The Impact of Online Game Addiction on Adolescent Mental Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- August 2021
- Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences 9(F):260-274
- 9(F):260-274
- CC BY-NC 4.0

- Airlangga University


Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Suwarsi Suwarsi
- Eko Mindarsih
- Melanie Reboldera Adolfo
- Alev Ustundag
- Vildan Caymaz
- Amani Kappi
- Rania Rabie El-Etreby

- Warda El Shahat Hamed
- Mohsen Saffari
- Kamolthip Ruckwongpatr

- Moushami Giree

- Mehmet Enes SAĞAR
- Tuğba ÖZÇELİK

- Widya Rahma Syari
- Edo Gusdiansyah
- Ferina Agustia Yuarta
- Ira Nurmala
- Child Adolesc Ment Health

- Sally M. Gainsbury
- Int J Environ Res Publ Health

- Lutz Wartberg

- Elisa Dwi Pertiwi

- Evana Nisa'ul Ammar

- Hyunsuk Jeong
- Hyeon Woo Yim

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 28 November 2022
Psychological treatments for excessive gaming: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Jueun Kim 1 ,
- Sunmin Lee 1 ,
- Dojin Lee 1 ,
- Sungryul Shim 2 ,
- Daniel Balva 3 ,
- Kee-Hong Choi 4 ,
- Jeanyung Chey 5 ,
- Suk-Ho Shin 6 &
- Woo-Young Ahn 5
Scientific Reports volume 12 , Article number: 20485 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
4754 Accesses
3 Citations
4 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Human behaviour
Despite widespread public interest in problematic gaming interventions, questions regarding the empirical status of treatment efficacy persist. We conducted pairwise and network meta-analyses based on 17 psychological intervention studies on excessive gaming ( n = 745 participants). The pairwise meta-analysis showed that psychological interventions reduce excessive gaming more than the inactive control (standardized mean difference [SMD] = 1.70, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.27 to 2.12) and active control (SMD = 0.88, 95% CI 0.21 to 1.56). The network meta-analysis showed that a combined treatment of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Mindfulness was the most effective intervention in reducing excessive gaming, followed by a combined CBT and Family intervention, Mindfulness, and then CBT as a standalone treatment. Due to the limited number of included studies and resulting identified methodological concerns, the current results should be interpreted as preliminary to help support future research focused on excessive gaming interventions. Recommendations for improving the methodological rigor are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Why do adults seek treatment for gaming (disorder)? A qualitative study
A randomized controlled trial on a self-guided Internet-based intervention for gambling problems
The interplay between mental health and dosage for gaming disorder risk: a brief report
Introduction.
Excessive gaming refers to an inability to control one’s gaming habits due to a significant immersion in games. Such an immersion may result in experienced difficulties in one’s daily life 1 , including health problems 2 , poor academic or job performance 3 , 4 , and poor social relationships 5 . Although there is debate regarding whether excessive gaming is a mental disorder, the 11th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) included Gaming Disorder as a disorder in 2019 6 . While there is no formal diagnosis for Gaming Disorder listed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), the DSM-5 included Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) as a condition for further study 7 . In the time since the DSM-5’s publication, research on excessive gaming has widely continued. Although gaming disorder’s prevalence appears to be considerably heterogeneous by country, results from a systematic review of 53 studies conducted between 2009 and 2019 indicated a global prevalence of excessive gaming of 3.05% 8 . More specifically, a recent study found that Egypt had the highest IGD prevalence rate of 10.9%, followed by Saudi Arabia (8.8%), Indonesia (6.1%), and India (3.8%) among medical students 9 .
While the demand for treatment of excessive gaming has increased in several countries 10 , standard treatment guidelines for problematic gaming are still lacking. For example, a survey in Australia and New Zealand revealed that psychiatrics— particularly child psychiatrists, reported greater frequency of excessive gaming in their practice, yet 43% of the 289 surveyed psychiatrists reported that they were not well informed of treatment modalities for managing excessive gaming 11 . Similarly, 87% of mental health professionals working in addiction-related institutions in Switzerland reported a significant need for professional training in excessive gaming interventions 12 . However, established services for the treatment of gaming remain scarce and disjointed.
