University Writing Program
- Peer Review
- Collaborative Writing
- Writing for Metacognition
- Supporting Multilingual Writers
- Alternatives to Grading
- Making Feedback Matter
- Responding to Multilingual Writers’ Texts
- Model Library
Written by Rebecca Wilbanks
Peer review is a workhorse of the writing classroom, for good reason. Students receive feedback from each other without the need for the instructor to comment on every submission. In commenting on each other’s work, they develop critical judgment that they can bring to bear on their own writing. Working peer review into the schedule requires students to complete a draft ahead of the final deadline and sets the expectation that they will revise. Students benefit from seeing how others executed similar writing tasks. Finally, the skills that students practice during peer review—soliciting, providing, receiving, and responding to feedback—are essential to success in both scholarly and professional contexts.
While students often report that they found peer review to be valuable, students and faculty sometimes worry that peer feedback may be inaccurate or unhelpful. These concerns are valid: for peer review to be successful, students must receive clear instructions about what aspects of the text to focus on and training in how to formulate responses to peer drafts. The class must develop a shared sense of standards and a language to articulate them. The good news is that when peer review is supported in these ways, substantial evidence supports peer review’s benefits. With appropriate preparation, Melzer and Bean report that three or more students collectively produce feedback analogous to that of an instructor. Some classes even use a rigorous peer review system to generate grades for assignments .
It’s best to put the guidelines for your peer review in writing. These guidelines could take the form of a set of questions for students to respond to, a rubric to fill out (usually the same rubric that will be used to grade the assignment), or instructions for writing a response letter to the writer. Students will also benefit from seeing examples of helpful (and less helpful) feedback comments. You can use these sample comments to push students to provide greater specificity in their feedback (Less helpful: “Nice work. You did a really good job on this assignment.” More helpful: “I really like how you responded to the claims of Author X.”)

