7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
The push against homework is not just about the hours spent on completing assignments; it’s about rethinking the role of education in fostering the well-rounded development of young individuals. Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities. The debate also highlights the importance of allowing children to have enough free time for play, exploration, and family interaction, which are crucial for their social and emotional development.
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
As we delve into this discussion, we explore various facets of why reducing or even eliminating homework could be beneficial. We consider the research, weigh the pros and cons, and examine alternative approaches to traditional homework that can enhance learning without overburdening students.
Once you’ve finished this article, you’ll know:

Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
Here are the insights and opinions from various experts in the educational field on this topic:
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Let’s delve into the reasons against assigning homework to students. Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices.
1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences
This data paints a concerning picture. Students, already navigating a world filled with various stressors, find themselves further burdened by homework demands. The direct correlation between excessive homework and health issues indicates a need for reevaluation. The goal should be to ensure that homework if assigned, adds value to students’ learning experiences without compromising their health and well-being.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
4. Consumption of Free Time
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
In conclusion, the conventional homework paradigm needs reevaluation, particularly concerning students with learning disabilities. By understanding and addressing their unique challenges, educators can create a more inclusive and supportive educational environment. This approach not only aids in their academic growth but also nurtures their confidence and overall development, ensuring that they receive an equitable and empathetic educational experience.
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
7. issues with homework enforcement, reliability, and temptation to cheat, addressing opposing views on homework practices, 1. improvement of academic performance, 2. reinforcement of learning, 3. development of time management skills, 4. preparation for future academic challenges, 5. parental involvement in education, exploring alternatives to homework and finding a middle ground, alternatives to traditional homework, ideas for minimizing homework, useful resources, leave a comment cancel reply.

Is homework a necessary evil?
After decades of debate, researchers are still sorting out the truth about homework’s pros and cons. One point they can agree on: Quality assignments matter.
By Kirsten Weir
March 2016, Vol 47, No. 3
Print version: page 36

- Schools and Classrooms
Homework battles have raged for decades. For as long as kids have been whining about doing their homework, parents and education reformers have complained that homework's benefits are dubious. Meanwhile many teachers argue that take-home lessons are key to helping students learn. Now, as schools are shifting to the new (and hotly debated) Common Core curriculum standards, educators, administrators and researchers are turning a fresh eye toward the question of homework's value.
But when it comes to deciphering the research literature on the subject, homework is anything but an open book.
The 10-minute rule
In many ways, homework seems like common sense. Spend more time practicing multiplication or studying Spanish vocabulary and you should get better at math or Spanish. But it may not be that simple.
Homework can indeed produce academic benefits, such as increased understanding and retention of the material, says Duke University social psychologist Harris Cooper, PhD, one of the nation's leading homework researchers. But not all students benefit. In a review of studies published from 1987 to 2003, Cooper and his colleagues found that homework was linked to better test scores in high school and, to a lesser degree, in middle school. Yet they found only faint evidence that homework provided academic benefit in elementary school ( Review of Educational Research , 2006).
Then again, test scores aren't everything. Homework proponents also cite the nonacademic advantages it might confer, such as the development of personal responsibility, good study habits and time-management skills. But as to hard evidence of those benefits, "the jury is still out," says Mollie Galloway, PhD, associate professor of educational leadership at Lewis & Clark College in Portland, Oregon. "I think there's a focus on assigning homework because [teachers] think it has these positive outcomes for study skills and habits. But we don't know for sure that's the case."
Even when homework is helpful, there can be too much of a good thing. "There is a limit to how much kids can benefit from home study," Cooper says. He agrees with an oft-cited rule of thumb that students should do no more than 10 minutes a night per grade level — from about 10 minutes in first grade up to a maximum of about two hours in high school. Both the National Education Association and National Parent Teacher Association support that limit.
Beyond that point, kids don't absorb much useful information, Cooper says. In fact, too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress.
In a recent study of Spanish students, Rubén Fernández-Alonso, PhD, and colleagues found that students who were regularly assigned math and science homework scored higher on standardized tests. But when kids reported having more than 90 to 100 minutes of homework per day, scores declined ( Journal of Educational Psychology , 2015).
"At all grade levels, doing other things after school can have positive effects," Cooper says. "To the extent that homework denies access to other leisure and community activities, it's not serving the child's best interest."
Children of all ages need down time in order to thrive, says Denise Pope, PhD, a professor of education at Stanford University and a co-founder of Challenge Success, a program that partners with secondary schools to implement policies that improve students' academic engagement and well-being.
"Little kids and big kids need unstructured time for play each day," she says. Certainly, time for physical activity is important for kids' health and well-being. But even time spent on social media can help give busy kids' brains a break, she says.
All over the map
But are teachers sticking to the 10-minute rule? Studies attempting to quantify time spent on homework are all over the map, in part because of wide variations in methodology, Pope says.
A 2014 report by the Brookings Institution examined the question of homework, comparing data from a variety of sources. That report cited findings from a 2012 survey of first-year college students in which 38.4 percent reported spending six hours or more per week on homework during their last year of high school. That was down from 49.5 percent in 1986 ( The Brown Center Report on American Education , 2014).
The Brookings report also explored survey data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress, which asked 9-, 13- and 17-year-old students how much homework they'd done the previous night. They found that between 1984 and 2012, there was a slight increase in homework for 9-year-olds, but homework amounts for 13- and 17-year-olds stayed roughly the same, or even decreased slightly.
Yet other evidence suggests that some kids might be taking home much more work than they can handle. Robert Pressman, PhD, and colleagues recently investigated the 10-minute rule among more than 1,100 students, and found that elementary-school kids were receiving up to three times as much homework as recommended. As homework load increased, so did family stress, the researchers found ( American Journal of Family Therapy , 2015).
Many high school students also seem to be exceeding the recommended amounts of homework. Pope and Galloway recently surveyed more than 4,300 students from 10 high-achieving high schools. Students reported bringing home an average of just over three hours of homework nightly ( Journal of Experiential Education , 2013).
On the positive side, students who spent more time on homework in that study did report being more behaviorally engaged in school — for instance, giving more effort and paying more attention in class, Galloway says. But they were not more invested in the homework itself. They also reported greater academic stress and less time to balance family, friends and extracurricular activities. They experienced more physical health problems as well, such as headaches, stomach troubles and sleep deprivation. "Three hours per night is too much," Galloway says.
In the high-achieving schools Pope and Galloway studied, more than 90 percent of the students go on to college. There's often intense pressure to succeed academically, from both parents and peers. On top of that, kids in these communities are often overloaded with extracurricular activities, including sports and clubs. "They're very busy," Pope says. "Some kids have up to 40 hours a week — a full-time job's worth — of extracurricular activities." And homework is yet one more commitment on top of all the others.
"Homework has perennially acted as a source of stress for students, so that piece of it is not new," Galloway says. "But especially in upper-middle-class communities, where the focus is on getting ahead, I think the pressure on students has been ratcheted up."
Yet homework can be a problem at the other end of the socioeconomic spectrum as well. Kids from wealthier homes are more likely to have resources such as computers, Internet connections, dedicated areas to do schoolwork and parents who tend to be more educated and more available to help them with tricky assignments. Kids from disadvantaged homes are more likely to work at afterschool jobs, or to be home without supervision in the evenings while their parents work multiple jobs, says Lea Theodore, PhD, a professor of school psychology at the College of William and Mary in Williamsburg, Virginia. They are less likely to have computers or a quiet place to do homework in peace.
"Homework can highlight those inequities," she says.
Quantity vs. quality
One point researchers agree on is that for all students, homework quality matters. But too many kids are feeling a lack of engagement with their take-home assignments, many experts say. In Pope and Galloway's research, only 20 percent to 30 percent of students said they felt their homework was useful or meaningful.
"Students are assigned a lot of busywork. They're naming it as a primary stressor, but they don't feel it's supporting their learning," Galloway says.
"Homework that's busywork is not good for anyone," Cooper agrees. Still, he says, different subjects call for different kinds of assignments. "Things like vocabulary and spelling are learned through practice. Other kinds of courses require more integration of material and drawing on different skills."
But critics say those skills can be developed with many fewer hours of homework each week. Why assign 50 math problems, Pope asks, when 10 would be just as constructive? One Advanced Placement biology teacher she worked with through Challenge Success experimented with cutting his homework assignments by a third, and then by half. "Test scores didn't go down," she says. "You can have a rigorous course and not have a crazy homework load."
Still, changing the culture of homework won't be easy. Teachers-to-be get little instruction in homework during their training, Pope says. And despite some vocal parents arguing that kids bring home too much homework, many others get nervous if they think their child doesn't have enough. "Teachers feel pressured to give homework because parents expect it to come home," says Galloway. "When it doesn't, there's this idea that the school might not be doing its job."
Galloway argues teachers and school administrators need to set clear goals when it comes to homework — and parents and students should be in on the discussion, too. "It should be a broader conversation within the community, asking what's the purpose of homework? Why are we giving it? Who is it serving? Who is it not serving?"
Until schools and communities agree to take a hard look at those questions, those backpacks full of take-home assignments will probably keep stirring up more feelings than facts.
Further reading
- Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987-2003. Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 1–62. doi: 10.3102/00346543076001001
- Galloway, M., Connor, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The Journal of Experimental Education, 81 (4), 490–510. doi: 10.1080/00220973.2012.745469
- Pope, D., Brown, M., & Miles, S. (2015). Overloaded and underprepared: Strategies for stronger schools and healthy, successful kids . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Letters to the Editor
- Send us a letter

The Dark Side of Homework: Why It’s Harmful and What the Statistics Say
Pencils down, backpacks zipped—the after-school battle that’s eroding our children’s well-being and widening educational gaps has a name: homework. This seemingly innocuous academic tradition has become a contentious issue in recent years, sparking debates among educators, parents, and policymakers alike. As we delve into the dark side of homework, we’ll explore its history, examine its impact on students, and consider alternatives that could reshape the future of education.
The practice of assigning homework has been a cornerstone of education for centuries, with its roots tracing back to the early days of formal schooling. Initially conceived as a way to reinforce classroom learning and instill discipline, homework has evolved into a complex and often controversial aspect of modern education. Today, the homework debate rages on, with proponents arguing for its necessity in academic achievement and critics pointing to its detrimental effects on student well-being and family life.
The importance of examining homework’s impact on students cannot be overstated. As our understanding of child development and learning processes advances, it’s crucial to reevaluate long-standing educational practices. The homework question touches on fundamental issues of equity, mental health, and the very purpose of education itself. By critically analyzing the role of homework in our educational system, we can work towards creating more effective and supportive learning environments for all students.
The Negative Effects of Homework on Student Well-being
One of the most significant concerns surrounding homework is its impact on student well-being. The Alarming Reality: What Percent of Students Are Stressed by Homework? reveals that a staggering number of students experience stress and anxiety related to their after-school assignments. This stress can manifest in various ways, from physical symptoms like headaches and stomach aches to emotional distress and feelings of overwhelm.
The pressure to complete homework often comes at the expense of valuable family time and social interactions. As students struggle to balance their academic responsibilities with extracurricular activities and personal interests, family dinners become rushed affairs, and quality time with loved ones becomes a luxury. This erosion of family connections can have long-lasting effects on a child’s emotional development and sense of security.
Moreover, the time-consuming nature of homework can significantly impact students’ sleep patterns and physical health. Late nights spent completing assignments lead to sleep deprivation, which in turn affects cognitive function, mood regulation, and overall well-being. Understanding Homeostatic Imbalance and Stress: A Comprehensive Guide with Worksheet Answers sheds light on how disrupted sleep patterns can contribute to a cascade of health issues.
Perhaps most concerning is the potential for homework to diminish students’ interest in learning and contribute to academic burnout. When learning becomes synonymous with tedious, repetitive tasks, students may lose their natural curiosity and enthusiasm for education. This disengagement can have far-reaching consequences, affecting not only academic performance but also future career aspirations and lifelong learning attitudes.
Homework and Academic Performance: A Surprising Relationship
Contrary to popular belief, the relationship between homework and academic achievement is not as straightforward as one might assume. Numerous studies have shown a limited correlation between homework and improved performance, particularly for younger students. This surprising finding challenges the long-held assumption that more homework inevitably leads to better academic outcomes.
The law of diminishing returns applies to homework as well. While some homework may be beneficial, there comes a point where additional assignments yield little to no academic benefit. This threshold varies depending on the student’s age, with high school students generally able to handle more homework than elementary or middle school students. However, even for older students, excessive homework can lead to burnout and decreased motivation.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of homework differs across age groups. For younger children, homework has been shown to have minimal impact on academic achievement. As students progress through middle and high school, homework can become more beneficial, but only when it’s carefully designed and appropriately challenging.
The quality of homework assignments is far more important than quantity. Meaningful, engaging tasks that reinforce classroom learning or encourage independent exploration are more likely to yield positive results than rote memorization or busywork. Educators and policymakers must focus on creating homework policies that prioritize quality over quantity, ensuring that out-of-school assignments truly contribute to student learning and growth.
Stress and Homework: What the Statistics Reveal
The statistics surrounding homework-related stress are alarming. Studies have consistently shown that a high percentage of students report experiencing stress and anxiety due to homework demands. In some surveys, as many as 70-80% of students indicate that homework is a significant source of stress in their lives.
When comparing stress levels across different educational systems, it becomes clear that homework practices vary widely. Countries with high-performing education systems, such as Finland, often assign less homework than their counterparts, challenging the notion that more homework equates to better academic outcomes. These international comparisons provide valuable insights into alternative approaches to education that prioritize student well-being alongside academic achievement.
The long-term effects of academic stress on mental health are a growing concern among researchers and mental health professionals. Chronic stress during childhood and adolescence can lead to increased risk of anxiety disorders, depression, and other mental health issues later in life. Overcoming Math Stress: Strategies for Confidence and Success in Mathematics explores how subject-specific stress, such as math anxiety, can have lasting impacts on students’ academic and personal lives.
Interestingly, gender differences in homework-related stress have been observed in various studies. Girls often report higher levels of stress and anxiety related to homework compared to boys. This disparity may be attributed to societal expectations, differences in coping strategies, or other factors that require further investigation to fully understand and address.
The Equity Issue: How Homework Perpetuates Inequality
One of the most troubling aspects of homework is its potential to exacerbate existing educational inequalities. Students from different socioeconomic backgrounds often face vastly different circumstances when it comes to completing homework assignments. Disparities in home resources and support can significantly impact a student’s ability to succeed academically.
For students from low-income families, homework can present numerous challenges. Limited access to technology, quiet study spaces, or academic resources can make completing assignments difficult or impossible. Parents working multiple jobs may have less time to assist with homework, putting their children at a disadvantage compared to peers with more available parental support. The Pervasive Daily Stress of Poverty: Unraveling Its Impact on Brain Development highlights how these socioeconomic factors can have far-reaching effects on a child’s cognitive development and academic potential.
Homework’s role in widening the achievement gap is a critical concern. As students from privileged backgrounds benefit from additional resources and support, those from disadvantaged backgrounds may fall further behind. This cycle can perpetuate and even amplify existing inequalities, making it increasingly difficult for students from low-income families to achieve academic success and social mobility.
Cultural biases in homework assignments can further compound these issues. Assignments that assume certain cultural knowledge or experiences may inadvertently disadvantage students from diverse backgrounds. Educators must be mindful of these potential biases and strive to create inclusive, culturally responsive homework practices that support all students’ learning and growth.
Alternatives to Traditional Homework
As the drawbacks of traditional homework become increasingly apparent, educators and researchers are exploring alternative approaches to out-of-school learning. Project-based learning approaches offer one promising alternative, encouraging students to engage in long-term, interdisciplinary projects that foster creativity, critical thinking, and real-world problem-solving skills.
The flipped classroom model is another innovative approach that reimagines the role of homework. In this model, students engage with instructional content at home through videos or readings, while class time is devoted to collaborative problem-solving and hands-on activities. This approach allows for more personalized instruction and support during school hours, potentially reducing the need for extensive homework assignments.
Personalized learning strategies, facilitated by advancements in educational technology, offer yet another alternative to traditional homework. These approaches tailor assignments to individual students’ needs, interests, and learning styles, potentially increasing engagement and reducing unnecessary stress. Gloria’s Study Challenge: The Impact of One More Hour and the Hidden Costs of Interruptions explores how personalized study strategies can impact learning outcomes.
Emphasizing in-class practice and collaboration is another way to reduce the burden of homework while still promoting learning and skill development. By providing more opportunities for guided practice during school hours, teachers can ensure that students receive immediate feedback and support, potentially reducing the need for extensive at-home practice.
Conclusion: Rethinking Homework for a Better Educational Future
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the traditional approach to homework is fraught with challenges. From its negative impact on student well-being to its potential to exacerbate educational inequalities, homework as we know it may be doing more harm than good. The limited correlation between homework and academic achievement, particularly for younger students, further calls into question the value of extensive out-of-school assignments.
A balanced approach to out-of-school learning is crucial. While some form of independent practice and exploration outside of school hours may be beneficial, it’s essential to consider the quality, quantity, and purpose of these assignments. Educators and policymakers must prioritize student well-being, equity, and meaningful learning experiences when developing homework policies.
The need for education reform and policy changes is clear. Is Homework Necessary? Examining the Debate and Its Impact on Student Well-being delves deeper into this question, challenging long-held assumptions about the role of homework in education. As we move forward, it’s crucial to consider alternative approaches that support student learning without sacrificing their mental health, family time, or love of learning.
Encouraging further research and discussion on homework practices is essential for developing evidence-based policies that truly serve students’ best interests. By critically examining our current practices and remaining open to innovative approaches, we can work towards an educational system that nurtures well-rounded, engaged, and lifelong learners.
As we conclude this exploration of the dark side of homework, it’s clear that the time has come to reevaluate our approach to out-of-school learning. By addressing the stress, inequity, and limited benefits associated with traditional homework, we can pave the way for a more effective, equitable, and student-centered education system. The Power of Playtime: How Recess Reduces Stress in Students reminds us of the importance of balance in education, highlighting the need for policies that support both academic growth and overall well-being.
The homework debate is far from over, but by continuing to question, research, and innovate, we can work towards educational practices that truly serve the needs of all students. As parents, educators, and policymakers, it’s our responsibility to ensure that our children’s education nurtures their curiosity, supports their well-being, and prepares them for success in an ever-changing world. Let’s reimagine homework not as a nightly battle, but as an opportunity for meaningful learning, growth, and discovery.
References:
1. Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research, 76(1), 1-62.
2. Galloway, M., Conner, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The Journal of Experimental Education, 81(4), 490-510.
3. OECD (2014). Does homework perpetuate inequities in education? PISA in Focus, No. 46, OECD Publishing, Paris.
4. Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2000). The end of homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning. Beacon Press.
5. Marzano, R. J., & Pickering, D. J. (2007). Special topic: The case for and against homework. Educational Leadership, 64(6), 74-79.
6. Vatterott, C. (2018). Rethinking homework: Best practices that support diverse needs. ASCD.
7. Kohn, A. (2006). The homework myth: Why our kids get too much of a bad thing. Da Capo Press.
8. Pressman, R. M., Sugarman, D. B., Nemon, M. L., Desjarlais, J., Owens, J. A., & Schettini-Evans, A. (2015). Homework and family stress: With consideration of parents’ self confidence, educational level, and cultural background. The American Journal of Family Therapy, 43(4), 297-313.
9. Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge.
10. Sahlberg, P. (2015). Finnish lessons 2.0: What can the world learn from educational change in Finland? Teachers College Press.
Similar Posts