Literature has identified a variety of treatments for excessive gaming, but no meta-analysis has yet been conducted on effectiveness of the indicated interventions. The only meta-analysis to date has focused on CBT 13 , and while results demonstrated excellent efficacy in reducing excessive gaming. However, the study did not compare the intervention with other treatment options. Given that gaming behavior is commonly affected by cognitive and behavioral factors as well as social and familial factors 14 , 15 , 16 , it would also be important to examine the effectiveness of treatment approaches that reflect social and familial influences. While two systematic reviews examined diverse therapeutic approaches, they primarily reported methodological concerns of the current literature and did not assess the weight of evidence 17 , 18 . Given that studies in this area are rapidly evolving and studies employing rigorous methodological approaches have since emerged 19 , 20 , a meta-analytic study that analyzes and synthesizes the current stage of methodological limitations while also providing a comprehensive comparison of intervention options is warranted.
In conducting such a study, undertaking a traditional pairwise meta-analysis is vital to assess overall effectiveness of diverse interventions. Particularly, moderator and subgroup analyses in pairwise meta-analysis provide necessary information as to whether effect sizes vary as a function of study characteristics. Furthermore, to obtain a better understanding of the superiority and inferiority of all clinical trials in excessive gaming psychological interventions, it is useful to employ a network meta-analysis, which allows for a ranking and hierarchy of the included interventions. While a traditional pair-wise analysis synthesizes direct evidence of one intervention compared with one control condition, a network meta-analysis incorporates multiple comparisons in one analysis regardless of whether the original studies used them as control groups. It enters all treatment and control arms of each study, and makes estimates of the differences in interventions by using direct evidence (e.g., direct estimates where two interventions were compared) and indirect evidence (e.g., generated comparisons between interventions from evidence loops in a network 21 . Recent meta-analytic studies on treatments for other health concerns and disorders have used this analysis to optimize all available evidence and build treatment hierarchies 22 , 23 , 24 .
In this study, the authors used a traditional pairwise meta-analysis and network meta-analysis to clarify the overall and relative effectiveness of psychological treatments for excessive gaming. The authors also conducted a moderator analysis to examine potential differences in treatment efficacy between Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) and non-RCTs, age groups, regions, and research qualities. Finally, the authors examined follow-up treatment efficacy and treatment effectiveness on common comorbid symptoms and characteristics (e.g., depression, anxiety, and impulsivity).
The protocol for this review has been registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Review (PROSPERO 2021: CRD 42021231205) and is available for review via the following link: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?RecordID=231205 . Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) network meta-analysis checklist 25 is included in Supplementary Material 1 .
Identification and selection of studies
The authors searched seven databases, which included ProQuest, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, PsycINFO, Research Information Sharing Service (RISS), and DBpia. Given that a substantial number of studies have been published particularly in East Asia and exclusion of literature from the area in languages other than English has been discussed as a major limitation in previous reviews 17 , 18 , the authors gave special attention to gaming treatment studies in English and other languages from that geographical area. Additionally, the authors searched Google Scholar to ensure that no studies were accidentally excluded. The authors conducted extensive searches for studies published in peer-reviewed journals between the first available year (year 2002) and October 31, 2022, using the following search terms: “internet”, or “video”, or “online”, or “computer”, and “game”, or “games”, or “gaming”, and “addiction”, or “addictions”, or “disorder”, “disorders”, or “problem”, or “problems”, or “problematic”, or “disease”, or “diseases”, or “excessive”, or “pathological”, or “addicted”, and “treatment”, or “treatments”, or “intervention”, or “interventions”, or “efficacy”, or “effectiveness”, or “effective”, or “clinical”, or “therapy”, or “therapies”. Search strategies applied to each database is provided in Supplementary Material 2 .
