Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide

How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”
The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, what is your plagiarism score.

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
The 31 Literary Devices You Must Know
General Education

Need to analyze The Scarlet Letter or To Kill a Mockingbird for English class, but fumbling for the right vocabulary and concepts for literary devices? You've come to the right place. To successfully interpret and analyze literary texts, you'll first need to have a solid foundation in literary terms and their definitions.
In this article, we'll help you get familiar with most commonly used literary devices in prose and poetry. We'll give you a clear definition of each of the terms we discuss along with examples of literary elements and the context in which they most often appear (comedic writing, drama, or other).
Before we get to the list of literary devices, however, we have a quick refresher on what literary devices are and how understanding them will help you analyze works of literature.
What Are Literary Devices and Why Should You Know Them?
Literary devices are techniques that writers use to create a special and pointed effect in their writing, to convey information, or to help readers understand their writing on a deeper level.
Often, literary devices are used in writing for emphasis or clarity. Authors will also use literary devices to get readers to connect more strongly with either a story as a whole or specific characters or themes.
So why is it important to know different literary devices and terms? Aside from helping you get good grades on your literary analysis homework, there are several benefits to knowing the techniques authors commonly use.
Being able to identify when different literary techniques are being used helps you understand the motivation behind the author's choices. For example, being able to identify symbols in a story can help you figure out why the author might have chosen to insert these focal points and what these might suggest in regard to her attitude toward certain characters, plot points, and events.
In addition, being able to identify literary devices can make a written work's overall meaning or purpose clearer to you. For instance, let's say you're planning to read (or re-read) The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe by C.S. Lewis. By knowing that this particular book is a religious allegory with references to Christ (represented by the character Aslan) and Judas (represented by Edmund), it will be clearer to you why Lewis uses certain language to describe certain characters and why certain events happen the way they do.
Finally, literary techniques are important to know because they make texts more interesting and more fun to read. If you were to read a novel without knowing any literary devices, chances are you wouldn't be able to detect many of the layers of meaning interwoven into the story via different techniques.
Now that we've gone over why you should spend some time learning literary devices, let's take a look at some of the most important literary elements to know.
List of Literary Devices: 31 Literary Terms You Should Know
Below is a list of literary devices, most of which you'll often come across in both prose and poetry. We explain what each literary term is and give you an example of how it's used. This literary elements list is arranged in alphabetical order.
An allegory is a story that is used to represent a more general message about real-life (historical) issues and/or events. It is typically an entire book, novel, play, etc.
Example: George Orwell's dystopian book Animal Farm is an allegory for the events preceding the Russian Revolution and the Stalinist era in early 20th century Russia. In the story, animals on a farm practice animalism, which is essentially communism. Many characters correspond to actual historical figures: Old Major represents both the founder of communism Karl Marx and the Russian communist leader Vladimir Lenin; the farmer, Mr. Jones, is the Russian Czar; the boar Napoleon stands for Joseph Stalin; and the pig Snowball represents Leon Trotsky.
Alliteration
Alliteration is a series of words or phrases that all (or almost all) start with the same sound. These sounds are typically consonants to give more stress to that syllable. You'll often come across alliteration in poetry, titles of books and poems ( Jane Austen is a fan of this device, for example—just look at Pride and Prejudice and Sense and Sensibility ), and tongue twisters.
Example: "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers." In this tongue twister, the "p" sound is repeated at the beginning of all major words.
Allusion is when an author makes an indirect reference to a figure, place, event, or idea originating from outside the text. Many allusions make reference to previous works of literature or art.
Example: "Stop acting so smart—it's not like you're Einstein or something." This is an allusion to the famous real-life theoretical physicist Albert Einstein.
Anachronism
An anachronism occurs when there is an (intentional) error in the chronology or timeline of a text. This could be a character who appears in a different time period than when he actually lived, or a technology that appears before it was invented. Anachronisms are often used for comedic effect.
Example: A Renaissance king who says, "That's dope, dude!" would be an anachronism, since this type of language is very modern and not actually from the Renaissance period.
Anaphora is when a word or phrase is repeated at the beginning of multiple sentences throughout a piece of writing. It's used to emphasize the repeated phrase and evoke strong feelings in the audience.
Example: A famous example of anaphora is Winston Churchill's "We Shall Fight on the Beaches" speech. Throughout this speech, he repeats the phrase "we shall fight" while listing numerous places where the British army will continue battling during WWII. He did this to rally both troops and the British people and to give them confidence that they would still win the war.
Anthropomorphism
An anthropomorphism occurs when something nonhuman, such as an animal, place, or inanimate object, behaves in a human-like way.
Example: Children's cartoons have many examples of anthropomorphism. For example, Mickey and Minnie Mouse can speak, wear clothes, sing, dance, drive cars, etc. Real mice can't do any of these things, but the two mouse characters behave much more like humans than mice.
Asyndeton is when the writer leaves out conjunctions (such as "and," "or," "but," and "for") in a group of words or phrases so that the meaning of the phrase or sentence is emphasized. It is often used for speeches since sentences containing asyndeton can have a powerful, memorable rhythm.
Example: Abraham Lincoln ends the Gettysburg Address with the phrase "...and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the Earth." By leaving out certain conjunctions, he ends the speech on a more powerful, melodic note.
Colloquialism
Colloquialism is the use of informal language and slang. It's often used by authors to lend a sense of realism to their characters and dialogue. Forms of colloquialism include words, phrases, and contractions that aren't real words (such as "gonna" and "ain't").
Example: "Hey, what's up, man?" This piece of dialogue is an example of a colloquialism, since it uses common everyday words and phrases, namely "what's up" and "man."
An epigraph is when an author inserts a famous quotation, poem, song, or other short passage or text at the beginning of a larger text (e.g., a book, chapter, etc.). An epigraph is typically written by a different writer (with credit given) and used as a way to introduce overarching themes or messages in the work. Some pieces of literature, such as Herman Melville's 1851 novel Moby-Dick , incorporate multiple epigraphs throughout.
Example: At the beginning of Ernest Hemingway's book The Sun Also Rises is an epigraph that consists of a quotation from poet Gertrude Stein, which reads, "You are all a lost generation," and a passage from the Bible.
Epistrophe is similar to anaphora, but in this case, the repeated word or phrase appears at the end of successive statements. Like anaphora, it is used to evoke an emotional response from the audience.
Example: In Lyndon B. Johnson's speech, "The American Promise," he repeats the word "problem" in a use of epistrophe: "There is no Negro problem. There is no Southern problem. There is no Northern problem. There is only an American problem."

A euphemism is when a more mild or indirect word or expression is used in place of another word or phrase that is considered harsh, blunt, vulgar, or unpleasant.
Example: "I'm so sorry, but he didn't make it." The phrase "didn't make it" is a more polite and less blunt way of saying that someone has died.
A flashback is an interruption in a narrative that depicts events that have already occurred, either before the present time or before the time at which the narration takes place. This device is often used to give the reader more background information and details about specific characters, events, plot points, and so on.
Example: Most of the novel Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë is a flashback from the point of view of the housekeeper, Nelly Dean, as she engages in a conversation with a visitor named Lockwood. In this story, Nelly narrates Catherine Earnshaw's and Heathcliff's childhoods, the pair's budding romance, and their tragic demise.
Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is when an author indirectly hints at—through things such as dialogue, description, or characters' actions—what's to come later on in the story. This device is often used to introduce tension to a narrative.
Example: Say you're reading a fictionalized account of Amelia Earhart. Before she embarks on her (what we know to be unfortunate) plane ride, a friend says to her, "Be safe. Wouldn't want you getting lost—or worse." This line would be an example of foreshadowing because it implies that something bad ("or worse") will happen to Earhart.
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement that's not meant to be taken literally by the reader. It is often used for comedic effect and/or emphasis.
Example: "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse." The speaker will not literally eat an entire horse (and most likely couldn't ), but this hyperbole emphasizes how starved the speaker feels.
Imagery is when an author describes a scene, thing, or idea so that it appeals to our senses (taste, smell, sight, touch, or hearing). This device is often used to help the reader clearly visualize parts of the story by creating a strong mental picture.
Example: Here's an example of imagery taken from William Wordsworth's famous poem "I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud":
When all at once I saw a crowd, A host of golden Daffodils; Beside the Lake, beneath the trees, Fluttering and dancing in the breeze.
Irony is when a statement is used to express an opposite meaning than the one literally expressed by it. There are three types of irony in literature:
- Verbal irony: When someone says something but means the opposite (similar to sarcasm).
- Situational irony: When something happens that's the opposite of what was expected or intended to happen.
- Dramatic irony: When the audience is aware of the true intentions or outcomes, while the characters are not . As a result, certain actions and/or events take on different meanings for the audience than they do for the characters involved.
- Verbal irony: One example of this type of irony can be found in Edgar Allan Poe's "The Cask of Amontillado." In this short story, a man named Montresor plans to get revenge on another man named Fortunato. As they toast, Montresor says, "And I, Fortunato—I drink to your long life." This statement is ironic because we the readers already know by this point that Montresor plans to kill Fortunato.
- Situational irony: A girl wakes up late for school and quickly rushes to get there. As soon as she arrives, though, she realizes that it's Saturday and there is no school.
- Dramatic irony: In William Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet , Romeo commits suicide in order to be with Juliet; however, the audience (unlike poor Romeo) knows that Juliet is not actually dead—just asleep.

Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition is the comparing and contrasting of two or more different (usually opposite) ideas, characters, objects, etc. This literary device is often used to help create a clearer picture of the characteristics of one object or idea by comparing it with those of another.
Example: One of the most famous literary examples of juxtaposition is the opening passage from Charles Dickens' novel A Tale of Two Cities :
"It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair …"
Malapropism
Malapropism happens when an incorrect word is used in place of a word that has a similar sound. This misuse of the word typically results in a statement that is both nonsensical and humorous; as a result, this device is commonly used in comedic writing.
Example: "I just can't wait to dance the flamingo!" Here, a character has accidentally called the flamenco (a type of dance) the flamingo (an animal).
Metaphor/Simile
Metaphors are when ideas, actions, or objects are described in non-literal terms. In short, it's when an author compares one thing to another. The two things being described usually share something in common but are unalike in all other respects.
A simile is a type of metaphor in which an object, idea, character, action, etc., is compared to another thing using the words "as" or "like."
Both metaphors and similes are often used in writing for clarity or emphasis.
"What light through yonder window breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun." In this line from Romeo and Juliet , Romeo compares Juliet to the sun. However, because Romeo doesn't use the words "as" or "like," it is not a simile—just a metaphor.
"She is as vicious as a lion." Since this statement uses the word "as" to make a comparison between "she" and "a lion," it is a simile.
A metonym is when a related word or phrase is substituted for the actual thing to which it's referring. This device is usually used for poetic or rhetorical effect .
Example: "The pen is mightier than the sword." This statement, which was coined by Edward Bulwer-Lytton in 1839, contains two examples of metonymy: "the pen" refers to "the written word," and "the sword" refers to "military force/violence."
Mood is the general feeling the writer wants the audience to have. The writer can achieve this through description, setting, dialogue, and word choice .
Example: Here's a passage from J.R.R. Tolkien's The Hobbit: "It had a perfectly round door like a porthole, painted green, with a shiny yellow brass knob in the exact middle. The door opened on to a tube-shaped hall like a tunnel: a very comfortable tunnel without smoke, with panelled walls, and floors tiled and carpeted, provided with polished chairs, and lots and lots of pegs for hats and coats -- the hobbit was fond of visitors." In this passage, Tolkien uses detailed description to set create a cozy, comforting mood. From the writing, you can see that the hobbit's home is well-cared for and designed to provide comfort.
Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is a word (or group of words) that represents a sound and actually resembles or imitates the sound it stands for. It is often used for dramatic, realistic, or poetic effect.
Examples: Buzz, boom, chirp, creak, sizzle, zoom, etc.
An oxymoron is a combination of two words that, together, express a contradictory meaning. This device is often used for emphasis, for humor, to create tension, or to illustrate a paradox (see next entry for more information on paradoxes).
Examples: Deafening silence, organized chaos, cruelly kind, insanely logical, etc.
A paradox is a statement that appears illogical or self-contradictory but, upon investigation, might actually be true or plausible.
Note that a paradox is different from an oxymoron: a paradox is an entire phrase or sentence, whereas an oxymoron is a combination of just two words.
Example: Here's a famous paradoxical sentence: "This statement is false." If the statement is true, then it isn't actually false (as it suggests). But if it's false, then the statement is true! Thus, this statement is a paradox because it is both true and false at the same time.
Personification
Personification is when a nonhuman figure or other abstract concept or element is described as having human-like qualities or characteristics. (Unlike anthropomorphism where non-human figures become human-like characters, with personification, the object/figure is simply described as being human-like.) Personification is used to help the reader create a clearer mental picture of the scene or object being described.
Example: "The wind moaned, beckoning me to come outside." In this example, the wind—a nonhuman element—is being described as if it is human (it "moans" and "beckons").
Repetition is when a word or phrase is written multiple times, usually for the purpose of emphasis. It is often used in poetry (for purposes of rhythm as well).
Example: When Lin-Manuel Miranda, who wrote the score for the hit musical Hamilton, gave his speech at the 2016 Tony's, he recited a poem he'd written that included the following line:
And love is love is love is love is love is love is love is love cannot be killed or swept aside.
Satire is genre of writing that criticizes something , such as a person, behavior, belief, government, or society. Satire often employs irony, humor, and hyperbole to make its point.
Example: The Onion is a satirical newspaper and digital media company. It uses satire to parody common news features such as opinion columns, editorial cartoons, and click bait headlines.
A type of monologue that's often used in dramas, a soliloquy is when a character speaks aloud to himself (and to the audience), thereby revealing his inner thoughts and feelings.
Example: In Romeo and Juliet , Juliet's speech on the balcony that begins with, "O Romeo, Romeo! Wherefore art thou Romeo?" is a soliloquy, as she is speaking aloud to herself (remember that she doesn't realize Romeo's there listening!).
Symbolism refers to the use of an object, figure, event, situation, or other idea in a written work to represent something else— typically a broader message or deeper meaning that differs from its literal meaning.
The things used for symbolism are called "symbols," and they'll often appear multiple times throughout a text, sometimes changing in meaning as the plot progresses.
Example: In F. Scott Fitzgerald's 1925 novel The Great Gatsby , the green light that sits across from Gatsby's mansion symbolizes Gatsby's hopes and dreams .
A synecdoche is a literary device in which part of something is used to represent the whole, or vice versa. It's similar to a metonym (see above); however, a metonym doesn't have to represent the whole—just something associated with the word used.
Example: "Help me out, I need some hands!" In this case, "hands" is being used to refer to people (the whole human, essentially).
While mood is what the audience is supposed to feel, tone is the writer or narrator's attitude towards a subject . A good writer will always want the audience to feel the mood they're trying to evoke, but the audience may not always agree with the narrator's tone, especially if the narrator is an unsympathetic character or has viewpoints that differ from those of the reader.
Example: In an essay disdaining Americans and some of the sites they visit as tourists, Rudyard Kipling begins with the line, "Today I am in the Yellowstone Park, and I wish I were dead." If you enjoy Yellowstone and/or national parks, you may not agree with the author's tone in this piece.

How to Identify and Analyze Literary Devices: 4 Tips
In order to fully interpret pieces of literature, you have to understand a lot about literary devices in the texts you read. Here are our top tips for identifying and analyzing different literary techniques:
Tip 1: Read Closely and Carefully
First off, you'll need to make sure that you're reading very carefully. Resist the temptation to skim or skip any sections of the text. If you do this, you might miss some literary devices being used and, as a result, will be unable to accurately interpret the text.
If there are any passages in the work that make you feel especially emotional, curious, intrigued, or just plain interested, check that area again for any literary devices at play.
It's also a good idea to reread any parts you thought were confusing or that you didn't totally understand on a first read-through. Doing this ensures that you have a solid grasp of the passage (and text as a whole) and will be able to analyze it appropriately.
Tip 2: Memorize Common Literary Terms
You won't be able to identify literary elements in texts if you don't know what they are or how they're used, so spend some time memorizing the literary elements list above. Knowing these (and how they look in writing) will allow you to more easily pinpoint these techniques in various types of written works.
Tip 3: Know the Author's Intended Audience
Knowing what kind of audience an author intended her work to have can help you figure out what types of literary devices might be at play.
For example, if you were trying to analyze a children's book, you'd want to be on the lookout for child-appropriate devices, such as repetition and alliteration.
Tip 4: Take Notes and Bookmark Key Passages and Pages
This is one of the most important tips to know, especially if you're reading and analyzing works for English class. As you read, take notes on the work in a notebook or on a computer. Write down any passages, paragraphs, conversations, descriptions, etc., that jump out at you or that contain a literary device you were able to identify.
You can also take notes directly in the book, if possible (but don't do this if you're borrowing a book from the library!). I recommend circling keywords and important phrases, as well as starring interesting or particularly effective passages and paragraphs.
Lastly, use sticky notes or post-its to bookmark pages that are interesting to you or that have some kind of notable literary device. This will help you go back to them later should you need to revisit some of what you've found for a paper you plan to write.
What's Next?
Looking for more in-depth explorations and examples of literary devices? Join us as we delve into imagery , personification , rhetorical devices , tone words and mood , and different points of view in literature, as well as some more poetry-specific terms like assonance and iambic pentameter .
Reading The Great Gatsby for class or even just for fun? Then you'll definitely want to check out our expert guides on the biggest themes in this classic book, from love and relationships to money and materialism .
Got questions about Arthur Miller's The Crucible ? Read our in-depth articles to learn about the most important themes in this play and get a complete rundown of all the characters .
For more information on your favorite works of literature, take a look at our collection of high-quality book guides and our guide to the 9 literary elements that appear in every story !

These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Hannah received her MA in Japanese Studies from the University of Michigan and holds a bachelor's degree from the University of Southern California. From 2013 to 2015, she taught English in Japan via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft , Book Design
Last updated on May 22, 2024
100 Literary Devices With Examples: The Ultimate List
About the author.
Reedsy's editorial team is a diverse group of industry experts devoted to helping authors write and publish beautiful books.
About Martin Cavannagh
Head of Content at Reedsy, Martin has spent over eight years helping writers turn their ambitions into reality. As a voice in the indie publishing space, he has written for a number of outlets and spoken at conferences, including the 2024 Writers Summit at the London Book Fair.
Literary devices are perhaps the greatest tools that writers have in literature. Just think — Shakespeare could have written: Everyone has a role in life.
Instead, he used a literary device and penned what is likely the most famous metaphor in literature:
All the world’s a stage
And all the men and women merely players
And the rest is history.

What are literary devices?
A literary device is a writing technique that writers use to express ideas, convey meaning, and highlight important themes in a piece of text. A metaphor, like we mentioned earlier, is a famous example of a literary device.
These devices serve a wide range of purposes in literature. Some might work on an intellectual level, while others have a more emotional effect. They may also work subtly to improve the flow of your writing. No matter what, if you're looking to inject something special into your prose, literary devices are a great place to start.
How to identify literary devices
A writer using a literary device is quite different from a reader identifying it. Often, an author’s use of a literary device is subtle by design —you only feel its effect, and not its presence.
Therefore, we’ve structured this post for both purposes:
- If you’re a reader, we’ve included examples for each literary device to make it easier for you to identify them in the wild.
- If you’re a writer, we’ve included exercises for the literary devices, so that you can practice using them in your works.
Let’s get to it.
100 common literary devices, with examples
1. alliteration.
Alliteration describes a series of words in quick succession that all start with the same letter or sound. It lends a pleasing cadence to prose and Hamlet and the dollar as currency in Macbeth .
Example: “ One short sleepe past, wee wake eternally,
And death shall be no more; death, thou shalt die.” — “Death, Be Not Proud” by John Donne
Exercise: Pick a letter and write a sentence where every word starts with that letter or one that sounds similar.
2. Anaphora
Anaphora is the repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of a series of clauses or sentences. It’s often seen in poetry and speeches, intended to provoke an emotional response in its audience.
Example: Martin Luther King’s 1963 “I Have A Dream” speech.
“I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed.
"… and I have a dream that one day on the red hills of Georgia the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit together at the table of brotherhood.
"… I have a dream that little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin, but by the content of their character.”
Exercise: Pick a famous phrase and write a paragraph elaborating on an idea, beginning each sentence with that phrase.
Related term: repetition
3. Anastrophe
Anastrophe is a figure of speech wherein the traditional sentence structure is reversed. So a typical verb-subject-adjective sentence such as “Are you ready?” becomes a Yoda-esque adjective-verb-subject question: “Ready, are you?” Or a standard adjective-noun pairing like “tall mountain” becomes “mountain tall.”
Example: “Deep into that darkness peering, long I stood there wondering, fearing.” — “The Raven” by Edgar Allan Poe
Exercise: Write a standard verb-subject-adjective sentence or adjective-noun pairing then flip the order to create an anastrophe. How does it change the meaning or feeling of the sentence?
4. Chiasmus
Chiasmus is when two or more parallel clauses are inverted. “Why would I do that?” you may be wondering. Well, a chiasmus might sound confusing and unnecessary in theory, but it's much more convincing in practice — and in fact, you've likely already come across it before.
Example: “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.” — John F. Kennedy
5. Congeries
Congeries is a fancy literary term for creating a list. The items in your list can be words, ideas, or phrases, and by displaying them this way helps prove or emphasize a point — or even create a sense of irony. Occasionally, it’s also called piling as the words are “piling up.”
Example: "Apart from better sanitation and medicine and education and irrigation and public health and roads and a freshwater system and baths and public order, what have the Romans done for us?" — Monty Python’s Life of Brian
6. Cumulative sentence
A cumulative sentence (or “loose sentence”) is one that starts with an independent clause, but then has additional or modifying clauses. They’re often used for contextual or clarifying details. This may sound complex, but even, “I ran to the store to buy milk, bread, and toilet paper” is a cumulative sentence, because the first clause, “I ran to the store,” is a complete sentence, while the rest tells us extra information about your run to the store.
Example: “It was a large bottle of gin Albert Cousins had brought to the party, yes, but it was in no way large enough to fill all the cups, and in certain cases to fill them many times over, for the more than one hundred guests, some of whom were dancing not four feet in front of him.” – Commonwealth by Ann Patchett
Example: Write three sentences that are related to each other. Can you combine the information into a cumulative sentence?

FREE RESOURCE
Literary Devices Cheatsheet
Master these 40+ devices to level up your writing skills.
7. Epistrophe
Epistrophe is the opposite of anaphora, with this time a word or phrase being repeated at the end of a sentence. Though its placement in a sentence is different it serves the same purpose—creating emphasis—as an anaphora does.
Example: “I’ll be ever’where – wherever you look. Wherever they’s a fight so hungry people can eat, I’ll be there. Wherever they’s a cop beatin’ up a guy, I’ll be there . If Casy knowed, why, I’ll be in the way guys yell when they’re mad an’ – I’ll be in the way kids laugh when they’re hungry an’ they know supper’s ready. An’ when our folks eat the stuff they raise an’ live in the houses they build, why, I’ll be there .” — The Grapes of Wrath by John Steinbeck
Related terms: repetition, anaphora
Exercise: Write a paragraph where a phrase or a word is repeated at the end of every sentence, emphasizing the point you’re trying to make.
8. Erotesis
Erotesis is a close cousin of the rhetorical question. Rather than a question asked without expectation of an answer, this is when the question (and the asker) confidently expects a response that is either negative or affirmative.
Example: “ Do you then really think that you have committed your follies in order to spare your son them?” — Siddhartha by Herman Hesse
Related term: rhetorical question
9. Hyperbaton
Hyperbaton is the inversion of words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence that differs from how they would normally be arranged. It comes from the Greek hyperbatos, which means “transposed” or “inverted.” While it is similar to anastrophe, it doesn’t have the same specific structure and allows you to rearrange your sentences in whatever order you want.
Example: “Object there was none. Passion there was none. I loved the old man. He had never wronged me. He had never given me insult. For his gold I had no desire.” — “The Tell-Tale Heart” by Edgar Allan Poe
Related terms: anastrophe, epistrophe
10. Isocolon
If you’re a neat freak who likes things just so , isocolon is the literary device for you. This is when two or more phrases or clauses have similar structure, rhythm, and even length — such that, when stacked up on top of each other, they would line up perfectly. Isocolon often crops up in brand slogans and famous sayings; the quick, balanced rhythm makes the phrase catchier and more memorable.
Example: Veni, vidi, vici (“I came, I saw, I conquered”)
11. Litotes
Litotes (pronounced lie-toe-teez ) is the signature literary device of the double negative. Writers use litotes to express certain sentiments through their opposites, by saying that that opposite is not the case. Don’t worry, it makes more sense with the examples. 😉
Examples: “You won’t be sorry” (meaning you’ll be happy); “you’re not wrong” (meaning you’re right); “I didn’t not like it” (meaning I did)
12. Malapropism
If Shakespeare is the king of metaphors, Michael Scott is the king of malapropisms . A malapropism is when similar-sounding words replace their appropriate counterparts, typically to comic effect — one of the most commonly cited is “dance a flamingo,” rather than a “flamenco.” Malapropisms are often employed in dialogue when a character flubs up their speech.
Example: “I am not to be truffled with.”
Exercise: Choose a famous or common phrase and see if you can replace a word with a similar sounding one that changes the meaning.