Chronic Stress in Students: Signs, Solutions, and Support Strategies
Silently screaming through their smiles, students across the globe navigate a minefield of expectations, deadlines, and digital noise that threatens to consume their very essence. This silent struggle is the face of chronic stress, a pervasive issue that has become increasingly common among students of all ages. As the demands of modern education continue to…

College Student Stress: Understanding and Managing the Pressure Cooker
College life is often portrayed as an exciting and transformative period, but for many students, it can feel more like navigating a pressure cooker. The stress experienced by college students has become a growing concern in recent years, with far-reaching implications for their academic success, mental health, and overall well-being. As we delve into this…

Workplace Stress Safety Talks: Top 5 Essential Strategies for a Healthier Work Environment
Silence the deafening roar of workplace chaos with five potent strategies that transform stress into success, one safety talk at a time. In today’s fast-paced work environment, the importance of addressing workplace stress through safety talks cannot be overstated. As organizations strive to maintain productivity and employee well-being, implementing effective stress management strategies has become…

Academic Stress: Causes, Effects, and Coping Strategies for Students
Academic stress is a pervasive issue that affects students across all educational levels, from elementary school to higher education. This phenomenon has become increasingly prevalent in recent years, with studies showing alarming rates of stress-related symptoms among students worldwide. Understanding the causes, effects, and coping strategies for academic stress is crucial for students, educators, and…

Too Much Light Stressing Your Plants: Recognizing and Preventing Light Stress
Bathed in an unforgiving glow, your leafy companions silently scream for mercy as they wilt under the relentless assault of misguided kindness. This haunting image serves as a stark reminder of the delicate balance required in plant care, particularly when it comes to light exposure. While light is essential for photosynthesis and growth, too much…

Homework Stress: The Hidden Toll on Students and Its Impact
Pencils snap, tears fall, and midnight oil burns as students nationwide grapple with an invisible epidemic that’s turning education into a battleground of anxiety and exhaustion. This silent struggle, rooted in the seemingly innocuous practice of assigning homework, has become a growing concern for educators, parents, and students alike. While homework has long been considered…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
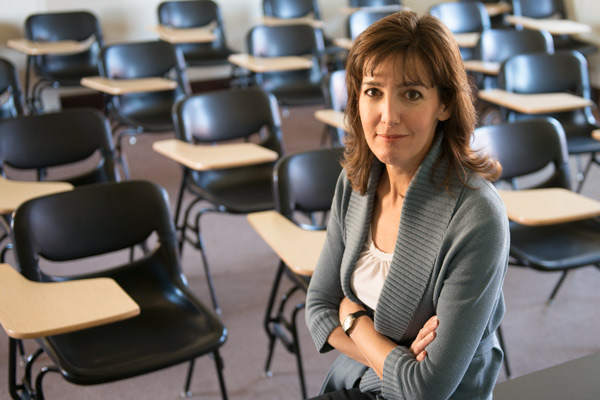

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
* Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
* Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Media Contacts
Denise Pope, Stanford Graduate School of Education: (650) 725-7412, [email protected] Clifton B. Parker, Stanford News Service: (650) 725-0224, [email protected]
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
share this!
August 16, 2021
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

In six new rogue worlds, Webb Telescope finds more star birth clues
14 minutes ago

3D shapes of viral proteins point to previously unknown roles
11 hours ago

Darwin's fear was unjustified: Study suggests fossil record gaps not a major issue

Using machine learning to speed up simulations of irregularly shaped particles

Closing the RNA loop holds promise for more stable, effective RNA therapies
12 hours ago
Scientists use evolution to bioengineer new pathways to sustainable energy and pharmaceuticals

Dual protein analysis approach provides potential way to slow cancer growth

Biomass-based polymer can capture and release CO₂ without high pressure or extreme temperatures

Microscopic fossilized shells reveal ancient climate change patterns

Sound drives 'quantum jumps' between electron orbits
Relevant physicsforums posts, incandescent bulbs in teaching.
Aug 21, 2024
How to explain Bell's theorem to non-scientists
Aug 18, 2024
Free Abstract Algebra curriculum in Urdu and Hindi
Aug 17, 2024
Sources to study basic logic for precocious 10-year old?
Jul 21, 2024
Kumon Math and Similar Programs
Jul 19, 2024
AAPT 2024 Summer Meeting Boston, MA (July 2024) - are you going?
Jul 4, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

More academic freedom leads to more innovation, reports study

Statistical analysis can detect when ChatGPT is used to cheat on multiple-choice chemistry exams
Aug 14, 2024

Larger teams in academic research worsen career prospects, study finds

The 'knowledge curse': More isn't necessarily better
Aug 7, 2024

Visiting an art exhibition can make you think more socially and openly—but for how long?
Aug 6, 2024

Autonomy boosts college student attendance and performance
Jul 31, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.
It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
The Cult of Homework
America’s devotion to the practice stems in part from the fact that it’s what today’s parents and teachers grew up with themselves.

America has long had a fickle relationship with homework. A century or so ago, progressive reformers argued that it made kids unduly stressed , which later led in some cases to district-level bans on it for all grades under seventh. This anti-homework sentiment faded, though, amid mid-century fears that the U.S. was falling behind the Soviet Union (which led to more homework), only to resurface in the 1960s and ’70s, when a more open culture came to see homework as stifling play and creativity (which led to less). But this didn’t last either: In the ’80s, government researchers blamed America’s schools for its economic troubles and recommended ramping homework up once more.
The 21st century has so far been a homework-heavy era, with American teenagers now averaging about twice as much time spent on homework each day as their predecessors did in the 1990s . Even little kids are asked to bring school home with them. A 2015 study , for instance, found that kindergarteners, who researchers tend to agree shouldn’t have any take-home work, were spending about 25 minutes a night on it.
But not without pushback. As many children, not to mention their parents and teachers, are drained by their daily workload, some schools and districts are rethinking how homework should work—and some teachers are doing away with it entirely. They’re reviewing the research on homework (which, it should be noted, is contested) and concluding that it’s time to revisit the subject.
Read: My daughter’s homework is killing me
Hillsborough, California, an affluent suburb of San Francisco, is one district that has changed its ways. The district, which includes three elementary schools and a middle school, worked with teachers and convened panels of parents in order to come up with a homework policy that would allow students more unscheduled time to spend with their families or to play. In August 2017, it rolled out an updated policy, which emphasized that homework should be “meaningful” and banned due dates that fell on the day after a weekend or a break.
“The first year was a bit bumpy,” says Louann Carlomagno, the district’s superintendent. She says the adjustment was at times hard for the teachers, some of whom had been doing their job in a similar fashion for a quarter of a century. Parents’ expectations were also an issue. Carlomagno says they took some time to “realize that it was okay not to have an hour of homework for a second grader—that was new.”
Most of the way through year two, though, the policy appears to be working more smoothly. “The students do seem to be less stressed based on conversations I’ve had with parents,” Carlomagno says. It also helps that the students performed just as well on the state standardized test last year as they have in the past.
Earlier this year, the district of Somerville, Massachusetts, also rewrote its homework policy, reducing the amount of homework its elementary and middle schoolers may receive. In grades six through eight, for example, homework is capped at an hour a night and can only be assigned two to three nights a week.
Jack Schneider, an education professor at the University of Massachusetts at Lowell whose daughter attends school in Somerville, is generally pleased with the new policy. But, he says, it’s part of a bigger, worrisome pattern. “The origin for this was general parental dissatisfaction, which not surprisingly was coming from a particular demographic,” Schneider says. “Middle-class white parents tend to be more vocal about concerns about homework … They feel entitled enough to voice their opinions.”
Schneider is all for revisiting taken-for-granted practices like homework, but thinks districts need to take care to be inclusive in that process. “I hear approximately zero middle-class white parents talking about how homework done best in grades K through two actually strengthens the connection between home and school for young people and their families,” he says. Because many of these parents already feel connected to their school community, this benefit of homework can seem redundant. “They don’t need it,” Schneider says, “so they’re not advocating for it.”
That doesn’t mean, necessarily, that homework is more vital in low-income districts. In fact, there are different, but just as compelling, reasons it can be burdensome in these communities as well. Allison Wienhold, who teaches high-school Spanish in the small town of Dunkerton, Iowa, has phased out homework assignments over the past three years. Her thinking: Some of her students, she says, have little time for homework because they’re working 30 hours a week or responsible for looking after younger siblings.
As educators reduce or eliminate the homework they assign, it’s worth asking what amount and what kind of homework is best for students. It turns out that there’s some disagreement about this among researchers, who tend to fall in one of two camps.
In the first camp is Harris Cooper, a professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University. Cooper conducted a review of the existing research on homework in the mid-2000s , and found that, up to a point, the amount of homework students reported doing correlates with their performance on in-class tests. This correlation, the review found, was stronger for older students than for younger ones.
This conclusion is generally accepted among educators, in part because it’s compatible with “the 10-minute rule,” a rule of thumb popular among teachers suggesting that the proper amount of homework is approximately 10 minutes per night, per grade level—that is, 10 minutes a night for first graders, 20 minutes a night for second graders, and so on, up to two hours a night for high schoolers.
In Cooper’s eyes, homework isn’t overly burdensome for the typical American kid. He points to a 2014 Brookings Institution report that found “little evidence that the homework load has increased for the average student”; onerous amounts of homework, it determined, are indeed out there, but relatively rare. Moreover, the report noted that most parents think their children get the right amount of homework, and that parents who are worried about under-assigning outnumber those who are worried about over-assigning. Cooper says that those latter worries tend to come from a small number of communities with “concerns about being competitive for the most selective colleges and universities.”
According to Alfie Kohn, squarely in camp two, most of the conclusions listed in the previous three paragraphs are questionable. Kohn, the author of The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing , considers homework to be a “reliable extinguisher of curiosity,” and has several complaints with the evidence that Cooper and others cite in favor of it. Kohn notes, among other things, that Cooper’s 2006 meta-analysis doesn’t establish causation, and that its central correlation is based on children’s (potentially unreliable) self-reporting of how much time they spend doing homework. (Kohn’s prolific writing on the subject alleges numerous other methodological faults.)
In fact, other correlations make a compelling case that homework doesn’t help. Some countries whose students regularly outperform American kids on standardized tests, such as Japan and Denmark, send their kids home with less schoolwork , while students from some countries with higher homework loads than the U.S., such as Thailand and Greece, fare worse on tests. (Of course, international comparisons can be fraught because so many factors, in education systems and in societies at large, might shape students’ success.)
Kohn also takes issue with the way achievement is commonly assessed. “If all you want is to cram kids’ heads with facts for tomorrow’s tests that they’re going to forget by next week, yeah, if you give them more time and make them do the cramming at night, that could raise the scores,” he says. “But if you’re interested in kids who know how to think or enjoy learning, then homework isn’t merely ineffective, but counterproductive.”
His concern is, in a way, a philosophical one. “The practice of homework assumes that only academic growth matters, to the point that having kids work on that most of the school day isn’t enough,” Kohn says. What about homework’s effect on quality time spent with family? On long-term information retention? On critical-thinking skills? On social development? On success later in life? On happiness? The research is quiet on these questions.
Another problem is that research tends to focus on homework’s quantity rather than its quality, because the former is much easier to measure than the latter. While experts generally agree that the substance of an assignment matters greatly (and that a lot of homework is uninspiring busywork), there isn’t a catchall rule for what’s best—the answer is often specific to a certain curriculum or even an individual student.
Given that homework’s benefits are so narrowly defined (and even then, contested), it’s a bit surprising that assigning so much of it is often a classroom default, and that more isn’t done to make the homework that is assigned more enriching. A number of things are preserving this state of affairs—things that have little to do with whether homework helps students learn.
Jack Schneider, the Massachusetts parent and professor, thinks it’s important to consider the generational inertia of the practice. “The vast majority of parents of public-school students themselves are graduates of the public education system,” he says. “Therefore, their views of what is legitimate have been shaped already by the system that they would ostensibly be critiquing.” In other words, many parents’ own history with homework might lead them to expect the same for their children, and anything less is often taken as an indicator that a school or a teacher isn’t rigorous enough. (This dovetails with—and complicates—the finding that most parents think their children have the right amount of homework.)
Barbara Stengel, an education professor at Vanderbilt University’s Peabody College, brought up two developments in the educational system that might be keeping homework rote and unexciting. The first is the importance placed in the past few decades on standardized testing, which looms over many public-school classroom decisions and frequently discourages teachers from trying out more creative homework assignments. “They could do it, but they’re afraid to do it, because they’re getting pressure every day about test scores,” Stengel says.
Second, she notes that the profession of teaching, with its relatively low wages and lack of autonomy, struggles to attract and support some of the people who might reimagine homework, as well as other aspects of education. “Part of why we get less interesting homework is because some of the people who would really have pushed the limits of that are no longer in teaching,” she says.
“In general, we have no imagination when it comes to homework,” Stengel says. She wishes teachers had the time and resources to remake homework into something that actually engages students. “If we had kids reading—anything, the sports page, anything that they’re able to read—that’s the best single thing. If we had kids going to the zoo, if we had kids going to parks after school, if we had them doing all of those things, their test scores would improve. But they’re not. They’re going home and doing homework that is not expanding what they think about.”
“Exploratory” is one word Mike Simpson used when describing the types of homework he’d like his students to undertake. Simpson is the head of the Stone Independent School, a tiny private high school in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, that opened in 2017. “We were lucky to start a school a year and a half ago,” Simpson says, “so it’s been easy to say we aren’t going to assign worksheets, we aren’t going assign regurgitative problem sets.” For instance, a half-dozen students recently built a 25-foot trebuchet on campus.
Simpson says he thinks it’s a shame that the things students have to do at home are often the least fulfilling parts of schooling: “When our students can’t make the connection between the work they’re doing at 11 o’clock at night on a Tuesday to the way they want their lives to be, I think we begin to lose the plot.”
When I talked with other teachers who did homework makeovers in their classrooms, I heard few regrets. Brandy Young, a second-grade teacher in Joshua, Texas, stopped assigning take-home packets of worksheets three years ago, and instead started asking her students to do 20 minutes of pleasure reading a night. She says she’s pleased with the results, but she’s noticed something funny. “Some kids,” she says, “really do like homework.” She’s started putting out a bucket of it for students to draw from voluntarily—whether because they want an additional challenge or something to pass the time at home.
Chris Bronke, a high-school English teacher in the Chicago suburb of Downers Grove, told me something similar. This school year, he eliminated homework for his class of freshmen, and now mostly lets students study on their own or in small groups during class time. It’s usually up to them what they work on each day, and Bronke has been impressed by how they’ve managed their time.
In fact, some of them willingly spend time on assignments at home, whether because they’re particularly engaged, because they prefer to do some deeper thinking outside school, or because they needed to spend time in class that day preparing for, say, a biology test the following period. “They’re making meaningful decisions about their time that I don’t think education really ever gives students the experience, nor the practice, of doing,” Bronke said.
The typical prescription offered by those overwhelmed with homework is to assign less of it—to subtract. But perhaps a more useful approach, for many classrooms, would be to create homework only when teachers and students believe it’s actually needed to further the learning that takes place in class—to start with nothing, and add as necessary.
About the Author

