
- October 11, 2023
- Education Advice

Ph.D. vs. Doctorate: What are the Differences?
UOTP Marketing

For those who have a deep-seated attitude, pursuing a doctoral degree can be a tough yet beneficial journey. Currently enrolled in a doctorate program means that a person has already scooched over college admissions, went through high stake tests and exams, and finished all those research papers and long hours spent in university libraries hitting the books. While studying for a doctorate entails asserting oneself to an extensive amount of quality time and money , its significance and purpose usually pave the way to a lucrative end.
After having finished the Master’s Degree , students begin to think about their next step in their academic career. Then, paradoxically, while navigating through academia, they find themselves baffled by the immense terms and terminologies used to label specific degrees. Because the terms “Doctorate” and “Ph.D.” are somehow interlocked and overlap, and because “PhD” is sometimes used inconsistently, it can lead to considerable confusion. Ph.D. vs. Doctorate? You might wonder what their difference is, and why they are important. E xplaining what each of these terms stands for, the difference between them, and why they are valuable, can help you steer yourself down the right path from the outset.
Doctorate Degree vs. Ph.D.

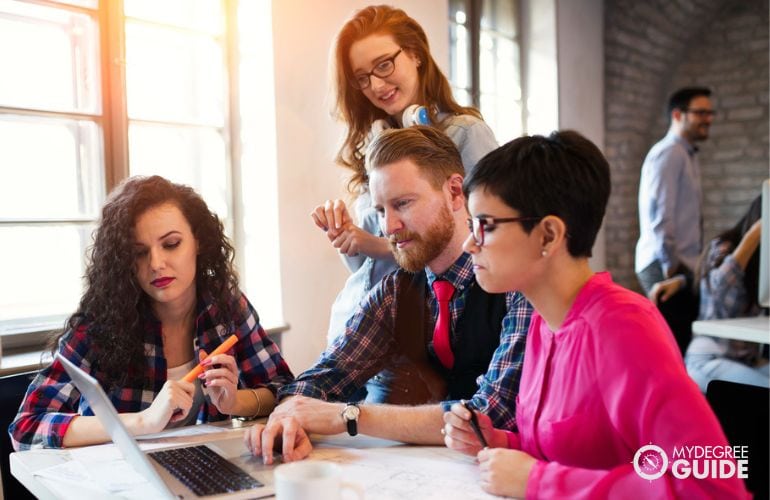
At first glance, it is pretty easy to confuse these two terms. But it is important for everyone to be able to make a distinction between the two. In this article, we will discuss the difference between Ph.D. and Doctorate in detail in order to get rid of any confusion you may have. In the academic world, the terms Doctorate and Ph.D. are currently used interchangeably. Both of them are the top cap of the ladder. However, a doctorate is mostly used as an umbrella term covering many fields ranging from professional degrees, humanities, and scientific disciplines.
A Ph.D. or Doctor of Philosophy, on the other hand, is a subcategory of a doctoral degree, it is much more distinct and clear-cut and is usually narrower in nature encompassing only humanities and scientific fields. In plain English, when someone says they are enrolling on a doctoral degree, it means they are doing a Ph.D. in a specific field. So, technically, in common parlance, there is no difference between the two terms.
But at the other end of the spectrum, one should be careful not to confuse a professional doctoral degree with a Ph.D. The former is more practical and is designed to prepare students to apply existing knowledge to find solutions to real-life problems and has a direct application to a particular profession.
A Ph.D. is theoretical by nature and is more academic and research-focused. it is often fixed on disseminating knowledge by conducting authentic research which means reviewing and identifying gaps in current literature and evaluating the relevance of existing and emerging theories within a particular field.
What Is a Ph.D. Degree and Why Should You Go for It?
Students who acquire a Ph.D. are justly proud — they wear it as a badge of identity in the academic elite. Traditionally, a Ph.D. was associated with teaching, which from Latin licentia docendi meant “license to teach”. However, the concept of Ph.D. has been on shifting sands nowadays and has become a more general term that isn’t necessarily confined to teaching only.
The Value of a PhD

Obtaining a Ph.D. helps you capitalize on the emerging academic opportunities making you more easily identifiable to employers or businesses seeking to fill professional, higher-level job positions. Many of these career options, conversely, are not available to those who do not belong to the Ph.D. club. While pursuing a Ph.D. requires devoting a tremendous effort and time and making significant personal sacrifices pushing the boundaries of knowledge, it’s all in service of the area of study you’re most passionate and zealous about. Ultimately, once you’ve attained your Ph.D., you will have achieved the pinnacle of education— something not too many people have or are able to accomplish.
FREE RESOURCE

A Guide to Choosing and Applying to Ph.D. Programs
Learn everything you need to know about selecting and applying to Ph.D. programs. Learn tips and tricks for a successful application and find your ideal program today!
What Is a Doctorate Degree?
A doctoral or doctorate degree is usually the most advanced degree one can earn in an academic discipline. Many pursue a doctorate degree to increase their professional credibility, be acknowledged as an expert in a specific field, and improve their resume.
A doctorate degree is a graduate-level credential that is usually earned after multiple years of graduate school. Earning a doctoral degree requires a significant level of research and work. In order to get this degree, one has to research a subject thoroughly, conduct new research and analysis, and provide a solution or interpretation into the field. But what types of doctoral degrees are available?
Types of Doctorate Degrees
There are two categories of doctorate degrees: an academic degree and a professional doctorate degree. An academic degree focuses on research, data analysis, and the evaluation of theory. A professional doctorate degree, on the other hand, is considered a terminal degree, which means that one has achieved the most advanced degree in the field. This degree is specifically designed for working professionals who want to grow in their careers.
Professional Doctorate Degrees
A professional doctorate is designed for working professionals who have experience in the field and want to increase their knowledge, improve their credibility, and advance their careers. This degree focuses on applying research to practical issues, coming up with interpretation and solutions, as well as designing effective professional practices within a particular field.
Professional doctoral degrees include:
Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
The DBA degree is ideal for students who already have a general business background and are interested in delving deeper into the practical and theoretical aspects that underpin business education. More to the point, in DBA you will develop the ability to solve real-life problems, discover the relevant expertise to innovate and uphold complex business issues and so much more. Upon completion, DBA students will possess enhanced leadership and strategic skills as well as the tools to propel their careers in today’s marketplace. The Business Administration industry is keen on finding such graduates with business skills and this is indicated by the immense job positions currently available.
Doctor of Education (Ed.D.)
If you are interested in setting your eyes on creating lifelong learning among your students, making a positive influence in educational culture, contributing to the growing body of research in the education realm , or just enhancing your subject matter expertise, the Doctor of Education program ticks all the boxes. This degree maintains a rigorous approach in academic education that prepares graduates to showcase the skills and expertise to devise solutions in tackling the challenges in contemporary education practice and become transformational leaders in the industry.
Doctor of Computer Science (DCS)
The demand for computer scientists has reached its peak and it is among the most sought-after positions nowadays. With a degree in DCS, you will have the opportunity to design, apply innovative experiments, predict trends and, ultimately, develop a richer understanding and contribute to your area of expertise. After all, who doesn’t want an exciting and financially stable career?
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. we will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours. if there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:.
By clicking the Send me more information button above, I represent that I am 18+ years of age, that I have read and agreed to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy , and agree to receive email marketing and phone calls from UOTP. I understand that my consent is not required to apply for online degree enrollment. To speak with a representative without providing consent, please call +1 (202) 274-2300
- We value your privacy.
Doctor of Medicine (M.D.)
The Doctor of Medicine degree is designed to prepare you for various medical challenges in different settings nationally and internationally. This program will further develop your critical thinking and clinical reasoning skills required for safe, high-quality medical practices. It will also improve your leadership, communication, and teamwork skills for collaborative patient care.
Doctor of Optometry (O.D.)
This professional degree typically requires four years of study. It focuses on basic biological sciences such as anatomy and physiology, microbiology, neuroanatomy, and so on. This doctoral degree will prepare, educate, and train professionals to practice at the highest level of proficiency, professionalism, and integrity.
Doctor of Psychology (PsyD)
The Doctoral of Psychology degree concentrates on the clinical and applied aspects of psychology. This type of doctorate prepares students for professional practice and clinical placement. This degree will be highly beneficial when working directly with patients who need psychology services. In addition, this degree allows doctors of psychology to confidently function as researchers and clinicians.
How to Choose a Ph.D. Program?
Choosing a Ph.D. program can be pretty challenging; it is a big academic decision and investment that requires commitment and perseverance. But how can you pick the right Ph.D. program for you? Well, there are some tips to help you choose the best fit for your goals and preferences:
- Think about the reasons why you want a Ph.D., what you expect to gain from it, and whether it is compatible with your professional goals.
- Consider your research environment.
- Take your time to research, compare, and consider multiple opportunities carefully.
- Pick a subject that interests and motivates you but is also practical.
- Ask your professors and other scholars in the field for advice.
All in all, the terms “Doctorate’’ and “Ph.D.” are in essence the same, which means all Ph.D. students are Doctoral students as well. On the other hand, earning a Ph.D. degree is no joke. If anything, Ph.D. students have the tenacity, patience, persistence, and years of hard work that you can vouch for. Ultimately, deciding what type of doctoral degree you should hop on, depends on your career goals, what you are passionate about and how you are going to achieve it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a doctorate and a ph.d..
In academic contexts, the terms “Doctorate” and “Ph.D.” are often used interchangeably, but there is a distinction. A Doctorate is an umbrella term covering a wide range of fields, including professional degrees, humanities, and scientific disciplines. A Ph.D., or Doctor of Philosophy, is a specific type of doctoral degree, typically focused on research and academic pursuits in the humanities and scientific fields.
Why should I pursue a Ph.D.?
Pursuing a Ph.D. can be a valuable endeavor, as it opens up academic and research opportunities, enhances your expertise in a specific field, and makes you more attractive to employers seeking candidates for high-level positions. It’s a chance to push the boundaries of knowledge and become an expert in your chosen study area.
What are the benefits of a professional doctorate?
Professional doctorate degrees, such as Doctor of Business Administration (DBA) or Doctor of Education (Ed.D.), are designed for working professionals who want to apply research to practical issues in their field. These degrees can enhance your career prospects, leadership skills, and problem-solving abilities within your profession.
How do I choose the right Ph.D. program?
To choose the right Ph.D. program, consider your career goals, research environment, and personal interests. Take your time to research and compare programs, seek advice from professors and experts in your field, and ensure that the program aligns with your professional aspirations.
What are the main differences between academic and professional doctorate degrees?
Academic doctorate degrees focus on research, theory evaluation, and data analysis, often leading to careers in academia or research. Professional doctorate degrees are more practical, designed for working professionals, and concentrate on applying research to real-world problems within a specific field.
Can I earn a Ph.D. in any field?
Ph.D. programs are available in various fields, including humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, engineering, and more. However, the specific availability of Ph.D. programs may vary by field and university.
Is a Ph.D. a challenging journey?
Yes, pursuing a Ph.D. can be a challenging journey that requires dedication, patience, and years of hard work. It involves conducting original research, writing a dissertation, and often teaching or assisting in courses. It’s a significant commitment, but it can be highly rewarding.
What are the potential career opportunities after earning a Ph.D.?
With a Ph.D., you can pursue careers in academia as a professor or researcher, work in research and development roles in various industries, or take on leadership positions in organizations. The specific career path will depend on your field of study and personal interests.
Share it with your friends!
Explore more.

Accounting vs. Finance Degree: Which Major to Choose?

12 Important Bookkeeping Skills You Need for a Successful Career
Recent resources.

How Long Does It Take to Become a Full-Stack Developer?

14 Essential Web Developer Skills You Need to Master

How to Become a Software Developer?

10 Essential Cybersecurity Skills You Must Have
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
Chat with an Admissions Officer Now!

- Associates Degree
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Faculty & Staff
- Accreditation
- Student Experience
QUICK LINKS
- Admission Requirements
- Military Students
- Financial Aid
- Jul 22, 2022
- 11 min read
Is a PhD Worth It? The Pros and Cons of Getting a Doctorate
To get a PhD or not to get a PhD? That is the question.
Valerie David
Lifestyle and Career Expert
Reviewed by Hayley Ramsey

