetry to serialized novels are included in these periodicals. Thus this resource provides a wide array of views for study. The collection contains overwhelmingly English and US publications, with 4 German, 1 French periodical and 1 Icelandic periodical. An online archive of digitized, full-image journal articles, Periodicals Archive Online (formerly PCI Full Text) offers unprecedented access to international, scholarly literature in the humanities and social sciences disciplines from 1802 to 2000. Many journals are non-English. Oxford has access to Collections 0–9, Jisc Collection and Jisc Collection 2. Contents includes The Spectator from 1828 to 2000. Note that Periodicals Archive Online is separate from other ProQuest databases such as British Periodicals. Recommend a journalIf the Bodleian Libraries don't have the journal or article you are looking for, you can make a recommendation by completing the form below ( Oxford Single-Sign On required).
Journal articles via inter-library loansIf you are looking for a particular journal article which is not in the Bodleian Libraries, we may be able to source it through Oxford's inter-library loan service.
BrowZine is an alternative way to browse many of the ejournals subscribed to by the Bodleian Libraries. Coverage is from 2005 onwards. For those wishing to learn more, we recommend the following guide:
Tables of contents and alerts
Website feedback Accessibility Statement - https://visit.bodleian.ox.ac.uk/accessibility Google Analytics - Bodleian Libraries use Google Analytics cookies on this web site. Google Analytics anonymously tracks individual visitor behaviour on this web site so that we can see how LibGuides is being used. We only use this information for monitoring and improving our websites and content for the benefit of our users (you). You can opt out of Google Analytics cookies completely (from all websites) by visiting https://tools.google.com/dlpage/gaoptout © Bodleian Libraries 2021. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Licence
 Most Read in LiteratureFrom Shakespeare's plays to modern literary trends, explore a collection of our most read recent articles and chapters from our literature portfolio. Enhance your knowledge with free access to these highlights from our books and journals until December 2022. Browse our collectionsBrowse our journals, browse our books, affiliations.
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers OnlySign In or Create an Account This PDF is available to Subscribers Only For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.  Literature in English: Literary Research Journals
English JournalsThe MLA International Bibliography , the primary database for literature research, indexes more than 4400 journals. If you would like to browse the content of highly cited literature journals here is a list of the most frequently cited journals. If you are looking for articles and chapters on a particular topic, it is more efficient to search the MLA database.
Open Access Resources: English Literature
OA Resources by SubjectLocate Open Access resources online by subject.
Open Access Journals for English LiteratureThe following is a list of suggested peer-reviewed and open access journals related to the discipline of English Literature.
Electronic Libraries, repositories and directoriesThe following is a list of suggested open access sites offering scholarly eBooks and eDocuments related to the discipline of English Literature.
Lectures/Speeches/Podcasts
Subject Guide
 Reviews of Peer-Reviewed Journals in the Humanities and Social SciencesWe give you the scuttlebutt on academic journals—aiding you in selecting the right journal for publication—in reviews that are sometimes snarky, sometimes lengthy, always helpful. Written by Princeton University graduate students and Wendy Laura Belcher. Category Archives: Literary Studies Journals
 MLN (Modern Language Notes)For those interested in publishing articles that explore French, German, Hispanic, or Italian literature, film, theory and pedagogy. MLN may not be quite as well-known … Continue reading →  PMLA (Publications of the Modern Language Association)For those interested publishing articles that discuss timely and culturally relevant literature and archival materials. For those looking to make broad connections (not close reading) … Continue reading →  Journal of Modern LiteratureFor those interested in publishing articles that deal with literature from any language or tradition, 1900-present. Ranked 19 out of all literature journals by Google … Continue reading →  French ForumFor those interested in publishing articles on French and Francophone Literature and films of all periods but preferably post-1900. Founded by Virginia and Raymond La … Continue reading →  Essays in RomanticismFor those interested in publishing articles that engage some aspect of Romantic literature (mainly British or, in a few instances, German)—often complicating or developing a … Continue reading →  Comparative Literature StudiesFor those interested in publishing articles of a comparative nature on literary history, the history of ideas, critical theory, studies between authors, and literary relations … Continue reading →  Modernism/modernityFor those interested in publishing articles that, as the journal’s name suggest, deal with either Modernism or the more broadly defined concept of modernity. As … Continue reading →  The Eighteenth Century: Theory and InterpretationFor those interested in publishing articles on literature of the eighteenth century, mainly British (but articles can have New World or colonial connections), often with … Continue reading →  Nineteenth-Century French StudiesFor those who would like to publish scholarly articles on nineteenth-century French literature, culture, and social/political issues. NCFS is independent journal that purports to publish … Continue reading → Philosophy and LiteratureFor those who wish to publish articles in which they address an aesthetic object (usually literature) with an attitude explicitly attuned to formal concerns and … Continue reading →  French StudiesFor those interested in publishing articles that concern a broad range of topics in French and Francophone literature, film, culture, and theory from the medieval … Continue reading →  Modern PhilologyFor those interested in publishing articles that speak to an aesthetic problem in a canonical text written before 1900 by a Western author, that deeply … Continue reading →  For those interested in publishing very formal articles that directly take up narrative theory and narratology and who are ready to subordinate their politics and … Continue reading →  MELUS (Multi-Ethnic Literature of the United States)For those with articles that provincialize or problematize the idea of the U.S. and its literary output. MELUS is a quarterly journal, and one of … Continue reading →  African American ReviewFor those with articles that have something substantial and innovative to say about canonical and non-canonical African American Literary texts; this journal is an especially … Continue reading →  Callaloo: A Journal of African Diaspora Arts and LettersFor those interested in publishing articles that creatively and/or critically engage with the work of African Americans and peoples of African descent throughout the African Diaspora. … Continue reading →  Victorian Literature and Culture (stub)Submit here if you have a really interesting, interdisciplinary article about Science, Race/Imperialism, Gender (mostly women), Death, Religion, Sympathy, Victorian institutions (museums, pawnshops, libraries, etc), … Continue reading →  Victorians Institute Journal (stub)For those interested in publishing close readings of a single work of a popular Victorian author, especially Hardy or Dickens.  Victorian Review (stub)For those interested in publishing an article on a lesser known Victorian author or text, or one on an obscure topic in relation to a … Continue reading →  Nineteenth Century Literature (stub)For those interested in publishing articles with very broad claims about an author, discourse, or text.  Dickens Studies Annual (stub)For those interested in publishing articles with close readings of any of Dickens’s novels or short stories or of his life and legacy. Eighteenth-Century LifeSubmit here if you’re writing about a canonical British author, have a historical (not theoretical) perspective, and want to talk about the author’s journals and … Continue reading → Eighteenth-Century StudiesSubmit here if you have a substantial amount of historical or contemporary (aka 18th century) theoretical background or if you’re writing about something global (not … Continue reading → Journal of Postcolonial WritingFor those interested in publishing on texts written in English after 1950, particularly on an individual postcolonial author or text; a critique of contemporary postcolonial … Continue reading → Comparative LiteratureFor those interested in publishing theoretically rigorous articles with large claims on different national or linguistic literatures and with a focus on transmission or circulation. … Continue reading →  SEL: Studies in English Literature, 1500-1900Submit here if you don’t mind waiting for the annual issue on your time period; if you’re working in the 19th century, submit if you have … Continue reading →  Tulsa Studies in Women’s LiteratureSubmit here if you’re writing about women (especially multiple works by a single author) and talk really explicitly about the larger implications of your argument. … Continue reading → ELH (English Literary History)For those interested in publishing a traditionally structured article (historical/ theoretical background followed by close reading); if you’re working in the 19th century, write about … Continue reading → Journal of Teaching and Research in English Literature About the JournalThe Journal of Teaching and Research in English Literature (JTREL), launched in July 2009, is an international double-blind peer-reviewed open-access journal dedicated to supporting scholarly exchange among teachers and researchers of Literature written in English. It aims to publish high-quality, original research articles, reviews, author interviews and poems. It welcomes contributions not only from well-known senior scholars but also from early-career researchers. The journal is published online four times a year by the Literature Special Interest Group of the English Language Teachers’ Association of India (ELTAI), Chennai, India. It does not charge any access or publication fees. Articles can be submitted throughout the year. Email your original unpublished research papers to [email protected] . Current IssueResearch articles, sinclair and coulthard’s ‘irf’ model in a one-to-one classroom: an analysis, aboriginal voices in australian literature, facets of mythological elements depicted in amish tripathi’s shiva trilogy, excavations from ground reality: exploring colonial aspects in k. n. panicker’s karimkutty, feline perspective and indianness in nilanjana roy’s the wildings, make a submission, information.
  American Research Journal of English and Literature[email protected] | ISSN-2378-9026 American Research Journal of English and Literature is an international, peer-reviewed, open access online journal. English literature is the study of literature written in the English language. It includes some of history's most famous writers: James Joyce (Ireland), William Shakespeare (England), Mark Twain (United States), Arthur Conan Doyle (Scotland), Dylan Thomas (Wales), and Vladimir Nabokov (Russia), just to name a few. English literature dates back more than five centuries. This represents writers not only from different parts of the world and time periods, but it covers every major genre and style of writing as well. The journal welcomes and publishes insightful English Literature related research articles in the form of original articles, review articles, short reviews, short notes etc. Given below are some of the key (but not limited) topics of this journal.