What to Ask of Student Reviewers
As you design the peer review, consider how you will balance these different options:
- Asking students to identify elements in the text. This approach allows students to check that expected elements of the text are present and legible to the audience. E.g.: Highlight the sentence(s) where the author states their thesis; or, identify the part of the text where the author explains the significance of their findings. In doing so, students practice recognizing the expected components of the genre they are working in, the different forms these components may take, and they help each other spot when a component is missing or underdeveloped.
- Asking students to record their reactions as a reader. This option harnesses the power of peer review to provide a real audience. Here are some examples of reader-response comments: “Oh, now I see why you brought up [x]; it seems like your point is [y]”; “I’m having trouble with this sentence; I had to go back and read it a couple times”; “I understand this paragraph to be saying [x]…”; “This is a really neat point; I hadn’t thought of making that connection before.” This approach is based on the idea that understanding how one’s writing is coming across to readers and making changes accordingly is an essential part of the revision process.
- Asking students to make judgments and/ or give advice. Students may evaluate the work with a rubric or be asked to summarize what is working well and what the student should prioritize for revision. This approach requires more training and practice with models to ensure that students and faculty have a shared understanding of how to apply the assessment criteria, and will be more successful as students gain more exposure to the genre they are working in. In these peer review guidelines from an upper-level writing course, you can see how I incorporated identification, reader-response, and evaluation.
How to Structure a Peer Review Session
- A workshop with the entire class or section. In this case, everyone reads and comments on the same draft(s), often ahead of time. This format allows the instructor to guide the conversation and may be particularly helpful at the beginning of the semester. You may use the workshop format to review a sample assignment from a previous semester as practice before students review each other’s work.
- As an alternative to having each student read and comment on each draft individually, Melzer and Bean suggest having groups exchange papers with other groups, and collaboratively write responses to each paper.
- Asynchronous and online. By using the peer review function on Canvas, or online platforms such as Peerceptiv, CPR, or Eli review, instructors can assign peer review as a homework assignment and avoid taking up class time. Applications designed expressly for peer review include features that encourage high quality review; for example, CPR requires students to pass a “calibration test” (in which they give feedback on models that have already been graded by the instructor), while Peerceptiv allows students to rate the quality of peer reviews during the revision process in an anonymous system that awards points for helpful feedback.
How to Get the Most out of Peer Review
Here are a few other suggestions to make peer review as effective as possible:
- Give students feedback on their feedback. If students are working in class, you can circulate through the different groups, reinforce insightful comments, and ask follow-up questions to get them to add depth or consider new aspects. You can also spot-check peer reviews and highlight examples of good feedback or ways to improve comments in class. Finally, you might ask students what feedback was most helpful during the revision process and recognize reviewers who do especially good work.
- Be aware that some students may put their energy into editing the paper, focusing on grammar and sentence structure rather than higher-level issues. This is especially likely when English is not the first language of the author being reviewed. Make sure to emphasize that the goal of peer review is to focus on higher-level concerns, and recurring issues of expression that affect readability—not to line-edit. The Sweetland Center for Writing at the University of Michigan has guidelines and evaluation criteria for peer reviews tailored for situations involving multilingual students.
- To encourage students to make use of the feedback, consider giving students time in class after the peer review to start working on their revisions or make notes about how they will begin.
Cited and Recommended Sources
- Corbett, Steven J., et al., editors. Peer Pressure, Peer Power: Theory and Practice in Peer Review and Response for the Writing Classroom . First edition, Fountainhead Press, 2014.
- Corbett, Steven J., and Michelle LaFrance, editors. Student Peer Review and Response: A Critical Sourcebook . Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2018.
- Double, Kit S., et al. “The Impact of Peer Assessment on Academic Performance: A Meta-Analysis of Control Group Studies.” Educational Psychology Review , vol. 32, no. 2, June 2020, pp. 481–509. Springer Link , https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-019-09510-3 .
- Huisman, Bart, et al. “Peer Feedback on Academic Writing: Undergraduate Students’ Peer Feedback Role, Peer Feedback Perceptions and Essay Performance.” Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , vol. 43, no. 6, Aug. 2018, pp. 955–68. Taylor and Francis+NEJM , https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2018.1424318 .
- Lundstrom, Kristi, and Wendy Baker. “To Give Is Better than to Receive: The Benefits of Peer Review to the Reviewer’s Own Writing.” Journal of Second Language Writing , vol. 18, no. 1, Mar. 2009, pp. 30–43. ScienceDirect , https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2008.06.002 .
- Melzer, Dan, and John C. Bean. Engaging Ideas: The Professor’s Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom . 3rd ed., Jossey-Bass, 2021, https://www.amazon.com/Engaging-Ideas-Professors-Integrating-Classroom/dp/1119705401 .
- Price, Edward, et al. “Validity of Peer Grading Using Calibrated Peer Review in a Guided-Inquiry, Conceptual Physics Course.” Physical Review Physics Education Research , vol. 12, no. 2, Dec. 2016, p. 020145. APS , https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevPhysEducRes.12.020145 .
- Rahimi, Mohammad. “Is Training Student Reviewers Worth Its While? A Study of How Training Influences the Quality of Students’ Feedback and Writing.” Language Teaching Research , vol. 17, no. 1, Jan. 2013, pp. 67–89. SAGE Journals , https://doi.org/10.1177/1362168812459151 .
- Using Peer Review to Improve Student Writing. University of Michigan Sweetland Center for Writing. Accessed 15 Jan. 2023.
- van den Berg, Ineke, et al. “Designing Student Peer Assessment in Higher Education: Analysis of Written and Oral Peer Feedback.” Teaching in Higher Education , vol. 11, no. 2, Apr. 2006, pp. 135–47. srhe.tandfonline.com (Atypon) , https://doi.org/10.1080/13562510500527685 .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Peer Review? | Types & Examples
What Is Peer Review? | Types & Examples
Published on December 17, 2021 by Tegan George . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Peer review, sometimes referred to as refereeing , is the process of evaluating submissions to an academic journal. Using strict criteria, a panel of reviewers in the same subject area decides whether to accept each submission for publication.
Peer-reviewed articles are considered a highly credible source due to the stringent process they go through before publication.
There are various types of peer review. The main difference between them is to what extent the authors, reviewers, and editors know each other’s identities. The most common types are:
- Single-blind review
- Double-blind review
- Triple-blind review
Collaborative review
Open review.
Relatedly, peer assessment is a process where your peers provide you with feedback on something you’ve written, based on a set of criteria or benchmarks from an instructor. They then give constructive feedback, compliments, or guidance to help you improve your draft.
Table of contents
What is the purpose of peer review, types of peer review, the peer review process, providing feedback to your peers, peer review example, advantages of peer review, criticisms of peer review, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about peer reviews.
Many academic fields use peer review, largely to determine whether a manuscript is suitable for publication. Peer review enhances the credibility of the manuscript. For this reason, academic journals are among the most credible sources you can refer to.
However, peer review is also common in non-academic settings. The United Nations, the European Union, and many individual nations use peer review to evaluate grant applications. It is also widely used in medical and health-related fields as a teaching or quality-of-care measure.
Peer assessment is often used in the classroom as a pedagogical tool. Both receiving feedback and providing it are thought to enhance the learning process, helping students think critically and collaboratively.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Depending on the journal, there are several types of peer review.
Single-blind peer review
The most common type of peer review is single-blind (or single anonymized) review . Here, the names of the reviewers are not known by the author.
While this gives the reviewers the ability to give feedback without the possibility of interference from the author, there has been substantial criticism of this method in the last few years. Many argue that single-blind reviewing can lead to poaching or intellectual theft or that anonymized comments cause reviewers to be too harsh.
Double-blind peer review
In double-blind (or double anonymized) review , both the author and the reviewers are anonymous.
Arguments for double-blind review highlight that this mitigates any risk of prejudice on the side of the reviewer, while protecting the nature of the process. In theory, it also leads to manuscripts being published on merit rather than on the reputation of the author.
Triple-blind peer review
While triple-blind (or triple anonymized) review —where the identities of the author, reviewers, and editors are all anonymized—does exist, it is difficult to carry out in practice.
Proponents of adopting triple-blind review for journal submissions argue that it minimizes potential conflicts of interest and biases. However, ensuring anonymity is logistically challenging, and current editing software is not always able to fully anonymize everyone involved in the process.
In collaborative review , authors and reviewers interact with each other directly throughout the process. However, the identity of the reviewer is not known to the author. This gives all parties the opportunity to resolve any inconsistencies or contradictions in real time, and provides them a rich forum for discussion. It can mitigate the need for multiple rounds of editing and minimize back-and-forth.
Collaborative review can be time- and resource-intensive for the journal, however. For these collaborations to occur, there has to be a set system in place, often a technological platform, with staff monitoring and fixing any bugs or glitches.
Lastly, in open review , all parties know each other’s identities throughout the process. Often, open review can also include feedback from a larger audience, such as an online forum, or reviewer feedback included as part of the final published product.
While many argue that greater transparency prevents plagiarism or unnecessary harshness, there is also concern about the quality of future scholarship if reviewers feel they have to censor their comments.
In general, the peer review process includes the following steps:
- First, the author submits the manuscript to the editor.
- Reject the manuscript and send it back to the author, or
- Send it onward to the selected peer reviewer(s)
- Next, the peer review process occurs. The reviewer provides feedback, addressing any major or minor issues with the manuscript, and gives their advice regarding what edits should be made.
- Lastly, the edited manuscript is sent back to the author. They input the edits and resubmit it to the editor for publication.
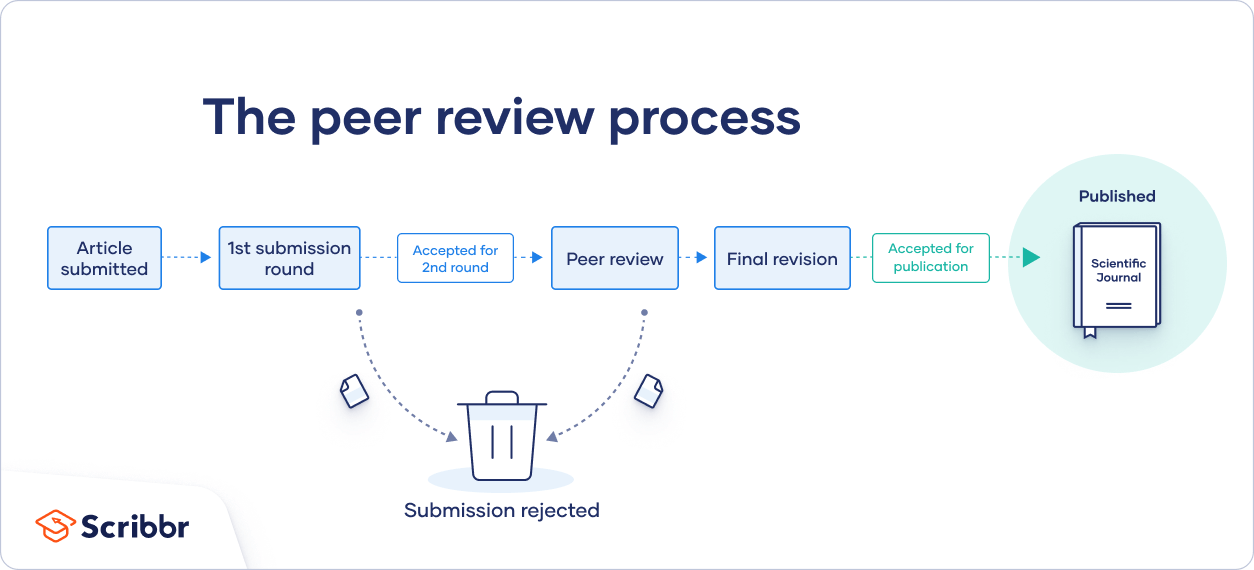
In an effort to be transparent, many journals are now disclosing who reviewed each article in the published product. There are also increasing opportunities for collaboration and feedback, with some journals allowing open communication between reviewers and authors.
It can seem daunting at first to conduct a peer review or peer assessment. If you’re not sure where to start, there are several best practices you can use.
Summarize the argument in your own words
Summarizing the main argument helps the author see how their argument is interpreted by readers, and gives you a jumping-off point for providing feedback. If you’re having trouble doing this, it’s a sign that the argument needs to be clearer, more concise, or worded differently.
If the author sees that you’ve interpreted their argument differently than they intended, they have an opportunity to address any misunderstandings when they get the manuscript back.
Separate your feedback into major and minor issues
It can be challenging to keep feedback organized. One strategy is to start out with any major issues and then flow into the more minor points. It’s often helpful to keep your feedback in a numbered list, so the author has concrete points to refer back to.
Major issues typically consist of any problems with the style, flow, or key points of the manuscript. Minor issues include spelling errors, citation errors, or other smaller, easy-to-apply feedback.
Tip: Try not to focus too much on the minor issues. If the manuscript has a lot of typos, consider making a note that the author should address spelling and grammar issues, rather than going through and fixing each one.
The best feedback you can provide is anything that helps them strengthen their argument or resolve major stylistic issues.
Give the type of feedback that you would like to receive
No one likes being criticized, and it can be difficult to give honest feedback without sounding overly harsh or critical. One strategy you can use here is the “compliment sandwich,” where you “sandwich” your constructive criticism between two compliments.
Be sure you are giving concrete, actionable feedback that will help the author submit a successful final draft. While you shouldn’t tell them exactly what they should do, your feedback should help them resolve any issues they may have overlooked.
As a rule of thumb, your feedback should be:
- Easy to understand
- Constructive
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Below is a brief annotated research example. You can view examples of peer feedback by hovering over the highlighted sections.
Influence of phone use on sleep
Studies show that teens from the US are getting less sleep than they were a decade ago (Johnson, 2019) . On average, teens only slept for 6 hours a night in 2021, compared to 8 hours a night in 2011. Johnson mentions several potential causes, such as increased anxiety, changed diets, and increased phone use.
The current study focuses on the effect phone use before bedtime has on the number of hours of sleep teens are getting.
For this study, a sample of 300 teens was recruited using social media, such as Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat. The first week, all teens were allowed to use their phone the way they normally would, in order to obtain a baseline.
The sample was then divided into 3 groups:
- Group 1 was not allowed to use their phone before bedtime.
- Group 2 used their phone for 1 hour before bedtime.
- Group 3 used their phone for 3 hours before bedtime.
All participants were asked to go to sleep around 10 p.m. to control for variation in bedtime . In the morning, their Fitbit showed the number of hours they’d slept. They kept track of these numbers themselves for 1 week.
Two independent t tests were used in order to compare Group 1 and Group 2, and Group 1 and Group 3. The first t test showed no significant difference ( p > .05) between the number of hours for Group 1 ( M = 7.8, SD = 0.6) and Group 2 ( M = 7.0, SD = 0.8). The second t test showed a significant difference ( p < .01) between the average difference for Group 1 ( M = 7.8, SD = 0.6) and Group 3 ( M = 6.1, SD = 1.5).
This shows that teens sleep fewer hours a night if they use their phone for over an hour before bedtime, compared to teens who use their phone for 0 to 1 hours.
Peer review is an established and hallowed process in academia, dating back hundreds of years. It provides various fields of study with metrics, expectations, and guidance to ensure published work is consistent with predetermined standards.
- Protects the quality of published research
Peer review can stop obviously problematic, falsified, or otherwise untrustworthy research from being published. Any content that raises red flags for reviewers can be closely examined in the review stage, preventing plagiarized or duplicated research from being published.
- Gives you access to feedback from experts in your field
Peer review represents an excellent opportunity to get feedback from renowned experts in your field and to improve your writing through their feedback and guidance. Experts with knowledge about your subject matter can give you feedback on both style and content, and they may also suggest avenues for further research that you hadn’t yet considered.
- Helps you identify any weaknesses in your argument
Peer review acts as a first defense, helping you ensure your argument is clear and that there are no gaps, vague terms, or unanswered questions for readers who weren’t involved in the research process. This way, you’ll end up with a more robust, more cohesive article.
While peer review is a widely accepted metric for credibility, it’s not without its drawbacks.
- Reviewer bias
The more transparent double-blind system is not yet very common, which can lead to bias in reviewing. A common criticism is that an excellent paper by a new researcher may be declined, while an objectively lower-quality submission by an established researcher would be accepted.
- Delays in publication
The thoroughness of the peer review process can lead to significant delays in publishing time. Research that was current at the time of submission may not be as current by the time it’s published. There is also high risk of publication bias , where journals are more likely to publish studies with positive findings than studies with negative findings.
- Risk of human error
By its very nature, peer review carries a risk of human error. In particular, falsification often cannot be detected, given that reviewers would have to replicate entire experiments to ensure the validity of results.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Thematic analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Cohort study
- Ethnography
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Conformity bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Availability heuristic
- Attrition bias
- Social desirability bias
Peer review is a process of evaluating submissions to an academic journal. Utilizing rigorous criteria, a panel of reviewers in the same subject area decide whether to accept each submission for publication. For this reason, academic journals are often considered among the most credible sources you can use in a research project– provided that the journal itself is trustworthy and well-regarded.
In general, the peer review process follows the following steps:
- Reject the manuscript and send it back to author, or
- Send it onward to the selected peer reviewer(s)
- Next, the peer review process occurs. The reviewer provides feedback, addressing any major or minor issues with the manuscript, and gives their advice regarding what edits should be made.
- Lastly, the edited manuscript is sent back to the author. They input the edits, and resubmit it to the editor for publication.
Peer review can stop obviously problematic, falsified, or otherwise untrustworthy research from being published. It also represents an excellent opportunity to get feedback from renowned experts in your field. It acts as a first defense, helping you ensure your argument is clear and that there are no gaps, vague terms, or unanswered questions for readers who weren’t involved in the research process.
Peer-reviewed articles are considered a highly credible source due to this stringent process they go through before publication.
Many academic fields use peer review , largely to determine whether a manuscript is suitable for publication. Peer review enhances the credibility of the published manuscript.
However, peer review is also common in non-academic settings. The United Nations, the European Union, and many individual nations use peer review to evaluate grant applications. It is also widely used in medical and health-related fields as a teaching or quality-of-care measure.
A credible source should pass the CRAAP test and follow these guidelines:
- The information should be up to date and current.
- The author and publication should be a trusted authority on the subject you are researching.
- The sources the author cited should be easy to find, clear, and unbiased.
- For a web source, the URL and layout should signify that it is trustworthy.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, June 22). What Is Peer Review? | Types & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 30, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/peer-review/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what are credible sources & how to spot them | examples, ethical considerations in research | types & examples, applying the craap test & evaluating sources, what is your plagiarism score.
- Peer Review Checklist
Each essay is made up of multiple parts. In order to have a strong essay each part must be logical and effective. In many cases essays will be written with a strong thesis, but the rest of the paper will be lacking; making the paper ineffective. An essay is only as strong as its weakest point.