Entering the job market for the first time can be a stressful experience, especially if you don't feel completely prepared. When deciding how to take those first steps toward your ultimate career , and how to give yourself a chance at the best jobs, you may find yourself asking: “Should I do a PhD?”.
While academics looking forward to a life of learning may consider this a no-brainer, there are important factors for everyone to consider. Finances, job prospects and quality of life issues can greatly affect the success of furthering your education.
To help you decide if the time and effort of a PhD is worth it, here are the major benefits and disadvantages of getting that doctorate.
After four or more years of intellectual pursuits, adding a PhD may seem like overkill. Before you make your choice, let's look at all the benefits that are exclusive to earning the most advanced degree.
1. You can contribute new knowledge to the world
Embarking on a PhD programme means delving into your preferred subject in a much deeper way than you have in any of your previous studies. The beauty of this advanced degree is that it allows you to sail in uncharted waters. Your goal is to find new information, draw new conclusions and, hopefully, make a significant contribution to your field.
Your intensive research, travel, collaboration and study will lead you on an unpredictable path to telling a story that no one has heard before. For some students, this pursuit of knowledge and discovery is enough to make all the hard work of earning a PhD worth it.
2. You'll have access to more prestigious jobs
One of the key benefits of a PhD is that it opens doors to careers at the highest levels. This can include leadership positions in science and engineering, government roles in economics and political science, and prestigious teaching posts for English and arts majors. Even if an advanced degree isn't required for the job you want, that PhD can give you an extra air of authority in your field and an edge over other candidates.
Another obvious upside to continuing your postgraduate studies is that landing these powerful positions can lead to large financial rewards. Some areas of study, like medicine and the law, tend to be more lucrative, but it can also depend on the type of job. For example, a university professor or researcher post can pay well for a wide variety of disciplines. Check out sites like the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the National Careers Service to investigate potential salaries.
3. Employers look for candidates with your superior writing skills
A study arranged by the National Commission on Writing discovered that blue-chip businesses (long-standing companies with stable stock growth) are spending more than $3 billion a year on remedial writing course for current employees. This includes staff with undergraduate degrees.
So, when a hiring manager peruses your résumé and sees that you've earned a PhD, they'll know immediately that you've spent years honing your skills at compiling research, organizing mountains of data and writing about your results in a cohesive and persuasive way. This will clearly set you apart from your competition, while landing your dream job will prove that pursuing that advanced degree was worth it.
4. You'll improve on all your soft skills
While pursuing your undergraduate degree, you likely noticed that you were learning more than just the subject matter taught in each class. Completing your studies also required time management skills , focus and problem solving .
Getting a doctorate degree requires even more of the soft skills that employers look for in applicants . Your intensive study and finished thesis should lead to improvements in your problem solving, critical thinking , patience and adaptability . These desirable skills won't just help you land a job but also excel in whatever career you choose to pursue .
5. You'll collect an extensive network of professional colleagues
When weighing the pros and cons of earning a PhD, consider all the professional contacts you'll make during the course of your studies. Working closely with professors, department heads, experts in your field, as well as fellow researchers, helps you develop an important resource. This network of colleagues can provide continual assistance with references, job leads, career advice and collaboration.
6. You can wait for a more favorable job market
Job prospects may not look that promising when you've completed your undergraduate degree, or even after you've been in the workforce for a few years. While there's no guarantee things will improve after a delay, some students may appreciate the benefit of a steady graduate assistant salary while they work on enhancing their résumé with a doctorate.
If you couldn't get a good internship during or after your undergrad studies, the PhD work also gives you the time to build that professional network . These contacts could prove to be the key to breaking into a specialized or highly competitive field.
You may still be thinking about all that time and commitment and wondering, “Is a PhD worth it?”. While there are always positive results from improving your education, there are some downsides to getting your doctorate.
1. It's expensive
This is a substantial factor for many students when weighing the merits of pursuing a PhD versus entering the job market right away. If you already have student loans , continuing your education will just increase your burden and add substantial pressure when you eventually begin your job search.
If cost is a concern, investigate graduate assistant jobs that help with expenses. Some programmes offer tuition assistance in return for teaching or research work. For those who already work full time and are hoping a PhD will help them advance in their career, consider keeping that job and pursuing your studies on a part-time basis.
2. Getting a PhD can be a lonely experience
Despite your interactions with professors and other students, pursuing a doctoral degree is ultimately a solitary pursuit. Your thesis topic is unique to you, and you'll spend a lot of time alone doing research and writing. Your social life can suffer, especially if you're also working in addition to your studies.
Career experts often talk about the necessity of work-life balance for physical and mental health, and this is just as important for PhD students as anyone else. It may take you a little longer to complete your degree, but it's worth taking the time to visit family and hang out with your friends. These positive interactions can help you stay motivated through the most tedious parts of your work.
3. You'll experience extreme stress and frustration
Pursuing a PhD may seem like a noble and interesting endeavor, and extended life as a student can appear more attractive than wading into the job market. You must be aware, however, that getting a doctorate can be a very stressful and frustrating experience.
A topic that seemed intriguing at first may not live up to years of scrutiny, causing boredom at best or requiring a complete thesis change at worst. Not all programmes are well-run, either, and you may have a supervisor who is too critical, offers poor advice or is just unavailable and unhelpful.
The difficulties of a PhD programme lead to rather substantial dropout rates. In the US alone, only 57% of PhD students obtained their degree within a decade of enrolling. If you want to be in the successful half of those stats, take extra time to review your choice of supervisor and topic focus. Ask every professor you have for advice on making the right decisions and talk with current graduate students to see what their experience has been.
4. There may be limited job openings
While getting a PhD can qualify you for better and higher-paying jobs , it can also put you in a position where you're competing for an extremely limited number of job openings. This is especially true of university jobs, where the number of advanced degree graduates far outpaces the need for full-time instructors, researchers and administrators.
Earning your PhD with a very obscure thesis in a niche speciality can also limit your options. When there are only a handful of jobs that suit your expertise, and they're already occupied, it can make you feel that your doctorate was a waste of time. Consider the job market before you make decisions about getting another degree. If you're determined to study in a niche area, think ahead of time about related fields or industries where your knowledge and skills will also prove useful to employers.
5. There may be little to no financial reward
While most studies concur that having a PhD increases your income potential substantially over the lifetime of your career, it's not a guarantee of job security or a financial windfall. A study by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) found that 5 years after earning their doctorates , 45% of grads in Germany were still on temporary contracts and 13% ended up in lowly occupations.
Other European countries, including Slovakia, Belgium and Spain, had similar results. In the US, in fields like engineering, the difference in pay scales between employees with a master's degree and a PhD was a mere 7%. When that small bump in salary is weighed against the amount of debt taken on in order to get your degree, you may decide it's not worth it.
6. You could lose out on valuable job experience
New forms of technology continue to change how organizations operate, and those changes can happen fast. If you've already spent several years in school, toiling away in solitary study of obscure subjects can cause you to fall further behind in learning the skills you'll actually need for a future career.
Before you invest in getting a PhD, research your chosen field and learn which type of degree will give you the most value. Many scientific, financial and computing careers rely more on skills acquired on the job, rather than in coursework that can quickly become outdated.
Questions to ask yourself
You’ve listed out the pros and cons, but that still may not be enough to help make your decision. When it comes to a life-altering change like getting a doctorate, it’s okay to take enough time to ask yourself specific questions to ensure you’re making the right move. Consider asking yourself the following:
- Why do I want to get a PhD?
- Do I have the pre-requisites to move forward to a PhD?
- What are my strengths and limitations?
- Am I financially prepared?
- Am I mentally prepared?
- How will this affect my relationship with my family or friends?
- Where will I study?
- What am I trying to achieve?
- What jobs will be available to me after I get my PhD?
- Are there other options or avenues to consider?
Unfortunately, you may not have the answer to every one of these questions, because let’s face it, you don’t know what you don’t know. You might not know how it will affect your relationship with family or friends, but why not ask them? Reach out to those closest to you and see how you pursuing this degree could trickle down to them and allow that to play into your decision. Evaluate the answers to these questions and use it to help you make an educated decision on your future moving forward.
The best PhD degrees
If you’ve weighed out the pros and cons, asked all the important questions, and now you’re set on getting your PhD, congratulations! To help you along the way, let’s look at a list of the most valuable PhD programs to start you on your way to this degree.
- Criminal Justice
- Engineering
- Cybersecurity
- Business Administration
These fields are rapidly growing and are among the highest-paying doctorate degrees in 2022 , so they might be worth considering as you start your journey.
Key takeaways
Pursuing your PhD requires an incredible amount of commitment, and it's important to take the necessary time to make the decision. As you’re evaluating a doctorate degree, remember the following:
- Evaluate the pros and cons list right from the beginning to ensure you’re weighing out both sides of the coin.
- Ask yourself the necessary questions. A doctorate degree commitment can affect more than just you, so be sure you’re factoring that into your decision.
- Review specifically which PhD would be best for you and your field progression.
- Research your chosen field carefully and evaluate the job market before you finalize your degree choice.
- Once you’ve selected your degree, stay focused and stay driven. It’s going to be a hard few years, but it will be worth the work!
Who knows, this may prompt you to move on to postgraduate study — never stop achieving!
Have you decided to pursue your PhD, or are you still considering your options? Join us in the comments below and let us know what’s stopping or encouraging you from getting a PhD.
Originally published on July 24, 2019. Updated by Shalie Reich.
Continuing Education
Courses and Qualifications
Doctorate vs. PhD: Understanding the Key Differences [2024]
If you’re interested in pursuing a doctoral degree, you may wonder about the differences between a doctorate vs. PhD.

A doctorate and a PhD are both terminal degrees that allow you to develop specialized knowledge and skills in your chosen field. But these degrees typically have different areas of focus, requirements, and career outcomes.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Understanding the difference between PhD and doctorate can help you pick the degree that most aligns with your career aspirations and interests.
What’s the Difference Between Doctorate vs. PhD Degrees?

A doctorate and a Ph.D. are the highest college degrees students can earn. Graduates of both types of programs receive the title of “doctor” and may qualify for specialized careers in their fields.
But, while doctorate programs focus on professional competencies and knowledge, PhD programs prioritize academic research.
What Is a Doctorate Degree?

A doctorate degree is a professional degree that enables students to become experts in a specific field or industry. This degree focuses on applying academic research and theories in the workplace to improve performance and solve problems.
Courses vary by field and program but typically emphasize professional skills like collaboration, leadership, and project management. Additionally, many doctorate programs require students to complete a capstone project that addresses real issues affecting their industry.
Graduates often qualify for advanced administrative, leadership, and managerial positions in their fields.
What Is a PhD Degree?

A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree is an opportunity to strengthen your academic research skills and generate original knowledge. This degree trains students to become independent scholars who conduct cutting-edge research in their areas of expertise.
PhD curriculums cover advanced concepts and theories in a discipline. They also teach students qualitative and quantitative methodologies to design studies and conduct research. Additionally, most PhD programs require students to produce a dissertation that contributes fresh knowledge to the field.
Current professionals with PhDs often work as academic researchers and professors. They may also secure government and industry jobs.
Key Differences Between a PhD vs. Doctorate Degree
What’s a PhD degree ? What’s a doctorate degree? The main difference between a doctorate and a PhD is their area of focus. A doctorate prioritizes applied knowledge and professional skills, while a PhD emphasizes academic research. Let’s compare some more differences between a professional doctoral degree vs. PhD.

A doctorate enables students to become expert practitioners in their discipline. Students study existing concepts and theories and learn how to apply these ideas in the workplace.
By contrast, a PhD prepares students to conduct innovative research and educate others.
Goals and Outcomes

Doctorate programs help prepare students for senior administrative and leadership positions in their industries. They also help students enhance their professional competencies and tackle industry-specific challenges.
Students who pursue PhDs aim to advance their disciplines by generating new knowledge. They may also publish peer-reviewed research and teach undergraduate courses.
Student Population

Doctorate degrees are designed for current or aspiring working professionals who want to become industry leaders. These programs also enable students to increase their knowledge and credibility.
PhD programs attract students who want to expand their knowledge of research methodologies and theories. These learners also frequently pursue academic careers.
Admissions Requirements
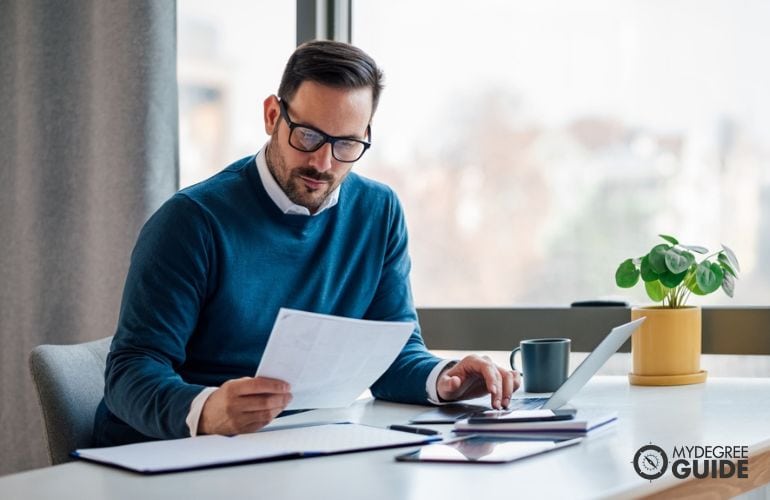

Doctorate and PhD programs typically require students to have bachelor’s and master’s degrees.
Additionally, prospective doctorate students may be asked to provide evidence of work experience, while PhD students might demonstrate their research abilities with a writing sample.
Program Length
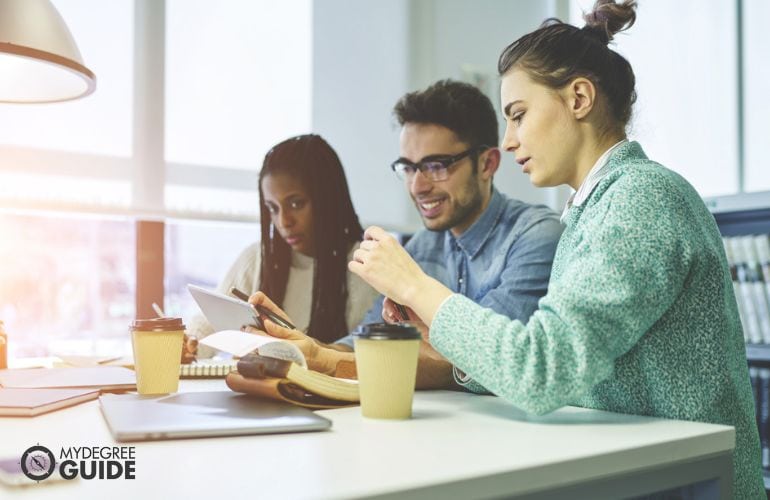

Requirements vary by program, but full-time students typically complete a doctorate in 3 to 5 years. Programs that require a capstone project may take longer. For those considering quick degrees, a number of universities now offer accelerated doctoral programs online .
PhD programs often take 4 to 7 years to finish. The speed at which students research and write their dissertations can significantly impact the timeline.
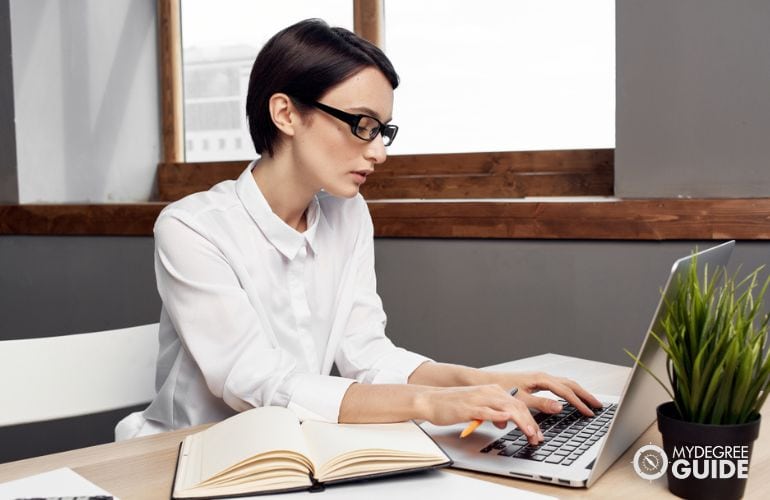

The curriculum for doctorate programs typically centers on practical skills and contemporary issues in the field. Topics may include communication, ethics, and leadership.
PhD programs offer classes on research methods, theories, and disciplinary trends. Students also learn how to write journal articles and present at conferences.
Assessment and Completion Requirements
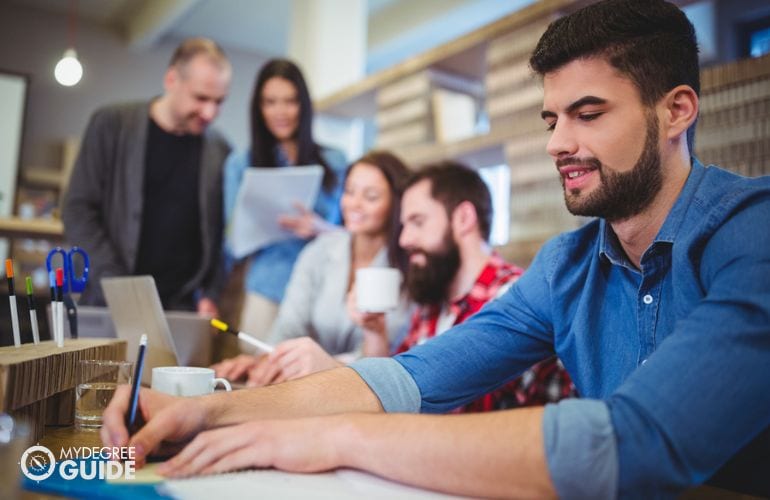

Doctorate and PhD students both complete 2 or more years of coursework. They also demonstrate their knowledge during comprehensive exams.
Doctorate students may produce a capstone project that applies their knowledge to real problems. By contrast, PhD students write dissertations based on original research.
If You Have a PhD, Are You a Doctor?

Is a PhD a doctor ? While graduates who earn a PhD are referred to as doctors, a PhD is different from a Doctor of Medicine (MD).
Doctors with MDs are medical doctors who can legally prescribe medications, perform surgery, and treat patients. They typically apply existing medical knowledge instead of conducting research. Doctors with PhDs don’t have any of these abilities. Instead, they have specialized knowledge and perform academic research in a particular field.
PhD or Doctorate Degree – Which Is Right for You?
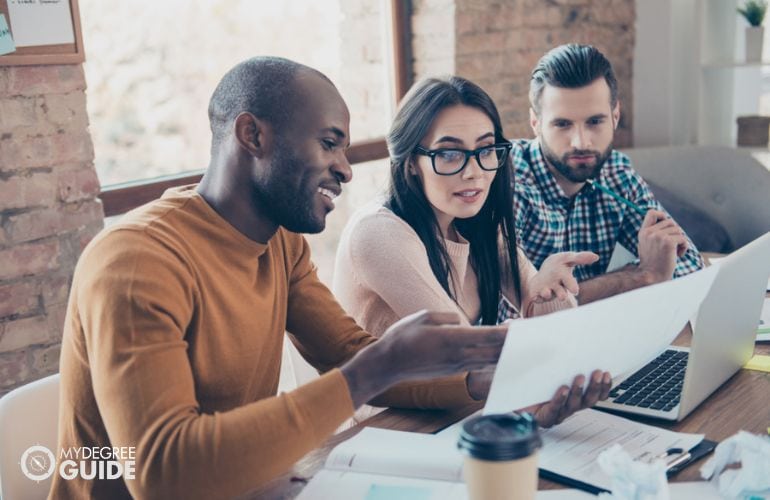

Understanding the difference between a doctorate and a PhD can help you select the right degree for you.
Professional doctorate degrees help students become leading practitioners and problem solvers. By contrast, PhD degrees enable students to hone their research skills and learn advanced concepts. Both degrees allow you to enrich your understanding of your chosen discipline or profession. They also help you boost your credentials and develop new skills.
After you decide between a doctorate degree vs. PhD, you can explore program options from accredited schools to find the best fit.