13. Onomatopoeia
Amusingly, onomatopoeia (itself a difficult-to-pronounce word) refers to words that sound like the thing they’re referring to. Well-known instances of onomatopoeia include whiz, buzz, snap, grunt, etc.
Example: The excellent children's book Click, Clack, Moo: Cows That Type . “Farmer Brown has a problem. His cows like to type. All day long he hears: Click, clack, moo. Click, clack, moo. Clickety, clack, moo. ”
Exercise: Take some time to listen to the sounds around you and write down what you hear. Now try to use those sounds in a short paragraph or story.
14. Oxymoron
An oxymoron comes from two contradictory words that describe one thing. While juxtaposition contrasts two story elements, oxymorons are about the actual words you are using.
Example: "Parting is such sweet sorrow.” — Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare. (Find 100 more examples of oxymorons here .)
Related terms: juxtaposition, paradox
Exercise: Choose two words with opposite meanings and see if you can use them in a sentence to create a coherent oxymoron.

15. Parallelism
Parallelism is all about your sentence structure. It’s when similar ideas, sounds, phrases, or words are arranged in a way that is harmonious or creates a parallel, hence the name. It can add rhythm and meter to any piece of writing and can often be found in poetry.
Example: “ That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” — Neil Armstrong
Which famous author do you write like?
Find out which literary luminary is your stylistic soulmate. Takes one minute!
16. Polysyndeton
Instead of using a single conjunction in lengthy statements, polysyndeton uses several in succession for a dramatic effect . This one is definitely for authors looking to add a bit of artistic flair to their writing, or who are hoping to portray a particular (usually naïve) sort of voice.
Example: “Luster came away from the flower tree and we went along the fence and they stopped and we stopped and I looked through the fence while Luster was hunting in the grass.” — The Sound and the Fury by William Faulkner
Exercise: Write three or four independent sentences. Try combining them using conjunctions. What kind of effect does this have on the overall meaning and tone of the piece?
17. Portmanteau
A portmanteau is when two words are combined to form a new word which refers to a single concept that retains the meanings of both the original words. Modern language is full of portmanteaus. In fact, the portmanteau is itself a portmanteau. It’s a combination of the French porter (to carry) and manteau (cloak).
Example: Brunch (breakfast and lunch); cosplay (costume and roleplay); listicle (list and article); romcom (romance and comedy)
Exercise: Pick two words that are often used together to describe a single concept. See if there’s a way to combine them and create a single word that encompasses the meaning of both.
18. Repetition
Repetition , repetition, repetition… where would we be without it? Though too much repetition is rarely a good thing, occasional repetition can be used quite effectively to drill home a point, or to create a certain atmosphere. For example, horror writers often use repetition to make the reader feel trapped and scared.
Example: In The Shining , Jack Torrance types over and over again on his pages, “All work and no play makes Jack a dull boy.” In this case, obsessive repetition demonstrates the character’s unraveling mind.
Related term: anaphora
Exercise: Repetition can be used to call attention to an idea or phrase. Pick an idea you want to emphasize and write a few sentences about it. Are there any places where you can add repetition to make it more impactful?

19. Tautology
A tautology is when a sentence or short paragraph repeats a word or phrase, expressing the same idea twice. Often, this is a sign that you should trim your work to remove the redundancy (such as “frozen ice”) but can also be used for poetic emphasis.
Example: "But the fact is I was napping, and so gently you came rapping, And so faintly you came tapping, tapping at my chamber door" – “The Raven” by Edgar Allan Poe
20. Tmesis
Tmesis is when a word or phrase is broken up by an interjecting word, such as abso-freaking-lutely. It’s used to draw out and emphasize the idea, often with a humorous or sarcastic slant.
Example: "This is not Romeo, he's some-other-where." – Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
21. Allegory
An allegory is a type of narrative that uses characters and plot to depict abstract ideas and themes. In an allegorical story, things represent more than they appear to on the surface. Many children's fables, such as The Tortoise and the Hare , are simple allegories about morality — but allegories can also be dark, complex, and controversial.
Example: Animal Farm by George Orwell. This dystopian novella is one of modern literature’s best-known allegories. A commentary on the events leading up to Stalin's rise and the formation of the Soviet Union, the pigs at the heart of the novel represent figures such as Stalin, Trotsky, and Molotov.
Exercise: Pick a major trend or problem in the world and consider what defines it. Try and create a story where that trend plays out on a smaller scale.
For more inspiration for how to use allegories to explore your themes, check out this guide on themes.
22. Anecdote
An anecdote is like a short story within a story. Sometimes, they are incredibly short—only a line or two—and their purpose is to add a character’s perspective, knowledge, or experience to a situation. They can be inspirational, humorous, or be used to inspire actions in others. Since anecdotes are so short, don’t expect them to be part of a main story. They’re usually told by a character and part of the dialogue.
Example: Marcel Proust’s Swann’s Way , part of his series of novels, In Search of Lost Time, deals with the themes of remembrance and memory. In one section of this book, to illustrate these ideas, the main character recalls an important memory of eating a madeleine cookie. “Many years had elapsed during which nothing of Combray, save what was comprised in the theatre and the drama of my going to bed there, had any existence for me, when one day in winter, as I came home, my mother, seeing that I was cold, offered me some tea, a thing I did not ordinarily take. I declined at first, and then, for no particular reason, changed my mind. She sent out for one of those short, plump little cakes called ‘petites madeleines,’ which look as though they had been moulded in the fluted scallop of a pilgrim’s shell.”
23. Deus Ex Machina
Literally meaning “god in the machine” in Greek, deus ex machina is a plot device where an impossible situation is solved by the appearance of an unexpected or unheard of character, action, object, or event. This brings about a quick and usually happy resolution for a story and can be used to surprise an audience, provide comic relief, or provide a fix for a complicated plot. However, deus ex machinas aren’t always looked upon favorably and can sometimes be seen as lazy writing, so they should be used sparingly and with great thought.
Example: William Golding’s famous novel of a group of British boys marooned on a desert island is resolved with a deus ex machina. At the climax of The Lord of the Flies, as all threads converge and Ralph is about to be killed by Jack, a naval officer arrives to rescue the boys and bring them back to civilization. It’s an altogether unexpected and bloodless ending for a story about the boys’ descent into savagery.
Exercise: Consider the ending of your favorite book or movie and then write an alternate ending that uses a deus ex machina to resolve the main conflict. How does this affect the overall story in terms of theme and tone?
If you struggle to write consistently, sign up for our How to Write a Novel course to finish a novel in just 3 months.

NEW REEDSY COURSE
How to Write a Novel
Enroll in our course and become an author in three months.
24. Dramatic irony
Dramatic irony is when the readers know more about the situation going on than at least one of the characters involved. This creates a difference between the ways the audience and the characters perceive unfolding events. For instance, if we know that one character is having an affair, when that character speaks to their spouse, we will pick up on the lies and double-meanings of their words, while the spouse may take them at face value.
Example: In Titanic , the audience knows from the beginning of the movie that the boat will sink. This creates wry humor when characters remark on the safety of the ship.
25. Exposition
Exposition is when the narrative provides background information in order to help the reader understand what’s going on. When used in conjunction with description and dialogue, this literary device provides a richer understanding of the characters, setting, and events. Be careful, though — too much exposition will quickly become boring, thus undercutting the emotional impact of your work.
Example: “The Dursley’s had everything they wanted, but they also had a secret, and their greatest fear was that somebody would discover it.” – Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone by J.K. Rowling
Exercise: Pick your favorite story and write a short paragraph introducing it to someone who knows nothing about it.
26. Flashback
Flashbacks to previous events split up present-day scenes in a story, usually to build suspense toward a big reveal. Flashbacks are also an interesting way to present exposition for your story, gradually revealing to the reader what happened in the past.
Example: Every other chapter in the first part of Gone Girl is a flashback, with Amy’s old diary entries describing her relationship with her husband before she disappeared.
Related term: foreshadowing
27. Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is when the author hints at events yet to come in a story. Similar to flashbacks (and often used in conjunction with them), this technique is also used to create tension or suspense — giving readers just enough breadcrumbs to keep them hungry for more.
Example: One popular method of foreshadowing is through partial reveals — the narrator leaves out key facts to prompt readers’ curiosity. Jeffrey Eugenides does this in The Virgin Suicides : “On the morning the last Lisbon daughter took her turn at suicide — it was Mary this time, and sleeping pills, like Therese, the two paramedics arrived at the house knowing exactly where the knife drawer was, and the gas oven, and the beam in the basement from which it was possible to tie a rope.”
Related term: flashback
Exercise: Go back to your favorite book or movie. Can you identify any instances of foreshadowing in the early portions of the story for events that happen in the future?
28. Frame story
A frame story is any part of the story that "frames" another part of it, such as one character telling another about their past, or someone uncovering a diary or a series of news articles that then tell the readers what happened. Since the frame story supports the rest of the plot, it is mainly used at the beginning and the end of the narrative, or in small interludes between chapters or short stories.
Example: In The Name of the Wind by Patrick Rothfuss, Kvothe is telling Chronicler the story of his life over the span of three days. Most of the novel is the story he is telling, while the frame is any part that takes place in the inn.
29. In Medias Res
In medias res is a Latin term that means "in the midst of things" and is a way of starting a narrative without exposition or contextual information . It launches straight into a scene or action that is already unfolding.
Example: “Many years later, as he faced the firing squad, Colonel Aureliano Buendía was to remember that distant afternoon when his father took him to discover ice.” — The opening line of One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel García Márquez
Exercise: Pick a story you enjoy and rewrite the opening scene so that it starts in the middle of the story.
30. Point of view
Point of view is, of course, the mode of narration in a story. There are many POVs an author can choose, and each one will have a different impact on the reading experience.
Example: Second person POV is uncommon because it directly addresses the reader — not an easy narrative style to pull off. One popular novel that manages to employ this perspective successfully is Bright Lights, Big City by Jay McInerney: “You are not the kind of guy who would be at a place like this at this time of the morning. But here you are, and you cannot say that the terrain is entirely unfamiliar, although the details are fuzzy.”
Exercise: Write a short passage in either first, second, or third person. Then rewrite that passage in the other two points of view, only changing the pronouns. How does the change in POV affect the tone and feel of the story?

FREE COURSE
Understanding Point of View
Learn to master different POVs and choose the best for your story.
31. Soliloquy
Soliloquy involves a character speaking their thoughts aloud, usually at length (and often in a Shakespeare play). The character in question may be alone or in the company of others, but they’re not speaking for the benefit of other people; the purpose of a soliloquy is for a character to reflect independently.
Example: Hamlet’s “to be or not to be” speech, in which he ruminates on the nature of life and death, is a classic dramatic soliloquy.
Exercise: Pick a character from your favorite book or movie and write a soliloquy from their point of view where they consider their thoughts and feelings on an important part of their story or character arc.
Which writing app is right for you?
Find out here! Takes 30 seconds
Tone refers to the overall mood and message of your book. It’s established through a variety of means, including voice, characterization, symbolism, and themes. Tone sets the feelings you want your readers to take away from the story.
Example: No matter how serious things get in The Good Place , there is always a chance for a character to redeem themselves by improving their behavior. The tone remains hopeful for the future of humanity in the face of overwhelming odds.
Exercise: Write a short paragraph in an upbeat tone. Now using the same situation you came up with, rewrite that passage in a darker or sadder tone.
33. Tragicomedy
Tragicomedy is just what it sounds like: a blend of tragedy and comedy. Tragicomedy helps an audience process darker themes by allowing them to laugh at the situation even when circumstances are bleak.
Example: Lemony Snicket’s A Series of Unfortunate Events uses wordplay, absurd situations, and over-the-top characters to provide humor in an otherwise tragic story.
34. Allusion
An allusion is a reference to a person, place, thing, concept, or other literary work that a reader is likely to recognize. A lot of meaning can be packed into an allusion and it’s often used to add depth to a story. Many works of classic Western literature will use allusions to the Bible to expand on or criticize the morals of their time.
Example: “The two knitting women increase his anxiety by gazing at him and all the other sailors with knowing unconcern. Their eerie looks suggest that they know what will happen (the men dying), yet don’t care.” The two women knitting in this passage from Joseph Conrad’s Heart of Darkness are a reference to the Fates from Greek mythology, who decide the fate of humanity by spinning and cutting the threads of life.
Exercise: In a relatively simple piece of writing, see how many times you can use allusions. Go completely crazy. Once you’re finished, try to cut it down to a more reasonable amount and watch for how it creates deeper meaning in your piece.
35. Analogy
An analogy connects two seemingly unrelated concepts to show their similarities and expand on a thought or idea. They are similar to metaphors and similes, but usually take the comparison much further than either of these literary devices as they are used to support a claim rather than provide imagery.
Example: “ It has been well said that an author who expects results from a first novel is in a position similar to that of a man who drops a rose petal down the Grand Canyon of Arizona and listens for the echo.” — P.G. Wodehouse
Exercise: Pick two seemingly unrelated nouns and try to connect them with a verb to create an analogy.
36. Anthropomorphism
To anthropomorphize is to apply human traits or qualities to a non-human thing such as objects, animals, or the weather. But unlike personification, in which this is done through figurative description, anthropomorphism is literal: a sun with a smiling face, for example, or talking dogs in a cartoon.
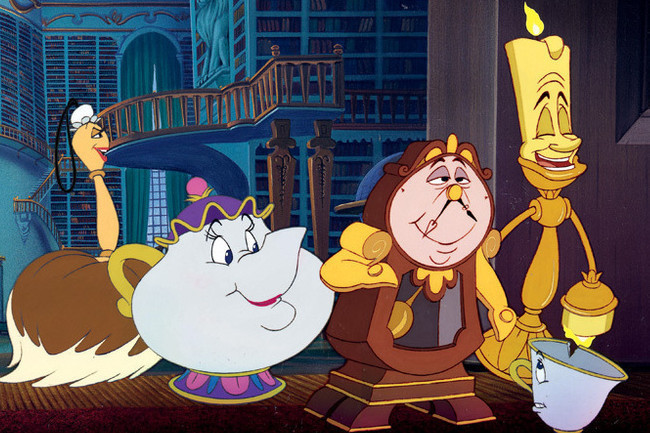
Examples: In Disney’s Beauty and the Beast , Mrs. Potts the teapot, Cogsworth the clock, and Lumière the candlestick are all household objects that act and behave like humans (which, of course, they were when they weren’t under a spell).
Related term: personification
Exercise: Pick a non-human object and describe it as if it was human, literally ascribing human thoughts, feelings, and senses to it.

37. Aphorism
An aphorism is a universally accepted truth stated in a concise, to-the-point way. Aphorisms are typically witty and memorable, often becoming adages or proverbs as people repeat them over and over.
Example: “To err is human, to forgive divine.” — Alexander Pope
38. Archetype
An archetype is a “universal symbol” that brings familiarity and context to a story. It can be a character, a setting, a theme, or an action. Archetypes represent feelings and situations that are shared across cultures and time periods, and are therefore instantly recognizable to any audience — for instance, the innocent child character, or the theme of the inevitability of death.
Example: Superman is a heroic archetype: noble, self-sacrificing, and drawn to righting injustice whenever he sees it.
Exercise: Pick an archetype — either a character or a theme — and use it to write a short piece centered around that idea.
To learn more about archetypes, check out these 12 common ones that all writers should know.
A cliché is a saying or idea that is used so often it becomes seen as unoriginal. These phrases might become so universal that, despite their once intriguing nature, they're now looked down upon as uninteresting and overused.
Examples: Some common cliches you might have encountered are phrases like “easy as pie” and “light as a feather.” Some lines from famous books and movies have become so popular that they are now in and of themselves cliches such as Darth Vader’s stunning revelation from The Empire Strikes Back, “Luke, I am your father.” Also, many classic lines of Shakespeare are now considered cliches like, “All that glitters is not gold” from The Merchant of Venice.
Exercise: Write a short passage using as many cliches as possible. Now try to cut them out and replace them with more original phrasing. See how the two passages compare.
40. Colloquialism
Colloquialism is the use of casual and informal language in writing, which can also include slang. Writers use colloquialisms to provide context to settings and characters, and to make their writing sound more authentic, especially in spoken form . Imagine reading a YA novel that takes place in modern America, and the characters speak to each other like this:
“Good morning, Sue. I hope that you slept well and are prepared for this morning’s science exam.”
It’s not realistic. Colloquialisms help create believable dialogue:
“Hey Sue, what’d you get up to last night? This science test is gonna suck.”
Example: Trainspotting by Irvine Welsh takes place in Scotland, a fact made undeniably obvious by the dialect: “Thing is, as ye git aulder, this character-deficiency gig becomes mair sapping. Thir wis a time ah used tae say tae aw the teachers, bosses, dole punters, poll-tax guys, magistrates, when they telt me ah was deficient: ’Hi, cool it, gadge, ah’m jist me, jist intae a different sort ay gig fae youse but, ken?’”
Exercise: Write a dialogue between two characters as formally as possible. Now take that conversation and make it more colloquial. Imagine that you’re having this conversation with a friend. Mimic your own speech patterns as you write.
41. Euphemism
A euphemism is an indirect, “polite” way of describing something too inappropriate or awkward to address directly. However, most people will still understand the truth about what's happening.
Example: When an elderly person is forced to retire, some might say they’re being “put out to pasture.”
Exercise: Write a paragraph where you say things very directly. Now rewrite that paragraph using only euphemisms.
42. Hyperbole
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement that emphasizes the significance of the statement’s actual meaning. When a friend says, "Oh my god, I haven't seen you in a million years," that's hyperbole.
Example: “At that time Bogotá was a remote, lugubrious city where an insomniac rain had been falling since the beginning of the 16th century.” — Living to Tell the Tale by Gabriel García Márquez
Exercise: Tall tales often make use of hyperbole to tell an exaggerated story. Use hyperbole to relate a completely mundane event or experience to turn it into a tall tale.
43. Hypophora
Hypophora is much like a rhetorical question, wherein someone asks a question that doesn't require an answer. However, in hypophora, the person raises a question and answers it immediately themselves (hence the prefix hypo, meaning 'under' or 'before'). It’s often used when characters are reasoning something aloud.
Example: “Do you always watch for the longest day of the year and then miss it? I always watch for the longest day in the year and then miss it.” — Daisy in The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald

An idiom is a saying that uses figurative language whose meaning differs from what it literally says. These phrases originate from common cultural experiences, even if that experience has long ago been forgotten. Without cultural context, idioms don’t often make sense and can be the toughest part for non-native speakers to understand.
Example: In everyday use, idioms are fairly common. We say things like, “It’s raining cats and dogs” to say that it’s downpouring.
Exercise: Idioms are often used in dialogue. Write a conversation between two people where idioms are used to express their main points.
45. Imagery
Imagery appeals to readers’ senses through highly descriptive language. It’s crucial for any writer hoping to follow the rule of "show, don’t tell," as strong imagery truly paints a picture of the scene at hand.
Example: “In the hard-packed dirt of the midway, after the glaring lights are out and the people have gone to bed, you will find a veritable treasure of popcorn fragments, frozen custard dribblings, candied apples abandoned by tired children, sugar fluff crystals, salted almonds, popsicles, partially gnawed ice cream cones and wooden sticks of lollipops.” — Charlotte's Web by E.B. White
Exercise: Choose an object, image, or idea and use the five senses to describe it.

