

50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
In this useful lesson, we’ll explore direct and indirect speech through 50 simple examples. These two ways of speaking help us share what someone else said. Think of direct speech as using the speaker’s exact words, like quoting a friend. Indirect speech , on the other hand, involves changing the original words a bit, as if you’re telling a story about what was said. This lesson is great for anyone looking to get better at English, offering clear examples to make learning easier.
Rules to Make Direct and Indirect Speech
When converting direct speech into indirect speech, it’s important to follow specific rules to ensure the sentence still conveys the original meaning. Here are the key rules:
- Change in Pronouns : Pronouns often need to be changed according to the context and the point of view of the reporting verb. For example, “ I am going ” (direct) might become “ He said he was going ” (indirect).
- Tense Shifts : The tense of the verb in direct speech usually changes when converting to indirect speech. If the reporting verb is in the past tense , the tense in the reported speech shifts back as well. For instance, “ She said, ‘I am eating ‘” changes to “ She said she was eating “.
- Time and Place Words : Words indicating time and place in direct speech are often adjusted in indirect speech. “Here” may change to “there,” “today” to “ that day ,” “tomorrow” to “ the next day ,” etc.
- Question Form : If the direct speech is a question, the indirect form does not use a question format. Instead, it integrates the question into a statement, often using “if” or “whether” for yes/no questions, and ‘wh’ words ( what, when, where, why, who ) for questions that require more detailed answers. For example, “ He asked, ‘Are you coming? ‘” becomes “ He asked if I was coming .”
- No Quotes : In indirect speech, quotation marks are not used. The sentence is integrated into a larger statement, which often starts with verbs like said, asked, or told.
- Exclamations and Commands : Exclamatory sentences and commands in direct speech are transformed into statements or requests in indirect speech. For instance, “He said, ‘How beautiful!'” becomes “He exclaimed that it was beautiful.” Commands like “He said, ‘Sit down!'” change to “He ordered me to sit down.”
- Modal Verbs : Modal verbs can also change in indirect speech, especially might, could, would, and should, depending on the context and the necessity to maintain the original sentence’s meaning.
Remember, the goal of these changes is to maintain the essence of the original statement while adapting it to the grammatical and contextual framework of indirect speech.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
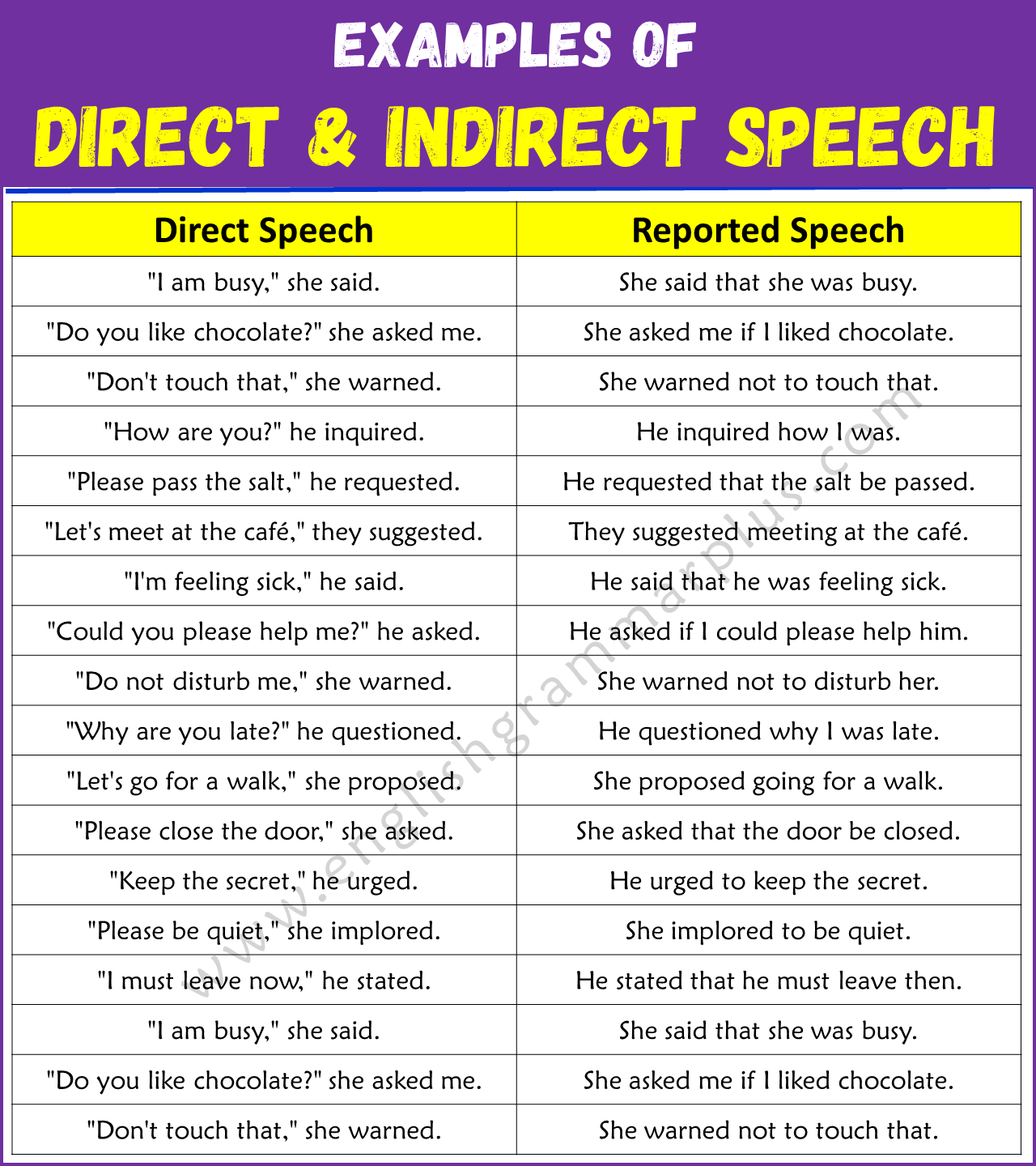
1. Direct: “I am busy,” she said.
Indirect: She said that she was busy.
2. Direct: “We will go tomorrow,” they said.
Indirect: They said that they would go the next day.
3. Direct: “He can play the guitar,” Mike said.
Indirect: Mike said that he could play the guitar.
4. Direct: “Do you like chocolate?” she asked me.
Indirect: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
5. Direct: “Please open the window,” John requested.
Indirect: John requested that the window be opened.
6. Direct: “I have finished my homework,” he announced.
Indirect: He announced that he had finished his homework.
7. Direct: “Don’t touch that,” she warned.
Indirect: She warned not to touch that.
8. Direct: “How are you?” he inquired.
Indirect: He inquired how I was.
9. Direct: “I will help you,” she promised.
Indirect: She promised that she would help me.
10. Direct: “I didn’t see him yesterday,” Tom confessed.
Indirect: Tom confessed that he hadn’t seen him the day before.
11. Direct: “I am going to the market,” Alex said.
Indirect: Alex said that he was going to the market.
12. Direct: “We saw a movie last night,” they told me.
Indirect: They told me that they had seen a movie the night before.
13. Direct: “Can you drive a car?” she questioned.
Indirect: She questioned whether I could drive a car.
14. Direct: “Please pass the salt,” he requested.
Indirect: He requested that the salt be passed.
15. Direct: “I have been to Spain,” she mentioned.
Indirect: She mentioned that she had been to Spain.
16. Direct: “Stay away from the dog,” he cautioned.
Indirect: He cautioned to stay away from the dog.
17. Direct: “Where did you buy this?” she inquired.
Indirect: She inquired where I had bought that.
18. Direct: “I’ll call you tonight,” he promised.
Indirect: He promised that he would call me that night.
19. Direct: “I didn’t take your book,” Sarah insisted.
Indirect: Sarah insisted that she hadn’t taken my book.
20. Direct: “Let’s meet at the café,” they suggested.
Indirect: They suggested meeting at the café.
21. Direct: “I’m feeling sick,” he said.
Indirect: He said that he was feeling sick.
22. Direct: “I won the match,” she exclaimed.
Indirect: She exclaimed that she had won the match.
23. Direct: “Could you please help me?” he asked.
Indirect: He asked if I could please help him.
24. Direct: “Turn off the lights,” she commanded.
Indirect: She commanded that the lights be turned off.
25. Direct: “I’ll see you tomorrow,” he said.
Indirect: He said that he would see me the next day.
26. Direct: “We’re moving to a new city,” they announced.
Indirect: They announced that they were moving to a new city.
27. Direct: “Do not disturb me,” she warned.
Indirect: She warned not to disturb her.
28. Direct: “Why are you late?” he questioned.
Indirect: He questioned why I was late.
29. Direct: “I’ll handle the situation,” she assured.
Indirect: She assured that she would handle the situation.
30. Direct: “I’ve never been to Asia,” he stated.
Indirect: He stated that he had never been to Asia.
31. Direct: “Let’s go for a walk,” she proposed.
Indirect: She proposed going for a walk.
32. Direct: “I am learning Spanish,” he mentioned.
Indirect: He mentioned that he was learning Spanish.
33. Direct: “Please close the door,” she asked.
Indirect: She asked that the door be closed.
34. Direct: “I will join you later,” he promised.
Indirect: He promised that he would join me later.
35. Direct: “I lost my wallet,” she declared.
Indirect: She declared that she had lost her wallet.
36. Direct: “Keep the secret,” he urged.
Indirect: He urged to keep the secret.
37. Direct: “Where is the nearest bank?” she inquired.
Indirect: She inquired where the nearest bank was.
38. Direct: “I might go to the concert,” he speculated.
Indirect: He speculated that he might go to the concert.
39. Direct: “Please be quiet,” she implored.
Indirect: She implored to be quiet.
40. Direct: “I will finish the project by Monday,” he assured.
Indirect: He assured that he would finish the project by Monday.
41. Direct: “Don’t forget to lock the door,” she reminded.
Indirect: She reminded to not forget to lock the door.
42. Direct: “How do you solve this problem?” he pondered.
Indirect: He pondered how to solve that problem.
43. Direct: “I can’t believe I won!” he exclaimed.
Indirect: He exclaimed that he couldn’t believe he had won.
44. Direct: “Would you like some coffee?” she offered.
Indirect: She offered if I would like some coffee.
45. Direct: “I must leave now,” he stated.
Indirect: He stated that he must leave then.
46. Direct: “We’re adopting a puppy,” they shared.
Indirect: They shared that they were adopting a puppy.
47. Direct: “Never speak to me again,” she commanded.
Indirect: She commanded never to speak to her again.
48. Direct: “When will you return the book?” he asked.
Indirect: He asked when I would return the book.
49. Direct: “I’ll think about your offer,” she considered.
Indirect: She considered that she would think about the offer.
50. Direct: “Please bring me a glass of water,” he requested.
Indirect: He requested that a glass of water be brought to him.
Post navigation
Previous post.
No comments yet. Why don’t you start the discussion?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Direct and Indirect Speech: Useful Rules and Examples
Are you having trouble understanding the difference between direct and indirect speech? Direct speech is when you quote someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. This can be a tricky concept to grasp, but with a little practice, you’ll be able to use both forms of speech with ease.

Direct and Indirect Speech
When someone speaks, we can report what they said in two ways: direct speech and indirect speech. Direct speech is when we quote the exact words that were spoken, while indirect speech is when we report what was said without using the speaker’s exact words. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I love pizza,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he loved pizza.
Using direct speech can make your writing more engaging and can help to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion. However, indirect speech can be useful when you want to summarize what someone said or when you don’t have the exact words that were spoken.
To change direct speech to indirect speech, you need to follow some rules. Firstly, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb. Secondly, you need to change the pronouns and adverbs in the reported speech to match the new speaker. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will go to the park,” said Sarah. Indirect speech: Sarah said that she would go to the park.
It’s important to note that when you use indirect speech, you need to use reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked” to indicate who is speaking. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is it?” asked Tom. Indirect speech: Tom asked what time it was.
In summary, understanding direct and indirect speech is crucial for effective communication and writing. Direct speech can be used to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion, while indirect speech can be useful when summarizing what someone said. By following the rules for changing direct speech to indirect speech, you can accurately report what was said while maintaining clarity and readability in your writing.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech
When it comes to reporting speech, there are two ways to go about it: direct and indirect speech. Direct speech is when you report someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. Here are some of the key differences between direct and indirect speech:
Change of Pronouns
In direct speech, the pronouns used are those of the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the pronouns have to be changed to reflect the perspective of the reporter. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.
- Indirect speech: John said he was going to the store.
In the above example, the pronoun “I” changes to “he” in indirect speech.
Change of Tenses
Another major difference between direct and indirect speech is the change of tenses. In direct speech, the verb tense used is the same as that used by the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the verb tense may change depending on the context. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am studying for my exams,” said Sarah.
- Indirect speech: Sarah said she was studying for her exams.
In the above example, the present continuous tense “am studying” changes to the past continuous tense “was studying” in indirect speech.
Change of Time and Place References
When reporting indirect speech, the time and place references may also change. For example:
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” said Tom.
- Indirect speech: Tom said he would meet you at the park the next day.
In the above example, “tomorrow” changes to “the next day” in indirect speech.
Overall, it is important to understand the differences between direct and indirect speech to report speech accurately and effectively. By following the rules of direct and indirect speech, you can convey the intended message of the original speaker.
Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
When you need to report what someone said in your own words, you can use indirect speech. To convert direct speech into indirect speech, you need to follow a few rules.
Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks
The first step is to remove the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. This is because indirect speech does not use the exact words of the speaker.
Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker
To indicate that you are reporting what someone said, you need to use a reporting verb such as “said,” “asked,” “told,” or “exclaimed.” You also need to use a linker such as “that” or “whether” to connect the reporting verb to the reported speech.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I love ice cream,” said Mary.
- Indirect speech: Mary said that she loved ice cream.
Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb
When you use indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb.
- Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
Step 4: Change the Pronouns
You also need to change the pronouns in the reported speech to match the subject of the reporting verb.
- Direct speech: “Are you busy now?” Tina asked me.
- Indirect speech: Tina asked whether I was busy then.
By following these rules, you can convert direct speech into indirect speech and report what someone said in your own words.
Converting Indirect Speech Into Direct Speech
Converting indirect speech into direct speech involves changing the reported speech to its original form as spoken by the speaker. Here are the steps to follow when converting indirect speech into direct speech:
- Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb used in the indirect speech. This will help you determine the tense of the direct speech.
- Change the pronouns: The next step is to change the pronouns in the indirect speech to match the person speaking in the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “She said that she was going to the store,” the direct speech would be “I am going to the store,” if you are the person speaking.
- Change the tense: Change the tense of the verbs in the indirect speech to match the tense of the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “He said that he would visit tomorrow,” the direct speech would be “He says he will visit tomorrow.”
- Remove the reporting verb and conjunction: In direct speech, there is no need for a reporting verb or conjunction. Simply remove them from the indirect speech to get the direct speech.
Here is an example to illustrate the process:
Indirect Speech: John said that he was tired and wanted to go home.
Direct Speech: “I am tired and want to go home,” John said.
By following these steps, you can easily convert indirect speech into direct speech.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech are two ways to report what someone has said. Direct speech reports the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech reports the meaning of what was said. Here are some examples of both types of speech:
Direct Speech Examples
Direct speech is used when you want to report the exact words spoken by someone. It is usually enclosed in quotation marks and is often used in dialogue.
- “I am going to the store,” said Sarah.
- “It’s a beautiful day,” exclaimed John.
- “Please turn off the lights,” Mom told me.
- “I will meet you at the library,” said Tom.
- “We are going to the beach tomorrow,” announced Mary.
Indirect Speech Examples
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, is used to report what someone said without using their exact words. It is often used in news reports, academic writing, and in situations where you want to paraphrase what someone said.
Here are some examples of indirect speech:
- Sarah said that she was going to the store.
- John exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- Mom told me to turn off the lights.
- Tom said that he would meet me at the library.
- Mary announced that they were going to the beach tomorrow.
In indirect speech, the verb tense may change to reflect the time of the reported speech. For example, “I am going to the store” becomes “Sarah said that she was going to the store.” Additionally, the pronouns and possessive adjectives may also change to reflect the speaker and the person being spoken about.
Overall, both direct and indirect speech are important tools for reporting what someone has said. By using these techniques, you can accurately convey the meaning of what was said while also adding your own interpretation and analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech refer to the ways in which we communicate what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, using quotation marks to indicate that you are quoting someone. Indirect speech, on the other hand, involves reporting what someone has said without using their exact words.
How do you convert direct speech to indirect speech?
To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb, such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.” For example, “I love ice cream,” said Mary (direct speech) can be converted to “Mary said that she loved ice cream” (indirect speech).
What is the difference between direct speech and indirect speech?
The main difference between direct speech and indirect speech is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. Direct speech is usually enclosed in quotation marks, while indirect speech is not.
What are some examples of direct and indirect speech?
Some examples of direct speech include “I am going to the store,” said John and “I love pizza,” exclaimed Sarah. Some examples of indirect speech include John said that he was going to the store and Sarah exclaimed that she loved pizza .
What are the rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech?
The rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech include changing the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb and use appropriate reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.”
What is a summary of direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions and introduce a reporting verb.
You might also like:
- List of Adjectives
- Predicate Adjective
- Superlative Adjectives
Related Posts:

This website is AMNAZING
MY NAAMEE IS KISHU AND I WANTED TO TELL THERE ARE NO EXERCISES AVAILLABLEE BY YOUR WEBSITE PLEASE ADD THEM SSOON FOR OUR STUDENTS CONVIENCE IM A EIGHT GRADER LOVED YOUR EXPLABATIO
sure cries l miss my friend
he saiad,” we are all sinners”. convert into indirect speech
He said that they were all sinners.

100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
Reported speech: tense shifts.
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
Reported speech: question format.
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
Reported speech quiz.