The authors included studies that recruited individuals who were excessively engaging in gaming, according to cutoff scores for different game addiction scales. Since there is not yet an existing consensus on operational definitions for excessive gaming, the authors included studies that recruited individuals who met high-risk cutoff score according to the scales used in each respective study (e.g., Internet Addiction Test [modified in game environments] > 70). The authors also sought studies that provided pretest and posttest scores from the game addiction scales in both the intervention and control groups. Studies meeting the following criteria were excluded: (a) the study targeted excessive Internet use but did not exactly target excessive gaming; (b) the study provided a prevention program rather than an intervention program; (c) the study provided insufficient data to perform an analysis of the effect sizes and follow-up contact to the authors of such studies did not yield the information necessary for inclusion within this paper; and (d) the study conducted undefinable types of intervention with unclear psychological orientations (e.g., art therapy with an undefined psychological intervention, fitness programs, etc.).
Two authors (D.L. and S.L.) independently screened the titles and abstracts of articles identified by the electronic searches and excluded irrelevant studies. A content expert (J.K.) examined the intervention descriptions to determine intervention types that were eligible for this review. All treatments were primarily classified based on the treatment theory, protocol, and descriptions about the procedures presented in each paper. D.L. and S.L.—both of whom have been in clinical training for 2 years categorized treatment type, to which J.K., a licensed psychologist, cross-checked and confirmed the categorization. The authors resolved disagreements through discussion. The specific example of intervention type classification is provided in Supplementary Material 3 .
Risk of bias and data extraction
Three independent authors assessed the following risks of bias among the included studies. The authors used the Risk of Bias 2.0 (RoB 2) tool for RCT studies and the Risk Of Bias In Non-Randomized Studies of Intervention (ROBINS-I) tool for non-RCT studies. The RoB 2 evaluates biases of (a) randomization processes; (b) deviations from intended interventions; (c) missing outcome data; (d) measurement of the outcome; and (e) selection of the reported result, and it categorizes the risk of bias in each dimension into three levels (low risk, moderate risk, and high risk). The ROBINS-I evaluates biases of (a) confounding variables; (b) selection of participants; (c) classification of interventions; (d) deviations from intended interventions; (e) missing data; (f) measurement of outcomes; and (g) selection of the reported result, and it categorizes the risk of bias in each dimension into five levels (low risk, moderate risk, serious risk, critical risk, and no information). After two authors (D.L. and S.L.) assessed each study, another author (J.K.) cross-checked the assessment.
For each study, the authors collected descriptive data, which included the sample size as well as participants’ ages, and regions where the studies were conducted. The authors also collected clinical data, including whether the study design was a RCT, types of treatment and control, treatment duration, and the number of treatment sessions. Finally, the authors collected data on the follow-up periods and the measurement tools used in each study.
Data analysis
The authors employed separate pairwise meta-analyses in active control and inactive control studies using R-package “meta” 26 and employed a random-effects model due to expected heterogeneity among studies. A random-effects model assumes that included studies comprise random samples from the larger population and attempt to generalize findings 27 . The authors categorized inactive control groups including no treatment and wait-list control and categorized active control groups including pseudo training (e.g., a classic stimulus-control compatibility training) and other types of psychological interventions (e.g., Behavioral Therapy, CBT, etc.). The authors also used the bias-corrected standardized mean change score (Hedges’ g ) due to small sample sizes with the corresponding 95% confidence interval 28 . The authors’ primary effectiveness outcome was a mean score change on game addiction scales from pre-treatment to post-treatment. Hedges’ g effect sizes were interpreted as small ( g = 0.15), medium ( g = 0.40) and large ( g = 0.75), as suggested by Cohen 29 . The authors used a conservative estimate of r = 0.70 for the correlation between pre-and post-treatment measures 30 , and to test heterogeneity, the authors calculated Higgins’ I 2 , which is the percentage of variability in effect estimates due to heterogeneity among studies rather than chance. I 2 > 75% is considered substantial heterogeneity 31 .