Show, Don't Tell
Master the golden rule of writing in 10 five-minute lessons.
Irony creates a contrast between how things seem and how they really are. There are three types of literary irony: dramatic (when readers know what will happen before characters do), situational (when readers expect a certain outcome, only to be surprised by a turn of events), and verbal (when the intended meaning of a statement is the opposite of what was said).
Example: This opening scene from Orson Welles’ A Touch of Evil is a great example of how dramatic irony can create tension.
47. Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition places two or more dissimilar characters, themes, concepts, etc. side by side, and the profound contrast highlights their differences. Why is juxtaposition such an effective literary device? Well, because sometimes the best way for us to understand something is by understanding what it’s not .
Example: In the opening lines of A Tale of Two Cities , Charles Dickens uses juxtaposition to emphasize the societal disparity that led to the French Revolution: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness…”
Related terms: oxymoron, paradox
Exercise: Pick two ideas, objects, places, or people that seem like complete opposites. Introduce them side by side in the beginning of your piece and highlight their similarities and differences throughout.
48. Metaphor
A metaphor compares two similar things by saying that one of them is the other. As you'd likely expect, when it comes to literary devices, this one is a heavy hitter. And if a standard metaphor doesn't do the trick, a writer can always try an extended metaphor: a metaphor that expands on the initial comparison through more elaborate parallels .
Example: Metaphors are literature’s bread and butter (metaphor intended) — good luck finding a novel that is free of them. Here’s one from Frances Hardinge’s A Face Like Glass : “Wishes are thorns, he told himself sharply. They do us no good, just stick into our skin and hurt us.”
Related term: simile
Exercise: Write two lists: one with tangible objects and the other concepts. Mixing and matching, try to create metaphors where you describe the concepts using physical objects.
One metaphor example not enough? Check out this post , which has 97 of ‘em!
49. Metonymy
Metonymy is like symbolism, but even more so. A metonym doesn’t just symbolize something else, it comes to serve as a synonym for that thing or things — typically, a single object embodies an entire institution.
Examples: “The crown” representing the monarchy, “Washington” representing the U.S. government.
Related term: synecdoche
Exercise: Create a list of ten common metonymies you might encounter in everyday life and speech.
Whatever form a motif takes, it recurs throughout the novel and helps develop the theme of the narrative . This might be a symbol, concept, or image.
Example: In Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy, trains are an omnipresent motif that symbolize transition, derailment, and ultimately violent death and destruction.
Related term: symbol
Exercise: Pick a famous book or movie and see if you can identify any common motifs within it.
51. Non sequitur
Non sequiturs are statements that don't logically follow what precedes them. They’ll often be quite absurd and can lend humor to a story. But they’re just not good for making jokes. They can highlight missing information or a miscommunication between characters and even be used for dramatic effect.
Example: “It was a spring day, the sort that gives people hope: all soft winds and delicate smells of warm earth. Suicide weather.” — Girl, Interrupted by Susanna Kaysen
Exercise: Write a conversation that gets entirely derailed by seemingly unrelated non sequiturs.
52. Paradox
Paradox derives from the Greek word paradoxon , which means “beyond belief.” It’s a statement that asks people to think outside the box by providing seemingly illogical — and yet actually true — premises.
Example: In George Orwell’s 1984 , the slogan of the totalitarian government is built on paradoxes: “War is Peace, Freedom is Slavery, Ignorance is Strength.” While we might read these statements as obviously contradictory, in the context of Orwell’s novel, these blatantly corrupt sentiments have become an accepted truth.
Related terms: oxymoron, juxtaposition
Exercise: Try writing your own paradox. First, think of two opposing ideas that can be juxtaposed against each other. Then, create a situation where these contradictions coexist with each other. What can you gather from this unique perspective?
53. Personification
Personification uses human traits to describe non-human things. Again, while the aforementioned anthropomorphism actually applies these traits to non-human things, personification means the behavior of the thing does not actually change. It's personhood in figurative language only.
Example: “Just before it was dark, as they passed a great island of Sargasso weed that heaved and swung in the light sea as though the ocean were making love with something under a yellow blanket, his small line was taken by a dolphin.” — The Old Man and the Sea by Ernest Hemingway
Related term: anthropomorphism
Exercise: Pick a non-human object and describe it using human traits, this time using similes and metaphors rather than directly ascribing human traits to it.
54. Rhetorical question
A rhetorical question is asked to create an effect rather than to solicit an answer from the listener or reader. Often it has an obvious answer and the point of asking is to create emphasis. It’s a great way to get an audience to consider the topic at hand and make a statement.
Example: “If you prick us, do we not bleed? If you tickle us, do we not laugh? If you poison us, do we not die? And if you wrong us, shall we not revenge?” — The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare
Writers use satire to make fun of some aspect of human nature or society — usually through exaggeration, ridicule, or irony. There are countless ways to satirize something; most of the time, you know it when you read it.
Example: The famous adventure novel Gulliver’s Travels by Jonathan Swift is a classic example of satire, poking fun at “travelers' tales,” the government, and indeed human nature itself.
A simile draws resemblance between two things by saying “Thing A is like Thing B,” or “Thing A is as [adjective] as Thing B.” Unlike a metaphor, a similar does not posit that these things are the same, only that they are alike. As a result, it is probably the most common literary device in writing — you can almost always recognize a simile through the use of “like” or “as.”
Example: There are two similes in this description from Circe by Madeline Miller: “The ships were golden and huge as leviathans, their rails carved from ivory and horn. They were towed by grinning dolphins or else crewed by fifty black-haired nereids, faces silver as moonlight.”
Related term: metaphor
57. Symbolism
Authors turn to tangible symbols to represent abstract concepts and ideas in their stories Symbols typically derive from objects or non-humans — for instance, a dove might represent peace, or a raven might represent death.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , Fitzgerald uses the eyes of Doctor T.J. Eckleburg (actually a faded optometrist's billboard) to represent God and his judgment of the Jazz Age.
Related term: motif
Exercise: Choose an object that you want to represent something — like an idea or concept. Now, write a poem or short story centered around that symbol.
58. Synecdoche
Synecdoche is the usage of a part to represent the whole. That is, rather than an object or title that’s merely associated with the larger concept (as in metonymy), synecdoche must actually be attached in some way: either to the name, or to the larger whole itself.
Examples: “Stanford won the game” ( Stanford referring to the full title of the Stanford football team) or “Nice wheels you got there” ( wheels referring to the entire car)
Related term: metonymy
Zeugma is when one word is used to ascribe two separate meanings to two other words. This literary device is great for adding humor and figurative flair as it tends to surprise the reader. And it’s just a fun type of wordplay.
Example: “ Yet time and her aunt moved slowly — and her patience and her ideas were nearly worn out before the tete-a-tete was over.” — Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen
60. Zoomorphism
Zoomorphism is when you take animal traits and assign them to anything that’s not an animal. It’s the opposite of anthropomorphism and personification, and can be either a physical manifestation, such as a god appearing as an animal, or a comparison, like calling someone a busy bee .
Example: When vampires turn into bats, their bat form is an instance of zoomorphism.
Exercise: Describe a human or object by using traits that are usually associated with animals.
Related terms: anthropomorphism, personification
61. Enjambment
French for “straddle,” enjambment denotes the continuation of a sentence from one poetic line to the next. It’s the opposite of an end-stopped line.
Example : The first line in T.S. Eilot’s “The Waste Land” is an example of enjambment:
“April is the cruellest month, breeding
Lilacs out of the dead land, mixing.”
Related terms: end-stop
62. Euphony
Euphony is the acoustic effect of a combination of words that’s pleasing to the ear. Indeed, it leads by example: if you say “euphony” out loud, the assonance of the word itself is harmonious.
Example: “Shall I compare thee to a summer’s day? / Thou art more lovely and more temperate.”
Related terms: cacophony, alliteration
63. Pathetic fallacy
Pathetic fallacy is a form of personification, where an author gives human emotions to an inanimate object.
Example: “The sky wept.”
64. Anagram
If you like puzzles, you might have already heard of an anagram : a new word or phrase a writer can form by re-ordering the letters of another word. Note that an anagram is not the same as a palindrome or a semordnilap, as the letters need to come in a different order, and not simply read back to front.
Example: “brag” is an anagram of “grab,” and vice versa. We can go on. “Night” is an anagram of “thing”!
Related terms: palindrome, semordnilap
65. Antithesis
Made up of two different words (“anti” and “thesis”), antithesis is a literary device that juxtaposes opposing ideas, words, or images. Usually, these two contrasting ideas will be written with similar grammatical structure for dramatic effect.
Example: Neil Armstrong perhaps unintentionally created an example of antithesis when he famously said, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.”
Related terms: juxtaposition
66. Circumlocution
Circumlocution is the opposite of saying something directly: instead, it’s when a writer states something in an ambiguous, unclear, or roundabout way. “Talking in circles” is the end result.
Example: Look to any politicians for examples of circumlocution. The pigs in George Orwell’s Animal Farm , for instance, vaguely say in many words, “For the time being it has been found necessary to make a readjustment of rations,” in order to mask the fact that they’ve simply stolen food from the other animals.
Related terms: periphrasis
67. Epigraph
In literature, an epigraph is the quotation (or sometimes the phrase) at the beginning of a book or chapter. It’s entirely optional on the author’s part, but can offer a thematic direction for the reader.
Example: In The Sun Also Rises , Ernest Hemingway uses Gertrude Stein’s “You are all a lost generation” quote to kick off a chapter.
Related terms: intertextuality
Mood in writing refers to the emotions that the writer makes a reader feel through the text. Many factors contribute to this effect, but the writer’s use of language is perhaps the most primary of them.
Example: When you read an Agatha Christie novel, what do you feel? Happy? Excited? Joyous? Probably not. You’re more likely to be nervous, anxious, and tense because of her stories — and that’s in part due to the suspenseful mood she successfully creates through her language.
Related terms: atmosphere
69. Diction
Diction refers to the words that an author chooses to put in writing. This linguistic choice helps the writer express an idea, or achieve a certain effect. In speech, it also refers to the style of enunciation.
Example: The diction that an author chooses for their characters is important, and can tell you about the characters themselves — whether they’re rich or poor, where they’re from, and how old they are. “
Related terms: tone, dialogue, narrative voice
70. Vignette
As a literary device, a vignette is a short scene without a beginning, middle, or end. Instead, it starts in medias res and captures a certain moment in time or is a character-creating detail.
Example: The cold opens of many sitcoms are great examples of vignettes. They are short scenes unrelated to the main plot of the episode, but set the humorous mood that will follow.
Related terms: in medias res
A foil character is a supporting character whose main purpose is to provide contrast to the protagonist in some shape or form, whether it’s the protagonist’s traits, dreams, or goals.
Example: In Pride and Prejudice , Mr. Wickham serves as Mr. Darcy’s foil. Without Wickham’s decadent, gold-digging ways, we’d never learn the extent of Darcy’s honesty, or his goodness.
72. Antistrophe
The term antistrophe describes a specific type of repetition — that of a word, or a phrase, repeating at the end of consecutive sentences. You’ll commonly see it used in poetry, although books and speeches will also make use of it.
Example: “Wherever there's a fight so hungry people can eat, I’ll be there. Wherever they’s a cop beatin’ up a guy, I’ll be there. […] An’ when our folks eat the stuff they raise an’ live in the houses they build — why, I’ll be there.” — John Steinbeck, Grapes of Wrath
73. Polyptoton
As you’re reading this post, do you find it readable? Congrats: you just encountered a case of polyptoton , which is otherwise known as the repetition of two words that share the shame root (“reading” and “readable,” for instance, “trick” and “trickery,” or “ignorant” and “ignorance.”)
Example: In the phrase, “Who shall watch the watchmen?”, the repetition of “watch” and “watchmen” is an example of polyptoton.
74. Anthimeria
Anthimeria captures the act of turning a word from one part of speech into another: for instance, when an author uses a word that was originally a noun as a verb.
Example: “Chill” is perhaps a popular example by now. Originally a noun, it’s now used everywhere as a verb that means “to relax.”
75. Double entendre
A double entendre is exactly what it says on the tin: a word with two, or double, meanings. What’s more? Often the second meaning is something a tad risqué.
Example: William Shakespeare was a master when it came to double entendres. Just take Mercutio’s statement: “Ask for me tomorrow, and you shall find me a grave man.” Here, the word “grave” pulls double duty, as it means both to be “serious” and hints at death.
Related terms: pun
76. Paraprosdokian
Paraprosdokian literally means “against expectations” in Greek—so you might be able to guess how it functions as a literary device. Yep, that’s right: it describes a sentence with an unexpected ending.
Example: As Oscar Wilde once said, “Some cause happiness wherever they go. Others, whenever they go.”
Related terms: paradoxical
77. Intertextuality
Whenever a text is referenced, either directly or indirectly, in another text, that’s an instance of intertextuality : the derived relationship between two works.
Example: Every reference that the musical “Hamilton” makes to another musical is an example of intertextuality.
78. Palindrome
A palindrome is the easiest literary device on your eyes: it’s a word or phrase that you can read the same either backward or forward.
Example: “Madam, I’m Adam” is exactly the same read backward as it is read forward. “Radar,” meanwhile, is an example of a word that’s a palindrome. Or the famous “Redrum” from The Shining .
79. Spoonerism
If you’ve ever mispronounced a phrase before, you might’ve accidentally created a spoonerism , which refers to a person swapping the sound of two or more words.
Example: You’d be committing a spoonerism if, instead of “bunny rabbit,” you said “runny babbit.”
80. Ellipsis
As a narrative device, an ellipsis means the omission of certain words or parts of the plot, so as to give the readers an opportunity to fill in the gaps themselves.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald lets the ellipsis form a time lapse that is up to the reader to interpret: “ ... I was standing beside his bed and he was sitting up between the sheets, clad in his underwear, with a great portfolio in his hands.”
81. Parataxi
Literally, a parataxi describes the placing of consecutive words without a connecting word to show the relationship between them. It is different from hypotaxi, as you’ll soon see.
Example: “I came, I saw, I conquered.” — Julius Caesar.
Related terms: hypotaxi
82. Hypotaxi
A hypotaxi is the opposite of a parataxi in that it adds connecting words (or conjunctions) to show readers exactly what the relationship between two clauses is.
Example: In the sentence, “I ate an apple because I was hungry,” the word ‘because’ makes it a hypotaxi.
Related terms: parataxi
Aporia captures the moment when the speaker pretends not to know something, or expresses doubt, in order to prove a point. Often this confusion is completely feigned when used rhetorically, bordering on irony, although sometimes it can be genuine.
Example: As Elizabeth Barrett Browning once asked, “How do I love thee?”. Or, like when someone replies “I don’t know, can you?” when you ask if you can use the bathroom.
Related terms: irony
84. Asyndeton
We’ve covered polysyndetons. Now get ready for its sibling, the asyndeton , which describes the act of intentionally omitting conjunctions in a sentence.
Example: “Live, laugh, love.”
Related terms: polysyndeton, syndeton, parataxi
85. Meiosis
Nope, this isn’t the kind of meiosis you learned about in high school biology! In literature, meiosis is instead a rhetorical device where the speaker understates something to belittle a undermine or situation.
Example: You’d be using meiosis if you said “Oh, it’s only a scratch” to describe a deep, gaping wound that’s bleeding out of the bone.
86. Paralipsis
A paralipsis is what it’s called when you emphasize something about a situation, person, or topic by claiming that you don’t know much about it. Yes, it’s a little passive-aggressive, if that’s what you’re also thinking right now.
Example: “Of course, that’s not to mention my most hated enemy’s billion-dollar debt, nor their complete unwillingness to pay it.”
Related terms: apophasis
87. Overstatement
An overstatement is the best literary device of all time. There’s nothing better in the world than an overstatement (which is when you exaggerate your language to make your point in some shape or form).
Example: “This is officially the worst day of my life,” one says, upon accidentally dropping one’s ice cream cone on the ground with a splat.
Related terms: understatement
88. Apophasis
As another rhetorical device that’s just slightly passive-aggressive, an apophasis does the trick of bringing up a subject by denying that you’re bringing it up.
Example: “We won’t speak of his absolute inability to be a decent human being. Nor will we even begin to speak of his atrocious gambling problem.”
89. Cacophony
The opposite of euphony, cacophony is the term used to describe a combination of discordant tones that do not sound good together.
Example: You’ll see this literary device used a lot in poetry, for instance, in Samuel Taylor Coleridge’s “The Rime of the Ancient Mariner”:
"With throats unslaked, with black lips baked,
Agape they heard me call:
Related terms: euphony
90. Connotation
Connotation refers to what an author or speaker implies through the use of a particular word. It’s usually non-literal, and up to the reader to interpret.
Example: The connotation of the word “miserly” is quite negative, and evokes the image of a Grinch hoarding money, while “frugal” connotes someone who’s merely thoughtful about saving money.
91. Dysphemism
When you choose to use an offensive or derogatory term in place of a neutral or agreeable one, you’re using a dysphemism .
Example: “He’s a nerd” instead of positively describing that someone is smart or factually stating that someone often studies is an instance of a dysphemism.
Related terms: euphemism
92. Hyperbaton
Inverting the regular sequence of words is called a hyperbaton . Authors generally do this to call emphasis to a certain phrase, or part of the sentence.
Example: Yoda from Star Wars is a famous abuser of hyperbaton, with his Go you must’s and Miss them, do not’s .
Related terms: anastrophe
93. Metanoia
In literature, metanoia is a self-correction, or when a writer deliberately takes back a statement they just made in order to re-state it.
Example: In the Hippocratic Oath that doctors take before getting their credentials, they promise “To help, or, at least, to do no harm.” The second half of it is the instance of metanoia.
You know them. You love them. Yes, puns , or jokes that are wordplays on the different meanings or sounds of a word, are also literary devices that authors use to add humor to a piece of writing.
Example: “Denial isn’t just a river in Egypt.”
95. Parenthesis
Parentheses are a form of punctuation, but when used in literature, they can insert information that authors would like to add for detail.
Example: Author Sarah Vowell once wrote in her book, Take the Cannoli , "I have a similar affection for the parenthesis (but I always take most of my parentheses out, so as not to call undue attention to the glaring fact that I cannot think in complete sentences, that I think only in short fragments or long, run-on thought relays that the literati call stream of consciousness but I still like to think of as disdain for the finality of the period)."
96. Synesthesia
Like its psychological definition, synesthesia in literature describes the conflation of two senses. This might materialize in the author using one sense to describe another, or blend the two altogether.
Example: "The silence that dwells in the forest is not so black." — Oscar Wilde
97. Eutrepismus
Eutrepismus is a long word for a simple concept: stating your points in a numbered list, so as to structure your speech, or dialogue.
Example: “Firstly, you’ll want to read this post. Secondly, you’ll want to memorize every single literary device on it.”
98. Epizeuxis
Epizeuxis is another hard-to-spell-and-pronounce literary device that captures a very simple concept: it’s the repetition of a word to emphasize it.
Example: “Hark, hark! The Lark!” — William Shakespeare

99. Narrative voice
Narrative voice is the voice from which a story in literature is told. It encompasses all of the decisions that an author makes in regards to voice, including tone, word choice, and diction.
Example: First-person books like Catcher in the Rye provide good examples of books written in a strong narrative voice.
100. Syllepsis
We saved one of the most obscure (and best!) literary devices for last. Syllepsis is another form of wordplay (similar to a pun) where a word, usually a verb, is used in multiple ways.
Example: “She blew my nose, and then she blew my mind.” — The Rolling Stones
Related terms: zeugma, pun
Readers and writers alike can get a lot out of understanding literary devices and how they're used. Readers can use them to gain insight into the author’s intended meaning behind their work, while writers can use literary devices to better connect with readers. But whatever your motivation for learning them, you certainly won't be sorry you did! (Not least because you'll recognize the device I just used in that sentence 😉)
6 responses
Ron B. Saunders says:
16/01/2019 – 19:26
Paraprosdokians are also delightful literary devices for creating surprise or intrigue. They cause a reader to rethink a concept or traditional expectation. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraprosdokian)
ManhattanMinx says:
17/01/2019 – 02:07
That's pore, not pour. Shame.....
↪️ Coline Harmon replied:
14/06/2019 – 19:06
It was a Malapropism
↪️ JC JC replied:
23/10/2019 – 00:02
Yeah ManhattanMinx. It's a Malepropism!
↪️ jesus replied:
07/11/2019 – 13:24
Susan McGrath says:
10/03/2020 – 10:56
"But whatever your motivation for learning them, you certainly won't be sorry you did! (Not least because you'll recognize the device I just used in that sentence. 😏)" Litote
Comments are currently closed.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

450+ Powerful Adjectives to Describe a Person (With Examples)
Want a handy list to help you bring your characters to life? Discover words that describe physical attributes, dispositions, and emotions.

How to Plot a Novel Like a NYT Bestselling Author
Need to plot your novel? Follow these 7 steps from New York Times bestselling author Caroline Leavitt.

How to Write an Autobiography: The Story of Your Life
Want to write your autobiography but aren’t sure where to start? This step-by-step guide will take you from opening lines to publishing it for everyone to read.

What is the Climax of a Story? Examples & Tips
The climax is perhaps a story's most crucial moment, but many writers struggle to stick the landing. Let's see what makes for a great story climax.

What is Tone in Literature? Definition & Examples
We show you, with supporting examples, how tone in literature influences readers' emotions and perceptions of a text.

Writing Cozy Mysteries: 7 Essential Tips & Tropes
We show you how to write a compelling cozy mystery with advice from published authors and supporting examples from literature.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

- Ask LitCharts AI
- Discussion Question Generator
- Essay Prompt Generator
- Quiz Question Generator