- What is a PhD?
Written by Mark Bennett
A PhD is a doctoral research degree and the highest level of academic qualification you can achieve. The degree normally takes between three and four years of full-time work towards a thesis offering an original contribution to your subject.
This page explains what a PhD is, what it involves and what you need to know if you’re considering applying for a PhD research project , or enrolling on a doctoral programme .
On this page
The meaning of a phd.
The PhD can take on something of a mythic status. Are they only for geniuses? Do you have to discover something incredible? Does the qualification make you an academic? And are higher research degrees just for people who want to be academics?
Even the full title, ‘Doctor of Philosophy’, has a somewhat mysterious ring to it. Do you become a doctor? Yes, but not that kind of doctor. Do you have to study Philosophy? No (not unless you want to) .
So, before going any further, let's explain what the term 'PhD' actually means and what defines a doctorate.
What does PhD stand for?
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term ‘philosophy’ does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to ‘lover of wisdom’.
What is a doctorate?
A doctorate is any qualification that awards a doctoral degree. In order to qualify for one you need to produce advanced work that makes a significant new contribution to knowledge in your field. Doing so earns you the title 'Doctor' – hence the name.
So, is a PhD different to a doctorate? No. A PhD is a type of doctorate .
The PhD is the most common type of doctorate and is awarded in almost all subjects at universities around the world. Other doctorates tend to be more specialised or for more practical and professional projects.
Essentially, all PhDs are doctorates, but not all doctorates are PhDs.
Do you need a Masters to get a PhD?
Not necessarily. It's common for students in Arts and the Humanities to complete an MA (Master of Arts) before starting a PhD in order to acquire research experience and techniques. Students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) don't always need an MS/MSc (Master of Science) to do a PhD as you'll gain training in lab techniques and other skills during your undergraduate degree.
Whether a Masters is a requirement for a PhD also varies by country. Australian PhDs may require a Masters as the equivalent of their own 'honours year' (where students work on research). US PhD programmes often include a Masters.
We have a whole guide dedicated to helping you decide whether a PhD without a Masters is the right route for you.
The origin of the PhD
Despite its name, the PhD isn't actually an Ancient Greek degree. Instead it's a much more recent development. The PhD as we know it was developed in nineteenth-century Germany, alongside the modern research university.
Higher education had traditionally focussed on mastery of an existing body of scholarship and the highest academic rank available was, appropriately enough, a Masters degree.
As the focus shifted more onto the production of new knowledge and ideas, the PhD degree was brought in to recognise those who demonstrated the necessary skills and expertise.
The PhD process – what's required to get a PhD?
The typical length of a PhD is three to four years full-time, or five to six years part-time.
Unlike most Masters courses (or all undergraduate programmes), a PhD is a pure research degree. But that doesn’t mean you’ll just spend years locked away in a library or laboratory. In fact, the modern PhD is a diverse and varied qualification with many different components.
Whereas the second or third year of a taught degree look quite a lot like the first (with more modules and coursework at a higher level) a PhD moves through a series of stages.
A typical PhD normally involves:
- Carrying out a literature review (a survey of current scholarship in your field).
- Conducting original research and collecting your results .
- Producing a thesis that presents your conclusions.
- Writing up your thesis and submitting it as a dissertation .
- Defending your thesis in an oral viva voce exam.
These stages vary a little between subjects and universities, but they tend to fall into the same sequence over the three years of a typical full-time PhD.
The first year of a PhD
The beginning of a PhD is all about finding your feet as a researcher and getting a solid grounding in the current scholarship that relates to your topic.
You’ll have initial meetings with your supervisor and discuss a plan of action based on your research proposal.
The first step in this will almost certainly be carrying out your literature review . With the guidance of your supervisor you’ll begin surveying and evaluating existing scholarship. This will help situate your research and ensure your work is original.
Your literature review will provide a logical jumping off point for the beginning of your own research and the gathering of results . This could involve designing and implementing experiments, or getting stuck into a pile of primary sources.
The year may end with an MPhil upgrade . This occurs when PhD students are initially registered for an MPhil degree and then ‘upgraded’ to PhD candidates upon making sufficient progress. You’ll submit material from your literature review, or a draft of your research findings and discuss these with members of your department in an upgrade exam . All being well, you’ll then continue with your research as a PhD student.
PhDs in other countries
The information on the page is based on the UK. Most countries follow a similar format, but there are some differences. In the USA , for example, PhD students complete reading assignments and examinations before beginning their research. You can find out more in our guides to PhD study around the world .
The second year of a PhD
Your second year will probably be when you do most of your core research. The process for this will vary depending on your field, but your main focus will be on gathering results from experiments, archival research, surveys or other means.
As your research develops, so will the thesis (or argument) you base upon it. You may even begin writing up chapters or other pieces that will eventually form part of your dissertation .
You’ll still be having regular meetings with your supervisor. They’ll check your progress, provide feedback on your ideas and probably read any drafts your produce.
The second year is also an important stage for your development as a scholar. You’ll be well versed in current research and have begun to collect some important data or develop insights of your own. But you won’t yet be faced with the demanding and time-intensive task of finalising your dissertation.
So, this part of your PhD is a perfect time to think about presenting your work at academic conferences , gaining teaching experience or perhaps even selecting some material for publication in an academic journal. You can read more about these kinds of activities below.
The third year of a PhD
The third year of a PhD is sometimes referred to as the writing up phase.
Traditionally, this is the final part of your doctorate, during which your main task will be pulling together your results and honing your thesis into a dissertation .
In reality, it’s not always as simple as that.
It’s not uncommon for final year PhD students to still be fine-tuning experiments, collecting results or chasing up a few extra sources. This is particularly likely if you spend part of your second year focussing on professional development.
In fact, some students actually take all or part of a fourth year to finalise their dissertation. Whether you are able to do this will depend on the terms of your enrolment – and perhaps your PhD funding .
Eventually though, you are going to be faced with writing up your thesis and submitting your dissertation.
Your supervisor will be very involved in this process. They’ll read through your final draft and let you know when they think your PhD is ready for submission.
All that’s left then is your final viva voce oral exam. This is a formal discussion and defence of your thesis involving at least one internal and external examiner. It’s normally the only assessment procedure for a PhD. Once you’ve passed, you’ve done it!
Looking for more information about the stages of a PhD?
How do you go about completing a literature review? What's it like to do PhD research? And what actually happens at an MPhil upgrade? You can find out more in our detailed guide to the PhD journey .
Doing a PhD – what's it actually like?
You can think of the ‘stages’ outlined above as the basic ‘roadmap’ for a PhD, but the actual ‘journey’ you’ll take as a research student involves a lot of other sights, a few optional destinations and at least one very important fellow passenger.
Carrying out research
Unsurprisingly, you’ll spend most of your time as a PhD researcher… researching your PhD. But this can involve a surprisingly wide range of activities.
The classic image of a student working away in the lab, or sitting with a pile of books in the library is true some of the time – particularly when you’re monitoring experiments or conducting your literature review.
Your PhD can take you much further afield though. You may find yourself visiting archives or facilities to examine their data or look at rare source materials. You could even have the opportunity to spend an extended period ‘in residence’ at a research centre or other institution beyond your university.
Research is also far from being a solitary activity. You’ll have regular discussions with your supervisor (see below) but you may also work with other students from time to time.
This is particularly likely if you’re part of a larger laboratory or workshop group studying the same broad area. But it’s also common to collaborate with students whose projects are more individual. You might work on shorter projects of joint interest, or be part of teams organising events and presentations.
Many universities also run regular internal presentation and discussion groups – a perfect way to get to know other PhD students in your department and offer feedback on each other’s work in progress.
Working with your supervisor
All PhD projects are completed with the guidance of at least one academic supervisor . They will be your main point of contact and support throughout the PhD.
Your supervisor will be an expert in your general area of research, but they won’t have researched on your exact topic before (if they had, your project wouldn’t be original enough for a PhD).
As such, it’s better to think of your supervisor as a mentor, rather than a teacher.
As a PhD student you’re now an independent and original scholar, pushing the boundaries of your field beyond what is currently known (and taught) about it. You’re doing all of this for the first time, of course. But your supervisor isn’t.
They’ll know what’s involved in managing an advanced research project over three years (or more). They’ll know how best to succeed, but they’ll also know what can go wrong and how to spot the warning signs before it does.
Perhaps most importantly, they’ll be someone with the time and expertise to listen to your ideas and help provide feedback and encouragement as you develop your thesis.
Exact supervision arrangements vary between universities and between projects:
- In Science and Technology projects it’s common for a supervisor to be the lead investigator on a wider research project, with responsibility for a laboratory or workshop that includes several PhD students and other researchers.
- In Arts and Humanities subjects, a supervisor’s research is more separate from their students’. They may supervise more than one PhD at a time, but each project is essentially separate.
It’s also becoming increasingly common for PhD students to have two (or more) supervisors. The first is usually responsible for guiding your academic research whilst the second is more concerned with the administration of your PhD – ensuring you complete any necessary training and stay on track with your project’s timetable.
However you’re supervised, you’ll have regular meetings to discuss work and check your progress. Your supervisor will also provide feedback on work during your PhD and will play an important role as you near completion: reading your final dissertation draft, helping you select an external examiner and (hopefully) taking you out for a celebratory drink afterwards!
Professional development, networking and communication
Traditionally, the PhD has been viewed as a training process, preparing students for careers in academic research.
As such, it often includes opportunities to pick up additional skills and experiences that are an important part of a scholarly CV. Academics don’t just do research after all. They also teach students, administrate departments – and supervise PhDs.
The modern PhD is also viewed as a more flexible qualification. Not all doctoral graduates end up working in higher education. Many follow alternative careers that are either related to their subject of specialism or draw upon the advanced research skills their PhD has developed.
PhD programmes have begun to reflect this. Many now emphasise transferrable skills or include specific training units designed to help students communicate and apply their research beyond the university.
What all of this means is that very few PhD experiences are just about researching and writing up a thesis.
The likelihood is that you’ll also do some (or all) of the following during your PhD:
The work is usually paid and is increasingly accompanied by formal training and evaluation.
Conference presentation
As a PhD student you’ll be at the cutting edge of your field, doing original research and producing new results. This means that your work will be interest to other scholars and that your results could be worth presenting at academic conferences .
Doing this is very worthwhile, whatever your career plans. You’ll develop transferrable skills in public speaking and presenting, gain feedback on your results and begin to be recognised as an expert in your area.
Conferences are also great places to network with other students and academics.
Publication
As well as presenting your research, you may also have the opportunity to publish work in academic journals, books, or other media. This can be a challenging process.
Your work will be judged according to the same high standards as any other scholar’s and will normally go through extensive peer review processes. But it’s also highly rewarding. Seeing your work ‘in print’ is an incredible validation of your PhD research and a definite boost to your academic CV.
Public engagement and communication
Academic work may be associated with the myth of the ‘ivory tower’ – an insular community of experts focussing on obscure topics of little interest outside the university. But this is far from the case. More and more emphasis is being placed on the ‘impact’ of research and its wider benefits to the public – with funding decisions being made accordingly.
Thankfully, there are plenty of opportunities to try your hand at public engagement as a PhD student. Universities are often involved in local events and initiatives to communicate the benefits of their research, ranging from workshops in local schools to public lectures and presentations.
Some PhD programmes include structured training in order to help students with activities such as the above. Your supervisor may also be able to help by identifying suitable conferences and public engagement opportunities, or by involving you in appropriate university events and public engagement initiatives.
These experiences will be an important part of your development as a researchers - and will enhance the value of your PhD regardless of your career plans.
What is a PhD for – and who should study one?
So, you know what a PhD actually is, what’s involved in completing one and what you might get up to whilst you do. That just leaves one final question: should you do a PhD?
Unfortunately, it’s not a question we can answer for you.
A PhD is difficult and uniquely challenging. It requires at least three years of hard work and dedication after you’ve already completed an undergraduate degree (and probably a Masters degree too).
You’ll need to support yourself during those years and, whilst you will be building up an impressive set of skills, you won’t be directly progressing in a career.
But a PhD is also immensely rewarding. It’s your chance to make a genuine contribution to the sum of human knowledge and produce work that other researchers can (and will) build on in future. However obscure your topic feels, there’s really no such thing as a useless PhD.
A PhD is also something to be incredibly proud of. A proportionately tiny number of people go on to do academic work at this level. Whatever you end up doing after your doctorate you’ll have an impressive qualification – and a title to match. What’s more, non-academic careers and professions are increasingly recognising the unique skills and experience a PhD brings.
Other PhDs - do degree titles matter?
The PhD is the oldest and most common form of higher research degree, but a few alternatives are available. Some, such as the DPhil are essentially identical to a PhD. Others, such as the Professional Doctorate or DBA are slightly different. You can find out more in our guide to types of PhD .
Is a PhD for me?
There’s more advice on the value of a PhD – and good reasons for studying one – elsewhere in this section. But the following are some quick tips if you’re just beginning to consider a PhD.
Speak to your lecturers / tutors
The best people to ask about PhD study are people who’ve earned one. Ask staff at your current or previous university about their experience of doctoral research – what they enjoyed, what they didn’t and what their tips might be.
If you’re considering a PhD for an academic career, ask about that too. Are job prospects good in your field? And what’s it really like to work at a university?
Speak to current PhD students
Want to know what it’s like studying a PhD right now? Or what it’s like doing research at a particular university? Ask someone who knows.
Current PhD students were just like you a year or two ago and most will be happy to answer questions.
If you can’t get in touch with any students ‘face to face’, pop over to the Postgraduate Forum – you’ll find plenty of students there who are happy to chat about postgraduate research.
Take a look at advertised projects and programmes
This may seem like a strange suggestion. After all, you’re only going to study one PhD, so what’s the point of reading about lots of others?
Well, looking at the details of different PhD projects is a great way to get a general sense of what PhD research is like. You’ll see what different PhDs tend to have in common and what kinds of unique opportunity might be available to you.
And, with thousands of PhDs in our database , you’re already in a great place to start.

Read our other advice articles
Finally, you can also check out some of the other advice on the FindAPhD website. We’ve looked at some good (and bad) reasons for studying a PhD as well as the value of a doctorate to different career paths.
More generally, you can read our in-depth look at a typical PhD journey , or find out more about specific aspects of doctoral study such as working with a supervisor or writing your dissertation .
We add new articles all the time – the best way to stay up to date is by signing up for our free PhD opportunity newsletter .
Ready to find your PhD?
Head on over to our PhD search listings to learn what opportunities are on offer within your discipline.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

What happens during a typical PhD, and when? We've summarised the main milestones of a doctoral research journey.

The PhD thesis is the most important part of a doctoral degree. This page will introduce you to what you need to know about the PhD dissertation.

This page will give you an idea of what to expect from your routine as a PhD student, explaining how your daily life will look at you progress through a doctoral degree.

PhD fees can vary based on subject, university and location. Use our guide to find out the PhD fees in the UK and other destinations, as well as doctoral living costs.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .

What is a PhD?
- Types of Doctorates
- A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest globally recognized postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award.
- PhDs are awarded to candidates who undertake original and extensive research in a particular field of study.
- Full time PhD programmes typically last three to four years, whilst part time PhD programmes typically last six to seven years.
- A PhD can lead to an academia teaching role or a career in research. A PhD can also equip you with skills suitable for a wide range of jobs unrelated to your research topic or academia.
Definition of a PhD – A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD , Ph.D or a DPhil ) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible.
PhDs differ from undergraduate and master’s degrees in that PhDs are entirely research-based rather than involving taught modules (although doctoral training centres (DTCs) offer programmes that start with a year of lecture-based teaching to help develop your research skills prior to starting your project).
In most English-speaking countries, those that complete a PhD use the title “Doctor” (typically abbreviated to Dr) in front of their names and are referred to as such within academic and/or research settings. Those that work in fields outside of academia may decide not to use the formal doctor title but use post-nominal letters (e.g. John Smith PhD); it’s unusual though for someone to use both the Doctor title and post-nominal letters in their name.
PhD vs Doctorate
A PhD and a professional doctorate are both research-based terminal degrees.
However, where a PhD focuses on original research mostly around theoretical concepts, a professional doctorate focuses on examining existing knowledge to solve real-life, practical problems.
While there is much crossover between the two, a PhD is generally better suited for an individual to wants to advance the knowledge and understanding in their field, and a professional doctorate degree is better suited to a working professional who wants to better be able to apply knowledge and understanding to their field.
What Are the Entry Requirements for a PhD?
To be accepted on to a PhD programme, students usually need to hold at least a high ( 2:1 and above ) undergraduate degree that is related to the field of research that they want to pursue. A PhD candidate may also be expected to hold a Master’s degree , however, this does not mean you must have one, as it is still possible to enrol into a PhD without a Master’s .
Self-funded courses may sometimes be more relaxed in relation to entry requirements . It may be possible to be accepted onto a self-funded PhD programme with lower grades, though these students typically demonstrate their suitability for the role through professional work experience.
Whilst a distance learning project is possible , most PhD candidates will carry out their research over at least three years based at their university, with regular contact with two academic supervisors (primary and secondary). This is particularly the case for lab-based projects, however, some PhD projects require spending time on-site away from university (e.g. at a specialist research lab or at a collaborating institution abroad).
How Long Does a PhD Take?
Typically, full-time PhDs last 3-4 years and part-time PhDs last 6-7 years. However, at the discretion of the university, the thesis writing-up period can be extended by up to four years.
Although most doctoral programmes start in September or October, they are generally much more flexible than taught-courses and can start at any time of the year.
How Much Does a PhD Cost?
Tuition fees for UK and EU students vary between £3,000 and £6,000 per year, with the average tuition fee of £4,712 per year for 2023/24 programmes.
Tuition fees increase considerably for international students, varying between £16,000 to £25,000 per year, with an average tuition fee of £19,600 per year .
Nonetheless, most students will secure PhD funding in the form of studentships, scholarships and bursaries to help pay for these fees. These funding opportunities can either be partial, which cover tuition fees only, or full, which cover both tuition fees and living expenses.
UK national students can also apply for Doctoral Loans from Student Finance England if they are unable to secure funding.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Does a PhD Involve?
To be awarded a PhD, a doctoral student is required to produce a substantial body of work that adds new knowledge to their chosen field.
A PhD programme will typically involve four key stages:
Stage 1: Literature Review
The first year of a PhD involves attending regular meetings with your supervisors and carrying out a search on previously published work in your subject area. This search will be used to produce a literature review which should set the context of the project by explaining the foundation of what is currently known within the field of research, what recent developments have occurred, and where the gaps in knowledge are. In most cases, this will be an extension of your research proposal should you have produced one as part of your application. The literature review should conclude by outlining the overarching aims and objectives of the research project. This stage of setting achievable goals which are original and contribute to the field of research is an essential first step in a successful PhD.
The supervisor is the main point of contact through the duration of a PhD – but remember: they are there to mentor, not to teach, or do it for you . It will be your responsibility to plan, execute and monitor your own work as well as to identify gaps in your own knowledge and address them.
Stage 2: Research
The second year (and prehapse some of your third year) is when you work on your research. Having identified novel research questions from your review of the literature, this is where you collect your data to help answer these questions. How you do this will depend on the nature of your doctoral research: for example, you may design and run experiments in a lab alongside other PhD students or visit excavation sites in remote regions of the world. You should check in regularly with your supervisors to update them and run any ideas or issues past them.
Have the structure and chapters of your thesis in mind as you develop and tackle your research questions. Working with a view of publishing your work will be very valuable later on.
Stage 3: Write up of Thesis
The next key stage of a PhD is writing a doctoral thesis , which typically takes from anywhere between three months to one year. A thesis is a substantial body of work that describes the work and outcomes of the research over the previous two to three years. It should tell a detailed story of the PhD project – focusing on:
- The motivations for the research questions identified from the literature review.
- The methodologies used, results obtained, and a comprehensive analysis and discussion of the findings.
- A detailed discussion of the key findings with an emphasis on the original contributions made to your field of research and how this has been impactful.
There is no universal rule for the length of a PhD thesis, but general guidelines set the word count between 80,000 to 100,000 words.
For your thesis to be successful, it needs to adequately defend your argument and provide a unique or increased insight into your field that was not previously available.
Stage 4: Attending the Viva
A viva voce , most commonly referred to as just a ‘ viva ‘, is an interview-style examination where the PhD student is required to engage in a critical appraisal of their work and defend their thesis against at least two examiners. The examiners will ask questions to check the PhD student has an in-depth understanding of the ideas and theories proposed in their thesis, and whether they have developed the research skills that would be expected of them.
The viva is one of the final steps in achieving a PhD, and typically lasts at least two hours, but this duration can vary depending on the examiners, the university and the PhD project itself.
Once you have done the viva – you’re on the home stretch. You will typically be asked to make some amendments to your thesis based on the examiner’s feedback. You are then ready to submit your final thesis for either:
- PhD – If you pass the requirements you will be awarded a PhD degree (most common outcome),
- MPhil – If you failed to meet requirements for a PhD, you may be downgraded to an MPhil degree (uncommon outcome),
- Fail – No award is given, typically for cases of plagiarism (extremely uncommon outcome).
What Is It Like to Undertake a PhD?
We’re often asked what it is like to undertake a PhD study. Unfortunately, this isn’t a simple answer to this question as every research project is different.
To help give insight into the life of a PhD student, we’ve interviewed PhD students at various stages of their programmes and put together a series of PhD Student Interviews . Check out the link to find out what a PhD is like and what advice they have to offer you.
What Are the Benefits of A PhD?
A PhD is the highest globally recognised postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award. The degree, which is awarded to candidates who demonstrate original and independent research in a particular field of study, is not only invaluable in itself, but sets you up with invaluable skills and traits.
Career Opportunities
First, a PhD prepares you for a career in academia if you wish to continue in this area. This takes form as a career in the Higher Education sector, typically as a lecturer working their way to becoming a professor leading research on the subject you’ve studied and trained in.
Second, a PhD also enables the opportunity for landing a job in a research & development role outside of the academic environment. Examples of this include laboratory work for a private or third sector company, a governmental role and research for commercial and industrial applications.
Transferable Skills
Finally, in possessing a PhD degree, you can show to employers that you have vital skills that make you an asset to any company. Three examples of the transferable skills that you gain through a PhD are effective communication, time management, and report writing.
- Communication – presenting your work in written and oral forms using journal papers and podium presentations, shows your ability to share complex ideas effectively and to those with less background knowledge than you. Communication is key in the professional environment, regardless of the job.
- Time management – The ability to prioritise and organise tasks is a tremendous asset in the professional industry. A PhD holder can use their qualification to demonstrate that they are able to manage their time, arrange and follow a plan, and stick to deadlines.
- Report writing – Condensing three years of work into a thesis demonstrates your ability to filter through massive amounts of information, identify the key points, and get these points across to the reader. The ability to ‘cut out the waffle’ or ‘get to the point’ is a huge asset in the professional industry.
Aside from the above, you also get to refer to yourself as a Doctor and add fancy initials after your name!
What Can I Do After a PhD?
One of the most desirable postdoctoral fields is working within independent Research and Development (R&D) labs and new emerging companies. Both industries, especially R&D labs, have dedicated groups of PhD graduates who lead research activities, design new products and take part in crucial strategic meetings. Not only is this a stimulating line of work, but the average salaries in R&D labs and emerging start-ups are lucrative. In comparison, an undergraduate with five years of experience within their given field will, on average, likely earn less than a new PhD graduate taking on a R&D position.
It’s a common misunderstanding that PhDs only opens the door for an academic career such as university lecturers and training providers. Although obtaining a PhD opens these doors, the opportunities extend far beyond educational roles. In fact, recent data from the UK’s Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) indicates only 23% of PhD graduates take a position in educational roles . This low percentage is primarily because PhD graduates have a wide range of skills that make them suitable for a broad spectrum of roles. This is being seen first hand by the increasing number of PhD graduates who are entering alternative roles such as research, writing, law and investment banking.
How Do I Find a PhD?
We appreciate that finding a PhD programme to undertake can be a relatively daunting process. According to Higher Education Student Statistics , over 22,000 PhDs were awarded in 2016/17 within the United Kingdom alone. Clearly there are a huge number of PhD programmes available. This can sometimes be confusing for prospective doctorates, particularly when different programmes are advertised in different places. Often, it is difficult to know where to look or where to even start. We’ve put together a list of useful sources to find the latest PhD programmes:
- A great place to start is with our comprehensive and up-to-date database of available PhD positions .
- Assuming you are still at university, speak to an existing PhD supervisor within your department.
- Attend as many postgraduate open days as you can. Whilst there, speak to current PhD students and career advisors to get an awareness of what PhDs are on offer.
- Visit the postgraduate section of university websites and the PhD Research Council section of the UKRI website.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Doctoral Degrees
A doctoral degree requires the satisfactory completion of an approved program of advanced study and original research of high quality..
Please note that the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) and Doctor of Science (ScD) degrees are awarded interchangeably by all departments in the School of Engineering and the School of Science, except in the fields of biology, cognitive science, neuroscience, medical engineering, and medical physics. This means that, excepting the departments outlined above, the coursework and expectations to earn a Doctor of Philosophy and for a Doctor of Science degree from these schools are generally the same. Doctoral students may choose which degree they wish to complete.
Applicants interested in graduate education should apply to the department or graduate program conducting research in the area of interest. Some departments require a doctoral candidate to take a “minor” program outside of the student’s principal field of study; if you wish to apply to one of these departments, please consider additional fields you may like to pursue.
Below is a list of programs and departments that offer doctoral-level degrees.
| Program | Application Opens | Application Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| September 1 | December 1 | |
| September 15 | January 7 | |
| September 15 | December 15 | |
| October 1 | December 1 | |
| September 1 | December 1 | |
| September 5 | November 13 | |
| September 15 | December 1 | |
| September 15 | December 1 | |
| October 1 | December 1 | |
| September 15 | December 1 | |
| September 1 | December 1 | |
| September 15 | December 15 | |
| September 16 | December 15 | |
| August 1 | December 1 | |
| September 15 | December 10 | |
| September 15 | December 15 | |
| September 15 | December 15 | |
| September 1 | December 1 | |
| September 14 | December 15 | |
| September 15 | December 15 | |
| October 1 | December 1 | |
| September | December 1 | |
| | October 1 | December 15 |
| September 15 | December 15 | |
| September 15 | December 15 | |
| September 15 | January 2 | |
| September 15 | December 15 | |
| October 9 | December 15 | |
| October 1 | January 15 | |
| September 5 | December 15 |
This site uses cookies to give you the best possible experience. By browsing our website, you agree to our use of cookies.
If you require further information, please visit the Privacy Policy page.
- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer
- Saved Articles
- Newsletters
Should All Ph.D.'s Be Called 'Doctor'? Female Academics Say Yes
Please try again
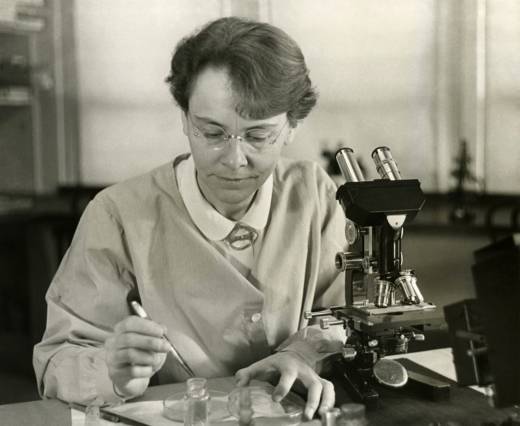

