Review Paper vs. Research Paper: Main Differences
Doing a paper is difficult, so learn the difference between a review paper vs. research paper, to determine which one is ideal for you.
A research paper and a review paper are two very specific types of papers. They have different motives, goals, and prerequisites. The elements found in research papers and review papers differ. The research paper is based on originality, therefore the paper takes into consideration the author’s original research, whereas the review paper is founded on an existing collection of knowledge.
This article will walk you through the main differences between a review paper vs. research paper, allowing you to correctly determine which one is ideal for your work.

What is a review paper?
A review paper project tries to provide readers with an overview of an existing collection of knowledge by reviewing a book or an article and examining its content, structure, style, and statements. Reviews, such as peer reviews, can be used to examine and assess the work of other authors, rating the work by comparing it to the work of others. A review article is frequently written for a large readership, which is why it is usually brief.
Review papers can be classified into three types:
- Narrative: a collection of and attempt to communicate all known information about a certain topic. It is based on research that has previously been completed and published.
- Meta-analysis: a method of comparing and combining the findings of past research studies. It is done routinely to evaluate the efficacy of a particular initiative or method of treatment.
- Systematic: a search of all known scientific information on a topic to find a solution to a specific issue or problem.
What is a research paper?
A research paper entails writing on research that has been performed by themselves, usually something new and done mostly from scratch since it has to be original research. It incorporates the research parameters, as well as the assessment, interpretation and important findings of the research.
Writing a research paper involves several phases and different aspects, such as: selecting a topic, developing a hypothesis, conducting research, testing the hypothesis, drawing conclusions, and publishing a paper supporting or denying the hypothesis.
Review paper vs. Research paper
Now that you have a basic understanding of both sorts of papers, it is time to compare and contrast the main differences between review paper vs. research paper.
| A thorough examination of something with the goal of implementing change if appropriate. E.g. a review of an article or other published work. | A methodical examination and analysis of materials and sources to establish facts and generate new findings. | |
| The word limit is often around 3000 and 5000 words. Based on the journal, a lengthier or fairly shorter review paper may also be published. | Normally runs between 3000 and 6000 words, depending on the journal requirement. The word limit for certain publications may potentially be increased to 12,000. | |
| To collect and critically examine information about a certain subject. | To present new information and findings. | |
| Existing literature and other work sources. | Raw data and original research. | |
| The author will select a topic and then synthesize the existing sources of information for that topic by providing an overview of its current understanding. | The researchers develop a research question, acquire raw data, then execute their own research. The research paper is then created utilizing the data analysis and interpretations. |
These are the main differences, however, there may be others:
- A research paper is usually more detailed and thorough than a review paper.
- A research paper is usually peer-reviewed, but a review paper is not always.
- In general, a research paper is more formal than a review paper.
- A research paper’s tone is normally objective, but a review paper’s tone can be more subjective.
- A research paper is normally written in APA style, however, a review paper may be written in a different format.
Add visual impact to your posters with scientific illustrations and graphics
Using infographics and illustrations may assist to make dense information more accessible and understood, they can bring interest and engagement to a research study or presentation. Use Mind The Graph to turn your work into remarkable work.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
About Jessica Abbadia
Jessica Abbadia is a lawyer that has been working in Digital Marketing since 2020, improving organic performance for apps and websites in various regions through ASO and SEO. Currently developing scientific and intellectual knowledge for the community's benefit. Jessica is an animal rights activist who enjoys reading and drinking strong coffee.
Content tags
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is the Difference Between Research Papers and Review Papers?
Researchers often have to write different types of articles, from review papers to review papers and more, each with its own purpose and structure. This makes it critical for students and researchers to understand the nuances of good writing and develop the skills required to write various kinds of academic text. With so many different types of academic writing to pursue – scholarly articles, commentaries, book reviews, case reports, clinical study reports – it is common for students and early career researchers to get confused. So in this article, we will explain what is a review paper and what is a research paper, while summarizing the similarities and difference between review papers and research papers.
Table of Contents
What is a Review Paper ?
A review paper offers an overview of previously published work and does not contain any new research findings. It evaluates and summarizes information or knowledge that is already available in various published formats like journals, books, or other publications, all of which is referred to as secondary literature. Well-written review papers play a crucial role in helping students and researchers understand existing knowledge in a specific field or a research topic they are interested in. By providing a comprehensive overview of previous studies, methodologies, findings, and trends, they help researchers identify gaps in a specific field of study opening up new avenues for future research.
What is a Research Paper ?
A research paper is based on original research and primary sources of data. Unlike review papers, researchers writing research papers need to report new findings derived from empirical research or experimentation. It requires the author to draw inferences or make assumptions based on experiments, surveys, interviews, or questionnaires employed to collect and analyze data. Research papers also typically follow the recommended IMRAD format, which includes an abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Through research papers, authors address a specific research question or hypothesis with the aim of contributing novel insights to the field.
Similarities between research papers and review papers
Research papers and review papers share several similarities, which makes it understandable that it is this pair of academic documents that are often most confused.
- Research papers and review papers are written by scholars and intended for an academic audience; they’re written with the aim of contributing to the existing body of knowledge in a particular field and can be published in peer reviewed journals.
- Both research papers and review papers require a comprehensive understanding of all the latest, relevant literature on a specific topic. This means authors must conduct a thorough review of existing studies, theories, and methodologies in their own subject and related areas to inform their own research or analysis.
- Research papers and review papers both adhere to specific formatting and citation styles dictated by the target journal. This ensures consistency and allows readers to easily locate and reference the sources cited in the papers.
These similarities highlight the rigorous, scholarly nature of both research papers and review papers, which requires both research integrity and a commitment to further knowledge in a field. However, these two types of academic writing are more different than one would think.
Differences between research papers and review papers
Though often used interchangeably to refer to academic content, research papers and review papers are quite different. They have different purposes, specific structure and writing styles, and citation formats given that they aim to communicate different kinds of information. Here are four key differences between research papers and review papers:
- Purpose: Review papers evaluate existing research, identify trends, and discuss the current state of knowledge on a specific topic; they are based on the study of previously published literature. On the other hand, research paperscontain original research work undertaken by the author, who is required to contribute new knowledge to the research field.
- Structure: Research papers typically follow a structured format, including key sections like the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Meanwhile, review papers may have a more flexible structure, allowing authors to organize the content based on thematic or chronological approaches. However, they generally include an introduction, main body discussing various aspects of the topic, and a conclusion.
- Methodology: Research papers involve the collection of data, experimentation, or analysis of existing data to answer specific research questions. However, review papers do not involve original data collection; instead, they extensively analyze and summarize existing studies, often using systematic literature review methods.
- Citation style: Research papers rely on primary sources to support and justify their own findings, emphasizing recent and relevant research. Review papers incorporate a wide range of primary and secondary sources to present a comprehensive overview of the topic and support the evaluation and synthesis of existing literature.
In summary, it’s important to understand the key differences between research papers and review papers. By mastering the art of writing both research papers and review papers, students and researchers can make more meaningful contributions to their chosen disciplines. All the best!
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What are the Best Research Funding Sources

What are Experimental Groups in Research
- Study resources
- Calendar - Graduate
- Calendar - Undergraduate
- Class schedules
- Class cancellations
- Course registration
- Important academic dates
- More academic resources
- Campus services
- IT services
- Job opportunities
- Safety & prevention
- Mental health support
- Student Service Centre (Birks)
- All campus services
- Calendar of events
- Latest news
- Media Relations
- Faculties, Schools & Colleges
- Arts and Science
- Gina Cody School of Engineering and Computer Science
- John Molson School of Business
- School of Graduate Studies
- All Schools, Colleges & Departments.
- Directories
- My Library account Renew books and more
- Book a study room or scanner Reserve a space for your group online
- Interlibrary loans (Colombo) Request books from external libraries
- Zotero (formerly RefWorks) Manage your citations and create bibliographies
- Article/Chapter Scan & Deliver Request a PDF of an article/chapter we have in our physical collection
- Contactless Book Pickup Request books, DVDs and more from our physical collection while the Library is closed
- WebPrint Upload documents to print on campus
- Course reserves Online course readings
- Spectrum Deposit a thesis or article
- Sofia Discovery tool
- Databases by subject
- Course Reserves
- E-journals via Browzine
- E-journals via Sofia
- Article/chapter scan
- Intercampus delivery of bound periodicals/microforms
- Interlibrary loans
- Spectrum Research Repository
- Special Collections & Archives
- Additional resources & services
- Subject & course guides
- Borrowing & renewing
- Open Educational Resources Guide
- Instructional Services
- General guides for users
- Ask a librarian
- Research Skills Tutorial
- Quick Things for Digital Knowledge
- Critical Toolkit for Navigating Information
- Bibliometrics & research impact guide
- Concordia University Press
- Copyright guide
- Copyright guide for thesis preparation
- Digital scholarship
- Digital preservation
- Open Access
- ORCiD at Concordia
- Research data management guide
- Scholarship of Teaching & Learning
- Systematic Reviews
- Borrow (laptops, tablets, equipment)
- Connect (netname, Wi-Fi, guest accounts)
- Desktop computers, software & availability maps
- Group study, presentation practice & classrooms
- Printers, copiers & scanners
- Technology Sandbox
- Visualization Studio
- Webster Library
- Vanier Library
- Grey Nuns Reading Room
- Study spaces
- Floor plans
- Book a group study room/scanner
- Room booking for academic events
- Exhibitions
- Librarians & staff
- Work with us
- Memberships & collaborations
- Indigenous Student Librarian program
- Wikipedian in residence
- Researcher in residence
- Feedback & improvement
- Annual reports & fast facts
- Strategic Plan 2016/21
- Library Services Fund
- Giving to the Library
- Policies & Code of Conduct
- My Library account
- Book a study room or scanner
- Interlibrary loans (Colombo)
- Zotero (formerly RefWorks)
- Article/Chapter Scan & Deliver
- Contactless Book Pickup
- Course reserves
Review vs. Research Articles
How can you tell if you are looking at a research paper, review paper or a systematic review examples and article characteristics are provided below to help you figure it out., research papers.
A research article describes a study that was performed by the article’s author(s). It explains the methodology of the study, such as how data was collected and analyzed, and clarifies what the results mean. Each step of the study is reported in detail so that other researchers can repeat the experiment.
To determine if a paper is a research article, examine its wording. Research articles describe actions taken by the researcher(s) during the experimental process. Look for statements like “we tested,” “I measured,” or “we investigated.” Research articles also describe the outcomes of studies. Check for phrases like “the study found” or “the results indicate.” Next, look closely at the formatting of the article. Research papers are divided into sections that occur in a particular order: abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, and references.
Let's take a closer look at this research paper by Bacon et al. published in the International Journal of Hypertension :

Review Papers
Review articles do not describe original research conducted by the author(s). Instead, they give an overview of a specific subject by examining previously published studies on the topic. The author searches for and selects studies on the subject and then tries to make sense of their findings. In particular, review articles look at whether the outcomes of the chosen studies are similar, and if they are not, attempt to explain the conflicting results. By interpreting the findings of previous studies, review articles are able to present the current knowledge and understanding of a specific topic.
Since review articles summarize the research on a particular topic, students should read them for background information before consulting detailed, technical research articles. Furthermore, review articles are a useful starting point for a research project because their reference lists can be used to find additional articles on the subject.
Let's take a closer look at this review paper by Bacon et al. published in Sports Medicine :

