Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.

How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Spring 2024)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
| Above Average (4) | Sufficient (3) | Developing (2) | Needs improvement (1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Thesis supported by relevant information and ideas | The central purpose of the student work is clear and supporting ideas always are always well-focused. Details are relevant, enrich the work. | The central purpose of the student work is clear and ideas are almost always focused in a way that supports the thesis. Relevant details illustrate the author’s ideas. | The central purpose of the student work is identified. Ideas are mostly focused in a way that supports the thesis. | The purpose of the student work is not well-defined. A number of central ideas do not support the thesis. Thoughts appear disconnected. |
| (Sequencing of elements/ ideas) | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which flows naturally and is engaging to the audience. | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which is followed by the reader with little or no difficulty. | Information and ideas are presented in an order that the audience can mostly follow. | Information and ideas are poorly sequenced. The audience has difficulty following the thread of thought. |
| (Correctness of grammar and spelling) | Minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. | The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by spelling and/or grammatical errors. | Grammatical and/or spelling errors distract from the work. | The readability of the work is seriously hampered by spelling and/or grammatical errors. |
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper
| The audience is able to easily identify the central message of the work and is engaged by the paper’s clear focus and relevant details. Information is presented logically and naturally. There are minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. : The audience is easily able to identify the focus of the student work which is supported by relevant ideas and supporting details. Information is presented in a logical manner that is easily followed. The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by errors. : The audience can identify the central purpose of the student work without little difficulty and supporting ideas are present and clear. The information is presented in an orderly fashion that can be followed with little difficulty. Grammatical and spelling errors distract from the work. : The audience cannot clearly or easily identify the central ideas or purpose of the student work. Information is presented in a disorganized fashion causing the audience to have difficulty following the author’s ideas. The readability of the work is seriously hampered by errors. |
Single-Point Rubric
| Advanced (evidence of exceeding standards) | Criteria described a proficient level | Concerns (things that need work) |
|---|---|---|
| Criteria #1: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #2: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #3: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #4: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| 90-100 points | 80-90 points | <80 points |
More examples:
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.

Writing Rubrics [Examples, Best Practices, & Free Templates]
Writing rubrics are essential tools for teachers.
Rubrics can improve both teaching and learning. This guide will explain writing rubrics, their benefits, and how to create and use them effectively.
What Is a Writing Rubric?

Table of Contents
A writing rubric is a scoring guide used to evaluate written work.
It lists criteria and describes levels of quality from excellent to poor. Rubrics provide a standardized way to assess writing.
They make expectations clear and grading consistent.
Key Components of a Writing Rubric
- Criteria : Specific aspects of writing being evaluated (e.g., grammar, organization).
- Descriptors : Detailed descriptions of what each level of performance looks like.
- Scoring Levels : Typically, a range (e.g., 1-4 or 1-6) showing levels of mastery.
Example Breakdown
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grammar | No errors | Few minor errors | Several errors | Many errors |
| Organization | Clear and logical | Mostly clear | Somewhat clear | Not clear |
| Content | Thorough and insightful | Good, but not thorough | Basic, lacks insight | Incomplete or off-topic |
Benefits of Using Writing Rubrics
Writing rubrics offer many advantages:
- Clarity : Rubrics clarify expectations for students. They know what is required for each level of performance.
- Consistency : Rubrics standardize grading. This ensures fairness and consistency across different students and assignments.
- Feedback : Rubrics provide detailed feedback. Students understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Efficiency : Rubrics streamline the grading process. Teachers can evaluate work more quickly and systematically.
- Self-Assessment : Students can use rubrics to self-assess. This promotes reflection and responsibility for their learning.
Examples of Writing Rubrics
Here are some examples of writing rubrics.
Narrative Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Story Elements | Well-developed | Developed, some details | Basic, missing details | Underdeveloped |
| Creativity | Highly creative | Creative | Some creativity | Lacks creativity |
| Grammar | No errors | Few minor errors | Several errors | Many errors |
| Organization | Clear and logical | Mostly clear | Somewhat clear | Not clear |
| Language Use | Rich and varied | Varied | Limited | Basic or inappropriate |
Persuasive Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argument | Strong and convincing | Convincing, some gaps | Basic, lacks support | Weak or unsupported |
| Evidence | Strong and relevant | Relevant, but not strong | Some relevant, weak | Irrelevant or missing |
| Grammar | No errors | Few minor errors | Several errors | Many errors |
| Organization | Clear and logical | Mostly clear | Somewhat clear | Not clear |
| Language Use | Persuasive and engaging | Engaging | Somewhat engaging | Not engaging |
Best Practices for Creating Writing Rubrics
Let’s look at some best practices for creating useful writing rubrics.
1. Define Clear Criteria
Identify specific aspects of writing to evaluate. Be clear and precise.
The criteria should reflect the key components of the writing task. For example, for a narrative essay, criteria might include plot development, character depth, and use of descriptive language.
Clear criteria help students understand what is expected and allow teachers to provide targeted feedback.
Insider Tip : Collaborate with colleagues to establish consistent criteria across grade levels. This ensures uniformity in expectations and assessments.
2. Use Detailed Descriptors
Describe what each level of performance looks like.
This ensures transparency and clarity. Avoid vague language. Instead of saying “good,” describe what “good” entails. For example, “Few minor grammatical errors that do not impede readability.”
Detailed descriptors help students gauge their performance accurately.
Insider Tip : Use student work samples to illustrate each performance level. This provides concrete examples and helps students visualize expectations.
3. Involve Students
Involve students in the rubric creation process. This increases their understanding and buy-in.
Ask for their input on what they think is important in their writing.
This collaborative approach not only demystifies the grading process but also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility in students.
Insider Tip : Conduct a workshop where students help create a rubric for an upcoming assignment. This interactive session can clarify doubts and make students more invested in their work.
4. Align with Objectives
Ensure the rubric aligns with learning objectives. This ensures relevance and focus.
If the objective is to enhance persuasive writing skills, the rubric should emphasize argument strength, evidence quality, and persuasive techniques.
Alignment ensures that the assessment directly supports instructional goals.
Insider Tip : Regularly revisit and update rubrics to reflect changes in curriculum and instructional priorities. This keeps the rubrics relevant and effective.
5. Review and Revise
Regularly review and revise rubrics. Ensure they remain accurate and effective.
Solicit feedback from students and colleagues. Continuous improvement of rubrics ensures they remain a valuable tool for both assessment and instruction.
Insider Tip : After using a rubric, take notes on its effectiveness. Were students confused by any criteria? Did the rubric cover all necessary aspects of the assignment? Use these observations to make adjustments.
6. Be Consistent
Use the rubric consistently across all assignments.
This ensures fairness and reliability. Consistency in applying the rubric helps build trust with students and maintains the integrity of the assessment process.
Insider Tip : Develop a grading checklist to accompany the rubric. This can help ensure that all criteria are consistently applied and none are overlooked during the grading process.
7. Provide Examples
Provide examples of each performance level.
This helps students understand expectations. Use annotated examples to show why a particular piece of writing meets a specific level.
This visual and practical demonstration can be more effective than descriptions alone.
Insider Tip : Create a portfolio of exemplar works for different assignments. This can be a valuable resource for both new and experienced teachers to standardize grading.
How to Use Writing Rubrics Effectively
Here is how to use writing rubrics like the pros.
1. Introduce Rubrics Early
Introduce rubrics at the beginning of the assignment.
Explain each criterion and performance level. This upfront clarity helps students understand what is expected and guides their work from the start.
Insider Tip : Conduct a rubric walkthrough session where you discuss each part of the rubric in detail. Allow students to ask questions and provide examples to illustrate each criterion.
2. Use Rubrics as a Teaching Tool
Use rubrics to teach writing skills. Discuss what constitutes good writing and why.
This can be an opportunity to reinforce lessons on grammar, organization, and other writing components.
Insider Tip : Pair the rubric with writing workshops. Use the rubric to critique sample essays and show students how to apply the rubric to improve their own writing.
3. Provide Feedback
Use the rubric to give detailed feedback. Highlight strengths and areas for improvement.
This targeted feedback helps students understand their performance and learn how to improve.