On the first day of class, Debbie Gale Mitchell, a chemistry professor at the University of Denver, introduced herself to her students, telling them about her Ph.D. and her research. She told her students they could call her either “Dr. Mitchell” or “Debbie.” A male colleague had told her that he went by his first name and that students were friendlier as a result, so Mitchell decided to try it. Many students chose to call her “Debbie.”
Then one day a student asked if she thought she’d ever get a Ph.D.
“I discovered that for me, the use of my title is VITAL to remind students that I am qualified to be their professor,” Mitchell wrote on Twitter.
Mitchell’s story was just one among hundreds shared last summer on social media calling attention to the way gender affects how professionals are addressed, especially those who hold a doctorate.
The discussion comes at a time when research studies into gender bias are increasingly confirming that how a person is addressed is linked to perceptions of their status.
The Twitter conversation branched from multiple roots. On June 7, Eric Kelderman, reporter for the Chronicle of Higher Education, sent out a critical tweet of a female academic who responded to his media inquiry by suggesting that he should have used “Professor” or “Doctor” (the tweet has since been deleted). The next day, a doctor from the U.K., David Naumann, criticized doctors, medical or otherwise, who use their title in a nonprofessional setting. And a few days later the Globe and Mail, a Canadian newspaper, announced revised style guidelines wherein only medical doctors would be referred to using “Dr.”, a convention that is already used most of the time by the Associated Press and news outlets that follow AP Style (including KQED). What followed was an explosion of opinions and experiences revolving around titles, expertise, and gender and racial bias.
Many Ph.D. holders are fine with reserving the title for medical doctors in common parlance, viewing insistence on the title as arrogant and elitist, and do not use their titles even in a scholarly setting. But for women and people of color, an academic title can be a tool to remind others of their expertise in a world that often undermines it.
Some Ph.D. holders who insist on titles say that they actually prefer their first names. But given the discrepancy in usage, some women feel they must use and defend their titles, especially where the alternative is a gendered title like “Ms.”, “Mrs.”, or “Miss”. Fern Riddell, a Ph.D.-holding historian, wrote:
My title is Dr Fern Riddell, not Ms or Miss Riddell. I have it because I am an expert, and my life and career consist of being that expert in as many different ways as possible. I worked hard to earned my authority, and I will not give it up to anyone. — Dr Fern Riddell (@FernRiddell) June 13, 2018
Following backlash to the tweet, which described her as “arrogant” and “immodest,” Riddell coined the hashtag #ImmodestWomen, encouraging hundreds of women to change their Twitter handles to include “Dr.” or share experiences of bias. Riddell later wrote about the rationale behind the hashtag, saying that “we define women by their ability to be well behaved.” #ImmodestWomen was “retaliation.”
The tweets show “Dr.” is preferred by many women because it is both unrelated to marital status and gender-neutral, unlike “Mrs.”, “Miss”, or “Ms”. Several tweets described situations where a woman’s husband or colleague was referred to as “Dr.” (whether or not he actually had a doctorate) while she got “Mrs.” or a first name.
My pastor has her PhD. She was interviewed by a local newspaper along with another male member of clergy, NOT a PhD.. HE was referred to as “Reverend Smith”, SHE was called “Paula”. Seriously. — Head To Toe Organizers (@HTTOrganizers) June 11, 2018
In other anecdotes, female doctors (M.D. and Ph.D. alike) were met with utter confusion when they answered the phone to a caller looking for “Dr.”, or presented an airline ticket bearing the title. Even in 2018, with women making up 34 percent of active physicians and more than half of medical school matriculants and doctorate recipients , many people assume that “Dr.” refers to a man.
Bias in forms of address and use of titles is not limited to gender, many participants in the Twitter discussion pointed out. People of color with doctorates are also often not given the courtesy of their title, which echoes a long history of racially biased uses of titles. History professor Charles W. McKinney wrote:
Wanna know why my students will always call me “Dr. McKinney”? Because one day in 1980 I went to the store with my 75 yr old Grandmother Melida Thomas. Clerk greeted two 20 yr old, white women in front of us with “Mrs” and said “Well, hello Melida” to my Grandmother. That’s why. — Charles W. McKinney (@kmt188) June 10, 2018
The bias reflected in these stories is backed up by data. Last year, a study from the Mayo Clinic found that female doctors were introduced by their first names, rather than a professional title, much more often than male doctors. And on June 25, researchers from Cornell University published results showing that female professionals are half as likely as their male colleagues to be referred to by their last names, a practice that is associated in the study with lower status.
“The way that we speak about others influences and is influenced by the way that we think about them,” wrote Stav Atir and Melissa J. Ferguson, authors of the recent paper.
Atir and Ferguson described eight different studies, covering forms of address in professor evaluations, talk radio and under experimental conditions. Across the board, female professionals were less likely to be referred to solely by their last name. They even found that fictional researchers who were described with last name only were perceived as better known, more eminent, higher status, and more deserving of awards.
Thanks for signing up for the newsletter.
The researchers proposed several explanations for their results. It may be more culturally common to refer to men by their last names because they are thought to be more permanent, since women may change their last names when they marry. Alternatively, it could be that speakers use first names to identify a subject’s gender, and this is more common for women in male-dominated professions, where male is the assumed default. This type of bias could even result from attempts to highlight women’s participation by identifying their gender using first names.
“The consequences may be ironic,” wrote Atir and Ferguson, “leading to lower judgments of eminence, status, and deservingness.”
As Mitchell, the chemistry professor from the University of Denver, and other academics related on Twitter, one way of fighting this type of bias is to insist upon the title “Dr.”
But other Ph.D. holders question whether insisting on titles is the best strategy. Meena Kandasamy, a poet and writer with a Ph.D. in sociolinguistics, rarely uses her title and did not change her Twitter handle. She questioned the practice of elevating those who earned doctorates over those who have not had the opportunity to do so:
For every one of us who has managed to float up and breathe from that cesspool with a doctorate degree above our heads–we must remember our sisters sent home, their dreams crushed, their futures messed up, academia behaving like one petty thug-gang to have the backs of a few men — meena kandasamy (@meenakandasamy) June 14, 2018
Critics argue that titles do not necessarily reflect how hard one has worked or even level of expertise, and that the most equal solution is fewer titles, not more. But supporters say that claiming the titles is the best choice under the present circumstances. Elissa Harbert, a musicologist, wrote:
I support #ImmodestWomen . As a PhD and professor, I currently use Dr. as my title professionally. My relationships with students improved when I switched to Dr., even though in a perfect world I’d use my first name. It’s not a perfect world. — Dr. Elissa Harbert (@KyrieElissa) June 14, 2018
In some instances, women are less likely to exhibit bias in form of address. The Mayo Clinic study found female medical doctors introduced both men and women with a title more than 95 percent of the time. Men introduced their female colleagues with a title 49 percent of time, compared with 72 percent of the time for a male colleague. In the Atir and Ferguson study, male speakers on talk radio referred to women by last name less than half as often as they did for men, while female speakers did not have such a strong contrast. In other research on gender bias in academia and medicine, women were just as likely to treat men and women differently. As research epidemiologist Chelsea Polis related, implicit bias can extend to usage of titles for speakers and writers of any gender:
I was once quoted in a story where all men w/PhDs were “Dr. X” & all women w/PhDs were untitled. Writer (a woman) was mortified when I pointed it out. Claiming our titles publicly raises consciousness than women can/do have these credentials. I want young girls/women to see that. — Chelsea Polis, PhD (@cbpolis) June 10, 2018
While the evidence points to persistent bias in professional forms of address, the solution is not so clear. Highlighting women with doctorates, medical or otherwise, may provide an important reminder that woman are now earning nearly half of medical and research-based doctoral degrees. But bias in use of doctoral titles is just one example of the larger issue of gender bias, as Atir and Ferguson’s study demonstrates.
“We find evidence of a gender bias in the way that we speak about professionals in a variety of domains,” wrote Atir and Ferguson. Addressing the problem may require attention to bias in all arenas, from the classroom to the boardroom.
To learn more about how we use your information, please read our privacy policy.
Amy R. Goetz, PhD
- Pediatric Psychology
Program Director, Acute Care Psychology
Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine
Phone: 832-822-1854
Languages: English
Departments: Pediatric Psychology
Office locations:
Get to know amy r. goetz, phd.
Dr. Goetz is an Assistant Professor of Pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine and a licensed clinical psychologist at Texas Children’s Hospital. She provides assessment and treatment for children and adolescents in acute patient care settings such as the Emergency Center, Intensive Outpatient Program and Bridge Clinic. In addition, Dr. Goetz engages in program development and quality improvement efforts in her role as the Program Director of Acute Care Psychology. She works with interdisciplinary teams to develop, implement and evaluate programs of care. She has a passion for improving the availability and accessibility of mental health services for children and adolescents.
Clinical Interests
Behavioral intervention, suicide prevention, early childhood mental health
| School | Education | Degree | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USDA Children's Nutrition Research Center/Baylor College of Medicine | Post-doctoral Fellowship | 2020 | |
| Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center | Post-doctoral Fellowship | 2019 | |
| University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee | PhD | Doctor of Philosophy in Psychology | 2017 |
| Baylor College of Medicine | Internship | Pediatric/Child-Clinical Psychology | 2017 |
| University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee | Masters | Master of Science in Psychology | 2013 |
| Florida State University | Bachelors | Bachelor of Science in Psychology | 2011 |
* Texas Children’s Hospital physicians’ licenses and credentials are reviewed prior to practicing at any of our facilities. Sections titled From the Doctor, Professional Organizations and Publications were provided by the physician’s office and were not verified by Texas Children’s Hospital.
Research interests
Clinical program development, suicide risk assessment and management
Oblath, R., Twohy, E., Higdon, C., Duncan, A., Folk, J.B., Schiel, M.A., Grewal, S., Hawks, J.L., Martinez, W., Coble, K., Edwards, S., Goetz, A. , Remtekkar, U., Kulkwarni, C.A., Khan, S., Doan, B.T., Nallpula, K., Fornari, V.M., Fortuna, L.R., & Myers, K. The provision and utilization of telehealth within academic mental health clinics in North America during the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAACAP Open , 2023, 1(3), 218-229
Goetz, A.R. , Jindal, I., Moreno, J.P., Puyau, M., Adolph, A., Butte, N., & Bacha, F. The roles of sleep and eating patterns in adiposity gain among preschool-aged children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition , 2022, 116(5), 1334-1342
Goetz, A.R. , Rybak, T.M., Peugh, J.K., & Stark, L.J. Early life determinants of excess weight in children born heavy. Pediatric Obesity, 2020, 15(2)

Can a PhD be called Doctor? Doctoral Degree Titles
If someone holds a PhD, they are able to call themselves Doctor. The doctor title is very prestigious and often projects expertise and respect in those who decide to use it.
A person with a PhD can be called Dr. However, many people with PhD degrees choose not to use their official titles unless they are communicating in an official capacity or are working in a professional role where they use their PhD.
I reserve the use my PhD title when I am giving a talk as it provides immediate credibility whereas, I do not often use my doctor title in many other instances.
When I first got my PhD I used my doctor title a lot more than I do now. I guess, the novelty has worn off and I have decided that it is not something that defines who I am as a person and, therefore, I would only use it in an official capacity.
Should PhDs use the title “doctor” after their doctorate?
It is a personal choice for a PhD holder to use the title of “doctor”.
In many countries, it is common practice to use the title when referring to someone with a doctoral degree.
The title of doctor holds a significant level of prestige, and it generally signifies a high level of education and expertise in a particular field. Which is why it is important to use it in an official capacity.
Those who have earned a PhD have spent many years researching, writing and defending their work and have earned the right to use the title if so desired.
The title of doctor can also be used by medical professionals, and it is important to clarify the intended meaning when using the title to avoid confusion.
The decision to use the title of doctor is a personal one that should be made with an understanding of its significance and potential implications.
Even though the original use of the doctor title was for scholars, nowadays there are several different professional qualifications that can use the doctor title.
There are many honorific doctor titles, including those found in the table below.
| Medical doctors | Pharmacists | Dentists |
| Veterinary surgeons | Lawyers (Doctor of Juris) | Podiatrists |
| Naturopath’s | Chiropractors |
The use of the doctor term for many healthcare-related qualifications can cause a fair bit of confusion about what qualification the person has achieved.
If you have any doubt about what degree a person holds look at the letters after their name.
If you want to know more about the doctor title check out my other article:
- How to use the PhD title and all the little doctorate “rules”
- Is a PhD a Doctor? [The full guide]
When can a PhD student be called doctor? After their dissertation?
A PhD student can be called doctor after successfully completing all the requirements of their program, including passing their dissertation defense.
More specifically, many universities only allow you to use the doctoral title after confirmation of your degree.
The University of Adelaide says that you can use it from your conferral date:
Students can be conferred on one of five dates during the year and for PhD students the conferral date will be the first available following the completion of all the academic requirements of your degree, including final thesis lodgement and the disbursement of any outstanding financial obligations to the University.
Personally, I felt comfortable using the doctor title as soon as I receive my notification letter from the University referring to me as Dr Stapleton. It was from this moment that I started using the doctor title.
There would be nothing wrong with someone using the doctor title after they have successfully defended their PhD – it just comes down to a matter of personal preference.
The title “Doctor” can still be used informally for those who hold other doctoral degrees such as a JD (Doctor of Law) or an EdD (Doctor of Education).
A PhD student can only be referred as a “Doctor” upon the completion of their doctoral program and after receiving their degree.
Why is PhD called doctor of philosophy?
A Ph.D. is called a Doctor of Philosophy because historically, philosophy was considered the foundation of all knowledge.

The word “philosophy” itself means the love of wisdom, and the pursuit of truth through reason and logic.
In medieval Europe, philosophy encompassed all forms of intellectual inquiry, including:
- mathematics,
- and history.
As universities developed and specialized in particular disciplines, the title of Doctor of Philosophy became associated with the highest level of academic achievement in any field.
This means that a Ph.D. is not limited to the study of philosophy but refers to any individual who has demonstrated the ability to conduct original research in their chosen field and make a significant contribution to advancing knowledge.
A Ph.D. signifies not only mastery of a specific subject but also the ability to think deeply and critically about complex problems. There are now many professional doctorates that include the doctor titleIn recognition of the hard work and deep thinking required to complete.
Wrapping up
Yes, PhD holders can be called Doctor.
Once you’ve completed a PhD and been conferred by your university and institution you can officially use the Dr title before your name and the PhD tag after your name.
Many doctoral degree holders only use their academic title in official settings such as academia and official duties.
Even though I was very excited about receiving my doctor title, after a couple of years the novelty wears off and I only use my official titles in the same way that someone would want to include Mr, Mrs, or Ms.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


Listen Live

Special Coverage: Democratic National Convention
Scott Detrow hosts NPR’s coverage with NPR National Political and White House Correspondents present during all days of the convention.
- Health Care
- Higher Education

Who gets to be called ‘doctor’?
Go to med school, earn an m.d. and the “dr.” honorific gets tacked on to your last name. some women — and ph.d.s — say they get the courtesy title, and respect, less often..

We call physicians "doctor." Should we do the same for people with PhDs? (Credit: Bigstock)
This story is from The Pulse , a weekly health and science podcast.
Subscribe on Apple Podcasts , Stitcher or wherever you get your podcasts.
Molecular biologist Adam Ruben has a Ph.D.
There was one time when he made a conscious choice to refer to himself as Dr. Ruben — when he emailed an airline to complain about a messed up flight.
“We had to spend a night in some city and I was trying to get a refund for our hotel bill, so I signed the email Dr. Ruben,” he said. “And I know that’s kind of an icky thing to do but I have heard that you get better service when you use the term doctor.”
It kind of worked: He got his refund — after three months.
“It’s not outright wrong and the world should forgive me,” he said.
Ruben has been thinking about the doctor honorific for a while. He polled his friends and acquaintances with Ph.D.s on Facebook and Twitter about whether or not they call themselves doctor.
Some said they’ve earned it. Others said it seems a little pretentious.
“A surprising number of people all had the same concern about using the term doctor: if they were going to be on an airplane when somebody needs a doctor,” Ruben said.
This sort of happened to Ruben several years ago, but when he was on the ground.
Besides being a biologist, he’s also a writer and comedian. He was at a Story Collider storytelling event, performing for an audience of mostly graduate students.
“And somebody actually had a medical emergency in the middle of the show. He fainted and needed an ambulance,” Ruben recalled.
As he described it at the time, someone asked if there was a doctor in the room and about 200 people with Ph.D.s kind of looked around at each other frantically.
Some EMTs helped the guy. He was okay in the end and the show went on .
Subscribe to The Pulse
Stories about the people and places at the heart of health and science.
After checking in on social media, Ruben wrote about his informal poll for the journal Science. He heard from female engineers with Ph.D.s who said they are under-represented in their field, and feel like they need to put doctor in front of their names to get the same respect that male engineers get.
Epidemiologist Beth Linas also earned a Ph.D., and she wants media outlets to refer to people with Ph.D.s as doctor, especially if we’re interviewing them about their area of expertise.
“Someone comes up [to me] on the street and says hello to me, they can address me as Beth, but if I’m being called upon for my background in infectious disease, epidemiology or digital health which is the other area that I study, I think I should be recognized as Dr. Beth Linas.”
Linas has been thinking about this issue and wrote a commentary about the congressional hearings with Supreme Court nominee Brett Kavanaugh and research psychologist Christine Blasey Ford, who accused Kavanaugh of sexually assaulting her when they were in high school.
“There was a lot of chatter online and on Twitter about how in written media, she wasn’t being addressed as Doctor Ford, I started noticing it in other publications and other outlets,” said Linas.
Some NPR listeners complained about the “insidious bias” of the radio network calling Kavanaugh “Judge Kavanaugh” but not calling Ford “Dr. Ford.”
The NPR ombudsman explained that like many media outlets, NPR follows the Associated Press stylebook, which says if someone practices medicine, NPR calls them doctor. If it’s someone with a Ph.D., it’s up to the individual media outlet.
On the radio, we don’t have a lot of time, and every word counts. Saying someone is a doctor or saying they have a Ph.D. can be a little vague. Ultimately that doesn’t give the listener much information. So for clear and efficient communication, our policy at “The Pulse” is to introduce someone as an epidemiologist, or pediatrician — being specific about a person’s expertise when we can.
Linas said her concern comes from an issue of representation.
“There are a lot of women, and particularly women of color that really struggle to make their way in science and stay in science, and we face a lot of obstacles, and I think it’s important for women also to be recognized.”
There’s a study that backs her up: researchers found that male doctors introduce their male colleagues as “Dr.” around 70 percent of the time, but introduce their female colleagues as doctor a little less than half the time.
Linas says if media outlets refer to people with Ph.D.s as doctor, especially when we’re interviewing them about their area of expertise, then it shouldn’t be that hard to tell who is the kind of doctor who can help you when someone needs an ambulance — and who’s best suited to give you statistics on the next flu outbreak.
WHYY is your source for fact-based, in-depth journalism and information. As a nonprofit organization, we rely on financial support from readers like you. Please give today.
Brought to you by The Pulse

Hosted by Maiken Scott
Subscribe for free
More segments from what we call things and why it matters, for some people who stutter, fluent speech is overrated, what makes addiction a disease, should we call little girls beautiful, you may also like.