The authors conducted moderator analyses as a function of RCT status (RCT versus non-RCT), age group (adolescents versus adults), region (Eastern versus Western), and research quality (high versus low). The authors divided high versus low quality studies using median values of research quality scores (RCT: low [0–2] versus high [3–5], non-RCT: low [0–4] versus high [5]). The authors calculated Cochran’s Q for heterogeneity: A significant Q value indicates a potentially important moderator variable. For the subgroup analyses of follow-up periods and other outcomes, the authors conducted separate pairwise analyses in 1- to 3-month follow-up studies and in 4- to 6-month follow-up studies and separate analyses in depression, anxiety, and impulsivity outcome studies.
The authors sought to further explore relative effectiveness of treatment types and performed a frequentist network meta-analysis using the R-package “netmeta” 4.0.4 version 26 . To examine whether transitivity and consistency assumptions for network meta-analysis were met, the authors assessed global and local inconsistency. To test network heterogeneity, the authors calculated Cochran’s Q to compare the effect of a single study with the pooled effect of the entire study. The authors drew the geometry plot of the network meta-analysis through the netgraph function in “netmeta”, and the thicker lines between the treatments indicated a greater number of studies.
The authors presented the treatment rankings based on estimates using the surface area under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) 32 . The SUCRA ranged from 0 to 100%, with higher scores indicating greater probability of more optimal treatment. The authors also generated a league table to present relative effectiveness between all possible comparisons between treatments. When weighted mean difference for pairwise comparisons is bigger than 0, it favors the column-defining treatment. Finally, funnel plots and Egger’s test were used to examine publication bias.
Included studies and their characteristics
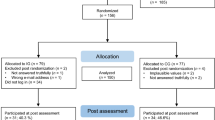
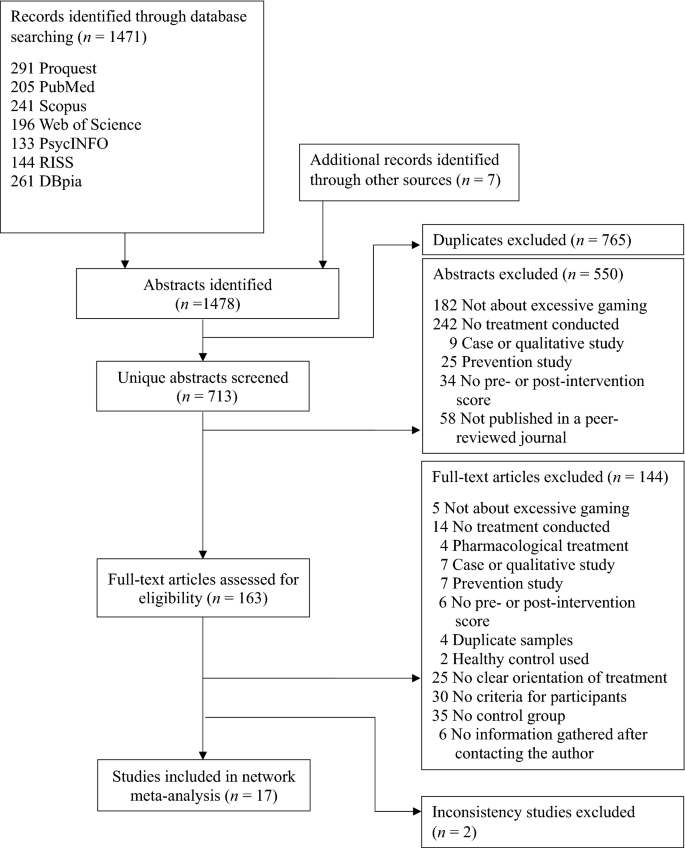
Figure 1 presents the flow diagram of the study selection process. The authors identified 1471 abstracts in electronic searches and identified an additional seven abstracts through secondary/manual searches (total n = 1478). After excluding duplicates ( n = 765) and studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria based on the study abstract ( n = 550), the authors retrieved studies with potential to meet the inclusion criteria for full review ( n = 163). Of these, 144 studies were excluded due to not meeting inclusion criteria based on full-text articles, leaving 19 remaining studies. Of the 19, two studies did meet this paper’s inclusion criteria but were excluded from this network meta-analysis 33 , 34 because the consistency assumption between direct and indirect estimates was not met at the time of this study's consideration based on previous studies 35 , 36 . Therefore, a total of 17 studies were included in this network meta-analysis, covering a total of 745 participants 36 .