Insider Tip : Instead of just marking scores, add comments next to each criterion on the rubric. This personalized feedback can be more impactful and instructive for students.
4. Encourage Self-Assessment
Encourage students to use rubrics to self-assess.
This promotes reflection and growth. Before submitting their work, ask students to evaluate their own writing against the rubric.
This practice fosters self-awareness and critical thinking.
Insider Tip : Incorporate self-assessment as a mandatory step in the assignment process. Provide a simplified version of the rubric for students to use during self-assessment.
5. Use Rubrics for Peer Assessment
Use rubrics for peer assessment. This allows students to learn from each other.
Peer assessments can provide new perspectives and reinforce learning.
Insider Tip : Conduct a peer assessment workshop. Train students on how to use the rubric to evaluate each other’s work constructively. This can improve the quality of peer feedback.
6. Reflect and Improve
Reflect on the effectiveness of the rubric. Make adjustments as needed for future assignments.
Continuous reflection ensures that rubrics remain relevant and effective tools for assessment and learning.
Insider Tip : After an assignment, hold a debrief session with students to gather their feedback on the rubric. Use their insights to make improvements.
Check out this video about using writing rubrics:
Common Mistakes with Writing Rubrics
Creating and using writing rubrics can be incredibly effective, but there are common mistakes that can undermine their effectiveness.
Here are some pitfalls to avoid:
1. Vague Criteria
Vague criteria can confuse students and lead to inconsistent grading.
Ensure that each criterion is specific and clearly defined. Ambiguous terms like “good” or “satisfactory” should be replaced with concrete descriptions of what those levels of performance look like.
2. Overly Complex Rubrics
While detail is important, overly complex rubrics can be overwhelming for both students and teachers.
Too many criteria and performance levels can complicate the grading process and make it difficult for students to understand what is expected.
Keep rubrics concise and focused on the most important aspects of the assignment.
3. Inconsistent Application
Applying the rubric inconsistently can lead to unfair grading.
Ensure that you apply the rubric in the same way for all students and all assignments. Consistency builds trust and ensures that grades accurately reflect student performance.
4. Ignoring Student Input
Ignoring student input when creating rubrics can result in criteria that do not align with student understanding or priorities.
Involving students in the creation process can enhance their understanding and engagement with the rubric.
5. Failing to Update Rubrics
Rubrics should evolve to reflect changes in instructional goals and student needs.
Failing to update rubrics can result in outdated criteria that no longer align with current teaching objectives.
Regularly review and revise rubrics to keep them relevant and effective.
6. Lack of Examples
Without examples, students may struggle to understand the expectations for each performance level.
Providing annotated examples of work that meets each criterion can help students visualize what is required and guide their efforts more effectively.
7. Not Providing Feedback
Rubrics should be used as a tool for feedback, not just scoring.
Simply assigning a score without providing detailed feedback can leave students unclear about their strengths and areas for improvement.
Use the rubric to give comprehensive feedback that guides students’ growth.
8. Overlooking Self-Assessment and Peer Assessment
Self-assessment and peer assessment are valuable components of the learning process.
Overlooking these opportunities can limit students’ ability to reflect on their own work and learn from their peers.
Encourage students to use the rubric for self and peer assessment to deepen their understanding and enhance their skills.
What Is a Holistic Scoring Rubric for Writing?
A holistic scoring rubric for writing is a type of rubric that evaluates a piece of writing as a whole rather than breaking it down into separate criteria
This approach provides a single overall score based on the general impression of the writing’s quality and effectiveness.
Here’s a closer look at holistic scoring rubrics.

Key Features of Holistic Scoring Rubrics
- Single Overall Score : Assigns one score based on the overall quality of the writing.
- General Criteria : Focuses on the overall effectiveness, coherence, and impact of the writing.
- Descriptors : Uses broad descriptors for each score level to capture the general characteristics of the writing.
Example Holistic Scoring Rubric
| Score | Description |
|---|---|
| 5 | : Exceptionally clear, engaging, and well-organized writing. Demonstrates excellent control of language, grammar, and style. |
| 4 | : Clear and well-organized writing. Minor errors do not detract from the overall quality. Demonstrates good control of language and style. |
| 3 | : Satisfactory writing with some organizational issues. Contains a few errors that may distract but do not impede understanding. |
| 2 | : Basic writing that lacks organization and contains several errors. Demonstrates limited control of language and style. |
| 1 | : Unclear and poorly organized writing. Contains numerous errors that impede understanding. Demonstrates poor control of language and style. |
Advantages of Holistic Scoring Rubrics
- Efficiency : Faster to use because it involves a single overall judgment rather than multiple criteria.
- Flexibility : Allows for a more intuitive assessment of the writing’s overall impact and effectiveness.
- Comprehensiveness : Captures the overall quality of writing, considering all elements together.
Disadvantages of Holistic Scoring Rubrics
- Less Detailed Feedback : Provides a general score without specific feedback on individual aspects of writing.
- Subjectivity : Can be more subjective, as it relies on the assessor’s overall impression rather than specific criteria.
- Limited Diagnostic Use : Less useful for identifying specific areas of strength and weakness for instructional purposes.
When to Use Holistic Scoring Rubrics
- Quick Assessments : When a quick, overall evaluation is needed.
- Standardized Testing : Often used in standardized testing scenarios where consistency and efficiency are priorities.
- Initial Impressions : Useful for providing an initial overall impression before more detailed analysis.
Free Writing Rubric Templates
Feel free to use the following writing rubric templates.
You can easily copy and paste them into a Word Document. Please do credit this website on any written, printed, or published use.
Otherwise, go wild.
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well-developed, engaging, and clear plot, characters, and setting. | Developed plot, characters, and setting with some details missing. | Basic plot, characters, and setting; lacks details. | Underdeveloped plot, characters, and setting. | |
| Highly creative and original. | Creative with some originality. | Some creativity but lacks originality. | Lacks creativity and originality. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Rich, varied, and appropriate language. | Varied and appropriate language. | Limited language variety. | Basic or inappropriate language. |
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strong, clear, and convincing argument. | Convincing argument with minor gaps. | Basic argument; lacks strong support. | Weak or unsupported argument. | |
| Strong, relevant, and well-integrated evidence. | Relevant evidence but not strong. | Some relevant evidence, but weak. | Irrelevant or missing evidence. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Persuasive and engaging language. | Engaging language. | Somewhat engaging language. | Not engaging language. |
Expository Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thorough, accurate, and insightful content. | Accurate content with some details missing. | Basic content; lacks depth. | Incomplete or inaccurate content. | |
| Clear and concise explanations. | Mostly clear explanations. | Somewhat clear explanations. | Unclear explanations. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Precise and appropriate language. | Appropriate language. | Limited language variety. | Basic or inappropriate language. |
Descriptive Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vivid and detailed imagery that engages the senses. | Detailed imagery with minor gaps. | Basic imagery; lacks vivid details. | Little to no imagery. | |
| Highly creative and original descriptions. | Creative with some originality. | Some creativity but lacks originality. | Lacks creativity and originality. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Rich, varied, and appropriate language. | Varied and appropriate language. | Limited language variety. | Basic or inappropriate language. |
Analytical Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insightful, thorough, and well-supported analysis. | Good analysis with some depth. | Basic analysis; lacks depth. | Weak or unsupported analysis. | |
| Strong, relevant, and well-integrated evidence. | Relevant evidence but not strong. | Some relevant evidence, but weak. | Irrelevant or missing evidence. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Precise and appropriate language. | Appropriate language. | Limited language variety. | Basic or inappropriate language. |
Final Thoughts: Writing Rubrics
I have a lot more resources for teaching on this site.
Check out some of the blog posts I’ve listed below. I think you might enjoy them.