 ARJ @ SOCIAL Social Connect @ARJInternational Journal of English Language, Literature and Translation Studies (IJELR) is a quarterly, Indexed, Refereed, and Peer Reviewed Open Access & Printed Journal ( Published in March, June, Sept, and December ) devoted to the critical and scholarly study of the new and the established Language, literatures in English around the world in its various manifestations as International English Literature, Postcolonial Literatures, Commonwealth Literature, New Literatures in English, and World Writing in English. It welcomes articles on the relationships among the new literatures and between the new and the established literatures. For submissions To submit an article to IJELR, please send us an email attachment to [email protected] , [email protected] All submissions must be received online, as email attachment. Before Submission, please check your article format : 1.Title 2. Author (s) Details 3.Abstract 4.Key Words, 5 Introductions/discussion 6.References/Work cited 7. Author Photograph (optional) Authors should be submitted article along with author agreement form Click here for download Journal Key Words: English Literature Journal, Print Journal, Linguistics Journal, Translation Journal, Indian English Literature Journal, Online English Journal, Indexed journal, English Language Journal, English Journal With Impact Factor NOTE: The submission must not have been previously published, nor should it be under consideration for publication elsewhere. We also have a strict policy against plagiarism. The plagiarism is checked through two methods: reviewer check and plagiarism prevention tool. All submissions will be checked by online software before being sent to reviewers. Editor in Chief having the right to publish or reject the article in pre or post publication updated on 01-08-2015
Focus and Scope IJELR publishes original papers, review papers, conceptual framework, analytical and simulation models, case studies, empirical research, technical notes, and book reviews in the fields of: Comparative Literature Critical Theory Cultural Studies Discourse and Inter language Pragmatics Discourse and Organization English Literature ELT and Related studies ESL, ESP,EFL etc., Interdisciplinary Approaches in Literature Interpreting Studies Literary Studies Literary Theory and Cultural Studies Literature and Media Literature in Translation Translation in Literature Translation Studies Translation and Globalization World Literature And other related themes Types of papers Accepting > Original Research Articles > Express Papers: Research Article Needs to Publish within short period (2-3 working days after submissions) > Review Articles > Short Communications > Case Studies > Letters to the editors and book reviewers > Abstracts/Full Papers of Seminars and symposia will also consider for publications © Copy Right www.ijelr.in , Andhra Pradesh, India Published by KY Publications, India doi: 10.33329/ijelr
Open access publishing is not without costs. IJELR therefore charges (See Below) as Article Processing Charge for each article accepted for publication after double-blind review. We routinely waive charges for authors from low-income countries. For other countries, article-processing charge waivers or discounts are granted on a case-by-case basis to authors with insufficient funds. Authors can apply for a waiver or discount during the submission process 
ISSN: 2456-7620 Email Id: [email protected]
International Journal of English Literature and Social Sciences (IJELS)(ISSN: 2456-7620) is a bi-monthly peer-reviewed refereed journal that invites Literature Essays, Review Articles, Research articles, case studies, conference proceedings and short communication in the field of English Literature, Humanities and Social Sciences. IJELS welcomes quality work that focuses on research, development, and review. After submission, all papers will be evaluated by experienced editorial members for their originality, Language perspective, and correctness, the relevance of topic and presentation quality. Why publish with us?
Submission open to Current Issue
Important Links:
IJELS Journal covers but is not limited to the following topics: Anthropology, applied linguistics studies, Arts, Business Studies, Communication Studies, communicative language teaching (CLT), comparative literature, computational linguistics, Corporate Governance, corpus linguistics, Criminology, critical theory today, Cross Cultural Studies, cross-cultural studies, Demography, Development Studies, discourse analysis, Economics, Education, English globalization, English language, English language testing and assessment, English literature, English speaking culture, English teaching and learning, Ethics, gender studies in language, Geography, History, Human Rights, Industrial Relations, Information Science, interdisciplinary approaches in literature, International Relations, Law, Library Science, Linguistics, Literature, literature and media, literature studies, Media Studies, methodology, Paralegal, Performing Arts, performing arts (music theater & dance), Philosophy, Political Science, Population Studies, Psychology, Public Administration, Religious Studies, second language acquisition, Social Welfare, Sociology, syllabus design and curriculum development, task-based language teaching (tblt), translation studies, Visual Arts, women studies, world literature..etc. Editor-In-Chief IJELS Journal For Authors
Important Links  Most Popular Articlese
Other related JournalsInternational journal of teaching, learning and education (ijtle)-issn: 2583-4371, international journal of english language, education and literature studies(ijeel)-issn: 2583-3812, international journal of language, literature and culture(ijllc)-issn: 2582-9823, international journal of advanced engineering, management and science (ijaems)-issn: 2454-1311.  About IJELS
 Social PluginCopyright @ 2020 IJELS(Infogain Publication)
Finding and Reading Journal Articles
Why are articles so important to research?
Journal articles are the academic's stock in trade, t he basic means of communicating research findings to an audience of one’s peers. That holds true across the disciplinary spectrum, so no matter where you land as a concentrator, you can expect to rely on them heavily. Regardless of the discipline, moreover, journal articles perform an important knowledge-updating function .  Textbooks and handbooks and manuals will have a secondary function for chemists and physicists and biologists, of course. But in the sciences, articles are the standard and preferred publication form. In the social sciences and humanities , where knowledge develops a little less rapidly or is driven less by issues of time-sensitivity , journal articles and books are more often used together. Not all important and influential ideas warrant book-length studies, and some inquiry is just better suited to the size and scope and concentrated discussion that the article format offers. Journal articles sometimes just present the most appropriate solution for communicating findings or making a convincing argument. A 20-page article may perfectly fit a researcher's needs. Sustaining that argument for 200 pages might be unnecessary -- or impossible. The quality of a research article and the legitimacy of its findings are verified by other scholars, prior to publication, through a rigorous evaluation method called peer-review . This seal of approval by other scholars doesn't mean that an article is the best, or truest, or last word on a topic. If that were the case, research on lots of things would cease. Peer review simply means other experts believe the methods, the evidence, the conclusions of an article have met important standards of legitimacy, reliability, and intellectual honesty. Searching the journal literature is part of being a responsible researcher at any level: professor, grad student, concentrator, first-year. Knowing why academic articles matter will help you make good decisions about what you find -- and what you choose to rely on in your work. Think of journal articles as the way you tap into the ongoing scholarly conversation , as a way of testing the currency of a finding, analysis, or argumentative position, and a way of bolstering the authority (or plausibility) of explanations you'll offer in the papers and projects you'll complete at Harvard.
Except where otherwise noted, this work is subject to a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which allows anyone to share and adapt our material as long as proper attribution is given. For details and exceptions, see the Harvard Library Copyright Policy ©2021 Presidents and Fellows of Harvard College. Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Scientific mapping and production analysis of digital comic, animation, and digital cartoon in education
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 1009 ( 2024 ) Cite this article Metrics details
Analyzing scientific mapping literature activity on digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons is essential for future research and development. The objective of the current study was to assess research activity in digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons. VOSviewer and Scopus were used to perform bibliometric analysis. The research was conducted from 2013 to 2023 and found 288 documents. In 2022, most research reports on digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons were published. China is the most productive region in terms of articles, with English being the most widely used language. The most common subject area is computer science, and the most common source is the journal Lecture Notes in Computer Science. The most productive author is Dong Hao Li. Zhejiang University is the most productive institution. Future research should concentrate on a single discipline and work with Google Scholar and Web of Science data for in-depth analysis. Similar content being viewed by others A bibliometric analysis of knowledge mapping in Chinese education digitalization research from 2012 to 2022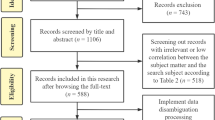 Education reform and change driven by digital technology: a bibliometric study from a global perspective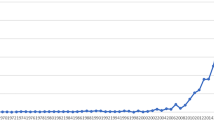 Social innovation and higher education: evolution and future promiseIntroduction. Educational technology in education applications like digital visual learning media has revolutionized conventional learning mechanisms (Shen and Ho, 2020 ). Digital visual learning media in education has become a trend in recent years. Comics, animations, and cartoons are visual learning media with similar characters. A comic is a single-panel illustration that depicts a story or journey (Alousque, 2020 ). Comics are increasingly prominent in entertainment, industry, culture, and the arts (Yamanishi et al. 2021 ). The students get simulant to discuss material or topics through the cartoons (Hansen and Skeiseid, 2022 ). Comics are a kind of animation that aims to amuse readers by introducing characters and telling a tale in a sequence closely tied to the image (Riwanto and Wulandari, 2018 ). Furthermore, animation is an illusion created by images and displayed on a computer screen (Cevahir et al. 2022 ). Cartoons are frequently used in education to assist students in developing their knowledge and improving their problem-solving skills (Gokkurt-Ozdemir et al. 2021 ). Cartoons are practical tools for reducing misconceptions among students in science classes. Then, comics can help students improve their literacy, language skills, and awareness of social issues (Das and Singh, 2022 ). Cartoons and animation have several educational benefits, including attracting attention, motivating students, and presenting information and explanations visually, making teaching more appealing (Appiah et al. 2022 ; Cevahir et al. 2022 ). Much research about digital multimedia has used the ADDIE model and focused on the scope of education. Digital cartoons, animation, and comics have been widely employed in education since the development of digital technology and the internet within the educational system. Much research explains the practical implementation of digital multimedia. Digital cartoons as visualization media can explain course topics well, so the students make courses enjoyable and increase their interest in course learning (Gokkurt-Ozdemir et al. 2021 ). Animation is frequently used in education, especially in Augmented Reality (AR). Science subject materials such as mathematics, chemistry, and physics-based animation with AR technology can increase students’ motivation and achievement levels. Digital comics are straightforward and feasible to increase students’ literature and motivation (Karlimah et al. 2021 ; Arafik et al. 2021 ). Digital technology is used in education as a media that significantly contributes to increased learning outcomes and 21 st -century skills such as critical thinking, analytical thinking, creative thinking, and problem-solving skills (Arafik et al. 2021 ; Yıldız et al. 2017 ). Over the past ten years, digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons have progressively become a part of learning media in humanities and social sciences research. This study aims to analyze the trends and recommendations of visual media education. In detail, this research uses bibliometric analysis to track the development of digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons in education. Data is taken from the Scopus database to answer the following research questions: Regarding research characteristics and features, what were the location, type of documents, sources, and authors of digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons in education research? In terms of application, what were the dominant subject areas and what are the contributions and differences between digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons in education research? Materials and MethodsScientific mapping uses bibliometric analysis to assess and quantify publications in a specific research field. The analysis results can help future researchers to understand the patterns and trends of research and find out the novelty (Kulakli and Osmanaj, 2020 ; Suprapto et al. 2021 ; Yang et al. 2017 ; Yanuarti and Suprapto, 2021 ; Zakhiyah et al. 2021 ). Data were collected from the Scopus database because it is one of the most significant sources of scientific kinds of literature, such as conference papers, book chapters, books, articles, and notes (Suprapto et al. 2021 ; Xie et al. 2020 ; Yanuarti and Suprapto, 2021 ; Zakhiyah et al. 2021 ). Data CollectionThe data were collected in October 2023. The authors input the keywords on the title and abstract: TITLE-ABS-KEY (digital AND comic OR animation OR digital AND cartoon) . The authors found 466 documents. Then, the data were collected from 2013–2023, and 288 documents were documented in .csv and .ris format. Data AnalysisVOSviewer used .ris metadata to visualize the network and determine the association between authors, documents, and keywords (Guleria and Kaur, 2021 ; Olandinrin et al. 2023 ; Van Eck and Waltman, 2020 ). Then .csv metadata used Microsoft Excel to categorize and plot the data about nation, affiliation, language, year of publication, and other data from the.csv file. VOSviewer and Microsoft Excel are all software used to analyze the data in bibliometric research (Prahani et al. 2022 ; Setyaningsih et al. 2018 ). Microsoft Excel was used to analyze RQ 1, using Microsoft Excel results, and RQ 2 was solved using VosViewer. Results and DiscussionResearch question 1—research characteristics and features, year-publication, language, and type of documents distribution. Figure 1 shows the year publication distribution of digital comic, animation, and digital cartoon research. Over the last decade, this research has fluctuated with no extreme decline. The average publication was 26 documents, and five years received publications above the average. The most recent publication year of digital comics, animation, and digital cartoon research was 2022, with 38 documents (see Fig. 1 ). The second-largest distribution, with 36 documents, occurs in 2020. There was a rapid spike in publications - doubling - in the first year of the pandemic, namely 2019 and 2020. The percentage of total documents (%TD) and total citations (%TC) is also illustrated in Fig. 1 . In 2020, the world experienced the COVID-19 pandemic, and there was a change in the learning system to online distance learning. Several institutions and grades use digital visual media and technology to support learning activities (Irfan et al. 2020 ).  Year-wise distribution of documents. Animation is an adequate distance teaching method and increases student motivation and participation (Azlan et al. 2020 ; Inangil et al. 2022 ). Digital comics are a popular source of reading history and science subject material that can increase students’ reading skills and motivation (Damopolii et al. 2021 ). Digital cartoons become increasingly popular during the pandemic, and several researchers use cartoons for their ADHD children (Jena and Devi, 2020 ). In addition, 2018 and 2020 were the top cited years. Citation on publication documents from 2021 to 2023 has the lowest percentage and declines yearly. Therefore, this research requires an increase in quantitative publications. Through the trends discussed above, future research can focus on digital technology that can be combined with visual media to measure student skills. English is the most common language, accounting for 270 documents or 93.75%. Chinese was used in digital-visual media research with five documents and a percentage of 1.74%. Each document in French, Russian, and Turkish gets three documents published. Dutch, Italian, and Spanish were used in a small percentage of the document (less than 1%) (see Fig. 2 ). Many sources and publishers used English as their standard international language. For example, Springer and Taylor & Francis Ltd published their English document. However, many sources-publisher used another language to publish their research document: Chinese-Editorial and Publishing Board of JIG, Italian-Universita degli Studi di Milano, Turkish-AVES, Portuguese-Research Centre in Education, Russian-Russian Psychological Society, Spanish- Fundacion para la Investigacion Social Avanzada , and Dutch-Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde .  Language used in documents. There are 288 digital comic, animation, and digital cartoon research documents, including 159 articles, 82 conference papers, 18 book chapters, 12 books, six conference reviews and reviews, and five documents of other types (see Fig. 3 ). The research documents were published from several sources (see Fig. 3 ). All articles and ten conference papers were published in the journal, and 61 were published in conference papers, books, and book series. Two documents were published in the trade journal.  Type of research document and sources. The source publishing and subject area of digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons40% of the top sources in visual media education research are journals and conference papers (see Table 1 ). The remaining 20% is published through a book series with Springer Verlag as publisher. Top cited documents in journal sources have the highest number of citations: ACM Transaction on Graphics (21 citations) and Multimedia Tools and Applications (14 citations). Two journals have many scopes of research that represent the implementation of digital visual media education (see Fig. 4 ). In this journal, researchers discuss several topics like distance and interactive learning (Guo et al. 2020 ) and implementing multimedia in learning activities (Li and Lu, 2023 ). However, the top cited authors in this source are not included among the top authors list (see the following subsection).  Aims and sources of ACM Transaction on Graphics and Multimedia Tools-Applications. Figure 5 represents several subject areas in digital visual media research related to computer science. Computer science is the subject area in top sources (89 documents) and top author (see following sub-section). Other research has concreated in social sciences (66 documents), engineering (40 documents), art & humanities (31 documents), and other subject areas: medicine, mathematics, decision sciences, psychology, BMA, physics-astronomy. The development of digital visual learning media has a significant impact on education. Research has impacted science, engineering, artificial intelligence, and other fields. Computer science is more closely related to mathematics, engineering, and science than many scientific fields. While social computing investigates the relationship between social behavior and computational systems, computational social science applies computer science theory to the social sciences.  Subject area of digital visual media research. The productive author, affiliation, and countries of digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons researchThe top ten authors with publications in digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons are listed in Table 2 . China and Hong Kong are all research-intensive countries with many publications. China has over 4600 animation industries and creates several scientific films, promoting scientific knowledge and ideological statements with animation effects and cartoons (Zhuang, 2023 ). Four Chinese researchers and three Hong Kong researchers from different affiliations participated in digital visual media education research. Li, D. from China has published more than other researchers (3 documents). Yu, Y from Hong Kong got the top citation and the highest h-index, and Wang W. from the US got the first rank for his publication documents. Several researchers got their gold publication years in the last decade. 2022 is the top publication year; two authors from China and the last one from the US participated (see the previous sub-section). In addition, 80% of affiliations’ top authors are included in the top ten affiliations. The University of Tokyo ranks second in top affiliations (see Table 3 ). Furthermore, there are three cluster co-authorships in this scope of research: Xu’s cluster (blue), Wu’s cluster (red), and Zhang’s cluster (green) (see Fig. 6 ). The largest cluster (red and green) contributed are related to the smallest cluster (blue). China-Hong Kong authors dominated three clusters. Xu and Wu researched computer graphics and deep learning.  A network visualization of co-authorship. There are four affiliations and three top authors are listed in Table 3 . In addition, China’s affiliation dominated this scope of research. On the other hand, Duke University and the University of Southern California have the top citations. Based on the discussion in this sub-section, the four biggest countries contributed to digital cartoons, animation, and digital comics: the US, China, Hong Kong, and Japan. The US and Japan are the top animation, cartoon, and comics industry makers. Many products from these countries were imported to China and Hong Kong. Figure 7 shows the distribution research worldwide. The dominant countries are China (48 docs) and the US (47 docs), which have top authors. In addition, The University of Tokyo and Zhejiang University contributed 23% to this scope of research. 8.64% of each document is from Hong Kong, the US, the Netherlands, and the UK. Based on Fig. 7 , it is known that research on comics, animation, and cartoons still needs to be improved. For example, in the Asian region, East Asia has significantly contributed to research - South Korea, Japan, Hong Kong, China, and Taiwan. In the Southeast Asia region, only three countries participated, namely Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand, with each publication having six documents. In addition, the only South Asian region is India, with 15 published documents.  The distribution of research in worldwide. Research Question 2- The visualization of co-occurrence-keywords of digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons The first top-cited document from the United Kingdom (the Queen Mary University of London and the University of Edinburgh) is about sketch images, DG methods, and deep learning. Five top-cited documents discuss various points of view and studies regarding visual media (see Table 4 ). Two papers discuss how to make digital visual media, such as DG methods and auto-painter. According to Li et al. ( 2017 ), implementing DG (Domain generalization) methods with photos, sketches, cartoons, and paintings presents a significant challenge for future research. Besides, Bleiker ( 2018 ) uses the cGAN model and Wasserstein distance to overcome model collapse and outperforms other image-to-image methods on various sketch datasets. Other research discusses another function of visual media, especially in politics, medicine, and disaster. Visual global politics has the function of visualizing and exploring several international events and politics as a resource to enhance students, scholars, and practitioners’ understanding (Liu et al. 2018 ). Bossu et al. ( 2018 ) conducted EMSC websites or the LastQuake app to reduce anxiety by providing timely information and services to eyewitnesses, potentially contributing to immediate global seismic risk reduction. The study conducted by Volante et al. ( 2016 ) suggests that virtual human appearance can affect critical emotional reactions and users’ perceptions of the virtual interlocutors. In other words, there are several clusters in visual media learning research. In Fig. 8 , six related clusters are visualized, while Fig. 9 presents the distribution of keywords used in research over the last ten years. In short, the latest research on visual media still needs to discuss more research regarding the implementation of digital technology to help create visual media and its benefits for students (changes in skills and measurement of knowledge) as users of visual learning media. How to Create Visual Media (Red) Currently, the animation is created using a computer. The animation looks more modern and has more volume (three-dimensional), high accuracy, and natural character element visualization thanks to interactive computer graphics (Wiana et al. 2018 ). As multimedia, text, audio, graphs, visual effects, sound effects, image texture, and interaction are all included in the animation, by the time the animation is produced, the shareability of co-participants experiences has already been established (Cantarutti, 2022 ). Interactive multimedia has the potential to accommodate users with a variety of learning styles and internet-based education. Figure 10 illustrates one method of creating motion graphics in visual media and e-learning (Wiana et al. 2018 ). 