Flow diagram of the study selection process.
Table 1 lists the characteristics of the 17 included studies. CBT ( n = 4), Behavioral Treatment (BT) + Mindfulness ( n = 4), and BT only ( n = 4) were most frequently studied, followed by CBT + Family Intervention ( n = 1), CBT + Mindfulness ( n = 1), virtual reality BT ( n = 1), Mindfulness ( n = 1), and Motivational Interviewing (MI) + BT ( n = 1). Seven studies were conducted in Korea and six were conducted in China, followed by Germany and Austria ( n = 1), Spain ( n = 1), the United States ( n = 1), and the Philippines ( n = 1). Twelve articles were written in English, and five articles were written in a language other than English. Nine studies conducted a follow-up assessment with periods ranging from one to three months, and two studies conducted a follow-up assessment with periods ranging four to six months. In one study 20 , the authors described their 6-month follow-up but did not present their outcome value, and thus only two studies were included in the four- to six-month follow-up analysis. Among the 17 included studies, eight had no treatment control group, five had an active control group (e.g., pseudo training, BT, and CBT), and four had a wait-list control group. Seven of the studies were RCT studies, and 10 were non-RCT studies.
Pairwise meta-analysis
The results of meta-analyses showed a large effect of all psychological treatments when compared to any type of comparison groups ( n = 17, g = 1.47, 95% CI [1.07, 1.86]). The treatment effects were separately provided according to active versus inactive comparison groups in Fig. 2 . The effects of psychological treatments were large when compared to the active control ( n = 5, g = 0.88, 95% CI [0.21, 1.56]) or inactive control ( n = 12, g = 1.70, 95% CI: [1.27, 2.12]). Substantial heterogeneity was evident in studies that were compared to both the active controls (I 2 = 72%, < 0.01) and inactive controls at p -value level of 0.05 (I 2 = 69%, p < 0.001).
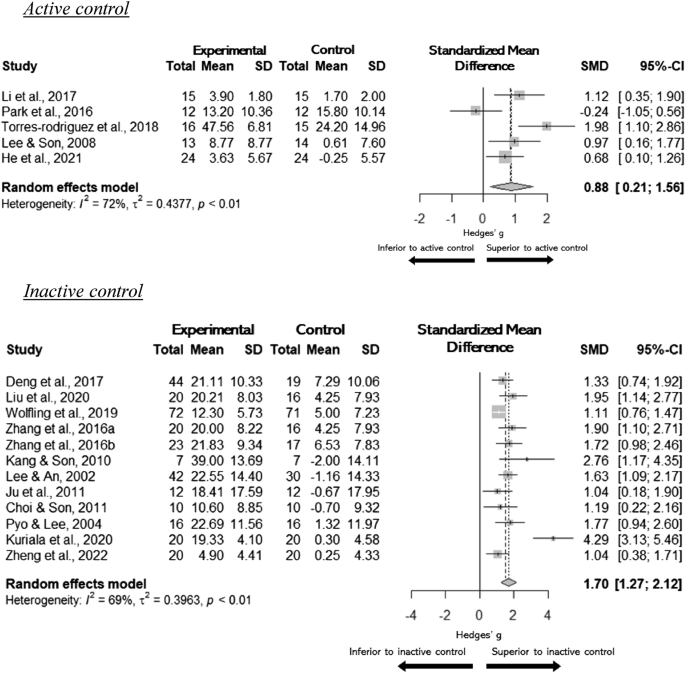
Pairwise Meta-analysis. Psychological treatment effects on excessive gaming by comparison group type (active and inactive controls). SMD standardized mean difference, SD standard deviation, CI confidence interval, I 2 = Higgins' I 2 .