Read This Next:
- Narrative Writing Graphic Organizer [Guide + Free Templates]
- 100 Best A Words for Kids (+ How to Use Them)
- 100 Best B Words For Kids (+How to Teach Them)
- 100 Dictation Word Ideas for Students and Kids
- 50 Tricky Words to Pronounce and Spell (How to Teach Them)
Essay Rubric: Grading Students Correctly
- Icon Calendar 10 July 2024
- Icon Page 2897 words
- Icon Clock 14 min read
Lectures and tutors provide specific requirements for students to meet when writing essays. Basically, an essay rubric helps tutors to analyze an overall quality of compositions written by students. In this case, a rubric refers to a scoring guide used to evaluate performance based on a set of criteria and standards. As such, useful marking schemes make an analysis process simple for lecturers as they focus on specific concepts related to a writing process. Moreover, an assessment table lists and organizes all of the criteria into one convenient paper. In other instances, students use assessment tables to enhance their writing skills by examining various requirements. Then, different types of essay rubrics vary from one educational level to another. Essentially, Master’s and Ph.D. grading schemes focus on examining complex thesis statements and other writing mechanics. However, high school evaluation tables examine basic writing concepts. In turn, guidelines on a common format for writing a good essay rubric and corresponding examples provided in this article can help students to evaluate their papers before submitting them to their teachers.
General Aspects
An essay rubric refers to a way for teachers to assess students’ composition writing skills and abilities. Basically, an evaluation scheme provides specific criteria to grade assignments. Moreover, the three basic elements of an essay rubric are criteria, performance levels, and descriptors. In this case, teachers use assessment guidelines to save time when evaluating and grading various papers. Hence, learners must use an essay rubric effectively to achieve desired goals and grades, while its general example is:
What Is an Essay Rubric and Its Purpose
According to its definition, an essay rubric is a structured evaluation tool that educators use to grade students’ compositions in a fair and consistent manner. The main purpose of an essay rubric in writing is to ensure consistent and fair grading by clearly defining what constitutes excellent, good, average, and poor performance (DeVries, 2023). This tool specifies a key criteria for grading various aspects of a written text, including a clarity of a thesis statement, an overall quality of a main argument, an organization of ideas, a particular use of evidence, and a correctness of grammar and mechanics. Moreover, an assessment grading helps students to understand their strengths to be proud of and weaknesses to be pointed out and guides them in improving their writing skills (Taylor et al., 2024). For teachers, such an assessment simplifies a grading process, making it more efficient and less subjective by providing a clear standard to follow. By using an essay rubric, both teachers and students can engage in a transparent, structured, and constructive evaluation process, enhancing an overall educational experience (Stevens & Levi, 2023). In turn, the length of an essay rubric depends on academic levels, types of papers, and specific requirements, while general guidelines are:
High School
- Length: 1-2 pages
- Word Count: 300-600 words
- Length: 1-3 pages
- Word Count: 300-900 words
University (Undergraduate)
- Length: 2-4 pages
- Word Count: 600-1,200 words
Master’s
- Length: 2-5 pages
- Word Count: 600-1,500 words
- Length: 3-6 pages
- Word Count: 900-1,800 words

| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Thesis Statement | A well-defined thesis statement is crucial as it sets a particular direction and purpose of an essay, making it clear what a writer intends to argue or explain. |
| Introduction | An introduction captures a reader’s interest and provides a framework for what a paper will cover, setting up a stage for arguments or ideas that follow after an opening paragraph. |
| Content | High-quality content demonstrates thorough understanding and research on a specific topic, providing valuable and relevant information that supports a thesis. |
| Organization | Effective organization ensures author’s ideas are presented in a clear, well-structure, and logical order, enhancing readability and an overall flow of a central argument. |
| Evidence and Support | Providing strong evidence and detailed analysis is essential for backing up main arguments, adding credibility and depth to a final document. |
| Conclusion | A strong conclusion ties all the main numbers together, reflects on potential implications of arguments, and reinforces a thesis, leaving a lasting impression on a reader. |
| Grammar and Mechanics | Proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation are vital for clarity and professionalism, making a whole text easy to read and understand. |
| Style and Tone | Correctness in writing style and author’s tone appropriate to a paper’s purpose and audience enhances an overall effectiveness of a particular text and engages a reader. |
| Citations and References | Accurate and complete citations and references are crucial for giving credit to sources, avoiding plagiarism, and allowing readers to follow up on the research. |
Note: Some elements of an essay rubric can be added, deled, or combined with each other because different types of papers, their requirements, and instructors’ choices affect a final assessment. To format an essay rubric, people create a table with criteria listed in rows, performance levels in columns, and detailed descriptors in each cell explaining principal expectations for each level of performance (Steven & Levi, 2023). Besides, the five main criteria in a rubric are thesis statement, content, organization, evidence and support, and grammar and mechanics. In turn, a good essay rubric is clear, specific, aligned with learning objectives, and provides detailed, consistent descriptors for each performance level.
Steps How to Write an Essay Rubric
In writing, the key elements of an essay rubric are clear criteria, defined performance levels, and detailed descriptors for each evaluation.
- Identify a Specific Purpose and Goals: Determine main objectives of an essay’s assignment and consider what skills and knowledge you want students to demonstrate.
- List a Key Criteria: Identify essential components that need to be evaluated, such as thesis statement, introduction, content, organization, evidence and support, conclusion, grammar and mechanics, writing style and tone, and citations and references.
- Define Performance Levels: Decide on a particular scale you will use to measure performance (e.g., Excellent, Good, Fair, Poor) and ensure each level is distinct and clearly defined.
- Create Descriptors for Each Criterion: Write detailed descriptions for what constitutes each level of performance for every criterion and be specific about what is expected at each level to avoid misunderstanding.
- Assign Number Values: Determine a specific range for each criterion and performance level and allocate numbers in a way that reflects an actual importance of each criterion in an overall assessment.
- Review and Revise: Examine a complete rubric to ensure it is comprehensive and clear and adjust any descriptions or number values that seem unclear or disproportionate.
- Test a Working Essay Rubric: Apply a grading scheme to a few sample compositions to see if it effectively differentiates between different levels of performance and make adjustments as necessary.
- Involve Peers for Feedback: Share marking criteria with colleagues or peers for feedback and insights on clarity and fairness that you might have overlooked.
- Provide Examples: Include examples of complete papers or writing excerpts at each performance level and help students to understand what is expected for grading.
- Communicate With Students: Share a complete rubric with students before they begin an assignment and explain each criterion and performance level so they understand how their work will be evaluated and what they need to do to achieve highest marks.
Essay Rubric Example
Organization
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay contains stiff topic sentences and a controlled organization.
Very Good/6 points: A paper contains a logical and appropriate organization. An author uses clear topic sentences.
Average/4 points: A composition contains a logical and appropriate organization. An author uses clear topic sentences.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text has an inconsistent organization.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A complete document shows an absence of a planned organization.
Grade: ___ .
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay shows the absence of a planned organization.
Very Good/6 points: A paper contains precise and varied sentence structures and word choices.
Average/4 points: A composition follows a limited but mostly correct sentence structure. There are different sentence structures and word choices.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text contains several awkward and unclear sentences. There are some problems with word choices.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): An author does not have apparent control over sentence structures and word choice.
Excellent/8 points: An essay’s content appears sophisticated and contains well-developed ideas.
Very Good/6 points: A paper’s content appears illustrative and balanced.
Average/4 points: A composition contains unbalanced content that requires more analysis.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text contains a lot of research information without analysis or commentary.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A complete document lacks relevant content and does not fit the thesis statement. Essay rubric rules are not followed.
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay contains a clearly stated and focused thesis statement.
Very Good/6 points: A paper comprises a clearly stated argument. However, a particular focus would have been sharper.
Average/4 points: A thesis statement phrasing sounds simple and lacks complexity. An author does not word the thesis correctly.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A thesis statement requires a clear objective and does not fit the theme in a paper’s content.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A thesis statement is not evident in an introduction paragraph.
Excellent/8 points: A submitted is clear and focused. An overall work holds a reader’s attention. Besides, relevant details and quotes enrich a thesis statement.
Very Good/6 points: A paper is mostly focused and contains a few useful details and quotes.
Average/4 points: An author begins a composition by defining an assigned topic. However, a particular development of ideas appears general.
Needs Improvement/2 points: An author fails to define an assigned topic well or focuses on several issues.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A complete document lacks a clear sense of a purpose or thesis statement. Readers have to make suggestions based on sketchy or missing ideas to understand an intended meaning. Essay rubric requirements are missed.