3D modeling software (Pillen and Matthews, 2022 ), MappleSim Software (Tsegay et al. 2022 ), Blender (De Vries et al. 2022 ), 3D printers, Sketchfab (Aristov et al. 2022 ), and other applications and software are frequently used to create digital cartoons, digital comics, and animation. In the previous discussion, we explained several examples of methods used by world researchers in creating their visual media. Factor and method animation, such as textures, decomposition, compression, and color, were part of the red cluster (Ding and Xie, 2020 ). The digital cartoons, animation, and digital comics are all types of images that require an algorithm and application or software to create (Wiana et al. 2018 ; Pillen and Matthews, 2022 ; Tsegay et al. 2022 ; De Vries et al. 2022 ; Aristov et al. 2022 ). Characteristics of Research Sample (Green) This cluster is focused on research sample characteristics such as adult, female, child, and male keywords. Visual media learning was used in behavior research and social science-humanities (see Fig. 11 ). For example, Volante et al. ( 2016 ) examines the interrelationship between visual media and social-emotional variables. The findings show that while harmful affect levels were much lower in the visually realistic condition, male participants showed higher arousal levels in all circumstances. Participants had varying responses regarding social-emotional variables such as shyness, presence, perceived personality, and enjoyment-joy. In addition, research focused on children, females, adults, and other characteristics around 2020. This cluster is also related to technology implementation and education in the next cluster. Technologies to support research (Dark Blue) In 2020, research focused on factors that go into creating digital multimedia, such as animation, cartoons, digital devices, AI and VR (see Fig. 12 ). Both can combine real-time and interactive visualization concepts (Chen et al. 2019 ; Prahani et al. 2022 ). Virtual reality can be applied to visualization and e-learning (Pangaribuan and Zulkarnain, 2021 ). Animation, comics, and cartoons are linked to deep learning, human-computer interaction, and education (see Figs. 13 and 14 ). As a type of multimedia digital learning, they have enabled students to use digital learning to learn anywhere and at any time (Cantarutti, 2022 ). Type of research (Blue) and learning systems (Green) Students’ participation, activity, and understanding can increase using digital visual media such as digital comics, animation, or digital cartoons (Suprapto et al. 2021 ; Yanuarti and Suprapto, 2021 ). That is related to the current condition in which devices and human activity users are integrated into technology (Prahani et al. 2022 ). There is currently game-based learning or gamification (Sukstrienwong, 2018 ). Digital visual media is also related to behavioral integrated surveys (see Fig. 15 ). Behavioral surveys are self-reported, subjective accounts of individual actions affecting well-being (Moss et al. 2023 ). They are crucial for identifying community issues, improving public awareness, and identifying potential solutions. Another function animation (Purple)  Visualization of keywords by clusters. 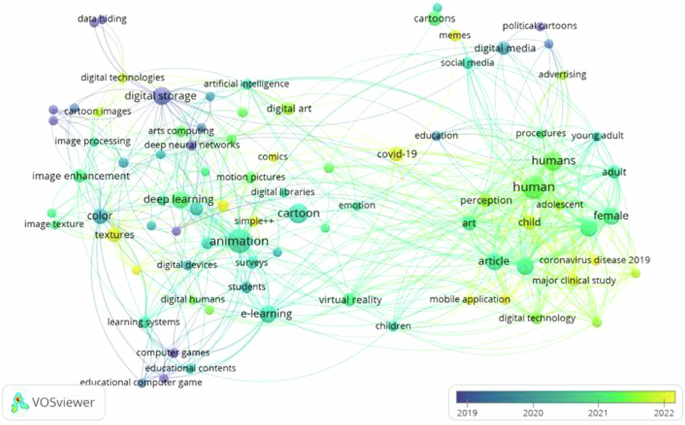 Visualization of keywords by year publication.  Cartoon and the making process. Digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons are most used in education research. It has recently been used as visual-digital media that increased multiple intelligence and literacy (Utomo and Ahsanah, 2020 ; Febriani et al. 2021 ; Kumar et al. 2019 ; Martzoukou, 2020 ). When learning combined with visual media, learners enjoy and are interested in watching digital media (digital cartoons, animation, or digital comics) so learners directly provide factual knowledge (Kühl, 2021 ). Implementing of digital media, such as digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons, is becoming more widespread (Ding and Xie, 2020 ). Digital comics are made in several stages to produce high-quality and compact comics. Bold colors can express more information and enhance the human visual experience (Chen et al. 2019 ; Chen et al. 2022 ). Liu et al. ( 2018 ) use visual media to improve the knowledge and awareness of students, academics, and practitioners of international events and politics. Table 5 informs the similarities and differences between digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons. Overall, there are similarities in several studies on digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons, such as using the same learning model. Several international researchers use (Problem-Based Learning) PBL and inquiry learning with digital visual media. They use a visual concept of digital media based on contextual problems with different dependent variables (indicators of students’ skills and knowledge). Many studies also report RnD research using pre-posttest design, interviews, and questionnaire models to analyze student responses using comics, animation, and digital cartoons. Jamal et al. ( 2019 ) reported using cartoon concepts in problem-based learning. Many international authors provide a scenario for students to discuss everyday life problems, but the cartoonization of these scenarios is not explicitly provided. The content activity in modules is similar but with different scenarios. 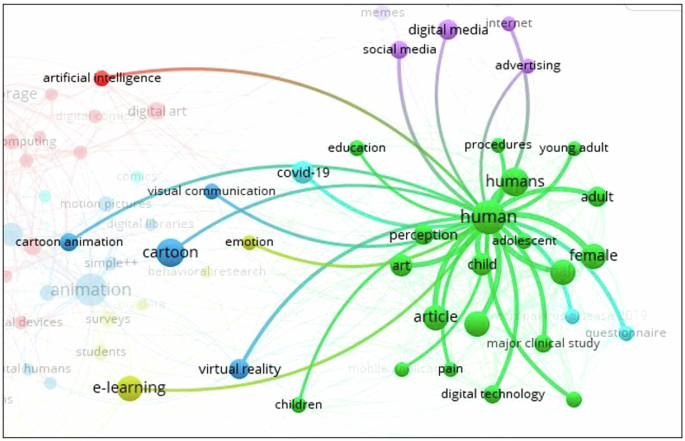 Visualization of human keywords.  Technology most used in research in VR and AI. ConclusionsThis study can complement future research by providing new information for librarians, researchers, educators, digital developers, and policymakers to advance digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons and create a Scopus document. The most recent research on digital comics, animation, and cartoons was published in 2022, primarily in China, and authored by Dong Hao Li. Zhejiang University is the most productive affiliation. The primary source for this research is the Journal Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons are different in their functions, devices, packaging, types, content, and access.  Animation and its visualize keywords.  Visualization of keywords on digital comic and cartoon. Further research can be developed based on the scope of computer science and social sciences, especially research on student behavior. Further research can also develop and integrate this product into various technologies such as AI, AR, and others. From 2013 to the present, studies about digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons have been conducted in education. Future researchers can collaborate with Google Scholar or the Web of Science data for in-depth analysis.  Research methods most used in research: questionaire and surveys. Data availabilityThe datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in this link: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.26335660 . This data set was proposed in xls. and csv. and process in VOSviewer and Microsoft Excel. Alousque IN (2020) The Metaphorical Representation of Brexit in Digital Political Cartoons. Vis. Commun. Q 27(1):3–12 Article Google Scholar Appiah B, Asamoah-Akuoko L, Samman E, Nam SH, Gyansa-Luterrodt M (2022) The impact of antimicrobial resistance awareness interventions involving schoolchildren, development of an animation and parents’ engagements: a pilot study. Antimicrob. Resist Infect. Control 11(1):1–10 Arafik M, Putra AP, Putro AAY, Nisa AF, Wiarsih N (2021) Development of digital comic technology applications design to increase children’s literature reading interest in elementary school. In 7th International Conference on Education and Technology, IEEE, New York, pp 277-281 Aristov MM, Geng H, Pavelic A, Berry JF (2022) A new library of 3D models and problems for teaching crystallographic symmetry generated through Blender for use with 3D printers or Sketchfab. J. Appl Crystallogr 55:172–179 Article ADS CAS Google Scholar Azlan CA, Wong JHD, Tan LK, Huri MSNA, Ung NM, Pallath V, Ng KH (2020) Teaching and learning of postgraduate medical physics using Internet-based e-learning during the COVID-19 pandemic–A case study from Malaysia. Phys. Med. 80:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.10.002 Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Bleiker R (2018) Visual Global Politics. Visual Global Politics . 1-398. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315856506 Bossu R, Roussel F, Fallou L, Landès M, Steed R, Mazet-Roux G, Dupont A, Frobert L, Petersen L (2018) LastQuake: From rapid information to global seismic risk reduction. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 28:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2018.02.024 Boy B, Bucher HJ, Christ K (2020) Audiovisual Science Communication on TV and YouTube. How Recipients Understand and Evaluate Science Videos. Front Comm. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomm.2020.608620 Cantarutti MN (2022) Responsive animation and the negotiation of (shared) self-deprecating attributes and experiences in interaction. Lang. Comm. 87:205–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.langcom.2022.08.002 Cevahir H, Özdemir M, Baturay MH (2022) The effect of animation-based worked examples supported with augmented reality on the academic achievement, attitude, and motivation of students towards learning programming. Part Educ. Res 9(3):226–247 Google Scholar Chen S, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Rosin PL, Lai Y, Gao L (2022) A rieview of image and video colorization: from analogies to deep learning. Vis. Inf. 6(3):51–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.visinf.2022.05.003 Chen Y, Wang Q, Chen H, Song X, Tang H, Tian M (2019) An overview of augmented reality technology. J Phys Conf Ser, 1237(022082) Damopolii I, Lumembang T, İlhan GO (2021) Digital comics in online learning during COVID-19: Its effect on student cognitive learning outcomes. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. (IJIM) 15(19):33–47. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v15i19.23395 Darmayanti R, Sugianto R, Baiduri B, Choirudin C, Wawan W (2022) Digital comic learning media based on character values on students’ critical thinking in solving mathematical problems in terms of learning styles. Al-Jabar. : J. Pendidik. Matematika 13(1):49–66 Das AK, Singh AK (2022) Comics: An alternative medium for education and social progress. ECS Trans. 107(1):8847–8854 De Vries RP, Sereno PC, Vidal D, Baumgart SL (2022) Reproducible digital restoration of fossils using blender. Front Earth Sci. 10:833379 Ding W, Xie YW (2020) Detection and Localization of the Copy-Paste in Digital Cartoon. In ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, pp 120-122 Enns A (2022) Time-Critical Animation: Comics, Cartoons, Computers. J. Sci. Technol. Arts 14(3):11–28. https://doi.org/10.34632/jsta.2022.11710 Febriani M, Prasandha D, Utami SPT, Setyaningsih NH, Yuniawan T, Sugiarto E (2021). The online comic development of Indonesian Folklore as a literature learning media for millennials. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol 1098. IOP Publishing, Bristol, p 032015 Gokkurt-Ozdemir B, Yildiz-Durak H, Karaoglan-Yilmaz FG, Yilmaz R (2021) The effects of digital concept cartoons and digital concept maps on eliminating middle school students’ misconceptions in the mathematics course: Experimental research. Inf. Educ. 20(2):205–229 Guleria D, Kaur G (2021) Bibliometric analysis of ecopreneurship using VOSviewer and R Studio Bibliometric 1989–2019. Libr. Hi Tech. 39:4 Guo J, Li C, Zhang G et al. (2020) Blockchain-enabled digital rights management for multimedia resources of online education. Multimed. Tools Appl 79:9735–9755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08059-1 Hansen KV, Skeiseid HV (2022) How to start a Focus Group: Using cartoons in adult focus groups to discuss consumers feedback expectations in food service settings. Int J Gastron Food Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgfs.2022.100582 Hiremath PS, Bhusnurmath RA (2014) RGB - Based Color Texture Image Classification Using Anisotropic Diffusion and LDBP. In: Murty, MN, He, X, Chillarige, RR, Weng, P (eds) Multi-disciplinary Trends in Artificial Intelligence. MIWAI 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science , 8875. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13365-2_10 Hung SJ, Young SSC (2017) A Preliminary Study of Using Avatars and Learning Companions for Junior High School Students in Enhancing Studying Chinese Classical Literature. In: Kantola, J, Barath, T, Nazir, S, Andre, T (eds) Advances in Human Factors, Business Management, Training and Education. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing , 498. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42070-7_19 Inangil D, Dincer B, Kabuk A (2022) Effectiveness of the use of animation and gamification in online distance education during pandemic. Comput. Inform. Nurs. 40(5):335–340. https://doi.org/10.1097/CIN.0000000000000902 Irfan M, Kusumaningrum B, Yulia Y, Widodo SA (2020) Challenges during the pandemic: use of e-learning in mathematics learning in higher education. Infin. J. 9(2):147–158. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v9i2.p147-158 Jamal SNB, Ibrahim NHB, Surif JB (2019) Concept cartoon in problem-based learning: A systematic literature review analysis. J. Technol. Sci. Educ. 9(1):51–58. https://doi.org/10.3926/jotse.542 Jena AK, Devi J (2020) Lockdown Area of COVID-19: How Does Cartoon Based E-Contents Effect on Learning Performance of Indian Elementary School Students with ADHD. Online Submiss. 8(4):189–201. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED608666 Jeromel A, Žalik B (2020) An efficient lossy cartoon image compression method. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 433–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08126-7 Kainz O, Jakab F, Kardoš S (2013) The computer animation in education. In 2013 IEEE 11th International Conference on Emerging eLearning Technologies and Applications (ICETA), pp 201-206 Karlimah K, Hamdu G, Pratiwi V, Herdiansah H, Kurniawan D (2021) The development of motion comic storyboard based on digital literacy and elementary school mathematics ability in the new normal era during covid-19 pandemic. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 1987(1):012026 Kühl T (2021) Prerequisite knowledge and time of testing in learning with animations and static pictures: Evidence for the expertise reversal effect. Learn Instr. 73:101457 Kulakli A, Osmanaj V (2020) Global research on big data in relation with Artificial Intelligence (A Bibliometric Study: 2008-2019). Int J. Online Biomed. Eng. 16(2):31–46 Kumar A, Vengatesan K, Rajesh M, Singhal A (2019) Teaching literacy through animation & multimedia. Int J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 8(5):73–76 CAS Google Scholar Leslie E (2017) Cloud Animation. Animation 12(3):230–243. https://doi.org/10.1177/1746847717740840 Li D, Yang Y, Song Y, Hospedales TM (2017) Deeper, Broader and Artier Domain Generalization. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 5543–5551 Li Y, Lu S (2023) Retraction Note: Research on physical education system model using multimedia technology. Multimed. Tools Appl 82:20705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13864-2 Liu Y, Qin Z, Wan T, Luo Z (2018) Auto-painter: Cartoon image generation from sketch by using conditional Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. Neurocomputing 311:78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.045 Martzoukou K (2020) “Maddie is online”: an educational video cartoon series on digital literacy and resilience for children. J. Res Innov. Teach. Learn 15(1):64–82 Miller CH (2019) Digital Storytelling 4e: A creator’s guide to interactive entertainment. CRC Press, Florida Book Google Scholar Miller J, Southern G (2014) Recommender system for animated video. Issues Inf. Syst. 15(2):321–327. https://doi.org/10.48009/2_iis_2014_321-327 Moss AJ, Rosenzweig C, Robinson J, Jaffe SN, Litman L (2023) Is it ethical to use Mechanical Turk for behavioral research? Relevant data from a representative survey of MTurk participants and wages. Behavior Research Methods . https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-022-02005-0 Nordin H (2021) Animation Vs. Comic Stripfor Digital Communication: A Mixed Method Approach through an Online Survey. Thesis, Umea University Olandinrin OT, Arif M, Rana MQ, Gyoh L (2023) Interrelations between construction ethics and innovation: A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer. Constr. Innov. 23:3 Olson JC (2008) The comic strip as a medium for promoting science literacy. California State University, Northridge Pangaribuan KR, Zulkarnain A (2021) Using the Concept of Timeframing to Implement Animation in the Motion Comic Adaptation of Bumi. In IMOVICCON Conference Proceeding, 2(1):35-39 Pillen A, Matthews EK (2022) Natural language modelled and printed in 3D: A multi-disciplinary approach. Humanit Soc. Sci. Commun. 9(1):1–11 Prahani BK, Nisa’ K, Amiruddin MZB, Suprapto N, Madlazim MS (2022) Analysis of the Top 100 Cited Publications in Earthquake Research During 1991 to 2021. Sci. Tsunami Hazards 41(1):77–94 Prahani BK, Nisa’ K, Jatmiko B, Suprapto N, Amelia T, Candrawati E (2022) The Comparison of the Top 100 Cited Publications of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality for the Last Thirty Years. Int J. Online Biomed. Eng. 18(6):13–29 Riwanto MA, Wulandari MP (2018) Efektivitas Penggunaan Media Komik Digital (Cartoon Story Maker) dalam Pembelajaran Tema Selalu Berhemat Energi. J. PANCAR 2(1):14–18 Saito S, Hu L, Ma C, Ibayashi H, Luo L, Li H (2018) 3D hair synthesis using volumetric variational autoencoders. ACM Trans. Graph. 208:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1145/3272127.3275019 . 37 , 6 Selmbacherova T, Sisler V, Brom C (2014) The impact of visual realism on the authenticity of educational simulation: A comparative study. 520-528 Setyaningsih I, Indarti N, Jie F (2018) Bibliometric analysis of the term ‘green manufacturing. Int J. Manag Concepts Philos. 11(3):315–339 Shen C-W, Ho H-T (2020) Technology-enhanced learning in higher education: A bibliometric analysis with latent semantic approach. Comput. Hum. Behav. 104:106177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.106177 Sukstrienwong A (2018) Animo math: The role-playing game in mathematical learning for children. TEM J. 7(1):147–154 Suprapto N, Sukarmin, Puspitawati RP, Erman, Savitri D, Ku CH, Mubarok H (2021) Research trend on technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) through bibliometric analysis (2015–2019). Int J. Eval. Res Educ. 10(4):1375–1385 Tatalovic M (2009) Science comics as tools for science education and communication: a brief, exploratory study. J Sci Commun. https://doi.org/10.22323/2.08040202 Tsegay MG, Pathak PM, Samantaray AK, Merzouki R (2022) Bond graph modeling of a spatial multi-section soft bionic robot. Mech. Mach. Theory 174:104902 Utomo DTP, Ahsanah F (2020) Utilizing Digital Comics in College Students’ Grammar Class. J. Engl. Lang. Teach. Linguist 5(3):393 Van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2020) VOSviewer manual. Retrieved from https://www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.6.16.pdf Volante M, Babu SV, Chaturvedi H, Newsome N, Ebrahimi E, Roy T, Daily SB, Fasolino T (2016) Effects of Virtual Human Appearance Fidelity on Emotion Contagion in Affective Inter-Personal Simulations. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 22(4):1326–1335. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2016.2518158 Article PubMed Google Scholar Wan J, Mougeot G, Yang X (2020) Dense feature pyramid network for cartoon dog parsing. Vis. Comput 36:2471–2483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01887-5 Wiana W, Barliana MS, Riyanto AA (2018) The effectiveness of using interactive multimedia based on motion graphic in concept mastering enhancement and fashion designing skill in digital format. Int J. Emerg. Technol. Learn 13(1):4–20 Xie L, Chen Z, Wang H, Zheng C, Jiang J (2020) Bibliometric and visualized analysis of scientific publications on atlantoaxial spine surgery based on web of science and VOSViewer. World Neurosurg. 137:435–442 Yamanishi R, Mori R, Matsushita M (2021) Representation of characters’ directed relationships in comics with speech-roles. Procedia Comp. Sci. 192:1541–1549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2021.08.158 Yang L, Sun T, Liu Y (2017) A bibliometric investigation of flipped classroom research during 2000-2015. Int J. Emerg. Technol. Learn 12(6):178–186 Yanuarti EA, Suprapto N (2021) Ten years of research on history of science (physics): A bibliometric analysis. Studies Philos. Sci. Educ. 2(1):7–16 Yıldız M, Çiftçi E, Karal H (2017) Bilişimsel düşünme ve programlama (Computational-thinking and programming). Eğitim Teknolojileri Okumaları (Educational Technology Readings) pp 75-86 Zakhiyah I, Suprapto N, Setyarsih W (2021) Prezi mind mapping media in physics learning: A bibliometric analysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2110(1):012015 Zhang YW, Zhou W, Wang Q, Chen, LL, Fang J (2014) Traditional culture protection system based on the virtual augmented reality technology. Applied Mechanics and Matherials. 513–517, 491–497. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.513-517.491 Zhuang M (2023) Animation of Experiment: The Science Education Film and Useful Animation in China. Animation 18(2):152–166. https://doi.org/10.1177/17468477231182914 Zimmerman B (2008) Creating comics fosters reading, writing and creativity. Educ. Dig. 74(4):55–57 Download references AcknowledgementsThanks to Universitas Negeri Surabaya to support this research. Author informationAuthors and affiliations. Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Surabaya, Indonesia Nadi Suprapto National Dong Hwa University, Hualien, Taiwan Khoirun Nisa’ National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taipei, Taiwan Imam Sya’roni & Alif Syaiful Adam You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar ContributionsConceptualization: [Nadi Suprapto]; literature search and data analysis: [Khoirun Nisa’, Alif S. Adam]; Writing - original draft preparation: [Nadi Suprapto, Imam Sya’roni]; Writing - review and editing: [Nadi Suprapto, Khoirun Nisa’]; Funding acquisition: [Nadi Suprapto]; Resources: [Alif S. Adam, Imam Sya’roni]; critically revised the work: [Khoirun Nisa’]. Corresponding authorCorrespondence to Nadi Suprapto . Ethics declarationsCompeting interests. The author(s) declare no competing interests. Ethical statementsAll the data used in this article are public data collected from the Scopus repository. This article might be containing personal information but not apart from the ethical approval and informed consent regulation. All the data collection factors follow all the statement in ethical approval and informed consent letter. Informed consentThis article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. Additional informationPublisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Rights and permissionsOpen Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ . Reprints and permissions About this articleCite this article. Suprapto, N., Nisa’, K., Sya’roni, I. et al. Scientific mapping and production analysis of digital comic, animation, and digital cartoon in education. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 1009 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03513-4 Download citation Received : 26 June 2023 Accepted : 26 July 2024 Published : 07 August 2024 DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03513-4 Share this articleAnyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative Quick links
Modeling the ecological footprint and assessing its influential factors: A systematic review
Cite this article
Various factors have been found responsible for the increment in ecological footprint resulting difficulties in maintaining environmental sustainability. This has been noticed through a modeling perspective. Identifying the factors affecting Ecological Footprint helps policymakers to formulate policies regarding sustainability. However, studies conducted based upon systematic reviews on Ecological Footprint through modeling are still limited. Objective: This study intends to identify influential factors associated with ecological footprint through a systematic review. Methods: ProQuest, Science Direct, Scopus, and Web of Science databases were used to search literature systematically. Particular keywords and Boolean operators were applied to dig out relevant studies for the review. Peer-reviewed research articles published in the English language till September 13, 2023, were incorporated for the analysis. Following the guidelines of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA), 1011 articles were identified from four different databases and only 37 research papers were eligible for this study. These articles were assessed and relevant information was extracted and then amalgamated into the systematic review. Results: Gross domestic product, urbanization, energy consumption, renewable energy, non-renewable energy, natural resources, bio-capacity, human capital, foreign direct investment, trade openness, and financial development were observed as key factors of the ecological footprint. Conclusion: Factors known to influence ecological footprint need to be addressed properly for environmental sustainability including widespread use of renewable energy. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access. Access this articleSubscribe and save.