- Literature Guides
- Poetry Guides
- Shakespeare Translations
- Literary Terms

Literary Devices & Terms
| # | G | W | X | Y |
An acrostic is a piece of writing in which a particular set of letters—typically the first letter of each line, word, or paragraph—spells out a word or phrase with special significance to the text. Acrostics... (read full acrostic explanation with examples) An acrostic is a piece of writing in which a particular set of letters—typically the first letter of each line,... (read more)
An allegory is a work that conveys a hidden meaning—usually moral, spiritual, or political—through the use of symbolic characters and events. The story of "The Tortoise and The Hare" is a well-known allegory with a... (read full allegory explanation with examples) An allegory is a work that conveys a hidden meaning—usually moral, spiritual, or political—through the use of symbolic characters and... (read more)
Alliteration is a figure of speech in which the same sound repeats in a group of words, such as the “b” sound in: “Bob brought the box of bricks to the basement.” The repeating sound... (read full alliteration explanation with examples) Alliteration is a figure of speech in which the same sound repeats in a group of words, such as the... (read more)
In literature, an allusion is an unexplained reference to someone or something outside of the text. Writers commonly allude to other literary works, famous individuals, historical events, or philosophical ideas, and they do so in... (read full allusion explanation with examples) In literature, an allusion is an unexplained reference to someone or something outside of the text. Writers commonly allude to... (read more)
An anachronism is a person or a thing placed in the wrong time period. For instance, if a novel set in Medieval England featured a trip to a movie-theater, that would be an anachronism. Although... (read full anachronism explanation with examples) An anachronism is a person or a thing placed in the wrong time period. For instance, if a novel set... (read more)
Anadiplosis is a figure of speech in which a word or group of words located at the end of one clause or sentence is repeated at or near the beginning of the following clause or... (read full anadiplosis explanation with examples) Anadiplosis is a figure of speech in which a word or group of words located at the end of one... (read more)
An analogy is a comparison that aims to explain a thing or idea by likening it to something else. For example, a career coach might say, "Being the successful boss or CEO of a company... (read full analogy explanation with examples) An analogy is a comparison that aims to explain a thing or idea by likening it to something else. For... (read more)
An anapest is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which two unstressed syllables are followed by a stressed syllable. The word "understand" is an anapest, with the unstressed syllables of "un" and "der" followed... (read full anapest explanation with examples) An anapest is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which two unstressed syllables are followed by a stressed syllable.... (read more)
Anaphora is a figure of speech in which words repeat at the beginning of successive clauses, phrases, or sentences. For example, Martin Luther King's famous "I Have a Dream" speech contains anaphora: "So let freedom... (read full anaphora explanation with examples) Anaphora is a figure of speech in which words repeat at the beginning of successive clauses, phrases, or sentences. For... (read more)
An antagonist is usually a character who opposes the protagonist (or main character) of a story, but the antagonist can also be a group of characters, institution, or force against which the protagonist must contend.... (read full antagonist explanation with examples) An antagonist is usually a character who opposes the protagonist (or main character) of a story, but the antagonist can... (read more)
Antanaclasis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated within a sentence, but the word or phrase means something different each time it appears. A famous example of antanaclasis is... (read full antanaclasis explanation with examples) Antanaclasis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated within a sentence, but the word... (read more)
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human characteristics, emotions, and behaviors to animals or other non-human things (including objects, plants, and supernatural beings). Some famous examples of anthropomorphism include Winnie the Pooh, the Little Engine that Could, and Simba from... (read full anthropomorphism explanation with examples) Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human characteristics, emotions, and behaviors to animals or other non-human things (including objects, plants, and supernatural beings). Some famous... (read more)
Antimetabole is a figure of speech in which a phrase is repeated, but with the order of words reversed. John F. Kennedy's words, "Ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you... (read full antimetabole explanation with examples) Antimetabole is a figure of speech in which a phrase is repeated, but with the order of words reversed. John... (read more)
Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance, Neil Armstrong used antithesis when he stepped onto the surface of the moon in 1969... (read full antithesis explanation with examples) Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance,... (read more)
An aphorism is a saying that concisely expresses a moral principle or an observation about the world, presenting it as a general or universal truth. The Rolling Stones are responsible for penning one of the... (read full aphorism explanation with examples) An aphorism is a saying that concisely expresses a moral principle or an observation about the world, presenting it as... (read more)
Aphorismus is a type of figure of speech that calls into question the way a word is used. Aphorismus is used not to question the meaning of a word, but whether it is actually appropriate... (read full aphorismus explanation with examples) Aphorismus is a type of figure of speech that calls into question the way a word is used. Aphorismus is... (read more)
Aporia is a rhetorical device in which a speaker expresses uncertainty or doubt—often pretended uncertainty or doubt—about something, usually as a way of proving a point. An example of aporia is the famous Elizabeth Barrett... (read full aporia explanation with examples) Aporia is a rhetorical device in which a speaker expresses uncertainty or doubt—often pretended uncertainty or doubt—about something, usually as... (read more)
Apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses someone (or something) that is not present or cannot respond in reality. The entity being addressed can be an absent, dead, or imaginary... (read full apostrophe explanation with examples) Apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses someone (or something) that is not present or... (read more)
Assonance is a figure of speech in which the same vowel sound repeats within a group of words. An example of assonance is: "Who gave Newt and Scooter the blue tuna? It was too soon!" (read full assonance explanation with examples) Assonance is a figure of speech in which the same vowel sound repeats within a group of words. An example... (read more)
An asyndeton (sometimes called asyndetism) is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and", "or", and "but" that join other words or clauses in a sentence into relationships of equal importance—are omitted.... (read full asyndeton explanation with examples) An asyndeton (sometimes called asyndetism) is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and", "or", and "but"... (read more)
A ballad is a type of poem that tells a story and was traditionally set to music. English language ballads are typically composed of four-line stanzas that follow an ABCB rhyme scheme. (read full ballad explanation with examples) A ballad is a type of poem that tells a story and was traditionally set to music. English language ballads... (read more)
A ballade is a form of lyric poetry that originated in medieval France. Ballades follow a strict rhyme scheme ("ababbcbc"), and typically have three eight-line stanzas followed by a shorter four-line stanza called an envoi.... (read full ballade explanation with examples) A ballade is a form of lyric poetry that originated in medieval France. Ballades follow a strict rhyme scheme ("ababbcbc"),... (read more)
Bildungsroman is a genre of novel that shows a young protagonist's journey from childhood to adulthood (or immaturity to maturity), with a focus on the trials and misfortunes that affect the character's growth. (read full bildungsroman explanation with examples) Bildungsroman is a genre of novel that shows a young protagonist's journey from childhood to adulthood (or immaturity to maturity),... (read more)
Blank verse is the name given to poetry that lacks rhymes but does follow a specific meter—a meter that is almost always iambic pentameter. Blank verse was particularly popular in English poetry written between the... (read full blank verse explanation with examples) Blank verse is the name given to poetry that lacks rhymes but does follow a specific meter—a meter that is... (read more)
A cacophony is a combination of words that sound harsh or unpleasant together, usually because they pack a lot of percussive or "explosive" consonants (like T, P, or K) into relatively little space. For instance, the... (read full cacophony explanation with examples) A cacophony is a combination of words that sound harsh or unpleasant together, usually because they pack a lot of... (read more)
A caesura is a pause that occurs within a line of poetry, usually marked by some form of punctuation such as a period, comma, ellipsis, or dash. A caesura doesn't have to be placed in... (read full caesura explanation with examples) A caesura is a pause that occurs within a line of poetry, usually marked by some form of punctuation such... (read more)
Catharsis is the process of releasing strong or pent-up emotions through art. Aristotle coined the term catharsis—which comes from the Greek kathairein meaning "to cleanse or purge"—to describe the release of emotional tension that he... (read full catharsis explanation with examples) Catharsis is the process of releasing strong or pent-up emotions through art. Aristotle coined the term catharsis—which comes from the... (read more)
Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through direct description, in which the character's qualities are described by a narrator, another character, or... (read full characterization explanation with examples) Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through... (read more)
Chiasmus is a figure of speech in which the grammar of one phrase is inverted in the following phrase, such that two key concepts from the original phrase reappear in the second phrase in inverted... (read full chiasmus explanation with examples) Chiasmus is a figure of speech in which the grammar of one phrase is inverted in the following phrase, such... (read more)
The word cinquain can refer to two different things. Historically, it referred to any stanza of five lines written in any type of verse. More recently, cinquain has come to refer to particular types of... (read full cinquain explanation with examples) The word cinquain can refer to two different things. Historically, it referred to any stanza of five lines written in... (read more)
A cliché is a phrase that, due to overuse, is seen as lacking in substance or originality. For example, telling a heartbroken friend that there are "Plenty of fish in the sea" is such a... (read full cliché explanation with examples) A cliché is a phrase that, due to overuse, is seen as lacking in substance or originality. For example, telling... (read more)
Climax is a figure of speech in which successive words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are arranged in ascending order of importance, as in "Look! Up in the sky! It's a bird! It's a plane! It's... (read full climax (figure of speech) explanation with examples) Climax is a figure of speech in which successive words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are arranged in ascending order of... (read more)
The climax of a plot is the story's central turning point—the moment of peak tension or conflict—which all the preceding plot developments have been leading up to. In a traditional "good vs. evil" story (like many superhero movies)... (read full climax (plot) explanation with examples) The climax of a plot is the story's central turning point—the moment of peak tension or conflict—which all the preceding plot... (read more)
Colloquialism is the use of informal words or phrases in writing or speech. Colloquialisms are usually defined in geographical terms, meaning that they are often defined by their use within a dialect, a regionally-defined variant... (read full colloquialism explanation with examples) Colloquialism is the use of informal words or phrases in writing or speech. Colloquialisms are usually defined in geographical terms,... (read more)
Common meter is a specific type of meter that is often used in lyric poetry. Common meter has two key traits: it alternates between lines of eight syllables and lines of six syllables, and it... (read full common meter explanation with examples) Common meter is a specific type of meter that is often used in lyric poetry. Common meter has two key... (read more)
A conceit is a fanciful metaphor, especially a highly elaborate or extended metaphor in which an unlikely, far-fetched, or strained comparison is made between two things. A famous example comes from John Donne's poem, "A... (read full conceit explanation with examples) A conceit is a fanciful metaphor, especially a highly elaborate or extended metaphor in which an unlikely, far-fetched, or strained... (read more)
Connotation is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary definition. Most words carry meanings, impressions, or associations apart from or beyond their literal meaning. For example, the... (read full connotation explanation with examples) Connotation is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary definition. Most words... (read more)
Consonance is a figure of speech in which the same consonant sound repeats within a group of words. An example of consonance is: "Traffic figures, on July Fourth, to be tough." (read full consonance explanation with examples) Consonance is a figure of speech in which the same consonant sound repeats within a group of words. An example... (read more)
A couplet is a unit of two lines of poetry, especially lines that use the same or similar meter, form a rhyme, or are separated from other lines by a double line break. (read full couplet explanation with examples) A couplet is a unit of two lines of poetry, especially lines that use the same or similar meter, form... (read more)
A dactyl is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by two unstressed syllables. The word “poetry” itself is a great example of a dactyl, with the stressed syllable... (read full dactyl explanation with examples) A dactyl is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by two unstressed syllables.... (read more)
Denotation is the literal meaning, or "dictionary definition," of a word. Denotation is defined in contrast to connotation, which is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary... (read full denotation explanation with examples) Denotation is the literal meaning, or "dictionary definition," of a word. Denotation is defined in contrast to connotation, which is... (read more)
The dénouement is the final section of a story's plot, in which loose ends are tied up, lingering questions are answered, and a sense of resolution is achieved. The shortest and most well known dénouement, it could be... (read full dénouement explanation with examples) The dénouement is the final section of a story's plot, in which loose ends are tied up, lingering questions are answered, and... (read more)
A deus ex machina is a plot device whereby an unsolvable conflict or point of tension is suddenly resolved by the unexpected appearance of an implausible character, object, action, ability, or event. For example, if... (read full deus ex machina explanation with examples) A deus ex machina is a plot device whereby an unsolvable conflict or point of tension is suddenly resolved by... (read more)
Diacope is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated with a small number of intervening words. The first line of Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy, "Happy families are all alike;... (read full diacope explanation with examples) Diacope is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated with a small number of intervening... (read more)
Dialogue is the exchange of spoken words between two or more characters in a book, play, or other written work. In prose writing, lines of dialogue are typically identified by the use of quotation marks... (read full dialogue explanation with examples) Dialogue is the exchange of spoken words between two or more characters in a book, play, or other written work.... (read more)
Diction is a writer's unique style of expression, especially his or her choice and arrangement of words. A writer's vocabulary, use of language to produce a specific tone or atmosphere, and ability to communicate clearly... (read full diction explanation with examples) Diction is a writer's unique style of expression, especially his or her choice and arrangement of words. A writer's vocabulary,... (read more)
Dramatic irony is a plot device often used in theater, literature, film, and television to highlight the difference between a character's understanding of a given situation, and that of the audience. More specifically, in dramatic... (read full dramatic irony explanation with examples) Dramatic irony is a plot device often used in theater, literature, film, and television to highlight the difference between a... (read more)
A dynamic character undergoes substantial internal changes as a result of one or more plot developments. The dynamic character's change can be extreme or subtle, as long as his or her development is important to... (read full dynamic character explanation with examples) A dynamic character undergoes substantial internal changes as a result of one or more plot developments. The dynamic character's change... (read more)
An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, especially one mourning the loss of someone who died. Elegies are defined by their subject matter, and don't have to follow any specific form in terms of... (read full elegy explanation with examples) An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, especially one mourning the loss of someone who died. Elegies are defined... (read more)
End rhyme refers to rhymes that occur in the final words of lines of poetry. For instance, these lines from Dorothy Parker's poem "Interview" use end rhyme: "The ladies men admire, I’ve heard, / Would shudder... (read full end rhyme explanation with examples) End rhyme refers to rhymes that occur in the final words of lines of poetry. For instance, these lines from... (read more)
An end-stopped line is a line of poetry in which a sentence or phrase comes to a conclusion at the end of the line. For example, the poet C.P. Cavafy uses end-stopped lines in his... (read full end-stopped line explanation with examples) An end-stopped line is a line of poetry in which a sentence or phrase comes to a conclusion at the... (read more)
Enjambment is the continuation of a sentence or clause across a line break. For example, the poet John Donne uses enjambment in his poem "The Good-Morrow" when he continues the opening sentence across the line... (read full enjambment explanation with examples) Enjambment is the continuation of a sentence or clause across a line break. For example, the poet John Donne uses... (read more)
An envoi is a brief concluding stanza at the end of a poem that can either summarize the preceding poem or serve as its dedication. The envoi tends to follow the same meter and rhyme... (read full envoi explanation with examples) An envoi is a brief concluding stanza at the end of a poem that can either summarize the preceding poem... (read more)
Epanalepsis is a figure of speech in which the beginning of a clause or sentence is repeated at the end of that same clause or sentence, with words intervening. The sentence "The king is dead,... (read full epanalepsis explanation with examples) Epanalepsis is a figure of speech in which the beginning of a clause or sentence is repeated at the end... (read more)
An epigram is a short and witty statement, usually written in verse, that conveys a single thought or observation. Epigrams typically end with a punchline or a satirical twist. (read full epigram explanation with examples) An epigram is a short and witty statement, usually written in verse, that conveys a single thought or observation. Epigrams... (read more)
An epigraph is a short quotation, phrase, or poem that is placed at the beginning of another piece of writing to encapsulate that work's main themes and to set the tone. For instance, the epigraph of Mary... (read full epigraph explanation with examples) An epigraph is a short quotation, phrase, or poem that is placed at the beginning of another piece of writing to... (read more)
Epistrophe is a figure of speech in which one or more words repeat at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences. In his Gettysburg Address, Abraham Lincoln urged the American people to ensure that,... (read full epistrophe explanation with examples) Epistrophe is a figure of speech in which one or more words repeat at the end of successive phrases, clauses,... (read more)
Epizeuxis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated in immediate succession, with no intervening words. In the play Hamlet, when Hamlet responds to a question about what he's reading... (read full epizeuxis explanation with examples) Epizeuxis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated in immediate succession, with no intervening... (read more)
Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the... (read full ethos explanation with examples) Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
Euphony is the combining of words that sound pleasant together or are easy to pronounce, usually because they contain lots of consonants with soft or muffled sounds (like L, M, N, and R) instead of consonants with harsh, percussive sounds (like... (read full euphony explanation with examples) Euphony is the combining of words that sound pleasant together or are easy to pronounce, usually because they contain lots of consonants with soft... (read more)
Exposition is the description or explanation of background information within a work of literature. Exposition can cover characters and their relationship to one another, the setting or time and place of events, as well as... (read full exposition explanation with examples) Exposition is the description or explanation of background information within a work of literature. Exposition can cover characters and their... (read more)
An extended metaphor is a metaphor that unfolds across multiple lines or even paragraphs of a text, making use of multiple interrelated metaphors within an overarching one. So while "life is a highway" is a... (read full extended metaphor explanation with examples) An extended metaphor is a metaphor that unfolds across multiple lines or even paragraphs of a text, making use of... (read more)
An external conflict is a problem, antagonism, or struggle that takes place between a character and an outside force. External conflict drives the action of a plot forward. (read full external conflict explanation with examples) An external conflict is a problem, antagonism, or struggle that takes place between a character and an outside force. External conflict... (read more)
The falling action of a story is the section of the plot following the climax, in which the tension stemming from the story's central conflict decreases and the story moves toward its conclusion. For instance, the traditional "good... (read full falling action explanation with examples) The falling action of a story is the section of the plot following the climax, in which the tension stemming from... (read more)
Figurative language is language that contains or uses figures of speech. When people use the term "figurative language," however, they often do so in a slightly narrower way. In this narrower definition, figurative language refers... (read full figurative language explanation with examples) Figurative language is language that contains or uses figures of speech. When people use the term "figurative language," however, they... (read more)
A figure of speech is a literary device in which language is used in an unusual—or "figured"—way in order to produce a stylistic effect. Figures of speech can be broken into two main groups: figures... (read full figure of speech explanation with examples) A figure of speech is a literary device in which language is used in an unusual—or "figured"—way in order to... (read more)
A character is said to be "flat" if it is one-dimensional or lacking in complexity. Typically, flat characters can be easily and accurately described using a single word (like "bully") or one short sentence (like "A naive... (read full flat character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "flat" if it is one-dimensional or lacking in complexity. Typically, flat characters can be easily... (read more)
Foreshadowing is a literary device in which authors hint at plot developments that don't actually occur until later in the story. Foreshadowing can be achieved directly or indirectly, by making explicit statements or leaving subtle... (read full foreshadowing explanation with examples) Foreshadowing is a literary device in which authors hint at plot developments that don't actually occur until later in the... (read more)
Formal verse is the name given to rhymed poetry that uses a strict meter (a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables). This two-line poem by Emily Dickinson is formal verse because it rhymes and... (read full formal verse explanation with examples) Formal verse is the name given to rhymed poetry that uses a strict meter (a regular pattern of stressed and... (read more)
Free verse is the name given to poetry that doesn’t use any strict meter or rhyme scheme. Because it has no set meter, poems written in free verse can have lines of any length, from... (read full free verse explanation with examples) Free verse is the name given to poetry that doesn’t use any strict meter or rhyme scheme. Because it has... (read more)
Hamartia is a literary term that refers to a tragic flaw or error that leads to a character's downfall. In the novel Frankenstein, Victor Frankenstein's arrogant conviction that he can usurp the roles of God... (read full hamartia explanation with examples) Hamartia is a literary term that refers to a tragic flaw or error that leads to a character's downfall. In... (read more)
Hubris refers to excessive pride or overconfidence, which drives a person to overstep limits in a way that leads to their downfall. In Greek mythology, the legend of Icarus involves an iconic case of hubris:... (read full hubris explanation with examples) Hubris refers to excessive pride or overconfidence, which drives a person to overstep limits in a way that leads to... (read more)
Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which a writer or speaker exaggerates for the sake of emphasis. Hyperbolic statements are usually quite obvious exaggerations intended to emphasize a point, rather than be taken literally.... (read full hyperbole explanation with examples) Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which a writer or speaker exaggerates for the sake of emphasis. Hyperbolic statements... (read more)
An iamb is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which one unstressed syllable is followed by a stressed syllable. The word "define" is an iamb, with the unstressed syllable of "de" followed by the... (read full iamb explanation with examples) An iamb is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which one unstressed syllable is followed by a stressed syllable.... (read more)
An idiom is a phrase that conveys a figurative meaning that is difficult or impossible to understand based solely on a literal interpretation of the words in the phrase. For example, saying that something is... (read full idiom explanation with examples) An idiom is a phrase that conveys a figurative meaning that is difficult or impossible to understand based solely on... (read more)
Imagery, in any sort of writing, refers to descriptive language that engages the human senses. For instance, the following lines from Robert Frost's poem "After Apple-Picking" contain imagery that engages the senses of touch, movement,... (read full imagery explanation with examples) Imagery, in any sort of writing, refers to descriptive language that engages the human senses. For instance, the following lines... (read more)
Internal rhyme is rhyme that occurs in the middle of lines of poetry, instead of at the ends of lines. A single line of poetry can contain internal rhyme (with multiple words in the same... (read full internal rhyme explanation with examples) Internal rhyme is rhyme that occurs in the middle of lines of poetry, instead of at the ends of lines.... (read more)
Irony is a literary device or event in which how things seem to be is in fact very different from how they actually are. If this seems like a loose definition, don't worry—it is. Irony is a... (read full irony explanation with examples) Irony is a literary device or event in which how things seem to be is in fact very different from how... (read more)
Juxtaposition occurs when an author places two things side by side as a way of highlighting their differences. Ideas, images, characters, and actions are all things that can be juxtaposed with one another. For example,... (read full juxtaposition explanation with examples) Juxtaposition occurs when an author places two things side by side as a way of highlighting their differences. Ideas, images,... (read more)
A kenning is a figure of speech in which two words are combined in order to form a poetic expression that refers to a person or a thing. For example, "whale-road" is a kenning for... (read full kenning explanation with examples) A kenning is a figure of speech in which two words are combined in order to form a poetic expression... (read more)
A line break is the termination of one line of poetry, and the beginning of a new line. (read full line break explanation with examples) A line break is the termination of one line of poetry, and the beginning of a new line. (read more)
Litotes is a figure of speech and a form of understatement in which a sentiment is expressed ironically by negating its contrary. For example, saying "It's not the best weather today" during a hurricane would... (read full litotes explanation with examples) Litotes is a figure of speech and a form of understatement in which a sentiment is expressed ironically by negating... (read more)
Logos, along with ethos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Logos is an argument that appeals to an audience's sense of logic... (read full logos explanation with examples) Logos, along with ethos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things by saying that one thing is the other. The comparison in a metaphor can be stated explicitly, as in the sentence "Love is... (read full metaphor explanation with examples) A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things by saying that one thing is the other.... (read more)
Meter is a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables that defines the rhythm of some poetry. These stress patterns are defined in groupings, called feet, of two or three syllables. A pattern of unstressed-stressed,... (read full meter explanation with examples) Meter is a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables that defines the rhythm of some poetry. These stress patterns... (read more)
Metonymy is a type of figurative language in which an object or concept is referred to not by its own name, but instead by the name of something closely associated with it. For example, in... (read full metonymy explanation with examples) Metonymy is a type of figurative language in which an object or concept is referred to not by its own... (read more)
The mood of a piece of writing is its general atmosphere or emotional complexion—in short, the array of feelings the work evokes in the reader. Every aspect of a piece of writing can influence its mood, from the... (read full mood explanation with examples) The mood of a piece of writing is its general atmosphere or emotional complexion—in short, the array of feelings the work evokes... (read more)
A motif is an element or idea that recurs throughout a work of literature. Motifs, which are often collections of related symbols, help develop the central themes of a book or play. For example, one... (read full motif explanation with examples) A motif is an element or idea that recurs throughout a work of literature. Motifs, which are often collections of... (read more)
A narrative is an account of connected events. Two writers describing the same set of events might craft very different narratives, depending on how they use different narrative elements, such as tone or point of view. For... (read full narrative explanation with examples) A narrative is an account of connected events. Two writers describing the same set of events might craft very different narratives,... (read more)
Onomatopoeia is a figure of speech in which words evoke the actual sound of the thing they refer to or describe. The “boom” of a firework exploding, the “tick tock” of a clock, and the... (read full onomatopoeia explanation with examples) Onomatopoeia is a figure of speech in which words evoke the actual sound of the thing they refer to or... (read more)
An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory terms or ideas are intentionally paired in order to make a point—particularly to reveal a deeper or hidden truth. The most recognizable oxymorons are... (read full oxymoron explanation with examples) An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory terms or ideas are intentionally paired in order to... (read more)
A paradox is a figure of speech that seems to contradict itself, but which, upon further examination, contains some kernel of truth or reason. Oscar Wilde's famous declaration that "Life is much too important to be... (read full paradox explanation with examples) A paradox is a figure of speech that seems to contradict itself, but which, upon further examination, contains some kernel... (read more)
Parallelism is a figure of speech in which two or more elements of a sentence (or series of sentences) have the same grammatical structure. These "parallel" elements can be used to intensify the rhythm of... (read full parallelism explanation with examples) Parallelism is a figure of speech in which two or more elements of a sentence (or series of sentences) have... (read more)
Parataxis is a figure of speech in which words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are set next to each other so that each element is equally important. Parataxis usually involves simple sentences or phrases whose relationships... (read full parataxis explanation with examples) Parataxis is a figure of speech in which words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are set next to each other so... (read more)
A parody is a work that mimics the style of another work, artist, or genre in an exaggerated way, usually for comic effect. Parodies can take many forms, including fiction, poetry, film, visual art, and... (read full parody explanation with examples) A parody is a work that mimics the style of another work, artist, or genre in an exaggerated way, usually... (read more)
Pathetic fallacy occurs when a writer attributes human emotions to things that aren't human, such as objects, weather, or animals. It is often used to make the environment reflect the inner experience of a narrator... (read full pathetic fallacy explanation with examples) Pathetic fallacy occurs when a writer attributes human emotions to things that aren't human, such as objects, weather, or animals.... (read more)
Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Pathos is an argument that appeals to an audience's emotions. When a... (read full pathos explanation with examples) Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
Personification is a type of figurative language in which non-human things are described as having human attributes, as in the sentence, "The rain poured down on the wedding guests, indifferent to their plans." Describing the... (read full personification explanation with examples) Personification is a type of figurative language in which non-human things are described as having human attributes, as in the... (read more)
Plot is the sequence of interconnected events within the story of a play, novel, film, epic, or other narrative literary work. More than simply an account of what happened, plot reveals the cause-and-effect relationships between... (read full plot explanation with examples) Plot is the sequence of interconnected events within the story of a play, novel, film, epic, or other narrative literary... (read more)
Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The three primary points of view are first person, in which the narrator tells a story from... (read full point of view explanation with examples) Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The... (read more)
Polyptoton is a figure of speech that involves the repetition of words derived from the same root (such as "blood" and "bleed"). For instance, the question, "Who shall watch the watchmen?" is an example of... (read full polyptoton explanation with examples) Polyptoton is a figure of speech that involves the repetition of words derived from the same root (such as "blood"... (read more)
Polysyndeton is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and," "or," and "but" that join other words or clauses in a sentence into relationships of equal importance—are used several times in close... (read full polysyndeton explanation with examples) Polysyndeton is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and," "or," and "but" that join other words... (read more)
The protagonist of a story is its main character, who has the sympathy and support of the audience. This character tends to be involved in or affected by most of the choices or conflicts that... (read full protagonist explanation with examples) The protagonist of a story is its main character, who has the sympathy and support of the audience. This character... (read more)
A pun is a figure of speech that plays with words that have multiple meanings, or that plays with words that sound similar but mean different things. The comic novelist Douglas Adams uses both types... (read full pun explanation with examples) A pun is a figure of speech that plays with words that have multiple meanings, or that plays with words... (read more)
A quatrain is a four-line stanza of poetry. It can be a single four-line stanza, meaning that it is a stand-alone poem of four lines, or it can be a four-line stanza that makes up... (read full quatrain explanation with examples) A quatrain is a four-line stanza of poetry. It can be a single four-line stanza, meaning that it is a... (read more)
A red herring is a piece of information in a story that distracts readers from an important truth, or leads them to mistakenly expect a particular outcome. Most often, the term red herring is used to refer... (read full red herring explanation with examples) A red herring is a piece of information in a story that distracts readers from an important truth, or leads them... (read more)
In a poem or song, a refrain is a line or group of lines that regularly repeat, usually at the end of a stanza in a poem or at the end of a verse in... (read full refrain explanation with examples) In a poem or song, a refrain is a line or group of lines that regularly repeat, usually at the... (read more)
Repetition is a literary device in which a word or phrase is repeated two or more times. Repetition occurs in so many different forms that it is usually not thought of as a single figure... (read full repetition explanation with examples) Repetition is a literary device in which a word or phrase is repeated two or more times. Repetition occurs in... (read more)
A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to get an answer—most commonly, it's asked to make a persuasive point. For example, if a... (read full rhetorical question explanation with examples) A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to... (read more)
A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in two or more words. Rhyming is particularly common in many types of poetry, especially at the ends of lines, and is a requirement in formal verse.... (read full rhyme explanation with examples) A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in two or more words. Rhyming is particularly common in many types... (read more)
A rhyme scheme is the pattern according to which end rhymes (rhymes located at the end of lines) are repeated in works poetry. Rhyme schemes are described using letters of the alphabet, such that all... (read full rhyme scheme explanation with examples) A rhyme scheme is the pattern according to which end rhymes (rhymes located at the end of lines) are repeated... (read more)
The rising action of a story is the section of the plot leading up to the climax, in which the tension stemming from the story's central conflict grows through successive plot developments. For example, in the story of "Little... (read full rising action explanation with examples) The rising action of a story is the section of the plot leading up to the climax, in which the tension stemming... (read more)
A character is said to be "round" if they are lifelike or complex. Round characters typically have fully fleshed-out and multi-faceted personalities, backgrounds, desires, and motivations. Jay Gatsby in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby... (read full round character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "round" if they are lifelike or complex. Round characters typically have fully fleshed-out and... (read more)
Satire is the use of humor, irony, sarcasm, or ridicule to criticize something or someone. Public figures, such as politicians, are often the subject of satire, but satirists can take aim at other targets as... (read full satire explanation with examples) Satire is the use of humor, irony, sarcasm, or ridicule to criticize something or someone. Public figures, such as politicians,... (read more)
A sestet is a six-line stanza of poetry. It can be any six-line stanza—one that is, itself, a whole poem, or one that makes up a part of a longer poem. Most commonly, the term... (read full sestet explanation with examples) A sestet is a six-line stanza of poetry. It can be any six-line stanza—one that is, itself, a whole poem,... (read more)
Setting is where and when a story or scene takes place. The where can be a real place like the city of New York, or it can be an imagined location, like Middle Earth in... (read full setting explanation with examples) Setting is where and when a story or scene takes place. The where can be a real place like the... (read more)
Sibilance is a figure of speech in which a hissing sound is created within a group of words through the repetition of "s" sounds. An example of sibilance is: "Sadly, Sam sold seven venomous serpents to Sally and... (read full sibilance explanation with examples) Sibilance is a figure of speech in which a hissing sound is created within a group of words through the repetition... (read more)
A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two unlike things. To make the comparison, similes most often use the connecting words "like" or "as," but can also use other words that indicate... (read full simile explanation with examples) A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two unlike things. To make the comparison, similes most often... (read more)
Traditionally, slant rhyme referred to a type of rhyme in which two words located at the end of a line of poetry themselves end in similar—but not identical—consonant sounds. For instance, the words "pact" and... (read full slant rhyme explanation with examples) Traditionally, slant rhyme referred to a type of rhyme in which two words located at the end of a line... (read more)
A soliloquy is a literary device, most often found in dramas, in which a character speaks to him or herself, relating his or her innermost thoughts and feelings as if thinking aloud. In some cases,... (read full soliloquy explanation with examples) A soliloquy is a literary device, most often found in dramas, in which a character speaks to him or herself,... (read more)
A sonnet is a type of fourteen-line poem. Traditionally, the fourteen lines of a sonnet consist of an octave (or two quatrains making up a stanza of 8 lines) and a sestet (a stanza of... (read full sonnet explanation with examples) A sonnet is a type of fourteen-line poem. Traditionally, the fourteen lines of a sonnet consist of an octave (or... (read more)
A spondee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which both syllables are stressed. The word "downtown" is a spondee, with the stressed syllable of "down" followed by another stressed syllable, “town”: Down-town. (read full spondee explanation with examples) A spondee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which both syllables are stressed. The word "downtown" is a... (read more)
A stanza is a group of lines form a smaller unit within a poem. A single stanza is usually set apart from other lines or stanza within a poem by a double line break or... (read full stanza explanation with examples) A stanza is a group of lines form a smaller unit within a poem. A single stanza is usually set... (read more)
A character is said to be "static" if they do not undergo any substantial internal changes as a result of the story's major plot developments. Antagonists are often static characters, but any character in a... (read full static character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "static" if they do not undergo any substantial internal changes as a result of... (read more)
Stream of consciousness is a style or technique of writing that tries to capture the natural flow of a character's extended thought process, often by incorporating sensory impressions, incomplete ideas, unusual syntax, and rough grammar. (read full stream of consciousness explanation with examples) Stream of consciousness is a style or technique of writing that tries to capture the natural flow of a character's... (read more)
A syllogism is a three-part logical argument, based on deductive reasoning, in which two premises are combined to arrive at a conclusion. So long as the premises of the syllogism are true and the syllogism... (read full syllogism explanation with examples) A syllogism is a three-part logical argument, based on deductive reasoning, in which two premises are combined to arrive at... (read more)
Symbolism is a literary device in which a writer uses one thing—usually a physical object or phenomenon—to represent something more abstract. A strong symbol usually shares a set of key characteristics with whatever it is... (read full symbolism explanation with examples) Symbolism is a literary device in which a writer uses one thing—usually a physical object or phenomenon—to represent something more... (read more)
Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which, most often, a part of something is used to refer to its whole. For example, "The captain commands one hundred sails" is a synecdoche that uses "sails"... (read full synecdoche explanation with examples) Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which, most often, a part of something is used to refer to its... (read more)
A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary themes is their universality, which is to say that themes are ideas that not only... (read full theme explanation with examples) A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary... (read more)
The tone of a piece of writing is its general character or attitude, which might be cheerful or depressive, sarcastic or sincere, comical or mournful, praising or critical, and so on. For instance, an editorial in a newspaper... (read full tone explanation with examples) The tone of a piece of writing is its general character or attitude, which might be cheerful or depressive, sarcastic or sincere, comical... (read more)
A tragic hero is a type of character in a tragedy, and is usually the protagonist. Tragic heroes typically have heroic traits that earn them the sympathy of the audience, but also have flaws or... (read full tragic hero explanation with examples) A tragic hero is a type of character in a tragedy, and is usually the protagonist. Tragic heroes typically have... (read more)
A trochee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by an unstressed syllable. The word "poet" is a trochee, with the stressed syllable of "po" followed by the... (read full trochee explanation with examples) A trochee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by an unstressed syllable.... (read more)
Understatement is a figure of speech in which something is expressed less strongly than would be expected, or in which something is presented as being smaller, worse, or lesser than it really is. Typically, understatement is... (read full understatement explanation with examples) Understatement is a figure of speech in which something is expressed less strongly than would be expected, or in which something... (read more)
Verbal irony occurs when the literal meaning of what someone says is different from—and often opposite to—what they actually mean. When there's a hurricane raging outside and someone remarks "what lovely weather we're having," this... (read full verbal irony explanation with examples) Verbal irony occurs when the literal meaning of what someone says is different from—and often opposite to—what they actually mean.... (read more)
A villanelle is a poem of nineteen lines, and which follows a strict form that consists of five tercets (three-line stanzas) followed by one quatrain (four-line stanza). Villanelles use a specific rhyme scheme of ABA... (read full villanelle explanation with examples) A villanelle is a poem of nineteen lines, and which follows a strict form that consists of five tercets (three-line... (read more)
A zeugma is a figure of speech in which one "governing" word or phrase modifies two distinct parts of a sentence. Often, the governing word will mean something different when applied to each part, as... (read full zeugma explanation with examples) A zeugma is a figure of speech in which one "governing" word or phrase modifies two distinct parts of a... (read more)