More Stories
Reporting on Parenthood Has Made Me Nervous About Having Kids
The Economic Principle That Helps Me Order at Restaurants

Join Our Discord Community!

daily dose of research
Carnoy & Levin
Showcases the relationship between schooling and work, which rejects the capitalist and Marxist lens of schooling.

featured contributor

This is why we should stop giving homework
At Human Restoration Project, one of the core systemic changes we suggest is the elimination of homework. Throughout this piece, I will outline several research studies and reports that demonstrate how the negative impact of homework is so evident that any mandated homework, outside of some minor catching up or for incredibly niche cases, simply does more harm than good.
I’ll summarize four main reasons why homework just flat out doesn’t make sense.
- Achievement, whether that be measured through standardized tests or general academic knowledge, isn’t correlated to assigning or completing homework.
- Homework is an inequitable practice that harms certain individuals more than others, to the detriment of those with less resources and to minor, if any, improvement for those with resources.
- It contributes to negative impacts at home with one’s family, peer relationships, and just general school-life balance, which causes far more problems than homework is meant to solve.
- And finally, it highlights and exacerbates our obsession with ultra-competitive college admissions and job opportunities, and other detrimental faults of making everything about getting ahead .
Does Homework Make Us Learn More?
Homework is such a ubiquitous part of school that it’s considered radical to even suggest that lessening it could be good teaching. It’s completely normal for families to spend extra hours each night, even on weekends, completing projects, reports, and worksheets. On average, teenagers spend about an hour a day completing homework, which is up 30-45 minutes from decades past. Kindergartners, who are usually saved from completing a lot of after school work, average about 25 minutes of homework a night (which to note, is 25 minutes too much than is recommended by child development experts).
The “10-minute rule”, endorsed by the National Parent Teacher Association and National Education Association, is incorporated into most school policies: there’s 10 minutes of homework per day per grade level – as in 20 minutes a day in second grade or 2 hours a day in 12th grade.
It’s so normalized that it was odd, when seemingly out of nowhere the President of Ireland recently suggested that homework should be banned . (And many experts were shocked at this suggestion.)
Numerous studies on homework reflect inconsistent results on what it exactly achieves. Homework is rarely shown to have any impact on achievement, whether that be measured through standardized testing or otherwise. As I’ll talk about later, the amount of marginal gains homework may lead to aren’t worth its negative trade-offs.
Let’s look at a quick summary of various studies:
- First off, the book National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling by David P. Baker and Gerald K. LeTendre draws on a 4 year investigation of schools in 47 countries. It’s the largest study of its type: looking at how schools operate, their pedagogy, their procedures, and the like. They made a shocking discovery: countries that assigned the least amount of homework: Denmark and the Czech Republic, had much higher test scores than those who assigned the most amount of homework: Iran and Thailand. The same work indicated that there was no correlation between academic achievement and homework with elementary students, and any moderate positive correlation in middle or high school diminished as more and more homework was assigned.
- A study in Contemporary Educational Psychology of 28,051 high school seniors concluded that quality of instruction, motivation, and ability are all correlated to a student’s academic success. However, homework’s effectiveness was marginal or perhaps even counterproductive: leading to more academic problems than it hoped to solve.
- The Teachers College Record published that homework added academic pressure and societal stress to those already experiencing pressures from other forces at home. This caused a further divide in academic performance from those with more privileged backgrounds. We’ll talk about this more later.
- A study in the Journal of Educational Psychology examined 2,342 student attitudes toward homework in foreign language classes. They found that time spent on homework had a significant negative impact on grades and standardized test scores. The researchers concluded that this may be because participants had to spend their time completing worksheets rather than spend time practicing skills on their own time.
- Some studies are more positive. In fact, a meta-analysis of 32 homework studies in the Review of Educational Research found that most studies indicated a positive correlation between achievement and doing homework. However, the researchers noted that generally these studies made it hard to draw causal conclusions due to how they were set up and conducted. There was so much variance that it was difficult to make a claim one way or another, even though the net result seemed positive. This often cited report led by Dr. Harris Cooper at Duke University is the most commonly used by proponents of the practice. But popular education critic Alfie Kohn believes that this study fails to establish, ironically, causation among other factors.
- And that said in a later published study in The High School Journal , researchers concluded that in all homework assigned, there were only modest linkages to improved math and science standardized test scores, with no difference in other subjects between those who were assigned homework and those who were not. None of the homework assigned had any bearing on grades. The only difference was for a few points on those particular subject’s standardized test scores.
All in all, the data is relatively inconclusive. Some educational experts suggest that there should be hours of homework in high school, some homework in middle school, and none in elementary school. Some call for the 10-minute rule. Others say that homework doesn’t work at all. It’s still fairly unstudied how achievement is impacted as a result of homework. But as Alfie Kohn says , “The better the research, the less likely one is to find any benefits from homework.” That said, when we couple this data with the other negative impacts of assigning homework: how it impacts those at the margins, leads to anxiety and stress, and takes away from important family time – it really makes us question why this is such a ubiquitous practice.
Or as Etta Kralovec and John Buell write in The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning,
‘Extensive classroom research of ‘time on task’ and international comparisons of year-round time for study suggest that additional homework might promote U.S. students’ achievement.’ This written statement by some of the top professionals in the field of homework research raises some difficult questions. More homework might promote student achievement? Are all our blood, sweat, and tears at the kitchen table over homework based on something that merely might be true? Our belief in the value of homework is akin to faith. We assume that it fosters a love of learning, better study habits, improved attitudes toward school, and greater self-discipline; we believe that better teachers assign more homework and that one sign of a good school is a good, enforced homework policy.
Our obsession with homework is likely rooted in select studies that imply it leads to higher test scores. The authors continue by deciphering this phenomena:
“[this is] a problem that routinely bedevils all the sciences: the relationship between correlation and causality. If A and B happen simultaneously, we do not know whether A causes B or B causes A, or whether both phenomena occur casually together or are individually determined by another set of variables…Thus far, most studies in this area have amounted to little more than crude correlations that cannot justify the sweeping conclusions some have derived from them.”
Alfie Kohn adds that even the correlation between achievement and homework doesn’t really matter. Saying,
“If all you want is to cram kids’ heads with facts for tomorrow’s tests that they’re going to forget by next week, yeah, if you give them more time and make them do the cramming at night, that could raise the scores…But if you’re interested in kids who know how to think or enjoy learning, then homework isn’t merely ineffective, but counterproductive… The practice of homework assumes that only academic growth matters, to the point that having kids work on that most of the school day isn’t enough…”

Ramping Up Inequity
Many justify the practice of assigning homework with the well-intentioned belief that we’ll make a more equitable society through high standards. However, it seems to be that these practices actually add to inequity. “Rigorous” private and preparatory schools – whether they be “no excuses” charters in marginalized communities or “college ready” elite suburban institutions, are notorious for extreme levels of homework assignment. Yet, many progressive schools who focus on holistic learning and self-actualization assign no homework and achieve the same levels of college and career success.
Perhaps this is because the largest predictor of college success has nothing to do with rigorous preparation, and everything to do with family income levels. 77% of students from high income families graduated from a highly competitive college, whereas 9% of students from low income families did the same .
It seems like by loading students up with mountains of homework each night in an attempt to get them into these colleges, we actually make their chances of success worse .

When assigning homework, it is common practice to recommend that families provide a quiet, well-lit place for the child to study. After all, it’s often difficult to complete assignments after a long day. Having this space, time, and energy must always be considered in the context of the family’s education, income, available time, and job security. For many people, jobs have become less secure and less well paid over the course of the last two decades.
In a United States context, we work the longest hours of any nation . Individuals in 2006 worked 11 hours longer than their counterparts in 1979. In 2020, 70% of children lived in households where both parents work. We are the only country in the industrial world without guaranteed family leave. And the results are staggering: 90% of women and 95% of men report work-family conflict . According to the Center for American Progress , “the United States today has the most family-hostile public policy in the developed world due to a long-standing political impasse.”
As a result, parents have much less time to connect with their children. This is not a call to a return to traditional family roles or to have stay-at-home parents – rather, our occupation-oriented society is structured inadequately which causes problems with how homework is meant to function.
For those who work in entry level positions, such as customer service and cashiers, there is an average 240% turnover per year due to lack of pay, poor conditions, work-life balance, and mismanagement. Family incomes continue to decline for lower- and middle-class Americans, leaving more families to work increased hours or multiple jobs. In other words, families, especially poor families, have less opportunities to spend time with their children, let alone foster academic “gains” via homework.

Even for students with ample resources who attend “elite schools”, the amount of homework is stressful. In a 2013 study in The Journal of Experiential Education, researchers conducted a survey of 4,317 students in 10 high-performing upper middle class high schools. These students had an average of more than 3 hours of homework a night. In comparison to their peers, they had more academic stress, notable physical health problems, and spent a worrying amount of time focused entirely on school and nothing else. Competitive advantage came at the cost of well-being and just being a kid.
A similar study in Frontiers of Psychology found that students pressured in the competitive college admissions process , who attended schools assigning hours of homework each night and promoting college-level courses and resume building extracurriculars, felt extreme stress. Two-thirds of the surveyed students reported turning to alcohol and drugs to cope.
In fact, a paper published by Dr. Suniya Luthar and her colleagues concluded that upper middle-class youth are actually more likely to be troubled than their middle class peers . There is an extreme problem with academic stress, where young people are engaging in a rat race toward the best possible educational future as determined by Ivy League colleges and scholarships. To add fuel to the fire, schools continue to add more and more homework to have students get ahead – which has a massively negative impact on both ends of the economic spectrum.
A 2012 study by Dr. Jonathan Daw indicated that their results,
“...imply that increases in the amount of homework assigned may increase the socioeconomic achievement gap in math, science, and reading in secondary school.”
In an effort to increase engagement with homework, teachers have been encouraged to create interesting, creative assignments. In fact, most researchers seem to agree that the quality of assignments matters a whole lot . After all, maybe assigning all of this homework won’t matter as long as it’s interesting and relevant to students? Although this has good intentions, rigorous homework with increased complexity places more impetus on parents. As researcher and author Gary Natrillo, an initial proponent of creative homework , stated later:
…not only was homework being assigned as suggested by all the ‘experts,’ but the teacher was obviously taking the homework seriously, making it challenging instead of routine and checking it each day and giving feedback. We were enveloped by the nightmare of near total implementation of the reform recommendations pertaining to homework…More creative homework tasks are a mixed blessing on the receiving end. On the one hand, they, of course, lead to higher engagement and interest for children and their parents. On the other hand, they require one to be well rested, a special condition of mind not often available to working parents…
Time is a luxury to most people. With increased working hours, in conjunction with extreme levels of stress, many people don’t have the necessary mindset to adequately supply children with the attention to detail for complex homework. As Kralovec and Buell state,
To put it plainly, I have discovered that after a day at work, the commute home, dinner preparations, and the prospect of baths, goodnight stories, and my own work ahead, there comes a time beyond which I cannot sustain my enthusiasm for the math brain teaser or the creative story task.
Americans are some of the most stressed people in the world. Mass shootings, health care affordability, discrimination, racism, sexual harassment, climate change, the presidential elections, and literally: staying informed on current events have caused roughly 70% of people to report moderate or extreme stress , with increased rates for people of color, LGBTQIA Americans, and other discriminated groups. 90% of high schoolers and college students report moderate or higher stress, with half reporting depression and a lack of energy and motivation .