Price excludes VAT (USA) Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout. Instant access to the full article PDF. Rent this article via DeepDyve Institutional subscriptions  Data availabilityThis systematic review has not used any raw or secondary data; therefore, data availability is not applicable. Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2015) The effect of energy consumption, urbanization, trade openness, industrial output, and the political stability on the environmental degradation in the MENA (Middle East and North African) region. Energy 84:382–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.03.004 Article Google Scholar Alola AA, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. SciTotal Environ 685:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.139 Article CAS Google Scholar Amer EAAA, Meyad EMA, Gao Y, Niu X, Chen N, Xu H, Zhang D (2022) Exploring the link between natural resources, urbanization, human capital, and ecological footprint: A case of GCC countries. Ecol Indic 144:109556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109556 Ashraf J (2022) The spillover effects of political risk, financial risk, and economic freedom on ecological footprint: Empirical evidence from Belt and Road Initiative countries. Borsa Istan Rev 22(5):873–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bir.2022.06.004 Awosusi AA, Adebayo TS, Altuntaş M, Agyekum EB, Zawbaa HM, Kamel S (2022) The dynamic impact of biomass and natural resources on ecological footprint in BRICS economies: A quantile regression evidence. Energy Report 8:1979–1994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.01.022 Baskurt B, Celik S, Aktan B (2022) Do foreign direct investments influence environmental degradation? Evidence from a panel autoregressive distributed lag model approach to low-, lower-middle-, upper-middle-, and high-income countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(21):31311–31329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17822-7 Chowdhury M, Shanto P, Ahmed A, Rumana R (2020) Does foreign direct investments impair the ecological footprint? New evidence from the panel quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(12):14372–14385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11518-0 Dursun E (2022) The Nexus among Civil Aviation, Energy Performance Efficiency and GDP in terms of Ecological Footprint: Evidence from France and Finland. Int J Energ Econ Policy 12(5):243–251. https://doi.org/10.32479/ijeep.13399 Elish E (2022) Gender gap and ecological footprint: Are there country variations? Evidence from quantile panel regression. J Chinese Econ Foreign Trade Stud 15(3):219–238. https://doi.org/10.1108/JCEFTS-08-2021-0042 GFN(2023). Global footprint network. https://www.footprintnetwork.org/licenses/public-data-package-free/ . (Accessed on October 22, 2023) Hamadeh N, Rompaey C, Metreau E (2023). World Bank Group country classifications by income level for FY24 (July 1, 2023-June 30, 2024). World Bank Blog. https://blogs.worldbank.org/en/opendata/new-world-bank-group-country-classifications-income-level-fy24 . (Accessed on April 18, 2024). Hao Y (2023) Heading towards sustainable environment: Does renewable and non-renewable energy generation matter for the effect of industrialization and urbanization on ecological footprint? Evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(12):34282–34295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24476-6 Hussain MM, Pal S, Villanthenkodath MA (2023) Towards sustainable development: The impact of transport infrastructure expenditure on the ecological footprint in India. Innov Green Dev 2(2):100037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.igd.2023.100037 Jiang G, Alvarado R, Murshed M, Tillaguango B, Toledo E, Méndez P, Isik C (2022) Effect of Agricultural Employment and Export Diversification Index on Environmental Pollution: Building the Agenda towards Sustainability. Sustainability 14(2):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14020677 Karasoy A (2021) How do remittances to the Philippines affect its environmental sustainability? Evidence based on the augmented ARDL approach. Nat Res Forum 45(2):120–137. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-8947.12218 Khan A, Ximei Wu (2022) Digital Economy and Environmental Sustainability: Do Information Communication and Technology (ICT) and Economic Complexity Matter? Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(19):12301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912301 Kibria MdG (2023) Ecological footprint in Bangladesh: Identifying the intensity of economic complexity and natural resources. Heliyon 9(4):e14747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14747 Kihombo S, Ahmed Z, Chen S, Adebayo T, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Linking financial development, economic growth, and ecological footprint: What is the role of technological innovation? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(43):61235–61245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14993-1 Kızılgöl Ö, Öndes H (2022) Factors affecting the ecological footprint: A study on the OECD countries. Sci Total Environ 849:157757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157757 Kutlar A, Gulmez A, Kabasakal A, Kutlar S (2022) Ecological footprint, energy usage, and economic progress relationship: The MINT countries. Econ Res-Ekonomska Istrazivanja 35(1):4457–4480. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2021.2013279 Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals Internal Med 151(4):W-65. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00136 Lin D, Wambersie L, Wackernagel M (2022). Nowcasting the World's footprint and bio-capacity for 2022. Global footprint network. https://www.overshootday.org/content/uploads/2022/06/Earth-Overshoot-Day-2022-Nowcast-Report.pdf (Accessed October 22, 2023) Mostafa MM (2010) A Bayesian approach to analyzing the ecological footprint of 140 nations. Ecol Indic 10(4):808–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2010.01.002 Nathaniel SP, Bekun FV, Faizulayev A (2021) Modelling the impact of energy consumption, natural resources, and urbanization on ecological footprint in south africa: Assessing the moderating role of human capital. Int J Energ Econ Policy 11(3):130–139. https://doi.org/10.32479/ijeep.11099 Pahlevan Sharif S, Mura P, Wijesinghe SN (2019). Systematic reviews in Asia: Introducing the “PRISMA” protocol to tourism and hospitality scholars. Quantitative Tourism Research in Asia: Current Status and Future Directions: 13–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2463-5_2 Qiao G, Yang D, Ahmad M, Ahmed Z (2022) Modeling for Insights: Does Fiscal Decentralization Impede Ecological Footprint? Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(16):10146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610146 Ramezani M, Abolhassani L, Foroushani NS, Burgess D, Aminizadeh M (2022) Ecological Footprint and Its Determinants in MENA Countries: A Spatial Econometric Approach. Sustainability 14(18):11708. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811708 Raza S, Qamar S, Ahmed M (2023) Asymmetric role of non-renewable energy consumption, ICT, and financial development on ecological footprints: Evidence from QARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(8):20746–20764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23549-w Wackernagel M, Rees W (1996) Our ecological footprint: reducing human impact on the earth. New society publishers, Canada Rout SK, Gupta M, Sahoo M (2022) The role of technological innovation and diffusion, energy consumption and financial development in affecting ecological footprint in BRICS: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci and Pollut Res 29:25318–25335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17734-6 Sabir S, Gorus M (2019) The impact of globalization on ecological footprint: Empirical evidence from the South Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(32):33387–33398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06458-3 Sahoo M, Sethi N (2021) The intermittent effects of renewable energy on ecological footprint: Evidence from developing countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(40):56401–56417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14600-3 Shujah-ur-Rahman CS, Saud S, Saleem N, Bari M (2019) Nexus between financial development, energy consumption, income level, and ecological footprint in CEE countries: Do human capital and biocapacity matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(31):31856–31872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06343-z Solarin S, Nathaniel S, Bekun F, Okunola A, Alhassan A (2021) Towards achieving environmental sustainability: Environmental quality versus economic growth in a developing economy on ecological footprint via dynamic simulations of ARDL. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(14):17942–17959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11637-8 Tang W, Zhong X, Liu S (2011) Analysis of major driving forces of ecological footprint based on the STRIPAT model and RR method: A case of Sichuan Province. Southwest China J Mount Sci 8(4):611–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-011-1021-2 Triki R, Kahouli B, Tissaoui K, Tlili H (2023) Assessing the Link between Environmental Quality, Green Finance, Health Expenditure, Renewable Energy, and Technology Innovation. Sustainability 15(5):4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054286 Uddin GA, Salahuddin M, Alam K, Gow J (2017) Ecological footprint and real income: Panel data evidence from the 27 highest emitting countries. Ecol Indic 77:166–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.01.003 Uddin I, Ullah A, Saqib N, Kousar R, Usman M (2023) Heterogeneous role of energy utilization, financial development, and economic development in ecological footprint: How far away are developing economies from developed ones. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(20):58378–58398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26584-3 Ullah A, Ahmed M, Raza SA, Ali S (2021) A threshold approach to sustainable development: Nonlinear relationship between renewable energy consumption, natural resource rent, and ecological footprint. J Environ Manag 295:113073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113073 Ullah A, Tekbaş M, Doğan M (2023) The Impact of Economic Growth, Natural Resources, Urbanization and Biocapacity on the Ecological Footprint: The Case of Turkey. Sustainability 15(17):12855. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712855 Wenlong Z, Nawaz M, Sibghatullah A, Ullah S, Chupradit S, Hieu V (2023) Impact of coal rents, transportation, electricity consumption, and economic globalization on ecological footprint in the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(15):43040–43055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20431-7 Wu D (2020) Spatially and temporally varying relationships between ecological footprint and influencing factors in China’s provinces Using Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR). J Clean Prod 261:121089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121089 Yang L, Danwana SB, Fadilul-lahYI, (2022) Achieving Environmental Sustainability in Africa: The Role of Renewable Energy Consumption, Natural Resources, and Government Effectiveness—Evidence from Symmetric and Asymmetric ARDL Models. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(13):8038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19138038 Zambrano-Monserrate MA, Ruano MA, Ormeño-Candelario V, Sanchez-Loor DA (2020) Global ecological footprint and spatial dependence between countries. J Environ Manag 272:111069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111069 Download references AcknowledgementsWe would like to extend our sincere gratitude to all the researchers whose articles were used in this study and to all anonymous reviewers for their constructive feedback. We would also like to thank members of the Central Department Research Committee, Central Department of Statistics, Tribhuvan University, Kirtipur, Kathmandu, Nepal for valuable comments and suggestions. The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. Author informationAuthors and affiliations. Amrit Science College Lainchour, Kathmandu, Nepal Surendra Raj Nepal Central Department of Statistics, Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Kirtipur, Nepal Srijan Lal Shrestha You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar ContributionsSurendra Raj Nepal (SRN) designed and conceptualized the study, developed a search strategy, executed searches, reviewed all the articles satisfying inclusion criteria, extracted relevant information from eligible articles, and drafted the manuscript. Srijan Lal Shrestha (SLS) supervised this review study as a part of ongoing Ph.D. research, verified extracted information, and reviewed, edited, and finalized the manuscript. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript. Corresponding authorCorrespondence to Surendra Raj Nepal . Ethics declarationsEthical approval and consent to participate. Not applicable. Consent to publishCompeting interests. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. Additional informationResponsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues Publisher's NoteSpringer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Rights and permissionsSpringer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law. Reprints and permissions About this articleNepal, S.R., Shrestha, S.L. Modeling the ecological footprint and assessing its influential factors: A systematic review. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34549-3 Download citation Received : 13 December 2023 Accepted : 24 July 2024 Published : 05 August 2024 DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34549-3 Share this articleAnyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Log in using your username and password
You are here