Human remains discovered at Philly construction site 8 years ago have been reburied, but issues still persist
Workers in Philly's Old City hit upon a historic cemetery with hundreds of people. It took years to study, identify and rebury them.

Advocates cheer new standards that could save horseshoe crabs from bloodletting
Up to 1 million horseshoe crabs in the U.S. are harvested for biomedical purposes. A synthetic alternative could mean less harvesting of the “living fossils.”
3 weeks ago

Three Pa. med schools tapped for medical marijuana research programs
The Health Department says it plans to approve five more partnerships between marijuana growers and research centers this summer.
5 years ago
About Alan Yu

Want a digest of WHYY’s programs, events & stories? Sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Together we can reach 100% of WHYY’s fiscal year goal
- Top Colleges
- Top Courses
- Entrance Exams
- Admission 2024
- Study Abroad
- Study in Canada
- Study in UK
- Study in USA
- Study in Australia
- Study in Germany
- IELTS Material
- Scholarships
- Sarkari Exam
- Visual Stories
- College Compare
- Write a review
- Login/ Register
- Login / Register
What's the Difference Between a PhD and a Doctorate?

Ria Ghosh ,
Aug 16, 2024 | PhD
Share it on:
PhD vs Doctorate degrees implies that students willing to pursue the career path of research and academics may pursue a PhD, and those who are looking for leadership and advanced roles may pursue a doctorate.

PhD vs Doctorate: The primary difference between a PhD and a Doctorate is that a PhD focuses on academic research while professional doctorate makes a significant and original contribution turning into a further professional practice.
A doctorate combines both coursework and a thesis of between 70,000 and 100,000 words. The PhD and Doctorate have academic requirements may be similar, but there are slight differences in career opportunities.
The difference between a PhD and a doctorate is that PhD programmes offer studies in a particular field with research aspects, providing opportunities in the academic field or any other field, including the government sector and doctorate programmes offer more advanced while a doctorate is a profession of leadership-focused and field-specified research, leading to even more progressive career paths.
Table of Contents
What is a PhD?
What is a doctorate, phd vs doctorate purpose, phd vs doctorate goals and outcomes, phd vs doctorate academic requirements/ eligibility, phd vs doctorate duration, phd vs doctorate completion requirements.
- PhD vs Doctorate Career Prospects
- PhD vs Doctorate: What to choose?
Top 5 Universities Offering PhD Courses
The Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is a university degree, which focuses on research, analysis, and theory. A PhD degree is earned in a specialized field of engineering, medicine, humanities, science, arts, management and so on.
A student can earn multiple PhDs to expand their knowledge and expertise in multiple domains. The Doctor of Philosophy is an branch of the academic doctorate degree. The PhD programs usually take at least 2 years of course work and 3-4 additional years of research and publication of the dissertation. The PhD programs in India
Read more: PhD Full Form
The Doctorate degree is a graduate-level college degree for individuals aspiring to work in a more practical environment, like leadership and managerial positions. This degree is considered the terminal degree, as this is the final level of education a professional can achieve in their respective field. There are 2 types of doctorate degrees such as academic and professional.
The professional doctorate is an applied doctorate with a specific profession, like medicine, surgery, and law. Here are some of the examples of the professional doctorate:
- Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
- Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS)
- Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD)
- Doctor of Podiatric Medicine (DPM)
- Doctor of Chiropractic (DC)
- Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM)
- Doctor of Naturopathic Medicine (ND)
- Juris Doctor (JD)
An academic doctorate is often referred as the following titles:
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)
- Doctor of Education (EdD)
- Doctor of Design (DDes)
- Doctor of Fine Arts (DFA)
- Doctor of Nursing Science (DNS)
- Doctor of Theology (ThD)
Read more: Top 5 PhD Fields After MBBS
Difference between PhD and Doctorate
Learning about a PhD or doctorate which is better, can be bewildering for students willing to pursue higher education.
PhD vs Doctorate in terms of research implies that the former is a particular type that majorly focuses on contribution to academics and original research, whereas the latter focuses on a broader category and comprises advanced degrees.
The purpose of a PhD is to conduct in-depth research through data analysis and assess related theories and ideas. A PhD student aims to test out their theories to contribute information and data findings to a specific discipline or field of study.
On the other hand, the main purpose of a Doctorate is to transform students into working professionals by providing them with practical knowledge in their preferred field of study. For working professionals, this degree helps to emphasize their credibility, influence and leadership capabilities.
The goal of a PhD student is to analyze theories accurately and create philosophical concepts in their field of study. They have to evaluate relevant information from contemporary and innovative sources to use in their research work. Finally, they must contribute to their field of study through their own research by analyzing current research material for informational gaps.
The goal and outcome of the Doctorate degree is to be able to apply academic knowledge to real-life situations and environments. This can be done when a student achieves a firm understanding of how to use existing solutions or create innovative solutions to solve complex problems.
The academic requirements for a PhD or Doctorate degree are almost similar. Aspiring students must have a Master’s degree with at least 55% aggregate marks in the field that is relevant to PhDs, or to the Doctorate. In some cases, candidates might require an Master of Philosophy (M.PHil) or Master of Psychology degree. There is also a selection process conducted by many educational institutions, where students need to appear for an entrance exam and interviews. Candidates having relevant working experience were given priority.
The duration of a PhD degree depends on various factors. The total time to complete the study can depend on the status of a student as a full or part-time student, timely completion of research stages, willingness to take up summer courses, etc. Hence, it can be expected for a student to complete the degree maximum within eight years, or a minimum of three to six years.
The time it takes to get a doctorate can depend on the specific course of study. Candidates can finish the degree within four to seven years if they are done with the initial academic requirements. Whereas, some educational institutions allow their students up to 10 years to complete the doctorate degree.
A PhD student has to submit a dissertation paper, which involves preparing, drafting and orally defending the argument of the dissertation in front of a committee of academic professionals. To achieve the required results, they have to do an extensive amount of research and documentation of the findings, literature, materials, reviews and conclusions.
To complete a doctorate program, a student has to draft a proposal that identifies and solves a problem. Based on this, they design a method to conduct their research and develop the solution. Similar to the PhD program, students must conduct extensive research, collect data, and defend their proposal orally in front of a committee.
PhD vs Doctorate Career Prospects
A PhD graduate can work in primary roles related to academics and research and other industries as well, such as Government and Nonprofits, Analysts, etc. This is because they have high expertise and opportunities in various career fields, including academics and research.
On the other hand, a doctorate is involved in advanced practice roles, including leadership roles in the fields of business, education, law, and medicine. They are well-suited for these roles as they have specific industry-centric knowledge that leads to more leadership roles and opportunities in specified sectors.
Read more: Ph.D vs MBBS
PhD vs Doctorate: What to Choose?
Candidates must have questions like "PhD or doctorate which is better", "Choosing between PhD and Doctorate", etc. Hence, here are some pointers that will help candidates to make a well-informed decision regarding this.
- Career Goals: Candidates must closely analyze their career goals while making the decision. They must think thoroughly about whether they want a career in academic research or opportunities for working in a practical environment.
- Budget: Students must also determine the costs of pursuing the degree program. They must know that the doctorate program is generally more expensive. For this, they need to compare and analyse both programs and select the one that best suits their academic goals and budget.
- Academic Progress: Aspirants must also consider how far along they are in their academic journey to decide between a Ph.D. vs. a doctorate. They must opt for the one that helps them achieve their career goals in the least amount of time.
- Coursework: Candidates must do thorough research on the coursework of their desired program to understand if that fits their career and academic interests or not. They can do so by researching about the professors, lectures, course offerings, academic opportunities, etc.
- Time Commitments: Students must be aware of the fact that both PhD and Doctorate degrees require an extensive amount of time for completion.
Read also: Ph.D Jobs, Scope, Salary in India
The top universities offering PhD courses are All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi Technological University, Ambedkar University Delhi, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, and IIT Delhi.
Some of the various PhD courses offered by the mentioned institutes are listed in the table below:
| University Name | Location | Courses Offered |
| Delhi | Ph.D. Biochemistry | |
| Ph.D. Biophysics | ||
| Ph.D. Pharmacology | ||
| Ph.D. Pathology | ||
| Ph.D. Pediatrics | ||
| Ph.D. Medical Oncology | ||
| Ph.D. Microbiology | ||
| Ph.D. Laboratory Medicine | ||
| Ph.D. Physiology | ||
| Ph.D. Biotechnology | ||
| Ph.D. Psychiatry | ||
| Ph.D. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance | ||
| Ph.D. Neurosurgery | ||
| Ph.D. Cardio Thoracic and Vascular Surgery | ||
| Ph.D. Biostatistics | ||
| Ph.D. Pediatric Surgery | ||
| Delhi Technological University | Delhi | Ph.D. Biotechnology |
| Delhi | Ph.D. English Language Education | |
| Ph.D. Film Studies | ||
| Ph.D. Literary Art | ||
| Ph.D. Human Ecology | ||
| Delhi | Ph.D. Vegetable Science | |
| Ph.D. Seed Science and Technology | ||
| Ph.D. Nematology | ||
| Ph.D. Plant Pathology | ||
| Ph.D. Plant Genetic Resources | ||
| Ph.D. Environmental Sciences | ||
| Ph.D. Microbiology | ||
| Ph.D. Agricultural Chemicals | ||
| Ph.D. Biochemistry | ||
| Ph.D. Molecular Biology and Biotechnology | ||
| Delhi | Ph.D. Biological Sciences | |
| Ph.D. Mathematics | ||
| Ph.D. Telecommunication Technology and Management | ||
| Ph.D. Opto-Electronics | ||
| Ph.D. Chemical Engineering | ||
| Ph.D. Energy Studies | ||
| Ph.D. Optical Metrology | ||
| Ph.D. Optical Metrology | ||
| Ph.D. Polymer Science and Technology | ||
| Ph.D. Industrial Tribology | ||
| Ph.D. Value Education in Engineering | ||
| Ph.D. Electrical Engineering | ||
| Ph.D. Humanities and Social Sciences | ||
| Ph.D. Chemistry | ||
| Ph.D. Rural Development and Technology |
Also Read: PhD Entrance Exam Syllabus
Q: What's the difference between a PhD and a Doctorate?
Q: How to choose between a PhD and a Doctorate?
Q: Which are the top 5 universities offering PhD courses?
Q: What is the purpose of a PhD and a Doctorate student?
Q: What are the career prospects of a PhD and a Doctorate student?
POST YOUR COMMENT
Top phd [doctor of philosophy] colleges.

Chennai,Tamil Nadu

IISc Bangalore
Bangalore,Karnataka

Mumbai,Maharashtra

Delhi,Delhi NCR

Kanpur,Uttar Pradesh

IIT Kharagpur
Kharagpur,West Bengal

IIT Roorkee
Roorkee,Uttarakhand

IIT Guwahati
Guwahati,Assam
PhD Fee Structure
Other category courses.
Engineering
Architecture
Agriculture
Paramedical
Computer Application
See Various PhD Colleges in India

Get Free Scholarship worth 25000 INR

- School of Nursing >
- Admissions >
- Graduate Admissions >
- Post-MS PhD
Post-MS Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Nursing Program - Admissions
The University at Buffalo's Post-Master's Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Nursing program is designed to prepare experienced nurses for leadership roles in nursing science and academia. This program equips nurse scholars to advance knowledge development, theory generation, and hypothesis testing to improve nursing practice and health care outcomes. All PhD program tracks are offered online, providing the flexibility needed for working professionals.
Jump to section
About our admissions process.
- The School of Nursing reserves the right to change admission and program criteria to meet prevailing accreditation and registration requirements.
- Students who have been dismissed from other nursing programs are not eligible for admission.
- An interview is required for all graduate programs as part of the review process. Qualified applicants will be notified of interview via email.
Admissions Information
Admissions requirements.
- Equivalent of a Bachelor of Science in nursing (BSN) and Master of Science in nursing (MSN) degree.
- Active U.S. RN license or foreign nursing license.
- Overall MSN GPA of 3.25.
Application Materials
- Online application.
- Application fee: $75
- Official transcripts from all colleges attended.
- Resume/curriculum vitae.
- Personal statement .
- Two scholarly writing samples.
- Three references.
Transcript Information
All application materials are submitted online through the application portal, except for official transcripts. Please do not upload any screenshots of transcripts.
Select the correct institution
Ensure that your transcripts are sent to SUNY University at Buffalo, not to SUNY Buffalo State University.
Please have official transcripts mailed to:
UB School of Nursing Beck Hall-Graduate Admissions 3435 Main Street Buffalo, New York 14214
Electronic transcripts can be:
- Emailed to [email protected].
- Uploaded via Parchment using the "University at Buffalo" option.
- Uploaded via National Student Clearinghouse using code: 002837.
International Applicants
Additional requirements for international applicants, all graduate nursing program applicants.
- SPEAK Test , TOEFL or IELTS scores (minimum scores and more information); UB TOEFL code: 2925.
- International Credentials/Transcripts/Proof of Degree/Translations. A WES document is strongly preferred.
- Upon admission to the program, you will be required to submit official transcripts/degrees/translations in a sealed envelope to the International Admission Office.
- Immigration and financial documents.
DNP Program Applicants
- Students applying to the DNP program are not eligible to obtain an F1 student visa. Visa requirements can be found here .
- If you do not have a US RN license, you must contact the state board of nursing to apply.
Application Deadlines
| Program | Term | Open | Close |
|---|---|---|---|
| PMH Advanced Certificate | Spring 2025 | 07/15/2024 | 10/15/2024 |
| Post-MS DNP (all) | Spring 2025 | 09/2/2024 | 01/02/2025 |
| Post-BS DNP CRNA | Summer 2025 | 07/15/2024 | 09/05/2024 |
| Post-BS DNP (AGNP, FNP, PMHNP) | Summer 2025 | 12/16/2024 | 04/01/2025 |
| PhD (Traditional and Early Assurance) | Fall 2025 | 12/16/2024 | 04/01/2025 |
| DNP Early Assurance | Fall 2025 | 12/16/2024 | 04/16/2025 |
| Post-BS DNP (AGNP, FNP, PMHNP) | Fall 2025 | 12/16/2024 | 6/16/2025 |
| Post-MS DNP (all) | Fall 2025 | 01/16/2025 | 6/16/2025 |
All documents must be received by the deadline.
Additional Information
Application tips series.

Letters of recommendation are a vital piece of your application. Here are some important tips for identifying recommenders.

Learn about filling out an application for the UB School of Nursing graduate programs.

Your resume is a vital piece of your application. Here are some important tips to remember when creating your resume.

Learn tips for writing a quality personal statement.

Learn tips for providing clear and high-quality transcripts will set you up for success during the application process.
Graduate Programs Information Sessions

Tanner Gelatt Assistant Director of Graduate Recruitment 202 Beck Hall 716-829-3765 [email protected] Schedule a meeting with Tanner.
The University at Buffalo is committed to ensuring equal access to its programs and activities. View UB's Notice of Discrimination here.
- PATIENT FORUM
- FOR PATIENTS AND CAREGIVERS
- FIND SUPPORT
- TREATMENT CENTER FINDER
- CLINICAL TRIAL FINDER
Stay Updated

National Make-a-Will Month - Create your free will today to support the melanoma community
News & press, in memoriam: jeffrey s. weber, md, phd..