Systematic Review Papers
A systematic review is a type of review article that tries to limit the occurrence of bias. Traditional, non-systematic reviews can be biased because they do not include all of the available papers on the review’s topic; only certain studies are discussed by the author. No formal process is used to decide which articles to include in the review. Consequently, unpublished articles, older papers, works in foreign languages, manuscripts published in small journals, and studies that conflict with the author’s beliefs can be overlooked or excluded. Since traditional reviews do not have to explain the techniques used to select the studies, it can be difficult to determine if the author’s bias affected the review’s findings.
Systematic reviews were developed to address the problem of bias. Unlike traditional reviews, which cover a broad topic, systematic reviews focus on a single question, such as if a particular intervention successfully treats a medical condition. Systematic reviews then track down all of the available studies that address the question, choose some to include in the review, and critique them using predetermined criteria. The studies are found, selected, and evaluated using a formal, scientific methodology in order to minimize the effect of the author’s bias. The methodology is clearly explained in the systematic review so that readers can form opinions about the quality of the review.
Let's take a closer look this systematic review paper by Vigano et al. published in Lancet Oncology :
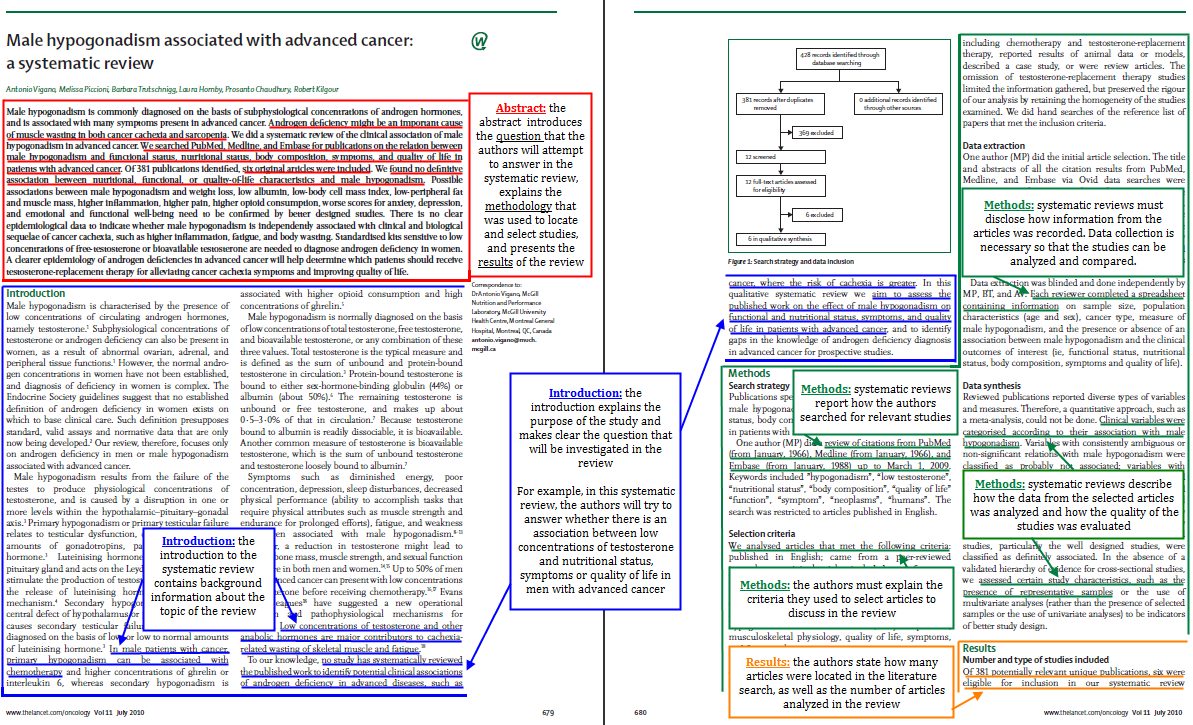
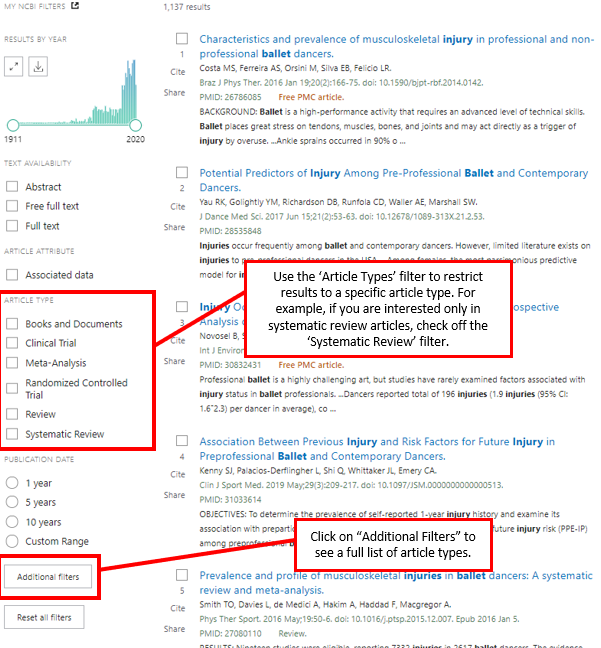
Finding Review and Research Papers in PubMed
Many databases have special features that allow the searcher to restrict results to articles that match specific criteria. In other words, only articles of a certain type will be displayed in the search results. These “limiters” can be useful when searching for research or review articles. PubMed has a limiter for article type, which is located on the left sidebar of the search results page. This limiter can filter the search results to show only review articles.
© Concordia University

Maxwell Library | Bridgewater State University
Today's Hours:
- Maxwell Library
- Scholarly Journals and Popular Magazines
- Differences in Research, Review, and Opinion Articles
Scholarly Journals and Popular Magazines: Differences in Research, Review, and Opinion Articles
- Where Do I Start?
- How Do I Find Peer-Reviewed Articles?
- How Do I Compare Periodical Types?
- Where Can I find More Information?
Research Articles, Reviews, and Opinion Pieces
Scholarly or research articles are written for experts in their fields. They are often peer-reviewed or reviewed by other experts in the field prior to publication. They often have terminology or jargon that is field specific. They are generally lengthy articles. Social science and science scholarly articles have similar structures as do arts and humanities scholarly articles. Not all items in a scholarly journal are peer reviewed. For example, an editorial opinion items can be published in a scholarly journal but the article itself is not scholarly. Scholarly journals may include book reviews or other content that have not been peer reviewed.
Empirical Study: (Original or Primary) based on observation, experimentation, or study. Clinical trials, clinical case studies, and most meta-analyses are empirical studies.
Review Article: (Secondary Sources) Article that summarizes the research in a particular subject, area, or topic. They often include a summary, an literature reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses.
Clinical case study (Primary or Original sources): These articles provide real cases from medical or clinical practice. They often include symptoms and diagnosis.
Clinical trials ( Health Research): Th ese articles are often based on large groups of people. They often include methods and control studies. They tend to be lengthy articles.
Opinion Piece: An opinion piece often includes personal thoughts, beliefs, or feelings or a judgement or conclusion based on facts. The goal may be to persuade or influence the reader that their position on this topic is the best.
Book review: Recent review of books in the field. They may be several pages but tend to be fairly short.
Social Science and Science Research Articles
The majority of social science and physical science articles include
- Journal Title and Author
- Abstract
- Introduction with a hypothesis or thesis
- Literature Review
- Methods/Methodology
- Results/Findings
Arts and Humanities Research Articles
In the Arts and Humanities, scholarly articles tend to be less formatted than in the social sciences and sciences. In the humanities, scholars are not conducting the same kinds of research experiments, but they are still using evidence to draw logical conclusions. Common sections of these articles include:
- an Introduction
- Discussion/Conclusion
- works cited/References/Bibliography
Research versus Review Articles
- 6 Article types that journals publish: A guide for early career researchers
- INFOGRAPHIC: 5 Differences between a research paper and a review paper
- Michigan State University. Empirical vs Review Articles
- UC Merced Library. Empirical & Review Articles
- << Previous: Where Do I Start?
- Next: How Do I Find Peer-Reviewed Articles? >>
- Last Updated: Jan 24, 2024 10:48 AM
- URL: https://library.bridgew.edu/scholarly
Phone: 508.531.1392 Text: 508.425.4096 Email: [email protected]
Feedback/Comments
Privacy Policy
Website Accessibility
Follow us on Facebook Follow us on Twitter

Differences Between Review Paper and Research Paper
A research paper includes original work while a review paper includes the summary of existing work which explains or solves a specific problem.
An integral part of a PhD dissertation or thesis is writing a research and review article, besides writing a thesis, proposal and synopsis. In addition, one also has to publish an article in a peer-reviewed journal which is indeed a tougher task, right!
Writing is an indispensable part of the doctorate degree and has significant value in honoring the same degree. A student when becoming a PhD candidate has to write a thesis statement, research proposal, synopsis of the doctorate, thesis, research article and review article, in chronological order.
If one fails to do so, they can’t get a degree. And that’s why writing is important. Nonetheless, students face problems while writing either research or review articles.
Supportive evidence suggests that students actually don’t know the basic and major differences between either so fail to publish both article types.
In the present piece of content, I will explain the importance of a review and research article as well as the differences between both. I am hoping that this article will add value to your knowledge and help you in your PhD.
Stay tuned.
What is a Review Paper?
What is a research paper, review vs research paper: differences, research article vs review article- similarities:, wrapping up: .
A review chapter or review articles add value to the thesis as well as existing knowledge. Universities are usually recommended to write and publish it. From students’ perspectives, review writing frightens them.
However, from a supervisors’ perspective, it should be precise, concise and nearly perfect.
Review writing is a tedious, frustrating and time-consuming process that needs special attention. The reason why it should be nearly perfect is that it supports researchers’ original work.
Technically, the review article comprises a summary of the existing research in a structured manner. Normally, it addresses the original research work and solves the existing problem by literature.
However, it can’t solve any existing problem, it doesn’t need wet-lab experimentation. It only shows the existing state of understanding of a topic. Notedly, an expert of the subject, experienced person, professor and professional scientist can usually write a review.
A research paper/article contributes original research or work of a researcher on the present topic, usually includes web lab work. Much like the review, a research article should be published in a peer-reviewed journal too.
Research article writing takes too much time as it includes research work additionally. Comprehensive writing is required to explain the materials & methods section and results & outcomes while the elaborative explanation is sufficient to introduce a topic.
Structurally a typical research article or paper has an introduction or background, Materials & Methods, Results & discussion and conclusion.
Depending upon the requirement of the journal and the depth or concentration of the research, the length of the article may vary, however, ordinarily is between 2 to 8 pages.
Much like the review article, an abstract and a list of references must be included in the article.
In summary, the research paper provides new knowledge in the relevant field and solves an existing problem by it.
Now quickly move to the important part of this article, what are the differences between the review and research paper?
A review article is certainly a comprehensive, in-depth and extensively well-written piece of information covering summaries of already present knowledge. While the research article constitutes an elaborative introduction of the topic and an in-depth explanation of how the research was conducted. It contributes new knowledge.
A review is written based on the already existing information and so considered as a secondary source of information, while the research paper has original research work supported by already existing sources.
In terms of length, a review article has an in-depth explanation and so are longer, normally, 10 to 20 pages whilst the research article has an elaborative explanation and to the point information on the problem, usually ranging from 2 to 8 pages.
The review article addresses the problem whilst the research article solves the problem, certainly.
The conclusion of the review article supports the already present findings while the result of the research article is supported by the existing research work.
The purpose of writing a research paper is to critically analyze already existing or previous work in the form of short summaries. And restricted to a specific topic.
On the other side, the research article includes the author’s own work in detail
Structurally, the review article has a single heading or sometimes a conclusion at the end of the article whilst the research article has sections like an introduction to the topic, materials & methods, results, discussion and final interpretation.
Steps in review article writing are,
- Topic finding
- Searching relevant sources
- Summarising each source
- Correlating them with the topic or problem
- Concluding the research.
Steps in research article writing are,
- Choosing a problem or gap in present findings
- Sample collection, experimentation and wet lab work
- Finding, collecting and organizing the data
- Correlating it with the present knowledge
- Stating results
- Final interpretation.
Normally, a subject expert or experienced person can write a review article while any student, or person having the original research work can write a research article.
The review article defines or clarifies a problem, explains it by compiling previous investigations and suggests problem-solving strategies or options. On the other hand, the research article has an original problem-solving statement supported by various chapters and previous research.
So the review article suggests possible outcomes to fill the knowledge gap while the research article provides evidence and new knowledge on how to fill the gap.
Summary:
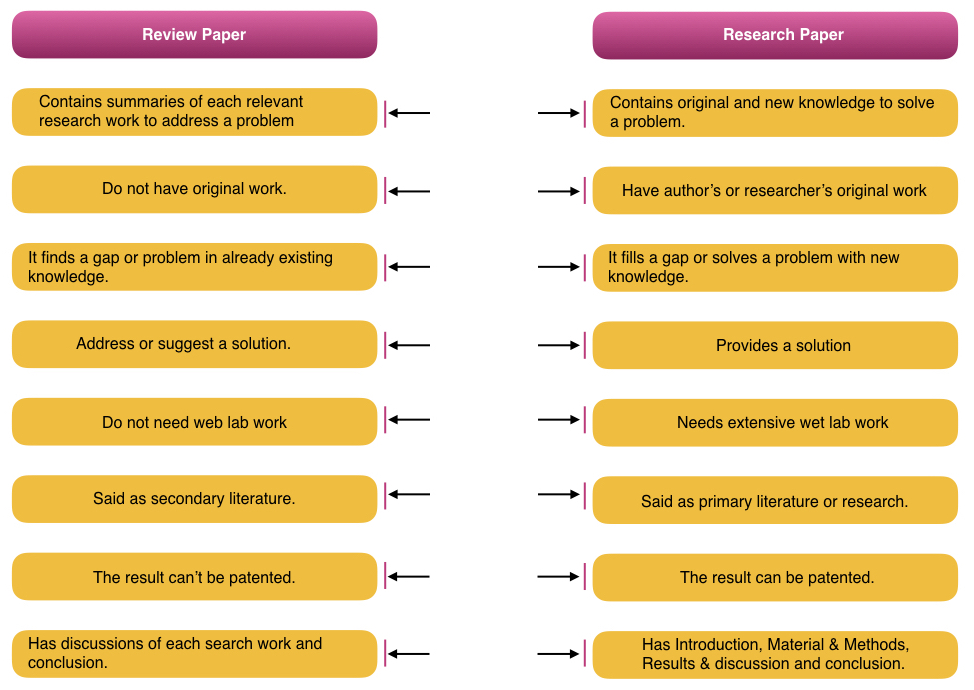
| Do not have original work. | Have author’s or researcher’s original work |
| Contains summaries of each relevant research work to address a problem | Contains original and new knowledge to solve a problem. |
| It finds a gap or problem in already existing knowledge. | It fills a gap or solves a problem with new knowledge. |
| Including comprehensive writing and elaborative explanation of each research work. | Including elaborative writing and comprehensive explanative of present research work. |
| Address or suggest a solution. | Provides a solution |
| Has discussions of each search work and conclusion. | Has Introduction, Material & Methods, Results & discussion and conclusion. |
| Do not need web lab work | Needs extensive wet lab work |
| Said as secondary literature. | Said as primary literature or research. |
| The result can’t be patented. | The result can be patented. |
Either document has been written for a different purpose which solves almost the same objective. Fortunately, there are several similarities in writing a research or review article. Hera re some,
Both have in-text citations, a references page, an abstract and contributors. Both also need a final conclusion too in order to address or solve a problem.
Research or review articles can be submitted or published in peer-reviewed journals.
Both require educational, professional, informal and research writing skills.
Importantly, both articles must be plagiarism-free, copying isn’t recommended.
Every PhD student must have written at least a single review and research article during their research or doctoral tenure to get an award. Achieving a successful publication needs critical writing skills and original research or findings.
The major difference between either is that the review article has summed information that directs one towards solving a problem and so does not include original work.
Whilst the research article actually proposes a way to solve a problem and so has original work.

Dr. Tushar Chauhan is a Scientist, Blogger and Scientific-writer. He has completed PhD in Genetics. Dr. Chauhan is a PhD coach and tutor.
Share this:

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on Linkedin
- Share via Email
About The Author

Dr Tushar Chauhan
Related posts.