In 2015, 1,100 parents were surveyed on the impact of homework on family life. Fights over homework were 200% more likely in families where parents didn’t have a college degree. Generally, these families believed that if their children didn’t understand a homework assignment then they must have been not paying attention at school. This led to young people feeling dumb or upset, and parents feeling like their child was lying or goofing off. The lead researcher noted,
All of our results indicate that homework as it is now being assigned discriminates against children whose parents don’t have a college degree, against parents who have English as a second language, against, essentially, parents who are poor.
Schooling is so integrated into family life that a group of researchers noted that “...homework tended to recreate the problems of school, such as status degradation.” An online survey of over 2,000 students and families found that 90% of students reported additional stress from homework, and 40% of families saw it as nothing more than busy work. Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish wrote the aptly titled The Case Against Homework which conducted interviews across the mid-2000s with families and children, citing just how many people are burdened with overscheduling homework featuring over-the-top assignments and constant work. One parent remarked,
I sit on Amy's bed until 11 p.m. quizzing her, knowing she's never going to use this later, and it feels like abuse," says Nina of Menlo Park, California, whose eleven-year-old goes to a Blue Ribbon public school and does at least three-and-a-half hours of homework each night. Nina also questions the amount of time spent on "creative" projects. "Amy had to visit the Mission in San Francisco and then make a model of it out of cardboard, penne pasta, and paint. But what was she supposed to be learning from this? All my daughter will remember is how tense we were in the garage making this thing. Then when she handed it in, the teacher dropped it and all the penne pasta flew off." These days, says Nina, "Amy's attitude about school has really soured." Nina's has, too. "Everything is an emergency and you feel like you're always at battle stations."
1/3rd of the families interviewed felt “crushed by the workload.” It didn’t matter if they lived in rural or suburban areas, or if they were rich or poor.
Learning this way is also simply ineffective because well, that’s just not how kids learn! Young people build upon prior knowledge. They use what they know to make what they’re currently doing easier. Adding more and more content to a student’s plate – having to connect the dots and build upon more information – especially with the distractions of home life is unrealistic. Plus, simply put…it’s just not fun! Why would I want to spend all of my free time on homework rather than hanging out with my friends or playing video games?
Even with all that said – if other countries demonstrate educational success on standardized testing with little to no assigned homework and limited school hours (nevermind the fact that this is measured through the questionable method of standardized testing), shouldn’t we take a step back and analyze the system as a whole, rather than figure out better homework policies? If other countries do this with limited to no homework , why can’t everyone else?
Investigating Systemic Problems
Perhaps the solution to academic achievement in America isn’t doubling down on increasing the work students do at home, but solving the underlying systemic inequities: the economic and discriminatory problems that plague our society. Yes, the United States tends to fall behind other countries on math and reading scores. Many countries impose increased workloads on students because they are afraid that they will fall behind economically with the standard of living to the rest of the world. But perhaps the problem with education doesn’t lie in not having enough “rigorous” methods, but with how easy it is for a family to simply live and be content.
Finland, frequently cited as a model education system which grew to prominence during the 2000s through popular scholars like Pasi Sahlberg, enjoys some of the highest standards of living in the world:
- Finland’s life expectancy is 81.8 years, compared to the US’ 78.7 years . Unlike Finland, there’s a notable difference between the richest and poorest Americans . The richest Americans are expected to live, on average, nearly 15 years longer than the poorest. Further, America’s life expectancy is declining, the only industrialized country with this statistic .
- Finland’s health care is rated best in the world and only spends $3,078 per capita, compared to $8,047 in the US.
- Finland has virtually no homelessness , compared to the 500,000 (and growing) homeless population in the United States .
- Finland has the lowest inequality levels in the EU , compared to the United States with one of the highest inequality levels in the world . Research has demonstrated that countries with lower inequality levels are happier and healthier .
These statistics reflect that potentially — instead of investing hundreds of millions of dollars in initiatives to increase national test scores , such as homework strategies, curriculum changes, and nationwide “raising the bar” initiatives — that we should invest in programs that improve our standard of living, such as universal healthcare and housing. The solution to test scores is rooted in solving underlying inequities in our societies — shining a light on our core issues — rather than making teachers solve all of our community’s problems.
This doesn’t mean that there’s no space for improving pedagogy, schooling, or curriculums, but at the end of the day the solution cannot solely be by improving education.

Creating Future Workers
Education often equates learning with work. As a teacher, I had to stop myself from behaving like an economics analyst: telling students to quit “wasting time”, stating that the purpose of the lesson is useful for securing a high salary career, seeing everything as prep for college and career (and college’s purpose as just for more earnings in a career), and making blanket assumptions that those who aren’t motivated will ultimately never contribute to society, taking on “low levels” of work that “aren’t as important” as other positions.
A common argument exists that the pressure of homework mirrors the real world – that we should assign homework because that’s “just the way things are.” If we want kids to succeed in the “real world”, they need to have this pressure.
But this mentality is unhealthy and unjust. The purpose of education should be to develop purpose. People live happier and healthier lives as a result of pursuing and developing a core purpose. Some people’s purpose is related to their line of work, but there is not necessarily a connection. However, the primary goal for education stated by districts, states, and the national government is to make “productive members of society” – those who are “prepared for the future” through “college and career readiness.” When we double down on economic principles, rather than look to developmental psychology and holistic care, to raise young people, it’s no wonder we’re seeing such horrific statistics related to childhood .
Further, the consistent pressure to solely learn for future economic gain raises generations of young people to believe that wealth is a measurement of success, and that specific lines of work create happiness. Teachers and parents are told to make their children “work hard” for future success and develop “grit.” Although grit is an important indicator of overcoming obstacles , it is not developed by enforcing grit through authoritarian classrooms or meaningless, long tasks like homework. In fact, an argument could be made that many Americans accept their dramatically poor work-life balance and lack of access to needs such as affordable health care by being brought up in a society that rewards tasks of “working through it” to “eventually achieve happiness.”
Many families have shifted from having children participate in common household chores and activities to have them exclusively focus on their school work. Americans have more difficulty than ever raising children, with increasing demands of time and rising childcare costs . When teachers provide more and more homework, they take away from the parents’ ability to structure their household according to their needs. In fact, children with chores show completely positive universal growth across the board , from time management skills to responsibility to managing a healthy work-life balance.
Of course, this is not to say that it is all the teacher’s fault. Educators face immense pressure to carry out governmental/school policies that place test scores at the forefront. Plus, most families had homework themselves – so continuing the practice only makes sense. Many of these policies require homework, and an educator’s employment is centered on enacting these changes. Barbara Stengel , an education professor, noted that the reason why so much homework isn’t necessarily interesting or applicable to a student’s lived experience is because “some of the people who would really have pushed the limits of that are no longer in teaching.” The constant pressure on teachers to raise test scores while simultaneously being overworked and underpaid is making many leave the profession. Etta Kralovec and John Buell add:
As more academic demands are placed on teachers, homework can help lengthen the school day and thus ensure ‘coverage’ — that is, the completion of the full curriculum that each teacher is supposed to cover during the school year…This in itself places pressure on teachers to create meaningful homework and often to assign large amounts of it so that the students’ parents will think the teacher is rigorous and the school has high academic standards. Extensive homework is frequently linked in our minds to high standards.
Therefore, there’s a connection to be made between the school- or work-life balance of children and the people who are tasked with teaching them. 8% of the teacher workforce leaves every year , with one of the primary reasons being poor work-life balance . Perhaps teachers see an increased desire to “work” students in their class and at home due to the pressures they face in their own occupation?

The more we equate work with learning, and the more we accept that a school’s primary purpose is to prepare workers, the less we actually succeed at promoting academics. Instead, we bolster the neoliberal tendencies of the United States (and others like it) to work hard, yet comparably to other countries’ lifestyle gains, achieve little.
This is why so many families demand that their children have ample amounts of homework. In fact, the majority of parents believe their students have just the right amount. They’re afraid that their kids are going to fall behind, doomed to a life within an increasingly hostile and inequitable society. They want the best for their children, and taking the risk of not assigning homework means that someone else may take that top slot. The same could be said for many parts of the “tracks toward college and career readiness” that professor William Deresiewicz refers to as “zombication” – lurching through each stage of the rat race in competitive admissions: a lot of assignments, difficult courses, sports, clubs, forced volunteerism, internships, and other things to pack our schedules.
The United States must examine the underlying inequities of peoples’ lives, rather than focus on increasing schools’ workloads and lessening children’s free time for mythical academic gains that lead to little change. Teacher preparation programs and popular authors need to stop promoting “interesting and fun ways to teach ‘x’!” and propose systemic changes that radically change the way education is done, including systemic changes to society at large. Only then will the United States actually see improved livelihoods and a better education system for all.
And what could be done instead? Much of the research and writing on homework tends to conclude that we should find a “happy middle ground” to continue the practice of homework, just in case it does indeed work. However, based on the decades of studies we have on this issue…I’m not really sure. It seems the best practice, by far, is to eliminate homework altogether outside of incredibly niche and rare scenarios. If a student asks for more things to do at home because they want to explore something that interests them, great! But that doesn’t need to be mandated homework.
Human Restoration Project believes that the four recommendations of the late educator and scholar Ken Robinson allows young people to learn for themselves and make the most of their lives:
- Let children spend time with their families. The single strongest predictor of academic success and fewer behavioral problems for a child, 3-12 years old, is eating as a family. Make planned time during the day to catch up with children, talking to them about what they’re learning, and encouraging them to achieve.
- Give children time to play outside or create something, preferably not always with a screen. Let them dive into their passions and plan a trip to a library, park, or museum. Explore free online resources to discover new skills and interests.
- Give children opportunities to read by themselves or with their family. One of the best ways to learn about the world is developing a lifelong love of reading. Children who prioritize reading are more motivated to learn and see drastically improved academic outcomes.
- Let children sleep! Elementary students should sleep at least 10 hours each night and adolescents, 9 hours. Being awake and ready to tackle each day keeps us energized and healthy.
If you’re interested in learning more, see The Case Against Homework by Nancy Kalish and Sara Bennett, The Homework Myth by Alfie Kohn, The End of Homework by Etta Kralovec and John Muelle, or one of the many citations linked in the show notes.
You can also watch a modified video version of this piece on our YouTube channel:
Anderson, J. (2019, December 3). Finland has the most efficient education system in the world. Quartz . https://qz.com/1759598/finland-has-the-most-efficient-education-system-in-the-world
APA. (2019a). Stress in America . https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2019/stress-america-2019.pdf
APA. (2019b). Stress in America TM 2019: Interactive Graphics . https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2019/interactive-graphics
Baker, D., & LeTendre, G. K. (2005). National differences, global similarities: World culture and the future of schooling . Stanford University Press.
Balingit, M. (2022, September 13). Wanted: Teachers. No training necessary. The Washington Post . https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2022/09/13/teacher-requirements-shortage-jobs/
Bennett, S., & Kalish, N. (2007). The Case Against Homework: How homework is hurting children and what parents can do about it . Harmony.
Byrnes, H. (2019a, April 11). U.S. leads among countries that spend the most on public health care. WLST . https://www.coloradoan.com/story/money/2019/04/11/countries-that-spend-the-most-on-public-health/39307147/
CDC. (2022, June 3). Data and statistics on children’s mental health . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/childrensmentalhealth/data.html
Chang, C. B., Wall, D., Tare, M., Golonka, E., & Vatz, K. (2014). Relationships of attitudes toward homework and time spent on homework to course outcomes: The case of foreign language learning. Journal of Educational Psychology , 106 (4), 1049–1065. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0036497
Chetty, R., Stepner, M., Abraham, S., Lin, S., Scuderi, B., Turner, N., Bergeron, A., & Cutler, D. (2016). The Association Between Income and Life Expectancy in the United States, 2001–2014: Association Between Income and Life Expectancy in the United States. JAMA , 315 (16). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.4226
Chores and children . (2018). https://www.aacap.org/AACAP/Families_and_Youth/Facts_for_Families/FFF-Guide/Chores_and_Children-125.aspx
Cool, V. A., & Keith, T. Z. (1991). Testing a model of school learning: Direct and indirect effects on academic achievement. Contemporary Educational Psychology , 16 (1), 28–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-476x(91)90004-5
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research , 76 (1), 1–62. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543076001001
Costa, P. N. da. (2019, May 29). America’s humongous wealth gap is widening further. Forbes . https://www.forbes.com/sites/pedrodacosta/2019/05/29/americas-humungous-wealth-gap-is-widening-further/?sh=327f1ac342ee
Costley, K. (2013). Does Homework Really Improve Achievement? Arkansas Tech University .
Covington, N. (2020, January 31). A progressive response to “Ed. Reform’s Lost Decade.” Human Restoration Project . https://medium.com/human-restoration-project/a-progressive-response-to-ed-reforms-lost-decade-fb640c16d893
Daniels, E., & Steres, M. (2011). Examining the effects of a school-wide reading culture on the engagement of middle school students. RMLE Online , 35 (2), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/19404476.2011.11462085
Deresiewicz, W. (2015). Excellent sheep: The miseducation of the American elite and the way to a meaningful life . Simon and Schuster.
Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The new psychology of success . Random House.
Esdal, L. Teacher turnover: An overview of the problem and why it matters . (2019, February 28). Education Evolving. https://www.educationevolving.org/blog/2019/02/teacher-turnover-overview-of-problem-and-why-it-matters
Finland - WID - World inequality database . (2016, June 23). WID - Wealth and Income Database. https://wid.world/country/finland/
Galloway, M., Conner, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The Journal of Experimental Education , 81 (4), 490–510. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2012.745469
Henly, J. R., Shaefer, H. L., & Waxman, E. (2006). Nonstandard work schedules: Employer‐ and employee‐driven flexibility in retail jobs. Social Service Review , 80 (4), 609–634. https://doi.org/10.1086/508478
Hofferth, S. L., & Sandberg, J. F. (2001). How American children spend their time. Journal of Marriage and Family , 63 (2), 295–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3737.2001.00295.x
Human Restoration Project. (n.d.). Research . Retrieved January 24, 2023, from https://www.humanrestorationproject.org/research
Indicators of Higher Education: Equity in the US . (2018). http://pellinstitute.org/downloads/publications-Indicators_of_Higher_Education_Equity_in_the_US_2018_Historical_Trend_Report.pdf&sa=D&source=docs&ust=1674598544982744&usg=AOvVaw3EdEhMRi9luOuJm0IKhMSF
Ken Robinson, TED. (2007). Do schools kill creativity? [Video]. In YouTube . https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iG9CE55wbtY
Kohn, A. (2007). The homework myth: Why our kids get too much of a bad thing . Da Capo Lifelong Books.
Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2001). The End of Homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning . Beacon Press.
Leonard, N. R., Gwadz, M. V., Ritchie, A., Linick, J. L., Cleland, C. M., Elliott, L., & Grethel, M. (2015). A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools. Frontiers in Psychology , 6 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01028
Livingston, G. (2019, February 20). The way U.S. teens spend their time is changing, but differences between boys and girls persist. Pew Research Center . https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/02/20/the-way-u-s-teens-spend-their-time-is-changing-but-differences-between-boys-and-girls-persist/
Luthar, S. S., Barkin, S. H., & Crossman, E. J. (2013). “I can, therefore I must”: Fragility in the upper-middle classes. Development and Psychopathology , 25 (4pt2), 1529–1549. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579413000758
Lynch, R. The economic and fiscal consequences of improving U.S. educational outcomes - Equitable growth . (2015, February 2). Washington Center for Equitable Growth. https://equitablegrowth.org/achievement-gap/
Mcdermott, R. P., Goldman, S. V., & Varenne, H. (1984a). When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework. Teachers College Record: The Voice of Scholarship in Education , 85 (3), 391–409. https://doi.org/10.1177/016146818408500310
McGuire, J. (2023). The President Of Ireland Wants To Get Rid Of Homework & Honestly, He's Onto Something. Romper. https://www.romper.com/life/president-of-ireland-michael-d-higgins-homework
Miller, C. C. (2018, December 25). The relentlessness of modern parenting. The New York Times . https://www.nytimes.com/2018/12/25/upshot/the-relentlessness-of-modern-parenting.html
Natriello, G., & McDill, E. L. (1986). Performance standards, student effort on homework, and academic achievement. Sociology of Education , 59 (1), 18. https://doi.org/10.2307/2112483
PBS NewsHour : Biggest Predictor of College Success is Family Income . (2015). America’s Promise. https://web.archive.org/web/20220807230624/americaspromise.org/news/pbs-newshour-biggest-predictor-college-success-family-income
Plante, T. (2018, December 3). Americans are stressed out, and it is getting worse . Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/do-the-right-thing/201812/americans-are-stressed-out-and-it-is-getting-worse
Pinsker, J. (2019, March 28). Does homework work? The Atlantic . https://www.theatlantic.com/education/archive/2019/03/homework-research-how-much/585889/
Pressman, R. M., Sugarman, D. B., Nemon, M. L., Desjarlais, J., Owens, J. A., & Schettini-Evans, A. (2015). Homework and family stress: With consideration of parents’ self confidence, educational level, and cultural background. The American Journal of Family Therapy , 43 (4), 297–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926187.2015.1061407
Sander, G. F. (2018). Finland’s homeless crisis nearly solved. How? By giving homes to all who need. The Christian Science Monitor . https://www.csmonitor.com/World/Europe/2018/0321/Finland-s-homeless-crisis-nearly-solved.-How-By-giving-homes-to-all-who-need
Smurthwaite, D. (2018, April 27). Why Overworking is Made in America and Work-Life Balance Lives in Europe . https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/why-overworking-made-america-work-life-balance-lives-dave-smurthwaite/
Taras, H., & Potts-Datema, W. (2005). Sleep and student performance at school. Journal of School Health , 75 (7), 248–254. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1746-1561.2005.00033.x
The State of Homelessness in America . (2019). https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/The-State-of-Homelessness-in-America.pdf
The three faces of work-family conflict . (2010, January 25). Center for American Progress. https://www.americanprogress.org/article/the-three-faces-of-work-family-conflict/
Walker, T. (2015). The great homework debate: What’s getting lost in the hype . NEA. https://www.nea.org/advocating-for-change/new-from-nea/great-homework-debate-whats-getting-lost-hype
Wallace, K. (2015, August 12). Kids have three times too much homework, study finds; what’s the cost? CNN . https://www.cnn.com/2015/08/12/health/homework-elementary-school-study/index.html
Weir, K. (2016). Is homework a necessary evil? https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/03/homework
Wilkinson, R. G. (2002). Unhealthy societies: The afflictions of inequality . Routledge.
Wilkinson, R., & Pickett, K. (2020). The inner level: How more equal societies reduce stress, restore sanity and improve everyone’s well-being . Penguin.
Woolf, S. H. (2019). Life expectancy and mortality rates in the United States, 1959-2017. JAMA , 322 (20), 1996–2016. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.16932

read this next

take a listen

Join the Movement
Stay informed.
I was just going to say that that is the ideal place to do it, because I think just biologically and whatever, when you're younger, you are more naturally a change agent, and have a better sense of vision, and have a longer time to be invested in the future, so that's actually the perfect place to be doing what you just said, Falami, is in schools, because that's where you've got this nexus of brilliance, and vision, and investment in 100 years from now or whatever. Not that we all can't be part of it, but you've got a nice concentration of people who are especially suited to creating that vision, and that change, and partnership with us elders.
Where's this from?