Moderator analysis
As shown in Table 2 , the moderator analysis suggested that effect sizes were larger in non-RCT studies ( n = 10, g = 1.60, 95% CI [1.36, 1.84]) than RCT studies ( n = 7, g = 1.26, 95% CI [0.30, 2.23]). However, the results of a Q-test for heterogeneity yielded insignificant results (Q = 0.44, df[Q] = 1, p = 0.51), indicating that no statistically significant difference in treatment efficacy at p level of 0.05 between RCT and non-RCT studies.
The results of Q-test for heterogeneity did not yield any significant results, indicating no significant differences in treatment efficacy between adults and adolescents (Q = 2.39, df[Q] = 1, p = 0.12), Western and Eastern regions (Q = 0.40, df[Q] = 1, p = 0.53), or low and high research qualities among RCT studies (Q = 2.25, df[Q] = 1, p = 0.13) and non-RCT studies (Q = 3.06, df[Q] = 1, p = 0.08).
Subgroup analysis
The results demonstrated that the treatment effect was Hedges’ g = 1.54 (95% CI [0.87, 2.21]) at 1-to-3-month follow-up and Hedges’ g = 1.23 (95% CI [0.77, 1.68]) 4- to-6-month follow-up. The results also showed that the treatment for excessive gaming was also effective on depression and anxiety. Specifically, treatment on depression was Hedges’ g = 0.52 (95% CI: [0.22, 0.81], p < 0.001), and anxiety was Hedges’ g = 0.60 (95% CI [0.11, 1.08], p = 0.02), which are medium and significant effects. However, the effect on impulsivity was insignificant, Hedges’ g = 0.26 (95% CI [− 0.14, 0.67], p = 0.20).
Network meta-analysis
As shown in Fig. 3 , a network plot represents a connected network of eight intervention types (CBT, BT + Mindfulness, BT, Virtual Reality BT, CBT + Mindfulness, CBT + Family, MI + BT, and Mindfulness) and three control group types (wait-list control, no treatment, treatment as usual). The widest width of nodes was observed when comparing BT + Mindfulness and no treatment, indicating that those two modules were most frequently compared. No evidence of global inconsistency based on a random effects design-by-treatment interaction model was found (Q = 8.5, df[Q] = 7, p = 0.29). Further, local tests of loop-specific inconsistency did not demonstrate inconsistency, indicating that the results from the direct and indirect estimates were largely in agreement ( p = 0.12- 0.78).
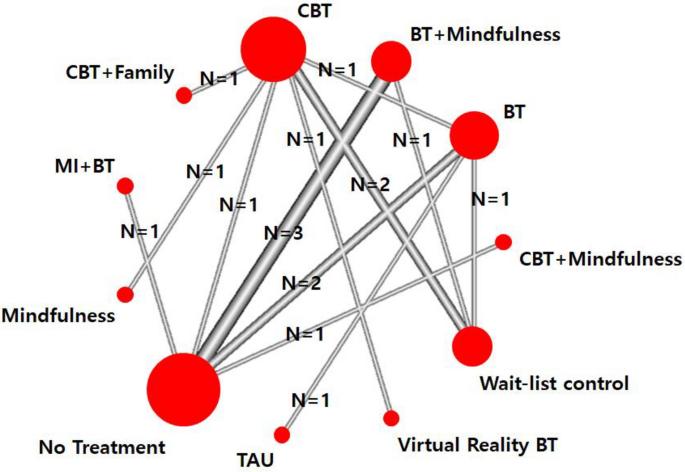
Network plot for excessive gaming interventions. Width of lines and size of circles are proportional to the number of studies in each comparison. BT behavioral therapy, CBT cognitive behavioral therapy, Family family intervention, MI motivational interviewing, TAU treatment as usual.