Using a checklist to complete your review will allow you to rate each of the parts in the paper according to their strength. There are many different peer review checklists, but the one below should be helpful for your assignment.
- Is the thesis clear?
- Does the author use his or her own ideas in the thesis and argument?
- Is the significance of the problem in the paper explained? Is the significance compelling?
- Are the ideas developed logically and thoroughly?
- Does the author use ethos effectively?
- Does the author use pathos effectively?
- Are different viewpoints acknowledged?
- Are objections effectively handled?
- Does the author give adequate explanations about sources used?
- Are the sources well-integrated into the paper, or do they seem to be added in just for the sake of adding sources?
- Is the word choice specific, concrete and interesting?
- Are the sentences clear?
- Is the overall organization of the argument effective?
- Are the transitions between paragraphs smooth?
- Are there any grammatical errors?
Based on the rubric found at: Grading Rubric Template (Word)
- Authored by : J. Indigo Eriksen. Provided by : Blue Ridge Community College. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of checklist. Authored by : Jurgen Appelo. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/hykfe7 . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Peer Review Checklist. Authored by : Robin Parent. Provided by : Utah State University English Department. Project : USU Open CourseWare Initiative. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Table of Contents
Instructor Resources (Access Requires Login)
- Overview of Instructor Resources
An Overview of the Writing Process
- Introduction to the Writing Process
- Introduction to Writing
- Your Role as a Learner
- What is an Essay?
- Reading to Write
- Defining the Writing Process
- Videos: Prewriting Techniques
- Thesis Statements
- Organizing an Essay
- Creating Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Editing and Proofreading
- Matters of Grammar, Mechanics, and Style
- Comparative Chart of Writing Strategies
Using Sources
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Formatting the Works Cited Page (MLA)
- Citing Paraphrases and Summaries (APA)
- APA Citation Style, 6th edition: General Style Guidelines
Definition Essay
- Definitional Argument Essay
- How to Write a Definition Essay
- Critical Thinking
- Video: Thesis Explained
- Effective Thesis Statements
- Student Sample: Definition Essay
Narrative Essay
- Introduction to Narrative Essay
- Student Sample: Narrative Essay
- "Shooting an Elephant" by George Orwell
- "Sixty-nine Cents" by Gary Shteyngart
- Video: The Danger of a Single Story
- How to Write an Annotation
- How to Write a Summary
- Writing for Success: Narration
Illustration/Example Essay
- Introduction to Illustration/Example Essay
- "She's Your Basic L.O.L. in N.A.D" by Perri Klass
- "April & Paris" by David Sedaris
- Writing for Success: Illustration/Example
- Student Sample: Illustration/Example Essay
Compare/Contrast Essay
- Introduction to Compare/Contrast Essay
- "Disability" by Nancy Mairs
- "Friending, Ancient or Otherwise" by Alex Wright
- "A South African Storm" by Allison Howard
- Writing for Success: Compare/Contrast
- Student Sample: Compare/Contrast Essay
Cause-and-Effect Essay
- Introduction to Cause-and-Effect Essay
- "Cultural Baggage" by Barbara Ehrenreich
- "Women in Science" by K.C. Cole
- Writing for Success: Cause and Effect
- Student Sample: Cause-and-Effect Essay
Argument Essay
- Introduction to Argument Essay
- Rogerian Argument
- "The Case Against Torture," by Alisa Soloman
- "The Case for Torture" by Michael Levin
- How to Write a Summary by Paraphrasing Source Material
- Writing for Success: Argument
- Student Sample: Argument Essay
- Grammar/Mechanics Mini-lessons
- Mini-lesson: Subjects and Verbs, Irregular Verbs, Subject Verb Agreement
- Mini-lesson: Sentence Types
- Mini-lesson: Fragments I
- Mini-lesson: Run-ons and Comma Splices I
- Mini-lesson: Comma Usage
- Mini-lesson: Parallelism
- Mini-lesson: The Apostrophe
- Mini-lesson: Capital Letters
- Grammar Practice - Interactive Quizzes
- De Copia - Demonstration of the Variety of Language
- Style Exercise: Voice
Peer Review Checklist
Janelle schwartz, english 201.
This is to give you an idea of the type of things you should be looking for and accomplishing in both your own paper and that of your peer(s). Use what follows as a kind of checklist for determining what is working effectively in a paper and what is not.
Introduction
Has the writer (either yourself or your classmate) clearly expressed the question (major claim, thesis) that he/she has selected to analyze? What is that question?
Is there any unnecessary information included in the introduction?
Having read the entire essay, suggest an alternate way to begin the essay.
Having read the entire essay, does the introduction fit the paper?
What are the main points that are being made in each paragraph? Briefly outline the point of each paragraph and sketch the evidence given in support for each.
How is the evidence linked to the main point of the paragraph? And to the main point of the essay?
Is there any unnecessary information throughout the body of the paper, such as plot summary, excessive quotation,
or unsupported claims?
Has the writer restated (not simply repeated) the major claim of the paper in light of its discussion throughout the paper? In other words, what should the reader have learned by the end of the argument?
What is your understanding of the initial question after reading the paper? Has this understanding been adequately expressed? And does it open up the major claim to the question of its implications? (Has this major claim ultimately been placed into a broader perspective or context?)
Suggest an alternate ending to the argument. General/Misc
Suggest an alternate title. Does it express “in a nutshell” the essay’s theme? Has it followed the proper “title: subtitle” format? [Note: This assumes the paper already has a title—thus, every paper must have a title!]
What confuses you about the draft? (For example, a certain word choice, the topic and/or its presentation, the explanation of something in particular.)
Does the flow of the essay break down at any point? In other words, does the essay become hard to read or lose its coherence? Where? And how might you fix it?
Does the essay remain within the chosen text(s)? If there are any generalizations, speculations, clichés, idiomatic expressions, or colloquialisms, underline them so that you can point them out to your peer(s).
What has the writer done well in his/her essay? Provide positive comments about the strength(s) of the essay.

- Writing Center
- Current Students
- Online Only Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Family
- Alumni & Friends
- Community & Business
- Student Life
- Video Introduction
- Become a Writing Assistant
- All Writers
- Graduate Students
- ELL Students
- Campus and Community
- Testimonials
- Encouraging Writing Center Use
- Incentives and Requirements
- Open Educational Resources
- How We Help
- Get to Know Us
- Conversation Partners Program
- Workshop Series
- Professors Talk Writing
- Computer Lab
- Starting a Writing Center
- A Note to Instructors
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Research Proposal
- Argument Essay
- Rhetorical Analysis
Argument Essay Peer Review