Reported Speech
Direct speech and reported speech (indirect speech), reported speech table of contents:, overview and definitions, reporting verbs.
- Using the word THAT
Reported speech – changes
Third person singular verbs, place and time expressions, tense backshift, no tense backshift, reporting questions, reporting orders and requests.
Click Here for Step-by-Step Rules, Stories and Exercises to Practice All English Tenses

| I have the package. |
| He says, "I have the package." |
| He says he has the package. |
- She says we should go.
- They told us to bring our stuff.
- He asked them the time.
- I explained the rules to her.
The word THAT
- She says they are full = She says that they are full
- I told them we could help = I told them that we could help
- I suggest we start = I suggest that we start
How to report
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| She says, "I like ice cream." | She says she likes ice cream. |
| They say, "You are right." | They say we are right. |
| He says, "My name is Gary." | He says his name is Gary. |
So when reporting speech we must apply this rule.
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| He says, "I work every day." | He says he works every day. |
| She says, "I am a big girl." | She says she is a big girl. |
| Bonnie says, "I have a question." | Bonnie says she has a question. |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| She said, "I work here." | She said she worked there. |
| They said, "We are eating now." | They said they were eating then. |
| You said, "She sings today." | You said she sang that day. |
| He said, "I will come tomorrow." | He said he would come the following day. |
A list of common place and time expressions
| this | that |
| these | those |
| here | there |
| now | then / at the time |
| today | that day / yesterday |
| yesterday | the day before / the previous day |
| a week ago / last week | a week before / the previous week |
| last month | the month before / the previous month |
| next year | the following year |
| in three years | three years from then |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| Ten minutes ago you said, "We have a lot of work today." | Ten minutes ago you said we had a lot of work today. |
| I am sorry. |
| He said he was sorry. |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| You said, "We are late." | You said we were late. |
| They said, "We have plans." | They said they had plans. |
| He said, "I work hard." | He said he worked hard. |
| She said, "I drink water." | She said she drank water. |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| He said, "I eat cheese." | He said he ate cheese. |
| He said, "I am eating cheese." | He said he was eating cheese. |
| He said, "I have eaten cheese." | He said he had eaten cheese. |
| He said, "I have been eating cheese." | He said he had been eating cheese. |
| He said, "I ate cheese." | He said he had eaten cheese. |
| He said, "I was eating cheese." | He said he had been eating cheese. |
(no change) | |
| He said, "I had eaten cheese." | He said he had eaten cheese. |
(no change) | |
| He said, "I had been eating cheese." | He said he had been eating cheese. |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| Will | Would |
| She said, "I will eat cheese." | She said she would eat cheese. |
Can | Could |
| She said, "I can eat cheese." | She said she could eat cheese. |
Must | Had to |
| She said, "I must eat cheese." | She said she had to eat cheese. |
Shall | Would |
| She said, "I shall eat cheese." | She said she would eat cheese. |
May | Might |
| She said, "I may eat cheese." | She said she might eat cheese. |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
Would | |
| She said, "I would eat cheese." | She said she would eat cheese. |
Could | |
| She said, "I could eat cheese." | She said she could eat cheese. |
Should | |
| She said, "I should eat cheese." | She said she should eat cheese. |
Might | |
| She said, "I might eat cheese." | She said she might eat cheese. |
Ought to | |
| She said, "I ought to eat cheese." | She said she ought to eat cheese. |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| You said, "The Earth is round." | You said the Earth is round. OR You said the Earth was round. |
| I said, "Rome is in Italy." | I said Rome is in Italy. OR I said Rome was in Italy. |
| She said, "People sleep at night." | She said people sleep at night. OR She said people slept at night. |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| You say, "I jog daily." | You say you jog daily. |
| You have said, "I jog daily." | You have said you jog daily. |
| You will say, "I jog daily." | You will say you jog daily. |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| She asked, "Are you well?" | She asked if I was well. |
| "Where do you live?" he asked me. | He asked me where I lived. |
| "Why don't we meet?" she asked me. | She asked me why we didn't meet. |
| I asked, "How does she make them?" | I asked how she made them. |
| They asked, "Where is the mall?" | They asked where the mall is. |
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| "Go home," she told me. | She told me to go home. |
| "Start talking," he told us. | He told us to start talking. |
| "Stop right there," they ordered us. | They ordered us to stop right there. |
| "Could you please open the door?" she asked me. | She asked me to open the door. |
| "Don't shout," I asked. | I asked them not to shout. |
Do online exercises and download a free worksheet.
Get the Reported Speech Illustrated Workbook: The easy way to teach and learn direct and reported speech. 148 pages of explanations, rules, exercises, stories, and lots of hands-on practice.
Get this illustrated workbook and you will receive the following items:
- Step-by-Step Workbook (148 pages)
- Full Answer Key (51 pages)
- Class Activities (52 pages)
- Final Test (10 pages)
- Rule Summary (23 pages)
Get Updates, Special Offers, and English Resources
Download your free gift (the first two chapters of english short stories book and workbook ) as soon as you join.
By submitting your email, you consent to receiving updates and newsletters from us and to the sharing of your personal data with third parties for the purposes of sending you communications. We will not spam you. You can unsubscribe at any time. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Return from Direct Speech and Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) to Easy English Grammar
Really Learn English Home
Top of this page
Please share this page with others:
- Spanish Version
- Textbooks and Workbooks
- Why Learn English
Downloads & Products
- English Short Stories Book and Workbook
- Stories and Exercises to Practice Grammar
- Online English Courses
Videos & Tips
- Learn English Videos
- ESL Lessons
Speaking & Pronunciation
- Learn To Speak English
- English Pronunciation
- English Reading Practice
- English Short Stories
- English Reading Comprehension
- Learn to Write in English
- Writing Tips
- Vocabulary Activities
- Building Vocabulary
- Vocabulary Games
- English Dictionaries
- English Spelling Rules
- Confusing Words
- English Grammar Center
- English Grammar Exercises
- English Tenses
- English Parts of Speech
- Parts of a Sentence
- Gerunds and Infinitives
- English Modal Verbs
Teaching Center
- How to Teach English
- Tips & Resources
Keep in Touch
- Ask Questions
- Learn English Blog
- About This Site
- Affiliate Program
- Useful Links
- Privacy Policy
- English Short Stories Book & Workbook
- ESL/EFL Resources for Teachers
- Free ESL/EFL Downloads
- Spanish Version (Español)
Downloads & Products:
Videos & tips:, speaking & pronunciation:, vocabulary:, teaching center:, keep in touch:.
Online English Courses: Interactive and Fun
Copyright © 2010-2023 Really-Learn-English.com. All rights reserved.
Direct And Indirect Speech | Rules For The Change Of Pronouns
A change in speaker may mean a change of pronoun .
- Alice: " I am going home."
- Mary: Alice said that she was going home.
In the example given above, Alice says I to refer to herself. Mary, talking about what Alice said, naturally uses she .
- Bill said that he didn’t like the party. (NOT Bill said that I didn’t like the party.)
Rules for the change of Pronouns
1. First person pronouns (I, we, me, mine, us, ours) normally change to the third person (he, she, they, his, her, their, him, her, them).
- He told her, " I want to meet your father."
- He told her that he wanted to meet her father.
2. There will be no change in the pronoun when the speaker reports his own words.
- I said, " I am going."
- I said that I was going.
3. Second person pronouns (you, yours) change according to the person of the object of the reporting verb .
- He told her, " I love you."
- He told her that he loved her.
- I told him , " You are a stupid."
- I told him that he was a stupid.
4. Third person pronouns do not normally change in the reported speech .
- She said, " I love him."
- She said that she loved him.
You can find more worksheets here
Sections in this article
Enter your email address to receive our lessons in your inbox:
Delivered by FeedBurner
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: direct speech
Direct speech is a representation of the actual words someone said. A direct speech report usually has a reporting verb in the past simple. The most common reporting verb is said . The reporting clause may come first or second.
reporting clause first | reported clause | reporting clause second |
| , | ||
| , | ||
| . | ||
| . |
The reporting clause may sometimes come in the middle of the reported clause, especially in literary styles:
“No,” she said , “I’ve never seen it before.”
‘Was it,’ he asked , ‘the first time you had spoken to Mrs Dalton?’
We can use adverbs with the reporting verb to describe the way someone said something. This is more common when the reporting clause comes second:
“I will not accept it!” he said angrily .
‘Can I speak to the doctor?’ she asked rather nervously .
Reported speech: punctuation
Reported speech: reporting and reported clauses
Direct speech: inversion of subject and reporting verb
In narratives, especially novels and short stories, when the reporting clause comes second, we often invert the subject (s) and reporting verb (v):
“Things have always been the same in this village,” [V] said [S] the old man .
‘Hold on! I’m coming!’ [V] cried [S] Maurice .
Direct speech: present simple and continuous reporting verbs
Informal narratives.
In informal conversation, we sometimes use the present simple in the reporting clause. This makes the direct speech more vivid and dramatic:
So then this guy says , “I’ve got something for you. Come over here.” And he picked up a box and he says , “Open that.”
We can make the direct speech even more vivid and dramatic by using the present continuous. This is very informal:
And he’s looking at me and he ’s asking , “Who are you?” and I said, “I’m your nephew” and he ’s mumbling , “I don’t know you. I’ve never seen you before in my life.”
In very informal conversation, people sometimes use says as a reporting verb for all persons ( I, you, she, he, we, they ):
She says , ‘What’s going on here?’ and I says , ‘Nothing. There’s nothing happening – everything’s okay.’
Many speakers consider the above examples to be incorrect. This applies especially to the use of says with all persons.
Newspaper headlines
We also use the present simple in newspaper headlines. This makes the reported words more dramatic:
‘I WON’T RESIGN,’ SAYS MINISTER
Say or tell ?

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
a newspaper, magazine, or online article that is in the form of a list
Never say die! (Idioms and phrases in newspapers)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
English Grammar & Vocabulary
Lessons & Practice Tests
Direct and Indirect Speech – Rules and Examples
13th June 2020 By Edify English Leave a Comment
Any word spoken by a speaker can be written in two different ways. Those two are direct and indirect speech. Direct Speech is when the speaker’s actual words are quoted and these words are put in inverted commas (“…..”) while Indirect Speech is when the speaker’s words are said indirectly with the same meaning without repeating the exact words. For Example, the statement in direct speech She said to me, “I am going to the park” changes into She told me that she was going to the park in indirect speech.

Basic Changes while changing from Direct speech to indirect speech
- The comma ( , )after the reporting verb is removed and the conjunction that is added in the indirect speech.
- If the direct speech contains ‘said to’ , it will be converted into ‘told’ in the indirect speech.
- The quotation marks (Inverted commas) are to be removed in the indirect speech.
- I becomes He/ She
- We becomes they
- You becomes He / She/ They
- Me becomes Him/ he r (Depending on the gender in the direct speech)
- My becomes His/ Her .
- Our becomes their
- Us becomes them
- Your becomes His/ her/ their .
Rules in changing a sentence from Direct and Indirect Speech
- Rule 1: The Verb in the simple present tense in the direct speech changes into the simple past tense in indirect speech
Example: He said to me, “I am happy” becomes He told me that he was happy
(The verb in the direct speech ‘am’ is converted into ‘was’.)
- Rule 2: The verb in the simple past tense becomes past perfect tense in indirect speech.
Example: He said to me, “I was happy” changes into He told me that he had been happy
- Rule 3: A present continuous tense in direct speech becomes past continuous tense in indirect speech.
Example: The peon said, “The professor is teaching in that classroom” changes into The peon said that the professor was teaching in that classroom.
- Rule 4: If the direct speech contains present perfect tense, it changes into the past perfect tense in indirect speech.
Example: She said, “I have passed the test” becomes She said that she had passed the test.
- Rule 5: If the direct speech contains a statement talking about a universal truth or a factual statement, there will be no change of tense in indirect speech.
Example: The teacher said, “The sun rises in the East” becomes The teacher said that the sun rises in the east in indirect speech.
Example: Samuel said, “I know the university’s address.” and the indirect speech for that is Samuel said that he knows the university’s address
Rules for converting Interrogatory sentences
- Rule 6: While converting interrogative sentences, the verb ‘said to’ becomes ‘asked’ and if/ whether will come in the place of ‘that’. The connecting word ‘that’ will not be used in indirect speech. Also, the interrogation mark (?) is not repeated in the indirect speech.
Example: He said to her, “Will you marry me?” changes into He asked her whether she would marry him in the indirect speech.
Rules for Converting Imperative Sentences
- Rule 7: During the conversion of imperative sentences, the verb “said to” is changed into ordered, advised, requested, suggested, proposed, etc. depending on the situation. Also, the connecting word ‘that’ is not used. Instead of that, ‘ to’ is used before the reporting verb.
Example: My father said to me, “prepare well for your examination” . It can be converted to My father advised me to prepare well for my examination.
Rules for Converting Exclamatory Sentences
- Rule 8: For exclamatory sentences, the verb is converted into: exclaimed with joy or sorrow or with surprise, wished, prayed, applauded,/ etc. The exclamatory words and the exclamation are not mentioned anymore in the indirect speech. For example,
Example: The coach said, “Hurrah! we won the match!” is changed as The coach exclaimed with joy that we had won the match.
These are the changes in helping verbs while changing from Direct and Indirect Speech
| Am/ Is | Was |
| Are | Were |
| Have/ Had/ Did | had |
| Do/ Does | Did |
| Will | Would |
| Shall | Should |
| Can | Could |
| May | Might |
| Must | Had to |
| Was/ Were | had been |
| Should | Should |
| Had | Had |
| Would | Would |
| Could | Could |
Note: There is no change in the helping verbs “would, should, could, might, had” in the direct speech and they remain the s ame in indirect speech as well.
Changes in Time and Place
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That Day |
| Tonight | That Night |
| Tomorrow | The next day/ The following day |
| The Day after tomorrow | In two days |
| The Day before yesterday | Two days before |
| Ago | Before |
| Next | The following |
| Last | The previous |
| Thus | So |
| This Evening | That Evening |
| Hence | Thence |
Cha nges in pronoun s
The changes in pronouns in indirect speech depends on the subject and the object of the reporting verb.
- Rule 1: The first person of reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting verb.
Example: She said, “I watched a movie” can be converted into She said that she had watched a movie . Hence, the first person in the direct speech “I” has become “she” based on the subject.
Had there been “he” instead of “she”, the first person in reported speech changes accordingly into “he”.
- Rule 2: The second person in reported speech changes based on the object of the reporting verb.
Example: She said to me, “You watched a movie” can be converted into She told me that I had watched a movie.
- Rule 3 : The third person in the reported speech remains unchanged.
Example: I said to her, “He will play Chess” can be converted into I told her that he would play Chess.
Stay tuned for more examples of direct and indirect speech.
For an extensive material on tenses, Click here
Follow us on Facebook
Share this:
Subscribe to blog via email.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.

What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said.
On this page:
Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker’s exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions.
1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually “said.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, “I am going to the store,” becomes “He said that he was going to the store.”
2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually “asked.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, “What time is it?” becomes “She asked what time it was.”
It’s important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples:
- Direct speech: “I will call you later.”Reported speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
- Direct speech: “I love pizza.”Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly.
Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include:
News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference.
Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer.
Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, “She told me that she was running late.”
Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the store now,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then.
In this example, the pronoun “I” is changed to “she” and the adverb “now” is changed to “then.”
2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day.
In this example, the present tense “will” is changed to the past tense “would.”
3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” or “inquire” depending on the context of the speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
In this example, the reporting verb “asked” is changed to “said” and “did” is changed to “had.”
Overall, when making reported speech, it’s important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker’s message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I love chocolate.” Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate.
Direct speech: “You should study harder.” Reported speech: He advised me to study harder.
Direct speech: “She is reading a book.” Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book.
2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct speech: “He is here.” Reported speech: She said he was there.
Note that the adverb “now” usually changes to “then” or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context.
It’s important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech:
Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I like pizza.” Reported speech: She said she liked pizza.
Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I am studying for my exam.” Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam.
Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I have finished my work.” Reported speech: She said she had finished her work.
Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I visited my grandparents last weekend.” Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend.
Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I will help you with your project.” Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project.
Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I can speak French.” Reported speech: She said she could speak French.
Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker’s perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech.
In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as “I heard that” or “It seems that” without using a reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she’s going to the cinema tonight.
However, it’s important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it’s generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible.
Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example:
Direct speech: “I think we should invest in renewable energy.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy.
Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is the meeting?” Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was.
Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech.
2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “ordered” or “told” followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Clean your room!” Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room.
Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech.
In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples:
Direct speech: “Will you go to the party with me?”Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: “Please bring me a glass of water.”Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water.
Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech:
Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include “asked,” “inquired,” “wondered,” and “wanted to know.”
Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker.
Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use “if” or “whether” to introduce the reported question.
Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word.
Here are some examples of reported questions:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: “Where are you going?”Reported speech: She wondered where I was going.
Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, “I am going to the store,” in reported speech you would say, “He/she said that he/she was going to the store.”
The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
- Direct speech: “I am hungry,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry.
- Direct speech: “Can you pass the salt, please?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt.
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the cinema,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema.
- Direct speech: “I have been working on this project for hours,” she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours.
- Direct speech: “What time does the train leave?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left.
- Direct speech: “I love playing the piano,” she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano.
- Direct speech: “I am going to the grocery store,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework.
- Direct speech: “I want to go to the beach,” she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach.
- Direct speech: “Do you need help with that?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that.
- Direct speech: “I can’t come to the party,” he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct speech: “Please don’t leave me,” she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her.
- Direct speech: “I have never been to London before,” he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before.
- Direct speech: “Where did you put my phone?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone.
- Direct speech: “I’m sorry for being late,” he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late.
- Direct speech: “I need some help with this math problem,” she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem.
- Direct speech: “I am going to study abroad next year,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year.
- Direct speech: “Can you give me a ride to the airport?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport.
- Direct speech: “I don’t know how to fix this,” he said. Reported speech: He said he didn’t know how to fix it.
- Direct speech: “I hate it when it rains,” she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- Phrases and Clauses
- Parts of a Sentence
- Modal Verbs
- Relative Clauses
- Confusing Words
- Online Grammar Quizzes
- Printable Grammar Worksheets
- Courses to purchase
- Grammar Book
- Grammar Blog
- Direct & Indirect Speech
Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech grammar rules vary so you need to understand them. We'll start by looking at what each one is. Note that indirect speech is also commonly knows as reported speech.
Definition of Direct Speech
Direct speech is when the words are given in exactly the way that the speaker said them. So in other words they are quoted with no change .
When presenting direct speech, the words are usually placed in quotation marks, with a comma after say(s) / said if it is used to present the speech. Say (s) / said can also be placed at the end of the quotation, in which case a comma comes before it.
Examples of Direct Speech:
- He said, "Don't take the car without asking me".
- John says, "I will help you with your work".
- "We are prepared to revise the law if we can", they said.
- The teacher said, "You must wear the proper uniform".
Definition of Indirect Speech
Indirect speech is also known as reported speech . You may also see it referred to as indirect discourse or indirect narration .
Indirect speech is the reporting of what someone else said in your own words but without changing the meaning of what was said.
Reporting verbs are used to present indirect speech. The common ones are:
- say(s)/said (that)
- told me (that)
That is in brackets as it can be omitted from the sentence, whether spoken or written.