Difference between M.D vs PhD

Doctorate vs PhD- differences and similarities
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
What is the difference between a review paper and a research paper?
I have been working on a review paper. After publication, how will it add on my academic research profile? When I will apply for MS or PHD admission, will it count as publication?
- publications
- review-articles
5 Answers 5
A review paper is likely also known as a "survey paper", where you read (i.e. survey) related works in the field and then comment on them. Usually, a review paper should be able to contribute a small amount of knowledge in its own right to the field by providing a taxonomy of work.
Another type of paper that reviews extensively related work but isn't actually a review paper is a "systematic review paper" in which you usually ask a meta-question about the field.
If it appears in a refereed, peer-reviewed journal, then yes, it is a publication. In fact, if done well, these works can often have pretty high impact and can be cited very frequently. However, as already noted, since they don't usually involve substantial original research they need to be augmented with traditional research papers. If a graduate student has only survey papers or systematic review papers, I'd wonder as a search committee reviewer if this student did nothing but read related work rather than working on research.
With respect to MS or PhD applications, I'd think that the fact that you have a publication at all is already a bonus point for you. Most students who apply to these programs don't have publications.
One important distinction should be made between papers in the humanities and the sciences. In the sciences, it would be much more important to have "original research" papers where new ground is broken. In the humanities, by contrast, the act of studying the existing literature and critically evaluating it may, in and of itself, be considered an act of research. (Similarly, in medicine, "meta-studies" in which the reports of various experiments are synthesized to produce overall results and recommendations may also be considered very important, although they augment direct clinical research, rather than substitute for it.)
I have limited experience regarding since I am still a graduate student but from what I understand, a review paper is also a research paper. However, unlike a piece of research, where you study the existing literature, develop research questions and hypotheses, collect data, run experiments/analysis and make inferences which accept or reject your hypotheses, a review article is a summarization and collation of existing articles in a given, specific research topic.
There has been some semi-formal writings on this already namely, this and this . The consensus, so far, seems to be that review articles make fine additions to your publication record but not as fine as articles where you actually did your own research.
I have little experience, because I am still an undergraduate student but from what I understand:
- Research paper: A paper in which results and discussion are derived from an experiment.
- Review paper: A paper in which results and discussion are not described.
- 4 Welcome to Academia SE. I have to disagree with your definitions. A research paper does not need to be based on an experiment (e.g., many mathematical papers). Also, a paper which does not describe (or derive) its results and discussions is just a very bad paper – this has nothing to do with the paper being a research or review paper. – Wrzlprmft ♦ Commented Nov 26, 2014 at 15:19
I would describe a review paper as different from a research paper. A research paper is one's original work that may be researched scientifically or otherwise, but a review paper is where someone goes through work already done/researched and gives suggestions as per that field of research. The suggestions would be if the objective, goal, problem were met by the researcher. Whether the research is of value now or in future, solutions to the problem, what is interesting, etc.
- Welcome to Academia SE. You seem to be confusing a review paper with a peer review. The downvotes you are receiving are likely due to this, i.e., to indicate that your answer is wrong. Do not take them personally. – Wrzlprmft ♦ Commented Oct 21, 2015 at 11:27
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged publications review-articles ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- Is "Alice loves candies" actually necessary for "Alice loves all sweet foods"?
- Is there a way to say "wink wink" or "nudge nudge" in German?
- Why do these finite group Dedekind matrices seem to have integer spectrum when specialized to the order of group elements?
- What is the translation of point man in French?
- Ways to paint a backbone on a tree
- chess game: loading images for the rooks
- What is the number ways to count tuples whose sum is zero?
- 1 amen for 2 berachot?
- What does it mean to have a truth value of a 'nothing' type instance?
- What makes a new chain jump other than a worn cassette?
- How would a culture living in an extremely vertical environment deal with dead bodies?
- Fourth order BVP partial differential equation
- What if something goes wrong during the seven minutes of terror?
- Very old fantasy adventure movie where the princess is captured by evil, for evil, and turned evil
- Restarted my computer and the display resolution changed
- What can cause a 24 volt solar panel to output 40 volt?
- If I purchase a house through an installment sale, can I use it as collateral for a loan?
- What is the trade union for postdocs working in Germany?
- A man hires someone to murders his wife, but she kills the attacker in self-defense. What crime has the husband committed?
- They come in twos
- How do you "stealth" a relativistic superweapon?
- What to do if sample size obtained is much larger than indicated in the power analysis?
- Why was I was allowed to bring 1.5 liters of liquid through security at Frankfurt Airport?
- Where exactly was this picture taken?
- Trending Categories

- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Difference between Research Paper and Review Paper
A research paper is written by students in which they have to conduct research on a given topic and then write the content. A review paper consists of reviews related to different articles that are already published. In this article, we will discuss the difference between a research paper and a review paper.
Research Paper
A research paper is an academic writing in which students have to collect information related to a given topic. They have to make an organized report regarding the subject which can include the research they have conducted or the research already done by other students. A peer review has to be conducted before publishing.
Steps to Write a Research Paper
Students have to follow the steps below to write a perfect research paper. These steps are discussed here.
The given assignment should be perfectly understood
Choose a topic, look for the sources of information.
- The thesis statement should be developed
- An outline of the research paper should be created
Write the first draft
Write the paragraphs properly, write the introduction, body text should be compelling, conclude the research paper, revise the research paper.
Before writing a research paper you have to understand the given assignment and then decide the specific tasks that you have to do to complete it. Here are the things that you need to do −
- Read the assignment and look for the topics that can create confusion
- Decide the length of the paper along with the options of formatting
- Make a bulleted list of all headings that you will add and then write about them
- Consider the deadline and decide the length of the research paper
Choose a topic about which you can get a large amount of content. The topic should be of your interest. You can do your own research or take help from research done by other people.
The next thing that you have to do is look for the sources from where you can get the information about the topic. Some of these sources can be discussions, books, journals, and websites. Look for the following −
- Heated debates
- Unique ideas
- Recent developments
- Overlooked but important topics
All these things will help you in devising questions related to your research topic.
Thesis statement should be developed
The next step is to develop a thesis statement which is an answer to the research question. Your answer should be supported by reasoning and pieces of evidence. The length of the thesis statement should be short and summarized.
Outline of the research paper should be created
Create an outline for the research which should include key topics, evidence, and arguments. They should be further divided into headings. This division will be helpful in writing the paper efficiently.
Write the first draft of the research paper with proper order and formatting. Your ideas should be clearly described and paragraphs should be ordered logically. You can start with the easiest or the most difficult topic. There can be situations where you have written a large amount of content for a topic. Rather than deleting it, take some part of it and paste it into another document which can be used later.
The paragraphs should be properly organized and it is better if you write each idea in a small and single paragraph. Each paragraph should not be more than three to four lines.
Now the time has come to write the introduction which should answer three questions related to your topics and these questions are what, why, and how.
This is the major part of your research paper and you may face difficulties in writing it. If you have created an outline, writing will be easy. The body text should be compelling so that the reader gets engaged in reading.
Write the conclusion of your research paper which should give a final touch to the content. Readers should understand the ways that you have used to write the paper. You can also include questions which your readers can try to answer.
Read the whole research paper and find if there is any spelling, grammatical, or factual mistakes. Check the structure of the paragraph and sentences. If there is a very long sentence, try to break it as it may become confusing for the readers.
Length of the Research Paper
The length of the research paper can be between 4,000 to 8,000 words. The minimum word count can be 2,000 and the maximum can go beyond 10,000 depending on the topic.
Review Papers
A review paper is an article which consists of surveys of the articles that are already published. No new experimental results are included in these articles. Other names of the review paper are literature review or review of literature. New conclusions can be drawn from the existing article. Review articles can explore new areas of research from the existing studies.
Steps to Write a Review Paper
Here are the steps that you have to follow to write a review paper.
Look for the aim of the article for which the review is to be written
Scope should be defined, look for the sources, choose title and keywords, topic should be introduced, critical discussion should be included, conclude the review paper.
Read the article and know about the aim and scope. All the articles do not accept reviews so you need to be very careful while choosing the article for which the review is to be written.
Find the research question and answer it with the aim of adding something new to the topic. The review should neither be too small nor too large. It should be managed easily.
You can look for the sources through search engines, books, and others. The search engines will provide a lot of sources which you can use to write the review.
Choose a proper title for your review article along with the keywords. The title will help to improve the number of views online. It will get more views if the correct readers view your article. The title should be concise, clear, and accurate and provide good information.
Write the introduction about the topic giving the reason for providing the review. The introduction should reach a large number of people which should also include non-specialists.
A critical discussion should also be included in the review paper. If the research topic is contradictory, a debate can also be included which should consist of arguments from both sides. The review paper should have the ability of resolving the conflict between contradictory studies.
A conclusion should be included at the end of the review paper. This should include the things that you have understood after studying the topic for which the review has been written.
Difference between Research paper and Review Paper
There are many differences between a research paper and a review paper and the table below includes them −
| Research Paper | Review Paper |
|---|---|
| The length of a research paper is large. | The length of the review paper is comparatively small. |
| Information is available in detail. | It is less comprehensive. |
| A research paper is written by one or more authors. | It is written by a single author. |
| A peer review is needed for the research paper. | No peer review is needed. |
| Publication of research papers is done in scholarly journals. | It can be published anywhere. |
| Scholars are the general audience of the research paper. | A review paper can be read by the general public. |
| A research paper is written to contribute to the literature. | A review paper is written to review the research. |
| The structure is complex. | The structure is comparatively easy. |
| It includes discussions and results. | These sections may not be included |
| It is organized around a central question. | It is organized around a central theme. |

- Related Articles
- Difference between Descriptive Research and Experimental Research
- Differences between E-paper and LCD
- Difference Between Correlational and Experimental Research
- Difference between Case Study and Action Research
- Make a list of various uses of papers. Observe currency notes carefully. Do you find any difference between currency paper and the paper in your notebook? Find out where currency paper is made.
- What do you mean by Blue litmus paper and Red litmus paper?
- Recycling of Paper
- Paper Chromatography - Principle, Procedure, and Applications
- If we tear the paper and then recycle it, it turns into paper again. So, is the tearing of paper a reversible change?
- Difference between Research Papers and Technical Articles for Journal Publication
- Which of the following will produce the maximum friction?(a) rubbing of sand paper on glazed paper(b) rubbing of sand paper on glass table top(c) rubbing of sand paper on aluminium frame(d) rubbing of sand paper on sand paper
- What is Litmus Paper?
- What is filter paper?
- The Value of Paper
- Rock Paper and Scissor Game Using Tkinter
Kickstart Your Career
Get certified by completing the course

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Literature Review vs Research Paper: What’s the Difference?
by Antony W
June 26, 2024

This is a complete student’s guide to understanding literature review vs research paper.
We’ll teach you what they’re, explain why they’re important, state the difference between the two, and link you to our comprehensive guide on how to write them.
Literature Review Writing Help
Writing a literature review for a thesis, a research paper, or as a standalone assignment takes time. Much of your time will go into research, not to mention you have other assignments to complete.
If you find writing in college or university overwhelming, get in touch with our literature review writers for hire at 25% discounts and enjoy the flexibility and convenience that comes with professional writing help. We’ll help you do everything, from research and outlining to custom writing and proofreading.
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review document is a secondary source of information that provides an overview of existing knowledge, which you can use to identify gaps or flaws in existing research. In literature review writing, students have to find and read existing publications such as journal articles, analyze the information, and then state their findings.
Credit: Pubrica
You’ll write a literature review to demonstrate your understanding on the topic, show gaps in existing research, and develop an effective methodology and a theoretical framework for your research project.
Your instructor may ask you to write a literature review as a standalone assignment. Even if that’s the case, the rules for writing a review paper don’t change.
In other words, you’ll still focus on evaluating the current research and find gaps around the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
There are three types of review papers and they’re a follows:
1. Meta-analysis
In meta-analysis review paper, you combine and compare answers from already published studies on a given subject.
2. Narrative Review
A narrative review paper looks into existing information or research already conducted on a given topic.
3. Systematic Review
You need to do three things if asked to write a systematic review paper.
First, read and understand the question asked. Second, look into research already conducted on the topic. Third, search for the answer to the question from the established research you just read.
What’s a Research Paper?
A research paper is an assignment in which you present your own argument, evaluation, or interpretation of an issue based on independent research.