Sport and Competition
Is too much homework unhealthy, a grassroots movement led by parents is backed by science..
Posted October 10, 2014

This is the question at the heart of the homework debate. The Washington Post education reporter Jay Mathews wrote a powerful article: “ Parents Saying No to Too Much Homework .” The story was inspired by a chapter in the new book, The Learning Habit: A Groundbreaking Approach to Homework and Parenting That Helps Our Children Succeed in School and Life . (Perigee, 2014)
The Learning Habit separates fact from fiction about homework and has started a grassroots movement led by parents. Instead of encouraging a homework revolt, it asks for parents to institute a regular, balanced homework routine . This includes having children stop doing academic homework after a reasonable amount of time. When children can’t understand the assignment, parents will not make the children sit for extended time and try to help them figure it out; they will write a note on the paper asking the teacher for extra help.
At the root of the movement is science. It’s not developmentally appropriate to ask a third grader to sit for 120 minutes and complete an academic assignment. It’s also not psychologically healthy to have a fourth grader in tears every night over homework. The focus on a "the whole child" approach is resonating with parents and administrators in school districts such as Barrington, Rhode Island.
So how much academic homework should a child have?
10 minutes per grade in school, and then children can move onto other activities. If they don’t understand the assignment or get frustrated, they should stop and read a book for the remaining time.
The facts are clear when it comes to academic homework . There is a point of diminishing returns, and it is anything over 10 minutes per grade. We now understand that the concept of “homework” involves balancing many opportunities that provide our kids with healthy learning experiences.. Activities such as neighborhood play, sports, dancing, family time, chores, and sleeping are equally important for whole-child enrichment. Additionally, children who participate in extra-curricular activities such as sports, dance, and clubs score higher on academic, social and emotional scales.
- All students work at a different pace.
- Think big picture. Forcing a child to complete a homework assignment, after they have spent a reasonable amount of time on it (10 minutes per grade), is not promoting balance.
- Keep academic homework time balanced and consistent. On nights children don’t have schoolwork, they will read. Reading is important for both ELA and Mathematics.
- No tears policy: When kids feel frustrated or don’t understand an academic assignment, they can choose to read a book instead and ask the teacher for extra help the next day.
GET THE FACTS ON HOMEWORK: Fact Sheet Balanced Homework Habit
For more information on The Learning Habit (Perigee) click HERE

Rebecca Jackson is a neuropsychological educator and the co-author of The Learning Habit
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Reasons Why Homework Is Bad For Students?

- Post author By admin
- October 12, 2022
Homework is a word that most students don’t want to hear. Because, after many hours of sitting in the same class, the last thing students get is more schoolwork over their precious weekends. Well, it is known to be a traditional schooling system. Lets now
Some feel that Homework is a necessary part of education. On the other hand, some believe that the time should be invested in extra activities. Many studies have found that most students are getting too much extra Homework and assignments that lead to many problems like stress, sleeping problems, and other problems related to health.
Typically in high schools, students take six classes a day, which means they receive 24.5 hours of homework weekly. But this is not the main problem. The problem with the school nowadays is that it promotes stress at a very high level by giving students extra work that most of the students don’t want to do.
There are plenty of reasons why Homework is bad for students, but in this Blog, we will look at the top 18 most crucial reasons.
Without wasting any time, let’s get started.
Table of Contents
18 Reasons Why Homework Is Bad For Students
There are many reasons why Homework is bad, but in this Blog, we will cover the top 18 reasons why Homework is bad for students.
- May lead to Stress Problems
No time for outside activities
Excessive homework cause depression, have no real impact on performance, homework control the student’s freedom.
- May break student’s confidence
No real benefit
The school became a full-time job, irrelevant content, lack of social skills , waste of time, no time for family, destroy sleep cycle.
- Excessive Homework encourages cheating
Can lower your grades
Counterproductivity.
- No time for daily exercise
Consume free time
May lead to stress problems..
Extra assignments given by high schools and universities to students may lead to unhealthy stress levels. If bombarded with countless work at the school and at home, students may feel anxiety and stress. I know students need to learn in the class, but they also get some time to explore other things outside the academic world.
This is obvious if you get work after work and fail to complete that work. You will automatically get stressed, and that gets worse over time.
According to the survey, 56 percent of the students think that Homework is the primary cause of stress. At the same time, the remaining students think that giving tests and getting good marks causes stress. Only 1 percent of the students think that Homework does not cause notable stress.
One of the main reasons Homework is bad is that you get no time to go outside and play something that will automatically boost your productivity and instantly kill stress. Doing outside activities will not only boost your productivity but also make you healthy physically as well as mentally.
Excessive Homework may cause Depression, which then affects students mentally and physically too. According to the studies, more than 39% of the students have experienced Depression daily. The main reason is that most students want more grades rather than doing Homework. When students are unable to attain their goals, then it is really hard to maintain their health, so as a result, they get depressed. All of these issues can have a negative impact on someone’s life.
Extra time spent on Homework does not have a real impact on performance. As a result, it’s more like you’re wasting time by doing the same thing repeatedly, which does not produce any result.
Childhood is meant to be enjoyed, but extra Homework makes it impossible. Instead of spending time on something else, students spend most of their time on Homework. As a result, Homework became the reason to control students’ freedom.
May break students’ confidence
If you’re doing the same thing repeatedly, you don’t get any result from this. Then the probability is high that you will lose your confidence. So, to boost your confidence, students should take some breaks and then get back to work.
A decrease in academic performance is directly connected to spending more time on Homework. Homework can help you get better marks, but it usually has a low return. As a result, there is no real benefit from the Homework.
This is the seventh reason why Homework is bad for the students.
In Chile, most school days start from 8 a.m and end at 4 p.m or later. Every day, students spend approximately 9 hours in school, like you’re doing a full-time job.
If the Homework has nothing to do with the topic or the subject, it should be prohibited. It is unfair to provide Homework that a student did not cover in the class and expect a better report.
Heavy homework activities may have a terrible effect on student life. Everyone needs some time for daily routine activity and quality time with their friends and family. But teachers assign heavy Homework during weekends. Then there is no choice but for the students to complete the task rather than be more social.
Most studies found that Homework is a waste of time that keeps people from doing things they want to do. Such as attending important events or sports. As a result, even if a student wants to attend or participate in such events, in such circumstances, students don’t have enough time due to workload.
This is the twelfth reason why Homework is bad and should be banned. In most parts of the world, students doest have time to spend with their family members. Well, the most difficult thing for today’s parents is that they don’t spend enough time with their children. Students start working on their homework as soon as they get back home. As a result, students barely have time to talk with their parents.
Even on the weekend, students work on their extra assignments and Homework. That being said, students miss weekends that they are supposed to spend with their family members. However, without work, students have more time for family.
In most cases, students don’t want to get up early in the morning. When you sleep for a longer period and wake up late in the morning, you would feel more relaxed and chill. But due to excessive amounts of Homework, students barely get 7 hours of sleep. As a result, Homework is the biggest concern that destroys the sleep cycle.
This is the thirteenth reason why Homework should be banned.
Excessive Homework encourages cheating
When students have an excessive amount of work to complete in a short period, it is really difficult for them to complete their Homework. As a result, to complete Homework in time, they copy from other students. Cheating is illegal in any school. If the teacher finds out that both assignments have relevant material, they get punished. That is why Homework is bad.
One of the main reasons Homework is bad is that many teachers cannot provide all the important information in the class, and parents can not help children. If you spend most of the time doing homework, you don’t get time to study. As a result, it can lower your grades.
Rather than improving education, a heavy homework load may affect the students’ performance. Students have too much stress to complete Homework every other night, which can affect the student’s performance in school. A homework load may counter your productivity skills.
No Time For Daily Workout
This is the seventeenth reason why Homework is bad. Well, exercise has many benefits, like if you work out daily then it can improve your mental health, and remove stress. On the other hand, some aerobic exercise can even help you with Depression. Students don’t have time for daily workouts due to an excessive homework load.
Everybody needs some free time to chill or relax, but what if you don’t have time to do anything? How do you feel? Well, the obvious answer is you feel very bad. That’s what students feel when they don’t have time to play or to spend some time with family, just because of frequently given Homework and assignments by the teachers.
Reasons Why Homework Is Bad & Should be Banned

Four main reasons why homework should be banned
- It creates family stress : Some parents argue with their children about getting Homework done or being frustrated with their inability to teach children about any topic.
- Students can do other important activities : Other activities include outdoor time, family bonding time, and other unscheduled play.
- Doesn’t increase academic achievement : According to many studies, Homework has weak links to get better academic achievements.
- Leads to more anxiety : It can cause more academic stress for students.
Conclusion: Why Homework is Bad
In this blog, we have learned 18 reasons why Homework is bad. I hope you understand why Homework is bad for the student; not only do students in the same city face this problem, but it’s a worldwide cause. Students also have the freedom to do other activities and have some free time to chill and relax.
This is the end of this Blog. I hope you like it. Also, Read: Best Homework Songs to Listen While Study
Q1. Is Homework Good or bad?
Ans. Too much of anything can harm you instead of helping you. So, if students get too much work, it can do more harm than good. Studies have shown that if a student gets less Homework, it’s good, but if it’s too much, it’s bad.
Q2. Why is too much Homework bad for mental health?
Ans. Studies conducted at Stanford University in 2013 have found that top-performing students are distracted and mostly spend more time on Homework than on improving academic skills. As a result, they experienced more stress, problems related to health, lack of social skills, and many more.
- australia (2)
- duolingo (13)
- Education (284)
- General (78)
- How To (18)
- IELTS (127)
- Latest Updates (162)
- Malta Visa (6)
- Permanent residency (1)
- Programming (31)
- Scholarship (1)
- Sponsored (4)
- Study Abroad (187)
- Technology (12)
- work permit (8)
Recent Posts


ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, the homework debate: the case against homework.

This post has been updated as of December 2017.
It’s not uncommon to hear students, parents, and even some teachers always complaining about homework. Why, then, is homework an inescapable part of the student experience? Worksheets, busy work, and reading assignments continue to be a mainstay of students’ evenings.
Whether from habit or comparison with out-of-class work time in other nations, our students are getting homework and, according to some of them, a LOT of it. Educators and policy makers must ask themselves—does assigning homework pay off?
Is there evidence that homework benefits students younger than high school?
The Scholastic article Is Homework Bad? references Alfie Kohn’s book The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing , in which he says, “There is no evidence to demonstrate that homework benefits students below high school age.”
The article goes on to note that those who oppose homework focus on the drawbacks of significant time spent on homework, identifying one major negative as homework’s intrusion into family time. They also point out that opponents believe schools have decided homework is necessary and thus assign it simply to assign some kind of homework, not because doing the work meets specifically-identified student needs.
“Busy work” does not help students learn
Students and parents appear to carry similar critiques of homework, specifically regarding assignments identified as busy work—long sheets of repetitive math problems, word searches, or reading logs seemingly designed to make children dislike books.
When asked how homework can negatively affect children, Nancy Kalish, author of The Case Against Homework: How Homework is Hurting Our Children and What We Can Do About It , says that many homework assignments are “simply busy work” that makes learning “a chore rather than a positive, constructive experience.”
Commenters on the piece, both parents and students, tended to agree. One student shared that on occasion they spent more time on homework than at school, while another commenter pointed out that, “We don’t give slow-working children a longer school day, but we consistently give them a longer homework day.”
Without feedback, homework is ineffective
The efficacy of the homework identified by Kalish has been studied by policy researchers as well. Gerald LeTendre, of Penn State’s Education Policy Studies department points out that the shotgun approach to homework, when students all receive the same photocopied assignment which is then checked as complete rather than discussed individually with the student, is “not very effective.” He goes on to say that, “If there’s no feedback and no monitoring, the homework is probably not effective.”
Researchers from the Curry School of Education at the University of Virginia had similar findings in their study, “ When Is Homework Worth The Time ?” According to UVAToday, these researchers reported no “substantive difference” in the grades of students related to homework completion.
As researcher Adam Maltese noted, “Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be.” The report further suggested that while not all homework is bad, the type and quality of assignments and their differentiation to specific learners appears to be an important point of future research.
If homework is assigned, it should heighten understanding of the subject
The Curry School of Education report did find a positive association between standardized test performance and time spent on homework, but standardized test performance shouldn’t be the end goal of assignments—a heightened understanding and capability with the content material should.
As such, it is important that if/when teachers assign homework assignments, it is done thoughtfully and carefully—and respectful of the maximum times suggested by the National Education Association, about 10 minutes per night starting in the first grade, with an additional 10 minutes per year after.
Continue reading — The Homework Debate: How Homework Benefits Students
Monica Fuglei is a graduate of the University of Nebraska in Omaha and a current adjunct faculty member of Arapahoe Community College in Colorado, where she teaches composition and creative writing.
You may also like to read
- The Homework Debate: How Homework Benefits Students
- Ending the Homework Debate: Expert Advice on What Works
- Advice on Creating Homework Policies
- Elementary Students and Homework: How Much Is Too Much?
- Homework in Middle School: Building a Foundation for Study Skills
- Homework Helps High School Students Most — But it Must Be Purposeful

Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: Leadership and Administration , Pros and Cons , Teacher-Parent Relationships
- Certificates in Administrative Leadership
- Teacher Resources for Social-Emotional Develo...
- Degrees and Certificates for Teachers & Educa...
Homework – Top 3 Pros and Cons
Pro/Con Arguments | Discussion Questions | Take Action | Sources | More Debates