Sentence Fluency
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay has a natural flow, rhythm, and cadence. Its sentences are well-built and have a wide-ranging and robust structure that enhances reading.
Very Good/6 points: Presented ideas mostly flow and motivate a compelling reading.
Average/4 points: A composition hums along with a balanced beat but tends to be more businesslike than musical. Besides, a particular flow of ideas tends to become more mechanical than fluid.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text appears irregular and hard to read.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): Readers have to go through a complete document several times to give this paper a fair interpretive reading.
Conventions
Excellent/8 points: An author demonstrates proper use of standard writing conventions, like spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar, usage, and paragraphing. A person also uses correct protocols in a way that improves an overall readability of an essay.
Very Good/6 points: An author demonstrates proper writing conventions and uses them correctly. One can read a paper with ease, and errors are rare. Few touch-ups can make a submitted composition ready for publishing.
Average/4 points: An author shows reasonable control over a short range of standard writing rules. A person also handles all the conventions and enhances readability. Writing errors in a presented composition tend to distract and impair legibility.
Needs Improvement/2 points: An author makes an effort to use various conventions, including spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar usage, and paragraphing. A provided text contains multiple errors.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): An author makes repetitive errors in spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar, usage, and paragraphing. Some mistakes distract readers and make it hard to understand discussed concepts. Essay rubric rules are not covered.
Presentation
Excellent/8 points: A particular form and presentation of a text enhance an overall readability of an essay and its flow of ideas.
Very Good/6 points: A chosen format has few mistakes and is easy to read.
Average/4 points: An author’s message is understandable in this format.
Needs Improvement/2 points: An author’s message is only comprehensible infrequently, and a provided text appears disorganized.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): Readers receive a distorted message due to difficulties connecting to a presentation of an entire text.
Final Grade: ___ .
Grading Scheme
- A+ = 60+ points
- F = less than 9
Differences in Education Levels
An overall quality of various types of texts changes at different education levels. In writing, an essay rubric works by providing a structured framework with specific criteria and performance levels to consistently evaluate and grade a finished paper. For instance, college students must write miscellaneous papers when compared to high school learners (Harrington et al., 2021). In this case, assessment criteria will change for these different education levels. For example, university and college compositions should have a debatable thesis statement with varying points of view (Mewburn et al., 2021). However, high school compositions should have simple phrases as thesis statements. Then, other requirements in a marking rubric will be more straightforward for high school students (DeVries, 2023). For Master’s and Ph.D. works, a writing criteria presented in a scoring evaluation should focus on examining a paper’s complexity. In turn, compositions for these two categories should have thesis statements that demonstrate a detailed analysis of defined topics that advance knowledge in a specific area of study.
Recommendations
When observing any essay rubric, people should remember to ensure clarity and specificity in each criterion and performance level. This clarity helps both an evaluator and a student to understand principal expectations and how a written document will be assessed (Ozfidan & Mitchell, 2022). Consistency in language and terminology across an essay rubric is crucial to avoid confusion and maintain fairness. Further on, it is essential to align a working scheme with learning objectives and goals of an essay’s assignment, ensuring all key components, such as thesis, content, organization, and grammar, are covered comprehensively (Stevens & Levi, 2023). Evaluators should also be aware of the weighting and scoring distribution, making sure they accurately reflect an actual importance of each criterion. Moreover, testing a rubric on sample essays before finalizing it can help to identify any mistakes or imbalances in scores. Essentially, providing concrete examples or descriptions for each performance level can guide students in understanding what is expected for each grade (Taylor et al., 2024). In turn, an essay rubric should be reviewed, revised, and updated after each educational year to remain relevant and aligned with current academic standards. Lastly, sharing and explaining grading assessment with students before they start their composition fosters transparency and helps them to put more of their efforts into meeting defined criteria, ultimately improving their writing and learning experience in general.
Common Mistakes
- Lack of Specificity: Descriptions for each criterion and performance level are too vague, leading to ambiguity and confusion for both graders and students.
- Overcomplicating a Rubric: Including too many criteria or overly complex descriptions that make a scoring assessment difficult to use effectively.
- Unbalanced Weighting: Assigning disproportionate number values to different criteria, which can mislead an overall assessment and not accurately reflect an actual importance of each component.
- Inconsistent Language: Using inconsistent terminology or descriptors across performance levels, which can confuse users and make a rubric less reliable.
- Not Aligning With Objectives: Failing to align a particular criteria and performance levels with specific goals and learning outcomes of an assignment.
- Omitting Key Components: Leaving out important criteria that are essential for evaluating a paper comprehensively, such as citations or a conclusion part.
- Lack of Examples: Not providing examples or concrete descriptions of what constitutes each performance level, making it harder for students to understand expectations.
- Ignoring Grammar and Mechanics: Overlooking an actual importance of grammar, spelling, and punctuation, which are crucial for clear and professional writing.
- Not Updating an Essay Rubric: Using outdated rubrics that do not reflect current educational standards or specific assignment needs.
- Insufficient Testing: Failing to test a grading scheme on some sample documents to ensure it effectively differentiates between levels of performance and provides fair assessments.
Essay rubrics help teachers, instructors, professors, and tutors to analyze an overall quality of compositions written by students. Basically, an assessment scheme makes an analysis process simple for lecturers, and it lists and organizes all of the criteria into one convenient paper. In other instances, students use such evaluation tools to improve their writing skills. However, they vary from one educational level to the other. Master’s and Ph.D. assessment schemes focus on examining complex thesis statements and other writing mechanics. However, high school grading criteria examine basic writing concepts. As such, the following are some of the tips that one must consider when preparing any rubric.
- Include all mechanics that relate to essay writing.
- Cover different requirements and their relevant grades.
- Follow clear and understandable statements.
DeVries, B. A. (2023). Literacy assessment and intervention for classroom teachers . Routledge.
Harrington, E. R., Lofgren, I. E., Gottschalk Druschke, C., Karraker, N. E., Reynolds, N., & McWilliams, S. R. (2021). Training graduate students in multiple genres of public and academic science writing: An assessment using an adaptable, interdisciplinary rubric. Frontiers in Environmental Science , 9 , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.715409
Mewburn, I., Firth, K., & Lehmann, S. (2021). Level up your essays: How to get better grades at university . NewSouth.
Ozfidan, B., & Mitchell, C. (2022). Assessment of students’ argumentative writing: A rubric development. Journal of Ethnic and Cultural Studies , 9 (2), 121–133. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejecs/1064
Stevens, D. D., & Levi, A. (2023). Introduction to rubrics: An assessment tool to save grading time, convey effective feedback, and promote student learning . Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group.
Taylor, B., Kisby, F., & Reedy, A. (2024). Rubrics in higher education: An exploration of undergraduate students’ understanding and perspectives. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2023.2299330
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Cite a Newspaper Article in APA 7 With Examples
- Icon Calendar 12 October 2020
- Icon Page 754 words

"Who Am I" Essay Examples & Student Guidelines
- Icon Calendar 10 October 2020
- Icon Page 5309 words
University Writing Program
- Collaborative Writing
- Writing for Metacognition
- Supporting Multilingual Writers
- Alternatives to Grading
- Making Feedback Matter
- Peer Review
- Responding to Multilingual Writers’ Texts
- Model Library
Written by Arthur Russell
Just about every discussion of rubrics begins with a caveat: writing rubrics are not a substitute for writing instruction. Rubrics are tools for communicating grading criteria and assessing student progress. Rubrics take a variety of forms, from grids to checklists , and measure a range of writing tasks, from conceptual design to sentence-level considerations.
As with any assessment tool, a rubric’s effectiveness is entirely dependent upon its design and its deployment in the classroom. Whatever form rubrics take, the criteria for assessment must be legible to all students—if students cannot decipher our rubrics, they are not useful.
When effectively integrated with writing instruction, rubrics can help instructors clarify their own expectations for written work, isolate specific elements as targets of instruction, and provide meaningful feedback and coaching to students. Well-designed rubrics will draw program learning outcomes, assignment prompts, course instruction and assessment into alignment.