Introduction During the last decade the Quebec Public Health Care System (QPHCS) had an important transformation in primary care planning activity. The increase of the service demand together with a significant reduction of supply in primary care may be at risk of reducing access to health care services, with a negative impact on costs and health outcomes. The aims of this systematic literature review are to map and aggregate existing literature and evidence on the primary care provided in Quebec, showing the benefits and limitations associated with the health policies developed in the last two decades, and highlighting areas of improvement. Methods and analysis PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science and CINAHL will be searched for articles and government reports between January 2000 and January 2022 using a prespecified search strategy. This protocol adheres to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis for Protocols and has been registered with PROSPERO. A wide range of electronic databases and grey literature sources will be systematically searched using predefined keywords. The review will include any study design, with the exclusion of protocols, with a focus on the analysis of health care policies, outcomes, costs and management of the primary health care services, published in either English or French languages. Two authors will independently screen titles, abstracts, full-text articles and select studies meeting the inclusion criteria. A customised data extraction form will be used to extract data from the included studies. Results will be presented in tabular format developed iteratively by the research team. Ethics and dissemination Research ethics approval is not required as exclusively secondary data will be used. Review findings will synthesise the characteristics and the impact of the reforms of QPHCS of the last two decades. Findings will therefore be disseminated in peer-reviewed journals, conference presentations and through discussions with stakeholders. PROSPERO registration number CRD42023421145.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ . https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068666 Statistics from Altmetric.comRequest permissions. If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways. Strengths and limitations of this studyThis systematic review protocol follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols guidelines. The search algorithm was developed by an experienced librarian and customised to four large databases, including any type of grey literature. The certainty of the evidence of this systematic review may be limited by the limited number of studies available and the possible low quality of the individual studies. We aim to create the most comprehensive systematic review providing a comprehensive view and analysis of the primary care in Quebec Public Health are System and its impact on costs, outcomes, accessibility, equity and health organisation. The systematic literature review will consider only studies published from 2000 onwards and those published in French and English languages. Primary health care services represent an important element in public health care systems. As reported by the WHO ‘Primary Health Care (PHC) is a whole-of-society approach to health that aims at ensuring the highest possible level of health and well-being and their equitable distribution by focusing on people’s needs and as early as possible along the continuum from health promotion and disease prevention to treatment, rehabilitation and palliative care, and as close as feasible to people’s everyday environment ’ . 1 PHC is the most inclusive, equitable, cost-effective and efficient approach to enhance people’s physical and mental health, as well as social well-being. A strong primary health care presents lower health costs, better population health, higher patient satisfaction, fewer inappropriate and unnecessary hospital admissions, better rates of screening and early detection of chronic diseases, better patient follow-up for patients, a better management of patients with multimorbidity and finally greater socioeconomic equity. 2–8 The PHC services include the general practitioners (GP) or family physicians, who represent generally the first point of contact of individuals with the healthcare system, and focus care on the individual within the community, delivering services across the entire spectrum of care (eg, mental health, preventive medicine, respiratory diseases). They play an important role in health promotion and illness prevention, coordinating care with other specialties and health professionals and advocating on behalf of their patients with respect to the care and services they need in all parts of the health care system. The importance of GPs for patients is highlighted in the international literature. 9–14 The physician’s personal commitment to the patient is one of the most important determinants of the patient’s sense of safety, and it has a large impact on the patient’s decision to consult a specialist or to access an emergency department (ED). 15 Canada has a decentralised and universal publicly funded health care system with the funding and administrations of health care primarily managed by the 13 provinces and territories and the entire country. Each province has its own insurance plan and each province receives money and assistance from the federal government on a per-capita basis. Each system is managed publicly and it is accessible to any citizen (universally). Each provincial government is responsible for the management, organisation and delivery of health care services for Canadians. The insurance plans developed by each province must meet the standards of the Canadian Health Act to access federal funds. Two reforms were introduced in the early 2000s (Family Medicine Group in 2003 and Bill 20 in 2015) aimed at maximising medical and financial resource use in order to improve the patient access in primary care. 16 17 However, actually the accessibility to primary care for patients still represents a public health issue in Québec ( online supplemental material S1 ). In addition, since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemics, the accessibility to primary health care worsened. 18 This problem was already reported previously 19–22 and it still represent a challenge for the government. 23 24 Supplemental materialThe aim of this work consists in studying, through this systematic literature review, the last two decades of the Quebec Public Health Care System (QPHCS) primary care and the impact of the reforms developed on health organisation, costs, health outcomes, accessibility, equity and services, considering health care system perspective. Methods and analysisThis protocol has been prepared using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Protocols guidelines, 25 as shown in PRISMA-P checklist ( online supplemental material S2 ). Important amendments made to the protocol will be documented and published alongside the results of the systematic review. Research questionThis systematic literature review will synthesise the scientific literature on interventions that have been developed in QPHCS, focusing on primary care and GPs activities, together with a collection of the evidence for assessing health outcomes, costs, equity and accessibility for Quebec adult population. Eligibility criteriaThe criteria for the study selection will be based on studies that will explicitly analyse the impact of any policy implementation or activity provided where GPs or family doctors are included, together with the information about corresponding health outcomes, costs, accessibility or performance on system organisation. Study design/characteristicsTarget studies will include meta-analysis, systematic review, randomised controlled trial, cohort study (prospective observational study), case-control study, cross-sectional study, case reports, series, quasi-experimental design, difference in difference analysis, natural experiments, regression discontinuity design that show the impact of GP activities on health outcomes, costs, accessibility, health organisation and management, services in QPHCS. We will also consider summary papers, government and public health reports and other analyses to identify relevant primary papers. Study protocols will not be considered in this systematic literature review. Information sourcesA research of academic databases including: PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) will be performed by an author experienced in conducting systematic reviews (FB). The search will look for potentially relevant articles using predefined strategies ( online supplemental material S3 ). A manual search of the reference lists of the studies will be performed in order to check for any additional possible relevant articles. The manual search will be based on backward snowballing search that will involve search of the reference list of the articles selected and identified. In addition, for some of the relevant journals a hand search will be performed to ensure a saturation of the literature. Grey literature will be included in order to explore all the available documentation published. Studies will be excluded if they do not investigate on QPHCS. Search strategyThe search strategy ( table 1 ) will be reviewed by the first (PL) and the second (J-DL) author, together with the supervision of the third author who is a medical librarian able to provide the support and the guidance on search terms and strategies (FB). The search strategy will combine MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) terms and free text words such as (Primary Health Care OR Primary Care OR Primary Healthcare OR Family Physicians OR Family Practitioner OR General Practitioners OR General Practice AND Health Services Needs and Demand OR Health Services Accessibility OR Delivery of Health Care OR Health Care Reform OR Health Policy OR Appointments and Schedules OR Mass Screening/organization and administration OR Outcome and Process Assessment, Health Care OR Quality Indicators, Health Care OR Waiting Lists OR Health Policy OR Healthcare Policy OR National Policy OR Healthcare Delivery OR delivery of care OR Health access OR Healthcare access OR Health Care Reform OR primary care demand OR Health demand OR care demand AND Quebec). The search strategy will have filters limiting studies to 2000 onwards, and studies published in English or French. The time limitation is chosen as by the early 2000s, the Family Medicine Groups were introduced as a new primary care model. The literature review searches will be updated at the end of the search process. In addition, using the Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timing and Study design strategy, 26 27 we elaborated the guiding question of this review to ensure the systematic search of available literature: ‘What is the impact of last two decades of primary health care reforms for GP activities on health outcomes, costs, equity and accessibility for Quebec adult population?’.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria Screening, data collection and extractionThe abstracts and full-text articles retrieved from the search strategy will be undertaken using Covidence ( www.covidence.org ), 28 an online systematic review tool recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration, and duplicates will be removed. Two authors (PL and J-DL) will independently assess titles and abstracts of records, and exclude articles that will not meet eligibility criteria. Disagreements between the selected papers made by the two authors will be resolved by discussion or by a third author SAK, J-BG, AC, MR or ET). Four authors will independently extract and record data from included studies using a predefined data extraction form (PL, J-DL, J-BG and MR). The authors will pilot the data extraction form with a sample of a limited number of papers (10) and amendments will be made as necessary. After the evaluation of piloting, the data extraction will be developed and completed. The data extraction form will include the information reported in the online supplemental material S4 . Other additional information will be included during the review process. If additional information will be required from the studies, study authors will be contacted. At the end of data extraction, four authors (PL, J-DL, J-BG and MR) will resolve any discrepancies that will be present by applying a consensus-based decision, or if necessary, discussion with a fifth author (AC). Data synthesis will be undertaken through a narrative approach, providing detailed written commentary on the data extracted previously. This will help in the understanding of the impact of GPs activity to the delivery of care and the related issues. In addition, summary tables will be used to present data in a structured format. We will use a convergent synthesis design to synthesise qualitative, quantitative and mixed-method results. 29 Thus, using a thematic synthesis procedure, we will synthesise the evidence from the selected studies. Quality assessmentTwo independent authors (PL and J-DL) will assess the methodological quality of eligible studies. Two independent authors will score the selected studies and disagreements will be resolved by a third author (SAK, J-BG, AC, MR or ET). For quality assessment we will use the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT), which is a critical appraisal tool that is designed for the appraisal stage of systematic mixed studies reviews that include qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods studies. It enables the appraisal of five categories of methodologies such as qualitative research, randomised controlled trials, non-randomised studies, quantitative descriptive studies, and mixed methods studies ( online supplemental material S5 ). 30 Cumulative evidenceWe will use the MMAT approach to assess the certainty of the evidence for each study, and will present the data results on the MMAT rating tables. To our knowledge, this systematic review will be the first to synthesise the available evidence on the impact of the last two decades’ reforms on primary health care organisations in Quebec evaluating several dimensions (eg, costs, health outcomes, services accessibility, equity). The results of this review will also inform policymakers and leaders of Quebec public health. Our results may highlight gaps in knowledge and guide future research concerned with the primary health care organisation in Quebec. Patient and public involvementPatients were not directly involved in the design of this study. As this is a protocol for a systematic literature review and no participant recruitment will take place, their involvement in the recruitment and dissemination of findings to participants was not applicable. Ethics and disseminationThis study does not require the ethical review as it is a systematic literature review. The objective is submitting this work and its future development to a peer-reviewed journal and presenting the main findings at Quebec government, national and international meetings and conferences. Ethics statementsPatient consent for publication. Not applicable.