From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. [ 1 ]
While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word “homework” dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home. Memorization exercises as homework continued through the Middle Ages and Enlightenment by monks and other scholars. [ 45 ]
In the 19th century, German students of the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given assignments to complete outside of the school day. This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann , who encountered the idea in Prussia. [ 45 ]
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies’ Home Journal , decried homework’s negative impact on children’s physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but the prevailing argument was that kids needed time to do household chores. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 45 ] [ 46 ]
Public opinion swayed again in favor of homework in the 1950s due to concerns about keeping up with the Soviet Union’s technological advances during the Cold War . And, in 1986, the US government included homework as an educational quality boosting tool. [ 3 ] [ 45 ]
A 2014 study found kindergarteners to fifth graders averaged 2.9 hours of homework per week, sixth to eighth graders 3.2 hours per teacher, and ninth to twelfth graders 3.5 hours per teacher. A 2014-2019 study found that teens spent about an hour a day on homework. [ 4 ] [ 44 ]
Beginning in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic complicated the very idea of homework as students were schooling remotely and many were doing all school work from home. Washington Post journalist Valerie Strauss asked, “Does homework work when kids are learning all day at home?” While students were mostly back in school buildings in fall 2021, the question remains of how effective homework is as an educational tool. [ 47 ]
Is Homework Beneficial?
Pro 1 Homework improves student achievement. Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicated that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” [ 6 ] Students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework on both standardized tests and grades. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take-home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school. [ 10 ] Read More
Pro 2 Homework helps to reinforce classroom learning, while developing good study habits and life skills. Students typically retain only 50% of the information teachers provide in class, and they need to apply that information in order to truly learn it. Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, co-founders of Teachers Who Tutor NYC, explained, “at-home assignments help students learn the material taught in class. Students require independent practice to internalize new concepts… [And] these assignments can provide valuable data for teachers about how well students understand the curriculum.” [ 11 ] [ 49 ] Elementary school students who were taught “strategies to organize and complete homework,” such as prioritizing homework activities, collecting study materials, note-taking, and following directions, showed increased grades and more positive comments on report cards. [ 17 ] Research by the City University of New York noted that “students who engage in self-regulatory processes while completing homework,” such as goal-setting, time management, and remaining focused, “are generally more motivated and are higher achievers than those who do not use these processes.” [ 18 ] Homework also helps students develop key skills that they’ll use throughout their lives: accountability, autonomy, discipline, time management, self-direction, critical thinking, and independent problem-solving. Freireich and Platzer noted that “homework helps students acquire the skills needed to plan, organize, and complete their work.” [ 12 ] [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 49 ] Read More
Pro 3 Homework allows parents to be involved with children’s learning. Thanks to take-home assignments, parents are able to track what their children are learning at school as well as their academic strengths and weaknesses. [ 12 ] Data from a nationwide sample of elementary school students show that parental involvement in homework can improve class performance, especially among economically disadvantaged African-American and Hispanic students. [ 20 ] Research from Johns Hopkins University found that an interactive homework process known as TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) improves student achievement: “Students in the TIPS group earned significantly higher report card grades after 18 weeks (1 TIPS assignment per week) than did non-TIPS students.” [ 21 ] Homework can also help clue parents in to the existence of any learning disabilities their children may have, allowing them to get help and adjust learning strategies as needed. Duke University Professor Harris Cooper noted, “Two parents once told me they refused to believe their child had a learning disability until homework revealed it to them.” [ 12 ] Read More
Con 1 Too much homework can be harmful. A poll of California high school students found that 59% thought they had too much homework. 82% of respondents said that they were “often or always stressed by schoolwork.” High-achieving high school students said too much homework leads to sleep deprivation and other health problems such as headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems. [ 24 ] [ 28 ] [ 29 ] Alfie Kohn, an education and parenting expert, said, “Kids should have a chance to just be kids… it’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.” [ 27 ] Emmy Kang, a mental health counselor, explained, “More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies.” [ 48 ] Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else’s homework, and 43% of college students engaged in “unauthorized collaboration” on out-of-class assignments. Even parents take shortcuts on homework: 43% of those surveyed admitted to having completed a child’s assignment for them. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] [ 32 ] Read More
Con 2 Homework exacerbates the digital divide or homework gap. Kiara Taylor, financial expert, defined the digital divide as “the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology and those that don’t. Though the term now encompasses the technical and financial ability to utilize available technology—along with access (or a lack of access) to the Internet—the gap it refers to is constantly shifting with the development of technology.” For students, this is often called the homework gap. [ 50 ] [ 51 ] 30% (about 15 to 16 million) public school students either did not have an adequate internet connection or an appropriate device, or both, for distance learning. Completing homework for these students is more complicated (having to find a safe place with an internet connection, or borrowing a laptop, for example) or impossible. [ 51 ] A Hispanic Heritage Foundation study found that 96.5% of students across the country needed to use the internet for homework, and nearly half reported they were sometimes unable to complete their homework due to lack of access to the internet or a computer, which often resulted in lower grades. [ 37 ] [ 38 ] One study concluded that homework increases social inequality because it “potentially serves as a mechanism to further advantage those students who already experience some privilege in the school system while further disadvantaging those who may already be in a marginalized position.” [ 39 ] Read More
Con 3 Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We’ve known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that “homework had no association with achievement gains” when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7 ] Fourth grade students who did no homework got roughly the same score on the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) math exam as those who did 30 minutes of homework a night. Students who did 45 minutes or more of homework a night actually did worse. [ 41 ] Temple University professor Kathryn Hirsh-Pasek said that homework is not the most effective tool for young learners to apply new information: “They’re learning way more important skills when they’re not doing their homework.” [ 42 ] In fact, homework may not be helpful at the high school level either. Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, stated, “I interviewed high school teachers who completely stopped giving homework and there was no downside, it was all upside.” He explains, “just because the same kids who get more homework do a little better on tests, doesn’t mean the homework made that happen.” [ 52 ] Read More
Discussion Questions
1. Is homework beneficial? Consider the study data, your personal experience, and other types of information. Explain your answer(s).
2. If homework were banned, what other educational strategies would help students learn classroom material? Explain your answer(s).
3. How has homework been helpful to you personally? How has homework been unhelpful to you personally? Make carefully considered lists for both sides.
Take Action
1. Examine an argument in favor of quality homework assignments from Janine Bempechat.
2. Explore Oxford Learning’s infographic on the effects of homework on students.
3. Consider Joseph Lathan’s argument that homework promotes inequality .
4. Consider how you felt about the issue before reading this article. After reading the pros and cons on this topic, has your thinking changed? If so, how? List two to three ways. If your thoughts have not changed, list two to three ways your better understanding of the “other side of the issue” now helps you better argue your position.
5. Push for the position and policies you support by writing US national senators and representatives .
| 1. | Tom Loveless, “Homework in America: Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report of American Education,” brookings.edu, Mar. 18, 2014 | |
| 2. | Edward Bok, “A National Crime at the Feet of American Parents,” , Jan. 1900 | |
| 3. | Tim Walker, “The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype,” neatoday.org, Sep. 23, 2015 | |
| 4. | University of Phoenix College of Education, “Homework Anxiety: Survey Reveals How Much Homework K-12 Students Are Assigned and Why Teachers Deem It Beneficial,” phoenix.edu, Feb. 24, 2014 | |
| 5. | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), “PISA in Focus No. 46: Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education?,” oecd.org, Dec. 2014 | |
| 6. | Adam V. Maltese, Robert H. Tai, and Xitao Fan, “When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math,” , 2012 | |
| 7. | Harris Cooper, Jorgianne Civey Robinson, and Erika A. Patall, “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003,” , 2006 | |
| 8. | Gökhan Bas, Cihad Sentürk, and Fatih Mehmet Cigerci, “Homework and Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analytic Review of Research,” , 2017 | |
| 9. | Huiyong Fan, Jianzhong Xu, Zhihui Cai, Jinbo He, and Xitao Fan, “Homework and Students’ Achievement in Math and Science: A 30-Year Meta-Analysis, 1986-2015,” , 2017 | |
| 10. | Charlene Marie Kalenkoski and Sabrina Wulff Pabilonia, “Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement?,” iza.og, Apr. 2014 | |
| 11. | Ron Kurtus, “Purpose of Homework,” school-for-champions.com, July 8, 2012 | |
| 12. | Harris Cooper, “Yes, Teachers Should Give Homework – The Benefits Are Many,” newsobserver.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 13. | Tammi A. Minke, “Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement,” repository.stcloudstate.edu, 2017 | |
| 14. | LakkshyaEducation.com, “How Does Homework Help Students: Suggestions From Experts,” LakkshyaEducation.com (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 15. | University of Montreal, “Do Kids Benefit from Homework?,” teaching.monster.com (accessed Aug. 30, 2018) | |
| 16. | Glenda Faye Pryor-Johnson, “Why Homework Is Actually Good for Kids,” memphisparent.com, Feb. 1, 2012 | |
| 17. | Joan M. Shepard, “Developing Responsibility for Completing and Handing in Daily Homework Assignments for Students in Grades Three, Four, and Five,” eric.ed.gov, 1999 | |
| 18. | Darshanand Ramdass and Barry J. Zimmerman, “Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework,” , 2011 | |
| 19. | US Department of Education, “Let’s Do Homework!,” ed.gov (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 20. | Loretta Waldman, “Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework,” phys.org, Apr. 12, 2014 | |
| 21. | Frances L. Van Voorhis, “Reflecting on the Homework Ritual: Assignments and Designs,” , June 2010 | |
| 22. | Roel J. F. J. Aries and Sofie J. Cabus, “Parental Homework Involvement Improves Test Scores? A Review of the Literature,” , June 2015 | |
| 23. | Jamie Ballard, “40% of People Say Elementary School Students Have Too Much Homework,” yougov.com, July 31, 2018 | |
| 24. | Stanford University, “Stanford Survey of Adolescent School Experiences Report: Mira Costa High School, Winter 2017,” stanford.edu, 2017 | |
| 25. | Cathy Vatterott, “Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs,” ascd.org, 2009 | |
| 26. | End the Race, “Homework: You Can Make a Difference,” racetonowhere.com (accessed Aug. 24, 2018) | |
| 27. | Elissa Strauss, “Opinion: Your Kid Is Right, Homework Is Pointless. Here’s What You Should Do Instead.,” cnn.com, Jan. 28, 2020 | |
| 28. | Jeanne Fratello, “Survey: Homework Is Biggest Source of Stress for Mira Costa Students,” digmb.com, Dec. 15, 2017 | |
| 29. | Clifton B. Parker, “Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework,” stanford.edu, Mar. 10, 2014 | |
| 30. | AdCouncil, “Cheating Is a Personal Foul: Academic Cheating Background,” glass-castle.com (accessed Aug. 16, 2018) | |
| 31. | Jeffrey R. Young, “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame,” chronicle.com, Mar. 28, 2010 | |
| 32. | Robin McClure, “Do You Do Your Child’s Homework?,” verywellfamily.com, Mar. 14, 2018 | |
| 33. | Robert M. Pressman, David B. Sugarman, Melissa L. Nemon, Jennifer, Desjarlais, Judith A. Owens, and Allison Schettini-Evans, “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background,” , 2015 | |
| 34. | Heather Koball and Yang Jiang, “Basic Facts about Low-Income Children,” nccp.org, Jan. 2018 | |
| 35. | Meagan McGovern, “Homework Is for Rich Kids,” huffingtonpost.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 36. | H. Richard Milner IV, “Not All Students Have Access to Homework Help,” nytimes.com, Nov. 13, 2014 | |
| 37. | Claire McLaughlin, “The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’,” neatoday.org, Apr. 20, 2016 | |
| 38. | Doug Levin, “This Evening’s Homework Requires the Use of the Internet,” edtechstrategies.com, May 1, 2015 | |
| 39. | Amy Lutz and Lakshmi Jayaram, “Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework,” , June 2015 | |
| 40. | Sandra L. Hofferth and John F. Sandberg, “How American Children Spend Their Time,” psc.isr.umich.edu, Apr. 17, 2000 | |
| 41. | Alfie Kohn, “Does Homework Improve Learning?,” alfiekohn.org, 2006 | |
| 42. | Patrick A. Coleman, “Elementary School Homework Probably Isn’t Good for Kids,” fatherly.com, Feb. 8, 2018 | |
| 43. | Valerie Strauss, “Why This Superintendent Is Banning Homework – and Asking Kids to Read Instead,” washingtonpost.com, July 17, 2017 | |
| 44. | Pew Research Center, “The Way U.S. Teens Spend Their Time Is Changing, but Differences between Boys and Girls Persist,” pewresearch.org, Feb. 20, 2019 | |
| 45. | ThroughEducation, “The History of Homework: Why Was It Invented and Who Was behind It?,” , Feb. 14, 2020 | |
| 46. | History, “Why Homework Was Banned,” (accessed Feb. 24, 2022) | |
| 47. | Valerie Strauss, “Does Homework Work When Kids Are Learning All Day at Home?,” , Sep. 2, 2020 | |
| 48. | Sara M Moniuszko, “Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In,” , Aug. 17, 2021 | |
| 49. | Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, “The Worsening Homework Problem,” , Apr. 13, 2021 | |
| 50. | Kiara Taylor, “Digital Divide,” , Feb. 12, 2022 | |
| 51. | Marguerite Reardon, “The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind,” , May 5, 2021 | |
| 52. | Rachel Paula Abrahamson, “Why More and More Teachers Are Joining the Anti-Homework Movement,” , Sep. 10, 2021 |
More School Debate Topics
Should K-12 Students Dissect Animals in Science Classrooms? – Proponents say dissecting real animals is a better learning experience. Opponents say the practice is bad for the environment.
Should Students Have to Wear School Uniforms? – Proponents say uniforms may increase student safety. Opponents say uniforms restrict expression.
Should Corporal Punishment Be Used in K-12 Schools? – Proponents say corporal punishment is an appropriate discipline. Opponents say it inflicts long-lasting physical and mental harm on students.
ProCon/Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 325 N. LaSalle Street, Suite 200 Chicago, Illinois 60654 USA
Natalie Leppard Managing Editor [email protected]
© 2023 Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. All rights reserved
- Social Media
- Death Penalty
- School Uniforms
- Video Games
- Animal Testing
- Gun Control
- Banned Books
- Teachers’ Corner
Cite This Page
ProCon.org is the institutional or organization author for all ProCon.org pages. Proper citation depends on your preferred or required style manual. Below are the proper citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order): the Modern Language Association Style Manual (MLA), the Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago), the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA), and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Turabian). Here are the proper bibliographic citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order):
[Editor's Note: The APA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
[Editor’s Note: The MLA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School’s In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .

Home > Blog > Tips for Online Students > The Pros and Cons of Homework
School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: July 16, 2024
Published: January 23, 2020

Remember those nights when you’d find yourself staring at a mountain of homework, eyes drooping, wondering if you’d ever see the light at the end of the tunnel? The debate over homework’s role in education is as old as time. Is it a crucial tool for reinforcing learning or just an unnecessary burden?
For college students, this question takes on new dimensions. Juggling homework with the endless amount of classes, part-time jobs, and social lives can feel like walking on thin ice. The pressure to maintain grades, meet deadlines, and still find time for friends and relaxation can be overwhelming. So, is homework a friend or foe?

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
The homework dilemma.
A large amount of college students report feeling overwhelmed by their academic workload, leading to high levels of stress and anxiety. According to Research.com , 45% of college students in the U.S. experience “more than average” stress, with 36.5% citing stress as a major impediment to their academic performance. This stress often stems directly from the homework load, leading to symptoms like headaches, exhaustion, and difficulty sleeping. The intense pressure to manage homework alongside other responsibilities makes us question the true impact of homework on students’ overall well-being.
And then there’s the digital twist. A whopping 89% of students confessed to using AI tools like ChatGPT for their assignments. While these tools can be a godsend for quick answers and assistance, they can also undermine the personal effort and critical thinking necessary to truly understand the material.
On the brighter side, homework can be a powerful ally. According to Inside Higher Ed , structured assignments can actually help reduce stress by providing a clear learning roadmap and keeping students engaged with the material. But where’s the balance between helpful and harmful?
With these perspectives in mind, let’s dive into the pros and cons of homework for college students. By understanding both sides, we can find a middle ground that maximizes learning while keeping stress at bay.
The Pros of Homework
When thoughtfully assigned, homework can be a valuable tool in a student’s educational journey . Let’s explore how homework can be a beneficial companion to your studies:
Enhances Critical Thinking
Homework isn’t just busywork; it’s an opportunity to stretch your mental muscles. Those late-night problem sets and essays can actually encourage deeper understanding and application of concepts. Think of homework as a mental gym; each assignment is a new exercise, pushing you to analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information in ways that strengthen your critical thinking skills .
Time Management Skills
Do you ever juggle multiple deadlines and wonder how to keep it all together? Regular homework assignments can be a crash course in time management . They teach you to prioritize tasks, manage your schedule, and balance academic responsibilities with personal commitments. The ability to juggle various tasks is a skill that will serve you well beyond your college years.
Reinforcement of Learning
There’s a reason why practice makes perfect. Homework reinforces what you’ve learned in class, helping to cement concepts and theories in your mind. Understanding a concept during a lecture is one thing, but applying it through homework can deepen your comprehension and retention.
Preparation for Exams
Think of homework as a sound check and warm-up for exams. Regular assignments keep you engaged with the material, making it easier to review and prepare when exam time rolls around. By consistently working through problems and writing essays, you build a solid foundation that can make the difference between cramming and confident exam performance.
Encourages Independent Learning
Homework promotes a sense of responsibility and independence. It pushes you to tackle assignments on your own, encouraging problem-solving and self-discipline. This independence prepares you for the academic challenges ahead and the autonomy required in your professional and personal life.