Examples of Indirect Speech:
- He said (that) he would definitely buy it.
- Sheila told me (that) I had to come back in the afternoon.
- The council said (that) they will try and clear the rubbish.
- She told me (that) she was feeling unwell.
So the key difference between direct and indirect speech is that with direct speech the exact words are quoted but in indirect speech it is your own words .
Direct speech is fairly simple to use and understand as it involves just repeating what was said. There is not much to get confused about with the grammar, apart from getting say(s)/said correct.
But indirect or reported speech is more difficult so we will look at that in more detail now.
View more examples of direct and indirect speech >>
Direct and Indirect Speech Conversion
With direct and indirect speech, there are three main things you need to be aware of when converting one to the other:
- Changes in Tense
- Changes in Person and Pronouns
- Changes in Time Phrases
Changing Tenses
The tense of verbs when moving from direct to indirect speech do not necessarily change because if the circumstances of what someone said is the same, then it may be reported as that. For example:
- "I am feeling tired" (= Direct Speech )
- Present Continuous
- She said she is feeling tired (= Indirect Speech )
However, as we are reporting what was said in the past, we often change the tense. This rule for this is related to backshifting, which means shifting back a tense. So the present will go back to the past. Some modals also change.
Here are examples using the previous examples of indirect speech, showing you how they look like in direct speech:
Direct Speech
- "I want to meet you later".
- "You have to come back in the afternoon"
- "We like it a lot"
- "I have been mowing the lawn"
Indirect Speech
- He said he wanted to meet me later.
- Sheila told me I had to come back in the afternoon.
- They said they liked it a lot.
- He said he had been mowing the lawn.
There are more details on the site about changing tenses in indirect / reported speech:
Learn more about changing tenses >>
Changing Pronouns
Pronouns in indirect speech also need to be changed from what they were in the indirect speech, as well as of course adapting the first pronoun to fit the person who said the statement:
- " I want to meet you later".
- " You have to come back in the afternoon"
- " We like it a lot"
- " I have been walking with my wife"
- He said he had been walking with his wife.
Changing Time Phrases
You may also need to change phrases referring to time, though this depends on the context and when you are reporting the speech.
With these examples you have to assume the speech is being reported at a time in the future so the phrases such as 'yesterday' or 'tomorrow' would not makes sense any more in terms of the reported speech.
- She said, "I saw her yesterday ".
- He said, "He will bring the book tomorrow ".
- She said, "I'm going to London today ".
- He said, "We need your assistance now ".
- She said that she had seen her the day before .
- He said that he would bring the book the next day .
- She said she was going to London that day .
- He said they needed my assistance then .
Imperatives
Some different rules apply when turning direct speech using imperatives or commands into indirect speech. Check out the rules here:
Rules for Reported Speech Imperatives >>
More on Reported Speech:

Reported Speech Quiz - Practice forming indirect speech
This reported speech quiz gives you the chance to practice converting direct speech to reported speech, also known as indirect speech. This involves backshifting with the tenses.

Reported Speech Imperatives: Reporting commands in indirect speech
Reported speech imperatives, also known as reported commands, follow a slightly different structure to normal indirect speech. We use imperatives to give orders, advice, or make requests.

Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
In these examples of direct and indirect speech you are given a sentence in direct speech which is then connected to indirect speech.

Reported Speech Tenses Chart: How to convert tenses
Reported speech tenses may differ from the tense of the direct speech. The general rule for tenses in reported speech is that it changes to the past tense. This is called backshifting.
New! Comments
Any questions or comments about the grammar discussed on this page?
Post your comment here.

Sign up for free grammar tips, quizzes and lessons, straight into your inbox
Grammar Rules
Subscribe to grammar wiz:, grammar ebook.

This is an affiliate link
Recent Articles
Use of the bare infinitive.
Aug 02, 24 02:55 AM
Future Continuous Tense Quiz: Yes/No Questions
Jun 29, 24 11:04 AM
Future Continuous Affirmative Tense Quiz
Important pages.
Online Quizzes Grammar Lessons Courses Blog
Connect with Us
Search Site
Privacy Policy / Disclaimer / Terms of Use

Direct and Indirect Speech
Every day, people relay messages from one person to another. Whether it is to prove a point, describe an event, or disclose an opinion, we use the freedom of speech to share information. There are generally two ways of reporting a spoken idea: direct and indirect speech. This article shall explain and compare these two types of speech. Some examples are also provided to give you a more in-depth understanding.
Both direct and indirect speech are methods to narrate the words spoken by a specific person. The difference between them lies in how they are constructed and in the purpose of using them.
Direct Speech
In a direct speech , the actual words of the speaker are quoted explicitly. It is often used to relay something being said in the present tense. It can also be used to recall the exact words of the speaker when retelling a previous conversation. You can recognize a direct speech instantly because it has a text enclosed in a set of quotation marks. That text or idea is known as the reported speech .
- He says, “I want to adopt a dog.”
- Julia asks, “What do you want to have for dinner?”
- Penny answers, “I would like to have some soup.”
- “I have a new job,” Kyle says to us.
- “I will be working as a virtual assistant,” he added.
As you can see, direct speech can be presented in different tenses: past, present, or future. It depends on when the actual words were spoken and when the reporter is retelling them. Also, reporting verbs (say, ask, answer, etc.) are not necessarily placed before the quoted text. You can also place them after it.
This type of speech is often used in writing novels or telling a story. This is because it gives the text a more actual and realistic effect.
Indirect Speech
Indirect speech is usually used to relay what was being said by the speaker without directly quoting the original words. In this case, the tense of the sentence is typically changed. Reporting verbs, such as say, tell, ask, and others, are used as an introduction. The words of the original speaker will not be enclosed inside the quotation marks. Instead, the word “that” is used to connect the reporting verb to the reported text.
- He says that he wants to adopt a dog.
- Julia asks Penny what she wants for dinner.
- Penny answers that she would like to have some soup.
- Kyle told us that he got a new job.
- He added that he will be working as a virtual assistant.
The above sentences are actually converted from the previous examples of direct speech. Aside from eliminating the quotation marks, correct pronouns are also used. Additionally, the reporting verbs are now all found before the reported speech. The reporting verb is then followed with “that.”
Converting Direct to Indirect Speech
Now, let us specify the rules in converting direct speech to indirect speech. Here are the steps on how to do so:
1. Eliminate the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text.
The quotation marks are the primary indication of a direct speech. Therefore, it is crucial to take them out if you are forming an indirect one.
2. Retain the tense of the reporting verb and add the word “that” after it.
You have to retain the tense of the reporting verb to allow consistency of reports. Instead of placing a comma to separate the reporting clause from the reported one, the word “that” is added. However, if the reported speech is a yes-no question, you use “if” instead of “that.” If the question starts with who, what, when, where, etc., no additional words are needed. Instead, you have to rearrange the sentence into a declarative form.
- Direct Speech: She says, “I want to go to Paris.”
- Indirect Speech: She says that she wants to go to Paris.
- Direct Speech: She asks, “Do you want to go to Paris?”
- Indirect Speech: She asks me if I want to go to Paris.
- Direct Speech: “Ms. Thompson, where are you going?” I asked.
- Indirect Speech: I asked Ms. Thompson where she was going .
3. Change the tense of the verb in the reported speech, if needed.
If the reporting verb is in the past tense, you should change the tense of the verb inside the reported speech into its past tense. This is not necessary if the reporting verb is in the present or future tense.
- Direct Speech: He said , “I am watching a new TV series.”
- Indirect Speech: He said that he was watching a new TV series.
- Direct Speech: He says , “I am watching a new TV series.”
- Indirect Speech: He says that he is watching a new TV series.
Of course, you have to consider the correlation between the report and the idea on the quoted text. Sometimes, a change in tense is not needed even if the reporting verb is in the past tense.
- Direct Speech: He said, “I will be watching a new TV series.”
- Indirect Speech: He said that he will be watching a new TV series.
- Direct Speech: He said, “I watch TV series every night.”
- Indirect Speech: He said that he watches TV series every night.
For the first example, the quoted text is still about to happen. So, you don’t need to change the tense of the sentence inside the quotation. For the second example, watching TV series is implied as a habitual action. Therefore, you still have to retain the present tense of the verb.
4. Change the pronouns accordingly.
You should also change the pronoun based on who the speaker, doer, and receiver of the action is.
- Direct Speech: Wendy says, “Ron, y ou should take care of yourself .”
- Indirect Speech: Wendy told Ron that he should take care of himself .
Appropriate changing of pronouns is done to avoid misunderstanding the whole text. If pronouns are not changed, it might confuse the reader or the listener as to who is saying or doing the action.
The change in pronouns gives rise to changes in the plurality of the verb used. That being said, you have to consider and follow correct subject-verb agreement at all times.
Tense Changes in Indirect Speech

Verb Tenses Changes
Present Simple Tense into Past Simple Tense
For example:
- Direct speech: She always wears a coat.
- Reported speech: He said (that) she always wore a coat.
Present Continuous Tense into Past Continuous Tense
- Direct speech: I ‘m looking for my keys.
- Reported speech: She said that she was looking for her keys.
Present Perfect Tense into Past Perfect Tense
- Direct speech: She has written three letters for her friend.
- Reported speech: He said she had written three letters for her friend.
Past Simple Tense into Past Perfect Tense
- Direct speech: My friend gave me a bar of chocolate.
- Reported speech: He said that his friend had given him a bar of chocolate.
Past Continuous Tense into Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Direct speech: We were living in London.
- Reported speech: They said that they had been living in London.
Past Perfect Tense ( The tense remains unchanged )
- Direct speech: The bread had gone stale.
- Reported speech: She said the bread had gone stale.
Future Simple Tense (e.g. will ) into “ would “
- Direct speech: I will finish my report in two days.
- Reported speech: He said that he would finish his report in two days.
Future Progressive Tense (e.g. will be ) into “ would be “
- Direct speech: I will be making tea.
- Reported speech: He said (that) he would be making tea.
Future Perfect Tense (e.g. will have ) into “ would have “
- Direct speech: I will have called a doctor.
- Reported speech: He said (that) she would have called a doctor.
Future Perfect Tense (e.g. will have been ) into “ would have been “
- Direct speech: All the money will have been spent.
- Reported speech: He said (that) all the money would have been spent.
Other Verb Form Changes in Reported Speech
Can into Could
- Direct speech: I can speak English.
- Reported speech: She said she could speak English.
Could ( The verb remains unchanged)
- Direct speech: He could play in the match.
- Reported speech: They said he could play in the match.
Have to into Had to
- Direct speech: I have to submit this assignment by 3 pm tomorrow.
- Reported speech: She said she had to submit this assignment by 3 pm tomorrow.
Must into Must/Had to
- Direct speech: I must go to the bank and get some money.
- Reported speech: She said she must / had to go to the bank and get some money.
May into Might
- Direct speech: I may invite them to dinner.
- Reported speech: She said that she might invite them to the dinner.
Might (The verb remains unchanged)
- Direct speech: He might get a flight tomorrow.
- Reported speech: She said he might get a flight the next day.
Should (The verb remains unchanged)
- Direct speech: I should start a job.
- Reported speech: She said that she should start a job.
More interesting articles
- Changes in Time and Place in Reported Speech
- Changes of Pronouns in Reported Speech: Rules & Examples
- Direct Speech | What is Direct Speech? with Useful Examples
- No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
- Reported Commands and Requests in English
- Reported Questions: Direct and Indirect Questions
- Reported Speech Exercises – Reported Speech Worksheet
- Reported Speech: Important Grammar Rules and Examples
- Reporting Verbs in English Grammar
Literary English

Direct and Indirect Speech in English | A Complete Guide
Direct and indirect speech are two ways to report what someone else has said. In direct speech, the exact words spoken by a person are quoted within quotation marks. In indirect speech, the words of the speaker are reported without using their exact words and without using quotation marks. Instead, the reported speech is often introduced by verbs such as “said,” “told,” “asked,” etc. Indirect speech allows us to convey what someone else said without necessarily repeating their exact words, often to provide a summary or to integrate it into a larger narrative.
Direct Speech
Direct speech is also called reporting speech. There are two parts in a sentence in direct speech first part is known as reporting speech (in this sentence we know about reporting person) and the second part which is known as reported speech (indirect narration “example”, or indirect discourse). When we want to describe what someone said, one option is to use direct speech . We use direct speech when we simply repeat what someone says, putting the phrase between speech marks:
- Saif came in and said, “I’m really happy”.
As you can see, with direct speech it is common to use the verb ‘to say’ and ‘to says’ (‘said’ in the past). But you can also find other verbs used to indicate direct speech such as ‘ask’, ‘reply’, and ‘shout’.
Indirect Speech
In grammar, when we want to report what someone said, without speech marks and without necessarily using exactly the same words, we use indirect speech. It is also known as reported speech. Look at the following sentences:
- Direct speech: he says, “I am going to school.”
- Indirect speech: he says that he is going to school.
In above sentences, the reporter delivers the message of the boy using his real words (e.g.“I am going to school.”) In the indirect speech sentence, the reporter delivers his message but in his own words without any change in the meaning. Thus, both direct and indirect speeches are two different ways of reporting a statement of person. In simple words, quoting a person using your own words is called an indirect speech.
Basic Rules for Direct and Indirect Speeches
- When we change direct speech to indirect speech always we will replace inverted commas with word ‘ that’ .
- When we combine reporting and reported speech we use that between these sentences.
- If the first part of the sentence does not include word said then tense will not be changed.
- At the end of reporting speech if there is a comma then it will be removed.
- Say always will be changed into tell .
- Says always will be changed into tells .
- Said will be changed into told only in one condition when there is object in reporting speech.
- Direct : You said to Saif, “you are going to Lahore”.
- Indirect : you told Saif that he was going to Lahore.
Changes in the Person of Pronouns
1 st person 2 nd person 3 rd person
Subject Object No change
I, we, you he, she, it,
My, our, us, me your they and noun.
- 1 st person pronouns in reported speech are always changed according to the subject of the reporting speech.
- 2 nd person pronouns in reported speech are always changed according to the object of the reporting speech.
- 3 rd person pronouns in reported speech are not changed.
Important word changes
The above rules are mandatory for converting direct speech into indirect speech. Hence, they should be memorized thoroughly. The following examples cover all the aforementioned rules. So, focus on every sentence to know how the above-mentioned rules have been used here.
Some special words will be changed when direct speech changes into indirect speech
- Now into then
- Today into that day
- Yesterday into the previous day
- This into that
- Last night into the previous night
- Tomorrow into the next day
- These into those
- Here into there
- Next day into the following day
- Ago into before
- Come into go
- Will into would
- Shall into should
- May into might
- Can into could
- Good Morning, into greeted
- Good Evening, into greeted
- Good Day into greeted
- Madam into Respectfully
- Sir into Respectfully
Changes in Verbs
If the reporting speech is in present tense or future tense, then no change is required to be made in the verb of reported speech.
Direct Speech: he says, “I live in Pakistan”.
Indirect Speech: he tells that he lives in Pakistan.
Direct Speech: you say to me, “you will go to Lahore”.
Indirect Speech: you tell me that I shall go to Lahore.
Direct Speech: I say, “she was ill”.
Indirect Speech: I tell that she was ill.
How to Make Direct and Indirect Speeches in Different Tenses
Present indefinite will be changed into past into past indefinite tense.
(First form into second form)
- Direct: I said, “I go to school”.
- Indirect: I said that I went to school.
Present continues will be changed into past continues tense.
(is, am, are into was, were)
- Direct: Raza said, “I am a boy”.
- Indirect : Raza said that he was a boy.
Present perfect will be changed into past perfect tense.
(has, had into had)
- Indirect : You told Saif that he was going to Lahore.
Present perfect continues will be changed into past perfect continues tense.
(has been, have been into had been)
- Direct : The guard said to the passenger, “the train has come”
- Indirect : The guard told to the passenger that the train had come.
Past indefinite will be changed into past perfect tense.
(second form into had)
- Direct : Aslam said, “They played cricket”.
- Indirect: Aslam said that they had played cricket.
Past continues will be changed into past perfect continues tense.
(was, were into had been)
- Direct : The policeman said, “The thief has been stealing for two year”.
- Indirect : The policeman told that the thief had been stealing for two year.
Note : Past perfect, past perfect continues, future indefinite, future continues, future perfect, future perfect continues tense will not be changed.
Direct and Indirect Speech in Assertive Sentences
Sentences that make a declaration are called assertive sentences. These sentences may be positive, negative, false, or true statements. To convert such sentences into indirect speech, use the rules as declared above except said is sometimes replaced with told . Look at the following examples:
Direct Speech: She says, “I am writing a letter to my brother.”
Indirect Speech: She says that she is writing a letter to her brother.
Direct Speech: She says, “I was not writing a letter to my brother.”
Indirect Speech: She says that she was not writing a letter to her brother.
Direct Speech: She said to me, “I am writing a letter to my brother.”
Indirect Speech: She told me that she was writing a letter to her brother.
Direct and Indirect Speech in Imperative Sentences
Imperative sentences are sentences that give an order or a direct command. These sentences may be in the form of advice, appeal, request, or order. Mostly, it depends upon the forcefulness of the presenter. Thus, a full stop (.) or sign of exclamation (!) is used at the end of the sentence.
When we will be convert these types of sentences into indirect speech, follow the following rules along with the above-mentioned rules:
- Both sentences will be joined with the conjunction
- If in the reported sentence has word do not, then it will be changed with the word not to.
- Direct speech : Aslam said, “Do not beat him”.
- Indirect speech: Aslam ordered to not beat him.
The direct verb is changed according to indirect speech in case order the speaker gives a direct command. Then said will be changed into ordered For example:
- Direct Speech: The father said to me, “Sit down.”
- Indirect Speech: The father ordered me to sit down.
The direct verb is changed according to indirect speech in case request the speaker gives a request command. Then said will be changed into request.
For example:
- Direct Speech: The man said, “Please show me your pen.”
- Indirect Speech: the man requested to show him my door.
The direct verb is changed according to indirect speech in case guide the speaker gives a piece of advice. Then said will be changed into advised .
- Direct Speech: The headmaster said, “Write neat and clean.”
- Indirect Speech: the headmaster advised to write neat and clean.
The direct verb is changed according to indirect speech in case forbade the speaker stopped to do something. Then said will be changed into forbade .
- Direct Speech: The teacher said, “Don’t sit.”
- Indirect Speech: The teacher forbade to sit.
Optative & Exclamatory Sentences
The sentence, which expresses a prayer, keen wish, curse, happiness etc., is called an optative sentence . This kind of sentence generally starts with ‘may’ and ‘wish’. Sometimes, ‘may’ remains hidden.
The sentence, which expresses a sudden and deep excitement, wonder, shock, or sorrow, etc., is called an exclamatory sentence . In this kind of sentence must have exclamation mark (!) at the end of the sentence or in the central of the sentence.
- May you succeed in the test!
- May you get well soon!
- Would that I was rich!
When we will be converted these types of sentences into indirect speech, follow the following rules along with the above-mentioned rules:
In a prayer sentence said will be replaced by
When we will be changed direct speech to indirect speech always we will be replaced inverted commas that .
- Direct speech : He said, “May you live long”.
- Indirect speech : He prayed that I might live long.
In a hope sentence said will be replaced by
When we will be changed direct speech to indirect speech always we will be replaced inverted commas that .
- Direct speech: The father said, “May my son get first position”.
- Indirect speech: The father wished that his son might get first position.
In a glad & happy sentence, said will be replaced by exclaimed with joy or exclaimed with joyfully. And exclamatory mark (!) will be removed.
- Direct speech: The boys said, “Hurrah! We have won the match”.
- Indirect speech: The boys exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
In a sad or sorrow sentence, said will be replaced by exclaimed with sorrow or exclaimed with sorrowfully.
- Direct speech: The bagger said, “Ah! I am undone”.
- Indirect speech: The exclaimed with sorrow that he was undone.
Interrogative Sentences
Which sentences, ask questions, are called interrogative sentences. Every interrogative sentence has question mark (?) at the ends.
- Where are you going?
- Where did you live?
- Are you want to go with me?
To change interrogative sentences from direct speech into indirect speech, follow the following rules along with the above-mentioned rules:
When we will be changed sentence direct speech to indirect Said will be replaced by asked .
If interrogative sentence will be started from “ Wh ” mean when, whom, what, where, who, which, why, how, whose when we will be changed sentence direct speech to indirect speech inverted commas will not be replaced. Just it will be removed.
If the reported sentence will be started form helping verb, then if will be used in place of that .
After the changing sentence mark of interrogation (?) will be replaced with full stop (.).
Direct speech: He said to me, “Who are you”?
Indirect speech: He asked me who I was.
Direct speech: He said to me, “Where are you going”?
Indirect speech: He asked me where I was going.
Direct speech: Sunny said to me, “will you help me”?
Indirect speech: Sunny asked me if I would help him.
Direct and indirect Speech in Universal Sentence
Sentences which have natural truth or universal truth in the part of reported speech are called universal sentences .
- Allah is one.
- Honesty is the best policy.
To change universal sentences from direct speech into indirect speech, follow the following rules along with the above-mentioned rules:
When we will be changed sentence direct speech to indirect Said will be replaced by
When we will be changed direct speech to indirect speech always we will be replaced inverted commas with that .
Always remember that universal truth will never change so we will not be changed reported speech portion.
Direct speech: The teacher said to the boys, “The earth revolves around the sun”.
Indirect speech: The teacher told the boys that the earth revolves around the sun.
Direct speech: Saif said, “Allah is one”.
Indirect speech: Saif told that Allah is one.
Direct speech: She said to him, “Honesty is the best policy”.
Indirect speech: She told him that honesty is the best policy.
Direct speech: Sunny said to Farrukh, “The sun rises in the east”.
Indirect speech: Sunny told Farrukh that the sun rises in the east.
Onlymyenglish.com
Learn English
Direct and Indirect Speech
Table of Contents
What is Speech (Narration):
If we want to describe the speech of some other people with other people in our own words, that speech is called a Reported speech or Narration.
Types of Speech
In the English language, there are certain ways to express the spoken words between two people.
The speech has two main types, Direct speech , and Indirect speech , respectively.
These two ways of narration of spoken words are also called Direct and Indirect speech, also known as Direct and Indirect narrations.
Direct and indirect speech is majorly used in any conversations, scripts, or any biographies, etc. where one or more than one person converses with each other.
Direct speech:
It is also called straight speech or quoted speech, which is spoken or written directly in the text by the speaker, writer, or the first person, who is going to speak with anyone with him.
The spoken statements of the speaker normally come under the inverted commas notation, and a speaker who speaks these sentences may come like “he said/he said that.”
The speaker’s words or statements are mentioned in a single phrase pattern or direct discussion.
Indirect speech:
An Indirect speech is also called a reported speech, or secondary speech means the speech, which has spoken indirectly.
It is simply an overlook statement that is used to say about the incident that has happened in the past time.
The actual words of the speaker changed into the past tense and the sentence, and hence the reported speech of the direct speech does not come inside the inverted commas.
Reporting speech:
A person who is going to report the speech or a speech that comes in the first part of the direct speech is called a reporting speech.
- He says , “He cooks food”.
Reported speech:
Reported speech is a speech that is always in an inverted comma or quotation marks.
It is a second part of the direct speech sentence.
- He says, “He cooks food.”
Reporting verb:
The verb, which is used in a reporting speech to report something in a direct speech, is called a reporting verb.
- Zoya said , “I want to go there.”
Reported verb:
The verb which comes inside the reported speech is called reported verb, respectively.
- Zoya said, “I want to go there.”
As we start writing any direct and indirect conversation, we often use reported verbs like “say, tell, ask, inform, instruct, claim, suggest, enquire, etc.”
These reported verbs, whenever used in direct or indirect speech, change into the past simple form like said, told, asked, informed, instructed, claimed, suggested, enquired, etc.
But the verbs used in a speech between the inverted commas will remain as it is.
Examples of direct and indirect speech:
- Indirect speech: John said that she was looking so beautiful.
- Indirect : He said that he was not a culprit.
- Indirect : He said that she was working on that project.
- Indirect : The teacher asked if he completed his homework.
- Indirect : She says that she is an artist.
- Indirect : Sam told me that he was not coming with me.
- Indirect : He says that she is working on that project.