As a writer . . .
Step 1 : Underline your thesis statement.
Step 2: Include answers to the following two questions at the top of your draft:
- What questions do you have for your reviewer?
- List two concerns you have about your argument essay.
Step 3: When you receive your peer's feedback, read and consider it carefully.
Remember: you are not bound to accept everything your reader suggests; if you believe that the response comes as a result of misunderstanding your intentions, be sure that those intentions are clear. The problem can be either with the reader or the writer!
As a reviewer . . .
As you begin writing your peer review, remember that your peer will benefit more from constructive criticism than vague praise. A comment like "I got confused here" or "I saw your point clearly here" is more useful than "It looks okay to me." Point out ways your classmates can improve their work.
Step 1: Read your peer’s draft two times.
Read the draft once to get an overview of the paper, and a second time to provide constructive criticism for the author to use when revising the draft.
Step 2: Answer the following questions:
- What is the writer’s thesis statement? (Copy it here.)
- Is the thesis clear and well-supported?
- Is the paper overly general, or does the writer make specific claims and then back them up using logical reasoning and/or researched evidence?
- Does the writing “flow” smoothly? Note sentences or sections where flow could be improved.
- Is the essay reasonably free of sentence and spelling errors?
- Remember the MEAL plan – does each paragraph follow this basic structure? [M – Main idea; E – Evidence; A – Analysis; L – Link]
- Are all references to outside materials (direct quotations as well as very specific information that had to have come from reading others’ work) cited, both within the essay and on a Works Cited page?
- Has the writer used at least three scholarly sources (no Wikipedia, personal blogs, etc.)?
Step 3: Address your peer’s questions and concerns included at the top of the draft.
Step 4: Write a short paragraph about what the writer does especially well.
Step 5: Write a short paragraph about what you think the writer should do to improve the draft.
Your suggestions will be the most useful part of peer review for your classmates, so focus more of your time on these paragraphs; they will count for more of your peer review grade than the yes or no responses.
Hints for peer review:
- Point out the strengths in the essay.
- Address the larger issues first.
- Make specific suggestions for improvement.
- Be tactful but be candid and direct.
- Don’t be afraid to disagree with another reviewer.
- Make and receive comments in a useful way.
- Remember peer review is not an editing service; you should not focus on sentence-level errors like punctuation and spelling.

Contact Info
Kennesaw Campus 1000 Chastain Road Kennesaw, GA 30144
Marietta Campus 1100 South Marietta Pkwy Marietta, GA 30060
Campus Maps
Phone 470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
kennesaw.edu/info
Media Resources
Resources For
Related Links
- Financial Aid
- Degrees, Majors & Programs
- Job Opportunities
- Campus Security
- Global Education
- Sustainability
- Accessibility
470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
© 2024 Kennesaw State University. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Statement
- Accreditation
- Emergency Information
- Report a Concern
- Open Records
- Human Trafficking Notice

Engaging in Peer Review
There are times when we write in solitary and intend to keep our words private. However, in many cases, we use writing as a way of communicating. We send messages, present and explain ideas, share information, and make arguments. One way to improve the effectiveness of this written communication is through peer-review.
What is Peer-Review?
In the most general of terms, peer-review is the act of having another writer read what you have written and respond in terms of its effectiveness. This reader attempts to identify the writing's strengths and weaknesses, and then suggests strategies for revising it. The hope is that not only will the specific piece of writing be improved, but that future writing attempts will also be more successful. Peer-review happens with all types of writing, at any stage of the process, and with all levels of writers.
Sometimes peer-review is called a writing workshop.
What is a Writing Workshop?
Peer-review sessions are sometimes called writing workshops. For example, students in a writing class might bring a draft of some writing that they are working on to share with either a single classmate or a group, bringing as many copies of the draft as they will need. There is usually a worksheet to fill out or a set questions for each peer-review reader to answer about the piece of writing. The writer might also request that their readers pay special attention to places where he or she would like specific help. An entire class can get together after reading and responding to discuss the writing as a group, or a single writer and reader can privately discuss the response, or the response can be written and shared in that way only.
Whether peer-review happens in a classroom setting or not, there are some common guidelines to follow.
Common Guidelines for Peer-Review
While peer-review is used in multiple contexts, there are some common guidelines to follow in any peer-review situation.
If You are the Writer
If you are the writer, think of peer-review as a way to test how well your writing is working. Keep an open mind and be prepared for criticism. Even the best writers have room for improvement. Even so, it is still up to you whether or not to take the peer-review reader's advice. If more than one person reads for you, you might receive conflicting responses, but don't panic. Consider each response and decide for yourself if you should make changes and what those changes will be. Not all the advice you get will be good, but learning to make revision choices based on the response is part of becoming a better writer.
If You are the Reader
As a peer-review reader, you will have an opportunity to practice your critical reading skills while at the same time helping the writer improve their writing skills. Specifically, you will want to do as follows:
Read the draft through once
Start by reading the draft through once, beginning to end, to get a general sense of the essay as a whole. Don't write on the draft yet. Use a piece of scratch paper to make notes if needed.
Write a summary
After an initial reading, it is sometimes helpful to write a short summary. A well written essay should be easy to summarize, so if writing a summary is difficult, try to determine why and share that with the writer. Also, if your understanding of the writer's main idea(s) turns out to be different from what the writer intended, that will be a place they can focus their revision efforts.
Focus on large issues
Focus your review on the larger writing issues. For example, the misplacement of a few commas is less important than the reader's ability to understand the main point of the essay. And yet, if you do notice a recurring problem with grammar or spelling, especially to the extent that it interferes with your ability to follow the essay, make sure to mention it.

Be constructive
Be constructive with your criticisms. A comment such as "This paragraph was boring" isn't helpful. Remember, this writer is your peer, so treat him/her with the respect and care that they deserve. Explain your responses. "I liked this part" or "This section doesn't work" isn't enough. Keep in mind that you are trying to help the writer revise, so give him/her enough information to be able to understand your responses. Point to specific places that show what you mean. As much as possible, don't criticize something without also giving the writer some suggestion for a possible solution. Be specific and helpful.
Be positive
Don't focus only on the things that aren't working, but also point out the things that are.
With these common guidelines in mind, here are some specific questions that are useful when doing peer-review.
Questions to Use
When doing peer-review, there are different ways to focus a response. You can use questions that are about the qualities of an essay or the different parts of an essay.
Questions to Ask about the Qualities of an Essay
When doing a peer-review response to a piece of writing, one way to focus it is by answering a set of questions about the qualities of an essay. Such qualities would be:
Organization
- Is there a clearly stated purpose/objective?
- Are there effective transitions?
- Are the introduction and conclusion focused on the main point of the essay?
- As a reader, can you easily follow the writer's flow of ideas?
- Is each paragraph focused on a single idea?
- At any point in the essay, do you feel lost or confused?
- Do any of the ideas/paragraphs seem out of order, too early or too late to be as effective as they could?
Development and Support
- Is each main point/idea made by the writer clearly developed and explained?
- Is the support/evidence for each point/idea persuasive and appropriate?
- Is the connection between the support/evidence, main point/idea, and the overall point of the essay made clear?
- Is all evidence adequately cited?
- Are the topic and tone of the essay appropriate for the audience?
- Are the sentences and word choices varied?
Grammar and Mechanics
- Does the writer use proper grammar, punctuation, and spelling?
- Are there any issues with any of these elements that make the writing unreadable or confusing?
Revision Strategy Suggestions
- What are two or three main revision suggestions that you have for the writer?
Questions to Ask about the Parts of an Essay
When doing a peer-review response to a piece of writing, one way to focus it is by answering a set of questions about the parts of an essay. Such parts would be:
Introduction
- Is there an introduction?
- Is it effective?
- Is it concise?
- Is it interesting?
- Does the introduction give the reader a sense of the essay's objective and entice the reader to read on?
- Does it meet the objective stated in the introduction?
- Does it stay focused on this objective or are there places it strays?
- Is it organized logically?
- Is each idea thoroughly explained and supported with good evidence?
- Are there transitions and are they effective?
- Is there a conclusion?
- Does it work?
Peer-Review Online
Peer-review doesn't happen only in classrooms or in face-to-face situations. A writer can share a text with peer-review readers in the context of a Web classroom. In this context, the writer's text and the reader's response are shared electronically using file-sharing, e-mail attachments, or discussion forums/message boards.
When responding to a document in these ways, the specific method changes because the reader can't write directly on the document like they would if it were a paper copy. It is even more important in this context to make comments and suggestions clear by thoroughly explaining and citing specific examples from the text.
When working with an electronic version of a text, such as an e-mail attachment, the reader can open the document or copy/paste the text in Microsoft Word, or other word-processing software. In this way, the reader can add his or her comments, save and then send the revised document back to the writer, either through e-mail, file sharing, or posting in a discussion forum.
The reader's overall comments can be added either before or after the writer's section of text. If all the comments will be included at the end of the original text, it is still a good idea to make a note in the beginning directing the writer's attention to the end of the document. Specific comments can be inserted into appropriate places in the document, made clear by using all capital letters enclosed with parenthesis. Some word-processing software also has a highlighting feature that might be helpful.
Benefits of Peer Review
Peer-review has a reflexive benefit. Both the writer and the peer-review reader have something to gain. The writer profits from the feedback they get. In the act of reviewing, the peer-review reader further develops his/her own revision skills. Critically reading the work of another writer enables a reader to become more able to identify, diagnose, and solve some of their own writing issues.
Peer Review Worksheets
Here are a few worksheets that you can print out and use for a peer-review session.
Parts of an Essay
- My audience is:
- My purpose is:
- The main point I want to make in this text is:
- One or two things that I would appreciate your comments on are:
- After reading through the draft one time, write a summary of the text. Do you agree with the writer's assessment of the text's main idea?
- In the following sections, answer the questions that would be most helpful to the writer or that seem to address the most relevant revision concerns. Refer to specific places in their text, citing examples of what you mean. Use a separate piece of paper for your responses and comments. Also, write comments directly on the writer's draft where needed.
- Is it effective? Concise? Interesting?
- Is there a conclusion? Does it work?
Finally, what are two or three revision suggestions you have for the writer?
Qualities of an Essay
- After reading through the draft one time, write a summary of the text.
- In the following sections, answer the questions that would be most helpful to the writer or that seem to address the most relevant revision concerns. Use a separate piece of paper for your responses and comments. Also, write comments directly on the writer's draft where needed.
- Is the connection between the support/evidence, main point/idea, and the overall point of the essay made clear?Is all evidence adequately cited?
Salahub, Jill . (2007). Peer Review. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=43
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
College Essay Checklist: Are You Ready to Submit?
←Whom Should I Ask for Help with My College Essay?
How Long Should Your College Essay Be?→
The college admissions process is a human process. An admissions committee filled with real people will evaluate your application, and these people will choose whether to advocate for you to gain admission to the university. So in order to be accepted, you need to stand out from the other applicants and persuade the admissions committee to choose you over students with a similar academic profile. Luckily, college essays are specifically designed to be your tool to stand out in the admissions process.
Given that college essays are so important, it’s important to make sure that they are absolutely perfect before you submit them. How do you make sure your college essays are ready to send to colleges? Make sure you’ve gone through this checklist before you hit that “submit” button!
Why Are College Essays So Important?
A college application has many components – test scores, grades and coursework, your extracurricular profile, recommendation letters, interviews, and, of course, your essays. So why are the essays such an important part if there are so many other components of your application to consider?
Well, most colleges receive thousands of applicants, many of whom have similar academic and extracurricular profiles. In fact, for every spot in a selective university’s admitted class, there are at least four outstanding applicants with similar grades and test scores. So how do admissions committees choose among so many students who have such strong potential? They use their essays to decide who would best fit in with the campus community.
For this reason, your college essays aren’t just about showing off your abilities and accomplishments. It’s about showing who you are as a person, what your values are, and what you’re passionate about. That’s no small task for a short essay. Every word is going to count, so follow the checklist below to make sure that your essay is as strong as it can be.
College Essay Checklist: Before You Submit
1. does your essay share who you are and what you care about.
Your essay needs to be personal. It should share your personality, goals, and voice. Even if a prompt doesn’t explicitly ask you who you are and what you care about, you should use it as an opportunity to showcase your personal qualities. For example, take the following supplemental essay prompt from the University of Chicago’s 2020 Application:
What can actually be divided by zero?
At first glance, this prompt may seem confusing. After all, didn’t we all learn in elementary school math classes that nothing can be divided by zero? More abstract, philosophical prompts like this one are actually ripe opportunities for students to showcase who they are and how they think.
So if you answered a prompt like this very practically, e.g. explaining that the laws of mathematics prove that no real number can be divided by zero, you’re missing out on a key opportunity to show the admissions committee your capability for creativity and abstract thought. Instead of answering a prompt like this literally, you ought to think critically about your own life and see if you can metaphorically or rhetorically link the question to something you have gone through or accomplished.
Alternatively, if you’re more of a logical person and want to answer the question analytically, make sure that you are showcasing your knowledge of various theorems and strategies, and be sure to cite where you learned them. Either way, you are showing the admissions committee how your brain works and how you go about solving problems.
Remember: the goal of an essay is, first and foremost, to showcase yourself. There are no right or wrong answers in college essays, so as long your essay tells the committee something important about you.
2. Do your essays form a portfolio that accurately represents you?
While having to write so many essays is a lot of work, there is an upside. Having multiple essays means you can use each essay to display a different aspect of yourself and your accomplishments. That way, holistically, your application will give a very representative picture of who you are, and you won’t have to leave anything out.
So when you’re evaluating your essays, ask yourself: do your essays depict as many facets of yourself as possible? Specifically, have you repeated a story, experience or quality about yourself in any of the essays you’re going to send to the same college? If you have, then consider editing one of the essays to highlight something that you haven’t yet shared with the admissions committee. The more you can share with them in a limited amount of space, the easier it will be for the admissions committee to imagine how you would fit in at their university.