The Cons of Homework
Despite its potential benefits, homework can also have significant downsides. Let’s examine the challenges and drawbacks of homework:
Impact on Mental Health
Homework can be a double-edged sword when it comes to mental health . While it’s meant to reinforce learning, the sheer volume of assignments can lead to stress and anxiety. The constant pressure to meet deadlines and the fear of falling behind can create a relentless cycle of stress. Many students become overwhelmed, leading to burnout and negatively impacting their overall well-being.
Limited Time for Other Activities
College isn’t just about hitting the books. It’s also a time for personal growth, exploring new interests, and building social connections. Excessive homework can eat into the time you might otherwise spend on extracurricular activities, hobbies, or simply hanging out with friends. This lack of balance can lead to a less fulfilling college experience. Shouldn’t education be about more than just academics?
Quality Over Quantity
When it comes to homework, more isn’t always better. Piling on assignments can lead to diminished returns on learning. Instead of diving deep into a subject and gaining a thorough understanding, students might rush through tasks just to get them done. This focus on quantity over quality can undermine the educational value of homework.
Inequity in Education
Homework can sometimes exacerbate educational inequalities. Not all students can access the same resources and support systems at home. While some might have a quiet space and access to the internet, others might struggle with distractions and lack of resources. This disparity can put certain students at a disadvantage, making homework more of a burden than a learning tool.
Dependence on AI Tools
With the advent of AI tools like ChatGPT , homework has taken on a new dimension. While these tools can provide quick answers and assistance, they also pose the risk of students becoming overly reliant on technology. This dependence can take away from the actual learning process, as students might bypass the critical thinking and effort needed to truly understand the material. Is convenience worth the potential loss in learning?
Finding the Balance
Finding the right balance with homework means tackling assignments that challenge and support you. Instead of drowning in a sea of tasks, focus on quality over quantity. Choose projects that spark your critical thinking and connect to real-world situations. Flexibility is key here. Recognize that your circumstances are unique, and adjusting your approach can help reduce stress and create a more inclusive learning environment. Constructive feedback makes homework more than just a chore; it turns it into a tool for growth and improvement.
It’s also about living a well-rounded college life. Don’t let homework overshadow other important parts of your life, like extracurricular activities or personal downtime. Emphasize independent learning and use technology wisely to prepare for future challenges. By balancing thoughtful assignments with your personal needs, homework can shift from being a burden to becoming a helpful companion on your educational journey, enriching your academic and personal growth.
Homework has its pros and cons, especially for college students. It can enhance critical thinking, time management, and learning, but it also brings stress, impacts mental health, and can become overwhelming. Finding the right balance is key.
Focus on quality assignments, maintain flexibility, and make sure your homework complements rather than dominates your life. With a thoughtful approach, homework can support your educational journey, fostering both academic success and personal growth.
How can I manage my time effectively to balance homework and other activities?
Create a schedule that allocates specific times for homework, classes, and personal activities. Use planners or digital calendars to keep track of deadlines and prioritize tasks. Don’t forget to include breaks to avoid burnout.
How can I reduce the stress associated with homework?
To manage stress, practice mindfulness techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises. Break assignments into smaller, manageable tasks and tackle them one at a time. If needed, seek support from classmates, tutors, or mental health professionals.
Is using AI tools for homework cheating?
While AI tools like ChatGPT can be helpful for quick assistance, relying on them too much can hinder your learning process. Use them as a supplement rather than a replacement for your own effort and critical thinking.
How can teachers make homework more equitable?
Teachers can offer flexible deadlines, provide resources for students who lack them, and design assignments that account for different learning styles and home environments. Open communication between students and teachers can also help address individual challenges.
What are some strategies to make homework more meaningful?
Focus on quality over quantity by designing assignments that encourage deep thinking and application of knowledge. Integrate real-world problems to make homework more relevant and engaging. Provide constructive feedback to help students learn and grow from their assignments.
In this article
At UoPeople, our blog writers are thinkers, researchers, and experts dedicated to curating articles relevant to our mission: making higher education accessible to everyone. Read More
Why homework matters
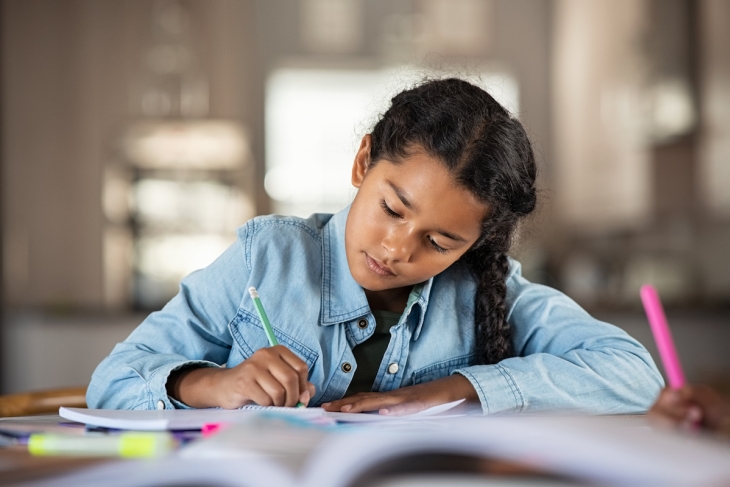

Homework is the perennial bogeyman of K–12 education. Any given year, you’ll find people arguing that students, especially those in elementary school, should have far less homework—or none at all . I have the opposite opinion. The longer I run schools—and it has now been more than sixteen years—the more convinced I am that homework is not only necessary, but a linchpin to effective K–12 education.
It is important to remember that kids only spend a fraction of their time in school. The learning that does or does not take place in the many hours outside of school has a monumental effect on children’s academic success and is a root cause of educational inequity.
The pandemic gave us a stark demonstration of this reality. Achievement gaps widened between affluent and low-income children not only because low-income students received less in-person or high-quality online instruction during the years of disrupted school, but also because children of college-educated and affluent parents were already less dependent on schools for learning. Affluent children are far more likely to have the privilege of tutors or other types of supplementary instruction, as well as a family culture of reading, and opportunities to travel, visit museums, and more. Homework is a powerful tool to help narrow these inequities, giving children from all backgrounds the opportunity to keep learning when they are not in school.
At Success Academy, the charter school network I founded and lead, we seek to develop students as lifelong learners who have the confidence and curiosity to pursue and build knowledge in all facets of their lives. Homework cultivates these mindsets and habits. Indeed, when teachers don’t assign homework, it reflects an unconscious conviction that kids can’t learn without adults. Kids internalize this message and come to believe they need their teacher to gain knowledge. In reality, they are more than capable of learning all sorts of things on their own. Discovering this fact can be both incredibly exciting and deeply empowering for them.
We also know that none of these benefits accrue when homework is mere busywork. Low-quality homework is likely what drives the mixed research evidence on the impact of homework on student achievement. It also sends the message to kids that doing it is simply an exercise in compliance and not worth their time. Homework must be challenging and purposeful for kids to recognize its value.
For this reason, at Success, we take great care with the design of our homework assignments, ensuring they are engaging and relevant to what takes place in class the next day. When done well, homework can be a form of the “flipped classroom”—a model developed by ed tech innovators to make large college lecture classes more engaging. In flipped classrooms, students learn everything they can on their own at home (in the original conception, via recorded lectures); class time builds on what they learned to address confusion and elevate their thinking to a more sophisticated level. It’s an approach that both respects kids’ capacity to learn independently, and assumes that out-of-class learning will drive the content and pace of the in-person lesson.
Students always need a “why” for the things we ask them to do, and designing homework this way is motivating for them because it gives them that clear why. Class is engaging and interesting when they are prepared; when they aren’t, they won’t have the satisfaction of participating.
At this point, some teachers may be saying, “I can’t get my kids to hand in a worksheet, let alone rely on them to learn on their own.” And of course, effective use of homework in class relies on creating a strong system of accountability for getting kids to do it. This can be hard for teachers. It’s uncomfortable to lean into students’ lives outside of school, and many educators feel they don’t have that right. But getting over that discomfort is best for kids.
Educators should embrace setting an exacting norm for completing homework. This should include a schoolwide grading policy—at Success schools, missing and incomplete homework assignments receive a zero; students can get partial credit for work handed in late; and middle and high schoolers can revise their homework for a better grade—as well as consistently and explicitly noticing when kids are or are not prepared and offering praise and consequences. Enlisting parents’ help in this area is also highly effective. I guarantee they will be grateful to be kept informed of how well their children are meeting their responsibilities!
Ultimately, minimizing homework or getting rid of it entirely denies children autonomy and prevents them from discovering what they are capable of. As we work to repair the academic damage from the last two-plus years, I encourage educators to focus not on the quantity of homework, but instead on its quality—and on using it effectively in class. By doing so, they will accelerate kids’ engagement with school, and propel them as assured, autonomous learners and thinkers who can thrive in college and beyond.

Eva Moskowitz is the CEO of Success Academy Charter Schools .
Related Content

Gadfly Bites 8/26/24—School choice reportage

Court cases shine light on state laws that obstruct effective school leadership

Ohio Charter News Weekly – 8.23.24
More From Forbes
Why homework doesn't seem to boost learning--and how it could.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Some schools are eliminating homework, citing research showing it doesn’t do much to boost achievement. But maybe teachers just need to assign a different kind of homework.
In 2016, a second-grade teacher in Texas delighted her students—and at least some of their parents—by announcing she would no longer assign homework. “Research has been unable to prove that homework improves student performance,” she explained.
The following year, the superintendent of a Florida school district serving 42,000 students eliminated homework for all elementary students and replaced it with twenty minutes of nightly reading, saying she was basing her decision on “solid research about what works best in improving academic achievement in students.”
Many other elementary schools seem to have quietly adopted similar policies. Critics have objected that even if homework doesn’t increase grades or test scores, it has other benefits, like fostering good study habits and providing parents with a window into what kids are doing in school.
Those arguments have merit, but why doesn’t homework boost academic achievement? The research cited by educators just doesn’t seem to make sense. If a child wants to learn to play the violin, it’s obvious she needs to practice at home between lessons (at least, it’s obvious to an adult). And psychologists have identified a range of strategies that help students learn, many of which seem ideally suited for homework assignments.
For example, there’s something called “ retrieval practice ,” which means trying to recall information you’ve already learned. The optimal time to engage in retrieval practice is not immediately after you’ve acquired information but after you’ve forgotten it a bit—like, perhaps, after school. A homework assignment could require students to answer questions about what was covered in class that day without consulting their notes. Research has found that retrieval practice and similar learning strategies are far more powerful than simply rereading or reviewing material.
One possible explanation for the general lack of a boost from homework is that few teachers know about this research. And most have gotten little training in how and why to assign homework. These are things that schools of education and teacher-prep programs typically don’t teach . So it’s quite possible that much of the homework teachers assign just isn’t particularly effective for many students.
Even if teachers do manage to assign effective homework, it may not show up on the measures of achievement used by researchers—for example, standardized reading test scores. Those tests are designed to measure general reading comprehension skills, not to assess how much students have learned in specific classes. Good homework assignments might have helped a student learn a lot about, say, Ancient Egypt. But if the reading passages on a test cover topics like life in the Arctic or the habits of the dormouse, that student’s test score may well not reflect what she’s learned.
The research relied on by those who oppose homework has actually found it has a modest positive effect at the middle and high school levels—just not in elementary school. But for the most part, the studies haven’t looked at whether it matters what kind of homework is assigned or whether there are different effects for different demographic student groups. Focusing on those distinctions could be illuminating.
A study that looked specifically at math homework , for example, found it boosted achievement more in elementary school than in middle school—just the opposite of the findings on homework in general. And while one study found that parental help with homework generally doesn’t boost students’ achievement—and can even have a negative effect— another concluded that economically disadvantaged students whose parents help with homework improve their performance significantly.
That seems to run counter to another frequent objection to homework, which is that it privileges kids who are already advantaged. Well-educated parents are better able to provide help, the argument goes, and it’s easier for affluent parents to provide a quiet space for kids to work in—along with a computer and internet access . While those things may be true, not assigning homework—or assigning ineffective homework—can end up privileging advantaged students even more.
Students from less educated families are most in need of the boost that effective homework can provide, because they’re less likely to acquire academic knowledge and vocabulary at home. And homework can provide a way for lower-income parents—who often don’t have time to volunteer in class or participate in parents’ organizations—to forge connections to their children’s schools. Rather than giving up on homework because of social inequities, schools could help parents support homework in ways that don’t depend on their own knowledge—for example, by recruiting others to help, as some low-income demographic groups have been able to do . Schools could also provide quiet study areas at the end of the day, and teachers could assign homework that doesn’t rely on technology.
Another argument against homework is that it causes students to feel overburdened and stressed. While that may be true at schools serving affluent populations, students at low-performing ones often don’t get much homework at all—even in high school. One study found that lower-income ninth-graders “consistently described receiving minimal homework—perhaps one or two worksheets or textbook pages, the occasional project, and 30 minutes of reading per night.” And if they didn’t complete assignments, there were few consequences. I discovered this myself when trying to tutor students in writing at a high-poverty high school. After I expressed surprise that none of the kids I was working with had completed a brief writing assignment, a teacher told me, “Oh yeah—I should have told you. Our students don’t really do homework.”
If and when disadvantaged students get to college, their relative lack of study skills and good homework habits can present a serious handicap. After noticing that black and Hispanic students were failing her course in disproportionate numbers, a professor at the University of North Carolina decided to make some changes , including giving homework assignments that required students to quiz themselves without consulting their notes. Performance improved across the board, but especially for students of color and the disadvantaged. The gap between black and white students was cut in half, and the gaps between Hispanic and white students—along with that between first-generation college students and others—closed completely.
There’s no reason this kind of support should wait until students get to college. To be most effective—both in terms of instilling good study habits and building students’ knowledge—homework assignments that boost learning should start in elementary school.
Some argue that young children just need time to chill after a long day at school. But the “ten-minute rule”—recommended by homework researchers—would have first graders doing ten minutes of homework, second graders twenty minutes, and so on. That leaves plenty of time for chilling, and even brief assignments could have a significant impact if they were well-designed.
But a fundamental problem with homework at the elementary level has to do with the curriculum, which—partly because of standardized testing— has narrowed to reading and math. Social studies and science have been marginalized or eliminated, especially in schools where test scores are low. Students spend hours every week practicing supposed reading comprehension skills like “making inferences” or identifying “author’s purpose”—the kinds of skills that the tests try to measure—with little or no attention paid to content.
But as research has established, the most important component in reading comprehension is knowledge of the topic you’re reading about. Classroom time—or homework time—spent on illusory comprehension “skills” would be far better spent building knowledge of the very subjects schools have eliminated. Even if teachers try to take advantage of retrieval practice—say, by asking students to recall what they’ve learned that day about “making comparisons” or “sequence of events”—it won’t have much impact.
If we want to harness the potential power of homework—particularly for disadvantaged students—we’ll need to educate teachers about what kind of assignments actually work. But first, we’ll need to start teaching kids something substantive about the world, beginning as early as possible.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

Why Is Homework Bad? How It Damages Students’ Mental Health
Why Is Homework Bad? Homework is considered to be an important part of the learning process. Yes, it can be helpful for students because it helps them to develop critical thinking, self-discipline, and also time management skills which are very important in life.
Homework plays an important role in their academic life and also prepares them for future challenges.
But on the other hand, it also has some drawbacks which are not good for students. I don’t say that homework is not good it can be good if students get enough homework.
But some teachers give students a lot of homework to do which can lead to stress, exhaustion, and a lack of motivation for learning.
It’s important to know these drawbacks and consider alternative ways of supporting students’ learning that do not rely so heavily on homework.
So, let’s take a closer look at the reasons why homework is bad.
If you want to get the Best homework help service from experts, then you can contact our expert who will provide you the best & top-notch homework help service within the given deadline.
20 Reasons Why Homework Is Bad
Table of Contents
Here are reasons why too much homework is bad :
- Less important
- Consume free time
- Is less important
- Teaches nothing
- There’s No Time for Life Outside of School
- Homework Is Busywork
- Homework Can’t Replace In-Class Education
- Because Students Can’t or Don’t Ask for Help
- Because Sometimes Parents Can’t Help
- Teaching Methods Keep Changing
- Because Homework Creates Unnecessary Struggles
- Because It Can Hurt Grades
- Because It Hurts Students With Problems
- Learning Should Be Fun
- Chronic Daily Headaches
- Lack of Socialization
- Loss of Creativity
- Too Difficult
- Distractions
10 Reasons Why Homework Is Bad?
School is an important part of students’ life. If students can’t go to school every day to gain the skills to be successful in life, this is the drawback for their entire life. It does not mean that they can’t do other think. It is also important that students should take a break from their education. In my opinion, most students get too much homework or assignment from their teachers, with a lot of homework or assignment students get unhealthy levels of stress and other health issues. Here are some reasons why homework is bad for students:
Depression
Kill the interest to learn.
- Affects Relationships With Parents
- Homework Is Harmful To Health

When teachers give a lot of homework to the students, it gives students a high level of stress. They feel stressed if they can’t complete their homework or assignment on time. This is a major source of anxiety.
When it comes to homework (especially if you want to be an IT specialist), many people work hard and struggle with issues such as a lack of information, poor time management skills, or a poor comprehension of the subject, all of which contribute to worry. It happens even more frequently when students are having trouble with their biochemistry homework or are unsure how to finish their philosophy tasks. This was the first reason why is homework bad.
The solution: parents and teachers should provide support and mentoring to students to help them avoid anxiousness.