In a research paper project, you’ll draw some conclusions from what experts have already done, find gaps in their studies, and then draw your own conclusions.
While a research paper is like an academic essay, it tends to be longer and more detailed.
Since they require extended research and attention to details, research papers can take a lot of time to write.
If well researched, your research paper can demonstrate your knowledge about a topic, your ability to engage with multiple sources, and your willingness to contribute original thoughts to an ongoing debate.
Types of Research Papers
There are two types of research papers and they’re as follows:
1. Analytical Research Papers
Similar to analytical essay , and usually in the form of a question, an analytical research paper looks at an issue from a neutral point and gives a clear analysis of the issue.
Your goal is to make the reader understand both sides of the issue in question and leave it to them to decide what side of the analysis to accept.
Unlike an argumentative research paper, an analytical research paper doesn’t include counterarguments. And you can only draw your conclusion based on the information stretched out all through the analysis.
2. Argumentative Research Papers
In an argumentative research paper, you state the subject under study, look into both sides of an issue, pick a stance, and then use solid evidence and objective reasons to defend your position.
In argumentative writing, your goal isn’t to persuade your audience to take an action.
Rather, it’s to convince them that your position on the research question is more accurate than the opposing point of views.
Regardless of the type of research paper that you write, you’ll have to follow the standard outline for the assignment to be acceptable for review and marking.
Also, all research paper, regardless of the research question under investigation must include a literature review.
Literature Review vs Research Paper
The table below shows the differences between a literature review (review paper) and a research paper.
| . Read it to learn how you can structure your review paper. | . Read it to learn how to write your research project. | |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. is there a literature review in a research paper.
A research paper assignment must include a literature review immediately after the introduction chapter.
The chapter is significant because your research work would otherwise be incomplete without knowledge of existing literature.
2. How Many Literature Review Should Be in Research Paper?
Your research paper should have only one literature review. Make sure you write the review based on the instructions from your teacher.
Before you start, check the required length, number of sources to summarize, and the format to use. Doing so will help you score top grades for the assignment.
3. What is the Difference Between Research and Literature?
Whereas literature focuses on gathering, reading, and summarizing information on already established studies, original research involves coming up with new concepts, theories, and ideas that might fill existing gaps in the available literature.
4. How Long is a Literature Review?
How long a literature review should be will depend on several factors, including the level of education, the length of the assignment, the target audience, and the purpose of the review.
For example, a 150-page dissertation can have a literature review of 40 pages on average.
Make sure you talk to your instructor to determine the required length of the assignment.
5. How Does a Literature Review Look Like?
Your literature review shouldn’t be a focus on original research or new information. Rather, it should give a clear overview of the already existing work on the selected topic.
The information to review can come from various sources, including scholarly journal articles , government reports, credible websites, and academic-based books.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
Research Paper Vs Review Paper | 50 Differences
50 Differences Between Research Article and a Review Article
A research paper is a piece of writing that reports facts, data, and other information on a specific topic. It is usually longer than a review paper and includes a detailed evaluation of the research. Whereas, a review paper is a shorter piece of writing that summarizes and evaluates the research on a specific topic. It is usually shorter than a research paper and does not include a detailed evaluation of the research. In this article, we have listed the 50 important differences between a review paper vs research article.
- A research paper is typically much longer than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more detailed and comprehensive than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more focused on a specific topic than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more analytical and critical than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more objective than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically written by one or more authors, while a review paper may be written by a single author.
- A research paper is typically peer-reviewed, while a review paper may not be.
- A research paper is typically published in a scholarly journal, while a review paper may be published in a variety of different publications.
- The audience for a research paper is typically other scholars, while the audience for a review paper may be the general public.
- The purpose of a research paper is typically to contribute to the scholarly literature, while the purpose of a review paper may be to provide an overview of the literature or to evaluate a particular research study.
- The structure of a research paper is typically more complex than the structure of a review paper.
- A research paper typically includes an abstract, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes a literature review, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes a methodology section, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes results and discussion sections, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes a conclusion, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper is typically organized around a central research question , while a review paper may be organized around a central theme.
- A research paper typically uses primary sources, while a review paper may use both primary and secondary sources.
- A research paper is typically based on empirical research, while a review paper may be based on either empirical or non-empirical research.
- A research paper is typically more formal than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically written in the third person, while a review paper may be written in the first person.
- A research paper typically uses formal language, while a review paper may use more informal language.
- A research paper is typically objective in tone, while a review paper may be more subjective in tone.
- A research paper typically uses APA style, while a review paper may use a different style.
- A research paper typically includes a title page, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes an abstract on the title page, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes keywords on the title page, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes an author note, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper is typically organized around a central research question, while a review paper may be organized around a central theme.
- A research paper is typically longer than a review paper.
I hope, this article would help you to know the differences between Research Paper and a Review Paper.
Also Read: What is a Research Design? Importance and Types

- Difference between
- evaluation review paper
- Research Paper
Working Sci-Hub Proxy Links 2024: Access Research Papers Easily
10 types of plagiarism – every academic writer should know – updated, the harsh reality: why revoked graduate degrees aren’t easily reclaimed, most popular, abstract template for research paper, top 50 research institutions in india: nirf rankings 2024, top 35 scopus indexed journals in english literature, how to create graphical abstract, list of research topics in environmental engineering, indo-russian joint research call for proposals 2024, newly accepted scopus indexed journals june 2024, best for you, 24 best online plagiarism checker free – 2024, what is phd, popular posts, top 10 scopus indexed agronomy and crop science journals, popular category.
- POSTDOC 317
- Interesting 257
- Journals 235
- Fellowship 133
- Research Methodology 102
- All Scopus Indexed Journals 93
Mail Subscription

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
Contact us: [email protected]
Google News
Copyright © 2024 iLovePhD. All rights reserved
- Artificial intelligence

Difference Between | Descriptive Analysis and Comparisons
Search form, difference between research paper and review paper.
Key Difference: The primary difference between a research paper and a review paper is that a research paper is based on the author’s original research and their analysis and interpretation of their research finishing, whereas a review paper collects and collates information on a particular topic from various different written publications.
A research paper involves writing about research that one has conducted themselves. It includes the parameters involved in the research as well as their analysis and interpretation of the research.
Writing a research paper involves many different steps such as selecting a topic, creating a hypothesis, doing research, testing the hypothesis, making conclusions, and writing a paper supporting or disproving the hypothesis.
A review paper, on the other hand, involves collection information from a variety of different sources. These sources can be primary or secondary. Primary sources can be people who have conducted research and have first hand information, whereas secondary sources are papers and documents that have covered the topic on hand.
A review paper collects and combines information from these various sources and presents in all in one place. The benefit of this that it makes information regarding a particular topic easier to find and reference. A student may be asked to support an argument or a hypothesis in a review paper by citing various works and sources of information.
Review papers can be categorized into three different types: -
- Narrative – which collects and attempts to explain any and all existing knowledge on a particular topic. It is based on research that is already conducted and published by someone else.
- Systematic – in which one searches all existing scientific literature on a topic and tries to find an answer to a particular question or problem.
- Meta-analysis – which compares and combines the findings of previously published studies. It is usually done in order to assess the effectiveness of an intervention or mode of treatment.
The job of a research paper is for one to be able to present new ideas and new information which can hep move science ahead, whereas a review paper allows one to combine ideas by collecting information from various sources, which makes information easier to find and refer to.
Comparison between Research Paper and Review Paper:
|
|
|
|
| Definition (Oxford Dictionaries) | The systematic investigation into and study of materials and sources in order to establish facts and reach new conclusions. | A formal assessment of something with the intention of instituting change if necessary. A critical appraisal of a book, play, film, etc. published in a newspaper or magazine. |
| Type | Academic Paper | Academic Paper |
| Used in | Schools, Colleges, Universities, Academies, certain fields of work and study, etc. | Schools, Colleges, Universities, Academies, certain fields of work and study, etc. |
| Based on | Original Research and Raw Data | Existing Literature and other sources of work |
| Purpose | To present new ideas, information, and research | To collect information about a particular topic in one place and to critically analyze that information |
| Type of source | Primary literature | Secondary literature |
Add new comment
Copyright © 2024, Difference Between | Descriptive Analysis and Comparisons
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- ScientificWorldJournal
- v.2024; 2024
- PMC10807936