3. Did you answer the prompt?
Okay, so we’ve talked a lot about making sure that your values, passions, and accomplishments are showcased in your essays, even if the prompt is more abstract. This is certainly important, but it’s also important to make sure you’re showcasing yourself in the context of the essay prompt that was given to you. In other words, you should be sure that at some point in your essay, you answer the essay prompt clearly. If you don’t, you risk coming across as a student who doesn’t know how to follow basic directions.
Moreover, you need to make sure that you answer every part of the essay prompt given. Some essay prompts will just have one part. Some will have many. If you have to answer an essay prompt with multiple parts, be sure you address all of them. Take the following essay prompts from the 2019-2020 College Application Cycle:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology , 2019-2020:
Tell us about the most significant challenge you’ve faced or something important that didn’t go according to plan. How did you manage the situation? (200-250 words)
University of California :
What would you say is your greatest talent or skill? How have you developed and demonstrated that talent over time? (350 words)
In both of these prompts, you are asked to respond to two related questions. If you were to answer the MIT prompt, you would need to not only describe a significant challenge but explain how you overcame it. For the University of California prompt, you’d not only need to explain your greatest skill but outline how you’ve cultivated it over time. If you miss any of those parts in your response, you will not have fully answered the prompt.
4. Did You Stay Within the Word Count?
Most main college essays (like the Common App essays) have a word limit of anywhere from 250-650 words. Supplemental essay prompts generally have word limit of 100-400 words. Either way, you need to make sure that you stay very close to the upper word limit in your response.
As a general rule, you should try to stay within 10% of the upper word limit. So if the word limit for one of your essays is 650 words, your essay shouldn’t be fewer than 585 words. Keep in mind that most online applications will cut off your essay at the word limit, so try not to go over the word count. However, on the other extreme, you don’t want to make your essay too short, as it may make it seem like you don’t care about the application. After all, every extra bit of space in your essays is an opportunity to further impress the admissions committee, so you should take advantage of it.
For some more details on how long your college essays should be, check out our previous post entitled How Long Should Your College Essay Be? What is the Ideal Length?
5. Did You Proofread?
Here are some things to look out for as you look over your essay:
Incorrect grammar and spelling mistakes. These can make a well-thought-out essay seem subpar in the eyes of an admissions committee.
Awkward or formal wording. Read your essay aloud and listen to how it sounds. If it doesn’t sound natural, then you’re likely not displaying your authentic self to the admissions committee. Consider shifting some of the wording to sound more like something you would actually say, even if it means you have to take out a bit of the advanced vocabulary and complex sentence structure.
Instances of telling, instead of showing. One of the biggest mistakes students make is to tell, instead of show. Here’s an example of telling: “It was a rainy and gloomy day.” Here’s an example of showing: “The gray clouds hovered ominously above the lake. I felt a drop. Then another. And another. It began pouring, and I frantically tried to row the canoe back to shore.” It’s much more engaging to read the second example, as you feel as if you’re there with the writer.
Repeated sentence structure and vocab. Do you use the same word over and over again? Do you begin lots of sentences in a row with “I”? As you’re reading your essay, make sure that you’re using varied language to keep things interesting.
Inconsistent style. While your language should be varied, your style shouldn’t. If you use contractions or acronyms, use them throughout the essay. If you begin the essay in past tense, keep it that way, or make sure there’s clear demarcation when you shift tenses.
Also, if you’re reused an essay from another school’s application, give it an extra read-through to make sure that you’ve replaced all of the mentions of and references to the other college. You don’t want the admissions committee from UC Berkeley reading about how thrilled you are to take advantage of the opportunities that Tufts has to offer. It would not bode well for your likelihood of acceptance to Berkeley.
Of course, it is okay to reuse essays if the prompts are similar, but just be sure to double and triple-check that it doesn’t seem like you’re reusing an essay meant for another college. Also, if you’re answering the famous “ Why This College ” essay, we at CollegeVine recommend that you not reuse another essay. This essay should include specific resources and opportunities that you plan to take advantage of at each university, so you shouldn’t be able to use the same essay for two different schools. In fact, if you’re able to reuse a “Why This College” essay, that’s a sign that you need to rework the essay and make it more specific to the college.
6. Did You Get a Second and Third Set of Eyes on Your Essay?
It’s important to get another person or two to read your essay before you submit. The best people to look at your essays are those who are well-versed in creative essay writing, but also people who know you well. Older peers who have gone through the admissions process successfully can offer some of the best advice. English or Communications teachers who know you well also make great proofreaders, as do writing-proficient friends and family.
If you’re not sure who to ask, you can also use our free peer essay review tool . You can get feedback on your essays, and improve your own writing skills by reviewing others’ essays.
7. Did You Revise and Proofread Again?
Once you’ve read through your essays and had others give suggestions, make the necessary edits and corrections. Then, be sure you proofread your essays one more time before you hit submit. You should try not to submit an essay that hasn’t been read at least a few times all the way through, without any changes. Consider even reading your essay out loud and printed out (have a pen at the ready!), as you may catch things you missed when reading silently.
Want help with your college essays to improve your admissions chances? Sign up for your free CollegeVine account and get access to our essay guides and courses. You can also get your essay peer-reviewed and improve your own writing skills by reviewing other students’ essays.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- Majors & Minors
- About Southwestern
- Library & IT
- Develop Your Career
- Life at Southwestern
- Scholarships/Financial Aid
- Student Organizations
- Study Abroad
- Academic Advising
- Billing & Payments
- mySouthwestern
- Pirate Card
- Registrar & Records
- Resources & Tools
- Safety & Security
- Student Life
- Parents Homepage
- Parent Council
- Rankings & Recognition
- Tactical Plan
- Academic Affairs
- Business Office
- Facilities Management
- Human Resources
- Notable Achievements
- Alumni Home
- Alumni Achievement
- Alumni Calendar
- Alumni Directory
- Class Years
- Local Chapters
- Make a Gift
- SU Ambassadors

Southwestern University announces its 2021–2026 Tactical Plan.