As shown in Fig. 4 , according to SUCRA, a combined intervention of CBT and Mindfulness ranked as the most optimal treatment (SUCRA = 97.1%) and demonstrated the largest probability of effectiveness when compared to and averaged over all competing treatments. A combined treatment of CBT and Family intervention ranked second (SUCRA = 90.2%), and Mindfulness intervention ranked third (SUCRA = 82.1%). As shown in Table 3 , according to league table, CBT + Mindfulness intervention showed positive weighted mean difference values in the lower diagonal, indicating greater effectiveness over all other interventions. The CBT + Mindfulness intervention was more effective than CBT + Family or Mindfulness interventions, but their differences were not significant (weighted mean differences = 0.23–1.11, 95% CI [− 1.39 to 2.68]). The top three ranked interventions (e.g., CBT + Mindfulness, CBT + Family intervention, and Mindfulness in a row) were statistically significantly superior to CBT as a standalone treatment as well as the rest of treatments.
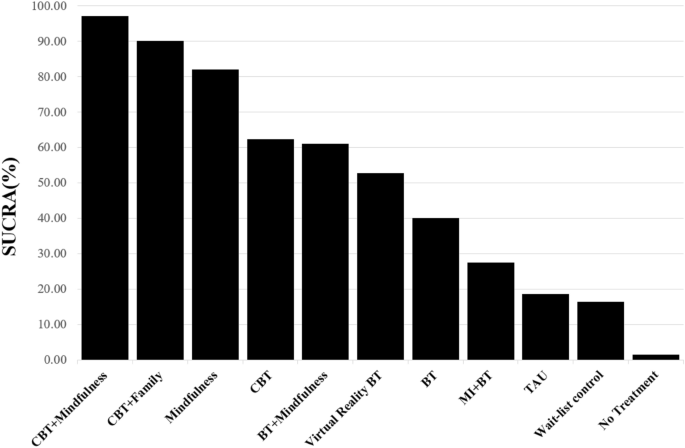
Surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) rankogram of excessive gaming. BT behavioral therapy, CBT cognitive behavioral therapy, Family family intervention, MI motivational interviewing, TAU treatment as usual.
Risk of bias
Figure 5 displays an overview of the risk of bias across all included studies. Of note was that in the RCT studies, bias due to missing outcome data was least problematic, indicating a low dropout rate (six out of seven studies). In contrast, bias due to deviations from intended interventions was most problematic, indicating that, in some studies, participants and trial personnel were not blinded and/or there was no information provided as to whether treatments adhered to intervention protocols (six out of seven studies). In the non-RCT studies, bias in the selection of participants in the study was least problematic, indicating that researchers did not select participants based on participant characteristics after the start of intervention (10 out of 10 studies). In contrast, bias in the measurement of outcomes was most problematic, indicating that participants and outcome assessors were not blinded and/or studies used self-reported measures without clinical interviews (10 out of 10 studies).
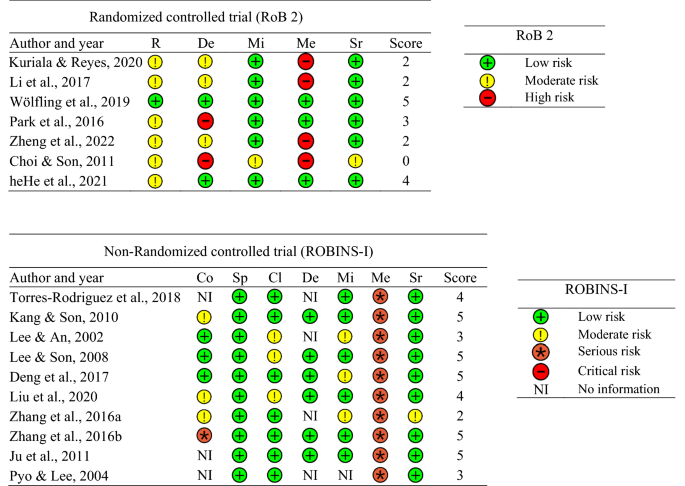
Overview of risk of bias results across all included studies. Cl bias in classification of interventions, Co bias due to confounding, De bias due to deviations from intended interventions, Me bias in measurement of the outcome, Mi bias due to missing outcome data, R bias arising from the randomization process, RoB risk of bias, ROBINS-I risk of bias in non-randomized studies of intervention, Sp bias in selection of participants in the study, Sr bias in selection of the reported result.