The Melanoma Research Foundation joins the melanoma community in expressing our profound condolences on the recent passing of Jeffrey S. Weber, MD, PhD. Dr. Weber was an internationally recognized and trailblazing pioneer in cancer immune therapy and melanoma and made countless contributions to these fields throughout his remarkable career. As an immunotherapy expert, Dr. Weber’s investigations and research findings have brought innovative advancements in melanoma treatment from the laboratory to clinical practice. Collectively, Dr. Weber’s contributions have greatly impacted the entire melanoma community and have enabled tremendous progress for countless patients, survivors and caregivers.
Dr. Weber was the esteemed deputy director of the Perlmutter Cancer Center and codirector of the Melanoma Research Program at NYU Langone Health. Prior to this most recent role, Dr. Weber also held leadership positions at H. Lee Moffit Cancer Center and USC’s Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center. He was a recognized leader in forging collaborative partnerships between basic scientists and clinical and translational investigators to advance cancer care. Throughout his decades long career, Dr. Weber led multiple practice changing clinical trials including the CheckMate 238 Phase III adjuvant nivolumab trial in stage III melanoma that established the first adjuvant use of anti-PD-1 antibodies. He also presented on the randomized Phase II trial of pembrolizumab and a personalized mRNA cancer vaccine compared to pembrolizumab alone in patients with melanoma. This was a landmark study in showing the first time randomized clinical data supporting the efficacy of a vaccine in preventing cancer relapse.
The MRF is incredibly honored and indebted to Dr. Weber for his many years of service to our community. In 2021, Dr. Weber helped produce a series of Animated Patient Videos that helped synthesize a variety of melanoma topics such as understanding, diagnosing and treating melanoma, an overview of genetic mutations of melanoma and TIL cell therapy and clinical trials for melanoma. This series continues to benefit melanoma patients, caregivers and survivors across the spectrum of their melanoma journey. In addition to his countless contributions to the melanoma patient community, Dr. Weber also helped steer the melanoma scientific community having served on the MRF’s Scientific Advisory Council and its Breakthrough Consortium – a network of 23 centers of excellence in melanoma that collaborate to accelerate the research and development of the most promising therapies in melanoma treatment. Dr. Weber served as an MRF grant reviewer and grant mentor and reviewed patient education materials. In 2019, the MRF honored Dr. Weber with its Humanitarian Award at that year’s New York City annual gala for his exceptional contributions to melanoma detection and treatment.
MRF’s Board Chair, Doug Brodman, offers, “It is with great sorrow that we have heard of Jeff’s passing. Jeff was a passionate doctor and researcher who had an immeasurable impact on the melanoma field. His work had an enormous impact on the survivorship of many melanoma patients, including myself. His legacy and work will carry on with all those he has touched personally through his career’s work.”
Our deepest condolences are extended to the family, friends, colleagues and patients of Dr. Weber’s and the countless cancer community members whose lives have been touched by his inspirational contributions.
TOGETHER WE CAN FUND THE FUTURE!
Donate what you can
YOUR GENEROSITY ADVANCES LIFE-SAVING MELANOMA RESEARCH.
TOGETHER WE CAN FUND THE FUTURE
DONATE WHAT YOU CAN
YOUR GENEROSITY ADVANCES LIFE-SAVING MELANOMA RESEARCH
Sign up for news and updates from the Melanoma Research Foundation
Name:
Become an Advocate
- Name * First Middle Last Suffix
- Professional Suffix
- Organization
- Address * Street Address Address Line 2 City State ZIP / Postal Code
- I identify as * Patient Survivor Thriver Caregiver Friend/Family Member Healthcare Provider Industry Professional Other
- I am interested in more information about… Advocacy News and Information Attending MRF's Annual Advocacy Summit and Hill Day Melanoma News and Information Melanoma Education and Patient Programs Research Miles for Melanoma 5k's Galas Fundraising
- Newly Diagnosed
- Treatment Center Finder
- Patient Forum
- Patient & Caregiver Meetings
- Connect with Others
- Survivorship
- Bereavement
- Financial Assistance
- Clinical Trials
- Diagnosis (Cutaneous)
- Treatment (Cutaneous)
- Resources (Cutaneous)
- Ocular Melanoma
- Diagnosis (Mucosal)
- Treatment (Mucosal)
- Resources (Mucosal)
- Diagnosis (Pediatric)
- Treatment (Pediatric)
- Resources (Pediatric)
- What Melanoma Looks Like
- Facts & Stats
- Cutaneous Melanoma
- Mucosal Melanoma
- Pediatric & AYA Melanoma
- Melanoma Prevention
- Melanoma Awareness
- Skin of Color & Melanoma
- Education Institute
- Provider Education
- Patient Meetings
- Research Grant RFPs
- Funded Research
- Supported Institutions
- VISION Registry
- MRF Breakthrough Consortium
- CURE Ocular Melanoma
- Pediatric & Mucosal Melanoma
- Scientific Meetings
- Partnerships
- Participate in Clinical Trials
- Advocate for Legislative Issues
- Review Grant Applications
- Scientific Leadership
- Federal Funding
- Take Action
- Advocacy News
- Advocacy Events
- Global Melanoma Coalition
- VISION Platform
- Planned Giving
- Memorial Giving
- Corporate Sponsorship
- Cause Marketing
- Merch Store
- Melanoma Awareness Month
- Miles for Melanoma
- Host an Event
- Patient Symposium
- Board of Directors
- SPOTlight Newsletter
- Eye on OM Newsletter
- Advocacy Newsletter
- Financials & Annual Reports
Robert Downey Jr. Opens Up About His Shocking MCU Return: We Want to "Get Victor von Doom Right"

Your changes have been saved
Email is sent
Email has already been sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
The Big Picture
- Robert Downey Jr. opens up about returning to the MCU as Doctor Doom.
- The actor's close ties with Kevin Feige and the Russo brothers led to the unexpected comeback.
- Downey's unconventional will also see him getting more involved with Bob Iger and Disney's theme parks.
“New mask, same task,” Robert Downey Jr announced at San Diego Comic-Con when he was introduced as the MCU's Doctor Doom along with returning directors Joe and Anthony Russo for Avengers: Doomsday and Avengers: Secret Wars . Fans for long have predicted the actor’s return to the MCU — however, no one could have predicted his return as a major multiverse villain after his iconic portrayal of Tony Stark aka Iron Man. Nonetheless, the casting has divided the fans. Some are hyperexcited for Downey’s return while others are disappointed to see another Marvel character's Romani heritage erased .
While the actor and the studio have been tight-lipped following the casting news, in a new conversation with The Hollywood Reporters’ Award Chatter podcast , Downey finally opened up about returning to the MCU. The idea was discussed "Probably a year ago because [Kevin] Feige and I have kept in touch," Downey revealed. Adding "We're pals. [Jon] Favreau, Feige, and I have kept in touch. I'm close with the Russo brothers. We have other business we're doing. So there's this little group of fellow travelers, and I had this instinct that I wanted to go to Bob Iger .” Downey then revealed that he had an idea to join forces with Disney, “outside of the cinematic universe , for how I could be of service to what's going on in the parks and all their location-based energy.” Downey then explained that one day Feige finally found a way to bring him back to the MCU. He explained:
“Susan and I were sitting down with Feige at one point, and he said, 'It just keeps occurring to me that, if you were to come back...' And Susan was like, 'Wait, wait, come back as what?'”
Kevin Feige Suggested Robert Downey Jr.’s Return as Doctor Doom

Feige and Downey’s friendship goes back to Iron Man , the first MCU movie. And when the Infinity Saga ended, Feige famously declared that Tony Stark’s legacy wouldn't be touched, ever. On the podcast, Downey reveals that Feige carefully thought it out before suggesting he return. Per Downey, Feige is “a very sophisticated, creative thinker about, 'How can we not go backwards? How can we not disappoint expectations? How can we continue to beat expectations?'” He went on to say:
And he brought up Victor von Doom, and I looked into this character, and I was like, 'Wow.' And later on, he goes, 'Let's get Victor von Doom right. Let's get that right.' So then I said to Kevin, 'Can I go talk to Bob Iger?' He goes, 'About?' I go, 'About everything.'"
After hearing Downey's pitch, Iger invited him and Feige to the Imagineering campus , and what they saw there really impressed them, “I can't say too much about it, but what is going on there right now is so beyond my expectation of what was possible, no wonder it was numinous to me.” The visit gave the Iron Man actor the feeling that "I can give a certain entertainment-seeking audience, something that they may have a hankering to have an experience of, in a way where I can continue to develop my interest in the future of entertainment. Where the hell else should you go but there?"
Avengers: Doomsday and Avengers: Secret Wars are set to release in 2026 and 2027, respectively. Downey's previous MCU projects are available on Disney+.

After being held captive in an Afghan cave, billionaire engineer Tony Stark creates a unique weaponized suit of armor to fight evil.
Watch on Disney+
- Robert Downey Jr
- Kevin Fiege
- Thoracic & Cardiac Surgeons
- Dr. Michael Saleeb Ibrahim
Dr. Michael Saleeb Ibrahim, MD/PhD
- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
- Specialties Ophthalmologists Gastroenterologists Otolaryngologists Cardiologists Endocrinologists Neurologists Urologists Plastic Surgeons Orthopaedic Surgeons Nephrologists Internal Medicine Doctors Pediatricians Family Medicine Doctors Urogynecologists Neurosurgeons OB/GYNs Cardiac Electrophysiologists Hand Surgeons Vascular Surgeons Psychiatrists View All CITIES New York Philadelphia Boston Seattle Chicago Houston Los Angeles Indianapolis Portland San Francisco Dallas Atlanta Washington Pittsburgh West Palm Beach St. Louis Charlotte San Antonio Phoenix San Diego View All INSURANCE Aetna Group AmeriHealth Blue Cross Blue Shield Empire Blue Cross Blue Shield Carefirst Inc. Group Cigna Health Group Emblem Health Ambetter Humana Group Independence Blue Cross Group Kaiser Foundation Group Unitedhealth Group Wellcare Group Oxford Health Plans Florida Blue Molina Healthcare Blue Cross Blue Shield of Illinois Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas Oscar Community Health Choice View All REASONS FOR VISIT Diabetes Breast Cancer Spine Surgery Cosmetic Surgery Lasik Weight Loss Surgery Prostate Issues Pain Management IVF Stroke Neuro-Ophthalmology Electromyography (EMG) Eyelid Surgery/Blepharoplasty Complex Diagnosis Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Concierge Medicine Oculoplastic Surgery Cataract Surgery Cornea & External Eye Disease Mohs Surgery View All
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Is it correct for a PhD holder to sign as "Dr. J. Doe, PhD"?
I have seen some of the PhD holders sign as "Dr. [First Name] [Surname], PhD".
Is it academically correct to write "Dr. Frank Amoani Arthur, PhD"?
- 28 Are you in Germany? If not you can do whatever you want. – Cape Code Commented Oct 8, 2016 at 5:42
- 3 In addition, "Dr. X Y, PhD" would be correct if the person actually holds two different doctoral degrees: a Dr. and a PhD. – lighthouse keeper Commented Oct 8, 2016 at 6:51
- 4 I would like to add that in some fields and (sub)cultures, adding the ", PhD" bit after your name may seem unnecessarily pretentious. – Gimelist Commented Oct 8, 2016 at 8:01
- 1 It certainly depends on the usage context. In a job talk title slide, naming the degree seems justified, while in a conference talk or in a twitter profile, it would look pretentious. – lighthouse keeper Commented Oct 8, 2016 at 8:09
- 1 @CapeCode Not just Germany. In The Netherlands it is a criminal offense to write your name like this. The law explicitly provides that you have to choose between either writing "dr." or writing "PhD". – Tom van der Zanden Commented Jun 22, 2021 at 7:54
7 Answers 7
There are two important points to note about name markers that refer to academic titles:
- You can have more than one of these markers in your name: Kay Doe, PhD, MD indicates a person who is both a doctor of philosophy and a doctor of medicine.
- The marker Dr. can very often be used as a variant of the post-positioned markers. If both of them are equivalent markers in your country, you can choose either marker to refer to your academic title.
These two observations make the suggested name form Dr. Kay Doe, PhD rather ambiguous.
Does it refer to a person with two doctor titles because there are two markers? Or do both markers refer to just one doctor title? But if so, why is that doctor referred to twice in one name? This may even lead to suspicion: Does the name bearer use two markers which refer to the same title with the intention to sound more impressive than their academic distinction actually warrants?
This ambiguity is avoided if you use only one title marker per title.
- 1 +1 for not asserting that something is "correct" or "incorrect" and instead focusing on what is the most effective for communication. – Thomas Commented Jun 21, 2021 at 22:43
- In Germany, we tend to list multiple doctor titles in front of the name, e.g. Dr. phil. D. med. Dr. h.c. Max Mustermann would declare a doctor of philosophy, a medical doctor and an honorary doctor all at once. But notably, these titles must match the precise expression of a title that has been awarded. So Dr. phil. X cannot be used instead of X, PhD , except if the awarding university explicitly declared it that way. Here you can find a list of examples (need to scroll down to a table). – xamid Commented Mar 27, 2023 at 5:59
In the US, at least the title doctor doesn't imply a medical doctor, though it includes that. My students would usually refer to me as Dr. Buffy. Someone not knowing that I hold a doctorate might call me Mr. Buffy, but Dr. Buffy is more specific.
If I wish to list my degrees after my name they aren't being used a title like Dr. or Ms.
So, being pedantic: Dr. Buffy, BA, MA, PhD. is just fine. In Germany, and places with a related academic culture, degrees are used more as titles so it is a bit different: Herr Doctor Professor Buffy.
Medical doctors (again in the US) insist on being called Doctor and have no difficulty with Dr. Foobar, MD. It would be extremely uncommon for them to be listed any other way.
- 5 "Herr Professor Doctor", actually. – Oleg Lobachev Commented Aug 1, 2018 at 15:07
- 1 Yes, Herr Student @OlegLobachev. Kidding of course. Thanks. In the US we would garble it, of course. As I did. I listed them in the order I did because of the order I earned them. I was Doktor before I was professor. – Buffy Commented Aug 1, 2018 at 15:12
- 2 There is a story of a quite famous mathematician (a professor) who was living with one of his students in a "romantic" relationship. He once is said to have informed her that she didn't need to refer to him with all of his titles as long as they were in private. Apocryphal? You judge. – Buffy Commented Aug 1, 2018 at 15:15
- 1 There's a reason why physicians are Dr. Foo, M.D. The Dr. part is for public appearances, so patients perceive that they're authoritative. The M.D. part is required by regulation in some places like hospitals and medical schools, as to disambiguate Ph.D., D.O., D.D.S./D.M.D., O.D., D.V.M. etc. which all have different rights/requirements when interacting with patients. My major US institution sticks both (Dr. Foo Bar, PhD) on everybody's e-mails and ID cards and computer accounts, even for non-medical people. – user71659 Commented Aug 2, 2018 at 7:02
I'm sure this must have been dealt with in previous questions, but the short answer is:
This is correct if you are both a medical doctor and an academic doctor. But just being an academic allows you to write Dr. (name) XOR (name) PhD.
- 12 This is not universally true. – Cape Code Commented Oct 8, 2016 at 7:23
If you have Dr. NAME only it might cause some confusion. I was once caught in a situation where I was asked to be on standby for assistance during a medical emergency because my boarding pass identified me as Dr. MYNAME. I had to explain that the Dr was for a PhD and not for medical practises. In my opinion the academic the title should be Dr. LASTNAME or Dr. LASTNAME M.D. for a medical practitioner Dr, LASTNAME PhD for an academic qualification Dr. LASTNAME HC for an honorary doctorate ( honororium causa )
As you can see from some of the answers here, there is substantial variation in use of academic titles and suffixes for degrees. It is certainly okay to use the suffix PhD if you have a PhD, and it would be hard to mount an argument that it is "incorrect" to use a suffix for a degree you actually have. There is wide variation in what is common practice in academia, but what is most important is to consider the following practical issues:
IMPORTANT --- avoid confusion with medical doctors: In most places, in an academic context the title "Dr" is fine for someone with a PhD (though in some countries they are distinct). However, in contexts outside academia it can cause confusion. In particular, for a person with a PhD who is not a medical doctor, it is often desirable to avoid using the title "Dr" in contexts where it might cause people to think that you are the appropriate contact person in a medical emergency ---e.g., " Dr O'Neill, this man is having a heart attack - do something! " So, for example, when I am checking into a plane, or in similar circumstances, I try to ensure that I am booked in as "Mr" not "Dr", notwithstanding that the latter title would apply in an academic context.
Academics rarely use the degree suffix: Because the PhD is so common among academics, we would rarely use this suffix outside of a CV. It is common for academics to use titles (e.g., Dr, Assoc Prof, Prof, etc.) in descriptions such as a signature block, staff page, etc. It is uncommon (but not incorrect) to additionally add the suffix "PhD". The main reason most academics leave this part off is because the degree is common among academics.
Dual use might clarify or it might confuse, depending on who is reading it: If you use both a title and a suffix for the same degree, that can potentially help to understand the source of the title, or it can look awkward or cause confusion. This really depends on the audience. In most cases, if you use the title "Dr" and the suffix "PhD" then people will assume that the title comes from the degree specified in the suffix, which is accurate here. It is perhaps a bit unusual to use both, but it is not unheard of.
I think in the US anyway, you can sign your name however you wish. In my case, I am a DVM and I have a Masters degree. I want my business cards to say Dr. MYNAME, DVM, MS. I have seen multiple DVMs that write their name the same way. I think it's good to know what kind of Dr. I am, and this helps others to know it also. Even if I didn't have the Masters degree, I would likely still want my business card to say Dr. MYNAME, DVM.
- 1 What is a DVM ? – astronat supports the strike Commented Jun 21, 2021 at 14:10
- 2 @astronat Doctor of Veterinary Medicine. – Bryan Krause ♦ Commented Jun 21, 2021 at 14:13
Dr Jones if he has a medical degree. Mark Jones, Ph.D. or Dr. Jones, if he has a Ph.D. Never Dr. Jones, Ph. D.
- 4 What if a PhD who is also a medical doctor? I think "Never" is too strong a word. – Nobody Commented Aug 1, 2018 at 6:34
- 5 @scaaahu Mark Jones, MD, PhD. – Nicole Hamilton Commented Aug 1, 2018 at 9:38
- 1 @NicoleHamilton That's a good one. – Nobody Commented Aug 1, 2018 at 9:45
- My major US university puts "Dr. Jones PhD" on everybody's ID cards, e-mails, computer accounts, directory, etc. It's because the medical school and hospital have all kinds of "Dr." running around and they need to make it easy to identify what responsibilities you have. – user71659 Commented Aug 2, 2018 at 7:07
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd titles ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- Until or before?
- Momentary solo circuit
- Faster simulation of two spins
- What is the origin of this quote on telling a big lie?
- veracity of matrix script
- What other goals could a space project with the primary goal of experience building with heavy lift rockets preform?
- Constructing a specific 2-variable function taking integer arguments whose value is odd/even only when arguments are equal
- Is there a good explanation for the existence of the C19 globular cluster with its very low metallicity?
- How common is it for external contractors to manage internal teams, and how can we navigate this situation?
- Do linguists have a noun for referring to pieces of commendatory language, as a sort of antonym of 'pejoratives'?
- Arranging people in a jeep.
- Stacked block problem & static friction
- Why are swimming goggles typically made from a different material than diving masks?
- Euler E152: "Analysin enim ineptam existimat"
- Why is global state harder to test? Doesn't reset the global state at the beginning of each test solves the problem?
- Handling Race Condition with Concurrent SOQL Queries in Salesforce Integration
- How to make two alignments in the environment align?
- How can flyby missions work?
- Reference of "she"
- Seven different digits are placed in a row. The products of the first 3, middle 3 and last 3 are all equal. What is the middle digit?
- Does "any computer(s) you have" refer to one or all the computers?
- result of a union between a decidable language and not recognizable one - disjoint
- For applying to a STEM research position at a U.S. research university, should a resume include a photo?
- Did polls adjust their methodology after overestimating Democrat's shares in the 2016 and 2020 presidential elections in the Rust Belt?
58. Deep Research Into the Gut Microbes That Keep Us Happy | Jennifer Bramen, PhD
by Anthony Effinger
The Think Neuro podcast from Pacific Neuroscience Institute takes you into the clinic, operating room and laboratory with doctors and surgeons who are tackling the most challenging brain diseases and disorders. Host: Anthony Effinger
Subscribe: Google Podcasts | Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Simplecast
Watch on YouTube
Episode 58: Show Notes
One thing that makes Pacific Neuroscience Institute an institute is research, and Jennifer Bramen spends all of her time doing just that. Dr. Bramen earned her PhD in neuroscience from UCLA. These days, she is particularly interested in the “gut biome”: all the organisms that live in our digestive system. Strange though it may seem, those bacteria have a lot to do with our brains.
That’s because the gut has its own nervous system, and it produces many of the neurotransmitters that regulate our stress levels and mood. But we can’t produce those compounds alone. We need a population of good bacteria to help. Sadly our modern diet of processed foods and cured meats, often consumed quickly at our desks, fosters bad bugs, which can push out the good ones.
The key, Dr. Bramen says, is to eat foods that aren’t over-processed, like fruits and vegetables, and to eat them slowly. We should also favor foods that the good bugs like to eat, too: kiwis, bananas and avocado, among them. Dr. Bramen takes two minutes before every meal to slow down her breath, activating the part of her nervous system that helps us digest food.
The bottom line: It takes a village (of bugs) to keep our guts and brains healthy. Dr. Bramen’s research is showing just how true that is.
About Dr. Bramen