Bullying in schools isn’t a new concept. without a doubt, Bullying has long-term harmful psychological consequences on children’s personalities. Although youngsters always find a way to make fun of their friends, there is no doubt that homework is detrimental to students who want to enhance their grades and academic performance. Why? In college or university, students treat nerds horribly, when A+ students refuse to help their students to cheat, it becomes a major source of bullying.
The solution: it’s critical to assign kids unique home responsibilities to avoid cheating and bullying.

This is the third reason Why Is Homework Bad. It has been proven over the last few years that young people spend a significant amount of time at school learning: they attend lectures, study books and materials, work on projects, solve geometry problems, and write essays. Without a doubt, academics take a lot of time, therefore students must prioritise their activities and often sacrifice their personal lives to complete their homework to a high standard. When people are focused on completing difficult activities, they lose motivation over time. Overall, it causes burnout, which makes it difficult for them to succeed.
The solution : assigning interesting and engaging activities that promote creativity is critical.

This is the fourth reason Why Is Homework Bad. According to researchers, home assignments promote sadness, and 39% of college students experience depression on a regular basis. When children are unable to attain their goals, whether it is to improve their grades or obtain positive comments from their teachers, they are unable to meet their development needs or learn other important life skills. All of these issues can have a negative impact on one’s general health and academic performance.
The solution is for parents to understand what motivates them to do homework, and for teachers to learn the art of teaching with SCDL.

Many students feel that if they do not complete their homework, then they may fail to deliver homework on time. Students should not have to take the stress of homework. They should learn educational content in a classroom and they have to explore other things when they are outside at school.
The solution: ensure that students fully comprehend the work or form student groups on social media to provide support.

This is the sixth reason Why Is Homework Bad. Sometimes homework kills the interest of students. As a result, homework becomes a full-time job, and a child loses interest in learning. Furthermore, a student requires a break from the instructional content in order to avoid becoming burnt out or losing interest in learning.
Affects Relationships With Parents

This is the seventh reason Why Is Homework Bad. While teachers do their best to engage students with a variety of activities, it’s difficult to recognize the genuine value in the homework projects that students bring home. It often happens that parents complete homework assignments, and they do not necessarily receive an A because:
- The educational program has changed, and parents’ awareness has deteriorated.
- Many parents forget what they learned in school and attempt to do chores from the perspective of an adult.
- Parents aren’t always the best teachers. They aren’t professionals at explaining the content, therefore doing so at home can be worse than failing the task.
- Homework is a frequent source of contention. Children don’t want to do it, and parents don’t know how to motivate their children to do it. Joint endeavours eventually come to a halt, resulting in disagreements and conflicts.
- As a result, the advantages of home duties as a learning tool are completely gone. Every year, the number of people who believe homework should be abolished rises.
Homework Is Harmful To Health.

This is the eighth reason Why Is Homework Bad. Every parent talks about how the ever-increasing academic load and stress testing are affecting their children’s health.
Children are sleepless due to their heavy workload, and they stay up late reading textbooks and worrying about their scores, and as a result, they have sleep issues. The relationships between sleep length, homework stress, and sleep hygiene in school-aged children.
We don’t have many healthy schoolchildren. Nearsightedness, gastritis, persistent tiredness, and postural abnormalities are all conditions that the youngster is likely to have.
So why don’t you spit on your homework and grades and do something more enjoyable?
Homework Takes Time Away

This is the nineth reason Why Is Homework Bad. Today’s kids are as busy as they’ve ever been. They spend too much time at school, then rush to the tutors, and then turn into the section on their way back. The schedule is very rigid, and every hour is taken into consideration.
In this study, psychologist Harris Cooper presents research that shows that homework is ineffective: if a child is given too much material, he will not learn it. In elementary school, children require no more than 20 minutes of extra classes, while older students require an hour and a half of homework.
For comparison, according to our hygienic requirements, an hour and a half is the volume for the second class. Graduates have three and a half hours to spend on lessons. After school, I was gone for over a half-day. And when is it appropriate to live?
Homework Teaches Nothing

This is the tenth reason Why Is Homework Bad. Life is completely detached from school education. Graduates who have spent years studying English are unable to link two words, have no idea which hemisphere they are in, and strongly believe in the power of homoeopathy. Homework follows the same pattern: it boggles kids’ minds with facts they can’t apply.
Consider how you learned in school and compare it to what you would learn in a Swiss school. It would be beneficial if homework helped bridge the gap between school and life. This, however, is not the case.
Why Kids Should Not Have Homework
When it comes to institutions that work with children, the effects of too much homework are even more severe than when it comes to high school students. Trainers should look for innovative ways to engage students and guarantee that they can easily relate to what they’re learning and find every subject enjoyable. The following are the primary reasons why children should not be assigned any homework:
Your Kid Should Read For Pleasure
Kids are always learning, your kid needs ample time outdoors.
If your child is busy with doing homework, he or she will not have time to broaden his or her knowledge base. Rather than assigning a large amount of homework, teachers should encourage students to read good books for enjoyment, practice poetry, paint images of familiar items, and pursue their own interests.
You are incorrect if you believe that a child can only learn through doing homework. Children in the twenty-first century learn in stages. Kids are constantly learning through the use of smartphones, computers at home, and reading platforms such as Kindle. For example, if you want your child to practice using specific terms, let him or her use the smartphone to seek up those words and create sentences about them. So, let’s get clever and let the kids be kids.
While the amount of time a child spends learning is important, so are outside activities. Giving children more time outside, according to education experts, is beneficial because it allows them to experiment with what they have learnt in class.
Take, for example, a scientific topic such as plant parts. Giving your child a lot of homework will result in a lot of homework stress. Instead, the teacher should have the students use their iPhones to identify flora in their complex. What’s more, you know what? “That tree looks like the one I read about yesterday,” the child will say to his or her guardian as they are being driven to school.
How Does Homework Affect Students And Their Social Life?
Outside of class, students have time for social and other activities, which allows them to clear their minds and bodies. on the other hand, Students who have several assignments to complete, have less time for their friends and relatives. Statistics show that too much homework has a detrimental impact on developing relationships and forming better bonds with classmates.
Students miss out on holidays and gatherings, which isolates them and makes them feel unsupported and discouraged. Combining coursework and jobs makes it even more difficult for college or university students to find time for themselves. Stress levels rise as a result of not having enough time to rest and socialize, which has an impact on academic performance and family relationships.
Submit Homework
In this blog, you have learned why is homework bad in detail. I hope you have understood why is homework bad easily. In my opinion, too much homework is bad students should not have so much homework to do. Students should also have time for outside activities because no one is intelligent in their studies. Some students are good at outdoor activities. Now if you need homework help from experts, then contact our experts for help.
Why Is Homework Bad FAQs
What are the negative effects of homework on students.
There are a lot of reasons homework can be affected negatively on students such as leading to stress, anxiety, depression, and sleep deprivation.
Why homework is bad for mental health?
Homework can contribute to students’ stress levels and anxiety which can lead to mental health problems such as anxiety and depression.
Why Is Homework A Waste Of Time?
Homework is a waste of time. It takes the enjoyment out of school and it takes up teacher time. Students need more free time for other activities such as sports, homework takes it away from spending time with family and friends.
Similar Articles

13 Best Tips To Write An Assignment
Whenever the new semester starts, you will get a lot of assignment writing tasks. Now you enter the new academic…

How To Do Homework Fast – 11 Tips To Do Homework Fast
Homework is one of the most important parts that have to be done by students. It has been around for…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Is Homework Good or Bad for Students?
It's mostly good, especially for the sciences, but it also can be bad
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
Homework isn't fun for students to do or for teachers to grade, so why do it? Here are some reasons why homework is good and why it's bad.
Why Homework Is Good
Here are 10 reasons why homework is good, especially for the sciences, such as chemistry:
- Doing homework teaches you how to learn on your own and work independently. You'll learn how to use resources such as texts, libraries, and the internet. No matter how well you thought you understood the material in class, there will be times when you'll get stuck doing homework. When you face the challenge, you learn how to get help, how to deal with frustration, and how to persevere.
- Homework helps you learn beyond the scope of the class. Example problems from teachers and textbooks show you how to do an assignment. The acid test is seeing whether you truly understand the material and can do the work on your own. In science classes, homework problems are critically important. You see concepts in a whole new light, so you'll know how equations work in general, not just how they work for a particular example. In chemistry, physics, and math, homework is truly important and not just busywork.
- It shows you what the teacher thinks is important to learn, so you'll have a better idea of what to expect on a quiz or test .
- It's often a significant part of your grade . If you don't do it, it could cost you , no matter how well you do on exams.
- Homework is a good opportunity to connect parents, classmates, and siblings with your education. The better your support network, the more likely you are to succeed in class.
- Homework, however tedious it might be, teaches responsibility and accountability. For some classes, homework is an essential part of learning the subject matter.
- Homework nips procrastination in the bud. One reason teachers give homework and attach a big part of your grade to it is to motivate you to keep up. If you fall behind, you could fail.
- How will you get all your work done before class? Homework teaches you time management and how to prioritize tasks.
- Homework reinforces the concepts taught in class. The more you work with them, the more likely you are to learn them.
- Homework can help boost self-esteem . Or, if it's not going well, it helps you identify problems before they get out of control.
Sometimes Homework Is Bad
So, homework is good because it can boost your grades , help you learn the material, and prepare you for tests. It's not always beneficial, however. Sometimes homework hurts more than it helps. Here are five ways homework can be bad:
- You need a break from a subject so you don't burn out or lose interest. Taking a break helps you learn.
- Too much homework can lead to copying and cheating.
- Homework that is pointless busywork can lead to a negative impression of a subject (not to mention a teacher).
- It takes time away from families, friends, jobs, and other ways to spend your time.
- Homework can hurt your grades. It forces you to make time management decisions, sometimes putting you in a no-win situation. Do you take the time to do the homework or spend it studying concepts or doing work for another subject? If you don't have the time for the homework, you could hurt your grades even if you ace the tests and understand the subject.
- How to Change Your Habits and Improve Your Grades
- Common Classroom Etiquette and Rules for Students
- 18 Ways to Practice Spelling Words
- How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- How Much Damage Do Bad Grades Do?
- Homework Guidelines for Elementary and Middle School Teachers
- 20 Tips for Success in High School
- Study Tips for Middle School Students
- Cheating with Technology
- The Many Definitions of a Glyph
- How to Overcome Math Anxiety
- Signs Your Child's Teacher Is a Bully
- How to Give an Impromptu Speech
- How to Deal With a Bad Report Card
- 5 Bubble Sheet Tips for Test Answers
- External and Internal Motivation

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. The researchers asked students whether they experienced physical symptoms of stress, such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep ...
Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices. 1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences. According to Gitnux, U.S. high school students who have over 20 hours of homework per week are 27% more likely to encounter health issues.
Even when homework is helpful, there can be too much of a good thing. "There is a limit to how much kids can benefit from home study," Cooper says. He agrees with an oft-cited rule of thumb that students should do no more than 10 minutes a night per grade level — from about 10 minutes in first grade up to a maximum of about two hours in high ...
Homework's role in widening the achievement gap is a critical concern. As students from privileged backgrounds benefit from additional resources and support, those from disadvantaged backgrounds may fall further behind. ... The homework myth: Why our kids get too much of a bad thing. Da Capo Press. 8. Pressman, R. M., Sugarman, D. B., Nemon ...
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects ...
The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night. "Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's ...
Kohn, the author of The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing, considers homework to be a "reliable extinguisher of curiosity," and has several complaints with the evidence ...
I'll summarize four main reasons why homework just flat out doesn't make sense. ... Why our kids get too much of a bad thing. Da Capo Lifelong Books. Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2001). The End of Homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning. Beacon Press.
Think big picture. Forcing a child to complete a homework assignment, after they have spent a reasonable amount of time on it (10 minutes per grade), is not promoting balance. Keep academic ...
There are many reasons why Homework is bad, but in this Blog, we will cover the top 18 reasons why Homework is bad for students. May lead to Stress Problems. No time for outside activities. Excessive Homework cause Depression. Have no real impact on performance.
According to UVAToday, these researchers reported no "substantive difference" in the grades of students related to homework completion. As researcher Adam Maltese noted, "Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be.". The report further suggested that while not all homework is bad, the type and quality ...
Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We've known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that "homework had no association with achievement gains" when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7]
Homework also helps students develop key skills that they'll use throughout their lives: Accountability. Autonomy. Discipline. Time management. Self-direction. Critical thinking. Independent problem-solving. The skills learned in homework can then be applied to other subjects and practical situations in students' daily lives.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. • Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered ...
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn. "Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of ...
Homework has its pros and cons, especially for college students. It can enhance critical thinking, time management, and learning, but it also brings stress, impacts mental health, and can become overwhelming. Finding the right balance is key. Focus on quality assignments, maintain flexibility, and make sure your homework complements rather than ...
Homework is the perennial bogeyman of K-12 education. Any given year, you'll find people arguing that students, especially those in elementary school, should have far less homework—or none at all.I have the opposite opinion. The longer I run schools—and it has now been more than sixteen years—the more convinced I am that homework is not only necessary, but a linchpin to effective K ...
The research cited by educators just doesn't seem to make sense. If a child wants to learn to play the violin, it's obvious she needs to practice at home between lessons (at least, it's ...
In my opinion, most students get too much homework or assignment from their teachers, with a lot of homework or assignment students get unhealthy levels of stress and other health issues. Here are some reasons why homework is bad for students: Anxiety. Bullying.
Probing Question: Is homework bad for kids? | Penn State University. Ask an eleven-year-old whether homework is a bad thing, and you'll likely be greeted with vigorous nodding and not a hint of ambiguity. But do grown-up experts agree? As with so many things, the answer is mixed.
Homework is a good opportunity to connect parents, classmates, and siblings with your education. The better your support network, the more likely you are to succeed in class. Homework, however tedious it might be, teaches responsibility and accountability. For some classes, homework is an essential part of learning the subject matter.