Some basic rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech:
Rule 1 : “no inverted commas.”.
The reported speech does not come into inverted commas or quotation in an indirect speech.
Example: Direct: He said, “I have completed my assignments yesterday.”
Indirect: He said that he had completed his assignments the previous day.
Rule 2: use of “that” conjunction
Using the conjunction word “that” in-between the reporting speech and reported speech in an indirect speech.
Example:
- He said, “I have completed my assignment yesterday.”
- He said that he had completed his assignment the previous day.
Rule 3: Change of tense
While writing a direct speech into an indirect speech, we have to change the tense of the reported speech because whatever we are writing in indirect speech has already happened in the past timing.
- If the tense of a reporting speech of direct speech is in the present tense or future tense , then the tense of the reported speech in indirect speech will not change. It may be in the present tense, past tense, or future tense, respectively.
- Indirect : He says that he is going to school. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : She says that she will not come with me. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : He says that he wrote a letter. (no change in tense)
If the tense of the reporting verb of direct speech is in the past tense, then the tense will change according to these criteria.
For the present tense:
Simple present tense will change into simple past tense..
Direct: He said, “They come to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they came to meet him.
Present continuous tense will change into past continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They are coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they were coming to meet her.
Present perfect tense will change into past perfect tense.
Direct: He said, “They have come to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him.
Present perfect continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They have been coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her.
For the past tense:
Simple past tense will change into the past perfect tense.
Direct: He said, “They came to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him.
Past continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They were coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her.
Past perfect tense and past perfect continuous tense will remain the same.
Direct: He said, “They had come to meet me.”
Direct: She said, “They had been coming to meet me.”
For the future tense:
There are no changes in the future tense sentences; only shall/will may change into would, can change into could.
- Direct: She said, “Can you come tomorrow.”
Indirect: She said that could he come on the next day
- Direct: He said, “I will never forgive you.”
Indirect: He said that he would never forgive me.
Rule 4: Changing the pronoun
The pronoun used as an indirect subject speech sometimes needs to be changed accordingly in indirect speech as of the reported verb of the direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the first person in reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting speech in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the second person in reported speech changes based on the report’s object in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the third person remains the same in the reported speech.
- Direct: He said, “ I am going to school.”
- Indirect: He said that he is going to school.
- Direct: She says, “ I will not come with you .”
- Indirect: She says that she will not come with me .
- Direct: They said, “ we are eating our tiffin box.”
- Indirect: They said that they were eating their tiffin box.
Rule 5: Changing the time
The mentioned time (not the timing) in a direct speech sentence will have to change in indirect speech like now becomes then, tomorrow becomes the next day, yesterday becomes the previous day, today becomes that day, later becomes soon.
- Direct: He told, “He is coming from Tokyo today .”
- Indirect: He told me that he was coming from Tokyo that day .
- Direct: She asked, “Will the parcel reach by tomorrow or not?”
- Indirect: She asked whether the parcel will reach by the next day or not.
- Direct: “The teacher has given some assignments yesterday ”, he reminds me.
- Indirect: He reminds me that the teacher had given some assignments on the previous day.
Conversion of statements from direct speech into Indirect speech:
Assertive sentences:.
Assertive sentences are simple statements that may be affirmative or negative.
If we are going to convert assertive sentences from direct speech into indirect speech, we have to replace “said” with “told” sometimes.
Here, the subject in direct speech refers to someone in his talk.
- Direct: He said to me, “she is working on this project.”
Indirect: He told me that she was working on that project.
- Direct: She said to me, “I’m going for a long drive.”
Indirect: She told me that she was going for a long drive.
Imperative sentences:
Imperative sentences are statements that deliver a command, order, request, appeal, or advice.
It depends on the speaker, how he delivers the message to the other person.
- Sit properly!
- Stand by my side!
- Come closer!
While converting these types of sentences cum statements from direct speech to indirect speech, we have to check the type of sentence, whether it is a command, order, request, or else.
- Direct: The teacher said to me, “Sit properly!”
Indirect: The teacher ordered me to sit properly.
- Direct: The Boss said to an office boy, “Bring one coffee for me.”
Indirect: The Boss commanded an office boy to bring a coffee for him.
Indirect: The teacher requested me to sit properly.
- Direct: The bartender said to me, “try this drink.”
Indirect: The bartender advised me to try that drink.
Interrogative sentences:
An interrogative sentence is a sentence which interrogates or ask questions.
Each interrogative sentence ends with an interrogative sign or a question mark sign “?”.
- What is your name?
- Can you do me a favor?
- Why are you laughing in the classroom?
While writing interrogative sentences from direct speech into indirect speech,
- the reporting verb “said” in the direct speech is changed into “asked” in the indirect speech because it asks the question to another person.
- If any reporting verb comes first in the reporting speech, then “If” is used despite “that.”
- In a reporting speech, if any wh-type question words are present, then no other words will be used, and the sentence ends with a full stop sign instead of a question mark.
- Indirect: He asked me what was my name.
- Indirect: She asked if he could do her a favor.
- Indirect: The teacher asked him why he was laughing in the classroom.
Exclamatory sentences:
Exclamatory sentences are those sentences that show emotions, feelings and ends with an exclamation mark!
- Congratulations! You have a baby girl.
- I am extremely sorry for your loss!
- Most welcome!
If any interjection comes in an exclamation sentence, then the exclamation sign removes in an indirect speech, and an exclamatory sentence gets converted into an assertive sentence.
The replacement of reporting verb “said” with exclaimed with (great wonder, sorrow, joy) exclaimed (joyfully, sorrowfully)
Replace with very or very great , if words like how or what comes at the beginning of the reported speech.
- Indirect: He exclaimed with joy that I had a baby girl.
- Indirect: She exclaimed with sorrow that she felt sorry for my loss.
- Indirect: They exclaimed with joy that most welcome.
You might also like

50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
Informal letter format in english.


Examples of a Sentence with Subject and Predicate

Question Tag

Wh-type Question Words | Wh Question Words
Vowels and consonants in english.
English Saga
Pronouns Changing Rules- Direct & Indirect Speech
Generally, “Personal Pronouns” are changed while converting the Direct Narration into Indirect Narration. These pronouns take their shape according to the pronouns used in the Reporting Speech of the Direct Narration.
Types of Personal Prono uns
The pronouns that are changed while converting Direct Narration into Indirect Narration, are called “Personal Pronouns”. Personal Pronouns are of 3 types:
Personal Pronouns of 1 st Person
The pronouns that a person uses for themselves, are called the Personal Pronouns of the 1 st Person, e.g. I, We.
Personal Pronouns of 2 nd Person
The pronouns that are used for a person with one talk, are called the Personal Pronouns of the 2 nd Person, e.g. You.
Personal Pronouns of 3 rd Person
The pronouns that are used for a person who is not present at that time about whom something is said, are called the Personal Pronouns of the 3 rd Person, e.g. He, She, It, They, etc.
Pronouns Changing Rules
Personal Pronouns of the Direct Narration are changed as follows to go into Indirect Narration:
- The Personal Pronouns of the 1 st Person (Reported Speech) are always changed their form according to the subject of the Reporting Speech of the Direct Narration.
- The Personal Pronouns of the 2 nd person (Reported Speech) are always changed according to the Reporting Speech object.
- There is no change in the form of Personal Pronouns of the 3 rd Person used in the Reported Speech of the Direct Narration.
Hint to Change personal Pronouns in Direct & Indirect Speech
The Pronouns Changing Rules can be summarized as “SON”. Because 1 st and 2 nd Personal Pronouns are changed according to the subject (S) and object (O) of the Reporting Speech of the Direct Narration, respectively. And 3 rd Personal Pronoun of the Direct Speech is non-changeable (N).

Example of the Change in the form of Personal Pronouns according to the Subject of the Reporting Speech with Explanation
- She said to me that she had received that telegram from my father the previous day.
Explanation of the Example
In this sentence, two Personal Pronouns (She, me) are used in the Reporting Speech. And Reported Speech also has two Personal Pronouns (I, Your). Since the pronouns of the Reported Speech are changed according to the pronouns of the Reporting Speech, therefore, Personal Pronoun of the 1st Person “I” is changed according to the subject “She” of the Reporting Speech and the Personal Pronoun of the 2nd Person “Your” is changed according to the object “me” of the Reporting Speech.
This is done by following the “SON” formula, which says that the Personal Pronoun of the 1 st Person is changed according to the subject of the Reporting Speech and the Personal Pronouns of the 2nd Person are changed according to the object of the Reporting Speech. And in this example, we have “she” as a subject and “me” as an object.
Examples of the Change in the form of Personal Pronouns according to the Subject of the Reporting Speech
- He says that he is ill.
- She says that her book is new.
- You say that your brother is very kind to you.
- They will say that they do not work hard.
- I will say that I have spoken the truth.
- She says to us that she is our neighbor.
- He says to us that he respects us.
- She says that she reads the book.
- They say that they love Pakistan.
- He will say that he does not mix with boys.
- You say that you respect your teacher.
- Faisal says that he will go to Karachi by the Khyber Mail.
- You say that you speak the truth.
- He will say that he has sent him a telegram.
- They will say that they are going to London.
- She says that she has visited Japan twice.
- He says that his father is a landlord.
- Your friends say that they will obey him.
- They say that they have done their duty.
- You say that you respect your elders.
- She says that she is sitting beside them.
Examples of the Change in the form of Personal Pronouns according to the Object of the Reporting Speech with an Explanation
- They say to me that I cannot help him.
In this sentence, two Personal Pronouns (They, me) are used in the Reporting Speech. And Reported Speech also has two Personal Pronouns (You, him). Since the pronouns of the Reported Speech are changed according to the pronouns of the Reporting Speech, therefore, Personal Pronoun of the 2nd Person “You” is changed according to the object of the Reporting Speech “me” and the Personal Pronoun of the 3rd Person “him” is non-changeable.
This is done by following the “SON” formula, which says that Personal Pronouns of the 2 nd Person are changed according to the object of the Reporting Speech and Personal Pronouns of the 3rd Person are non-changeable. And in this example, we have “They” as the subject and “me” as the object in the Reporting Speech.
Examples of the Change in the form of Personal Pronouns according to the Object of the Reporting Speech
- You will say to him that his brother beats them.
- We say to her that her uncle will not hate them.
- I shall say to him that he has broken the jug of that tea set.
- He says to me that he lives near my house.
- They will say to him that they do not know him.
- You say to him that you were his class fellow.
- She says to me that her son gives me two apples every day.
- He will say to you that he has come to you for help.
Direct Narration with Personal Pronouns of the 3 rd Person
When Direct Narration has Personal Pronouns of the 3 rd Person (he, she, it, they), then there is no change in the form of Personal Pronouns of the 3rd Person to convert the sentence into Indirect Narration.
Examples of Direct Narration with Personal Pronouns of the 3 rd Person
- They say to me that he cannot help her.
- You will say to him that her brother beats the stranger.
- We say to you that his uncle will not hate us.
- I shall say to you that he has broken the jug of that tea set.
- He says to you that he lives near your house.
- They will say to us that he does not know them.
- You say to me that he was my class fellow.
- She says to me that his son gives me two apples every day.
- She said to me that he had received that telegram from her father the previous day.
Similar Posts
Assertive sentences-direct & indirect speech.
An Assertive Sentence is the type of Sentence that defines some declaration. It may support some type of positivity,…
Optative Sentences-Direct & Indirect speech
Optative Sentence is that type of sentence that has a prayer, keen wish or curse, etc. Optative Sentences always…
Other Words Changing Rules-Direct & Indirect speech
Some words must be changed while going from Direct Narration to Indirect Narration to convey the same thing with…
Exclamatory Sentences-Direct & Indirect speech
An Exclamatory Sentence is a type of Sentence that must have some strong feelings, e.g; joy, sorrow, grief, wonder,…
Rule # 1 of Changes in the Tenses| Direct & Indirect Speech
All the tenses of the Reported Speech are changed while going from Direct Narration to Indirect Narration under a…
Rule #2 of Changes in the Tenses| Direct & Indirect speech
Rule number 2 of the Changes in the Tenses is about the effect of the Past Tense in the…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

100 + Direct and Indirect Speech Examples and Answers (2025)

Gain a deep understanding of 100+ examples of direct and indirect speech, along with detailed, step-by-step guides on converting between the two. Enhance the skill of maintaining correct tense, pronoun, and modal usage when transforming direct and indirect speech. Explore comprehensive examples to support your learning journey.
Direct Speech Examples
When a speech is quoted with exact words used by the speaker is called Direct speech or narration .
Direct Speech: Ravi says, “I am tired.”
The speech which is quoted above in actual words (“ I am tired” is called the Reported Speech and the verb (“ says “) that introduces speech is called the Reporting Verb. The above speech is called Direct Speech .
Indirect Speech Examples
On the other hand, when the speech is reported in the form of a narrative, without quoting the speaker’s actual words , it is called Indirect speech or narration.
Indirect Speech: Ravi says that he is tired.
The above speech is reported in the form of a narrative , without quoting the speaker’s actual words , but keeping the meaning the same. So, it is Indirect Speech
Direct and Indirect Speech with Examples of Punctuation Marks
Punctuating direct and indirect speech correctly is essential for clarity and grammatical correctness in writing. Let me provide examples of both with explanations:
Direct Speech:
Direct speech involves conveying the exact words spoken by a person. When punctuating direct speech, you enclose the spoken words within quotation marks and separate them from the rest of the sentence using commas, question marks, or exclamation marks as appropriate.
- Original sentence (Direct Speech): “I love reading,” she said.
- Explanation: The spoken words “I love reading” are enclosed within quotation marks. The comma after “reading” indicates the end of the spoken sentence but keeps the dialogue flowing within the sentence.
- Original sentence (Direct Speech): “What time is the meeting?” he asked.
- Explanation: The question asked is enclosed within quotation marks. The comma after “meeting” separates the spoken words from the attribution “he asked.”
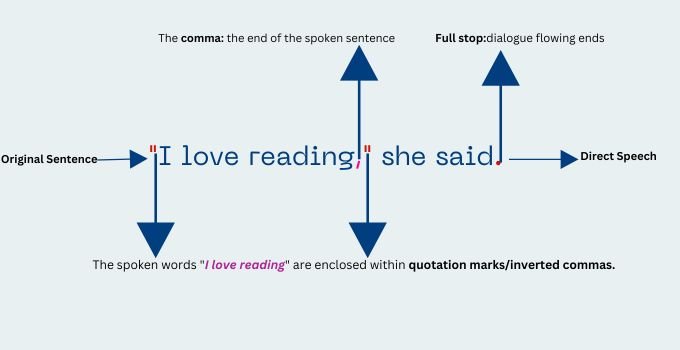
Indirect Speech:
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, involves reporting what someone said without quoting their exact words. When punctuating indirect speech, you do not use quotation marks. Instead, you change the verb tense and possibly pronouns to reflect the shift from direct to indirect speech.
- Original sentence: “I’ll be there at 3 PM,” she said.
- Indirect speech: She said she would be there at 3 PM.
- Explanation: In indirect speech, the verb tense changes from “I’ll” to “she would,” reflecting the shift from present to past tense. The spoken words are not enclosed within quotation marks, and the reporting verb “said” is used to attribute the speech.
- Original sentence: “I want to travel the world,” he exclaimed.
- Indirect speech: He exclaimed that he wanted to travel the world.
- Explanation: The verb tense changes from “want” to “wanted” in indirect speech. The spoken words are not enclosed within quotation marks, and the attribution “he exclaimed” is used to report the speech.