Writing a Scientific Review Article: Comprehensive Insights for Beginners
Ayodeji amobonye.
1 Department of Biotechnology and Food Science, Faculty of Applied Sciences, Durban University of Technology, P.O. Box 1334, KwaZulu-Natal, Durban 4000, South Africa
2 Writing Centre, Durban University of Technology, P.O. Box 1334 KwaZulu-Natal, Durban 4000, South Africa
Japareng Lalung
3 School of Industrial Technology, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Gelugor 11800, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Santhosh Pillai
Associated data.
The data and materials that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Review articles present comprehensive overview of relevant literature on specific themes and synthesise the studies related to these themes, with the aim of strengthening the foundation of knowledge and facilitating theory development. The significance of review articles in science is immeasurable as both students and researchers rely on these articles as the starting point for their research. Interestingly, many postgraduate students are expected to write review articles for journal publications as a way of demonstrating their ability to contribute to new knowledge in their respective fields. However, there is no comprehensive instructional framework to guide them on how to analyse and synthesise the literature in their niches into publishable review articles. The dearth of ample guidance or explicit training results in students having to learn all by themselves, usually by trial and error, which often leads to high rejection rates from publishing houses. Therefore, this article seeks to identify these challenges from a beginner's perspective and strives to plug the identified gaps and discrepancies. Thus, the purpose of this paper is to serve as a systematic guide for emerging scientists and to summarise the most important information on how to write and structure a publishable review article.
1. Introduction
Early scientists, spanning from the Ancient Egyptian civilization to the Scientific Revolution of the 16 th /17 th century, based their research on intuitions, personal observations, and personal insights. Thus, less time was spent on background reading as there was not much literature to refer to. This is well illustrated in the case of Sir Isaac Newton's apple tree and the theory of gravity, as well as Gregor Mendel's pea plants and the theory of inheritance. However, with the astronomical expansion in scientific knowledge and the emergence of the information age in the last century, new ideas are now being built on previously published works, thus the periodic need to appraise the huge amount of already published literature [ 1 ]. According to Birkle et al. [ 2 ], the Web of Science—an authoritative database of research publications and citations—covered more than 80 million scholarly materials. Hence, a critical review of prior and relevant literature is indispensable for any research endeavour as it provides the necessary framework needed for synthesising new knowledge and for highlighting new insights and perspectives [ 3 ].
Review papers are generally considered secondary research publications that sum up already existing works on a particular research topic or question and relate them to the current status of the topic. This makes review articles distinctly different from scientific research papers. While the primary aim of the latter is to develop new arguments by reporting original research, the former is focused on summarising and synthesising previous ideas, studies, and arguments, without adding new experimental contributions. Review articles basically describe the content and quality of knowledge that are currently available, with a special focus on the significance of the previous works. To this end, a review article cannot simply reiterate a subject matter, but it must contribute to the field of knowledge by synthesising available materials and offering a scholarly critique of theory [ 4 ]. Typically, these articles critically analyse both quantitative and qualitative studies by scrutinising experimental results, the discussion of the experimental data, and in some instances, previous review articles to propose new working theories. Thus, a review article is more than a mere exhaustive compilation of all that has been published on a topic; it must be a balanced, informative, perspective, and unbiased compendium of previous studies which may also include contrasting findings, inconsistencies, and conventional and current views on the subject [ 5 ].
Hence, the essence of a review article is measured by what is achieved, what is discovered, and how information is communicated to the reader [ 6 ]. According to Steward [ 7 ], a good literature review should be analytical, critical, comprehensive, selective, relevant, synthetic, and fully referenced. On the other hand, a review article is considered to be inadequate if it is lacking in focus or outcome, overgeneralised, opinionated, unbalanced, and uncritical [ 7 ]. Most review papers fail to meet these standards and thus can be viewed as mere summaries of previous works in a particular field of study. In one of the few studies that assessed the quality of review articles, none of the 50 papers that were analysed met the predefined criteria for a good review [ 8 ]. However, beginners must also realise that there is no bad writing in the true sense; there is only writing in evolution and under refinement. Literally, every piece of writing can be improved upon, right from the first draft until the final published manuscript. Hence, a paper can only be referred to as bad and unfixable when the author is not open to corrections or when the writer gives up on it.
According to Peat et al. [ 9 ], “everything is easy when you know how,” a maxim which applies to scientific writing in general and review writing in particular. In this regard, the authors emphasized that the writer should be open to learning and should also follow established rules instead of following a blind trial-and-error approach. In contrast to the popular belief that review articles should only be written by experienced scientists and researchers, recent trends have shown that many early-career scientists, especially postgraduate students, are currently expected to write review articles during the course of their studies. However, these scholars have little or no access to formal training on how to analyse and synthesise the research literature in their respective fields [ 10 ]. Consequently, students seeking guidance on how to write or improve their literature reviews are less likely to find published works on the subject, particularly in the science fields. Although various publications have dealt with the challenges of searching for literature, or writing literature reviews for dissertation/thesis purposes, there is little or no information on how to write a comprehensive review article for publication. In addition to the paucity of published information to guide the potential author, the lack of understanding of what constitutes a review paper compounds their challenges. Thus, the purpose of this paper is to serve as a guide for writing review papers for journal publishing. This work draws on the experience of the authors to assist early-career scientists/researchers in the “hard skill” of authoring review articles. Even though there is no single path to writing scientifically, or to writing reviews in particular, this paper attempts to simplify the process by looking at this subject from a beginner's perspective. Hence, this paper highlights the differences between the types of review articles in the sciences while also explaining the needs and purpose of writing review articles. Furthermore, it presents details on how to search for the literature as well as how to structure the manuscript to produce logical and coherent outputs. It is hoped that this work will ease prospective scientific writers into the challenging but rewarding art of writing review articles.
2. Benefits of Review Articles to the Author
Analysing literature gives an overview of the “WHs”: WHat has been reported in a particular field or topic, WHo the key writers are, WHat are the prevailing theories and hypotheses, WHat questions are being asked (and answered), and WHat methods and methodologies are appropriate and useful [ 11 ]. For new or aspiring researchers in a particular field, it can be quite challenging to get a comprehensive overview of their respective fields, especially the historical trends and what has been studied previously. As such, the importance of review articles to knowledge appraisal and contribution cannot be overemphasised, which is reflected in the constant demand for such articles in the research community. However, it is also important for the author, especially the first-time author, to recognise the importance of his/her investing time and effort into writing a quality review article.
Generally, literature reviews are undertaken for many reasons, mainly for publication and for dissertation purposes. The major purpose of literature reviews is to provide direction and information for the improvement of scientific knowledge. They also form a significant component in the research process and in academic assessment [ 12 ]. There may be, however, a thin line between a dissertation literature review and a published review article, given that with some modifications, a literature review can be transformed into a legitimate and publishable scholarly document. According to Gülpınar and Güçlü [ 6 ], the basic motivation for writing a review article is to make a comprehensive synthesis of the most appropriate literature on a specific research inquiry or topic. Thus, conducting a literature review assists in demonstrating the author's knowledge about a particular field of study, which may include but not be limited to its history, theories, key variables, vocabulary, phenomena, and methodologies [ 10 ]. Furthermore, publishing reviews is beneficial as it permits the researchers to examine different questions and, as a result, enhances the depth and diversity of their scientific reasoning [ 1 ]. In addition, writing review articles allows researchers to share insights with the scientific community while identifying knowledge gaps to be addressed in future research. The review writing process can also be a useful tool in training early-career scientists in leadership, coordination, project management, and other important soft skills necessary for success in the research world [ 13 ]. Another important reason for authoring reviews is that such publications have been observed to be remarkably influential, extending the reach of an author in multiple folds of what can be achieved by primary research papers [ 1 ]. The trend in science is for authors to receive more citations from their review articles than from their original research articles. According to Miranda and Garcia-Carpintero [ 14 ], review articles are, on average, three times more frequently cited than original research articles; they also asserted that a 20% increase in review authorship could result in a 40–80% increase in citations of the author. As a result, writing reviews can significantly impact a researcher's citation output and serve as a valuable channel to reach a wider scientific audience. In addition, the references cited in a review article also provide the reader with an opportunity to dig deeper into the topic of interest. Thus, review articles can serve as a valuable repository for consultation, increasing the visibility of the authors and resulting in more citations.
3. Types of Review Articles
The first step in writing a good literature review is to decide on the particular type of review to be written; hence, it is important to distinguish and understand the various types of review articles. Although scientific review articles have been classified according to various schemes, however, they are broadly categorised into narrative reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses [ 15 ]. It was observed that more authors—as well as publishers—were leaning towards systematic reviews and meta-analysis while downplaying narrative reviews; however, the three serve different aims and should all be considered equally important in science [ 1 ]. Bibliometric reviews and patent reviews, which are closely related to meta-analysis, have also gained significant attention recently. However, from another angle, a review could also be of two types. In the first class, authors could deal with a widely studied topic where there is already an accumulated body of knowledge that requires analysis and synthesis [ 3 ]. At the other end of the spectrum, the authors may have to address an emerging issue that would benefit from exposure to potential theoretical foundations; hence, their contribution would arise from the fresh theoretical foundations proposed in developing a conceptual model [ 3 ].
3.1. Narrative Reviews
Narrative reviewers are mainly focused on providing clarification and critical analysis on a particular topic or body of literature through interpretative synthesis, creativity, and expert judgement. According to Green et al. [ 16 ], a narrative review can be in the form of editorials, commentaries, and narrative overviews. However, editorials and commentaries are usually expert opinions; hence, a beginner is more likely to write a narrative overview, which is more general and is also referred to as an unsystematic narrative review. Similarly, the literature review section of most dissertations and empirical papers is typically narrative in nature. Typically, narrative reviews combine results from studies that may have different methodologies to address different questions or to formulate a broad theoretical formulation [ 1 ]. They are largely integrative as strong focus is placed on the assimilation and synthesis of various aspects in the review, which may involve comparing and contrasting research findings or deriving structured implications [ 17 ]. In addition, they are also qualitative studies because they do not follow strict selection processes; hence, choosing publications is relatively more subjective and unsystematic [ 18 ]. However, despite their popularity, there are concerns about their inherent subjectivity. In many instances, when the supporting data for narrative reviews are examined more closely, the evaluations provided by the author(s) become quite questionable [ 19 ]. Nevertheless, if the goal of the author is to formulate a new theory that connects diverse strands of research, a narrative method is most appropriate.
3.2. Systematic Reviews
In contrast to narrative reviews, which are generally descriptive, systematic reviews employ a systematic approach to summarise evidence on research questions. Hence, systematic reviews make use of precise and rigorous criteria to identify, evaluate, and subsequently synthesise all relevant literature on a particular topic [ 12 , 20 ]. As a result, systematic reviews are more likely to inspire research ideas by identifying knowledge gaps or inconsistencies, thus helping the researcher to clearly define the research hypotheses or questions [ 21 ]. Furthermore, systematic reviews may serve as independent research projects in their own right, as they follow a defined methodology to search and combine reliable results to synthesise a new database that can be used for a variety of purposes [ 22 ]. Typically, the peculiarities of the individual reviewer, different search engines, and information databases used all ensure that no two searches will yield the same systematic results even if the searches are conducted simultaneously and under identical criteria [ 11 ]. Hence, attempts are made at standardising the exercise via specific methods that would limit bias and chance effects, prevent duplications, and provide more accurate results upon which conclusions and decisions can be made.
The most established of these methods is the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines which objectively defined statements, guidelines, reporting checklists, and flowcharts for undertaking systematic reviews as well as meta-analysis [ 23 ]. Though mainly designed for research in medical sciences, the PRISMA approach has gained wide acceptance in other fields of science and is based on eight fundamental propositions. These include the explicit definition of the review question, an unambiguous outline of the study protocol, an objective and exhaustive systematic review of reputable literature, and an unambiguous identification of included literature based on defined selection criteria [ 24 ]. Other considerations include an unbiased appraisal of the quality of the selected studies (literature), organic synthesis of the evidence of the study, preparation of the manuscript based on the reporting guidelines, and periodic update of the review as new data emerge [ 24 ]. Other methods such as PRISMA-P (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analysis Protocols), MOOSE (Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology), and ROSES (Reporting Standards for Systematic Evidence Syntheses) have since been developed for systematic reviews (and meta-analysis), with most of them being derived from PRISMA.
Consequently, systematic reviews—unlike narrative reviews—must contain a methodology section which in addition to all that was highlighted above must fully describe the precise criteria used in formulating the research question and setting the inclusion or exclusion criteria used in selecting/accessing the literature. Similarly, the criteria for evaluating the quality of the literature included in the review as well as for analysing, synthesising, and disseminating the findings must be fully described in the methodology section.
3.3. Meta-Analysis
Meta-analyses are considered as more specialised forms of systematic reviews. Generally, they combine the results of many studies that use similar or closely related methods to address the same question or share a common quantitative evaluation method [ 25 ]. However, meta-analyses are also a step higher than other systematic reviews as they are focused on numerical data and involve the use of statistics in evaluating different studies and synthesising new knowledge. The major advantage of this type of review is the increased statistical power leading to more reliable results for inferring modest associations and a more comprehensive understanding of the true impact of a research study [ 26 ]. Unlike in traditional systematic reviews, research topics covered in meta-analyses must be mature enough to allow the inclusion of sufficient homogeneous empirical research in terms of subjects, interventions, and outcomes [ 27 , 28 ].
Being an advanced form of systematic review, meta-analyses must also have a distinct methodology section; hence, the standard procedures involved in the traditional systematic review (especially PRISMA) also apply in meta-analyses [ 23 ]. In addition to the common steps in formulating systematic reviews, meta-analyses are required to describe how nested and missing data are handled, the effect observed in each study, the confidence interval associated with each synthesised effect, and any potential for bias presented within the sample(s) [ 17 ]. According to Paul and Barari [ 28 ], a meta-analysis must also detail the final sample, the meta-analytic model, and the overall analysis, moderator analysis, and software employed. While the overall analysis involves the statistical characterization of the relationships between variables in the meta-analytic framework and their significance, the moderator analysis defines the different variables that may affect variations in the original studies [ 28 , 29 ]. It must also be noted that the accuracy and reliability of meta-analyses have both been significantly enhanced by the incorporation of statistical approaches such as Bayesian analysis [ 30 ], network analysis [ 31 ], and more recently, machine learning [ 32 ].
3.4. Bibliometric Review
A bibliometric review, commonly referred to as bibliometric analysis, is a systematic evaluation of published works within a specific field or discipline [ 33 ]. This bibliometric methodology involves the use of quantitative methods to analyse bibliometric data such as the characteristics and numbers of publications, units of citations, authorship, co-authorship, and journal impact factors [ 34 ]. Academics use bibliometric analysis with different objectives in mind, which includes uncovering emerging trends in article and journal performance, elaborating collaboration patterns and research constituents, evaluating the impact and influence of particular authors, publications, or research groups, and highlighting the intellectual framework of a certain field [ 35 ]. It is also used to inform policy and decision-making. Similarly to meta-analysis, bibliometric reviews rely upon quantitative techniques, thus avoiding the interpretation bias that could arise from the qualitative techniques of other types of reviews [ 36 ]. However, while bibliometric analysis synthesises the bibliometric and intellectual structure of a field by examining the social and structural linkages between various research parts, meta-analysis focuses on summarising empirical evidence by probing the direction and strength of effects and relationships among variables, especially in open research questions [ 37 , 38 ]. However, similarly to systematic review and meta-analysis, a bibliometric review also requires a well-detailed methodology section. The amount of data to be analysed in bibliometric analysis is quite massive, running to hundreds and tens of thousands in some cases. Although the data are objective in nature (e.g., number of citations and publications and occurrences of keywords and topics), the interpretation is usually carried out through both objective (e.g., performance analysis) and subjective (e.g., thematic analysis) evaluations [ 35 ]. However, the invention and availability of bibliometric software such as BibExcel, Gephi, Leximancer, and VOSviewer and scientific databases such as Dimensions, Web of Science, and Scopus have made this type of analysis more feasible.
3.5. Patent Review
Patent reviews provide a comprehensive analysis and critique of a specific patent or a group of related patents, thus presenting a concise understanding of the technology or innovation that is covered by the patent [ 39 ]. This type of article is useful for researchers as it also enhances their understanding of the legal, technical, and commercial aspects of an intellectual property/innovation; in addition, it is also important for stakeholders outside the research community including IP (intellectual property) specialists, legal professionals, and technology-transfer officers [ 40 ]. Typically, patent reviews encompass the scope, background, claims, legal implications, technical specifications, and potential commercial applications of the patent(s). The article may also include a discussion of the patent's strengths and weaknesses, as well as its potential impact on the industry or field in which it operates. Most times, reviews are time specified, they may be regionalised, and the data are usually retrieved via patent searches on databases such as that of the European Patent Office ( https://www.epo.org/searching.html ), United States Patent and Trademark Office ( https://patft.uspto.gov/ ), the World Intellectual Property Organization's PATENTSCOPE ( https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/structuredSearch.jsf ), Google Patent ( https://www.google.com/?tbm=pts ), and China National Intellectual Property Administration ( https://pss-system.cponline.cnipa.gov.cn/conventionalSearch ). According to Cerimi et al. [ 41 ], the retrieved data and analysed may include the patent number, patent status, filing date, application date, grant dates, inventor, assignee, and pending applications. While data analysis is usually carried out by general data software such as Microsoft Excel, an intelligence software solely dedicated to patent research and analysis, Orbit Intelligence has been found to be more efficient [ 39 ]. It is also mandatory to include a methodology section in a patent review, and this should be explicit, thorough, and precise to allow a clear understanding of how the analysis was carried out and how the conclusions were arrived at.
4. Searching Literature
One of the most challenging tasks in writing a review article on a subject is the search for relevant literature to populate the manuscript as the author is required to garner information from an endless number of sources. This is even more challenging as research outputs have been increasing astronomically, especially in the last decade, with thousands of new articles published annually in various fields. It is therefore imperative that the author must not only be aware of the overall trajectory in a field of investigation but must also be cognizant of recent studies so as not to publish outdated research or review articles. Basically, the search for the literature involves a coherent conceptual structuring of the topic itself and a thorough collation of evidence under the common themes which might reflect the histories, conflicts, standoffs, revolutions, and/or evolutions in the field [ 7 ]. To start the search process, the author must carefully identify and select broad keywords relevant to the subject; subsequently, the keywords should be developed to refine the search into specific subheadings that would facilitate the structure of the review.
Two main tactics have been identified for searching the literature, namely, systematic and snowballing [ 42 ]. The systematic approach involves searching literature with specific keywords (for example, cancer, antioxidant, and nanoparticles), which leads to an almost unmanageable and overwhelming list of possible sources [ 43 ]. The snowballing approach, however, involves the identification of a particular publication, followed by the compilation of a bibliography of articles based on the reference list of the identified publication [ 44 ]. Many times, it might be necessary to combine both approaches, but irrespective, the author must keep an accurate track and record of papers cited in the search. A simple and efficient strategy for populating the bibliography of review articles is to go through the abstract (and sometimes the conclusion) of a paper; if the abstract is related to the topic of discourse, the author might go ahead and read the entire article; otherwise, he/she is advised to move on [ 45 ]. Winchester and Salji [ 5 ] noted that to learn the background of the subject/topic to be reviewed, starting literature searches with academic textbooks or published review articles is imperative, especially for beginners. Furthermore, it would also assist in compiling the list of keywords, identifying areas of further exploration, and providing a glimpse of the current state of the research. However, past reviews ideally are not to serve as the foundation of a new review as they are written from someone else's viewpoint, which might have been tainted with some bias. Fortunately, the accessibility and search for the literature have been made relatively easier than they were a few decades ago as the current information age has placed an enormous volume of knowledge right at our fingertips [ 46 ]. Nevertheless, when gathering the literature from the Internet, authors should exercise utmost caution as much of the information may not be verified or peer-reviewed and thus may be unregulated and unreliable. For instance, Wikipedia, despite being a large repository of information with more than 6.7 million articles in the English language alone, is considered unreliable for scientific literature reviews, due to its openness to public editing [ 47 ]. However, in addition to peer-reviewed journal publications—which are most ideal—reviews can also be drawn from a wide range of other sources such as technical documents, in-house reports, conference abstracts, and conference proceedings. Similarly, “Google Scholar”—as against “Google” and other general search engines—is more appropriate as its searches are restricted to only academic articles produced by scholarly societies or/and publishers [ 48 ]. Furthermore, the various electronic databases, such as ScienceDirect, Web of Science, PubMed, and MEDLINE, many of which focus on specific fields of research, are also ideal options [ 49 ]. Advancement in computer indexing has remarkably expanded the ease and ability to search large databases for every potentially relevant article. In addition to searching by topic, literature search can be modified by time; however, there must be a balance between old papers and recent ones. The general consensus in science is that publications less than five years old are considered recent.
It is important, especially in systematic reviews and meta-analyses, that the specific method of running the computer searches be properly documented as there is the need to include this in the method (methodology) section of such papers. Typically, the method details the keywords, databases explored, search terms used, and the inclusion/exclusion criteria applied in the selection of data and any other specific decision/criteria. All of these will ensure the reproducibility and thoroughness of the search and the selection procedure. However, Randolph [ 10 ] noted that Internet searches might not give the exhaustive list of articles needed for a review article; hence, it is advised that authors search through the reference lists of articles that were obtained initially from the Internet search. After determining the relevant articles from the list, the author should read through the references of these articles and repeat the cycle until saturation is reached [ 10 ]. After populating the articles needed for the literature review, the next step is to analyse them individually and in their whole entirety. A systematic approach to this is to identify the key information within the papers, examine them in depth, and synthesise original perspectives by integrating the information and making inferences based on the findings. In this regard, it is imperative to link one source to the other in a logical manner, for instance, taking note of studies with similar methodologies, papers that agree, or results that are contradictory [ 42 ].
5. Structuring the Review Article
The title and abstract are the main selling points of a review article, as most readers will only peruse these two elements and usually go on to read the full paper if they are drawn in by either or both of the two. Tullu [ 50 ] recommends that the title of a scientific paper “should be descriptive, direct, accurate, appropriate, interesting, concise, precise, unique, and not be misleading.” In addition to providing “just enough details” to entice the reader, words in the titles are also used by electronic databases, journal websites, and search engines to index and retrieve a particular paper during a search [ 51 ]. Titles are of different types and must be chosen according to the topic under review. They are generally classified as descriptive, declarative, or interrogative and can also be grouped into compound, nominal, or full-sentence titles [ 50 ]. The subject of these categorisations has been extensively discussed in many articles; however, the reader must also be aware of the compound titles, which usually contain a main title and a subtitle. Typically, subtitles provide additional context—to the main title—and they may specify the geographic scope of the research, research methodology, or sample size [ 52 ].
Just like primary research articles, there are many debates about the optimum length of a review article's title. However, the general consensus is to keep the title as brief as possible while not being too general. A title length between 10 and 15 words is recommended, since longer titles can be more challenging to comprehend. Paiva et al. [ 53 ] observed that articles which contain 95 characters or less get more views and citations. However, emphasis must be placed on conciseness as the audience will be more satisfied if they can understand what exactly the review has contributed to the field, rather than just a hint about the general topic area. Authors should also endeavour to stick to the journal's specific requirements, especially regarding the length of the title and what they should or should not contain [ 9 ]. Thus, avoidance of filler words such as “a review on/of,” “an observation of,” or “a study of” is a very simple way to limit title length. In addition, abbreviations or acronyms should be avoided in the title, except the standard or commonly interpreted ones such as AIDS, DNA, HIV, and RNA. In summary, to write an effective title, the authors should consider the following points. What is the paper about? What was the methodology used? What were the highlights and major conclusions? Subsequently, the author should list all the keywords from these answers, construct a sentence from these keywords, and finally delete all redundant words from the sentence title. It is also possible to gain some ideas by scanning indices and article titles in major journals in the field. It is important to emphasise that a title is not chosen and set in stone, and the title is most likely to be continually revised and adjusted until the end of the writing process.
5.2. Abstract
The abstract, also referred to as the synopsis, is a summary of the full research paper; it is typically independent and can stand alone. For most readers, a publication does not exist beyond the abstract, partly because abstracts are often the only section of a paper that is made available to the readers at no cost, whereas the full paper may attract a payment or subscription [ 54 ]. Thus, the abstract is supposed to set the tone for the few readers who wish to read the rest of the paper. It has also been noted that the abstract gives the first impression of a research work to journal editors, conference scientific committees, or referees, who might outright reject the paper if the abstract is poorly written or inadequate [ 50 ]. Hence, it is imperative that the abstract succinctly represents the entire paper and projects it positively. Just like the title, abstracts have to be balanced, comprehensive, concise, functional, independent, precise, scholarly, and unbiased and not be misleading [ 55 ]. Basically, the abstract should be formulated using keywords from all the sections of the main manuscript. Thus, it is pertinent that the abstract conveys the focus, key message, rationale, and novelty of the paper without any compromise or exaggeration. Furthermore, the abstract must be consistent with the rest of the paper; as basic as this instruction might sound, it is not to be taken for granted. For example, a study by Vrijhoef and Steuten [ 56 ] revealed that 18–68% of 264 abstracts from some scientific journals contained information that was inconsistent with the main body of the publications.
Abstracts can either be structured or unstructured; in addition, they can further be classified as either descriptive or informative. Unstructured abstracts, which are used by many scientific journals, are free flowing with no predefined subheadings, while structured abstracts have specific subheadings/subsections under which the abstract needs to be composed. Structured abstracts have been noted to be more informative and are usually divided into subsections which include the study background/introduction, objectives, methodology design, results, and conclusions [ 57 ]. No matter the style chosen, the author must carefully conform to the instructions provided by the potential journal of submission, which may include but are not limited to the format, font size/style, word limit, and subheadings [ 58 ]. The word limit for abstracts in most scientific journals is typically between 150 and 300 words. It is also a general rule that abstracts do not contain any references whatsoever.
Typically, an abstract should be written in the active voice, and there is no such thing as a perfect abstract as it could always be improved on. It is advised that the author first makes an initial draft which would contain all the essential parts of the paper, which could then be polished subsequently. The draft should begin with a brief background which would lead to the research questions. It might also include a general overview of the methodology used (if applicable) and importantly, the major results/observations/highlights of the review paper. The abstract should end with one or few sentences about any implications, perspectives, or future research that may be developed from the review exercise. Finally, the authors should eliminate redundant words and edit the abstract to the correct word count permitted by the journal [ 59 ]. It is always beneficial to read previous abstracts published in the intended journal, related topics/subjects from other journals, and other reputable sources. Furthermore, the author should endeavour to get feedback on the abstract especially from peers and co-authors. As the abstract is the face of the whole paper, it is best that it is the last section to be finalised, as by this time, the author would have developed a clearer understanding of the findings and conclusions of the entire paper.
5.3. Graphical Abstracts
Since the mid-2000s, an increasing number of journals now require authors to provide a graphical abstract (GA) in addition to the traditional written abstract, to increase the accessibility of scientific publications to readers [ 60 ]. A study showed that publications with GA performed better than those without it, when the abstract views, total citations, and downloads were compared [ 61 ]. However, the GA should provide “a single, concise pictorial, and visual summary of the main findings of an article” [ 62 ]. Although they are meant to be a stand-alone summary of the whole paper, it has been noted that they are not so easily comprehensible without having read through the traditionally written abstract [ 63 ]. It is important to note that, like traditional abstracts, many reputable journals require GAs to adhere to certain specifications such as colour, dimension, quality, file size, and file format (usually JPEG/JPG, PDF, PNG, or TIFF). In addition, it is imperative to use engaging and accurate figures, all of which must be synthesised in order to accurately reflect the key message of the paper. Currently, there are various online or downloadable graphical tools that can be used for creating GAs, such as Microsoft Paint or PowerPoint, Mindthegraph, ChemDraw, CorelDraw, and BioRender.
5.4. Keywords
As a standard practice, journals require authors to select 4–8 keywords (or phrases), which are typically listed below the abstract. A good set of keywords will enable indexers and search engines to find relevant papers more easily and can be considered as a very concise abstract [ 64 ]. According to Dewan and Gupta [ 51 ], the selection of appropriate keywords will significantly enhance the retrieval, accession, and consequently, the citation of the review paper. Ideally, keywords can be variants of the terms/phrases used in the title, the abstract, and the main text, but they should ideally not be the exact words in the main title. Choosing the most appropriate keywords for a review article involves listing down the key terms and phrases in the article, including abbreviations. Subsequently, a quick review of the glossary/vocabulary/term list or indexing standard in the specific discipline will assist in selecting the best and most precise keywords that match those used in the databases from the list drawn. In addition, the keywords should not be broad or general terms (e.g., DNA, biology, and enzymes) but must be specific to the field or subfield of study as well as to the particular paper [ 65 ].
5.5. Introduction
The introduction of an article is the first major section of the manuscript, and it presents basic information to the reader without compelling them to study past publications. In addition, the introduction directs the reader to the main arguments and points developed in the main body of the article while clarifying the current state of knowledge in that particular area of research [ 12 ]. The introduction part of a review article is usually sectionalised into background information, a description of the main topic and finally a statement of the main purpose of the review [ 66 ]. Authors may begin the introduction with brief general statements—which provide background knowledge on the subject matter—that lead to more specific ones [ 67 ]. It is at this point that the reader's attention must be caught as the background knowledge must highlight the importance and justification for the subject being discussed, while also identifying the major problem to be addressed [ 68 ]. In addition, the background should be broad enough to attract even nonspecialists in the field to maximise the impact and widen the reach of the article. All of these should be done in the light of current literature; however, old references may also be used for historical purposes. A very important aspect of the introduction is clearly stating and establishing the research problem(s) and how a review of the particular topic contributes to those problem(s). Thus, the research gap which the paper intends to fill, the limitations of previous works and past reviews, if available, and the new knowledge to be contributed must all be highlighted. Inadequate information and the inability to clarify the problem will keep readers (who have the desire to obtain new information) from reading beyond the introduction [ 69 ]. It is also pertinent that the author establishes the purpose of reviewing the literature and defines the scope as well as the major synthesised point of view. Furthermore, a brief insight into the criteria used to select, evaluate, and analyse the literature, as well as the outline or sequence of the review, should be provided in the introduction. Subsequently, the specific objectives of the review article must be presented. The last part of the “introduction” section should focus on the solution, the way forward, the recommendations, and the further areas of research as deduced from the whole review process. According to DeMaria [ 70 ], clearly expressed or recommended solutions to an explicitly revealed problem are very important for the wholesomeness of the “introduction” section. It is believed that following these steps will give readers the opportunity to track the problems and the corresponding solution from their own perspective in the light of current literature. As against some suggestions that the introduction should be written only in present tenses, it is also believed that it could be done with other tenses in addition to the present tense. In this regard, general facts should be written in the present tense, specific research/work should be in the past tense, while the concluding statement should be in the past perfect or simple past. Furthermore, many of the abbreviations to be used in the rest of the manuscript and their explanations should be defined in this section.
5.6. Methodology
Writing a review article is equivalent to conducting a research study, with the information gathered by the author (reviewer) representing the data. Like all major studies, it involves conceptualisation, planning, implementation, and dissemination [ 71 ], all of which may be detailed in a methodology section, if necessary. Hence, the methodological section of a review paper (which can also be referred to as the review protocol) details how the relevant literature was selected and how it was analysed as well as summarised. The selection details may include, but are not limited to, the database consulted and the specific search terms used together with the inclusion/exclusion criteria. As earlier highlighted in Section 3 , a description of the methodology is required for all types of reviews except for narrative reviews. This is partly because unlike narrative reviews, all other review articles follow systematic approaches which must ensure significant reproducibility [ 72 ]. Therefore, where necessary, the methods of data extraction from the literature and data synthesis must also be highlighted as well. In some cases, it is important to show how data were combined by highlighting the statistical methods used, measures of effect, and tests performed, as well as demonstrating heterogeneity and publication bias [ 73 ].
The methodology should also detail the major databases consulted during the literature search, e.g., Dimensions, ScienceDirect, Web of Science, MEDLINE, and PubMed. For meta-analysis, it is imperative to highlight the software and/or package used, which could include Comprehensive Meta-Analysis, OpenMEE, Review Manager (RevMan), Stata, SAS, and R Studio. It is also necessary to state the mathematical methods used for the analysis; examples of these include the Bayesian analysis, the Mantel–Haenszel method, and the inverse variance method. The methodology should also state the number of authors that carried out the initial review stage of the study, as it has been recommended that at least two reviews should be done blindly and in parallel, especially when it comes to the acquisition and synthesis of data [ 74 ]. Finally, the quality and validity assessment of the publication used in the review must be stated and well clarified [ 73 ].
5.7. Main Body of the Review
Ideally, the main body of a publishable review should answer these questions: What is new (contribution)? Why so (logic)? So what (impact)? How well it is done (thoroughness)? The flow of the main body of a review article must be well organised to adequately maintain the attention of the readers as well as guide them through the section. It is recommended that the author should consider drawing a conceptual scheme of the main body first, using methods such as mind-mapping. This will help create a logical flow of thought and presentation, while also linking the various sections of the manuscript together. According to Moreira [ 75 ], “reports do not simply yield their findings, rather reviewers make them yield,” and thus, it is the author's responsibility to transform “resistant” texts into “docile” texts. Hence, after the search for the literature, the essential themes and key concepts of the review paper must be identified and synthesised together. This synthesis primarily involves creating hypotheses about the relationships between the concepts with the aim of increasing the understanding of the topic being reviewed. The important information from the various sources should not only be summarised, but the significance of studies must be related back to the initial question(s) posed by the review article. Furthermore, MacLure [ 76 ] stated that data are not just to be plainly “extracted intact” and “used exactly as extracted,” but must be modified, reconfigured, transformed, transposed, converted, tabulated, graphed, or manipulated to enable synthesis, combination, and comparison. Therefore, different pieces of information must be extracted from the reports in which they were previously deposited and then refined into the body of the new article [ 75 ]. To this end, adequate comparison and combination might require that “qualitative data be quantified” or/and “quantitative data may be qualitized” [ 77 ]. In order to accomplish all of these goals, the author may have to transform, paraphrase, generalize, specify, and reorder the text [ 78 ]. For comprehensiveness, the body paragraphs should be arranged in a similar order as it was initially stated in the abstract or/and introduction. Thus, the main body could be divided into thematic areas, each of which could be independently comprehensive and treated as a mini review. Similarly, the sections can also be arranged chronologically depending on the focus of the review. Furthermore, the abstractions should proceed from a wider general view of the literature being reviewed and then be narrowed down to the specifics. In the process, deep insights should also be provided between the topic of the review and the wider subject area, e.g., fungal enzymes and enzymes in general. The abstractions must also be discussed in more detail by presenting more specific information from the identified sources (with proper citations of course!). For example, it is important to identify and highlight contrary findings and rival interpretations as well as to point out areas of agreement or debate among different bodies of literature. Often, there are previous reviews on the same topic/concept; however, this does not prevent a new author from writing one on the same topic, especially if the previous reviews were written many years ago. However, it is important that the body of the new manuscript be written from a new angle that was not adequately covered in the past reviews and should also incorporate new studies that have accumulated since the last review(s). In addition, the new review might also highlight the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of the past studies. But the authors must not be excessively critical of the past reviews as this is regarded by many authors as a sign of poor professionalism [ 3 , 79 ]. Daft [ 79 ] emphasized that it is more important for a reviewer to state how their research builds on previous work instead of outright claiming that previous works are incompetent and inadequate. However, if a series of related papers on one topic have a common error or research flaw that needs rectification, the reviewer must point this out with the aim of moving the field forward [ 3 ]. Like every other scientific paper, the main body of a review article also needs to be consistent in style, for example, in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense. It is also important to note that tables and figures can serve as a powerful tool for highlighting key points in the body of the review, and they are now considered core elements of reviews. For more guidance and insights into what should make up the contents of a good review article, readers are also advised to get familiarised with the Boote and Beile [ 80 ] literature review scoring rubric as well as the review article checklist of Short [ 81 ].
5.8. Tables and Figures
An ideal review article should be logically structured and efficiently utilise illustrations, in the form of tables and figures, to convey the key findings and relationships in the study. According to Tay [ 13 ], illustrations often take a secondary role in review papers when compared to primary research papers which are focused on illustrations. However, illustrations are very important in review articles as they can serve as succinct means of communicating major findings and insights. Franzblau and Chung [ 82 ] pointed out that illustrations serve three major purposes in a scientific article: they simplify complex data and relationships for better understanding, they minimise reading time by summarising and bringing to focus on the key findings (or trends), and last, they help to reduce the overall word count. Hence, inserting and constructing illustrations in a review article is as meticulous as it is important. However, important decisions should be made on whether the charts, figures, or tables to be potentially inserted in the manuscript are indeed needed and how best to design them [ 83 ]. Illustrations should enhance the text while providing necessary information; thus, the information described in illustrations should not contradict that in the main text and should also not be a repetition of texts [ 84 ]. Furthermore, illustrations must be autonomous, meaning they ought to be intelligible without having to read the text portion of the manuscript; thus, the reader does not have to flip back and forth between the illustration and the main text in order to understand it [ 85 ]. It should be noted that tables or figures that directly reiterate the main text or contain extraneous information will only make a mess of the manuscript and discourage readers [ 86 ].
Kotz and Cals [ 87 ] recommend that the layout of tables and figures should be carefully designed in a clear manner with suitable layouts, which will allow them to be referred to logically and chronologically in the text. In addition, illustrations should only contain simple text, as lengthy details would contradict their initial objective, which was to provide simple examples or an overview. Furthermore, the use of abbreviations in illustrations, especially tables, should be avoided if possible. If not, the abbreviations should be defined explicitly in the footnotes or legends of the illustration [ 88 ]. Similarly, numerical values in tables and graphs should also be correctly approximated [ 84 ]. It is recommended that the number of tables and figures in the manuscript should not exceed the target journal's specification. According to Saver [ 89 ], they ideally should not account for more than one-third of the manuscript. Finally, the author(s) must seek permission and give credits for using an already published illustration when necessary. However, none of these are needed if the graphic is originally created by the author, but if it is a reproduced or an adapted illustration, the author must obtain permission from the copyright owner and include the necessary credit. One of the very important tools for designing illustrations is Creative Commons, a platform that provides a wide range of creative works which are available to the public for use and modification.
5.9. Conclusion/Future Perspectives
It has been observed that many reviews end abruptly with a short conclusion; however, a lot more can be included in this section in addition to what has been said in the major sections of the paper. Basically, the conclusion section of a review article should provide a summary of key findings from the main body of the manuscript. In this section, the author needs to revisit the critical points of the paper as well as highlight the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the inferences drawn in the article review. A good conclusion should highlight the relationship between the major points and the author's hypothesis as well as the relationship between the hypothesis and the broader discussion to demonstrate the significance of the review article in a larger context. In addition to giving a concise summary of the important findings that describe current knowledge, the conclusion must also offer a rationale for conducting future research [ 12 ]. Knowledge gaps should be identified, and themes should be logically developed in order to construct conceptual frameworks as well as present a way forward for future research in the field of study [ 11 ].
Furthermore, the author may have to justify the propositions made earlier in the manuscript, demonstrate how the paper extends past research works, and also suggest ways that the expounded theories can be empirically examined [ 3 ]. Unlike experimental studies which can only draw either a positive conclusion or ambiguous failure to reject the null hypothesis, four possible conclusions can be drawn from review articles [ 1 ]. First, the theory/hypothesis propounded may be correct after being proven from current evidence; second, the hypothesis may not be explicitly proven but is most probably the best guess. The third conclusion is that the currently available evidence does not permit a confident conclusion or a best guess, while the last conclusion is that the theory or hypothesis is false [ 1 ]. It is important not to present new information in the conclusion section which has link whatsoever with the rest of the manuscript. According to Harris et al. [ 90 ], the conclusions should, in essence, answer the question: if a reader were to remember one thing about the review, what would it be?
5.10. References
As it has been noted in different parts of this paper, authors must give the required credit to any work or source(s) of information that was included in the review article. This must include the in-text citations in the main body of the paper and the corresponding entries in the reference list. Ideally, this full bibliographical list is the last part of the review article, and it should contain all the books, book chapters, journal articles, reports, and other media, which were utilised in the manuscript. It has been noted that most journals and publishers have their own specific referencing styles which are all derived from the more popular styles such as the American Psychological Association (APA), Chicago, Harvard, Modern Language Association (MLA), and Vancouver styles. However, all these styles may be categorised into either the parenthetical or numerical referencing style. Although a few journals do not have strict referencing rules, it is the responsibility of the author to reference according to the style and instructions of the journal. Omissions and errors must be avoided at all costs, and this can be easily achieved by going over the references many times for due diligence [ 11 ]. According to Cronin et al. [ 12 ], a separate file for references can be created, and any work used in the manuscript can be added to this list immediately after being cited in the text [ 12 ]. In recent times, the emergence of various referencing management software applications such as Endnote, RefWorks, Mendeley, and Zotero has even made referencing easier. The majority of these software applications require little technical expertise, and many of them are free to use, while others may require a subscription. It is imperative, however, that even after using these software packages, the author must manually curate the references during the final draft, in order to avoid any errors, since these programs are not impervious to errors, particularly formatting errors.
6. Concluding Remarks
Writing a review article is a skill that needs to be learned; it is a rigorous but rewarding endeavour as it can provide a useful platform to project the emerging researcher or postgraduate student into the gratifying world of publishing. Thus, the reviewer must develop the ability to think critically, spot patterns in a large volume of information, and must be invested in writing without tiring. The prospective author must also be inspired and dedicated to the successful completion of the article while also ensuring that the review article is not just a mere list or summary of previous research. It is also important that the review process must be focused on the literature and not on the authors; thus, overt criticism of existing research and personal aspersions must be avoided at all costs. All ideas, sentences, words, and illustrations should be constructed in a way to avoid plagiarism; basically, this can be achieved by paraphrasing, summarising, and giving the necessary acknowledgments. Currently, there are many tools to track and detect plagiarism in manuscripts, ensuring that they fall within a reasonable similarity index (which is typically 15% or lower for most journals). Although the more popular of these tools, such as Turnitin and iThenticate, are subscription-based, there are many freely available web-based options as well. An ideal review article is supposed to motivate the research topic and describe its key concepts while delineating the boundaries of research. In this regard, experience-based information on how to methodologically develop acceptable and impactful review articles has been detailed in this paper. Furthermore, for a beginner, this guide has detailed “the why” and “the how” of authoring a good scientific review article. However, the information in this paper may as a whole or in parts be also applicable to other fields of research and to other writing endeavours such as writing literature review in theses, dissertations, and primary research articles. Finally, the intending authors must put all the basic rules of scientific writing and writing in general into cognizance. A comprehensive study of the articles cited within this paper and other related articles focused on scientific writing will further enhance the ability of the motivated beginner to deliver a good review article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of South Africa under grant number UID 138097. The authors would like to thank the Durban University of Technology for funding the postdoctoral fellowship of the first author, Dr. Ayodeji Amobonye.
Data Availability
Conflicts of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
"How Do I?" @JWULibrary