Starting Points
Course rubrics vs. assignment rubrics.
Instructors may choose to use a standard rubric for evaluating all written work completed in a course. Course rubrics provide instructors and students a shared language for communicating the values and expectations of written work over the course of an entire semester. Best practices suggest that establishing grading criteria with students well in advance helps instructors compose focused, revision-oriented feedback on drafts and final papers and better coach student writers. When deploying course rubrics in writing-intensive courses, consider using them to guide peer review and self-evaluation processes with students. The more often students work with established criteria, the more likely they are to respond to and incorporate feedback in future projects.
At the same time, not every assignment needs to assess every aspect of the writing process every time. Particularly early in the semester, instructors may develop assignment-specific rubrics that target one or two standards. Prioritizing a specific learning objective or writing process in an assignment rubric allows instructors to concentrate time spent on in-class writing instruction and encourages students to develop targeted aspects of their writing processes.
Developing Evaluation Criteria
- Establish clear categories. What specific learning objectives (i.e. critical and creative thinking, inquiry and analysis) and writing processes (i.e. summary, synthesis, source analysis, argument and response) are most critical to success for each assignment?
- Establish observable and measurable criteria of success. For example, consider what counts for “clarity” in written work. For a research paper, clarity might attend to purpose: a successful paper will have a well-defined purpose (thesis, takeaway), integrate and explain evidence to support all claims, and pay careful attention to purpose, context, and audience.
- Adopt student-friendly language. When using academic terminology and discipline-specific concepts, be sure to define and discuss these concepts with students. When in doubt , VALUE rubrics are excellent models of clearly defined learning objective and distinguishing criteria.
Sticking Points: Writing Rubrics in the Disciplines
Even the most carefully planned rubrics are not self-evident. The language we have adopted for writing assessment is itself a potential obstacle to student learning and success . What we count for “clarity” or “accuracy” or “insight” in academic writing, for instance, is likely shaped by our disciplinary expectations and measured by the standards of our respective fields. What counts for “good writing” is more subjective than our rubrics may suggest. Similarly, students arrive in our courses with their own understanding and experiences of academic writing that may or may not be reflected in our assignment prompts.
Defining the terms for success with students in class and in conference will go a long way toward bridging these gaps. We might even use rubrics as conversation starters, not only as an occasion to communicate our expectations for written work, but also as an opportunity to demystify the rhetorical contexts of discipline-specific writing with students.
Helpful Resources
For a short introduction to rubric design, the Creating Rubrics guide developed by Louise Pasternack (2014) for the Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation is an excellent resource. The step-by-step tutorials developed by North Carolina State University and DePaul Teaching Commons are especially useful for instructors preparing rubrics from scratch. On the use of rubrics for writing instruction and assignments in particular, Heidi Andrade’s “Teaching with Rubrics: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly” provides an instructive overview of the benefits and drawbacks of using rubrics. For a more in-depth introduction (with sample rubrics), Melzer and Bean’s “Using Rubrics to Develop and Apply Grading Criteria” in Engaging Ideas is essential reading.
Cited and Recommended Sources
- Andrade, Heidi Goodrich. “Teaching with Rubrics: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly.” College Teaching , vol. 53, no. 1, 2005, pp. 27–30, http://www.jstor.org/stable/27559213
- Athon, Amanda. “Designing Rubrics to Foster Students’ Diverse Language Backgrounds.” Journal of Basic Writing , vol. 38, No.1, 2019, pp. 78–103, https://doi.org/10.37514/JBW-J.2019.38.1.05
- Bennett, Cary. “Assessment Rubrics: Thinking inside the Boxes.” Learning and Teaching: The International Journal of Higher Education in the Social Sciences , vol. 9, no. 1, 2016, pp. 50–72, http://www.jstor.org/stable/24718020
- Broad, Bob. What We Really Value: Beyond Rubrics in Teaching and Assessing Writing . University Press of Colorado, 2003. https://doi-org.proxy1.library.jhu.edu/10.2307/j.ctt46nxvm
- Melzer, Dan, and John C. Bean. Engaging Ideas: The Professor’s Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom . 3rd ed., Jossey-Bass, 2021 (esp. pp. 253-277), https://ebookcentral-proquest-com.proxy1.library.jhu.edu/lib/jhu/detail.action?docID=6632622
- Pasternack, Louise. “Creating Rubrics,” The Innovative Instructor Blog , Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation, Johns Hopkins University, 21 Nov. 2014.
- Reynders, G., et al. “Rubrics to assess critical thinking and information processing in undergraduate STEM courses.” International Journal of STEM Education vol. 7, no. 9, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00208-5
- Turley, Eric D., and Chris W. Gallagher. “On the ‘Uses’ of Rubrics: Reframing the Great Rubric Debate.” The English Journal , vol. 97, no. 4, 2008, pp. 87–92, http://www.jstor.org/stable/30047253
- Wiggins, Grant. “The Constant Danger of Sacrificing Validity to Reliability: Making Writing Assessment Serve Writers.” Assessing Writing , vol. 1, no. 1, 1994, pp. 129-139, https://doi.org/10.1016/1075-2935(94)90008-6
Essay Papers Writing Online
Effective essay writing rubrics to enhance students’ skills and performance.

Essay writing is a fundamental skill that students must master to succeed academically. To help students improve their writing, educators often use rubrics as a tool for assessment and feedback. An essay writing rubric is a set of criteria that outlines what is expected in a well-crafted essay, providing students with clear guidelines for success.
Effective essay writing rubrics not only evaluate the quality of the content but also assess the organization, coherence, language use, and overall structure of an essay. By using a rubric, students can better understand what aspects of their writing need improvement and how to achieve higher grades.
This article will explore the importance of essay writing rubrics in academic success and provide tips on how students can use them to enhance their writing skills. By understanding and mastering the criteria outlined in a rubric, students can not only improve their writing but also excel in their academic endeavors.
Learn the Key Elements
When it comes to effective essay writing, understanding the key elements is essential for academic success. Here are some important elements to keep in mind:
- Thesis Statement: A clear and concise thesis statement that presents the main idea of your essay.
- Structure: A well-organized structure with introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Evidence: Use relevant evidence and examples to support your arguments.
- Analysis: Analyze the evidence provided and draw conclusions based on your analysis.
- Clarity and Coherence: Ensure that your essay is clear, coherent, and easy to follow.
By mastering these key elements, you can improve your essay writing skills and achieve academic success.
Elements of Effective Essay Writing
When it comes to writing a successful essay, there are several key elements that you should keep in mind to ensure your work is of high quality. Here are some essential aspects to consider:
| A strong thesis statement is the foundation of a well-written essay. It should clearly state the main argument or position you will be defending in your writing. | |
| Your essay should have a logical flow and be well-organized. Make sure your ideas are presented in a coherent manner, with each paragraph contributing to the overall argument. | |
| Your introduction should grab the reader’s attention and provide context for your argument, while the conclusion should summarize your main points and leave a lasting impression. | |
| To support your argument, use relevant evidence and examples to back up your claims. This will make your essay more persuasive and convincing. | |
| It is important to cite your sources properly to give credit where it is due and avoid plagiarism. Make sure to follow the appropriate citation style required by your academic institution. | |
| Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and coherent. Avoid jargon and convoluted sentences, and make sure your ideas are easy to follow for the reader. |
Understand the Importance
Understanding the importance of essay writing rubrics is crucial for academic success. Rubrics provide clear criteria for evaluating and assessing essays, which helps both students and instructors. They help students understand what is expected of them, leading to more focused and organized writing. Rubrics also provide consistency in grading, ensuring that all students are evaluated fairly and objectively. By using rubrics, students can see where they excel and where they need to improve, making the feedback process more constructive and impactful.
of Clear and Concise Rubrics
One key aspect of effective essay writing rubrics is the clarity and conciseness of the criteria they outline. Clear and concise rubrics provide students with a roadmap for success and make grading more efficient for instructors. When creating rubrics, it is essential to clearly define the expectations for each aspect of the essay, including content, organization, style, and grammar.
By using language that is straightforward and easy to understand, students can easily grasp what is expected of them and how they will be evaluated. Additionally, concise rubrics avoid confusion and ambiguity, which can lead to frustration and misunderstanding among students.