In both direct and indirect speech, proper punctuation and verb tense agreement are crucial for accurately conveying the speaker’s words and maintaining grammatical correctness within the sentence.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of All Tenses
In English grammar, examples of all tenses can be found in both direct and indirect speech, illustrating how verbs and structures change to reflect the shift in time.
1. Present Tense Examples
Direct: “I love chocolate,” she says . Indirect: She says that she lo ves chocolate.
Direct: “I am watching TV,” he says. Indirect: He says that he is watching TV.
Direct: “I have finished my homework,” she says. Indirect: She says that she has finished her homework.
Direct: “I have been studying for hours,” he says. Indirect: He says that he has been studying for hours.
Direct: “I played cricket,” he says . Indirect: He says that he played cricket.
Direct: “I shall visit New York,” he says . Indirect: He says that he will visit New York.
Direct: He says, “You will make a good result.” Indirect: He says that I shall make a good result.
Direct: They say, “We won the match.” Indirect: They say that they won the match.
2. Past Tense Examples
Direct: “I visited Paris last summer,” she said. Indirect: She said that she had visited Paris last summer.
Direct: “I was reading a book when you called,” he said. Indirect: He said that he had been reading a book when I called.
Direct: “I had already eaten dinner when she arrived,” she said. Indirect: She said that she had already eaten dinner when I arrived.
Direct: “I had been working on this project for months,” he said. Indirect: He said that he had been working on that project for months.
Direct: She said to me, “I am writing a letter now.” Indirect: She told me that she was writing a letter then.:
Direct: He said to me, “I shall not do it.” Indirect: He told me that he would not do it.
Direct: They said to us, “You make a mistake.” Indirect: They told us that we made a mistake
Direct: The doctor said to me, “You have brought the patient in time.” Indirect: The doctor told me that I had brought the patient in time.
Direct: Mother said , “I took tea.” Indirect: Mother said that she had taken tea.
Direct: My friend said to me, “you were doing a good job.” Indirect: My friend told me that I had been doing a good job.
Direct: The man said to me, “I had not seen you before.” Indirect: The man told me that he had not seen me before.
3. Future Tense Examples:
Direct: “I will call you tomorrow,” she will say. Indirect: She will say that she will call me tomorrow.
Direct: “I will be traveling to Europe next month,” he will say. Indirect: He will say that he will be traveling to Europe next month.
Direct: “I will have finished the project by Friday,” she will say. Indirect: She will say that she will have finished the project by Friday.
Direct: “I will have been studying for five hours by then,” he will say. Indirect: He will say that he will have been studying for five hours by then.
Direct: He will say , “I shall be there within an hour.” Indirect: He will say that he will be there for an hour.
Direct: Mother will say , “I made the fish curry.” Indirect: Mother will say that She made the fish curry.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples in Sentences
Direct: Sarah said, “I am going to the store.” Indirect: Sarah said that she was going to the store.
Direct: “The meeting starts at 9 AM,” announced the manager. Indirect: The manager announced that the meeting started at 9 AM.
Direct: Tom asked, “Did you finish your homework?” Indirect: Tom asked if I had finished my homework.
Direct: “I love watching movies,” she exclaimed. Indirect: She exclaimed that she loved watching movies.
Direct: “Don’t touch that!” shouted Mark. Indirect: Mark shouted not to touch that.
Direct: He said, “You are intelligent.” Indirect: He said that I was intelligent.
Direct: You will say, “I am right.” Indirect: You will say that you are right.
Direct: Rita said, “She is my favourite player.” Indirect: Rita said that she was her favourite player.
Direct: I said to you, ‘I wish to start a business next year.’ Indirect: I told you that I wished to start a business in the following years.
Direct: Mother said to her, “Are you feeling feverish?” Indirect: Mother inquired of her if she was feeling feverish.
Direct: She said to him, ‘Which of the books do you want to buy?’ Indirect: She asked him which of the books he wanted to buy.
Direct: The teacher said, “Boys, go to your classes.” Indirect: The teacher ordered the boys to go to their classes.
Direct: Mother said, ‘May you be happy.’ Indirect: Mother wished that I might be happy.
People Also Ask
| Direct and Indirect Speech with Examples | |
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of Modal Verbs
Direct: He said to me, “You may go. ” Indirect: He told me that I might go.
Direct: “I can swim,” she said . (can) Indirect: She said that she could swim. (can)
Direct: “You will attend the meeting tomorrow,” he said to me. Indirect: He told me that I would attend the meeting the next day.
Direct: You will attend the meeting tomorrow,” I said to him. Indirect: I told him that he would attend the meeting the next day.
Direct: “You should study harder,” he advised . (should) Indirect: He advised that I should study harder. (should)
Direct: “ May I borrow your pen?” she asked . (may) Indirect: She asked if she might borrow my pen. (may)
Direct: “We must finish this project by Friday,” he insisted. (must) Indirect: He insisted that we must finish the project by Friday. (must)
Direct: “You might want to consider that option,” she suggested. (might) Indirect : She suggested that I might want to consider that option. (might)
Direct: “I will help you with your homework,” she promised. (will) Indirect: She promised that she would help me with my homework. (will)
Direct: “You ought to apologize for your mistake,” he scolded. (ought to) Indirect: He scolded that I ought to apologize for my mistake. (ought to)
Direct: “ Can you lend me some money?” she requested. (can) Indirect: She requested if I could lend her some money. (can)
Direct: “You need to finish your chores before you go out,” he reminded. (need to) Indirect: He reminded me that I needed to finish my chores before going out. (need to)
Direct: “You are allowed to leave early today,” she informed. (are allowed to) Indirect: She informed that we were allowed to leave early that day. (are allowed to)
Direct to Indirect Speech Examples with Change of Pronouns
Direct: He said to me, “ I am ill.” Indirect: He told me that he was ill.
Direct: They will say to you, “ We have made it.” Indirect: They will tell you that they have made it.
Direct: You said to him, “ You are not like me.” Indirect: You told him that he was not like you.
Direct: He said to me, “ My name is John.” Indirect: He tells me that his name is John.
Direct: They said to me, “ This is our playground.” Indirect: They told me that that was their playground.
Direct: He says to me, “Elders give us blessings.” Indirect: He tells me that elders give them blessings.
Direct: He said to me, “ You are not smart .” Indirect: He told me that I was not smart.
Direct: She said to him, “ I am not your friend.” Indirect: She told him that she was not his friend.
Direct: He said to us, “ I shall give you money.” Indirect: He told us that he would give us money.
Direct: You said, “ He is right.” Indirect: You said that he was right.
Direct: I said, “ They will be late.” Indirect: I said that they would be late.
Change of Time & Place for Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
Direct: He said to me, “ This is my house.” Indirect: He told me that that was his house.
Direct: She said to him, “ These are golden flowers.” Indirect: She told him that those were golden flowers.
Direct: He said, “I have done it today .” Indirect: He said that he had done it that day.
Direct: She said to him, “I bought the book yesterday .” Indirect: She said that she had the book the previous day.
Direct: They said, ‘We will play now. ‘ Indirect: They said that they would play then .
Direct: You said, ‘ Here lives a lion.’ Indirect: You said that there lived a lion.
Direct: She always says, ‘I like these flowers.’ Indirect: She always says that she likes those flowers.
Direct: He said, ‘I will come here tomorrow. ‘ Indirect: He said that he would go there the next day .
Direct: I said, ‘You will get it today or tomorrow.’ Indirect: I said that you would get it that day or the next day.
Direct: He said to me, ‘ Come here .’ Indirect: He told me to go there.
Direct: He said, ‘I shall go there the day after tomorrow .’ Indirect: He said that he would go there in two day’s time.
Direct: He said to me, ‘I saw your sister two years ago. ‘ Indirect: He told me that he had seen my sister two years before.
Direct: He said to me, “I have no friend here .” Indirect: He told me that he had no friends here.
Direct: I said, ‘We cannot be happy in this world. Indirect: I said that we could not be happy in this world.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of Assertive Sentences
Direct: Peter says, “My mother teaches me English.” Indirect: Peter says that his (Peter’s) mother teaches him English.
Direct: Shyam will say, “I have done this work. Indirect: Shyam will say that he has done that work.
Direct: Bappa said to him, “I am ten years old.” Indirect: Bappa told him that he was ten years old.
Direct: Laltu said, “I am watching television now. Indirect: Laltu said that he was watching television then.
Direct: He said to me, “My mother is now sleeping.’ Indirect: He told me that his mother was sleeping then.
Direct: I said, “The teacher has taken me to the task. Indirect: I said that the teacher had taken me to the task.
Direct: Mother said to me, “I have taken the medicine twice today.” Indirect: Mother told me that she had taken the medicine twice that day.
Direct: My sister said to me, “The bird flew away. Indirect: My sister told me that the bird had flown away.
Direct: Namrata said, “They came here yesterday.’ Indirect: Namrata said that they had come there the previous day.
Direct: Jamuna said, “Lalan was listening to my words. Indirect: Jamuna said that Lalan had been listening to her words.
Direct: He said, “I shall take rice.” Indirect: He said that he would take rice.
Direct: They said, “We shall leave for Goa tomorrow.” Indirect: They said that they would leave for Goa the next day.
Direct: Ashisbabu said, “Now we shall start the ceremony.’ Indirect: Ashisbabu said that they should start the ceremony then.
Direct Indirect Examples of Universal Truth or Habitual Truth, Historical Truth
Direct: The teacher said to us, “Oil floats on water.” Indirect: The teacher told us that oil floats on water
Direct: Lopa said, “God is almighty.” Indirect: Lopa said that God is almighty.
Direct: Father said, “God is good.” Indirect: Father said that God is good.
Direct: Keats said, “Beauty is truth, truth beauty.” Indirect: Keats said that beauty is truth, truth beauty.
Direct: The teacher said, “The earth moves round the sun.” Indirect: The teacher said that the earth moves round the sun.
Direct: My grandfather said, “Honesty is the best policy.” Indirect: My grandfather said that honesty is the best policy.
Direct: Father said, “The sun rises in the east.” Indirect: Father said that the sun rises in the east.
Direct: Saurav said, “My grandfather recites the Geeta every morning.” Indirect: Saurav said that his grandfather recites the Geeta every morning.
Direct: Arindam’s uncle said, “I walk for half an hour every afternoon.” Indirect: Arindam’s uncle said that he walks for half an hour every afternoon.
Direct: He said, “Man is mortal.” Indirect: He said that man is mortal.
Direct: The old man said, “God is merciful.” Indirect: The old man said that God is merciful.
Direct: The teacher said, “Ashoka was a great emperor.” Indirect: The teacher said that Ashoka was a great emperor.
Direct: The student answered, “Lord Buddha died in his eightieth year.” Indirect: The student answered that Lord Buddha died in his eightieth year.
Direct: He said, “Babar was the first emperor of the Mughal empire.” Indirect: He said that Babar was the first emperor of the Mughal Empire.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of Interrogative Sentences
Direct: The boy said to me. “Is the mango sweet?” Indirect: The boy asked me whether(or, if) the mango was sweet.
Direct: Tanmay said to me, “Are you ill?” Indirect: Tanmay asked me whether (or, if) I was ill.
Direct: I said to him, “Do you know him?” Indirect: I asked him whether he knew him.
Direct: Rabin said to me, “Is there any problem?” Indirect: Rabin enquired of me if there was any problem.
Direct: I said to my brother, “Are you going to school?” Indirect: I asked my brother whether he was going to school.
Direct: The teacher said to the student. Did you come to school yesterday?” Indirect: The teacher enquired of the student whether he (the student) had come to school the day before.
Direct: I said to Binay, “Did you see Palash?” Indirect: I asked Binay whether he (Binay) had seen Palash.
Direct: His mother angrily said to him, “Do you know better than your elder brother?” Indirect: His mother asked him angrily whether he supposed that he knew better than his elder brother.
Direct: The judge said to the accused, “Have you anything to say in justification of your action?” Indirect: The judge wanted to know from the accused if he had anything to say in justification of his action.
Direct: Sadhan said to Nabin, “Have you read the letter?” Indirect: Sadhan asked Nabin if he had read the letter.
Direct: Santosh said to Seema, “Can you lend me a pen?” Indirect: Santosh asked Seema if she could lend him (Santosh) a pen.
Direct: The trainer said to Tarun, “Can you swim?” Indirect: The trainer asked Tarun whether he (Tarun) could swim.
Direct: The poet said, “Real happiness is only a dream.” Indirect: The poet said that real happiness is only a dream.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of “Wh-word”
Direct: He said to me, “What are you doing?” Indirect: He asked me what I was doing.
Direct: I said to him, “What is your name?” Indirect: I asked him what his name was.
Direct: The passerby said to me, “What is the time now by your watch?” Indirect: The passerby asked me what time it was then by my watch.
Direct: I said to Basu, “Where do you live?” Indirect: I asked Basu where he (Basu) lived.
Direct: Dinu said to Manu, “Where are you going?” Indirect: Dinu asked Manu where he (Manu) was going.
Direct: I said to Gopal, “Where is your pencil box?” Indirect: I enquired of Gopal where his (Gopal’s) pencil box was.
Direct: The passenger asked, “When will the train start?” Indirect: The passenger asked (or, wanted to know) when the train would start.
Direct: Ratan said to me, “How are you?” Indirect: Ratan wanted to know from me how I was.
Direct: Suman said to me, “How did you know this? Indirect: Suman enquired (asked) me how I had known that.
Direct: I said to the policeman, “Why did you strike the boy?” Indirect: I wanted to know from the policeman why he had struck the boy.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of Imperative Sentences
Direct: The teacher said to the students, “Sit down.” Indirect: The teacher told the students to sit down.
Direct: The commander-in-chief said to the soldiers, “March forward.” Indirect: The commander-in-chief ordered the soldiers to march forward.
Direct: The master said to his servant, Polish my shoes,” Indirect: The master ordered his servant to polish his master’s shoes.
Direct: Ratanbabu said to the man, “Leave the house at once,” Indirect: Ratanbaby ordered the man to leave the house at once.
Direct: The teacher said to his pupils, “Go out.” Indirect: The teacher told his pupils to go out.
Direct: Mother said to me, “Go to school at once.” Indirect: Mother ordered/urged me to go to school that very moment.
Direct: He said to Sujay. “Let’s have a cup of tea. Indirect: He invited Sujay to have a cup of tea with him.
Direct: Sunillbabe said to Sistab. Please lend me some money.” Indirect: Sunilbabe requested Sisibaba to lend him (Sababu) some money.
Direct: Father said, “Go on, apply for the job.” Indirect: Father advised/encouraged me to apply for the job.
Direct: The teacher said to the boy, “Don’t spit on the floor. Indirect: The teacher forbade the boy to spit on the floor.
Direct: I said to my brother, “Do not run in the sun.” Indirect: I advised my brother not to run in the sun. Or I forbade my brother to run in the sun.
Direct: The teacher said to me, “Do not waste time.” Indirect: The teacher advised me not to waste time.
Direct: He said to his sons, “Do not quarrel among yourselves.” Indirect: He advised his sons not to quarrel among themselves.
Direct Speech and Indirect Speech Examples with “Let”
Direct: Mukti said, “Let’s go for a walk.” Indirect: Mukti suggested that they should go for a walk.
Direct: The inspector said to the constable, “Let the man go.” Indirect: The inspector ordered the constable to let the man go.
Direct: Rama said, “Let’s arrange a musical party.” Indirect: Rama suggested that they should arrange a musical party.
Direct: The clergyman said, “The nations of the world should forget their differences and work together for peace.” Indirect: The clergyman suggested that the nations of the world should forget their differences and work together for peace.
Direct: Ramen said, “I must not delay any longer.” Indirect: Ramen said that he ought not to delay any longer.
Direct: He said, “I must return before 5 in the evening.” Indirect: He said that he must (or, would have to) return before 5 in the evening.
Direct: Rima said to me, “You ought to be careful when driving.” Indirect: Nima advised me to be careful when driving.
Direct: My father said, “You ought not to trust a man who is a habitual liar.” Indirect: My father warned me against trusting a man who was a habitual liar
Direct: Father said, “You should not be late in reaching school.” Indirect: Father advised me not to be late in reaching school. Or, Father said that I should not be late in reaching school.
Direct: Somen said, “It might rain tonight.” Indirect: Somen said that it might rain that night, Or Somen said that there was the possibility of rainfall that night,
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of Optative Sentences
Direct: He said, “May God bless you.’ Indirect: He prayed that God might bless him (or, me).
Direct: The priest said to the accused, “May God pardon your sins.” Indirect: The priest prayed to God that He might pardon his sins (or, the sins of the accused).
Direct: We said, “May Mother Teresa’s soul rest in peace.” Indirect: We prayed that Mother Teresa’s soul might rest in peace.
Direct: The retiring teacher said to his pupils, “I bid all of you goodbye.” Indirect: The retiring teacher bade goodbye (or, farewell) to all his pupils.
Direct: They said, “Long live Netaji.” Indirect: They prayed for Netaji’s long life.
Direct: My grandfather said to me, “May you be happy.” Indirect: My grandfather blessed me wishing that I might be happy. Or. My grandfather blessed me by wishing me a happy life. Or, My grandfather wished that I might be happy.
Direct: His father said to him, “May you prosper.” Indirect: His father wished him prosperity. Or. His father wished that he might prosper.
Direct: Ajay said to his brother, “Welcome home.” Indirect: Ajay bade his brother welcome.
Direct: Rahul said to his playmates, “Good morning, I hope you are quite well.” Indirect: Rahul wished his playmates a good morning and expressed his hope that they were quite well.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of Exclamatory Sentences
Direct: The students said, “Hurrah! Our school won the match.” Indirect: The students shouted with delight (exclaimed with joy) that their school had won the match.
Direct: He said, “Alas! I am ruined.” Indirect: He lamented that he was ruined.
Direct: He said, “What a fool I am !” Indirect: He reproached (feata lucuíba) himself for being such a big fool.
Direct: The audience said to the actor, “How wonderful is your acting !” Indirect: The audience expressed to the actor their appreciation of his fine acting.
Direct: Returning from the place of the accident, he said, “What a ghastly sight it was!” Indirect: Returning from the place of the accident he expressed his disgust at the ghastliness of the sight.
Direct: Looking at the Tajmahal the tourist said, “What an exquisitely beautiful creation !” Indirect: Looking at the Tajmahal the tourist exclaimed in wonder that it was indeed an extremely beautiful creation.
Direct: The youth said, “Alas! I am undone by the death of my father.” Indirect: The youth lamented that he was undone by his father’s death.
Direct: The coach of the team said to his players, “Bravo! You have played extremely well.” Indirect: The coach of the team cheered the players and said that they had played extremely well indeed.
Direct: Nabinbabu said to Sajal, “What a pity you could not succeed in spite of such great efforts !” Indirect: Nabinbabu expressed his sympathy for Sajal for not being successful in spite of his great efforts.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of More than one sentence
Direct: Sanu said to Sushama over the telephone, “I have got the tickets. Meet me at the station at 6.30 p.m.” Indirect: Sanu informed Sushama over the telephone that he had got the tickets and suggested that she meet him at the station at 6.30 p.m.
Direct: The supervisor of the examination said to the candidates, “Do not forget to put your names at the top of the page. Write down also the roll and the number.” Indirect: The supervisor of the examination advised the candidates not to forget to put their names at the top of the page and also reminded them to write down their roll and number therein.
Direct: Surabhi said to Mohan, “Let’s buy some flour. We will prepare bread at home.’ Indirect: Surabhi suggested to Mohan that they buy some flour and make bread themselves at home.
Direct: My assistant said to me, “You look tired. Why don’t you take a rest for a couple of days?” Indirect: My assistant told me that I looked tired, and suggested that I should take a rest for a couple of days.
Direct: My friend said to me, “Why don’t you open a bank account? I have opened one.” Indirect: My friend advised me to open a bank account and he also informed me that he had opened one.
Frequently Asked Questions Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
Q: What are the 10 examples of direct and indirect speech?
- Direct Speech: Rohan said, “She works hard.”
- Indirect Speech: Rohan said that she worked hard
- Direct Speech: Rohan said, “She is singing a song.”
- Indirect Speech: Rohan said that she was singing a song.
- Direct Speech: The guest said shouting, “We have arrived .”
- Indirect Speech: The guest said shouting that they had arrived.
- Direct Speech: My sister said, “It has been raining hard for 3 days”.
- Indirect Speech: My sister said that it had been raining hard for 3 days.
- Direct Speech: Father said, “I visited the Taj yesterday.”
- Indirect Speech: Father said that he had visited the Taj the previous day.
- Direct Speech: Boys said, “They were travelling in the park.”
- Indirect Speech: Boys said that they had been travelling in the park.
- Direct Speech: The reporters commented that the Kohinoor had been lost long ago.
- Indirect Speech: The reporters commented, “The Kohinoor had been lost long ago”.
- D i rect Speech: Jyotsna said, “ She had been doing the work for 3 hours”.
- Indirect Speech: Jyotsna said that she had been doing the work for 3 hours.
- Direct: The boy said to his mother, “ The sun rises in the East”. Indirect: The boy told his mother that the sun rises in the East. [ Universal Truth ]
- Direct: The monk answered, “ Man is mortal”. Indirect: The monk answered that man is mortal. [ Universal Truth ]
Q: What is direct and indirect speech with examples for Class 5?
Ans: When a sentence is quoted with the exact words used by the speaker, it is called a sentence in Direct Speech.
When the sentence is spoken or written in the form of a narrative without quoting the speaker’s actual words but keeping the meaning the same, it is called a sentence in Indirect Speech .
(1) I said to him that I had once seen him before. Ans: I said to him, “ I once saw you ago.”
(2) She said that she had a dream that night. Ans : She said, “I have a dream tonight.”
(3) The boy said. “We were playing.” Ans: The boy said that they had been playing.
(4) He told me that I should obey my parents. Ans: He said to me, “You will obey your parents.”
(5) Amal said to Bimal, “I gave you, my pen.” Ans: Amal told Bimal that he had given him his pen.
Q: What is the example of direct and indirect speech Class 9?
Ans: Direct: You say, ‘I am always busy.’ Indirect: You say that you are always busy.
Direct: The child will say, ‘Mum knows everything.’ Indirect: The child will say that Mum knows everything.
Direct: He said, ‘I need some money.’ Indirect: He said that he needed some money,
Direct: She said, ‘I am waiting for him.’ Indirect: She said that she was waiting for him.
Q: What are the 5 rules of indirect speech?
Ans: The five rules of indirect speech consist of Assertive sentences, Interrogative Sentences, Imperative Sentences, Optative Sentences, and Exclamatory sentences.
Related Posts:


20 Easy Examples of Direct Speech
Back to: Direct and Indirect Speech (Narration)
Table of Contents
Direct Speech Assertive Sentences Examples
Assertive sentence makes statement. It can be about a speaker’s thoughts and feelings or about day to day events, etc. assertive sentence always ends with full stop.
Direct Speech Interrogative Sentence Examples
Interrogative sentence asks question. We can form interrogative sentence with WH-question, yes/no question. Interrogative sentence in direct speech always ends with question mark.
Direct Speech Imperative sentence Examples:
We use imperative sentence to give order, advice, to instruct or to request something.
Direct Speech in Exclamatory Sentence Examples
Exclamatory sentence is used to convey or express emotions like joy, sorrow, pity, fear, wish etc. In case of Direct speech, exclamatory mark is used to show and stress on emotions in exclamatory sentence.

Direct and Indirect Speech
Ai generator.

Direct and Indirect Speech: Direct speech quotes the exact words spoken, using quotation marks, while indirect speech paraphrases the spoken words without quotes, often changing tenses and pronouns. Both forms are essential for effective communication, emphasizing clarity and context in reporting speech.
What is Direct Speech?
Direct speech refers to the exact words spoken by someone, presented within quotation marks and often accompanied by a speech tag that attributes the statement to the speaker. This method of reporting speech is used to convey the original words and the tone in which they were spoken, preserving the personal touch and specific expressions of the speaker.
For example , if John says, “I am going to the store,” the direct speech presentation would be:
John said, “I am going to the store.”
What is Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, is a method of conveying what someone said without quoting their exact words. Instead of using direct quotations, indirect speech summarizes or paraphrases the original statement. It often involves changes in verbs tenses, pronouns, and other elements to fit the grammatical context of the reporting sentence.
For example , consider the direct speech statement:
Tom said, “I am going to the gym now.” When converted into indirect speech, it becomes:
Tom said that he was going to the gym then.
Indirect speech does not use quotation marks and typically introduces the reported clause with conjunctions like “that,” although “that” can be omitted in informal contexts.
Rules of Direct and Indirect Speech
Rules for converting direct into indirect speech.
- Example : Direct: He said, “I am tired.”
- Indirect: He said that he was tired.
- Example : Direct: She says, “I am reading a book.”
- Indirect: She says that she is reading a book. (Note: When reporting in the present tense, as with ‘says’, the tense may not always change.)
- Example : Direct: “I will go there tomorrow,” John said.
- Indirect: John said that he would go there the next day.
- Example : Direct: She said, “I can solve the problem.”
- Indirect: She said that she could solve the problem.
- Example : Direct: He asked, “Are you coming?”
- Indirect: He asked if I was coming.
- Example : Direct: He said, “Close the door.”
- Indirect: He asked me to close the door.
- Example : Direct: She said, “What a beautiful day!”
- Indirect: She exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
Rules for converting Indirect Speech into Direct Speech
- Example : Indirect: He said that he was tired.
- Direct: He said, “I am tired.”
- Example : Indirect: She says that she is reading a book.
- Direct: She says, “I am reading a book.” (Note: Sometimes the tense doesn’t need to change if the reporting verb is in the present tense.)
- Example : Indirect: John said that he would go there the next day.
- Direct: John said, “I will go there tomorrow.”
- Example : Indirect: She said that she could solve the problem.
- Direct: She said, “I can solve the problem.”
- Example : Indirect: He asked if I was coming.
- Direct: He asked, “Are you coming?”
- Example : Indirect: He asked me to close the door.
- Direct: He said, “Close the door.”
- Example : Indirect: She exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- Direct: She said, “What a beautiful day!”
Difference Between Direct and Indirect Speech
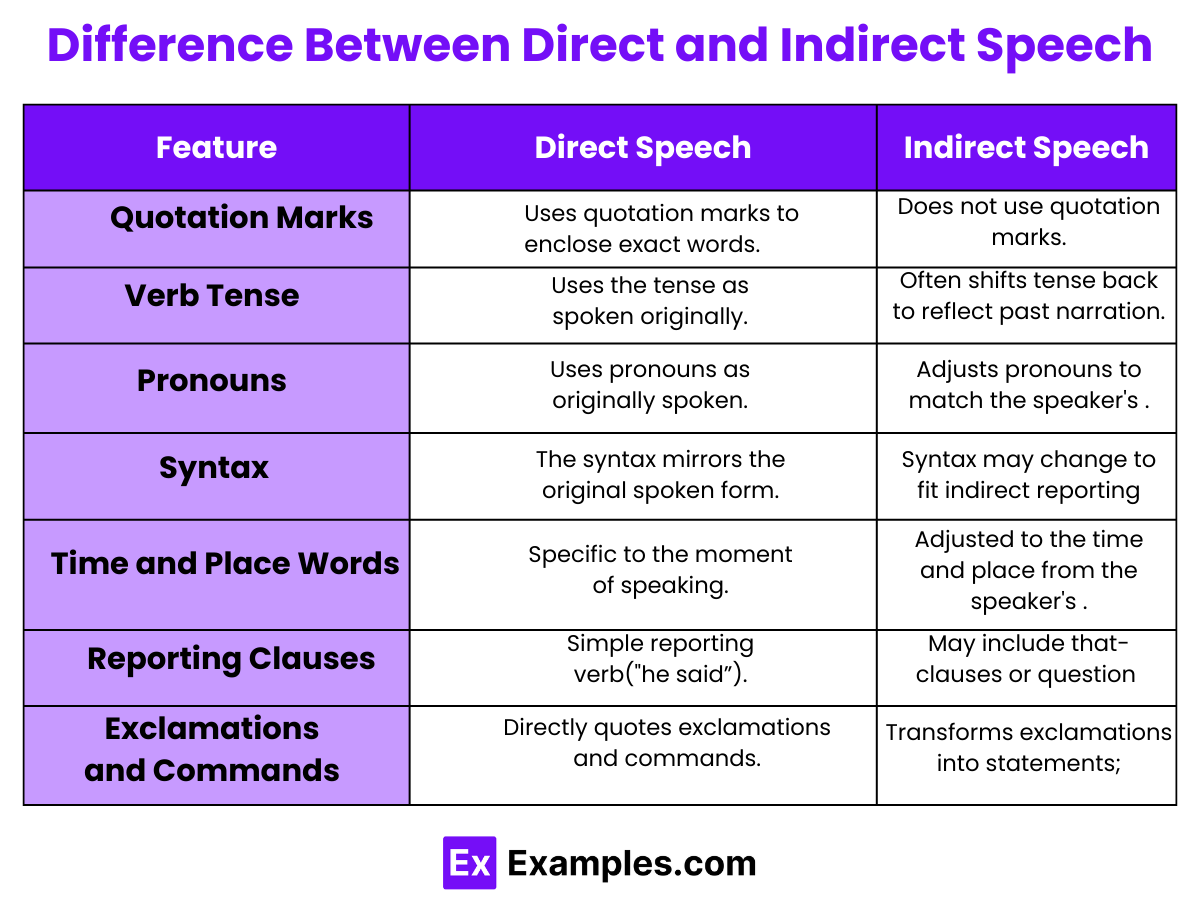
| Feature | Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|---|
| Uses quotation marks to enclose exact words. | Does not use quotation marks. | |
| Uses the tense as spoken originally. | Often shifts tense back to reflect past narration. | |
| Uses pronouns as originally spoken. | Adjusts pronouns to match the speaker’s perspective. | |
| The syntax mirrors the original spoken form. | Syntax may change to fit indirect reporting (e.g., question forms are changed). | |
| Specific to the moment of speaking. | Adjusted to the time and place from the speaker’s perspective. | |
| Simple reporting verb (“he said,” “she said”). | May include that-clauses or question words (if, whether). | |
| Directly quotes exclamations and commands. | Transforms exclamations into statements; commands into requests with infinitive verbs. |
This table should help you clearly see how the format, verbs, pronouns, and other elements differ between direct and indirect speech.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
1. Direct : “I love reading books,” Jane said. Indirect : Jane said that she loved reading books. 2. Direct : “We will go to the park,” they announced. Indirect : They announced that they would go to the park. 3. Direct : “I have finished my homework,” he told his mother. Indirect: He told his mother that he had finished his homework. 4. Direct : “Can you help me with this?” she asked. Indirect: She asked if I could help her with that. 5. Direct : “I am feeling sick today,” he whispered. Indirect: He whispered that he was feeling sick that day. 6. Direct : “I won’t be able to attend the meeting,” Laura said. Indirect: Laura said that she would not be able to attend the meeting. 7. Direct : “Please open the window,” she requested. Indirect: She requested him to open the window. 8. Direct : “Do not touch my phone,” he warned. Indirect: He warned not to touch his phone. 9. Direct : “I’ll call you tomorrow,” she promised. Indirect: She promised that she would call me the next day. 10. Direct : “What time does the concert start?” he asked. Indirect: He asked what time the concert started.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises with Answers
Direct to indirect speech exercises.
Convert the following sentences from direct to indirect speech:
Exercise 1 : “I am learning to play the piano,” she said. Answer 1 : How did she say she was learning to play the piano?
Exercise 2 : “Will you be attending the meeting?” he asked me. Answer 2 : How did he ask if I would be attending the meeting?
Exercise 3 : “I have seen that movie three times,” Alex told her. Answer 3 : How did Alex tell her that he had seen that movie three times?
Exercise 4 : “You should try the new Italian restaurant,” he recommended. Answer 4 : How did he recommend trying the new Italian restaurant?
Exercise 5 : “Please pass the salt,” she requested. Answer 5 : How did she request to pass the salt?
Exercise 6 : “I cannot come to your party,” Jane apologized. Answer 6 : How did Jane apologize that she could not come to the party?
Exercise 7 “Let’s meet at the mall,” they suggested. Answer 7 : How did they suggest meeting at the mall?
Exercise 8 : “Do you know where the station is?” he inquired. Answer 8 : How did he inquire if I knew where the station was?
Exercise 9 : “I must finish this book tonight,” she declared. Answer 9 : How did she declare that she must finish the book that night?
Exercise 10 : “I didn’t take your notebook,” he denied. Answer 10 : How did he deny taking my notebook?
Indirect to Direct Speech Exercises
Convert the following sentences from indirect to direct speech:
Exercise 11 : She said that she was learning to play the piano. Answer 11 : What did she say about learning to play the piano in direct speech?
Exercise 12 : He asked if I would be attending the meeting. Answer 12 : How did he ask about my attendance at the meeting in direct speech?
Exercise 13 : Alex told her that he had seen that movie three times. Answer 13 : What did Alex tell her about how many times he had seen the movie in direct speech?
Exercise 14 : He recommended trying the new Italian restaurant. Answer 14 : What did he say about trying the new Italian restaurant in direct speech?
Exercise 15 : She requested to pass the salt. Answer 15 : What did she request about the salt in direct speech?
Exercise 16 : Jane apologized that she could not come to the party. Answer 16 : What did Jane say when she apologized for not coming to the party in direct speech?
Exercise 17 : They suggested meeting at the mall. Answer 17 : What did they suggest about meeting in direct speech?
Exercise 18 : He inquired if I knew where the station was. Answer 18 : How did he inquire about the location of the station in direct speech?
Exercise 19 : She declared that she must finish the book that night. Answer 19 : What did she declare about finishing the book in direct speech?
Exercise 20 : He denied taking my notebook. Answer 20 : What did he say when he denied taking the notebook in direct speech?
FAQ’s
How do tenses change in indirect speech.
Tenses in indirect speech usually shift back (e.g., present to past) to reflect that the speaking occurred in the past.
Do pronouns always change in indirect speech?
Pronouns change in indirect speech to match the perspective of the speaker reporting the speech, ensuring clarity and coherence.
How do you convert a question from direct to indirect speech?
Questions in direct speech are converted by introducing a clause with ‘if’ or ‘whether’, and rearranging the syntax to statement form.
What happens to modal verbs in indirect speech?
Modal verbs often change in indirect speech, with ‘will’ becoming ‘would’ and ‘can’ changing to ‘could’, for example.
Can the verb tense remain the same in indirect speech?
Yes, if the reporting verb is in the present tense, the tense within the reported clause might not change.
What are the typical introductory verbs used in indirect speech?
Common verbs include ‘said’, ‘told’, ‘asked’, ‘replied’, ‘exclaimed’, and ‘advised’, depending on the nature of the speech.
How do you handle imperatives in indirect speech?
Imperatives are converted into infinitive structures, such as changing “Close the door” to “He asked her to close the door.”
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
GrammarSimple.Com
40 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Sentences
Table of Contents
Direct And Indirect Speech Examples
While using English, we use direct and indirect speeches quite often. If a sentence is expressed exactly as it came out of the mouth of the person who said it, it becomes a direct speech. However Indirect Speech (also called reported speech) refers to transmitting a sentence that someone has said. It is often used in daily language.
For example,
- Susan told me she ate pizza yesterday. (Indirect Speech)
Susan said, “I ate pizza yesterday.”. (Direct Speech)
- Mathilda told me she had to go out. (Indirect Speech)
Mathilda said: “I have to go out.”. (Direct Speech)
- Julie asked if the train had left when she arrived at the ticket office. (Indirect Speech)
Julie asked: “Did the train leave?” (Direct Speech)
| 1 | It is too late. | |
| I said it was too late. | ||
| 2 | I had taken Spanish lessons before. | |
| He said he had taken Spanish lessons before. | ||
| 3 | Did you do your homework? | |
| He asked me if I did (had done) my homework. | ||
| 4 | Please help me carry this! | |
| My mother asked me to help her carry that. | ||
| 5 | I like ice cream. | |
| He said that he liked ice cream. | ||
| 6 | I’II see you later. | |
| He said he would see me later. | ||
| 7 | I could swim when I was four. | |
| He said he could swim when he was four. | ||
| 8 | I should call my mother. | |
| He said he should call her mother. | ||
| 9 | I might be late. | |
| He said he might be late. | ||
| 10 | He said, “I was teaching earlier.” | |
| He said he had been teaching earlier. | ||
| 11 | Mary said, “I have been writing this essay.” | |
| Mary said that he had been writing that essay. | ||
| 12 | Michael said, “I may go there.’ | |
| Michael says that she may go there. | ||
| 13 | We can´t go the zoo next week. | |
| They said they couldn’t go to the zoo next week. | ||
| 14 | George is said, “I write a letter”. | |
| George is said that she wrote a letter. | ||
| 15 | I said, “He is driving a car” | |
| I said that he was driving a car. | ||
| 16 | I am reading a book, he explained. | |
| He explained that he was reading a book. | ||
| 17 | My father said, “I am cooking dinner.” | |
| My father said he was cooking dinner. | ||
| 18 | My sister said, “I had already eaten.” | |
| My sister said she had already eaten. | ||
| 19 | My boyfriend asked, “Do you like horror films?” | |
| Do you like horror films? my boyfriend asked. | ||
| 20 | I never get up late, my mother said. | |
| My mother said that she never got up late. |
| 21 | She said, “I might come early.” | |
| She said she might come early. | ||
| 22 | I am leaving home now.” | |
| He said that he left home then. | ||
| 23 | Are you living here? | |
| He asked me if I was living here. | ||
| 24 | I’m going to come. | |
| She said that she was going to come. | ||
| 25 | We can communicate smoothly. | |
| They said that they could communicate smothly. | ||
| 26 | I often enjoy myself. | |
| Mary will say that that she often enjoys herself. | ||
| 27 | Everything is going fine. | |
| The news says that everything is going fine. | ||
| 28 | My father was born in 1962. | |
| My father told us that he was born in 1962. | ||
| 29 | She said, “I’ve missed my train.” | |
| She said that she’d missed her train. | ||
| 30 | I’m sorry for the accident. | |
| Georger told Samuel (that) he was sorry for the accident. | ||
| 31 | He said, “I am a football player.” | |
| He said that he was a football player. | ||
| 32 | Michael said, “I will buy a new car.” | |
| Michael said that she will buy a new car. | ||
| 33 | Mark said, “Bill needs a pencil.” | |
| Mark said that Bill needed a pencil. | ||
| 34 | She said, “I went to the shopping center.” | |
| She said that she had gone to the shopping center. | ||
| 35 | I write poems. | |
| He says that he writes poems. | ||
| 36 | She said: “I would buy new house if I were rich”. | |
| She said that she would buy new house if she had been rich”. | ||
| 37 | May I go out? | |
| She wanted to know if she might go out. | ||
| 38 | She is American, she said. | |
| She said she was American. | ||
| 39 | My son, do the exercise.“ | |
| Sh told her son to do the exercise. | ||
| 40 | I don’t know what to do. | |
| Samuel added that he didn’t know what to do. |
Related Posts
Using LESS and Example Sentences
Synonyms of Better, Synonym words for Better
Relative Clauses and Example Sentences
About the author.
Englishfornoobs.com
English worksheets & lessons for beginners
Direct and Indirect speech: rules and examples
Direct and indirect speech with rules and examples, download all the grammar lessons in one click $27 $19.
In English, to report someone’s words or their own words, you can use direct or indirect speech. These may include statements, questions, orders, advice…
When moving from direct to indirect style, it is often necessary to change personal pronouns, demonstrative and possessive pronouns according to who says what:
- I → he / she
- me → him / her
- my → his / her
- this → that
- mine → his / hers
- ours → theirs
- our → their
Here are some examples:
| She says: “My dad likes onion soup.” | She says that dad likes onion soup. |
| Kevin said, ‘I’m tired.’ | Kevin said (that) was tired. |
| Have you ever been to Japan? | She asked if I had ever been to Japan. |
| Open the door! | He told to open the door. |
Note: That is often implied in indirect speech. It is not mandatory to use it, so it is indicated in brackets in this lesson.
Introductory verbs
To relate someone’s words to both direct and indirect speech, you need an introductory verb.
The two most frequent are tell and say, but there are many other possible ones like:
- want to know
Say or tell ?
Be careful to distinguish SAY from TELL . The two verbs may have the same meaning, but their use is different. With TELL, the interlocutor is quoted: the name or pronoun is placed immediately after tell (tell somebody something).
With SAY, the interlocutor is not necessarily quoted; if he is, he is introduced by the preposition to ( say something to somebody ):
- He says (that) he is English.
- He tells me (that) he is English.
However, tell is used in some expressions without mentioning a contact person:
- tell the truth
- tell a story
- tell the time
Note: the wording ‘ He said to me… ‘ is possible but seems clumsy. It is best to use ‘ He told me… ‘.
TIMES MODIFICATIONS
The shift to indirect speech leads to changes in the tense, depending on whether the verb is in the present tense or in the past tense.
If the introductory verb is in the present tense, the tense (or modal) does not change.
- “I’m sorry.” → He says he is sorry.
- “I hate driving” → He says he hates driving.
Be careful, if the statements reported are still true now you must not change the tense!
- He said this morning (that) he hates driving. (= He still hates driving now).
If the introductory verb is in the past, the verb tense changes:
Examples of major changes in time:
| Direct speeches | Indirect speeches |
|---|---|
| He said: “I happy” | He said (that) he happy. |
| He said: “I for my phone” | He said (that) he for his phone. |
| He said: “I Paris last year” | He said (that) he Paris the previous year. |
| He said: ” I in London for a long time “ | He said (that) he in London for a long time. |
| He said: “They the kitchen when I “ | He said (that) they the kitchen when he |
| He said: “I when the accident “ | He said (that) when the accident |
| He said:”I for one hours.” | He said (that) for one hours. |
| He said: “I a book when the light “ | He said (that) he a book when the light |
| He said: “I the door.” | He said (that) the door. |
| He said: “I a plane if I rich” | He said (that) he a plane if he rich. |
The modals could, should, would, might, needn’t, ought to, used to don’t change when used with indirect speech.
Those who change are will → would, can → could, may → might :
- I will come with you. → Tina promised she would come with me.
- I can help you. → He said he could help me.
- It may be a good idea. → I thought it might be a good idea.
| Direct speeches | Indirect speeches | |
|---|---|---|
| will | “They will call you.” | He told her that they would call her. |
| would* | “I would help, but I’m sick.” | She said (that) she would help but she was sick. |
| can | “I can do it.” | He said he could do it. |
| could* | “I could swim when I was four” | She said (that) she could swim when she was four. |
| should* | “I should call my mother” | She said (that) she should call her mother. |
| may | “May I go out?” | He wanted to know if he might go out. |
| must | “She must apply for the job.” | He said that she must/had to apply for the job. |
* do not change
TIME, PLACE AND DEMONSTRATIVE MARKERS
Expressions of time, place and demonstratives change if the context of indirect speech is different from that of direct speech.
She said “I saw him yesterday.” → She said she had seen him the day before.
| Direct speeches | Indirect speeches |
|---|---|
| Time marker | |
| today | that day |
| now | then |
| yesterday | the day before |
| … days ago | … days before |
| last week | the week before |
| next week | the following week |
| next year | the following year |
| tomorrow | the next day / the following day |
| Location marker | |
| here | there |
| Demonstrative | |
| this | that |
| these | those |
Orders and prohibitions to indirect speech
To relate an order or prohibition to indirect speech, verbs such as tell, order or forbid are used… Be careful, remember to replace Don’t by NOT when it is the main verb of the sentence!
For affirmative sentences, use to + infinitive
For negative sentences use not to + infinitive
- Don’t worry! → He told her not to worry.
- He said, “go to bed!” → He ordered the child to go to bed.
- Don’t marry him! → She forbade me to marry him.
- Please don’t be late. → She asked us not to be late.
Questions to the indirect speech
If there is an interrogative word like where/who/when/why… in direct speech, we keep it in indirect speech:
- What are you doing? → She asked me what I was doing.
- Who was that beautifl woman? → He asked me who that beautiful woman had been.
- Where do you live? → He wanted to know where I lived.
- “Why don’t you speak Spanish?” → He asked me why I didn’t speak Spanish.
If it is a closed-ended question or you have to answer yes/no, you use if or whether :
- “Do you like chocolate?” → She asked me if I liked chocolate.
- “Are you living here?” → She asked me if I was living here.
- “Have you ever been to Paris?” → He asked me if I had ever been to Paris.
When the question contains a modal, it is preterite in the reported question:
- How will he react? → He wondered how he would react.
Some examples of indirect questions:
- I wondered what they were talking about.
- I don’t know if they’ll come or not.
OTHER CHANGES
Expressions of advice such as must, should and ought are usually reported using the verbs advise or urge :
- “You must read this book.” → He advised / urged me to read that book.
The expression let’s is usually reported using the verb suggest, with gerund or with should:
- “Let’s go to the cinema.” → He suggested going to the cinema. OR He suggested that we should go to the cinema.
©Englishfornoobs.com
Tags: Grammar
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Join Pilot Waitlist