Jennifer Bramen , PhD, is a neuroscientist with expertise in neuroscience research, advanced neuroimaging, and non-pharmacological interventions for cognitive decline. She obtained her PhD in Neuroscience from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), where she also completed her postdoctoral research fellowship at the Laboratory of Neuroimaging (LONI).
Check Out More Think Neuro Podcast Episodes

31. Helping Patients and Advancing Science With a Psilocybin Trial | Karina Sergi, MS, MFT
In this episode we chat with Karina Sergi, a licensed therapist, trained the old-fashioned way, who has been exploring a new tool proven to help people who are struggling with persistent depression, addiction, and post-traumatic stress disorder: magic mushrooms.

42. Treating Brain Tumors – Guest Podcast | Dr. Daniel F. Kelly
Brain tumors don’t get the same amount of attention as the other types of cancers. But they are still very important to talk about. Dr. Daniel F. Kelly is a neurosurgeon and founder of Pacific Neuroscience Institute. Listen in to learn about Daniel’s non-linear path to becoming a neurosurgeon. You’ll also hear how the Pacific Neuroscience Institute uses keyhole surgery to reduce the amount of time patients need to stay in the hospital.

55. What Everyone Should Know About Strokes | Jason Tarpley, MD, PhD – Guest Podcast
Join us as Dr. Jason Tarpley joins the Your Healthy Dose podcast with Kym Douglas. A stroke can be debilitating and even deadly. Join us for “What You Need to Know About Strokes,” when podcast host Kym Douglas talks with physician Dr. Jason Tarpley about the various kinds of strokes, the need for speed in assessing someone who may be having a stroke, what BEFAST stands for, the latest options for treatment, and the best opportunities for prevention.
About the Author

Anthony Effinger
Think Neuro's host is Anthony Effinger, an award-winning journalist who is fascinated with neuroscience and the workings of the brain. Anthony spent 24 years at Bloomberg News, where he covered all aspects of finance, with forays into science and health. In 2006, the Association of Health Care Journalists awarded him first prize for Playing the Odds, an in-depth piece on the changing strategies used to treat prostate cancer. These days, he is a staff writer at Willamette Week, a Pulitzer Prize-winning newspaper in Portland, Oregon, where he lives with his wife and two children.
Last updated: August 21st, 2024
To give you the best possible experience, this site uses cookies and by continuing to use the site you agree that we can save them on your device.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A doctor of philosophy degree is designed to prepare people for research careers at a university or in industry, and teach students how to discover new knowledge within their academic discipline ...
Doctorate, or doctoral, is an umbrella term for many degrees — PhD among them — at the height of the academic ladder. Doctorate degrees fall under two categories, and here is where the confusion often lies. The first category, Research (also referred to as Academic) includes, among others: Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)**.
A Ph.D. or Doctor of Philosophy, on the other hand, is a subcategory of a doctoral degree, it is much more distinct and clear-cut and is usually narrower in nature encompassing only humanities and scientific fields. In plain English, when someone says they are enrolling on a doctoral degree, it means they are doing a Ph.D. in a specific field.
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD or DPhil; Latin: philosophiae doctor or doctor philosophiae) is a terminal degree that usually denotes the highest level of academic achievement in a given discipline and is awarded following a course of graduate study and original research.The name of the degree is most often abbreviated PhD (or, at times, as Ph.D. in North America), pronounced as three separate ...
3. You'll experience extreme stress and frustration. Pursuing a PhD may seem like a noble and interesting endeavor, and extended life as a student can appear more attractive than wading into the job market. You must be aware, however, that getting a doctorate can be a very stressful and frustrating experience.
A Doctor of Philosophy, often known as a PhD, is a terminal degree —or the highest possible academic degree you can earn in a subject. While PhD programs (or doctorate programs) are often structured to take between four and five years, some graduate students may take longer as they balance the responsibilities of coursework, original research ...
Doctorate and PhD students both complete 2 or more years of coursework. They also demonstrate their knowledge during comprehensive exams. Doctorate students may produce a capstone project that applies their knowledge to real problems. By contrast, PhD students write dissertations based on original research.
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term 'philosophy' does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to 'lover of wisdom'.
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
Definition of a PhD - A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD, Ph.D or a DPhil) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible. PhDs differ from undergraduate and master's degrees in that PhDs are ...
A PhD is a Doctor of Philosophy. In answer to the question, "Is a PhD a doctor," the answer is yes. Both a PhD and a professional doctorate like an EdD earn you the title of "doctor.". But there are differences between the types of doctoral degrees. Learn more about a PhD vs. a professional doctorate below.
The primary difference in coursework between Ph.D. and doctorate programs primarily involves the type of assignments the students complete. Ph.D. students mainly concentrate on a curriculum that emphasizes philosophical ideas, theories and research. The coursework of a doctorate focuses on practical applications, problem-solving and innovation.
This is possibly country dependent, but for Germany this is utterly wrong: "many also think that the MD is much more difficult to attain than a PhD" - Medical doctors get the equivalent of a "paper doctorate" thrown after them so they can be called "doctor" as part of their degree, while "real doctors" have to start a doctorate and carry out rigorous research to obtain the degree/academic title.
Academic doctorate. An academic doctorate, often called a PhD (short for Doctor of Philosophy), is a research degree that typically requires completing a dissertation. Students enrolled in a PhD program may be interested in working in academia as a professor or conducting research in their field. However, a growing number of PhD students go on ...
The answer here isn't straightforward, as it hinges on various factors, including: the discipline, the institution, and. whether you're a full-time or part-time student. For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you're juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 ...
A doctoral degree requires the satisfactory completion of an approved program of advanced study and original research of high quality. Please note that the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) and Doctor of Science (ScD) degrees are awarded interchangeably by all departments in the School of Engineering and the School of Science, except in the fields of biology, cognitive science, neuroscience, medical ...
A PhD program typically takes four to seven years, but a variety of factors can impact that timeline. A PhD, or doctorate degree, is the highest degree you can earn in certain disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, education, and mathematics. As a result, it often takes longer to earn than it does for a bachelor's or master's degree.
As a PhD and professor, I currently use Dr. as my title professionally. My relationships with students improved when I switched to Dr., even though in a perfect world I'd use my first name. It's not a perfect world. — Dr. Elissa Harbert (@KyrieElissa) June 14, 2018. In some instances, women are less likely to exhibit bias in form of address.
Get to know Amy R. Goetz, PhD About Dr. Goetz is an Assistant Professor of Pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine and a licensed clinical psychologist at Texas Children's Hospital. She provides assessment and treatment for children and adolescents in acute patient care settings such as the Emergency Center, Intensive Outpatient Program and ...
The Ph.D. is the most common research doctorate. Although the title stands for "doctor of philosophy," students can earn Ph.D.s in a wide range of subjects, including science and technology. In contrast, applied research doctorates often relate to specific fields, such as education, music, or social work.
By: Dr Andy Stapleton, PhD. Updated on: July 17, 2024. If someone holds a PhD, they are able to call themselves Doctor. The doctor title is very prestigious and often projects expertise and respect in those who decide to use it. A person with a PhD can be called Dr. However, many people with PhD degrees choose not to use their official titles ...
The NPR ombudsman explained that like many media outlets, NPR follows the Associated Press stylebook, which says if someone practices medicine, NPR calls them doctor. If it's someone with a Ph.D., it's up to the individual media outlet. On the radio, we don't have a lot of time, and every word counts. Saying someone is a doctor or saying ...
The time it takes to get a doctorate can depend on the specific course of study. Candidates can finish the degree within four to seven years if they are done with the initial academic requirements. Whereas, some educational institutions allow their students up to 10 years to complete the doctorate degree. PhD vs Doctorate Completion Requirements
The University at Buffalo's Post-Master's Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Nursing program is designed to prepare experienced nurses for leadership roles in nursing science and academia. This program equips nurse scholars to advance knowledge development, theory generation, and hypothesis testing to improve nursing practice and health care outcomes. All PhD program tracks are offered online ...
The Melanoma Research Foundation joins the melanoma community in expressing our profound condolences on the recent passing of Jeffrey S. Weber, MD, PhD. Dr. Weber was an internationally recognized and trailblazing pioneer in cancer immune therapy and melanoma and made countless contributions to these fields throughout his remarkable career. As an immunotherapy expert, Dr. Weber's
Nicole C. Wright, PhD, MPH. Associate Professor. CHOICES Director of Education. [email protected]. Office Address. 1503D Tidewater Building, 1440 Canal St, New Orleans, LA 70112. School of Medicine. Department. CHOICES. Biography. Dr. Wright earned her Master of Public Health (MPH) and Doctor of Philosophy from the University of Arizona. Her ...
Robert Downey Jr. opens up about returning to the MCU as Doctor Doom. The actor's close ties with Kevin Feige and the Russo brothers led to the unexpected comeback.
Dr. Michael Saleeb Ibrahim is a Castle Connolly Top Doctor whose specialty is Thoracic & Cardiac Surgery and is located in Philadelphia, PA. DOCTORS. Search Top Doctors By: Location; Specialty; ... Dr. Michael Saleeb Ibrahim, MD/PhD Thoracic & Cardiac Surgeon. Castle Connolly Top Doctor Since: 2024 ...
12. There are two important points to note about name markers that refer to academic titles: You can have more than one of these markers in your name: Kay Doe, PhD, MD indicates a person who is both a doctor of philosophy and a doctor of medicine. The marker Dr. can very often be used as a variant of the post-positioned markers.
Subscribe: Google Podcasts | Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Simplecast Watch on YouTube. Episode 58: Show Notes. One thing that makes Pacific Neuroscience Institute an institute is research, and Jennifer Bramen spends all of her time doing just that. Dr. Bramen earned her PhD in neuroscience from UCLA. These days, she is particularly interested in the "gut biome": all the organisms that live ...