Supplementary materialsSupplementary data. This web only file has been produced by the BMJ Publishing Group from an electronic file supplied by the author(s) and has not been edited for content.
Contributors PL and J-DL led the design, search strategy and conceptualisation of this work and drafted the protocol. FB performed the search strategy and provided the corresponding results. PL, J-DL, SAK, MR, ET, AC and J-BG were involved in the conceptualisation of the review design, inclusion and exclusion criteria and provided feedback on the methodology and the manuscript. PL, MR, ET, AC, J-BG and J-DL were involved in data extraction forms. All authors provided feedback on the manuscript and approval to the publishing of this protocol manuscript. Funding Université Laval - Fonds de démarrage Université Laval (Canada). Soutien à la recherche (SAR) Faculté des Sciences de l'administration - Volet 1A : Démarrage nouveau professeur adjoint (DC132416). Competing interests None declared. Patient and public involvement Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research. Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed. Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise. Read the full text or download the PDF:Information
InitiativesYou are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader. All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess . Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications. Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers. Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal. Original Submission Date Received: .
 Article Menu
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website. Please let us know what you think of our products and services. Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI. JSmol ViewerArtificial neural network application in construction and the built environment: a bibliometric analysis.  1. Introduction
2. Methodology: Multi-Stage Critical Literature Review2.1. phase 1: data collection, 2.2. phase 2: quantitative analysis stage, 2.3. phase 3: qualitative analysis stage, 3. quantitative analysis and scientometrics, 3.1. authorship analysis, 3.1.1. active countries, 3.1.2. co-authors analysis, 3.2. citation analysis, 3.2.1. journals citation analysis, 3.2.2. articles citation analysis, 3.3. authors’ keywords analysis, 3.3.1. co-occurrence analysis, 3.3.2. thematic clusters.
4.1. Energy Management in Buildings4.1.1. predicting energy consumption, 4.1.2. improving energy performance, 4.2. occupant comfort in buildings, 4.2.1. thermal comfort of occupants, 4.2.2. modelling occupant behavior, 4.3. design & construction optimization, 4.3.1. building design optimization, 4.3.2. construction material optimization, 4.4. cost prediction, 4.5. health and safety in construction, 4.5.1. safety of workers, 4.5.2. safety of structures, 4.6. soil mechanics, 5. discussion, 5.1. broadening the application ranges of ann into the current construction 4.0 technologies.
5.2. Constructing ANN Applications Research in Developing Countries5.3. potential areas for improvement in the application of neural networks.
6. Future Perspectives
6.1. Theoretical Implications6.2. practical implications, 7. conclusions, author contributions, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
Click here to enlarge figure
Share and CiteKaushik, A.K.; Islam, R.; Elbahy, S.; Arif, M. Artificial Neural Network Application in Construction and the Built Environment: A Bibliometric Analysis. Buildings 2024 , 14 , 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082423 Kaushik AK, Islam R, Elbahy S, Arif M. Artificial Neural Network Application in Construction and the Built Environment: A Bibliometric Analysis. Buildings . 2024; 14(8):2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082423 Kaushik, Amit Kant, Rubina Islam, Salma Elbahy, and Mohammed Arif. 2024. "Artificial Neural Network Application in Construction and the Built Environment: A Bibliometric Analysis" Buildings 14, no. 8: 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082423 Article MetricsArticle access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.  Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Australian Association for the Teaching of English (AATE) 5. English in Education (Wiley) 6. English World-Wide | A Journal of Varieties of English. 7. European Journal of English Studies- Taylor & Francis Online. 8. Journal of English for Academic Purposes - Elsevier B.V.
Language and Literature is an invaluable international peer-reviewed journal that covers the latest research in stylistics, defined as the study of style in literary and non-literary language. We publish theoretical, empirical and experimental research that aims to make a contribution to our understanding of style and its effects on readers.
English is delighted to announce its 2022 Postgraduate Essay Prize. It is open to all students currently registered on a PhD and writing on a topic in English Literature. Winners get a cash prize and publication in the journal, while all entries are considered for publication and receive specialist peer review. Explore the past winning essays.
Search the journal. More than three decades after its founding, the Journal of Modern Literature remains the most important and widely recognized scholarly serial in the field of modern literature. Each issue emphasizes scholarly studies of literature in all languages, as well as related arts and cultural artifacts, from 1900 to the present.
Journal overview. For more than a century, English Studies has been one of the defining publications in the field of 'English'. Unique in the range and quality of its coverage, it attracts contributions from leading scholars worldwide on the language, literature and culture of the English-speaking world from the Early Medieval period to the ...
Journal Rankings on Literature and Literary Theory. Agricultural and Biological Sciences (miscellaneous) Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology (miscellaneous) Business, Management and Accounting (miscellaneous) Economics, Econometrics and Finance (miscellaneous) Organizational Behavior and Human Resource Management.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Refereed/ Peer-Reviewed International Research Journal in the field of English Literature, Humanities and Social Sciences. Impact Factor: 5.66 ... CrossRef DOI: 10.22161/ijels. International Journal of English Literature and Social Sciences (IJELS) International Journal of English Literature and Social Sciences is a Bi-Monthly(6 Issue Per Year ...
The content of the journal consists of research articles and review essays of 5,000 to 7,000 words. Short reviews are not published. The target audience of the journal is scholars in the field of Literary and Cultural Studies. The main language medium is English but essays written in Afrikaans are also published. Peer Review Policy
Science Center Berlin for Social Research, Berlin Visitors. Welcome. The Criterion is refereed e-journal and is designed to publish theoretical articles and book reviews on English Language and Literature. The Criterion encourages interpretative criticism and fresh insights into new and established authors and texts and seeks to generate a ...
The Research Journal of English Language and Literature (RJELAL) is seeking volunteer full and junior members to join its National/International Editorial Board who support our mission, values, and commitment to provide a high-quality experience for our authors. Positions will begin January 1, 2023
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Take your research further with Artstor's 3+ million images. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and ...
PMLA is the journal of the Modern Language Association of America. Since 1884, PMLA has published members' essays judged to be of interest to scholars and teachers of language and literature. SEL: Studies in English Literature 1500-1900.
A regular publication of academic and research articles. A broad term that refers to items published in a series but the items are separate and standalone. Examples include indexes, yearbooks and some journals. A regular publication that includes articles, stories and other text. Magazines and newspapers are examples of these.
Most Read in Literature. From Shakespeare's plays to modern literary trends, explore a collection of our most read recent articles and chapters from our literature portfolio. Enhance your knowledge with free access to these highlights from our books and journals until December 2022.
The MLA International Bibliography, the primary database for literature research, indexes more than 4400 journals.If you would like to browse the content of highly cited literature journals here is a list of the most frequently cited journals. If you are looking for articles and chapters on a particular topic, it is more efficient to search the MLA database.
Open Access Journals for English Literature. The following is a list of suggested peer-reviewed and open access journals related to the discipline of English Literature. ... Missions and Global Christianity, Pastoral Studies, Religious Studies, Research Strategies, Spirituality, Theology << Previous: Education; Next: History >> Last Updated ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on ENGLISH LITERATURE. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on ...
Callaloo: A Journal of African Diaspora Arts and Letters. For those interested in publishing articles that creatively and/or critically engage with the work of African Americans and peoples of African descent throughout the African Diaspora. …. Continue reading →.
About the Journal. The Journal of Teaching and Research in English Literature (JTREL), launched in July 2009, is an international double-blind peer-reviewed open-access journal dedicated to supporting scholarly exchange among teachers and researchers of Literature written in English. It aims to publish high-quality, original research articles, reviews, author interviews and poems.
American Research Journal of English and Literature is an international, peer-reviewed, open access online journal. English literature is the study of literature written in the English language. It includes some of history's most famous writers: James Joyce (Ireland), William Shakespeare (England), Mark Twain (United States), Arthur Conan Doyle (Scotland), Dylan Thomas (Wales), and Vladimir ...
A Peer Reviewed International Research Journal ISSN-2349-9451(online): ISSN (PRINT): 2395-2628 ... Translation Journal, Indian English Literature Journal, Online English Journal, Indexed journal, English Language Journal, English Journal With Impact Factor. NOTE: The submission must not have been previously published, nor should it be under ...
International Journal of English Literature and Social Sciences (IJELS)(ISSN: 2456-7620) is a bi-monthly peer-reviewed refereed journal that invites Literature Essays, Review Articles, Research articles, case studies, conference proceedings and short communication in the field of English Literature, Humanities and Social Sciences. IJELS welcomes quality work that focuses on research ...
Journal articles are the academic's stock in trade, the basic means of communicating research findings to an audience of one's peers. That holds true across the disciplinary spectrum, so no matter where you land as a concentrator, you can expect to rely on them heavily. ... Searching the journal literature is part of being a responsible ...
Analyzing scientific mapping literature activity on digital comics, animation, and digital cartoons is essential for future research and development. The objective of the current study was to ...
Methods: ProQuest, Science Direct, Scopus, and Web of Science databases were used to search literature systematically. Particular keywords and Boolean operators were applied to dig out relevant studies for the review. Peer-reviewed research articles published in the English language till September 13, 2023, were incorporated for the analysis.
Background. Primary health care services represent an important element in public health care systems. As reported by the WHO 'Primary Health Care (PHC) is a whole-of-society approach to health that aims at ensuring the highest possible level of health and well-being and their equitable distribution by focusing on people's needs and as early as possible along the continuum from health ...
This research also identified the critical articles, countries, sources, and co-authors in the existing body of literature. The co-occurrence of author keywords analysis conducted in Section 3 revealed that energy management in buildings, cost estimates, occupant comfort in buildings, and building design optimization are themes that have ...