Sample Question
- JWU-Providence Library
Q. What's the difference between a research article and a review article?
- 35 about the library
- 29 articles & journals
- 1 Borrowing
- 8 citing sources
- 17 company & industry
- 11 computers
- 1 copyright compliance
- 5 countries & travel
- 2 course registration
- 50 databases
- 3 education
- 2 Interlibrary loan
- 5 job search
- 6 libguides
- 9 market research
- 25 my library account
- 12 requests
- 26 research basics
- 21 research topics
- 2 study rooms
- 16 technology
- 7 textbooks
- 42 university
- 3 video tutorial
- 1 writing_help
Answered By: Sarah Naomi Campbell Last Updated: Sep 07, 2018 Views: 215894
Watch this short video to learn about types of scholarly articles, including research articles and literature reviews!
Not in the mood for a video? Read on!
What's the difference between a research article and a review article?
Research articles , sometimes referred to as empirical or primary sources , report on original research. They will typically include sections such as an introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
Here is a more detailed explanation of research articles .
Review articles , sometimes called literature reviews or secondary sources , synthesize or analyze research already conducted in primary sources. They generally summarize the current state of research on a given topic.
Here is a more detailed explanation of review articles .
The video above was created by the Virginia Commonwealth University Libraries .
The defintions, and the linked detailed explanations, are paraphrased from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 6th ed .
The linked explanations are provided by the Mohawk Valley Community College Libraries .
Links & Files
- How do I find empirical articles in the library databases?
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 63 No 19
Comments (0)
Related topics.
- about the library
- articles & journals
- citing sources
- company & industry
- copyright compliance
- countries & travel
- course registration
- Interlibrary loan
- market research
- my library account
- research basics
- research topics
- study rooms
- video tutorial
- writing_help
Downcity Library:
111 Dorrance Street Providence, Rhode Island 02903
401-598-1121
Harborside Library:
321 Harborside Boulevard Providence, RI 02905
401-598-1466
- Location and Directions
- Off-Campus Access
- Staff Directory
- Student Employment
- Pay Bills and Fines
- Chat with a Librarian
- Course Reserves
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Study Rooms
- Research Appointment
- Culinary Museum