As part of Southwestern University’s Hispanic Serving Institution designation, first-generation student Brianna Gonzales ’24 has traveled the country to participate in a variety of prestigious programs.

Theatre and psychology double major Camille Krumwiede ’22 is showcasing skills learned at Southwestern through internships at And Just Like That… and Atlantic Pictures.

Through a seasoned blend of award-winning meal options, professional staff, and state-of-the-art facilities, Pirate Dining is enhancing the Southwestern Experience one meal at a time.

The bestselling college guide ranked Southwestern as one of the top 300 “best and most interesting” four-year universities in its annual list.

With the support of an SU alumnus and local honey producer, Layla Hoffen ’26 created BEE-Co, one of the most unique student organizations at Southwestern.

Spurred by her affection for horses, Gabby Guinn ’25 gives back to the community as an intern at the Ride On Center for Kids (ROCK).

Generous gift kicks off fundraising efforts for new athletic complex that will help bring football back to campus for the first time since 1950.

Pirate Athletics launches a new way to elevate the student-athlete experience at Southwestern.

Southwestern’s liberal arts education, wide array of majors and minors, and prime geographic location set students up for future success in the tech industry.

A conversation with Assistant Professor of Sociology Adriana Ponce.

Natalie Davis ’26 awarded with runner-up honors in ASIANetwork’s nationwide essay contest.

Expansive transformation of Mabee Commons honored for outstanding renovation project in national competition.

Nineteen students participate in seven thought-provoking projects funded by King Creativity Fund grants.

Alumnus debuts performance to complete masters of music composition program at Texas State University.

The Southwestern community will have exclusive access to expanded job resources through Indeed, the world’s #1 job site.

Jihan Schepmann ’24 will attend UT Southwestern this fall to begin organic chemistry Ph.D. program.