Home » Blog » General » Direct vs. Indirect Speech Examples: Unveiling the Variances and Usage

Direct vs. Indirect Speech Examples: Unveiling the Variances and Usage
I. introduction.
Welcome to my blog on Social Emotional Learning (SEL)! In today’s post, we will explore the difference between direct and indirect speech examples. But first, let’s briefly understand what SEL is and why it is important in our personal and professional lives.
A. Brief explanation of Social Emotional Learning (SEL)
Social Emotional Learning (SEL) is the process of acquiring and applying the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary to understand and manage emotions, set and achieve positive goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions.
B. Importance of SEL in personal and professional life
SEL plays a crucial role in our personal and professional lives. It helps us develop self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making abilities. These skills are essential for building healthy relationships, managing conflicts, and succeeding in various aspects of life.
C. Purpose of the blog post – exploring the difference between direct and indirect speech examples
In this blog post, we will focus on the difference between direct and indirect speech examples. Understanding and effectively using both forms of speech is vital for effective communication and enhancing our social and emotional skills.
II. Understanding Direct Speech
Direct speech is a form of speech where the exact words spoken by a person are quoted and presented within quotation marks. Let’s delve deeper into its definition, characteristics, and examples.
A. Definition of direct speech
Direct speech refers to the exact words spoken by someone, presented within quotation marks. It allows us to directly quote what someone said, capturing their tone, emotions, and intentions.
B. Characteristics and features of direct speech
Direct speech has the following characteristics:
- Quotation marks are used to indicate the exact words spoken.
- The verb tense and pronouns are used as per the original speaker.
- The sentence structure is preserved.
C. Examples of direct speech in everyday conversations
Direct speech can be observed in various types of conversations. Let’s explore some examples:
1. Simple statements
“I love ice cream,” said Sarah.
“I can’t wait for the weekend,” exclaimed John.
2. Questions
“Are you coming to the party?” asked Lisa.
“What time does the movie start?” inquired Tom.
3. Commands
“Please clean your room,” instructed the mother.
“Don’t forget to bring your umbrella,” reminded the teacher.
D. Importance of using direct speech in effective communication
Direct speech allows us to accurately convey the speaker’s words, emotions, and intentions. It adds authenticity and clarity to our communication, fostering better understanding and connection with others.
III. Unveiling Indirect Speech
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, is a form of speech where the speaker’s words are paraphrased or reported without using quotation marks. Let’s explore its definition, differences from direct speech, and examples.
A. Definition of indirect speech
Indirect speech refers to reporting or paraphrasing someone’s words without using quotation marks. It involves transforming the original speaker’s words into our own words while maintaining the meaning and essence of the message.
B. Key differences between direct and indirect speech
The key differences between direct and indirect speech are:
- Direct speech uses quotation marks, while indirect speech does not.
- Direct speech preserves the original speaker’s words, while indirect speech paraphrases or reports them.
- Direct speech maintains the original sentence structure, while indirect speech may require changes in tense, pronouns, and word order.
C. Examples of indirect speech in various contexts
Indirect speech can be observed in different contexts. Let’s explore some examples:
1. Reporting statements
Sarah said that she loved ice cream.
John exclaimed that he couldn’t wait for the weekend.
2. Reporting questions
Lisa asked if you were coming to the party.
Tom inquired about the movie’s starting time.
3. Reporting commands
The mother instructed to clean your room.
The teacher reminded not to forget to bring your umbrella.
D. Advantages and challenges of using indirect speech
Indirect speech offers certain advantages, such as allowing us to summarize or report longer conversations concisely. However, it can also pose challenges in accurately conveying the speaker’s tone, emotions, and intentions.
IV. Variances in Usage
Several factors influence the choice between direct and indirect speech. Let’s explore these factors and understand when to use each form of speech in different scenarios.
A. Factors influencing the choice between direct and indirect speech
The choice between direct and indirect speech is influenced by:
- Formality of the situation: Direct speech is often used in informal conversations, while indirect speech is more common in formal settings.
- Cultural norms and expectations: Different cultures have varying preferences for direct or indirect communication styles.
- Emotional impact and empathy: Direct speech may be more appropriate when conveying strong emotions, while indirect speech can be used to soften the impact or show empathy.
B. Appropriate usage of direct and indirect speech in different scenarios
Let’s explore the appropriate usage of direct and indirect speech in various scenarios:
1. Personal conversations
In personal conversations with friends and family, direct speech is often preferred as it allows for a more authentic and immediate exchange of thoughts and emotions.
2. Professional settings
In professional settings, indirect speech is commonly used to report conversations, summarize meetings, or convey information in a more formal and concise manner.
3. Educational contexts
In educational contexts, both direct and indirect speech can be used depending on the purpose and formality of the communication. Direct speech can be useful for role-playing or reenacting historical events, while indirect speech is often used in academic writing and research.
V. Enhancing Social Emotional Learning through Direct and Indirect Speech
Both direct and indirect speech play a significant role in developing social and emotional skills. Let’s explore the impact of these forms of speech on SEL and strategies for improving our communication skills.
A. Impact of direct and indirect speech on SEL skills
1. Active listening: Both direct and indirect speech require active listening skills to accurately understand and interpret the speaker’s words, emotions, and intentions.
2. Empathy and understanding: Indirect speech, in particular, allows us to show empathy and understanding by paraphrasing and summarizing the speaker’s words in a compassionate manner.
3. Conflict resolution: Both direct and indirect speech can be effective in resolving conflicts by promoting open and honest communication, understanding different perspectives, and finding common ground.
B. Strategies for developing effective direct and indirect speech skills
1. Active practice and role-playing: Engage in role-playing activities to practice both direct and indirect speech. This will help improve your listening, speaking, and paraphrasing skills.
2. Reflective listening exercises: Practice reflective listening by summarizing and paraphrasing what others say in your own words. This will enhance your understanding and empathy.
3. Mindful communication techniques: Develop mindfulness in your communication by being aware of your own words and their impact on others. Practice using direct and indirect speech consciously and purposefully.
VI. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between direct and indirect speech examples is essential for effective communication and enhancing our social and emotional skills. Both forms of speech have their advantages and appropriate usage in different scenarios. By mastering both direct and indirect speech, we can improve our active listening, empathy, and conflict resolution skills. So, let’s continue exploring Social Emotional Learning and communication skills to foster better connections and understanding in our personal and professional lives.
C. Encouragement to continue exploring SEL and communication skills
Start your EverydaySpeech Free trial today and embark on a journey of enhancing your Social Emotional Learning and communication skills. Sign up now at https://everydayspeech.com/start-free-trial/ .
Related Blog Posts:
Pragmatic language: enhancing social skills for meaningful interactions.
Pragmatic Language: Enhancing Social Skills for Meaningful Interactions Pragmatic Language: Enhancing Social Skills for Meaningful Interactions Introduction: Social skills play a crucial role in our daily interactions. They enable us to navigate social situations,...
Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12
Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12 Key Takeaways Strong social communication skills are crucial for academic success and building meaningful relationships in Grade 12. Social communication includes verbal and non-verbal communication,...
Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12 Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12 As students enter Grade 12, they are on the cusp of adulthood and preparing for the next chapter of their lives. While academic success...