- Aimlay Foundation
- Pharma Courses
- Become a Partner
- Medical Courses
- Life@Aimlay
- Web Stories

- Thesis Writing
- Law Admission
- Dissertation
- Honorary doctorate
- Educational Academy
- Management Courses
- Research Paper Writing
- YouTube Journal
PhD | Thesis Writing | Law Admission | Dissertation | Biography | Pharma | Honorary doctorate | Educational Academy | Management Courses | Research Paper Writing | YouTube Journal
Difference Between Research Paper and Review Paper?
- August 29, 2022
- Research Paper Writing , YouTube Journal
- No Comments

A research paper and a review paper writing are two different types of documents. They have different purposes, purposes, and requirements. Research papers and review papers contain different information. The r esearch paper contains original research work by the author, while the review paper is based on an existing source of knowledge.
In this blog, let’s discuss the differences between research and review paper writing .
What are Research Papers?
A research paper is a type of essay where the main purpose is that it should present new ideas and information to the audience. The author of the research paper must provide facts, figures, graphs, and other types of written information that can support his/her argument(s).
Research papers can be written on any topic, but they must be connected with one or more disciplines.
A good example is when science students write their research papers on cell division or DNA synthesis.
What are Review Papers?
A review paper writing aims to provide readers with an overview of an article or book by reviewing its content, structure, style, and arguments. Reviews can be used to evaluate other people’s work or to assess one’s own work by comparing it with another’s work (i.e., peer reviews). Review papers are usually shorter than research papers because they are intended for wider audiences.
Understanding the Main Difference:
Research papers and review papers are two different types of writing assignments you will encounter in your academic career.
Research paper writing: The research paper is a written piece that is required to answer the question, “What do we know about this topic?”
Review paper writing : The review paper is a written piece that is required to answer the question, “What do we not know about this topic?”

More about Research Papers:
- Research papers present essential information that has been gathered from many sources.
- The writer must cite his sources for all ideas used in this article. This can be done by using bibliographies or footnotes at the end of each page of your paper.
- A bibliography is a list of all sources used within your article; it should be placed at the end of your work or on an appendix page in the principal body.
- Footnotes cite specific puotes or references not found within the text itself.
- They should also be placed at the end of your work. Or on an appendix page if used as part of your principal body.
More about Review Papers :
- Review papers have a special role in scientific literature. They are one of the most common papers and are often used to measure an individual’s scientific contributions. It provides a summary of current knowledge on the subject while identifying gaps in that knowledge, and it may also offer suggestions for future research.
- Review papers are most often written by scientists publishing in peer-reviewed journals, although they can be written by anyone with access to relevant information about the subject matter.
- Review papers usually include an introduction and background information about their topic. It is related to other subjects, discussion of previous work on the subject, and research methods used to gather data from studies.
- Usually conducted by others who have studied the same thing, conclusions are supported by evidence from these studies and any additional information needed to understand their findings and draw conclusions from them.

What is a Literature Review? Is it similar to Review Papers?
A literature review is a scholarly document that discusses the current state of knowledge on a topic. It may evaluate existing research quality and determine which works should be included in an analysis or synthesis.
- A literature review can be conducted by anyone interested in a particular topic area. But it is usually performed by someone with some knowledge or training.
- The primary purpose of a literature review is to provide background information about a topic. So that the author can develop the ideas for a research paper or report. For this to happen, you need to know what your audience wants. You also need to understand what your audience wants from you.
- A literature review is a critique of current literature. A literature review is similar to a research paper , but it is not as long and detailed.
The main difference is that a literature review typically focuses on only one or two specific topics. Whereas a research paper can be more broadly focused and may include multiple sections.
How does a Review Paper help form a Research Paper?
A review paper is a summary of previous research on a topic. It can be either an objective or subjective analysis.
The purpose of the review is to summarize the findings of previous research. Also to determine whether the results are valid and reliable.