Furthermore, clear and concise rubrics help instructors provide more targeted feedback to students, allowing them to focus on specific areas for improvement. This ultimately leads to better learning outcomes and helps students develop their writing skills more effectively.
Implement Structured Guidelines
Structured guidelines are essential for effective essay writing. These guidelines provide a framework for organizing your thoughts, ideas, and arguments in a logical and coherent manner. By implementing structured guidelines, you can ensure that your essay is well-organized, cohesive, and easy to follow.
One important aspect of structured guidelines is creating an outline before you start writing. An outline helps you plan the structure of your essay, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. It also helps you organize your ideas and ensure that your arguments flow logically from one point to the next.
Another important aspect of structured guidelines is using transitions to connect your ideas and arguments. Transitions help readers follow the flow of your essay and understand how one point relates to the next. They also help maintain the coherence and clarity of your writing.
Finally, structured guidelines include formatting requirements such as word count, font size, spacing, and citation style. Adhering to these formatting requirements ensures that your essay meets academic standards and is visually appealing to readers.
for Academic Excellence
When aiming for academic excellence in essay writing, it is essential to adhere to rigorous standards and criteria set by the educational institution. The use of effective essay writing rubrics can greatly enhance the quality of academic work by providing clear guidelines and criteria for assessment.
Academic excellence in essay writing involves demonstrating a deep understanding of the subject matter, presenting a well-structured argument, and showcasing critical thinking skills. Rubrics can help students focus on key elements such as thesis development, evidence analysis, organization, and clarity of expression.
By following a well-designed rubric, students can ensure that their essays meet the desired academic standards and expectations. Feedback provided based on the rubric can also help students identify areas for improvement and guide them towards achieving academic success.
| Key Elements | Criteria |
| Thesis Development | Clear thesis statement that addresses the main argument |
| Evidence Analysis | Use of relevant and credible evidence to support arguments |
| Organization | Logical flow of ideas and effective paragraph structure |
| Clarity of Expression | Clear and concise writing style with proper grammar and punctuation |
Master the Art
Mastering the art of essay writing requires dedication, practice, and attention to detail. To become a proficient essay writer, one must develop strong writing skills, a clear and logical structure, as well as an effective argumentative style. Start by understanding the purpose of your essay and conducting thorough research to gather relevant information and evidence to support your claims.
Furthermore, pay close attention to grammar, punctuation, and spelling to ensure your work is polished and professional. Use essay writing rubrics as a guide to help you stay on track and meet the necessary criteria for academic success. Practice makes perfect, so don’t be afraid to revise and edit your work to improve your writing skills even further.
By mastering the art of essay writing through consistent practice and attention to detail, you can set yourself up for academic success and develop a valuable skill that will benefit you in various aspects of your life.
of Constructing Detailed Evaluations
Constructing detailed evaluations in essay writing rubrics is essential for providing specific feedback to students. When designing a rubric, it is important to consider the criteria that will be assessed and clearly define each level of performance. This involves breaking down the evaluation criteria into smaller, measurable components, which allows for more precise and accurate assessments.
Each criterion in the rubric should have a clear description of what is expected at each level of performance, from basic to proficient to advanced. This helps students understand the expectations and enables them to self-assess their work against the rubric. Additionally, including specific examples or descriptors for each level can further clarify the expectations and provide guidance to students.
Constructing detailed evaluations also involves ensuring that the rubric aligns with the learning objectives of the assignment. By mapping the evaluation criteria to the desired learning outcomes, instructors can ensure that the rubric accurately reflects what students are expected to demonstrate in their essays. This alignment helps students see the relevance of the assessment criteria and encourages them to strive for mastery of the material.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, creating and using rubrics.
A rubric is a scoring tool that explicitly describes the instructor’s performance expectations for an assignment or piece of work. A rubric identifies:
- criteria: the aspects of performance (e.g., argument, evidence, clarity) that will be assessed
- descriptors: the characteristics associated with each dimension (e.g., argument is demonstrable and original, evidence is diverse and compelling)
- performance levels: a rating scale that identifies students’ level of mastery within each criterion
Rubrics can be used to provide feedback to students on diverse types of assignments, from papers, projects, and oral presentations to artistic performances and group projects.
Benefitting from Rubrics
- reduce the time spent grading by allowing instructors to refer to a substantive description without writing long comments
- help instructors more clearly identify strengths and weaknesses across an entire class and adjust their instruction appropriately
- help to ensure consistency across time and across graders
- reduce the uncertainty which can accompany grading
- discourage complaints about grades
- understand instructors’ expectations and standards
- use instructor feedback to improve their performance
- monitor and assess their progress as they work towards clearly indicated goals
- recognize their strengths and weaknesses and direct their efforts accordingly
Examples of Rubrics
Here we are providing a sample set of rubrics designed by faculty at Carnegie Mellon and other institutions. Although your particular field of study or type of assessment may not be represented, viewing a rubric that is designed for a similar assessment may give you ideas for the kinds of criteria, descriptions, and performance levels you use on your own rubric.
- Example 1: Philosophy Paper This rubric was designed for student papers in a range of courses in philosophy (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Psychology Assignment Short, concept application homework assignment in cognitive psychology (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 3: Anthropology Writing Assignments This rubric was designed for a series of short writing assignments in anthropology (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 4: History Research Paper . This rubric was designed for essays and research papers in history (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 1: Capstone Project in Design This rubric describes the components and standards of performance from the research phase to the final presentation for a senior capstone project in design (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Engineering Design Project This rubric describes performance standards for three aspects of a team project: research and design, communication, and team work.
Oral Presentations
- Example 1: Oral Exam This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing performance on an oral exam in an upper-division course in history (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Oral Communication This rubric is adapted from Huba and Freed, 2000.
- Example 3: Group Presentations This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing group presentations in history (Carnegie Mellon).
Class Participation/Contributions
- Example 1: Discussion Class This rubric assesses the quality of student contributions to class discussions. This is appropriate for an undergraduate-level course (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Advanced Seminar This rubric is designed for assessing discussion performance in an advanced undergraduate or graduate seminar.
See also " Examples and Tools " section of this site for more rubrics.
CONTACT US to talk with an Eberly colleague in person!
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links

Creating Effective Rubrics: Examples and Best Practices
- Classroom Activities/Strategies/Guides
Rubrics are an essential component of assessing student learning effectively. A rubric is a scoring guide that clearly defines the expectations for student performance on a particular task or assignment. Teachers can use rubrics to both evaluate a student’s performance level and to provide feedback to that student. Because they provide a standardized way to assess learning, rubrics help to ensure grading is fair and consistent across all students.
It is important that rubrics are a clear, consistent evaluation of a student’s work. This can sometimes be hard to achieve because rubrics have the potential to become cumbersome and confusing. The best rubrics will typically include specific criteria relevant to the task or assignment at hand, as well as a set of descriptors that outline the different levels of performance that learners may achieve.
There are many different types and uses of rubrics, as well as many benefits of using rubrics. Therefore, learning how to create effective rubrics and the best practices for using rubrics is important for all educators to know. Some may think rubrics are only used in upper-level grades or only for essay assignments, but rubrics can be a beneficial tool for many different subjects and grade levels. All teachable content has learning goals and outcomes, and therefore all content can benefit from the use of good-quality rubrics.
Types of Rubrics
There are three main types of rubrics that are typically used in the education realm: analytic, holistic, and developmental. These three rubrics all pair differently with certain tasks or assignments, depending on the learning goals and desired outcomes for the assignment. While each have their advantages and disadvantages, they all have an appropriate place in a teacher’s assessment toolbox.
Analytic Rubric
Analytic rubrics focus on breaking down the work into specific components or criteria and then evaluating each of those components separately. Each individual component is usually scored on a separate scale, allowing for more detailed feedback on the strengths and weaknesses of the performance. Analytic rubrics are useful when there is a specific focus on particular skills or knowledge students are expected to demonstrate. Analytic rubrics are very specific and detailed, and for that reason, they can sometimes be seen as more complicated or complex to use.