- Quizzes, saving guides, requests, plus so much more.
Literary Devices: 30 Elements & Techniques for Writers (With Examples)

Every Author wants to write a good book . That’s a given.
But you don’t need to know the names and definitions of 30 or 40 literary devices to accomplish that goal.
Knowing the difference between alliteration, onomatopoeia, and hyperbole won’t make or break your book.
Literary devices are especially common in novels, where writers need to use flashbacks, foreshadowing, or figurative language to keep the reader enthralled.
But most nonfiction doesn’t need literary devices to be effective.
As an Author, your goal is to explain how your knowledge can solve a reader’s problems in a clear, concise manner. If you can toss in some good storytelling, so much the better.
Remember, being a good writer isn’t about checking off every writing trick on the list. It’s about expressing your information in an authentic, clear way.
This literary device crash course is a helpful tool, but if you want to publish a great book, devices shouldn’t be your primary focus.
What Are Literary Devices?
Literary devices, also known as literary elements, are techniques that writers use to convey their message more powerfully or to enhance their writing.
Many Authors use literary devices without even realizing it. For example, if you exaggerate and say, “This method has the potential to revolutionize the world,” that’s hyperbole. Your method may be impactful, but it probably isn’t really going to upend the way every single country does things.
More complicated literary devices are a common feature in fiction, but most nonfiction books don’t need them. A nonfiction Author’s job is to deliver information in an engaging way. “Engaging” doesn’t necessarily mean “literary.”
Still, literary devices can add a lot to a text when they’re used correctly.
For example, in The Great Gatsby , Fitzgerald uses the following metaphor to describe human struggle: “So we beat on, boats against the current…”
The image of boats fighting against the current is a powerful way to express the simple idea that “life is hard.”
Literary devices are especially effective when they’re used sparingly. Don’t overdo it.
If your entire book is written in metaphors, it’s not only going to be an overkill of flowery language, but it’s probably going to be confusing too.
If you can incorporate literary devices in a way that makes sense and adds something to the readers’ experience, great. But don’t force it.
30 Common Literary Devices
1. alliteration.
Alliteration is the repetition of initial consonant sounds within a group of words. For example, “Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers.”
Nonfiction Authors can use alliteration to create catchy chapter or subsection titles. For example, “4 Best Bets for Better Business.”
Alliteration is also particularly effective for highlighting concepts you want your readers to remember. For example, if the takeaway of your chapter is a pithy, one-line sentence, alliteration can really make it stand out. Think, “Clear communication is key.”
Be careful not to overuse alliteration, or your book will start to sound like a nursery rhyme.
2. Onomatopoeia
An onomatopoeia is a word that imitates, suggests, or resembles the sound it’s describing. Common onomatopoeias include “gurgle,” “hiss,” “boom,” “whir,” and “whizz.”
In storytelling, onomatopoeia is an effective way to draw your reader into the environment. For example, if you’re telling an anecdote about a meeting you had with a client, it’s more vivid to say, “He plopped a sugar cube into his coffee and slurped,” than to say, “He drank his coffee with sugar.”
3. Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is an advance warning about something that’s going to happen in the future.
In fiction, foreshadowing can be subtle. For example, something that happens in the first chapter of a murder mystery can come into play at the end of the book.
But in nonfiction, foreshadowing tends to be more obvious. Authors often use it to tell readers what they can expect to learn. For example, an Author might say, “We’re going to talk more about this example later,” or “I’ll discuss this at length in Chapter Three.”
4. Hyperbole
Hyperbole is an exaggeration that’s not meant to be taken literally. For example, if my friend surprised me by eating a lot of pizza, I might say, “Hey man, remember that time you ate, like, fifteen pizzas in one night?”
Good nonfiction Authors often use hyperbole to emphasize the power of their statements. For example, “We all know how miserable it can be to work 24/7.” Do we really all know that? And it’s impossible to literally work 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
Nonfiction Authors have to be careful with hyperbole, though. If you’re using data, you want it to seem credible. In nonfiction, readers often want precision, not exaggeration.
5. Oxymoron
An oxymoron is a figure of speech where seemingly contradictory terms appear together. For example, “the dumbest genius I know.”
Oxymorons are useful if you want to create an unexpected contrast. For example, “Your unhappiest customers are often your business’ happiest accident.”
6. Flashback
A flashback is a scene set in an earlier time than the main story. They’re often used to provide important context or backstory for an event you’re discussing.
Because most nonfiction books aren’t chronological ( unless it’s a memoir ), you probably won’t have many opportunities to use flashbacks. But in anecdotes, a touch of flashback can be effective.
For example, “My boss congratulated me for landing the largest account our company had ever seen. It was hard to believe that only seven months earlier, I was struggling to keep the few clients I already had.”
7. Point of View
Point of view is the perspective you use to tell your story.
A lot of nonfiction is written with a first-person point of view, which means writing from an “I” perspective. For example, “I’ve developed the following ten-point system to improve your finances.”
It’s much rarer, although possible, to write nonfiction from the third-person perspective. For example, “They saw how powerful their methods could be.” Sometimes co-authors choose this method to avoid first-person confusion.
Nonfiction writers occasionally use second person (“you”) to directly address their readers. For example, “You know how hard it can be to fire someone.”
8. Euphemism
A euphemism is a polite way of describing something indirectly.
Many Authors use euphemisms to vary their language or soften the blow of a difficult concept. For example, “passed away” is a euphemism for “died.”
Some Authors use euphemisms to keep their texts more palatable for a general audience.
For example, if an Author is writing about sexual harassment in the workplace, they may not want to repeat lewd phrases and could use euphemisms instead. Or, an Author who wants to avoid the political controversy around the term “abortion” might opt for “pregnancy termination.”
9. Colloquialism
A colloquialism is a word or phrase that’s not formal or literary. It tends to be used in ordinary or familiar conversation instead. For example, it’s more colloquial to say, “How’s it going?” instead of “How are you doing?”
Slang is also a form of colloquialism. If you say something was “awesome,” unless you literally mean it inspired awe, you’re being colloquial.
No matter how professional your audience is, some colloquialism can make your book feel more relatable. Readers like to feel as if they’re talking with the Author. Colloquialism can help you create that personal, one-on-one feeling.
10. Anthropomorphism
Anthropomorphism is when you give human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human creatures or things.
If you think of your dog as having a “funny personality,” you’re anthropomorphizing him. The same goes for your “stubborn” toaster or “cranky” computer.
In nonfiction, you generally won’t encounter a lot of opportunities for anthropomorphism, but some Authors may want to humanize their products or services. For example, your software may be “friendly” or “kind” to new users.
11. Anaphora
Anaphora is a rhetorical device where you repeat a word or phrase at the beginning of successive clauses. This is a great way to draw emphasis to a certain portion of text.
For example, Charles Dickens uses anaphora in the opening of A Tale of Two Cities : “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief…”
12. Anachronism
An anachronism is a chronological inconsistency where you juxtapose people, things, or sayings from different time periods. If you were reading a book about colonial America where characters talk about cars, that would be anachronistic.
In nonfiction, you might want to use anachronism to make it easier for a current audience to relate to people in your stories.
For example, if you’re writing about the history of the banking industry, you might refer to certain individuals as “influencers” or talk about ideas that were “trending.”
13. Malapropism
A malapropism is the mistaken use of a word in place of a similar-sounding one. This usually creates some kind of humorous effect. Imagine a person saying, “I know how to dance the flamingo,” instead of, “I know how to dance flamenco.”
There aren’t a lot of good reasons to use malapropism in nonfiction, but you could do this if you’re trying to amuse or delight your reader in an unexpected way. It’s a lot like using a pun.
For example, if you’re writing a book about sports, you might say, “The client and I saw things so eye-to-eye, it was almost like we had ESPN” (instead of “ESP”).
14. Figurative Language
Figurative language is language that dresses up your writing in an attempt to engage your readers. Figurative language is often more colorful, evocative, or dramatic.
For example, “She was chained to her desk for sixty hours a week.” Let’s hope not.
Still, it conjures a vivid image that’s more exciting for readers than, “She worked a lot.”

Figurative language is like taking your everyday language and putting it in a tuxedo.
15. Dramatic Irony
Irony is a literary technique where what appears to be the case differs radically from what is actually the case.
Dramatic irony is a type of irony that occurs when an audience understands the context more than the character in a story.
Let’s say you’re telling a story about an interaction with a client that didn’t go the way you expected. You might write, “Things seemed to be going well, but little did I know, she had already hired someone else.”
At the moment you were meeting with the client, you didn’t have that information. But now, the reader does. So, they get to follow along with the rest of the story, knowing more than you did at the time.
16. Verbal Irony
Verbal irony occurs when a person says one thing but means another. Sarcasm is a good example of verbal irony. For example, you might say, “It was a wonderful dinner,” when, in fact, the food was terrible, and your partner showed up an hour late.
Depending on the tone of your book, verbal irony can help create humor or make you more relatable.
17. Figure of Speech
Think of “figure of speech” as a kind of catch-all term for any word or phrase that’s used in a non-literal sense to create a dramatic effect.
For example, it’s a figure of speech to say that it was “raining cats and dogs” or that something stands “an ice cube’s chance in Hell” of happening.
A lot of the devices we’ve already discussed (e.g., alliteration, oxymoron, and metaphors) also fall into the category of figures of speech.
18. Metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things in an interesting way. It often highlights the similarities between two different ideas.
Take, for example, “The classroom was a zoo.” It wasn’t literally a zoo, but this metaphor expresses the wild energy of a room full of children.
Or, “the curtain of night fell.” Night doesn’t have a curtain, but we can all imagine darkness falling like one.
Metaphors form direct comparisons by saying something is something else. (Similes, explained below, form comparisons by saying something is like something else.)
Metaphors are a useful tool for “showing” your reader something instead of just “telling.” They help your reader see and feel the scene, and they paint a vivid picture.
If you use a metaphor, though, make sure it’s intelligible. There are a lot of bad ones out there. The point of a metaphor is to make a scene clearer, not to confuse your reader.
A simile is also a figure of speech that compares two different things in an interesting way. But unlike a metaphor, a simile uses comparison words like “like” or “as.”
“She was as bright as a lightbulb.”
“He was stubborn like a mule.”
Using similes can make your writing more interesting. The comparisons can spark your readers’ imagination while still getting your information across clearly.
20. Metonymy
Metonymy is a figure of speech in which a thing or concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
For example, a businessman is sometimes known as “a suit.”
Or, in William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar , “lend me your ears,” is a metonymy for “give me your full attention.”
People use metonymy all the time without being conscious of it. For example, if you get in a car wreck, you’re likely to say, “That car hit me,” instead of, “That car hit my car.”
If you’re writing in relatable, colloquial language, your book will probably have metonymy in it.
21. Synecdoche
Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which a part of something stands in for the whole or vice versa. It’s a subset of metonymy.
For example, if you have “hungry mouths to feed,” you actually need to feed people. Their mouths are just a stand-in for the whole person.
Or, you might say, “All of society was at the gala,” when you really mean, “All of high society was there.”
Typically, synecdoche will come out in your writing naturally. When you force synecdoche, it can sound strange.
For example, what do you think I mean when I say, “I sat on the legs?” I’m guessing a chair didn’t come to mind, even though “legs” is a part of the whole “chair.”
22. Aphorism
An aphorism is a concise statement of a general truth or principle. For example, “If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it.”
Most aphorisms are handed down over time, so chances are, you won’t coin your own. Think of these as the tried-and-true statements people already know.
For example, if you’re describing toxic leadership, you could quickly say, “After all, power corrupts,” and your audience would immediately know what you mean.
Aphorisms are great for emphasis because they’re quick, clear, and to the point. They aren’t flowery, and their simplicity makes them memorable.
23. Rhetorical Question
A rhetorical question is a question asked for effect, not because you want an answer.
“Do you want to make money? Do you want to sleep better at night? Do you want to run a successful company?”
Who wouldn’t say yes? (See what I did there?)
Be careful not to overuse rhetorical questions because too many can get tedious. But used sparingly, they’re a great way to invite your reader into the conversation and highlight the benefits of your knowledge.
24. Polysyndeton
Polysyndeton comes from the Ancient Greek for “many” and “bound together.” As its name implies, it’s a literary technique in which conjunctions (e.g., and, but, or) are used repeatedly in quick succession.
Here it is in action: “I wanted an employee who was self-motivated and enterprising and skilled. I needed someone who could write and talk and network like a pro.”
In most cases, you’ll use a regular list instead of polysyndeton (e.g., “I like cats, dogs, and ferrets.”). But when it’s used correctly, polysyndeton is useful for drawing emphasis to different aspects of a sentence.
One common way to use polysyndeton is, “You’ll find everything in this book, from billing and buying to marketing and sales.”
25. Consonance
Consonance occurs when you repeat consonant sounds throughout a particular word or phrase. Unlike alliteration, the repeated consonant doesn’t have to come at the beginning of the word.
“Do you like blue?” and “I wish I had a cushion to squash” are examples of consonance.
Consonance can help you build sentences and passages that have a nice rhythm. When a text flows smoothly, it can subconsciously propel readers forward and keep them reading.
26. Assonance
Assonance is similar to consonance, except it involves repeating vowel sounds. This is usually a subtler kind of echo. For example, the words “penitence” and “reticence” are assonant.
Like consonance, assonance can help you build compelling, rhythmic language.
27. Chiasmus
Chiasmus is a rhetorical device where grammatical constructions or concepts are repeated in reverse order.
For example, “Never let a kiss fool you or a fool kiss you.” Or, “The happiest and best moments go to the best and happiest employees.”
In nonfiction, chiasmus can be an effective way to make a significant point. It often works because it’s unexpected and punchy.
28. Litotes
Litotes is a figure of speech closely related to verbal irony. With litotes, you use understatement to emphasize your point. They often incorporate double negatives for effect.
For example, “You won’t be sorry” is the litotes way of saying, “You will be glad.”
If I say, “He wasn’t a bad singer,” you can probably assume that he was actually a good singer. But the negative construction conveys a different tone.
If hyperbole lends more force to your claims, litotes diminishes your statement. In nonfiction, there are situations where you might want to downplay your judgment.
Take this statement, for example: “He wasn’t the worst lawyer I had ever seen, but he could have been more organized.” You aren’t completely bashing the lawyer, but you’re still showing there’s room for improvement.
Still, I recommend using litotes sparingly if you don’t want people to think you’re constantly damning with faint praise.
29. Epigraph
An epigraph is a short quotation or saying at the beginning of a book or chapter, intended to suggest its theme.
For example, Mario Puzo’s The Godfather begins with a quotation from the French writer Balzac: “Behind every great fortune, there is a crime.”
An epigraph is a great way to honor a writer or thinker you admire. It also immediately puts your work in conversation with theirs. In nonfiction, an epigraph can be a great way to signal to readers, “Hey, Tim Ferriss’ book has informed mine!”
But don’t rely too heavily on epigraphs. The point of writing a book is to show that you are an expert. You don’t want to constantly defer to other Authors to contextualize your ideas.
Also, epigraphs are only effective when they are truly relevant to your book. Don’t just pick a person that you think readers will recognize. Pick a quotation that really adds something to your book.
30. Epistrophe
Epistrophe is the repetition of the same word or words at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences. It’s sometimes called epiphora or antistrophe.
Epistrophe is the cousin of anaphora, where the repetition happens at the beginning of successive phrases.
Abraham Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address is a great example of a text that uses epistrophe: “… that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.”
His repetition of “the people” really drives home the importance of “the people” to American government. They are central, no matter how you slice it.
Epistrophe can be very dramatic, and it’s a great way to draw attention to crucial concepts or words in your book. But because it’s so impactful, it should be used in moderation.

The Scribe Crew
Read this next.
Never Stop Launching [How to Make Your Book Successful]
Authors Receive Authority – What does ‘The Medium Is the Message’ Really Mean?
Audiobooks: Who Benefits Most and Why Authors Should Consider Them
What are you looking for?
Quick links.
Click here to find all our contact information
Literary devices list: examples of literary devices and how to use them
Learn about literary devices, including rhetorical devices and stylistic devices, and how you can use them to improve your communication skills. This content series is part of Semantix’s copywriting toolkit, which is designed to boost your language skills and equip you with a wealth of effective writing tools.