This can be done by examining the research methods used in the studies and their design, measurement and statistical analysis.
In addition to presenting information about a subject in its own right. Reviews also provide a context for future research by identifying areas that need to be addressed. Checks may be critical in identifying areas that require further investigation or discussion. They also help researchers focus their efforts on those areas that are most important to address.
Tips for Writing Research paper and Review paper:
A review paper has to be written. First, it includes the citations you might require while developing your research paper.
While writing a research paper , you should inquire about every question that comes to your mind. And follow through with them appropriately.
A review paper is not your final paper; it requires constant research and a table of contents, commonly known as the bibliography. With the help of a bibliography, you will have a clear list of items you need in-depth research. It will prevent you from getting confused and haphazard with your findings and research.
A research paper is a piece of writing that tries to answer a specific question. A review paper is typically shorter than a research paper and focuses on one main point or idea.
Share this Article
Send your query, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
Difference between Research Paper and Review Paper
Scholarly literature can be of different types. Many of them require researchers to perform an original study, whereas others are based on previously published research. Amateur researchers have quite a confusion understanding each type of scholarly literature and the difference between them.
Research Paper
When researchers partake in an original study or investigation of a unique topic, for example, a study of the prevalence of substance abuse in a specific community or geographical area, the findings of that study are presented as a research paper. The most essential component of a research paper is the analysis of the topic, evidence to support the study and the conclusion of the study. It can comprise of the answer to the reach question and may include a hypothesis, the resource requirement for the study and the method followed to reach the conclusion. The formatting of a research paper is fairly similar across all subjects and institutions, though it can vary from one region to another depending upon the pattern laid down by the publishing and educational bodies. This scholarly work is unique and bears no similarity to any other published work. Analysis of the data can vary from the use of software to authentic experiments.
Review Paper
Review papers are universal and can be focused upon a wide range of mediums, including articles in journals, books, magazines, and software. A review paper refers to the study and survey of a recently published Research paper on a specific topic or subject. For instance, climate change due to industrial waste has many scholarly Research paper. these papers can be reviewed by any other number of scholars for its merits. In order to write a review paper successfully, one needs to have knowledge of what other scholars have written on the subject and their thoughts on the subject, particularly in recent times. the reach papers act as a reference and source material for these review papers. These can be stimulating and extremely exhaustive with the intent for undertaking research by introducing challenging materials and facts. It should act as a summary of the original research paper with all its relevant literature on the topic.
Key differences between the Research paper and Review paper are given in the table below:
| Attributes | Research Paper | Review Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Its purpose is to report a detailed description of the original research study that is unique and specific to a subject | Its purpose is to critic and analyze a published literature on a specific topic. |
| Basis | It must always be based on original research work and must be the primary reference source on the topic | it must always be based upon published scholarly literature and contain no new information on the topic |
| Contents | The contents of this paper must be based on analysis and interpretation of original data from the research study | These contain simple and compact summary of the original research paper and should act as an overview on the topic. |
| Report | It reports every step undertaken for the study and include an abstract, well crafted hypothesis, its background studies, all methodology, conclusion and explanation of the findings | It reports commonalities among various research on the topic and the discrepancies with reasons for conflicting or varying results. |
| Length | More often it depends upon the journal publishing or educational authorities, but it can range from 3000 to 6000 words. | These generally have a limit of 3000 to 5000 words, but depending upon the merits of the paper it can be shorter. |
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Difference Between
- Write From Home
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

How to Write a Literature Review
- What is a literature review
How is a literature review different from a research paper?
- What should I do before starting my literature review?
- What type of literature review should I write and how should I organize it?
- What should I be aware of while writing the literature review?
- For more information on Literature Reviews
- More Research Help
The purpose of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument. The literature review is one part of a research paper. In a research paper, you use the literature review as a foundation and as support for the new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and analyze the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
- << Previous: What is a literature review
- Next: What should I do before starting my literature review? >>
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2021 11:35 AM
- URL: https://midway.libguides.com/LiteratureReview
RESEARCH HELP
- Research Guides
- Databases A-Z
- Journal Search
- Citation Help
LIBRARY SERVICES
- Accessibility
- Interlibrary Loan
- Study Rooms
INSTRUCTION SUPPORT
- Course Reserves
- Library Instruction
- Little Memorial Library
- 512 East Stephens Street
- 859.846.5316
- [email protected]


How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.

Blog, Article, Essay and Research Paper: What’s the Difference?
- Career Guide
- August 18, 2024

Writing can be confusing, especially when you’re faced with different formats like blogs, articles, essays and research papers. Each one has its own style and purpose and choosing the right one can be challenging. As a law student or graduate, you need to know which format works best for your needs, whether you’re sharing your thoughts on a blog, writing an article or doing in-depth research.
Understanding the differences between these formats is important for your academic work and for connecting with your readers. Let’s explore what makes each format unique so you can make the best choice for your writing.
- Purpose: A blog is typically informal, engaging and meant to share opinions, personal experiences or commentary on various topics. It is often used to connect with a broader audience, including peers, clients or the general public.
- Tone: Blogs are generally conversational and written in a casual tone, making them easy to read and accessible to a wide audience.
- Length: They are usually short to medium in length, ranging from 300 to 1500 words.
- Content: The content can vary widely, from tips and tutorials to opinions and news. For law students, calls for blogs might include summaries of recent legal developments, reflections on law school experiences or practical advice for budding lawyers.
- Structure: Blogs are often less rigid in structure, allowing for creative expression, including the use of headings, bullet points, images and links.
- Purpose: Articles are more formal and are often found in newspapers, magazines or online publications. They aim to inform, analyse or comment on a specific topic or issue.
- Tone: The tone is more formal than a blog but still accessible, aiming to inform or persuade the reader.
- Length: Articles are typically longer than blogs, often ranging from 800 to 2000 words.
- Content: The content is well-researched and often includes evidence, quotes from experts and a balanced discussion of the topic. For law students, articles might analyse a specific legal issue, case law or recent legislation.
- Structure: Articles have a clear structure, including an introduction, body and conclusion and may include subheadings to organise the content.
- Purpose: Essays are academic pieces that aim to explore, argue or analyse a particular topic or question in depth. They are often assigned as part of coursework in law schools.
- Tone: The tone is formal and academic, often requiring the use of legal jargon and citations.
- Length: Essays vary in length, typically ranging from 1000 to 3000 words, depending on the depth of analysis required.
- Content: Essays involve critical thinking and analysis, supported by evidence and references. They require a clear thesis statement and a logical argument that develops throughout the piece. For law students, essays may focus on legal theories, interpretations of statutes or case law analysis.
- Structure: Essays follow a structured format with an introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs and a conclusion. Proper citations and references are essential.
Research Paper
- Purpose: Research papers are comprehensive academic documents that present original research, analysis or findings on a specific topic. They are often required for advanced law courses or academic publications.
- Tone: The tone is highly formal and scholarly, with a strong emphasis on precision, detail and objectivity.
- Length: Research papers are the longest of the four, often exceeding 3000 words and can be much longer depending on the scope of the research.
- Content: Research papers require extensive research, including primary and secondary sources. They present a detailed analysis, supported by data, case studies or legal precedents. For law students, a research paper might involve an in-depth study of a legal issue, case or theory, often contributing new insights or perspectives to the field.
- Structure: Research papers have a strict structure, including an abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, findings, discussion and conclusion. Proper citation and adherence to academic standards are critical.
Each of these forms of writing serves a different purpose and audience. Blogs are informal and engaging, articles are informative and accessible, essays are analytical and structured, while research papers are comprehensive and scholarly. Understanding these differences will help law students and graduates choose the right format for their work and audience.

You might like

KC Gajapati Narayan Deo vs State of Orissa (1953)

Top 7 Law Entrance Exams in India 2025, Check Details

Starting an Independent Litigation Practice: Challenges and Tips for Young Lawyers
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Post Comment

IMAGES
COMMENTS
INFOGRAPHIC :5 Differences between a research paper and a review paper. There are different types of scholarly literature. Some of these require researchers to conduct an original study, whereas others can be based on previously published research. Understanding each of these types and also how they differ from one another can be rather ...
These are the main differences, however, there may be others: A research paper is usually more detailed and thorough than a review paper. A research paper is usually peer-reviewed, but a review paper is not always. In general, a research paper is more formal than a review paper. A research paper's tone is normally objective, but a review ...
Here are four key differences between research papers and review papers: Purpose: Review papers evaluate existing research, identify trends, and discuss the current state of knowledge on a specific topic; they are based on the study of previously published literature. On the other hand, research paperscontain original research work undertaken ...
The research paper will be based on the analysis and interpretation of this data. A review article or review paper is based on other published articles. It does not report original research. Review articles generally summarize the existing literature on a topic in an attempt to explain the current state of understanding on the topic.
A research article describes a study that was performed by the article's author (s). It explains the methodology of the study, such as how data was collected and analyzed, and clarifies what the results mean. Each step of the study is reported in detail so that other researchers can repeat the experiment. To determine if a paper is a research ...
The kind of research may vary depending on your field or the topic (experiments, survey, interview, questionnaire, etc.), but authors need to collect and analyze raw data and conduct an original study. The research paper will be based on the analysis and interpretation of this data. A review article or review paper is based on other published ...
Research versus Review Articles 6 Article types that journals publish: A guide for early career researchers INFOGRAPHIC: 5 Differences between a research paper and a review paper
A research paper, then, involves gathering evidence related directly towards a given argument. In contrast, a review paper, examines multiple sources that relate indirectly towards it. . III. The Main Purpose Behind the Two Types of Articles. The purpose of a research paper is to explore and expand upon an existing concept.
Research Paper vs Review Paper. A research paper is primarily based on original research; it outlines theories, methods and results related to a particular area of investigation. A review paper summarizes previously published studies, without adding new contributions. The purpose of writing a review paper is three-fold:
A research paper includes original work while a review paper includes the summary of existing work which explains or solves a specific problem. An integral part of a PhD dissertation or thesis is writing a research and review article, besides writing a thesis, proposal and synopsis. In addition, one also has to publish an article in a peer ...
The differences between a research paper and a review paper in the purpose, structure, and timeframe of writing it.Scientific Research Paper Checklist: https...
I have limited experience regarding since I am still a graduate student but from what I understand, a review paper is also a research paper. However, unlike a piece of research, where you study the existing literature, develop research questions and hypotheses, collect data, run experiments/analysis and make inferences which accept or reject your hypotheses, a review article is a summarization ...
The length of a research paper is large. The length of the review paper is comparatively small. Information is available in detail. It is less comprehensive. A research paper is written by one or more authors. It is written by a single author. A peer review is needed for the research paper. No peer review is needed.
The information you use to write a research paper comes from different sources and is often considered raw. Function. The purpose of a literature review is to help readers find what's already published on the subject in. The purpose of a research paper is to present your own unique research on a subject. Writing.
A research paper is typically objective in tone, while a review paper may be more subjective in tone. A research paper typically uses APA style, while a review paper may use a different style. A research paper typically includes a title page, while a review paper may not. A research paper typically includes an abstract on the title page, while ...
Tweet. Key Difference: The primary difference between a research paper and a review paper is that a research paper is based on the author's original research and their analysis and interpretation of their research finishing, whereas a review paper collects and collates information on a particular topic from various different written publications.
An ideal review article should be logically structured and efficiently utilise illustrations, in the form of tables and figures, to convey the key findings and relationships in the study. According to Tay , illustrations often take a secondary role in review papers when compared to primary research papers which are focused on illustrations ...
Review articles, sometimes called literature reviews or secondary sources, synthesize or analyze research already conducted in primary sources. They generally summarize the current state of research on a given topic. Here is a more detailed explanation of review articles. The video above was created by the Virginia Commonwealth University ...
A research paper and a review paper writing are two different types of documents. They have different purposes, purposes, and requirements. Research papers and review papers contain different information. The r esearch paper contains original research work by the author, while the review paper is based on an existing source of knowledge.
A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results. Writing a review of literature is to provide a ...
Key differences between the Research paper and Review paper are given in the table below: Attributes. Research Paper. Review Paper. Purpose. Its purpose is to report a detailed description of the original research study that is unique and specific to a subject. Its purpose is to critic and analyze a published literature on a specific topic. Basis.
What is the purpose of a literature review? Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
The literature review is one part of a research paper. In a research paper, you use the literature review as a foundation and as support for the new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and analyze the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal? A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand ...
Length: Research papers are the longest of the four, often exceeding 3000 words and can be much longer depending on the scope of the research. Content: Research papers require extensive research, including primary and secondary sources. They present a detailed analysis, supported by data, case studies or legal precedents. For law students, a ...
Wondering what to expect from your paper review appointment? Below are the types of assignments we review, along with sample feedback. Feedback will vary among writing instructional specialists but will consist of some of these: Explanations of errors; Links to resources; Questions or reactions from a reader's perspective; Recommended next steps
This review article addresses the critical need for a comprehensive synthesis of existing knowledge on well-being of low-income consumers. Focusing on Base of the Pyramid and Subsistence Marketplaces literature, we employed the SPAR-4-SLR protocol to structure our methodology and applied ADO-TCM framework for literature analysis.
Higher education institutions, as organizations that transform society, have a responsibility to contribute to the construction of a sustainable and resilient world that is aware of the collateral effects of technological advances. This is the initial phase of a research that aims to determine whether subjects in the complementary training area have a significant effect on ethical, social ...
In this paper, we review the modification method of sodium ion anode materials that are prepared using pitch-based carbon. The current status of pitch-based carbon preparation of anode materials for sodium-ion batteries by heteroatom doping, morphology construction, and composite materials is introduced.
(LeMusique/iStock via Getty Images) In the 2003 movie, "Something's Gotta Give," Jack Nicholson's character, Harry, is seen rolling on the floor, clutching his chest and sweating profusely, barely able to speak while his eyes roll back in his head.