Analytic rubrics are sometimes viewed as the most reliable assessment rubric because they tend to be more precise assessments and offer more specific and detailed feedback to students. Because of this, these rubrics are often better able to align with learning objects, which can promote deeper learning. Teachers who are using more targeted instruction will benefit from using a more targeted assessment.
Below, Jennifer Gonzalez of Cult of Pedagogy offers a playful example of rubrics assessing breakfast in bed:
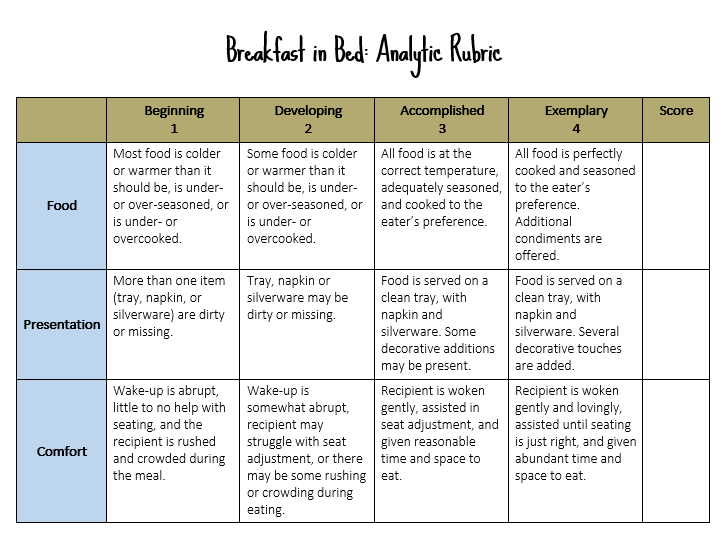
Holistic Rubric
Holistic rubrics provide a broader overall assessment of the quality of student work. They typically use a single scale to evaluate the work, ranging simply from one to five or from excellent to poor. Holistic rubrics are useful when the focus is on the overall quality of the work rather than on smaller, more specific components of the work.
Holistic rubrics can be used at any point in any subject when there is a task or assignment being assessed as a whole. For example, art classes often use a holistic grading rubric to assess broad categories such as creativity or composition. Whereas an English class may use a more analytical rubric for writing, a history class may use a holistic rubric when grading an essay for the overall success of argumentation, evidence, and organization. Holistic rubrics are often used with projects in many classes to evaluate the quality of the project on an overall scale from weak to exemplary.
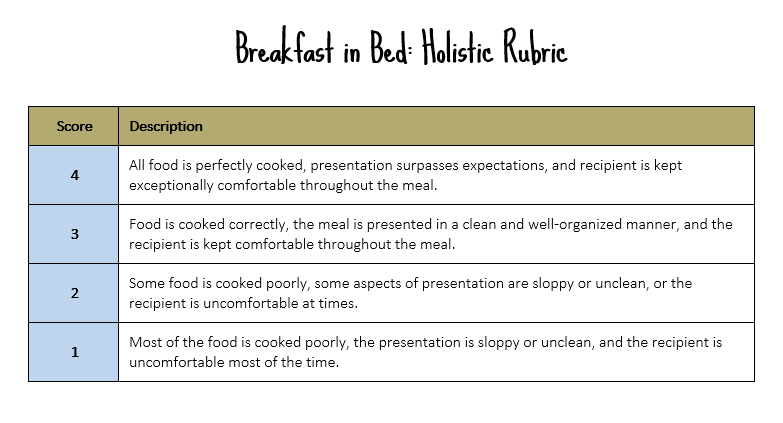
Developmental Rubric
Finally, developmental rubrics are used to assess a student’s progress or development over time. They are typically used in subjects like writing or language development, where progress is more gradual. Developmental rubrics are great for courses or assessments that require multiple assessments over a longer period of time. Within a developmental rubric, there are multiple levels of performance that show progress made from one level to the next over time.
Because developmental rubrics are focused on growth and development, they are often best used in courses to judge progress that has been made over a length of the course. For example, English classes may assess someone’s writing growth with a developmental rubric that ranges from weak to exemplary. Math classes may assess progress on categories such as problem-solving or mathematical reasoning with a rubric including emerging, developing, and proficient levels. Likewise, art classes may track progressions of creativity and technique with descriptors like beginner, intermediate, or advanced. As a student’s knowledge and skills develop over time, teachers will see a progression in learning and mastery of those concepts.
How to Design a Rubric
While each type of rubric may have its own step in how to design it, the overall process of designing a rubric should follow a standard pattern of steps. Writing a strong rubric takes time and attention to detail, but the outcome produces a more effective rubric that will offer more benefits to students and the teacher.
Plan your purpose and pick a rubric style . First, teachers must decide what they want to teach, what they want to assess, and then how they are going to assess it. Teachers must think all the way to the end even at the very beginning. This may determine what type of rubric will be designed.
Align the rubric with the task or assignment . Once a certain rubric has been chosen, teachers must identify the learning objectives of the assessment and determine the skills and knowledge the students need to demonstrate. If a teacher does not properly align the assessment with the assignment, then they are seemingly setting students up for failure.
Write clear and concise criteria and levels of performance . Long and wordy does not always mean detailed or superior. Sometimes the lengthy and complex rubrics may seem detailed, but instead overwhelm or confuse students. Teachers must develop the criteria and descriptors for each criterion, but doing so in a clear and concise way will help students better understand what is expected of them.
Provide specific and actionable feedback to students . Remember that rubrics and assessments are ultimately meant to be used as a tool for supporting student learning and growth. Therefore, rubrics should be used as a stepping stone, not an end point. Students should be able to do something with the feedback that has been presented to them on a rubric.
Reflect on what worked and be willing to revise . The first rubric designed for an assessment may not always be the final rubric used. Sometimes rubrics need edits or changes along the way, and it is better for the teacher to accept responsibility for those adjustments rather than risk inaccurately assessing students based on a poorly constructed rubric.
Online resources for rubrics are very common and range from simple rubric examples , to common core-aligned rubrics , to college university recommended rubrics. For example, NC State University offers best rubric practices and examples, including this example of a holistic rubric for a final paper:
: The audience is able to easily identify the focus of the work and is engaged by its clear focus and relevant details. Information is presented logically and naturally. There are no more than two mechanical errors or misspelled words to distract the reader. The audience is easily able to identify the focus of the student work, which is supported by relevant ideas and supporting details. Information is presented in a logical manner that is easily followed. There is minimal interruption to the work due to misspellings and/or mechanical errors. : The audience can identify the central purpose of the student work, and supporting ideas are present and clear. The information is presented in an orderly fashion that can be followed with little difficulty. There are some misspellings or mechanical errors, but they do not distract from the work. : The audience cannot clearly or easily identify the central ideas or purpose of the student work. Information is presented in a disorganized fashion, causing the audience to have difficulty following the author’s ideas. There are many misspellings and/or mechanical errors that negatively affect the audience’s ability to read the work. |
Within the last few years, the College Board switched its AP English Language and Composition rubric from a holistic grading scale of zero to nine to using an analytic rubric, which evaluates student performance based on three main scoring categories.
Using Rubrics for Assessment
To use rubrics to facilitate fair, efficient, and effective assessment of student work, there are several things to consider when implementing the rubrics. These include the purpose of the rubric, the placement within the lesson plan, and the people using the rubric.
First, one must consider what the intended purpose of the rubric is within the assessment. For example, rubrics can be used in different types of assessments, such as formative or summative. Both types of assessments are valuable for different reasons, and therefore rubrics should be used in both scenarios.
Another thing to consider when using rubrics is the placement of the rubric within the lesson plan. Providing the rubric at the beginning of a task or assessment can allow students to clearly see the requirements and expectations. Using a rubric in the middle of an assignment can provide more specific and actionable feedback for students before completing a project. Then, of course, using the rubric at the end of a lesson plan is where final and more formal assessment and reflection can take place.
Finally, teachers are not the only ones who can fill out and “assess” using a rubric. Allowing students to use rubrics for self-assessment and peer assessment teaches them vital skills of how to self-evaluate their work as well as how to offer constructive criticism and compliments to others.