FREE MATERIALS
Better doesn’t have to be harder, social skills lessons students actually enjoy.
Be the best educator you can be with no extra prep time needed. Sign up to get access to free samples from the best Social Skills and Social-Emotional educational platform.
Get Started Instantly for Free
Complete guided therapy.
The subscription associated with this email has been cancelled and is no longer active. To reactivate your subscription, please log in.
If you would like to make changes to your account, please log in using the button below and navigate to the settings page. If you’ve forgotten your password, you can reset it using the button below.
Unfortunately it looks like we’re not able to create your subscription at this time. Please contact support to have the issue resolved. We apologize for the inconvenience. Error: Web signup - customer email already exists
Welcome back! The subscription associated with this email was previously cancelled, but don’t fret! We make it easy to reactivate your subscription and pick up right where you left off. Note that subscription reactivations aren't eligible for free trials, but your purchase is protected by a 30 day money back guarantee. Let us know anytime within 30 days if you aren’t satisfied and we'll send you a full refund, no questions asked. Please press ‘Continue’ to enter your payment details and reactivate your subscription
Notice About Our SEL Curriculum
Our SEL Curriculum is currently in a soft product launch stage and is only available by Site License. A Site License is currently defined as a school-building minimum or a minimum cost of $3,000 for the first year of use. Individual SEL Curriculum licenses are not currently available based on the current version of this product.
By clicking continue below, you understand that access to our SEL curriculum is currently limited to the terms above.
How So-Called ‘Preferred Pronouns’ Threaten Free Speech

In J.R.R. Tolkien’s classic The Fellowship of the Ring , Boromir says concerning the one ring, “Is it not a strange fate that we should suffer so much fear and doubt for so small a thing? So small a thing!” In some ways, this encapsulates what some feel about the debate over so-called “preferred pronouns.” Are pronouns such a big deal? The answer is yes!
Pronouns are small words with big implications. When signifying persons, pronouns often carry other characteristics of the people they refer to, like number and gender. And until recently, most people understood gender to be binary (male or female). But now, an ever-growing list of pronouns have become expressions of one’s self-proclaimed identity, a claim that proponents insist everyone must affirm—or else.
Some people have lost their jobs or been threatened with termination because they decline to use certain pronouns due to the message about human nature that those terms inherently and unavoidably communicate. In other cases, people have been banned from common or public spaces—all because they believe what has been obvious to human society for thousands of years: that a man is a man, and a woman is a woman.
Let’s look at how pronouns are becoming a battleground for the radical gender ideology inundating our culture.
What is a pronoun?
To review a little grammar, according to Merriam-Webster , a pronoun is “a word that is used instead of a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns refer to either a noun that has already been mentioned or to a noun that does not need to be named specifically.” For example, instead of using someone’s name repeatedly (e.g., “Dave did this. Then, Dave did that.”), we could just say, “Dave did this. Then, he did that.” Or, a noun phrase like “the kids in orange shirts who dashed across the yard” could be replaced with “they” if you wanted to refer to the same kids multiple times. These are simple examples, but they show how often we use pronouns in English.
Pronouns and gender
In English, third-person singular pronouns can carry the implied gender of the noun they refer to. In my example above, Dave, a man, was referred to with the pronoun “he.” A woman would be referred to with a “she” pronoun. A rock would be called “it,” which doesn’t have an implied gender. First-person pronouns (I/we), second-person pronouns (you), and third-person plural pronouns (they) do not carry an implied gender.
For an individual whose gender is not known or isn’t necessary to determine, there is now debate over which third-person singular pronoun to use. Historically, we have used the pronoun “he” in a generic sense. In the past several decades, some have suggested replacing the generic “he” with “he or she,” “s/he,” or “she.” A generic statement might also use the pronoun “one” (e.g., “In such situations, one might like to do this.”). However, in any of these cases, whenever a particular person is in mind (Dave, Taylor, Molly, Bernice, Joey, etc.), the pronouns “he” or “she” have traditionally been used to refer back to that individual, reflecting the sex of the person being discussed.
Why are pronouns being debated?
Now, two major cultural trends have converged to question the foundational principles about gender and pronouns.
The first trend is that basic facts about sex, gender, and the gender binary are being denied. According to activists, no longer is gender determined by body and biology but by “gender identity,” which the World Health Organization defines as “a person’s deeply felt, internal and individual experience of gender, which may or may not correspond to the person’s physiology or designated sex at birth.” If an “internal and individual experience” is accepted as the source of one’s gender, then “gender” can come to mean whatever the individual claims, even without making reference to male or female categories.
The second trend, as theologian and historian Carl Trueman has noted , is that a new “modern self” has emerged. This modern self is defined by expressive individualism, where “authenticity is achieved by acting outwardly in accordance with one’s inward feelings.” It also demands that “society at large will recognize and affirm this behavior,” such that “any attempt to express disapproval is therefore a blow not simply against particular ways of behaving but against the right of that person to be whoever they wish to be.”
As you might imagine, such logic can move (and usually intends to move) well beyond the gender binary. For many in our modern culture, “gender” is no longer correlated to an empirical reality like the body but has become a mere expression of one’s own self-perception or self-declaration. It has become, like so many other things, a mode of expressive individualism.
This shift in thinking has changed how our culture demands that pronouns be used and has even sparked the invention of new “pronouns.” Instead of referring to the biological sex of an individual, pronouns are now demanded to reflect a person’s asserted gender identity. And with the growing number of asserted gender identities , the number of pronouns has grown at an even faster rate, as each gender identity can create its own set of pronouns.

What are ‘preferred pronouns’?
So-called “preferred pronouns” are the pronouns by which someone wants (or prefers) to be referred to by others. These pronouns could be ones that most people are familiar with like “he” or “she.” Some people who identify as “non-binary” (claiming to be neither male nor female) use “they” as their pronoun.
Some people will use a combination of different pronouns. They may even adopt multiple sets of pronouns that can change from moment to moment, over time, or depending on the setting. Some pronouns are even designed to communicate non-human identities.
Conceiving of pronouns as something to be specified by the individual (with a potentially infinite array of choices), rather than as words that are proper or improper to use depending on who or what is being referenced, is the first step in the activists’ attempt to redefine the relationship between sex and human identity. And that’s before you even get to which pronouns to use. All of this illustrates the message that viewing pronouns as “ preferred ” instead of proper is designed to communicate that every reality about human identity is rooted in one’s will rather than in nature.
What are neopronouns? What are noun-self pronouns?
A relatively recent but entirely predictable phenomenon in the world of pronouns is the invention of neopronouns . According to The New York Times , a neopronoun “can be a word created to serve as a pronoun without expressing gender.” Examples are ‘xe/xir/xirs,’ ‘ze/zir/zirs,’ ‘ey/em/eir,’ etc. (as opposed to ‘he/him/his’ or ‘she/her/hers’). With neopronouns, a person’s pronouns don’t need to reflect the gender binary. Gender becomes a creation of the individual and loses almost any connection to the physical world.
A subset of neopronouns is noun-self pronouns . The Times explains that noun-self pronouns are “a pre-existing word … drafted into use as a pronoun. Noun-self pronouns can refer to animals — so your pronouns can be ‘bun/bunself’ and ‘kitten/kittenself.’ Others refer to fantasy characters — ‘vamp/vampself,’ ‘prin/cess/princesself,’ ‘fae/faer/faeself’ — or even just common slang, like ‘Innit/Innits/Innitself.’” In other words, a noun-self pronoun doesn’t even need to reflect the fact that you are a human being.
While most people would consider neopronouns and noun-self pronouns outlandish, they reflect the culture’s expressive individualism that tries to root one’s identity in purely internal and psychological phenomena. If our understanding of sex and gender is severed from our embodied reality, there’s no stopping a person from identifying as the opposite sex, no sex, both sexes, or nonhuman things like animals , objects , fictional characters , or abstract concepts . Without the human body as the source of one’s identity, “I am a woman trapped in a man’s body” becomes just as plausible as “ I am a wolf trapped in a human body .” One’s identity is limited only by one’s imagination.
Pronouns and free speech
Words—including pronouns—have meaning. They carry a message with them. And this isn’t just the opinion of those who insist that pronouns reflect biological reality:
- A communications officer for GLAAD says that using a person’s “preferred pronouns” is a “really simple way to affirm their identity.”
- The Human Rights Campaign says that “using a person’s chosen name and pronouns is essential to affirming their identity and showing basic respect.”
- A resource page at the University of Wisconsin – Milwaukee says that using a person’s asserted pronouns is a way “to show your respect for their gender identity.”
- The National Child Traumatic Stress Network says that “using and validating the names, pronouns, and identities that youth share with you” is a part of parents’ and caregivers’ responsibility to “communicate” and actively affirm those identities.
Thus, even LGBT activists agree that pronouns are important because they carry a message when they are used.
Some might read all this and wonder, “So what? How is this going to affect me? I will simply use accurate pronouns.”
Unfortunately, radical gender ideology and its accompanying pronoun demands aren’t giving people that freedom. Many corporations and government officials label it offensive, discriminatory, and harmful not to use a person’s “preferred pronouns.” And, in the name of diversity and inclusion, this leads them to fire or “cancel” those who don’t toe the line. Ultimately, activists’ goals are to change the way you think, to punish any dissent, and to render it difficult (if not impossible) to communicate the truth that God created each of us either male or female.
Several Alliance Defending Freedom clients have already been punished because they declined to use pronouns about a person that are untrue, don’t reflect reality, and would reinforce ideas that are harmful to that individual. The fact is, if you believe that being a man matters, that being a woman matters, even that being human matters, you might be next.

Educators and pronouns
Teachers and professors have been frequent targets of government pronoun policies. Some public school districts and universities have adopted policies requiring staff to use students’ “preferred pronouns” or face punishment. Some policies even require teachers to lie to parents by actively hiding whether their child is using a different set of pronouns at school than they are at home. These policies violate the rights of teachers and parents.
Meriwether v. The Trustees of Shawnee State University
Dr. Nicholas Meriwether has served as a philosophy professor at Shawnee State University in Ohio for over 20 years with an unblemished record.
One day, a male student approached Dr. Meriwether after class, informing him that he identified as transgender and demanding that the professor refer to him as a woman with feminine titles and pronouns. Doing so would endorse an ideology that conflicts with Dr. Meriwether’s beliefs, would be untrue, and would force him to contradict his religious convictions. He tried to reach a compromise by using the student’s preferred first or last name, but this wasn’t enough.
Eventually, the university formally charged Dr. Meriwether and placed a written warning in his personnel file that threatened “further corrective actions” if he did not use the student’s chosen pronouns or stop using pronouns altogether—an impossible demand.
ADF filed suit on Dr. Meriwether’s behalf, and in 2021, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 6th Circuit ruled in his favor , saying that the university had violated the professor’s right to free speech. This led to a settlement in which the university agreed that it cannot force Dr. Meriwether to use pronouns and titles that differ from someone’s sex and agreed to remove the discipline from Dr. Meriwether’s files.
Vlaming v. West Point School Board
Peter Vlaming worked as a French teacher for almost seven years at West Point High School in Virginia. In 2018, one of Peter’s female students began to identify as male. Peter went out of his way to accommodate this student. He agreed to use the student’s preferred name and to avoid using pronouns to refer to the student. But Peter simply could not use male pronouns for a female student because it would communicate messages that contradict his core beliefs. This wasn’t good enough for the school district, and the district ultimately punished and fired Peter—not for what he said, but for what he could not say.
That’s why ADF filed a lawsuit to protect Peter’s constitutional right to not speak messages against his core beliefs. And thankfully, in December 2023, the Virginia Supreme Court reinstated Peter’s case and affirmed that Virginians have a right not to be forced to express messages that violate their beliefs. The case now returns to the trial court to be heard.
Parental rights and pronouns
In addition to teachers, parents who express concerns about these policies are being vilified and denied their right to direct the upbringing, education, and health care of their children.
T.F. and B.F. v. Kettle Moraine School District
Kettle Moraine School District in Wisconsin had a policy that instructed teachers and other adults at school to actively “socially transition” children by addressing them with incorrect names and pronouns immediately upon the child’s request, without parental consent, and even over their parents’ express objections and requests for a different therapeutic path.
The Wisconsin Institute for Law and Liberty and ADF filed a lawsuit against the district, and in October 2023, the Waukesha County Circuit Court ruled that Kettle Moraine’s policy violated parental rights . According to the court, without parental consent, the school district could neither “administer medicine to a student” nor “allow a student to participate in a sport.” So too could it “not change the pronoun of a student without parental consent without impinging on a fundamental liberty interest of the parents.”
Mead v. Rockford Public School District
In Michigan, ADF filed suit against a school district on behalf of Dan and Jennifer Mead after district employees began treating the couple’s middle-school daughter as a boy without their knowledge or consent and then taking steps to conceal these actions from the parents.
Employees had even altered some of the girl’s official records to remove references to the district’s new name and pronouns for her before sending the records home. The Meads only discovered the district’s actions when an employee unintentionally failed to completely alter a report about their daughter before sharing it with them.
Vitsaxaki v. Skaneateles Central School District
ADF attorneys filed suit against a New York school district after officials there began treating a middle-school girl as a boy without her mother’s knowledge or consent.
Jennifer Vitsaxaki withdrew her daughter from Skaneateles Central School District soon after she learned that school employees had begun to treat her daughter as a boy. Without notifying Mrs. Vitsaxaki or seeking her consent, employees began to refer to her daughter with a masculine name and third-person plural pronouns inconsistent with her daughter’s sex. When Mrs. Vitsaxaki confronted school officials, they defended their actions, citing district policy.
Pronouns in adoption and foster care
The effects of coercive pronoun policies are extending beyond education into other fields like foster care and adoption.
DeGross v. Hunter
In Washington, ADF is representing Shane and Jennifer DeGross, who had taken in vulnerable children for nine years as foster parents. But when the DeGrosses sought to renew their license in 2022, they learned that Washington had enacted new regulations requiring all foster parents to express the state’s views on human sexuality, including being required to use “preferred pronouns.”
When the DeGrosses said that they would love and support any child placed in their home but could not lie to a child about who they are, Washington officials rejected their application .
Wuoti v. Winters
Two families in Vermont, the Wuotis and the Gantts, had their foster-care licenses revoked for similar reasons. Despite the families’ track records of success and high praise from social workers who knew them, Vermont’s Department for Children and Families revoked their foster-care licenses after the couples expressed their belief—informed by their Christian faith and biological fact—that girls cannot become boys or vice versa.
They also expressed concern about the department’s policy requiring them to use “preferred pronouns,” take children to Pride parades, and push children to reject their bodies.
The wide reach of this pronoun issue
Because pronouns are a part of everyday speech, it should come as no surprise that government-mandated pronoun policies reach even further—from Catholic bookstores to Christian schools to faith-based health-care providers .
Thankfully, ADF continues to win many of these cases. No one should have to violate their conscience by being forced to speak a message about human nature contrary to their beliefs.
It is indeed a strange fate that small words like pronouns have become one of the biggest battlegrounds of identity politics today.
We can be sure that the logic of expressive individualism will not stop with attempts to enforce the use of opposite-sex pronouns, non-binary pronouns, and neopronouns. It will continue into noun-self pronouns or whatever may come after that.
Our human nature, and the pronouns we use to reflect it, need to be grounded in the empirical reality of one’s sex and the body. Only then can the disastrous “logic” of expressive individualism be brought to a halt.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Indirect: He inquired how I was. 9. Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Indirect: She promised that she would help me. 10. Direct: "I didn't see him yesterday," Tom confessed. Indirect: Tom confessed that he hadn't seen him the day before. 11. Direct: "I am going to the market," Alex said.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech. Change of Pronouns. Change of Tenses. Change of Time and Place References. Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech. Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks. Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker. Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb. Step 4: Change the Pronouns.
Rule #1. First person pronoun in direct speech (i.e. I, we) is changed according to the pronoun of reporting verb if pronoun in reporting verb is third person pronoun (i.e. he, she) For example: Direct speech: He said, " I don't want to shock people ". Reported speech: He said that he didn't want to shock people.
Here are the key aspects of converting direct speech into reported speech. Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns. Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, "I" in direct speech may become "he" or "she" in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example ...
Overview and definitions. Direct speech means to say exactly what someone else said. It is usually put inside quotation marks (". . ."). I have the package. He says, "I have the package." Reported speech (also called indirect speech ) means to say what someone else said, without actually quoting them.
1. First person pronouns (I, we, me, mine, us, ours) normally change to the third person (he, she, they, his, her, their, him, her, them). He told her, " I want to meet your father." He told her that he wanted to meet her father. 2. There will be no change in the pronoun when the speaker reports his own words. I said, " I am going."
Reported speech: direct speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Cha nges in pronoun s. The changes in pronouns in indirect speech depends on the subject and the object of the reporting verb. Rule 1: The first person of reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting verb. Example: She said, "I watched a movie" can be converted into She said that she had watched a movie.Hence, the first person in the direct speech "I" has become "she ...
When moving from direct to indirect style, it is often necessary to change personal pronouns, demonstrative and possessive pronouns according to who says what: I → he / she me → him / her my → his / her we → they this → that us → them mine → his / hers ours → theirs our → their Here are some examples: Direct speeches Indirect ...
Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then. In this example, the pronoun "I" is changed to "she" and the adverb "now" is changed to "then.". 2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here's an example:
Examples of Direct Speech: He said, "Don't take the car without asking me". John says, "I will help you with your work". "We are prepared to revise the law if we can", they said. ... Changing Pronouns. Pronouns in indirect speech also need to be changed from what they were in the indirect speech, as well as of course adapting the first pronoun ...
Here are the steps on how to do so: 1. Eliminate the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. The quotation marks are the primary indication of a direct speech. Therefore, it is crucial to take them out if you are forming an indirect one. 2. Retain the tense of the reporting verb and add the word "that" after it.
1 st person pronouns in reported speech are always changed according to the subject of the reporting speech.; 2 nd person pronouns in reported speech are always changed according to the object of the reporting speech.; 3 rd person pronouns in reported speech are not changed.; Important word changes. The above rules are mandatory for converting direct speech into indirect speech.
2. Examples of Indirect Speech. Basic Examples. Here's a simple conversion: Direct: John said, "I am going to the store.". Indirect: John said that he was going to the store. Complex Examples. For a more complex sentence: Direct: "I can't believe it," she whispered, "but I saw a unicorn in the garden.".
The pronoun used for representing the second person in reported speech changes based on the report's object in a direct speech. The pronoun used for representing the third person remains the same in the reported speech. Example: Direct: He said, "I am going to school." Indirect: He said that he is going to school.
The Pronouns Changing Rules can be summarized as "SON". Because 1 st and 2 nd Personal Pronouns are changed according to the subject (S) and object (O) of the Reporting Speech of the Direct Narration, respectively. And 3 rd Personal Pronoun of the Direct Speech is non-changeable (N). Pronouns are changed according to the "SON" formula ...
The speech which is quoted above in actual words ("I am tired" is called the Reported Speech and the verb ("says") that introduces speech is called the Reporting Verb.The above speech is called Direct Speech.. Indirect Speech Examples. On the other hand, when the speech is reported in the form of a narrative, without quoting the speaker's actual words, it is called Indirect speech or ...
Indirect speech, on the other hand, involves reporting someone's words without using their exact phrasing. It requires a change in verb tense, pronoun usage, and often the reporting verb and adverbs. For example: Indirect Speech: Sarah said that she was going to the park. In this example, Sarah's words are reported indirectly, with a change ...
Direct Speech Imperative sentence Examples: We use imperative sentence to give order, advice, to instruct or to request something. Mother told me, "Do your homework.". Father said, "Study more for your exam.". Ranju said, "Please, come with me.". The dwarf said to snow white, "Do not eat the apple.". The commander said to the ...
Direct and Indirect Speech: Direct speech quotes the exact words spoken, using quotation marks, while indirect speech paraphrases the spoken words without quotes, often changing tenses and pronouns. Both forms are essential for effective communication, emphasizing clarity and context in reporting speech.
Mathilda told me she had to go out. (Indirect Speech) Mathilda said: "I have to go out.". (Direct Speech) Julie asked if the train had left when she arrived at the ticket office. (Indirect Speech) Julie asked: "Did the train leave?" (Direct Speech) It is too late. I said it was too late.
In English, to report someone's words or their own words, you can use direct or indirect speech. These may include statements, questions, orders, advice… When moving from direct to indirect style, it is often necessary to change personal pronouns, demonstrative and possessive pronouns according to who says what: I → he / she; me → him / her
B. Characteristics and features of direct speech. Direct speech has the following characteristics: Quotation marks are used to indicate the exact words spoken. The verb tense and pronouns are used as per the original speaker. The sentence structure is preserved. C. Examples of direct speech in everyday conversations. Direct speech can be ...
Pronouns and free speech. Words—including pronouns—have meaning. They carry a message with them. And this isn't just the opinion of those who insist that pronouns reflect biological reality: A communications officer for GLAAD says that using a person's "preferred pronouns" is a "really simple way to affirm their identity."
There is a rich descriptive literature of speech and language differences in ASD. Beginning with the earliest accounts of the disorder, Kanner described the language of autistic children as monotonous and repetitious, noting that children often reversed personal pronouns (Kanner, 1968).