A command of more advanced writing techniques can take your writing to another level or give you the ability to capture the attention of a large audience with an engaging speech. Whether you’re a creative writing student, have a speech to write or you’re a professional writer, the toolkit provides a valuable resource, including definitions of literary devices and examples.
A toolkit for writers
A professional writer uses literary devices to make sure that their writing reads well, is remembered and gets the results they intend. This often means convincing a reader of an idea, getting them to buy a product or even changing their mind about something important.
Literary devices are a superpower when it comes to truly great writing, as has been proven for many, many years. That’s why Semantix has created a literary devices toolkit for copywriters, students and other writers who want to hone their craft. The toolkit is a content series that provides lists of literary devices, their definitions, examples and suggested uses. If your writing needs to really hit the mark, choose a literary device from the toolkit that fits your purpose and let it work its magic!
Examples of literary devices
| Alliteration | Repetition of the same initial consonant sound throughout a sentence, phrase or verse. Alliteration is popular in marketing text. | " on’t ream it. rive it." |
| Anadiplosis | The repetition of a word that ends one sentence, phrase or verse at the beginning of the next sentence, phrase or verse. | "Fear leads to . leads to . leads to suffering.” |
| The repetition of words at the beginning of successive sentences, phrases or verses. | " that one day on the red hills of Georgia, the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit down together at the table of brotherhood. that one day even the state of Mississippi, a state sweltering with the heat of injustice, sweltering with the heat of oppression will be transformed into an oasis of freedom and justice." - Martin Luther King Jr. | |
| Antanaclasis | A single word or phrase is repeated, but with two different meanings. | me.” - John Lennon |
| A phrase that uses a parallel grammar structure to emphasise important differences between opposing ideas, things or people. | "No pain, no gain." | |
| Antimetabole | The repetition of words from the first half of the sentence or phrase in the second half, but in reverse order. | "I know what I like, and I like what I know." |
| Aphorism | A short, witty phrase that expresses a generally accepted truth. | ''Tis better to have loved and lost than never to have loved at all." - Alfred, Lord Tennyson. |
| Assonance | The repetition of vowel sounds in words that are close to each other in a sentence, phrase or verse. | " h n , this is s sl ." |
| The reversed repetition of the grammatical structure of a sentence, phrase or clause. NB! Chiasmus and antanaclasis both have the reversed “ABBA” structure in common, but chiasmus can use synonymous words, whereas in antanaclasis the words have to be , just in reversed order. | “Who dotes, yet doubts, suspects, yet strongly loves.” - Shakespeare, Othello | |
| Conduplicatio | The repetition of an important word from anywhere in one sentence, phrase or verse at the beginning of the next sentence, phrase or verse. | “I am filled with a profound and abiding to the American people. is a word that I cherish. is what defines the humanity of the human being.” - used by Elie Weisel in his ‘The Perils of Indifference’ speech. |
| Diaphora | The repetition of a name, firstly as a proper noun to signify the person and then as a noun to signify its meaning. | "For your are not but man-made idols." |
| Diacope | Repetition broken up by one or more intervening words. | "I want a , a beautiful, lavish ." |
| Epanalepsis | The repetition of the first part of a sentence, phrase or verse at the end of the sentence, phrase or verse. | " is worse than doing ." |
| Epimone | The continual repetition of a phrase or question. | “ , sir!" - Charles Dickens, David Copperfield. |
| Epistrophe is the repetition of the final element of a structure. This could be the repetition of a single word or an entire clause or sentence. | "Here we go round , , ." - from a well-known children's nursery rhyme. | |
| Epizeuxis | The repetition of one word or phrase in immediate succession. | " !" |
| Hypophora | A sentence where the writer or speaker poses a question, and then immediately provides the answer. | "What did he want? He wanted to know how it worked." |
| Hyperbaton | Inverting the arrangement of common words. | "Some by virtue fall,’ which is an inversion of ’Some fall by virtue." - William Shakespeare, Measure for Measure. |
| Juxtaposition | Placing two elements side by side in a phrase to emphasise the contrast between the two. | "For , or ." - phrase used in some wedding vows. |
| Isocolon | A sentence composed of two or more phrases of similar structure and length that mean the same thing. | A bicolon has two phrases; a tricolon has three phrases; a tetracolon has four phrases. This description is an example of a tricolon! |
| Mesodiplosis | The repetition of a word or phrase in the middle of every sentence, phrase or verse. | "Me, you; us, them; you, him." |
| Metaphor | Making a comparison between two unsimilar things to signify something without using ‘like’ or ‘as’ as used in simile. | The term "I’m the of the family" to express being the unusual or non-conforming member of the family. |
| Parallelism | The repetition of grammatical elements, words or structures used to create impact by emphasising a parallel position between concepts. | "Don’t marry someone ve with, marry someone ." |
| Polyptoton | The repetition of words derived from the same root but used to mean different things. | "There is no end of it, the voiceless wailing, No end to the of flowers" - T.S.Eliot: The Dry Salvages |
| Syncope | Shortening words by omitting syllables or letters. | "The road extended the heath..." - William Wordsworth, The World Is Too Much with Us. |
| Synecdoche | Using part of an element to signify the whole. | "Boots on the ground" instead of "soldiers". |
Do rhetorical devices improve your writing?
Rhetorical and literary devices have been used for centuries by some of the world’s greatest writers. They provide a time-proven way to keep readers, or listeners, engaged and give your writing impact, rhythm and style.
There are many literary devices that writers can choose from and each one has a range of possible uses. Knowing which device will get the results you intend provides you with either a good starting place when you're looking for creative inspiration, or a way to add some extra impact to existing copy.
The best writers’ works are rich with rhetorical and literary devices... and that’s no accident. The right words can keep readers turning the pages of a book, convince minds or sell millions of products.
What is rhetoric and what are literary devices?
The term ‘rhetoric’ is used to describe language that’s designed to have a persuasive or dramatic effect, especially with regards to public speaking. This is because it’s shaped to appeal to an audience’s sense of logic, emotions, ethics or awareness of the passing of time.
A literary device is a structure used in language to create impact. There are many different literary devices to choose from, and each one can be used to create a different effect. When used properly, literary devices help readers and listeners to appreciate, interpret and remember words.
You might have used literary devices in your writing many times without realising it. We’re so used to reading and hearing them that they sometimes come naturally to talented writers. However, being able to use them purposely means being able to consciously control how your writing is likely to be received.
If you analyse the words of truly great speakers, you'll find that they make use of a plethora of literary devices to create their intended impact. For example, it’s no accident that the words in the ‘I have a dream’ speech by Martin Luther King have been remembered and quoted for decades. His delivery makes use of many literary devices, cleverly designed to deliver a powerful punch.
They can also be found in the books of great writers, who have used them to add impact, colour and beauty to their work. For example, the works of the most famous wordsmith of all time, William Shakespeare, are rich with finely crafted literary devices of all kinds.
The difference between literary and rhetorical devices
The terms literary device and rhetorical device are commonly used interchangeably. However, they aren’t exactly interchangeable terms. By definition, a rhetorical device is a technique used in writing or speech to convince a reader or listener of something, while a literary device is a technique used in writing or speech to express something. It’s easy to confuse the two and there are a lot of crossovers. For example, if writing expresses a concept well it’s usually able to convince a reader too, so it could be called either!
The difference between stylistic and rhetorical devices
The term stylistic device is used to describe figures of speech that involve non-literal language. For example, metaphor and simile. Therefore, a stylistic device can be used in the role of either a rhetorical device if it’s used to convince, or a literary device if it’s used to express something.
Our copywriting services
Crafting great writing takes time and it’s easy to make mistakes that can be costly. If you’re translating into other languages, the task becomes even more complex.
Literary devices can be used in every language but it’s often not as straightforward as substituting one word for another. A translator working in their first language can use the source copy’s literary device in translation but might have to change words or structures to achieve the intended effect. Poorly translated literary devices sometimes make no sense at all and can seriously damage the credibility of your material.
Our multilingual copywriters get our clients the best results from their marketing and other writing in more than 200 languages. With access to thousands of translators, we team you with a translator who is not only fluent in your target language, but one who knows your industry.
If you’d like to find out how to boost your business by using our multilingual copywriting services , or if you’d like some advice on which direction is right for your translation needs, contact us today.
Want to know more about our copywriting services?
Further reading.
- A Handlist of Rhetorical Terms – Richard Lanham, University of California Press, 2013
- Simplified Glossary of Literary Terms/Devices: An-easy-to use Source of Definitions, Examples and Exercises For Students and Teachers – Victor Igiri, 2022
- The Oxford Dictionary of Literary Terms (Oxford Quick Reference) 4th Edition – Chris Baldick, OUP Oxford, 2015
- The Elements of Eloquence – Mark Forsyth, Icon Books, 2013
- The Elements of Rhetoric - Ryan N S Topping, Angelico Press, 2016
- The Penguin Dictionary of Literary Terms and Literary Theory – J A Cuddon, Penguin, 2014
- The Rhetorical Device: Literary Resources for The Writer Vol. 1 of 2 – Paul F Kisak, CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2016
- Writing with Clarity and Style: A Guide to Rhetorical Devices for Contemporary Writers – Robert A Harris, Routledge, 2017
- The Use of Rhetorical Devices in Selected Speeches by Clinton & Trump: Discourse from the Electoral Campaign 2016 – Larissa Wolf, AV Akademikerverlag, 2018
- Studiobinder (online) ‘What is antithesis’ blog post
- Voltaire, The Project Gutenberg EBook of A Philosophical Dictionary, Volume 4 (of 10).
- The Crafting of Eloquence: How rhetorical and literary devices turn basic communication into soaring words of art.
- Toastmasters (online) ‘The Crafting of Eloquence’ blog post.
Related content

A guide to the literary device anaphora – for professional wordsmiths

Understanding chiasmus – examples and effects of a rhetorical device

Understanding epistrophe: examples and usage across genres

Any writer looking to master the art of storytelling will want to learn the literary devices in prose. Fiction and nonfiction writers rely on these devices to bring their stories to life, impact their readers, and uncover the core truths of life. You can, too, with mastery over the different literary devices!
If you’re not familiar with the common literary devices, start with this article for definitions and examples. You may also benefit from brushing up on the six elements of fiction , as most prose stories have them. Combined with the following literary devices in fiction and nonfiction, these framing elements can help you write a powerful story.
10 Important Literary Devices in Prose
We’ve included examples and explanations for each of these devices, pulling from both contemporary and classical literature. Whether you’re a writer, a student, or a literary connoisseur, familiarize yourself with the important literary devices in prose.
1. Parallelism (Parallel Plots)
Parallelism refers to the plotting of events that are similarly constructed but altogether separate.
Are you familiar with the phrase “history often repeats itself”? If so, then you’re already familiar with parallelism. Parallelism refers to the plotting of events that are similarly constructed but altogether separate. Sometimes these parallels develop on accident, but they are powerful tools for highlighting important events and themes.
A surprising example of parallelism comes in the form of the Harry Potter series. As an infant, Harry is almost killed by Voldemort but is protected by his mother’s love. Eighteen years later, Harry must die in order to defeat Voldemort, thus shouldering the burden of love himself.
What does this parallelism do for the story? Certainly, that’s open to interpretation. Perhaps it draws attention to the incompleteness of love without action: to defeat Voldemort (who personifies hatred), Harry can’t just be loved, he has to act on love—by sacrificing his own life, no less.
This is unrelated to grammatical parallelism , a different literary device.
2. Foil Characters
A foil refers to any two characters who are “opposites” of each other.
A foil refers to any two characters who are “opposites” of each other. These oppositions are often conceptual in nature: one character may be even-keeled and mild, like Benvolio in Romeo & Juliet, while another character may be quick-tempered and pugnacious, like Tybalt.
What do foil characters accomplish? In Romeo & Juliet , Benvolio and Tybalt are basically Romeo’s devil and angel. Benvolio discourages Romeo from fighting, as it would surely end in his own death and separation from Juliet, whereas Tybalt encourages fighting out of family loyalty.
Of course, foils can also be the protagonist and antagonist, especially if they are character opposites. A reader would be hard-pressed to find similarities between Harry Potter and Voldemort (except for their shared soul). If you can think of other embodiments of good versus evil, they are most assuredly foils as well.
Foil characters help establish important themes and binaries in your work.
Foil characters help establish important themes and binaries in your work. Because Shakespeare wrote Benvolio and Tybalt as foils, one of the themes in Romeo & Juliet is that of retribution: is it better to fight for honor or turn the other cheek for love?
When considering foil characters in your writing, consider which themes/morals you want to turn your attention towards. If you want to write about the theme of chaos versus order, and your protagonist is chaotic, you might want a foil character who’s orderly. If you want to write about this theme but it’s not central to the story, perhaps have two side characters represent chaos versus order.
Learn more about foil characters here:
What is a Foil Character? Exploring Contrast in Character Development
You’ll often hear that “diction” is just a fancy term for “word choice.” While this is true, it’s also reductive, and it doesn’t capture the full importance of select words in your story. Diction is one of the most important literary devices in prose, as every prose writer will use it.
Diction is best demonstrated through analyzing a passage of prose, so to see diction in action, let’s take apart the closing paragraphs of The Great Gatsby .

Take a look at the highlighted words, as well as the opposition between different highlights. F. Scott Fitzgerald juxtaposes many different emotions in this short, poignant passage, resulting in an ambivalent yet powerful musing on the passage of time. By focusing the diction of this passage on emotions both hopeful and hopeless, Fitzgerald masterfully closes one of the most important American novels.
For a further analysis of diction, as well as some great examples, check out our article expanding upon word choice in writing !
The mood of a story or passage refers to the overall emotional tone it invokes.
The mood of a story or passage refers to the overall emotional tone it invokes. When writers craft a mood in their work, they’re heightening the experience of their story by putting you in the characters’ shoes. Since mood requires using the right words throughout a scene, mood can be considered an extended form of diction.
The writer cultivates mood by making consistent language choices throughout a passage.
The writer cultivates mood by making consistent language choices throughout a passage of the story. Take, for example, the cliché “it was a dark and stormy night.” That phrase wasn’t clichéd when it was first written; in fact, it did a great job of opening Edward Bulwer-Lytton’s novel Paul Clifford . The narrator’s dark, bleak description of the weather brings the reader into the bleary, tumultuous life of its protagonist, building a mood in both setting and story.
Or, consider this excerpt from Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë:

Charlotte is quick to build the mood, keying in on Jane’s sombre beginnings before juxtaposing it against the ironic perfection of her siblings. Jane’s world is clear from the beginning: a cloudy house amidst a sunny street.
Learn more about this device at our article on mood in literature.
What is Mood in Literature? Creating Mood in Writing
5. Foreshadowing
A foreshadow refers to any time the writer hints towards later events in the story.
Foreshadowing is a powerful literary device in fiction, drawing readers ever-closer to the story’s climax. A foreshadow refers to any time the writer hints towards later events in the story, often underscoring the story’s suspense and conflict.
Sometimes foreshadowing is obvious, and sometimes you don’t notice it until rereading the story.
Sometimes foreshadowing is obvious, and sometimes you don’t notice it until rereading the story. For example, the foreshadowing in Harry Potter makes it fairly obvious that Harry will have to die. Once the idea of horcruxes, or “split souls,” was introduced in the books, it was only a matter of time before readers connected these horcruxes to the psychic connection Harry shared with Voldemort. His mission—to die and be reincarnated—becomes fairly obvious as the heptalogy comes to a close.
However, sometimes foreshadowing is much more discreet. In Jane Eyre , for example, it’s clear that many of the people in Jane’s life are keeping secrets from her. Rochester doesn’t let anyone know about his previous marriage but it gets alluded to several times, and St. John is reluctant to admit that he does not actually love Jane, foreshadowing Jane’s return to Rochester. All of this combines to reinforce Jane’s uncertain place in the world and the journey she must take to settle down.
6. In Media Res
In Media Res refers to writing a story starting from the middle
From the Latin “In the middle of things,” In Media Res is one of the literary devices in prose chiefly concerned with plot. In Media Res refers to writing a story starting from the middle; by throwing the reader into the center of events, the reader’s interest piques, and the storytelling bounces between flashback and present day.
Both fiction and nonfiction writers can use In Media Res, provided it makes sense to do so. For example, Margaret Atwood’s A Handmaid’s Tale begins in the middle of a dystopian society. Atwood leads us through the society’s establishment and the narrator’s capture, but all of this is in flashback, because the focus is on navigating the narrator’s escape from this evil world.
In Media Res applies well here, because the reader feels the full intensity of this dystopia from its start. Writers who are writing stories in either alternate worlds or very private worlds may benefit from this literary device in fiction, as it helps keep the reader interested and attentive.
7. Dramatic Irony
Dramatic irony occurs when the audience understands more about the situation than the story’s characters do.
Dramatic irony is a literary device in prose in which the audience understands more about the situation than the story’s characters do. This is an especially important literary device in fiction, as it often motivates the reader to keep reading.
We often see dramatic irony in stories which involve multiple points-of-view.
We often see dramatic irony in stories which involve multiple points-of-view. For example, the audience knows that Juliet is still alive, but when Romeo discovers her seemingly dead body, he kills himself in grief. How ironic, then, for Juliet to wake up to her lover’s passing, only to kill herself in equal grief. By using dramatic irony in the story, Shakespeare points towards the haphazardness of young love.
8. Vignette
A vignette is a passage of prose that’s primarily descriptive, rather than plot-driven.
A vignette (vin-yet) refers to a passage of prose that’s primarily descriptive, rather than plot-driven. Vignettes throw the reader into the scene and emotion, often building the mood of the story and developing the character’s lens. They are largely poetic passages with little plot advancement, but the flourishes of a well-written vignette can highlight your writing style and the story’s emotions.
The story snippets we’ve included are striking examples of vignettes. They don’t advance the plot, but they push the reader into the story’s mood. Additionally, the prose style itself is emotive and poetic, examining the nuances of life’s existential questions.
9. Flashback
A flashback refers to any interruption in the story where the narration goes back in time.
A flashback refers to any interruption in the story where the narration goes back in time. The reader may need information from previous events in order to understand the present-day story, and flashbacks drop the reader into the scene itself.
Flashbacks are often used in stories that begin In Media Res, such as The Handmaid’s Tale. While the main plot of the story focuses on the narrator’s struggles against Gilead, this narration frequently alternates with explanations for how Gilead established itself. The reader gets to see the bombing of Congress, the forced immigration of POC, and the environmental/fertility crisis which gives context for Gilead’s fearmongering. We also experience the narrator’s separation from her daughter and husband, supplying readers with the story’s highly emotive world.
10. Soliloquy
A soliloquy is a long speech with no audience in the story.
Soliloquy comes from the Latin for self (sol) and talking (loquy), and self-talking describes a soliloquy perfectly. A soliloquy is a long speech with no audience in the story. Soliloquies are synonymous with monologues, though a soliloquy is usually a brief passage in a chapter, and often much more poetic.
Shakespeare’s plays abound with soliloquies. Here’s an example, pulled from Scene II Act II of Romeo and Juliet .
But soft, what light through yonder window breaks? It is the East, and Juliet is the sun. Arise, fair sun, and kill the envious moon, Who is already sick and pale with grief That thou, her maid, art far more fair than she.
Romeo isn’t talking to anyone in particular, but no matter: his soliloquy is rife with emotion and metaphor, and one can’t help but blush when he expresses how his love for Juliet makes her like the sun to him.
As a literary device in prose, soliloquy offers insight into the characters’ emotions. Soliloquy doesn’t have to be in dialogue, it can also take the form of private thoughts, but a soliloquy must be an extended conversation with oneself that exposes the character’s own feelings and ideas.
Write Powerful Literary Devices in Prose with Writers.com
The literary devices in Jane Eyre , Romeo & Juliet, and The Great Gatsby help make these stories masterful works of fiction. By using these literary building blocks, your story will sparkle, too. Take a look at our upcoming courses in fiction and nonfiction , and take the next step in writing the great American novel. Happy writing!
Sean Glatch
So amazing to here, it has helped me
Thanks, it is helpful.💯
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Maths Acceleration
- English Advanced
- Maths Standard
- Maths Advanced
- Maths Extension 1
- Maths Standard 2
- Maths Extension 2
- UCAT Preparation
- English Standard
- English Common Module Study Guides
- UCAT Preparation Course Online
Select a year to see available courses
- Level 7 English
- Level 7 Maths
- Level 8 English
- Level 8 Maths
- Level 9 English
- Level 9 Maths
- Level 9 Science
- Level 10 English
- Level 10 Maths
- Level 10 Science
- VCE English Units 1/2
- VCE Biology Units 1/2
- VCE Chemistry Units 1/2
- VCE Physics Units 1/2
- VCE Maths Methods Units 1/2
- VCE English Units 3/4
- VCE Maths Methods Units 3/4
- VCE Biology Unit 3/4
- VCE Chemistry Unit 3/4
- VCE Physics Unit 3/4
- Castle Hill
- Strathfield
- Sydney City
- Eastwood (Coming soon)
- Liverpool (Coming soon)
- Inspirational Teachers
- Great Learning Environments
- Proven Results
- Jobs at Matrix
- Events and Seminars
- Book a Free Trial
The English Literary Techniques Toolkit for The HSC