Relive moments from the commencement ceremony for the Southwestern University Class of 2024.
Peer Review
Benefits of peer review, how does devoting class time to peer review help student writing.
- Peer review builds student investment in writing and helps students understand the relationship between their writing and their coursework in ways that undergraduates sometimes overlook. It forces students to engage with writing and encourages the self-reflexivity that fosters critical thinking skills. Students become lifelong thinkers and writers who learn to question their own work, values, and engagement instead of simply responding well to a prompt.
- Making the writing process more collaborative through peer review gives students opportunities to learn from one another and to think carefully about the role of writing in the course at hand . The goals of the assignment are clarified. By assessing whether or not individual student examples meet the requirements, students are forced to focus on goals instead of getting distracted entirely by grammar and mechanics or by their own anxiety.
- Studies have shown that even strong writers benefit from the process of peer review : students report that they learn as much or more from identifying and articulating weaknesses in a peer’s paper as from incorporating peers’ feedback into their own work.
- Peer review provides students with contemporary models of disciplinary writing . Because students often learn writing skills in English class, at least in high school, their models for “good writing” might be entirely general or ill-suited to your class. Peer review gives them a communal space to explore writing in the disciplines.
- Peer review allows students to clarify their own ideas as they explain them to classmates and as they formulate questions about their classmates’ writing. This is helpful to writers at all skill levels, in all classes, and at all stages of the writing process.
- Peer review provides professional experience for students having their writing reviewed. Peer review is the process by which professionals in the field publish, it’s how managers and co-workers provide feedback in the workplace, and it’s a skill with practical application.
- Last but not least, peer review minimizes last minute drafting and may cut down on common lower-level writing errors.
Cho, Kwangsu, Christian D. Schunn, and Davida Charney. “Commenting on Writing: Typology and Perceived Helpfulness of Comments from Novice Peer Reviewers and Subject Matter Experts.” Written Communication 23.3 (2006): 260-294.
Graff, Nelson. “Approaching Authentic Peer Review.” The English Journal 95.5 (2009): 81-89.
Nilson, Linda B. “Improving Student Peer Feedback.” College Teaching 51.1 (2003): 34-38.
“Using Peer Review to Help Students Improve Writing.” The Teaching Center . Washington University in St. Louis. n.d. Web. 1 June 2014.
- Request a Consultation
- Workshops and Virtual Conversations
- Technical Support
- Course Design and Preparation
- Observation & Feedback
Teaching Resources
Planning and Guiding In-Class Peer Review
Resource overview.
How to plan and guide in-class peer review.
Incorporating peer review into your course can help your students become better writers, readers, and collaborators. However, peer review must be planned and guided carefully.
The following suggestions for planning and guiding peer review are based on our approach to peer review. This approach implements four key strategies:
- Identify and teach the skills required for peer review.
- Teach peer review as an essential part of the writing process.
- Present peer review as an opportunity for students to learn how to write for an audience.
- Define the role of the peer-reviewer as that of a reader, not an evaluator.
These tips are are organized in four areas:
Before the Semester Starts
During the semester and before the first peer-review session, during and after peer-review sessions, peer review is challenging work.
The Center for Teaching and Learning provides sample worksheets (Peer Review Worksheet for Thesis-Driven Essay) that may be adapted to suit various types of courses and genres of writing.
1. Determine how peer review will fit into the course.
A. Decide which writing assignments will include a peer-review session. Given the time that is required to conduct peer-review sessions successfully (see below), in undergraduate courses, peer review will work best with papers of 5 pages or less. Instructors who want to incorporate peer-review sessions for longer papers will have to ask students to complete part of the work outside of class (e.g. reading peers’ papers and preparing written comments); such an approach is likely to be more successful if students first practice peer review during class, with the guidance of the instructor.
B. Decide when peer-review sessions will occur. The ideal time for peer review is after students have written a complete draft of a paper, but while there is still time for substantial revision.
Each peer-review session will require at least one class period. While it is possible to complete a session in one hour, a one-and-one-half hour class period is preferable (see below for a detailed discussion of how to structure peer-review sessions).
As you look over your course schedule, make time for a “mock” peer-review session before you ask students to review one another’s writing, so that they can learn to identify and begin practicing the skills necessary for peer review. Before the semester begins, furthermore, you should find a short sample paper that will serve as the focus of the “mock” peer review. You can also write this short paper yourself (for more detailed suggestions on how to set up a mock peer-review session, see below).
Instructors should schedule the first peer-review session early in the semester to give students time to get to know one another and to develop peer-review skills. The atmosphere of trust and mutual respect that is necessary for the success of peer-review sessions does not develop instantaneously. Ideally, the first peer-review session should focus on a short piece of writing, such as a paragraph or two, so that students develop comfort with giving and receiving feedback before taking on the task of reading longer papers.
2. Design peer-review worksheets that students will complete during each peer-review session.
These worksheets should include specific tasks that reviewers should complete during the session. The guidance you provide on the worksheets should help students stay “on task” during the session and should help them discern the amount of commenting that is desirable.
The role of the peer-reviewer should be that of a reader, not an evaluator or grader. Do not replicate the grading criteria when designing these worksheets. Your students will not necessarily be qualified to apply these criteria effectively, and they may feel uncomfortable if they are given the responsibility to pronounce an overall judgment on their peers’ work.
Peer-review worksheets should ask the reviewer to begin by offering a positive comment about the paper. After that point, the peer-reviewer role in commenting should be descriptive: each reviewer should describe his response to the paper. For example, a peer-reviewer might write: “I found this description very clear” or “I do not understand how this point relates to your thesis.” The worksheet should give students specific tasks to complete when recording their response to a paper (Nilson 2003). Where evaluation is required, it should be based on the reviewer’s impressions as a reader. Examples of specific tasks include:
- Indicate which parts of the paper the reader finds most or least effective, and why
- Identify or rephrase the thesis
- List the major points of support or evidence
- Indicate sentences or paragraphs that seem out of order, incompletely explained, or otherwise in need of revision
Performing these tasks should enable each peer-reviewer to provide the writer with a written response that will help the writer determine which parts of the paper are effective as is, and which are unclear, incomplete, or unconvincing.
Do not require students to tell the writer how to revise the paper. Advanced undergraduates, students who have been meeting in peer-review groups for an extended time, and graduate students may be able to handle adding more directive responses (e.g. suggesting that the writer make specific changes).
3. During the course-planning process, think carefully about the kind of comments that you will provide students when you review drafts and grade papers.
With your comments, you can model for your students the qualities you would like to see reflected in their comments as peer-reviewers. For example, you can give them examples of comments that are descriptive and specific.
4. Decide whether and how you will grade students’ contributions to peer-review sessions.
One way to communicate to students the importance of peer review and the skills it requires is to grade their contributions to the peer-review process. If you do grade students’ performances in peer review, you will need to decide ahead of time what exactly you will be grading and what criteria you will use to judge their achievement. Furthermore, you might decide to use a straightforward -√/ √/ √+ system, or you might assign a point-value to different aspects of the work required for peer review. You should then decide how to incorporate each peer-review score into the course grade or into the grade earned for each paper.
The following example illustrates a point-system approach to grading student performance in peer review:
Brought 2 copies of paper to class: 5 pts Provided peers with specific, constructive written feedback: 0-5 pts Participated actively in discussion of each paper: 0-5 pts Wrote specific response to peers’ feedback: 0-5 pts Total score for each peer-review session: 0-20 pts.
This example makes it clear that those students who do not bring a draft to be peer-reviewed would nevertheless earn points by acting as reviewers of their peers’ work. Of course, if you use such a point-system, you will need to explain to the students the criteria by which you judge their performance in each category. Providing students with graded examples will help to clarify these criteria.
Whatever you decide regarding whether and how you will grade each student’s performance in peer review, you should observe and evaluate what students are doing during peer review so that you can give them some feedback and suggestions for improvement throughout the semester (see below for further suggestions on how to observe and evaluate peer review).
1. Hold a “mock” peer-review session.
First, copy and distribute a brief sample paper. You can either use a paper submitted by a student in an earlier semester (block-out the name and ask the student’s permission to distribute the paper) or write a sample paper yourself, approximating a draft that would be typical of students in your course. Next, ask students to take 5 minutes to read the paper and 10 minutes to write some comments, using a peer-review worksheet. If time allows, you can ask students to work in groups of 3-4 to produce written comments; if you do so, give them an additional 5-10 minutes for group discussion.
After students have produced written comments individually or as a group, use a document camera or overhead projector to display a blank peer-review worksheet. Then, ask students to present their reviewing comments to the class and use these to write comments on the displayed worksheet. When necessary, follow-up with questions that help the students phrase their comments in more specific and constructive ways. For example, if a student comments, “I like the first paragraph,” you might ask, “can you tell the writer what you find effective or appealing about that paragraph? And why?” Your aim should be to help students understand that the point of their comments should be to describe their experience as readers with specific language, not to praise or condemn their peers or to tell the peer how they would write the paper. Note that while students often hesitate to give specific feedback to a writer face-to-face, they may actually be overly critical when critiquing something written by a writer who is not present. Therefore, it might be helpful to direct students to construct their comments as if the writer were indeed in the room, listening.
2. Teach students how to think about, respond to, and use comments by peer-reviewers.
Just as your students will need to learn and practice the skills involved in providing constructive feedback on their peers’ writing, they will also need to learn how to respond, as writers, to the feedback they receive. Therefore, you might consider including in the “mock” peer-review session, described above, an exercise in which you ask your students to put themselves in the position of the writer and come up with a plan for revision based on the comments that they and their classmates have formulated in response to the sample paper.
Students must learn how to approach a peer-review session with an open mind (and a thick skin, perhaps). Often, undergraduate students go into a peer-review session thinking that their papers are essentially “done” and need to be edited or changed only slightly. Thus they “hear” only those responses that confirm this view and they end up making very few changes to their papers after the peer-review session and before submitting the final draft to the instructor. Alternatively, they can become so discouraged by what they view as a negative response from a peer that they are not able to discern what is useful about those responses.
To help students resist the understandable temptation to become either discouraged or defensive during the peer-review session and to help them focus on listening carefully to their peers’ comments, it is useful to institute a rule that prohibits writers from speaking when peer-reviewers are offering feedback. An exception might be made in a case in which the writer does not understand a reviewer’s comments and needs to ask for more information.
In addition, instructors should require each writer to respond in writing to their peers’ comments. This written response can be recorded directly on the peer-review worksheet, or it can take the form of an informal letter (addressed to the peer-reviewers). Alternatively, instructors might require each writer to sketch out a plan for revision that 1) indicates any changes she will make in response to the reviewers’ comments and 2) explains any decisions she has made to disregard a specific comment or suggestion.The point of such writing exercises is to ask students to take their peers’ comments seriously and to think carefully about how readers respond to the choices they have made in their writing–even if that means determining that they will decide not to make changes based on those comments.
3. Assign three students to each peer-review group: maintain the same groups throughout the semester.
With groups of three, each student will be reviewing the papers of two peers during each peer-review session, but each group will discuss three papers (for detailed instructions on how to structure each session, see below).
It is best to assign students to groups, rather than to have them define the groups themselves. Students often want to form groups with friends, which may actually create difficulties. As you may want to explain to your students, it can be more difficult to provide honest feedback to a writer when that writer is a friend. Moreover, assigning students to the groups will allow the instructor to ensure that the groups are heterogeneous in terms of, for example, student ability, gender, race, and academic major. Such heterogeneity can enhance student learning in groups (Millis 2002).
Maintaining the groups throughout the semester will help your students build the trust that is necessary for peer review to be successful (Millis 2002). You should only reassign students to another group in the rare case when one or two group members drop the course. You should encourage your students to speak with you if they find that their peer-review groups are not functioning as well as desired, but you should also make it clear that you are interested in helping them find ways to work together to solve whatever problems have surfaced.
4. Ask each student to bring 2 copies of his or her paper to class on the designated day.
You can tell students that these copies are required, but if they do not bring copies of their own paper to class, they should come to class anyway, so that they can act as reviewers of other students’ papers.
1. Structure each peer-review session: give students clear instructions and time limits.
To start each session, distribute peer-review worksheets (see above), explain how students should complete the worksheets, set time limits, and ask each group to designate one person as a time-keeper to make sure that the group stays on schedule.
Peer-review sessions can be accomplished during one-hour classes, but instructors may find that a 90-minute class is preferable. If you teaching a one-hour or 50 minute class, consider asking students to read their peers’ papers before coming to class, then spending the first 10 minutes reviewing the paper and writing comments.
The following is a peer-review schedule that can work in a 90-minute class.
I. When papers are around three pages long, peer-reviewers should spend about 20-25 minutes reading and reviewing each paper: 15 minutes reading the paper (tell students to read each paper twice) and 5-10 minutes writing comments. You should lengthen the time limit when necessary, for instance when papers are longer or when they are written in a foreign language. This schedule will mean that during the first 45-50 minutes of class, each student will be reading and writing comments on papers written by two peers.
II. After all 3 students have finished commenting on the two papers submitted by their peers, the group should then devote 5-10 minutes to a “discussion” of each paper (spending a total of 15-30 minutes discussing three papers). During this discussion, the 2 reviewers should present spoken feedback to the writer. If reviewers feel uncomfortable with providing spoken feedback, they might start by reading their written comments out loud to the writer. Doing so can produce the added benefit of helping the reviewers clarify their written comments. As noted above, the writer of the paper should not speak during this discussion, except perhaps to ask a clarifying question.
2. Take an active role in observing the progress of each group and offering guidance when appropriate.
Even with clear instructions, peer-review sessions can go awry. Circulate throughout the session to make sure that the groups stay focused. Listen carefully to the spoken feedback, and use questions to help students make their comments as specific and descriptive as possible. For example, if you hear a student saying, “I was confused by the third paragraph,” you might prompt them to say more by asking, “Can you tell the writer where you got lost?” or “What word or phrase confused you? Why?” Students will soon learn to supply such details themselves.
Paying attention to how the groups are functioning overall can help you determine whether you need to give additional guidance to the class as a whole. For example, you might tell students that you noticed that many groups seem to be rushing through the spoken feedback period for each paper, and that even reviewers who wrote detailed and constructive comments on the worksheet are giving only cursory responses when speaking to the writer (e.g. “I thought you did a good job,” or “Your paper was interesting”). You might then remind them that they do not need to present an overall judgment of the paper, but they should try to say something specific that can help the writer revise the paper.
3. Have each student submit the completed peer-review worksheets when they turn-in the final drafts of their papers.
Whether or not you are grading the responses that reviewers and writers write on the peer-review worksheets, you should read the completed worksheets to get a sense of what students are actually doing during the peer-review sessions and how they are responding to one another’s comments. Having the students turn in the worksheets also helps you communicate to them that you are taking the peer-review process seriously. Instructors should also give students feedback on their performance during peer review so that they know what they are doing well and what they should try to improve upon.
4. Regularly assess how the peer-review sessions are going; seek and incorporate student input.
You should review completed peer-review worksheets when you grade papers not only to evaluate individual student performance, but also to gauge the success of the peer-review sessions and to determine what you might do to improve them.
Are students writing thoughtful comments that provide an adequate amount of detail? If not, spend some time in class before the next peer-review session giving students suggestions for how to phrase comments in a specific, constructive way.
Are students using the peer-review worksheets to develop thoughtful responses to peer comments? Are they coming up with plans for revision that take into account at least some of their peers’ comments? Again, if needed, give your students additional guidance and in-class activities that will lead them through the process of identifying potential aspects needing revision and coming up with a plan for revision that takes into account peer comments.
Around midterm, ask students to complete anonymous evaluation forms that include questions such as, “What is the most important insight that I have learned as a result of the peer-review process?” and “What can be done (by the instructor or by students, or both) to make the peer-review sessions run more smoothly?”
Be prepared to hear that the peer-review sessions are not functioning as well as you believe they are, and be open to making changes that incorporate your students’ observations and ideas. In other words, model the same open-mindedness to revision that you want them to display as writers during peer review.
Instructors who ask their students to review their peers’ writing should recall how difficult it is–even after years of experience–to accomplish with efficiency the tasks involved in responding to student writing: reading drafts of papers (usually multiple papers at one sitting), quickly discerning each draft’s strengths and most pressing problems, then formulating specific and well written comments that will help the writer improve the paper. It can also be difficult, even for experienced writers, to respond effectively to the comments they receive from reviewers of their work. It is essential, then, that you plan carefully the guidance you will give your students on how to conduct and utilize peer review, and that you give them a chance to reflect on the process.
Bean, John C. (2001). Engaging Ideas: The Professor’s Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Gottschalk, Katherine and Keith Hjortshoj (2004). “What Can You Do with Student Writing?” In The Elements of Teaching Writing: A Resource for Instructors in All Disciplines . Boston: Bedford/St. Martin’s.
Millis, Barbara J. (2002). “ Enhancing Learning-and More! Through Collaborative Learning. IDEA Paper 38 . The IDEA Center.
Nilson, Linda. (2003). “Improving Student Peer Feedback.” College Teaching, 51 (1 ), p. 34-38.
- Home News Tribune
- Courier News
- Jersey Mayhem
- NJ Politics
- National Politics
What to avoid in college application essays | College Connection
An important part of the Common Application, which is accepted by more than 1,000 colleges, is the personal essay. Students are given six options as prompts, as well as a seventh option which is to share an essay on a topic of choice. So, students can write about anything at all.
The essay is an integral part of the application, as it is typically viewed by all the schools to which a student applies. It is the one section where students have the opportunity to share what is unique about them and what qualities they will bring to their future college community.
To make their essay stand out, students should avoid some common pitfalls.
Do not cheat. That means students should not turn to ChatGPT or to another person to write their essay. This should go without saying but, sadly, it does need to be said. College admissions officers know what the “voice” of a teenager sounds like, and that’s exactly what they’re looking for.
More: Top colleges where 'B' students are accepted | College Connection
Do not write about mental health issues. Although many young people, as well as those in every age group, deal with such issues, it is important not to share that information. Due to privacy laws, colleges are not able to contact parents if students struggle with depression, substance abuse, or any other troubling behavior. Therefore, students should not raise a red flag, or they will most likely find their applications in the “rejected” pile.
Do not be redundant. One’s personal essay is not the place to itemize the extracurricular, volunteer, and work experiences that are all included in the Activities section of the Common App. If there is one activity that dominated a student’s high school experience and is particularly compelling, it can be the topic of the essay. But students must elaborate on how they were profoundly impacted by their engagement.
More: How where you live affects your college admissions chances | College Connection
Do not recycle successful essays that were submitted by prior applicants. Often, students turn to the multitude of articles showcasing essays written by students who were admitted to Ivy League and other elite institutions. What worked for a prior student will not be effective for another as it’s not their story. It’s vital for students to share their genuine story using their authentic voice. The key to writing a thoughtful, introspective essay is to start early, carefully consider the story you want to share, and then do so in your very own style.
Susan Alaimo is the founder & director of Collegebound Review, offering PSAT/SAT ® preparation & private college advising by Ivy League educated instructors. Visit CollegeboundReview.com or call 908-369-5362 .
Peer essay review Answered
Is it taking anyone else so long to get their essays edited right now? I have given up using the peer essay review because no one had edited it for a few days (normally it's 24 hours max) and I even fast-tracked it. Also I go to edit essays and it's the same ones over and over again.
Earn karma by helping others:
Hey @lilye !
Thanks for reaching out about this! As the 1/1 deadline draws closer, the essay submissions in peer review have increased, which may have caused some lag in getting your essay back. If you continue to have this issue and have not yet received your essay, please feel free to reach out to support @collegevine.com so we can take a closer look at your submission.
I hope that helps!
Thank you! That makes a lot of sense.
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, community guidelines.
To keep this community safe and supportive:
- Be kind and respectful!
- Keep posts relevant to college admissions and high school.
- Don’t ask “chance-me” questions. Use CollegeVine’s chancing instead!
How karma works