It is important that once a rubric has been used for assessment, the data generated be evaluated, processed, and used for future assignments. Because rubrics allow teachers to assess with fairness and objectivity, the results of rubrics offer teachers and students valuable feedback for teaching and learning.
Best Practices for Creating Effective Rubrics
Whether you are providing detailed feedback to a student on their essay, observing that a student needs improvement on a certain math skill, or assessing the overall quality of someone’s artwork, rubrics used effectively lead to less teacher stress and more student success. Creating clear, reliable, and valid rubrics might seem like a massive undertaking, but with a few simple steps and a few key strategies, rubrics can revolutionize a classroom .
Use clear and concise language . Students often struggle with heavy academic language, so providing clear instructions and understandable language can help students go into a task or assignment knowing exactly what is expected of them. This includes writing clear and concise criteria and levels of performance.
Know when to use what . Use different types of rubrics for different tasks or assignments. A teacher who uses a variety of assessments is a teacher who understands different students learn in different ways. Rubrics are not “one size fits all,” so know when to use different resources. The rubric must align with the task or assignment to be effective for both teachers and students.
Provide actionable feedback . A painful moment for a teacher is when a student looks at the number or letter at the top of a grade sheet, ignores the heartfelt feedback written on the page, and immediately tosses it into the trash can. Teachers can avoid this scenario by providing specific action steps for students to take once they have received their feedback.
Some of the common misconceptions when it comes to creating and using effective rubrics are that 1) any rubric will work for anything and that 2) rubrics are too hard to make. These two misconceptions lead people to the common mistake of taking to the Internet and downloading a rubric that looks like a good fit.
It is important to avoid these when creating rubrics because the reality is that not all rubrics will work for all assignments, but it is also not impossible to quickly and effectively create a rubric that is perfect for your specific needs. If using a rubric from another source, you must ensure the reliability and validity of the rubric. One might be better off creating a simple holistic rubric than using a detailed analytic rubric that needs a lot of checking or editing to fit your assignment.
Conclusion: The Importance of Rubrics in Education
Rubrics are an important assessment tool for evaluating student learning and provide a consistent, fair, and clear way to assess student work. While there are a number of different rubric resources available online, rubrics are also fairly easy for educators to create and personalize to their specific needs. Creating rubrics is an ongoing process, which means it is important to continually review and revise rubrics to ensure they are still meeting the needs of the students. Just as students need to make adjustments in their learning, teachers may also need to make adjustments from time to time in their assessments.
Subscribe to EDVIEW360 to gain access to podcast episodes, webinars and blog posts where top education thought leaders discuss hot topics in the industry.

COMMENTS
Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates. A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects ...
Essay Rubric Directions: Your essay will be graded based on this rubric. Consequently, use this rubric as a guide when writing your essay and check it again before you submit your essay. Traits 4 3 2 1 Focus & Details There is one clear, well-focused topic. Main ideas are clear and are well supported by detailed and accurate information.
Examples of Writing Rubrics. Here are some examples of writing rubrics. Narrative Writing Rubric. Criteria 4 (Excellent) 3 (Good) 2 (Fair) 1 (Poor) Story Elements: ... For example, for a narrative essay, criteria might include plot development, character depth, and use of descriptive language.
Try this rubric to make student expectations clear and end-of-project assessment easier. Learn more: Free Technology for Teachers. 100-Point Essay Rubric. Need an easy way to convert a scoring rubric to a letter grade? This example for essay writing earns students a final score out of 100 points. Learn more: Learn for Your Life. Drama ...
Graded rubrics are also a great map for the revision process and can show you where your strengths and weaknesses lie in writing. Studying rubrics can even make you a stronger writer. By considering the qualities that make up a strong essay, you can work to master the different areas and continually improve your writing. Essay rubric example
An essay rubric refers to a way for teachers to assess students' composition writing skills and abilities. Basically, an evaluation scheme provides specific criteria to grade assignments. Moreover, the three basic elements of an essay rubric are criteria, performance levels, and descriptors. In this case, teachers use assessment guidelines to ...
An essay rubric is a way teachers assess students' essay writing by using specific criteria to grade assignments. Essay rubrics save teachers time because all of the criteria are listed and organized into one convenient paper. If used effectively, rubrics can help improve students' writing. Below are two types of rubrics for essays.
Students can self-assess using the rubric as a checklist before. submitting their assignment. This sample rubric can also be found under the Turnitin tool in. Edit the assignment requirements column, performance level descriptions in each box, and. point values to align with a particular course assignment. Distribute the rubric to students.
Grading rubrics can be of great benefit to both you and your students. For you, a rubric saves time and decreases subjectivity. Specific criteria are explicitly stated, facilitating the grading process and increasing your objectivity. For students, the use of grading rubrics helps them to meet or exceed expectations, to view the grading process ...
Essay Writing Rubrics. Here are some essay writing rubrics to help you get started grading your students' essays. You will probably have to customize these rubrics to meet your goals and standards, but these should give you a decent place to start. Persuasive Essay Rubric 1 - This rubric mainly covers the structure of the essay: attention ...
Rubrics are tools for communicating grading criteria and assessing student progress. Rubrics take a variety of forms, from grids to checklists, and measure a range of writing tasks, from conceptual design to sentence-level considerations. As with any assessment tool, a rubric's effectiveness is entirely dependent upon its design and its ...
Demonstrates little understanding of author's voice. 24 points. Mechanics (20 points) Essay is written in complete sentences. Includes a clear beginning, middle, and end. All grammar, usage, punctuation, and spelling are correct. Essay is easy to follow; all details and examples are vivid and relevant to the topic.
Logical, compelling progression of ideas in essay;clear structure which enhances and showcases the central idea or theme and moves the reader through the text. Organization flows so smoothly the reader hardly thinks about it. Effective, mature, graceful transitions exist throughout the essay.
For example, an instructor may choose to give 30 points for an essay whose ideas are sufficiently complex, that marshals good reasons in support of a thesis, and whose argument is logical; and 20 points for well-constructed sentences and careful copy editing. ... For example, a partial analytic rubric for a single trait, "addresses a ...
Generic Rubric for Practice. The essay is unclear with no organization. The main points of the essay are ambiguous. Writing has minimal organization and a basic thesis statement. Writing follows a logical organization, but sometimes drifts from the thesis. Writing is clear, logical, and very organized around a developed thesis.
Most rubrics aren't exhaustive—see the note above on rubrics that are "too specific"—and a great way to see how different graders are handling "real-life" scenarios for an assignment is to have the entire team grade a few samples (including examples that seem more representative of an "A" or a "B") and compare everyone's ...
Evidence: Use relevant evidence and examples to support your arguments. Analysis: Analyze the evidence provided and draw conclusions based on your analysis. Clarity and Coherence: Ensure that your essay is clear, coherent, and easy to follow. By mastering these key elements, you can improve your essay writing skills and achieve academic success.
Holistic scoring is a quick method of evaluating a composition based on the reader's general impression of the overall quality of the writing—you can generally read a student's composition and assign a score to it in two or three minutes. Holistic scoring is usually based on a scale of 0-4, 0-5, or 0-6.
This rubric was designed for essays and research papers in history (Carnegie Mellon). Projects. Example 1: Capstone Project in Design This rubric describes the components and standards of performance from the research phase to the final presentation for a senior capstone project in design (Carnegie Mellon).
For example, art classes often use a holistic grading rubric to assess broad categories such as creativity or composition. Whereas an English class may use a more analytical rubric for writing, a history class may use a holistic rubric when grading an essay for the overall success of argumentation, evidence, and organization.
BASIC RUBRIC FOR ASSESSMENT OF ESSAYS ABOUT LITERATURE CRITERIA LEVELS OF MASTERY. Most paragraphs clearly relevant, supporting and explaining thesis. Essay reads coherently and all points are made according to a defined pattern. Paragraphs exceptionally well ordered to provide strong flow and synthesis of individual points.
This is a grading rubric an instructor uses to assess students' work on this type of. assignment. It is a sample rubric that needs to be edited to reflect the specifics of a. particular assignment. Students can self-assess using the rubric as a checklist before. submitting their assignment. This sample rubric can also be found under the ...