Guide Chapters
- 1. Literary Techniques Toolkit
- 2. Visual Techniques Toolkit
- 3. Film Techniques Toolkit
- 4. English Grammar Toolkit
All about the English Literary Techniques Toolkit
This Literary Techniques Toolkit is your essential resource for analysing written texts for English.
Students of all year levels should explore this page for techniques to enhance their discussion of texts and strengthen their repertoire of written techniques.
We are constantly adding to this reference to ensure that it is as detailed and comprehensive as possible to help you achieve your best in English.
What are English literary techniques?
Literary Techniques (NESA also refers to literary techniques and devices as figurative language ) are the techniques that composers use in their written texts to help convey or heighten meaning.
Rather than writing in plain language, composers give more emphasis to their ideas by utilising literary devices to make them stand out.
If you are after more practical advice about how to succeed in Year 11 and 12 English, you should read our Beginner’s Guide to Acing HSC English .
English Literary Techniques for the HSC
While the list below is a comprehensive list of literary techniques, Year 11 and 12 Matrix English Students have an extensive 30+ page Glossary of Techniques with detailed definitions and examples included at the end of each Matrix Theory Book. Please note that not all language and literary techniques are made equal! For guidance and practical strategies on how to effectively interweave literary analysis into your essay writing, check out our guide on writing body paragraphs and ‘layering analysis’.
Below is a list of the most common literary devices used in texts (the techniques underlined are clickable links that take you to expanded definitions and step-by-step tutorials on analysis):
Go to technique: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
| Literary Techniques Toolkit | |
| Literary Technique | Explanation and Example |
| An allegory is an extended metaphor where objects, persons and actions in a narrative are equated with meanings outside of the narrative. The meaning of an allegory can have moral, social, religious, or political significance, often relatable to the context of the author. A well-known example of an allegorical text is George Orwell’s Animal Farm. If you are analysing this text, you should read extracts as examples of allegories. For example, Napoleon is an allegorical counterpart of the Soviet leader Joseph Stalin. | |
| For example, in T.S. Eliot’s ‘The Hollow Men,’ there is an allusion to a celestial rose described by Dante in his Paradiso. At one point in Eliot’s poem the reader encounters the phrase ‘multifoliate rose,’ but Eliot does not mention Dante or the Paradiso by name. This is an allusion. Had Eliot quoted Dante’s Paradiso, then we would refer to this as a quotation (see below). | |
| Alliteration means the repetition of sounds at the start of a word in two or more words in close proximity. Alliteration is a real technique used in poetry, and, in some traditions, it is a unifying feature of the verse. For the most part, you should be careful identifying alliteration. It’s seldom used in prose, and when it is used in poetry, it often does not have a specific meaning, being rather a convention of the genre. Use with caution! The opening line of William Blake’s ‘The Tyger’ provides an example of alliteration: ‘Tyger, tyger, urning right,’ and this technique is used throughout the poem. | |
| A statement or aspect of a text that lacks a clear or singular meaning. Ambiguity in literary texts falls into four categories: Ambiguity is a higher order technique that can develop tension and uncertainty throughout. It is a technique you must know. ! | |
| A comparison of two things for the purpose of explanation or clarification. For example, The journalist is suggesting that we can understand aspects of the United States today by appreciating their similarity with aspects of the Roman Empire. | |
| An interesting or unique personal story or account. Composer’s use of anecdotes in both fiction and non-fiction texts to develop their ideas, demonstrate elements of a character’s personality, or add to their world. In Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire, Professor Dumbledore offers the following anecdote about his brother: “My own brother, Aberforth, was prosecuted for practising inappropriate charms on a goat. It was all over the papers, but did Aberforth hide? No, he did not! He held his head high and went about his business as usual! Of course, I’m not entirely sure he can read, so that may not have been bravery….” ( , P. 454) This anecdote is a clue to eagle-eyed readers that Aberforth, Dumbledore’s brother, is the barman of the Hog’s Head Tavern and the reason why Dumbledore knows so much about what happens there. | |
| In a text, an anomaly is something which deviates from what is normal or expected. | |
| The act of attributing human qualities to a non-human figure. Napoleon the pig in Animal Farm has been anthropomorphised – he speaks and acts like a person – and this allows Orwell to use him in an allegorical way. | |
| A rhetorical technique where a character speaks to an object, quality, or idea, or discusses somebody who is absent or dead. In ‘The Sunne Rising” by John Donne, the speaker refers to, “Busy old fool, unruly Sun, Here, the speaker takes a casual (colloquial) register and mocking tone to chide the sun for interrupting him and his lover in bed. | |
| An is a recurring idea, character, or object. Throughout literary history, there is a hero archetype, for example. Homer’s Penelope from and is considered the archetype of the faithful wife. While now understood as sexist and misogynistic, for many centuries Penelope was held up as an example of the perfect wife and used to restrict women’s behaviour and freedom. | |
| Assonance occurs when similar vowel sounds appear close together. This repetition can occur anywhere in the word, not only at the start. An example of assonance is ‘she sells sea shells by sea shore.’ Like alliteration, assonance can contribute particular meanings or effects, but is often simply an organising feature. Again, use with caution! | |
| Bricolage | This is a term usually used to describe modern texts that are constructed from pre-existing material, often belonging to multiple sources and text types. Alain De Botton’s can be broadly considered a bricolage text. This pluralistic method of representation, which reflects de Botton’s postmodernist context, suggests that there are multiple, equally valuable versions of reality – those found in art and those that we experience individually. |
| Cliché | An over-used, common expression. For example, the statements “brave as a lion” or “opposites attract” are clichés that define personal traits and relationships, respectively. |
| Repetition of consonants throughout a sentence or phrase. For example, John Keat’s “Ode to a Nightingale” employs half-rhyming consonance in the first stanza. We can see this in the first two lines: “My heart aches, and a drowsy numbness pains There is consonance in the “n” sounds in the first line and the “k” sounds in the second. | |
| . This is often done to accentuate their unique individual qualities. Paradox, antithesis, oxymoron, juxtaposition, contrast in description are all techniques that employ contrast. For example, In Shakespeare’s Henry IV, Pt 1, there is a consistent contrasting occurring between Henry, the title character, who is old and stern; his young son, Hal, or is wild, unpredictable and intelligent; and, the quick-tempered and stubborn Hotspur, Hal’s rival for the throne. Shakespeare contrasts these figures to discuss the ideal qualities of a king. | |
| Dialect | A dialect is a form of English spoken by a particular group, such as a group of people from a particular region. If your text is written in a certain dialect, you could explain why the author has chosen to adopt this language. If a character speaks in a particular dialect, that is part of their characterisation and suggests where they come from and their socio-economic status. In , Orwell includes dialogue from a woman speaking in cockney English, a dialect historically associated with East London and the working class. From this, the reader can infer that the Proles in Orwell’s novel are descendants of Cockney speakers, an inference even the novel’s protagonist would not be able to make. |
| Dialogue is one of the major techniques you will refer to, and it is often good to refer to it in connection with other techniques. For example, you may refer to the diction in a speaker’s dialogue, which will suggest their level of education. Dialogue can be used to infer a speaker’s intentions, as well as their personality (are they assertive or restrained when speaking to other people?). | |
| The selective choice of words and style of expression by an author. Diction refers to the construction of expressions which allows a text to fulfill its purpose. It can impact the tone and representation of characters and setting. In the ‘Love Song Of J. Alfred Prufrock’, T.S Eliot utilises diction to convey the decay of humanity. His careful choice of language, particularly in “I have measured out my life with coffee spoons;/I know the voices dying with a dying fall.” Through comparing the quantity of life he has remaining to coffee spoons, Eliot is able to emphasise the degradation and fragility of human life. | |
| Any text that instructs the reader or is obviously delivering a moral message. For example, Jane Austen’s is considered by some to be a didactic text because it presents examples of how a young woman should and shouldn’t behave. | |
| This refers to the use of words or expressions that are considered deictic – meaning they require on the context of other words to develop clear meaning. the most common examples of this are “me” or “here.” These words require us to know, or at least assume we know, contextual information to develop meaning. For example, in the sentence, “I talk about writing from here.” You, the reader, will assume that “I” am a teacher at Matrix and that by “here” I mean that I am writing from or at one of the Matrix campuses. Composers can manipulate and disorientate their readers by disrupting deixis in their texts. TS Eliot utilises deixis extensively in ‘The Hollow Men.’ He refers to an unknown “I” and “we” and numerous places connoted as “here” to disorientate the reader. | |
| A disjunct is a type of adverb that modifies a whole sentence. They function in a similar way to introductory clauses and introduce examples or observations by commenting on them. Jane Austen begins with a disjunct “It is a truth acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife.” The initial clause about acknowledged truth is modified by “universally” to make it hyperbolic and satirise the regency conventions of marriage. | |
| Related to Disjuncts, see above, a disjunction is a conjunction (e.g. usually ‘either’ or ‘either….or’, but also ‘but’ or ‘yet’) that dramatically interrupts the rhythm of the sentence to introduce a contrast. For example, in the Great Gatsby by Fitzgerald Nick Carraway observes that: “Conduct may be founded on the hard rock or the wet marshes, but after a certain point I don’t care what it’s founded on.” In this quotation, ‘but’ is used to dramatically dismiss the religious allusion in the previous clause. | |
| Ellipsis | Ellipsis is sometimes used to truncate quotations that are long by using three consecutive periods (…). In literature, Ellipsis can be employed in a variety of different ways. Most commonly, a dramatic pause is signalled by (…) creates tension or suggests words can’t be spoken. For example, if a character were to suggest doubt about what another has just said they might respond with, “…Sure…,” where the pauses convey the speaker’s scepticism. In , Virginia Woolf employs ellipsis to convey the unease at the Ramsay dinner table: “Why don’t some of you take up botany?.. With all those legs and arms why doesn’t one of you . . .?” So they would talk as usual, laughing, among the children. ” In addition, Woolf uses a different form of ellipsis in the second chapter of the novel, “Time Passes”. Here, she uses parenthetical insertions [in square parenthesis] to denote a passing of time – 10 years – and significant events and interrupt the narrative in each section. For example, in section 6 Woolf represents both Prue Ramsay’s marriage and subsequent death in two parenthetical remarks that bookend a description of summer: “[Prue Ramsay, leaning on her father’s arm, was given in marriage. What, people said, could have been more fitting? And, they added, how beautiful she looked!]” and then, “[Prue Ramsay died that summer in some illness connected with childbirth, which was indeed a tragedy, people said, everything, they said, had promised so well.]” |
| Words that stir the readers’ emotions. For example, Prince Hamlet’s self-indulgent rant in Scene to of Shakespeare’s Hamlet uses emotive language to describe how depressed he is: “O God! God! | |
| A poetic technique, when a sentence or phrase runs over more than one line (or stanza). Enjambment is an interesting technique. Visually, this gives the sense that the poem flows between lines. However, in utterance, enjambment leads to a pause between lines when spoken aloud. This effect is known as a . Composers often use this to disrupt the flow or a poem or contrast distinct images or ideas. In The Love Song of J Alfred Prufrock by TS Eliot, the persona states: This use of enjambment conveys a romantic image of a night sky only to contrast it with the macabre image of an unconscious patient about to undergo surgery. This is jarring contrast further emphasized by the rejet. | |
| Mild expression used to replace a harsh one. For example, an embarrassed student might tell their parent that they had a “working lunch” rather than admitting to having been given a lunchtime detention for poor behaviour. | |
| Exclamatory sentence ending in “!” to convey high emotion. In Eliot’s ‘The Love Song of J Alfred Prufrock’ the persona’s insecurities about their appearance are conveyed with the exclamation: “(They will say: “How his hair is growing thin!”)” | |
| Metaphor, metonymy, hyperbole, simile, personification, assonance, alliteration, consonance, onomatopoeia, etc. These devices have a powerful impact as they work on our senses to strengthen the subject matter of the text. You will find specific examples of the above techniques throughout this toolkit. | |
| Form | Purpose and features of a text influence its construction and will suggest its structure. |
| A flashback is a scene appearing in a text that occurs earlier than the main narrative. Flashbacks can have many effects. A significant flashback occurs in George Orwell’s , in Part Two, Chapter 7. In this scene, a traumatic dream causes a flashback in the protagonist Winston Smith. The flashback concerns painful memories involving his family. The spontaneous nature of this flashback suggests that Winston has gone to lengths to repress the traumatic memory involving his family. It is also a narrative device. By revealing new details about Winston’s past, Orwell keeps the reader engaged and interested. | |
| Incomplete sentences used to increase tension or urgency, or reflect the way people speak to each other. Sentence fragments are sentences that cannot stand on their own. A single noun is a sentence fragment, as is a subordinate clause, such as ‘That he knew better.’ If you’re trying to identify a sentence fragment, just ask yourself whether it could stand on its own, or whether it needs some other element to complete it. In the previous example, we could add ‘I said that he knew better.’ Sentence fragments can convey many things. T.S. Eliot used fragmentation in tandem with symbolism to explore non-mimetic forms of expression, for example in ‘The Hollow Men’. Fragmentation will usually convey notions of destruction and decay, so when interpreting instances of it think about what sorts of themes your author is exploring. | |
| Gaps & silences | What is not said; whose voice isn’t heard and whose voice dominates? |
| Humour | Incongruity, parody, satire, exaggeration, irony, puns etc. used to lighten the overall tone. |
| . This is a simple technique, so refer to it sparingly. In , Jane Austen uses hyperbole in Elton’s comment that, “I have no hesitation in saying — at least if my friend feels at all as I do — I have not the smallest doubt that, could he see his little effusion honoured as I see it, (looking at the book again, and replacing it on the table), he would consider it as the proudest moment of his life,” to convey the growing misunderstanding between Elton, Harriet, and Emma about who fanices whom. | |
| Icons | A single person, object or image that represents complex ideas and feelings. |
| Imagery is language that evokes one of the five senses, and you must always refer to the specific kind. In other words, never use simply ‘imagery,’ but always ‘olfactory imagery,’ ‘tactile imagery,’ ‘visual imagery,’ ‘auditory imagery’ or ‘gustatory imagery.’ Occasionally, students, noticing that ‘visual imagery’ is something of a tautology, omit the adjective ‘visual’ when referring to this category. They shouldn’t, though. Always be specific. | |
| Forceful use of the verb at the start of sentence or phrase. The imperative mood is one of the grammatical moods in English. Other moods include the indicative (as in ‘That cat is suspicious’) and the interrogative (‘Is that cat suspicious?’). The imperative mood is useful to refer to since it’s the mood for commands (e.g. ‘Go to bed!’ ‘Shut the door!). If a speaker uses the imperative, then he or she may be an authority figure. Before the third section of Orwell’s , Winston and Julia are caught. A man named Mr. Charrington, whom Winston had believed was a gentle shopkeeper, turns out to be a member of the secret police. Mr. Charrington’s authority in the secret police is indicated by his use of the imperative to command another officer when he first enters the room. | |
| A poetic form that uses repetition, rhythm, and/or rhyme to convey a sense of magic or magical power. The song of the Weird Sisters, or Three Witches, in Shakespeare’s Macbeth (1606) is a good example of an incantation: Double, double toil and trouble; | |
| This reference can be an explicit quotation or implied and inferred by allusion. For example, much of the meaning in Margaret Edson’s play is developed through constant intertextual references to the poetry of John Donne. | |
| , as opposed to slowly building up to this action. This is an ancient technique, and it has a number of meanings. Most obviously, it’s a hook to draw the reader in. It can also be used to disorientate. Homer’s , the first text of western literature, begins in medias res. t begins in medias res, many years after Prospero and his daughter, Miranda, have been stranded on Caliban’s Isle after Antonio’s treachery. | |
| For example In Fitzgerald’sThe Great Gatsby, Nick Carraway’s assertion that, “I’m inclined to reserve all judgments, a habit that has opened up many curious natures to me and also made me the victim of not a few veteran bores,” is ironic because he is not, in fact, reserving judgement on those he calls “veteran bores.” | |
| In Act 3, Scene 4 of Shakespeare’s , the eponymous Prince holds up images of his father and uncle to illustrate Hamlet’s feelings about their differences through juxtaposition: “Look here upon this picture and on this, | |
| Level of language (also known as Register) | This refers to the level of sophistication of a piece of language. We expect a high register in formal contexts, while we might expect lower registers in more familiar contexts. High register is signalled by conceptual, ‘bigger’ vocabulary and complex, lengthy syntax. The common registers we refer to are: slang, colloquial, informal or formal. Consider the following greetings: |
| Sequential – in chronological order. In a linear narrative, authors simply tell the reader what happens in their story chronologically. The linear narrative of a bank robbery might begin with the bandits approaching in their car and move through all the noteworthy incidents until their inevitable capture and arrest. While it begins , Shakespeare’s is a linear narrative. The non-linear version might begin in media res during a shootout, and move backwards to explain how the robbers arrived in their predicament, before moving forward to the resolution of the story. Margaret Atwood’s is a non-linear text. | |
| Metaphor is one of the most fundamental figures of speech, and indeed aspects of language itself. Literary texts are typically dense in metaphor. In the cases of writers such as Shakespeare, it is impossible to understand the text without constantly unpacking metaphors. In Shakespeare’s Henry IV, Pt 1, Sir John Fallstaff on the homonyms “son” and “sun” to develop the metaphor of Prince Hal as the Sun, the ruler of the heavens: “If then thou be son to me, here lies the point: why, being son to me, art thou so pointed at? Shall the blessed sun of heaven prove a micher and eat blackberries? . . . Shall the son of England prove a thief and take purses?” (2.4.359-67) | |
| A word or name that is used in the place of something it is closely related to. The Kremlin, for example, has long been conventionally used as a metonym for the Russian government. A student might say, “I’m going to Matrix.” But they really mean that they are going to the Matrix Hurstville Campus. In this usage, the proper noun, “Matrix,” is metonymic with all of the Matrix campuses. | |
| The certainty which a speaker employs in their language. = Certainty. “It will hail today.” (also called ) = doubt that something that should occur will occur. “It ought to rain today.” = Uncertainty. “It may rain today.” | |
| A motif is an image, sound, figure, character archetype or object which has a symbolic reference to a particular theme or idea. A motif is a recurring symbol with a figurative meaning and is quite easy to spot due to its prominence. In Great Gatsby, Fitzgerald utilises the recurring motif of weather to reflect the emotions experienced by the characters. When Daisy and Gatsy reunite it is pouring however when there love reignites the sun is just coming out. | |
| Non-linear | Non-sequential narrative, events do not occur in chronological order. See, above. |
| Onomatopoeia | A word that echoes the sound it represents. The reader hears what is happening. Sometimes this can be overt, as in “the drip-dripping and plip-plopping of a tap.” Other times, this can be more subtle, such as in “The murmurous haunt of flies on summer eve” from John Keats’ ‘Ode to a Nightingale.” This example is specifically known as mechanical onomatopoeia because the sound of the word imitates the same sound being referenced – “murmurous” sounds like the low buzz of a swarm of flies. |
| Paradox | A statement that is self-contradictory or logically unacceptable but has valid reasoning based on a true premise. It is a juxtaposition of contradictory-yet-interrelated ideas which have a hidden truth. In George Orwell’s Nineteen Eighty-Four, The Party’s slogan “War is peace, freedom is slavery, and ignorance is strength,” is a clear example of a paradox whereby each idea contradicts the other. Thus, Orwell clearly utilises contradictory statements throughout his novel to place emphasis on a society controlled by a totalitarian government. |
| Conscious imitation for a satiric purpose. Parody is a style that mocks the serious manner and characteristic features of literary works through imitation. Parodies work by exaggerating certain traits common to the work. In George Orwell’s Winston reads a heretical political tract called ‘The Theory and Practice of Oligarchical Collectivism’. This tract is clearly a parody of political writing and in particular the theoretical writing of communist revolutionaries like Vladimir Lenin, Leon Trotsky, and Joseph Stalin. Orwell’s aim is to subvert the self-important, vague, and even contradictory style found in these texts. | |
| Pathetic fallacy is the attribution of human emotions to nonhuman objects, particularly objects of nature. Note that the term should just apply to the ascription of emotions, not thoughts or other properties. The term was invented by the English writer John Ruskin, and is widely used in literature. In Dickens’ Pip’s misery is reflected in the weather which surrounds him: “It was wretched weather; stormy and wet, stormy and wet; and mud, mud, mud, deep in all the streets. Day after day, a vast heavy veil had been driving over London from the East, and it drove still, as if in the East there were an Eternity of cloud and wind. So furious had been the gusts, that high buildings in town had had the lead stripped off their roofs; and in the country, trees had been torn up, and sails of windmills carried away; and gloomy accounts had come in from the coast, of shipwreck and death. Violent blasts of rain had accompanied these rages of wind, and the day just closed as I sat down to read had been the worst of all.” | |
| First, second or third person. refers to the speaker himself or a group that includes the speaker (i.e., I, me, we and us). T.S. Eliot’s ‘Journey of the Magi’ is a first person narrative. refers to the speaker’s audience (i.e., you). Italo Calvino’s is a narrative in the second person. refers to everybody else (e.g., he, him, she, her, it, they, them), including all other nouns (e.g. James, Swedish, fish, mice). Jane Austen’s Emma is written in the third person. Some texts might shift between different perspectives throughout. T.S. Eliot’s ‘Preludes’ is relatively unusual in that it switches between first, second, and third person throughout. | |
| Circumlocution. That is, the use of a longer expression for an idea where a shorter one might suffice. Periphrasis is widespread, and often quite significant as a technique. Writers sometimes use periphrasis to refer to an object or person in a more creative way, or to avoid repetition. In Shakespeare’s , Polonius often speaks periphrastically, from which the reader can infer much about his character. | |
| Human characteristics given to a non-human object. Inanimate objects take on a life. Personification is usually well-understood by students. It is a specific kind of metaphor in which human attributes are applied to nonhumans. Note that unlike pathetic fallacy, personification involves the application of any form of an attribute, not just emotions. Like other forms of metaphor, it is widely used in literature, as well as daily life. In John Donne’s ‘Death, be Not Proud,’ Donne personifies Death. | |
| A particular way of looking at individuals, issues, events, texts, facts etc. | |
| Harsh sounds in a sentence or phrase. While this can be used to draw attention to specific things in the sentence, more often than not it is purely an aesthetic device. Use this technique with caution. | |
| A pun is formed by exploiting two different meanings of the same sound. Richard’s famous soliloquy at the start of Mod A text Richard III includes a pun. Speaking at the end of a battle, Richard declares that ‘Now is the winter of our discontent / Made glorious summer by this sun of York.’ The sun of York brings this summer, and ‘sun’ is, of course, a pun on ‘son’ as Edward is the first son of the York family – and thus the rightful heir to the throne (according to the Yorks). | |
| Reference | Reference is a very broad term. It simply means mentioning, usually clearly and unambiguously, something else, whether it is a historical event, another author, another text, or even a set of ideas. ‘No! I am not Prince Hamlet’ is a reference to Shakespeare’s in his T.S. Eliot’s poem, ‘The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock.’ |
| See | |
| An effect of enjambment. The rejet is the disjunction between the appearance of a poem flowing between lines on a page and the pause that speakers unconsciously insert between lines when first reading a poem aloud. See . | |
| . Repetition does matter, but it is an extremely easy technique to identify, so you should refer to it sparingly, and always analyse it further. Never point out that repetition of a term emphasises the term. Instead, think critically about what the repetition actually suggests. A famous example of repetition comes at the end of T.S. Eliot’s ‘The Hollow Men’: Declaring that this repetition ‘highlights’ or ‘emphasises’ Eliot’s idea tells the reader nothing. To begin with, what is the idea? Repetition here has to be interpreted in the context of the central themes of the poem. You could begin by thinking about how this repetition relates to the cycles of revolution alluded to elsewhere in the poem, or to the scientific theories, including the theory of entropy, Eliot appears to explore. . | |
| How a composer conveys meaning through textual features. This is a key concept in works of art. . | |
| Rhyme is one of the most familiar techniques, and there is little to be said about it. Rhyme is often more of an organising feature and used to please aesthetically rather than to create meaning. Be careful in attributing meaning to rhyme in verse. It usually doesn’t mean anything. | |
| . In satire, common human behaviours, beliefs, and vices are held up to shame and scorn. Satire is often considered a high form of comedy. Satire is often employed for biting social or political commentary. Queen Elizabeth I banned satire in 1599 to curb criticism of her reign in print. Satire is often a part of Shakespeare’s plays, such as in the historical play, Henry IV, Part 1. Many critics argue that the character of Falstaff is a satirical representation of Sir John Oldcastle, a Lollard (the pre-cursor to protestants) who was executed for treason and heresy. Falstaff’s character was originally called, John Oldcastle, but complaints by a prominent Lord, William Brooke, 10th Baron Cobham, forced Shakespeare to rename him. | |
| Location of a story – internal and external. | |
| The repetition of soft consonant sounds, such as “s” sounds. This is often used to create a sinister or sensuous tone or mood. For example, in John Keats’ ‘Hyperion’ he develops a sinister mood through sibilance in the description, “Instead of thrones, hard flint they sat upon Couches of rugged stone, and slaty ridge Stubborn’d with iron.” | |
| , but rather than identifying the tenor and vehicle, tend to make the comparison using ‘like’ or ‘as,’ while metaphors tend to use a form of the verb ‘to be.’ King Hamlet uses simile to emphasise his sufferings in hell, declaring to Hamlet that the details of his tortures would: | |
| . Symbolism is a very important technique, and in some texts, it is the central technique. A symbol is any visual object that by convention signifies something else, whether it be another object, an idea, a process, or an emotion. The letters of the alphabet are therefore symbols, in that they represent speech sounds. Numbers are symbols. Although all language is symbolic, literary symbolism usually refers more specifically to the use of objects to represent ideas and emotions. The Eliot poems set for study in Module B are all heavily symbolic. Consider the following example, from the opening of Eliot’s ‘The Hollow Men’: A first step in interpreting the symbolism is to think about the ideas the objects conventionally imply. ‘Hollow’ and ‘dried’ and ‘dry’ all evoke aridity. This suggests the poem might be concerned with decline and decay. Eliot was influenced by Frazer’s , which he cited in the notes to his most famous poem, The Waste Land. (A reader wanting to push her analysis further would look into how the symbols evoking aridity reflect Frazer’s theory that a number of important religions, including Christianity, had their origins in prehistoric fertility cults.) | |
| Syntax is one of the main components of language. It refers to the organisation of words and phrases in a sentence, as well as their structural relations. For example, in the English sentence ‘John thanked the president,’ we know that John is the one doing the thanking since English syntax usually follows a subject, verb, object order. ‘John’ is the subject, ‘thanked’ is the verb, and ‘the president’ is the object. If I swap the roles, the nouns of English syntax change the meaning of the sentence: ‘The president thanked John.’Therefore, when referring to syntax as a technique, you need to provide further analysis. Some strategies you can take to assess this are: is a marker of a high education. This could imply a narrative voice that is well-educated. might be a marker of poor education, as might fragmented or incomplete syntax. | |
| Tense | Present, past, future (events are predicted). This is an important and commonplace feature of grammar that students should be familiar. Tense is an important aspect of narrative form and can tell the audience when things are occurring. T.S Eliot’s ‘Preludes’ is written in the present continuous tense in sections I and II but then is written in the past tense in sections III and IV. |
| The organic unit of a text. Its use of universal themes. This is an essential part of Year 11 and Year 12 Module B. | |
| Message or moral of a story – makes us ponder bigger issues in life. | |
| The way composer or character feels – conveyed by word choice. Tone is a very common technique and useful to discuss in your responses. There are many different ways to describe the tone of a text. Here is an . | |
| Word choice or Diction | Emotive, forceful, factual, descriptive, blunt, graphic, disturbing, informative etc. E.g. use of forceful verbs ‘insist’ & ‘demand’ can be very persuasive. Diction is a useful technique to discuss, especially if you are using it to convey information about the characterisation of that person. For example, in Shakespeare’s , Iago’s bestial and demonic diction is adopted by Othello as the play progresses, symbolising the loss of Othello’s nobility. |
| Zoomorphism | The attribution of animal properties to non-animals. This technique is more common than many people expect. It is used, for example, in Eliot’s ‘Prufrock’: The fog appears to be compared with a dog, which is suggested by the actions of the fog and the diction throughout, such as the word ‘muzzle.’ This somewhat uncanny image is difficult to interpret, but at the least relates to the disorientation caused to the speaker by the urban environment. |
If you want to take your analysis further and expand your awareness of literary techniques, read the blog post: Understanding Literary Techniques: How to Analyse Poetry and Prose to learn how to analyse literary techniques in poetry and prose with reference to all the major techniques.
When you write an essay identifying the techniques used by a composer, you need to explain how that technique is creating meaning in the text. It is not enough to just cite a literary term. You need to discuss the device or technique in detail. This process is called literary analysis and it is an important skill that Matrix English students are taught in the Matrix English courses.
Great marks in essays and writing tasks are earned through the detailed analysis of your texts and not merely listing examples and techniques. You can learn more about how to analyse texts in our Beginner’s Guide to Acing HSC English .
The Visual Techniques Toolkit
© Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au, 2023. Unauthorised use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.
Related courses
Year 11 english advanced.
Year 11 English Advanced tutoring at Matrix will help your child improve their English skills and confidence.
Learning methods available
Year 11 English Advanced Online
Year 11 english advanced term, year 12 english advanced holiday.
Year 12 English Advanced tutoring at Matrix will help you gain strong reading and writing skills for the HSC.
Year 12 English Advanced Online
Year 12 english advanced term, more essential guides.