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Expert and peer essay review Essay livestreams Get started. 10,000+ Essays reviewed | 25.7 hrs Avg. return time | 4.8/5 Avg.rating. ... Recommended if you have a rough or strong draft with ideas for revisions to submit a top notch essay! The essay review can be applied to college applications, scholarship applications, common app essays, direct ...
Hello, I'm Andrea Dardello, and I developed the C.A.R.E.S Feedback Method. This is a five-step process, which helps students peer review their assignments. Now that you're in your groups, I'd you to try the C.A.R.E.S Method. Fill out the worksheet I gave you while each person is presenting. This process works best in groups of three or four.
Written by Rebecca Wilbanks. Peer review is a workhorse of the writing classroom, for good reason. Students receive feedback from each other without the need for the instructor to comment on every submission. In commenting on each other's work, they develop critical judgment that they can bring to bear on their own writing.
In short, this pattern of commenting encourages reviewers to 1. describe what they are reading and understanding from the text, 2. evaluate how well the text is working based on the rubric, assignment sheet, or class material, and 3. suggest next steps for improvement. Putting these three moves together in a comment helps your partner ...
Make your peer review feedback more effective and purposeful by applying these strategies: Be a reader. Remember you are the reader, not the writer, editor, or grader of the work. As you make suggestions, remember your role, and offer a reader's perspective (e.g., "This statistic seemed confusing to me as a reader.
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom. Here's how your outline might look: 1. Summary of the research and your overall impression. In your own words, summarize what the manuscript ...
Essays guidance and peer review. Submit your own essay for a review in less than 6 hours on the world's first entirely free college essay review system. Q&A with experts. Ask questions and get quick and helpful answers from CollegeVine experts and a community of supportive peers.
The most common types are: Single-blind review. Double-blind review. Triple-blind review. Collaborative review. Open review. Relatedly, peer assessment is a process where your peers provide you with feedback on something you've written, based on a set of criteria or benchmarks from an instructor.
Peer Review Checklist. Each essay is made up of multiple parts. In order to have a strong essay each part must be logical and effective. In many cases essays will be written with a strong thesis, but the rest of the paper will be lacking; making the paper ineffective. An essay is only as strong as its weakest point.
Your essay is very important to your application — especially if you're applying to selective colleges. You should also take advantage of the following free resources: Peer Essay Review. Become a stronger writer by reviewing your peers' essays and get your essay reviewed as well for free. Essay Livestreams.
Janelle Schwartz, English 201. This is to give you an idea of the type of things you should be looking for and accomplishing in both your own paper and that of your peer (s). Use what follows as a kind of checklist for determining what is working effectively in a paper and what is not. Introduction. Has the writer (either yourself or your ...
Step 3: Address your peer's questions and concerns included at the top of the draft. Step 4: Write a short paragraph about what the writer does especially well. Step 5: Write a short paragraph about what you think the writer should do to improve the draft. Your suggestions will be the most useful part of peer review for your classmates, so ...
Effective Peer Review. When requiring your students to write essays, peer review provides your students with the opportunity to receive feedback from other readers familiar with the assignment, in addition to your feedback. This can provide students with more suggestions and ideas for revisions, potentially increasing the quality of their drafts.
Engaging in Peer Review. There are times when we write in solitary and intend to keep our words private. However, in many cases, we use writing as a way of communicating. We send messages, present and explain ideas, share information, and make arguments. One way to improve the effectiveness of this written communication is through peer-review.
Most main college essays (like the Common App essays) have a word limit of anywhere from 250-650 words. Supplemental essay prompts generally have word limit of 100-400 words. Either way, you need to make sure that you stay very close to the upper word limit in your response. As a general rule, you should try to stay within 10% of the upper word ...
Peer review gives them a communal space to explore writing in the disciplines. Peer review allows students to clarify their own ideas as they explain them to classmates and as they formulate questions about their classmates' writing. This is helpful to writers at all skill levels, in all classes, and at all stages of the writing process.
Guided Questions for Peer Review. How is the thesis structured? Does it follow the teacher's instructions? How can the thesis be more specific and complex? How can the writer demonstrate why their argument is significant? Does the thesis provide an outline of where the paper goes? How do the ideas in the paper progress?
Sophie Alina. 5.0. 7 years of experience. B.A. Math, Vanderbilt University, Cornelius Vanderbilt Scholar | SMU M.Ed. | Vanderbilt Ph.D student. Review starting at $100. Return time. Standard delivery up to 48 hours. Also offers 12 hour return time. 12 hour return available.
The Center for Teaching and Learning provides sample worksheets (Peer Review Worksheet for Thesis-Driven Essay) that may be adapted to suit various types of courses and genres of writing. Before the Semester Starts 1. Determine how peer review will fit into the course. A. Decide which writing assignments will include a peer-review session.
Peer Essay Reviews. If you use the peer essay review feature on CollegeVine, how do you usually rate the reviews of your essays? I try to rate every review as 5/5, as long as they gave some helpful advice and looks like they spent at least 15 minutes on it. Recently, I've been reviewing more essays to earn some extra karma.
During the college essay writing process, there were a few days that were dedicated to peer reviews. There were two types of peer reviews: one where we were in groups of four other students assigned by Mrs. Larson and ones with our table partner. Prior to doing the peer reviews in groups of four, I was thinking: I'm doing fine.
An important part of the Common Application, which is accepted by more than 1,000 colleges, is the personal essay. Students are given six options as prompts, as well as a seventh option which is ...
Hey there! I completely understand how stressful the college essay process can be. Finding a good reviewer can make a huge difference. When looking for a potential reviewer, consider someone who is familiar with the college admissions process, has strong writing and editing skills, and can provide honest and unbiased feedback. People who might fit this description include teachers, high school ...
As the 1/1 deadline draws closer, the essay submissions in peer review have increased, which may have caused some lag in getting your essay back. If you continue to have this issue and have not yet received your essay, please feel free to reach out to support @collegevine.com so we can take a closer look at your submission. I hope that helps!