English Grammar Toolkit

The Beginner's Guide to Acing HSC English
Ultimate List of High School Student Maths Hacks | Success Secrets

Visual Techniques for English Essays: A Complete Guide
Visual techniques in English may be something you are familiar with, but it also may be completely new to you, and that’s okay! In HSC, QCE, ATAR, and other English curriculums, you have to use visual techniques to discuss images in books, videos, or book covers and analyse the visual and interpretation techniques within them, for meaning. The visual techniques outlined in this article focus mainly on images rather than film clips as these are likely to come across in your external HSC system. Still, these techniques can easily be transferred to film clips.
What Are Visual Techniques in English?
Visual techniques are the elements of an image, video, or artwork that help to create meaning. They are used by different artists and creators for many reasons, but we analyse them to help us discern and create meaning from text when writing English essays .
Essential English Visual Techniques
Analysing visual techniques in your English essays is vital for success in your career as an English student. Many other things can help you get an A in English as well, but here we are focusing on breaking down different visual techniques. The different techniques are listed and expanded upon below.
1. Composition
Composition is what an image is made up of . This includes things like where an object is placed, how it is framed, and the colour and lighting techniques used. Composition broadly refers to the image as a whole and what you see when you look at it.
Using this in an essay could look like this: The Mona Lisa is a picture of a woman’s torso taking up the majority of the piece in front of a nature background.
Colour is the colours used in an image and what they can symbolise. Oftentimes different colours will evoke different emotions in the audience. For example, purple is a colour of royalty, wealth and luxury, whereas red represents passion, lust and anger.
Colour also includes the tone of the colour, if it is bright and vivid or dull and de-saturated. Using this in an essay could look like: The deep, saturated colours used in the Mona Lisa evoke feelings of calm and peace.
If you are a visual learner , you may already be using this without even knowing it! This could be through colour-coding different subjects or thoughts, or working better with diagrams and colours built into your notes.
3. Symbolism
Symbolism is the use of one object or image to represent another more complex concept. Things like religious symbolism and animal symbolism are often used.
Using this in an essay could look like: Frida Kahlo’s use of the hummingbird in Self Portrait with Thorn Necklace and Hummingbird symbolises hope in her culture.
Texture refers to the literal texture of an object. Is it rough or smooth? Does it have different ridges and feelings across the object?
Using this in an essay could look like: Van Gogh’s Starry Night has a heavy texture throughout the image.
5. Perspective
Perspective is how a three-dimensional object is placed on a two-dimensional surface. In artworks, perspective also changes the angle at which you, as the viewer, perceive the object.
Using this in an essay could look like: In Self Portrait with Thorn Necklace and Hummingbird, the viewer is placed in a front-on perspective, looking directly at Kahlo.
6. Lighting
Lighting is how an image is lit or not lit. This can include natural lighting like sunlight or open windows, man-made lighting like lamps or torches, or feature lighting like coloured lights or spotlights. Lighting has a major impact on the mood and atmosphere of a piece of art.
Framing includes the camera shots and angles used across images and film to foster differing audience reactions and emotions. These techniques include a close-up, extreme close-up, mid shots, aerial shots, and many more.
Using this in an essay could look like this: The artist uses an extreme close-up of the subject to create a feeling of tension and unease in the viewer.
8. Proportion and Scale
Proportion is the size of the different parts of an object in relation to each other. Scale is the size of one object to another in the same artwork.
Using this in an essay could look like: The artist uses realistic proportions across the image. The artist plays with scale to create a more surrealist feel in the image.
9. Point of View
Point of view refers to how the shot is framed in reference to the viewer or a character. For example, is the audience placed level with, above or below the subject of the image.
Using this in an essay could look like: The point of view in the image places the viewer looking down at the subject.
10. Text and Typography
Text and typography are the words used within an image to convey a literal or figurative message. This is influenced by the colour, size, and font of the text as well as its repetition throughout the image.
Using this in an essay could look like: The text within the image conveys both its literal message based on the words, and a subliminal message based on the wider context of the whole image.
Need extra help with English assignments?

Ready to take your visual analysis skills to the next level? Sign up for our English tutoring services today and get personalised guidance and support from experienced academic personal trainers.
Whether you need help with literary analysis, essay writing, or visual techniques in literature, our team is here to help you succeed. Contact us now to schedule your first session and start achieving your academic goals!
Recent Posts
- 7 Effective Time Management Tips For Students
- How to Write a Comparative Essay: Structure, Tips & Examples
- How to Analyse a Text for English Class: 7 Textual Analysis Tips
- Cameron McEvoy and A Team Tuition Unite to Empower Young Minds
- Our 4 Most In-Demand Subjects for HSC Tutoring
- Advice For Parents
- Foundations of Learning
- How to Succeed
- Neurodivergent Learning
- ATAR for University Admissions
- Career Paths
- High School Programs and Classes
- Transformation Stories
Privacy Overview

- Services for education institutions
- Academic subject areas
- Peer connection
- Evidence of Studiosity impact
- Case studies from our partners
- Research Hub
- The Tracey Bretag Integrity Prize
- The Studiosity Symposium
- Studiosity for English learners
- Video case studies
- Meet the online team
Academic Advisory Board
Meet the board.
- Social responsibility
- Meet the team
- Join the team

How to structure paragraphs using the PEEL method
Sophia Gardner
Sep 1, 2023
You may have heard of the acronym PEEL for essays, but what exactly does it mean? And how can it help you? We’re here to explain it all, plus give you some tips on how to nail your next essay.
There’s certainly an art to writing essays. If you haven’t written one for a while, or if you would like to hone your academic writing skills, the PEEL paragraph method is an easy way to get your point across in a clear and concise way, that is easily digestible to the reader.
So, what exactly is PEEL ?

The PEEL paragraph method is a technique used in writing to help structure paragraphs in a way that presents a single clear and focused argument, which links back to the essay topic or thesis statement.
It’s good practice to dedicate each paragraph to one aspect of your argument, and the PEEL structure simplifies this for you.
It allows you to create a paragraph that is easy and accessible for others to understand. Remember, when you’re writing something, it’s not just you who is reading it - you need to consider the reader and how they are going to be digesting this new information.
What does PEEL stand for?
P = Point: start your paragraph with a clear topic sentence that establishes what your paragraph is going to be about. Your point should support your essay argument or thesis statement.
E = Evidence/Example: here you should use a piece of evidence or an example that helps to reaffirm your initial point and develop the argument.
E = Explain: next you need to explain exactly how your evidence/example supports your point, giving further information to ensure that your reader understands its relevance.
L = Link: to finish the paragraph off, you need to link the point you’ve just made back to your essay question, topic, or thesis.
Download a free PEEL paragraph planner below. 👇

Studiosity English specialist Ellen, says says students often underestimate the importance of a well-structured paragraph.
PEEL in practice
Here’s an example of what you might include in a PEEL structured paragraph:
Topic: Should infants be given iPads? Thesis/argument: Infants should not be given iPads.
Point : Infants should not be given iPads, because studies show children under two can face developmental delays if they are exposed to too much screen time.
Evidence/Example: A recent paediatric study showed that infants who are exposed to too much screen time may experience delays in speech development.
Explanation: The reason infants are facing these delays is because screen time is replacing other key developmental activities.
Link: The evidence suggests that infants who have a lot of screen time experience negative consequences in their speech development, and therefore they should not be exposed to iPads at such a young age.
Once you’ve written your PEEL paragraph, do a checklist to ensure you have covered off all four elements of the PEEL structure. Your point should be a clear introduction to the argument you are making in this paragraph; your example or evidence should be strong and relevant (ask yourself, have you chosen the best example?); your explanation should be demonstrate why your evidence is important and how it conveys meaning; and your link should summarise the point you’ve just made and link back to the broader essay argument or topic.

Keep your paragraphs clear, focused, and not too long. If you find your paragraphs are getting lengthy, take a look at how you could split them into multiple paragraphs, and ensure you’re creating a new paragraph for each new idea you introduce to the essay.
Finally, it’s important to always proofread your paragraph. Read it once, twice, and then read it again. Check your paragraph for spelling, grammar, language and sentence flow. A good way to do this is to read it aloud to yourself, and if it sounds clunky or unclear, consider rewriting it.
That’s it! We hope this helps explain the PEEL method and how it can help you with your next essay. 😊
You might also like: Proofreading vs editing: what's the difference? How to get easy marks in an exam 5 study hacks that actually work
Topics: English , Writing , Grammar
About Studiosity
Asking for feedback on your work is an essential part of learning. So when you want to better understand a concept or check you're on the right track, we're here for you.
Find out if you have free access through your institution here .
Recent Posts
Posts by topic.
- Students (85)
- Higher education (66)
- Student Experience (46)
- University (46)
- Education (41)
- online study (34)
- Learning (28)
- Tertiary education (28)
- Educators (27)
- Interview (27)
- Research (24)
- Parents (23)
- English (18)
- High School (18)
- Technology (17)
- students first (17)
- Podcast (16)
- Writing (16)
- Student stories (14)
- Homework (13)
- Assignment Help (12)
- Education policy (12)
- Formative feedback (12)
- Literacy (12)
- academic integrity (12)
- student wellbeing (12)
- Events (11)
- Academic Advisory Board (10)
- Studiosity (10)
- covid19 (10)
- international student (10)
- Australia (9)
- Health and Wellbeing (9)
- Learning trends (9)
- Student satisfaction (9)
- Teaching (9)
- Secondary education (8)
- Equality (7)
- Science (7)
- Student retention (7)
- UK students (7)
- staff wellbeing (7)
- Student support (6)
- UK Higher Education (6)
- academic services (6)
- online learning (6)
- CanHigherEd (5)
- Online Tutoring (5)
- Workload (5)
- belonging (5)
- CVs and cover letters (4)
- Internet (4)
- Mathematics (4)
- Partnerships (4)
- School holidays (4)
- Student performance (4)
- Widening Participation (4)
- student success (4)
- #InthisTogether (3)
- Grammar (3)
- University of Exeter (3)
- teaching & learning (3)
- Charity (2)
- Government (2)
- Mentors (2)
- Primary education (2)
- Subject Specialists (2)
- accessibility (2)
- community (2)
- diversity (2)
- plagiarism prevention (2)
- student stress (2)
- webinar (2)
- Biology (1)
- Careers (1)
- Chemistry (1)
- EU students (1)
- First years (1)
- Indigenous Strategy (1)
- Nutrition (1)
- Teacher (1)
- academic support (1)
- academic writing (1)
- business schools (1)
- choice of language (1)
- dyslexia (1)
- ethical AI (1)
- job help (1)
- library services (1)
- podcasts (1)
- reflection (1)
- university of west of england (1)
- July 2015 (12)
- March 2020 (11)
- June 2020 (10)
- July 2020 (8)
- September 2020 (8)
- March 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (7)
- October 2019 (7)
- April 2020 (7)
- May 2018 (6)
- April 2019 (6)
- May 2020 (6)
- September 2022 (6)
- June 2015 (5)
- August 2015 (5)
- December 2017 (5)
- March 2018 (5)
- February 2020 (5)
- March 2021 (5)
- June 2021 (5)
- July 2016 (4)
- March 2017 (4)
- October 2017 (4)
- February 2018 (4)
- August 2018 (4)
- May 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (4)
- March 2024 (4)
- February 2015 (3)
- May 2015 (3)
- September 2015 (3)
- December 2015 (3)
- January 2016 (3)
- April 2016 (3)
- October 2016 (3)
- December 2016 (3)
- April 2017 (3)
- September 2017 (3)
- April 2018 (3)
- October 2018 (3)
- March 2019 (3)
- January 2020 (3)
- October 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (3)
- June 2022 (3)
- October 2022 (3)
- November 2022 (3)
- August 2023 (3)
- November 2023 (3)
- April 2024 (3)
- July 2024 (3)
- March 2016 (2)
- May 2016 (2)
- August 2016 (2)
- July 2017 (2)
- January 2018 (2)
- November 2018 (2)
- December 2018 (2)
- February 2019 (2)
- June 2019 (2)
- September 2019 (2)
- January 2021 (2)
- February 2021 (2)
- April 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (2)
- September 2021 (2)
- December 2021 (2)
- August 2022 (2)
- February 2023 (2)
- March 2023 (2)
- May 2023 (2)
- December 2023 (2)
- June 2024 (2)
- August 2024 (2)
- October 2008 (1)
- August 2013 (1)
- October 2015 (1)
- February 2016 (1)
- June 2016 (1)
- September 2016 (1)
- November 2016 (1)
- January 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (1)
- June 2017 (1)
- August 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (1)
- June 2018 (1)
- September 2018 (1)
- January 2019 (1)
- November 2019 (1)
- December 2019 (1)
- August 2020 (1)
- December 2020 (1)
- May 2021 (1)
- February 2022 (1)
- March 2022 (1)
- July 2022 (1)
- December 2022 (1)
- January 2023 (1)
- June 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- September 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (1)
- February 2024 (1)
Studiosity is personalised study help, anytime, anywhere. We partner with institutions to extend their core academic skills support online with timely, after-hours help for all their students, at scale - regardless of their background, study mode or location.
Now you can subscribe to our educator newsletter, for insights and free downloads straight to your inbox:

ABN 41 114 279 668
Student zone, assignment calculator, calendars and organisers, study survival guides, free practice tests, student faqs, download our mobile app, student sign in, success stories.
Student Reviews & Testimonials
Specialist Sign In
Meet our specialists
Meet the team, media and research, student reviews.
Read more on Google

Studiosity acknowledges the Traditional Indigenous Custodians of country throughout Australia, and all lands where we work, and recognises their continuing connection to land, waters, and culture. We pay our respects to Elders past and present.
Contact • FAQ • Privacy • Accessibility • Acceptable Use • Terms of Use AI-for-Learning Polic y • Academic Integrity Policy
You are using an outdated browser. This site may not look the way it was intended for you. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience and security.
London School of Journalism
- Tel: +44 (0) 20 7432 8140
- [email protected]
- Student log in
Search courses
English literature essays, an english literature essay archive, written by our students, with subjects ranging from shakespeare to artistotle, and from dickens to hemingway, essay subjects in alphabetical order:.
- Aristotle: Poetics
Margaret Atwood
Margaret atwood 'gertrude talks back'.
- Matthew Arnold
John Bunyan: The Pilgrim's Progress and Geoffrey Chaucer: The Canterbury Tales
- Jonathan Bayliss
- Lewis Carroll, Samuel Beckett
- Saul Bellow and Ken Kesey
- Castiglione: The Courtier
- Joseph Conrad: Heart of Darkness
- Kate Chopin: The Awakening
- T S Eliot, Albert Camus
- Charles Dickens
- John Donne: Love poetry
- John Dryden: Translation of Ovid
- T S Eliot: Four Quartets
- Henry Fielding
- William Faulkner: Sartoris
- Graham Greene: Brighton Rock
- Ibsen, Lawrence, Galsworthy
- Jonathan Swift and John Gay
- Oliver Goldsmith
- Ernest Hemingway
- Nathaniel Hawthorne: The Scarlet Letter
Thomas Hardy: Tess of the d'Urbervilles
- Carl Gustav Jung
James Joyce: A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man
- Jon Jost: American independent film-maker
- Jamaica Kincaid, Merle Hodge, George Lamming
- Rudyard Kipling: Kim
- D. H. Lawrence: Women in Love
Henry Lawson: 'Eureka!'
- Ian McEwan: The Cement Garden
- Jennifer Maiden: The Winter Baby
- Machiavelli: The Prince
- Toni Morrison: Beloved and Jazz
R K Narayan
- R K Narayan: The English Teacher
- R K Narayan: The Guide
- Alexander Pope: The Rape of the Lock
- Brian Patten
- Harold Pinter
- Sylvia Plath and Alice Walker
Jean Rhys: Wide Sargasso Sea. Charlotte Bronte: Jane Eyre
- Edmund Spenser: The Faerie Queene
- Shakespeare: Antony and Cleopatra
- Shakespeare: Coriolanus
- Shakespeare: Hamlet
- Shakespeare: Measure for Measure
Shakespeare: Shakespeare's Women
Shakespeare: the winter's tale and the tempest.
- Shakespeare: Twelfth Night
- Sir Philip Sidney: Astrophil and Stella
- Tom Stoppard
William Styron: Sophie's Choice
- William Wordsworth
Miscellaneous
- Alice, Harry Potter and the computer game
Indian women's writing
- New York! New York!
- Photography and the New Native American Aesthetic
- Renaissance poetry
- Renaissance tragedy and investigator heroes
- Romanticism
- Studying English Literature
- The Age of Reason
- The author, the text, and the reader
- The Spy in the Computer
- What is literary writing?
- Margaret Atwood: Bodily Harm and The Handmaid's Tale
- Margaret Atwood 'Gertrude Talks Back'
- John Bunyan: The Pilgrim's Progress and Geoffrey Chaucer: The Canterbury Tales
- Thomas Hardy: Tess of the d'Urbervilles
- James Joyce: A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man: Will McManus
- James Joyce: A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man: Ian Mackean
- James Joyce: A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man: Ben Foley
- Henry Lawson: 'Eureka!'
- R K Narayan's vision of life
- Jean Rhys: Wide Sargasso Sea. Charlotte Bronte: Jane Eyre: Doubles
- Jean Rhys: Wide Sargasso Sea. Charlotte Bronte: Jane Eyre: Symbolism
- Shakespeare: Shakespeare's Women
- Shakespeare: The Winter's Tale and The Tempest
- William Wordsworth and Lucy
- Indian women's writing
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Advance articles
- The ALH Review
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Why Submit?
- About American Literary History
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Terms and Conditions
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

- < Previous
Progressive Originalism and the New Canon Wars
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Almas Khan, Progressive Originalism and the New Canon Wars, American Literary History , Volume 36, Issue 3, Fall 2024, Pages 809–814, https://doi.org/10.1093/alh/ajae074
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This essay responds to Geoffrey Kirsch’s review essay “What’s Past is Prologue: Democracy in the Age of Originalism” by evaluating how the three texts Kirsch reviews—Kermit Roosevelt, III’s The Nation That Never Was: Reconstructing America’s Story (2022), Cass R. Sunstein’s How to Interpret the Constitution (2023), and D. Berton Emerson and Gregory Laski’s edited collection Democracies in America: Keywords for the Nineteenth Century and Today (2023)—engage with progressive originalism. Drawing inspiration from civil rights activists including Frederick Douglass, progressive originalists seek to recast an ostensibly conservative method of constitutional interpretation grounded in what the “founding fathers” or a historical public thought or intended. Roosevelt’s and Sunstein’s books reveal the potential and limits of both progressive originalism and insular disciplinary conversations about constitutional interpretation. Contrastingly, the multidisciplinary Democracies in America has a more expansive conception of whose voices should matter when interpreting the Constitution through a progressive originalist lens. A comparative analysis of the three books also demonstrates the value of literature and literary historians in an age characterized by the ascendancy of historical approaches to constitutional interpretation and a revival of the “canon wars.”
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Short-term Access
To purchase short-term access, please sign in to your personal account above.
Don't already have a personal account? Register
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1468-4365
- Print ISSN 0896-7148
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis, nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Literary devices are techniques that writers use to create a special and pointed effect in their writing, to convey information, or to help readers understand their writing on a deeper level. Often, literary devices are used in writing for emphasis or clarity.
A literary device is a writing technique that writers use to express ideas, convey meaning, and highlight important themes in a piece of text. A metaphor, like we mentioned earlier, is a famous example of a literary device. These devices serve a wide range of purposes in literature.
Literary devices and terms are the techniques and elements—from figures of speech to narrative devices to poetic meters—that writers use to create narrative literature, poetry, speeches, or any other form of writing.
Learn how to write a literary analysis by examining the author's use of literary devices and discover the elements of a strong analytical essay.
Literary devices are specific techniques that allow a writer to convey a deeper meaning that goes beyond what's on the page. Literary devices work alongside plot and characters to elevate a story and prompt reflection on life, society, and what it means to be human.
Literary devices, also known as literary elements, are techniques that writers use to convey their message more powerfully or to enhance their writing. Many Authors use literary devices without even realizing it.
Literary devices are ways of taking writing beyond its straightforward, literal meaning. In that sense, they are techniques for helping guide the reader in how to read the piece.
By definition, a rhetorical device is a technique used in writing or speech to convince a reader or listener of something, while a literary device is a technique used in writing or speech to express something.
Learn about some of the most common literary elements and how to identify them, plus how to use literary devices in your own writing.
In this article, we'll share how to perform literary analysis on any text, as well as how to write a literary analysis essay (including worksheets for writing your thesis statement and body paragraphs).
Literary devices are techniques and tools used by writers to convey meaning, create a particular mood or tone, and enhance the overall effect of their writing. We use these literary devices in creative writing such as literature and poetry. These are also used in non-fiction works and other types of communication.
Instead, the best writers understand that writing is a process: it takes time; sustained attention; and a willingness to change, expand, and even delete words as one writes. Good writing also takes a willingness to seek feedback from peers and mentors and to accept and use the advice they give.
These are the best literary devices in prose to make your fiction and nonfiction sparkle. From Great Gatsby to Jane Eyre, read our analysis.
A literary analysis essay asks you to make an original argument about a poem, play, or work of fiction and support that argument with research and evidence from your careful reading of the text.
The introduction to your literary analysis essay should try to arouse interest in your reader. To bring immediate focus to your subject, you may want to use a quotation, a provocative question, a personal anecdote, a startling statement, or a combination of these.
Your free go-to reference list of literary techniques and what they are for the HSC. Learn the techniques used in texts to express artistic meaning through the use of language. Find detailed explanations of essential literary techniques complete with relevant examples.
Other possible synonyms within written narratives are literary technique or literary device, though these can also broadly refer to non-narrative writing strategies, as might be used in academic or essay writing, as well as poetic devices such as assonance, metre, or rhyme scheme.
Discover the essential visual techniques for English and enhance your literary analysis skills by learning how to analyse images with this comprehensive guide.
How To Write A Literature (Literary) Essay | Easy and Simple Technique - YouTube. Caitlin Jessica. 12.1K subscribers. Subscribed. 2.9K. 105K views 4 years ago. In only 15 minutes I will teach...
The PEEL paragraph method is a technique used in writing to help structure paragraphs in a way that presents a single clear and focused argument, which links back to the essay topic or thesis statement. It's good practice to dedicate each paragraph to one aspect of your argument, and the PEEL structure simplifies this for you.
q. r. s. t. u. v. w. x. y. z. misc. Aristotle: Poetics. Complexity and pleasure: Aristotle's 'complex plot' and the pleasure element in tragedy. Souvik Mukherjee examines Aristotle's Poetics and other works in order to elucidate Aristotle's view of a successful tragedy (2,100 words) Margaret Atwood.
A comparative analysis of the three books also demonstrates the value of literature and literary historians in an age characterized by the ascendancy of historical approaches to constitutional interpretation and a revival of the "canon wars.". Issue Section: Essay-Review. Launched a decade after the Constitution's signing in 1787, the USS ...