Funnel plots and Egger’s test showed no evidence of publication in network meta-analyses. Funnel plots were reasonably symmetric and the result from Egger’s test for sample bias were not significant ( p = 0.22; see Supplementary Material 4 ).
In this pairwise and network meta-analyses, the authors assessed data from 17 trials and analyzed the overall and relative effectiveness of eight types of psychological treatments for reducing excessive gaming. The pairwise meta-analysis results indicated large overall effectiveness of psychological treatments in reducing excessive gaming. Although the effectiveness was smaller when compared to the active controls than when compared to the inactive controls, both effect sizes were still large. However, this result needs to be interpreted with caution because there are only seven existing RCT studies and several existing low-quality studies. Network meta-analysis results indicated that a combined treatment of CBT and Mindfulness was the most effective, followed by a combined therapy of CBT and Family intervention, Mindfulness, and then CBT as a standalone treatment, however, this finding was based on a limited number of studies. Overall, the findings suggest that psychological treatments for excessive gaming is promising, but replications are warranted, with additional attention being placed on addressing methodological concerns.
The large effect of psychological treatments in reducing excessive gaming seems encouraging but the stability and robustness of the results need to be confirmed. These authors’ moderator analysis indicated that the effect size of non-RCT studies was not significantly different from that of RCT studies. The authors conducted a moderator analysis using the research quality score (high vs low) and found that research quality did not moderate the treatment effect. The authors also examined publication bias using both funnel plots and Egger’s test and found no evidence of publication bias in network meta-analysis. Because most of the studies included in the review were from Asian countries, the authors examined the generalizability of the finding by testing moderator analysis by regions and found no significant difference of treatment effect sizes between Eastern and Western countries. Finally, although limited studies exist, treatment benefits did not greatly diminish after 1–6 months of follow-ups, indicating possible lasting effects.
Network meta-analysis findings provide some preliminary support for the notion that a combined treatment of CBT and Mindfulness and a combined treatment of CBT and Family intervention are most effective in addressing individuals’ gaming behaviors. These combined therapies were significantly more effective than the CBT standalone approach. CBT has been studied and found to be highly effective in addiction treatment—particularly in reducing excessive gaming due to its attention to stimulus control and cognitive restructuring 13 . However, adding Mindfulness and family intervention may have been more effective than CBT alone, given that gaming is affected not only by individual characteristics, but also external stress or family factors.
Mindfulness generally focuses on helping individuals to cope with negative affective states through mindful reappraisal and aims to reduce stress through mindful relaxation training. The effectiveness of Mindfulness has been validated in other substance and behavioral addiction studies such as alcohol 37 , gambling 38 , and Internet 39 addiction treatments. Indulging in excessive gaming is often associated with the motivation to escape from a stressful reality 40 , and mindful exercises are likely to help gamers not depend on gaming as a coping strategy.
Because excessive gaming is often entangled with family environments or parenting-related concerns—particularly with adolescents, addressing appropriate parent–adolescent communication and parenting styles within excessive gaming interventions are likely to increase treatment efficacy 41 , 42 , 43 . Based on a qualitative study focused on interviews with excessive gamers 43 , and per reports from interviewed gamers, parental guidance to support regulatory control and encouragement to participate in other activities are important factors to reduce excessive gaming. However, at the same time, if parents excessively restrict their children’s behavior, children will feel increased stress and may further escape into the online world through gaming 44 as a means of coping with their stress. Our study indicates that appropriate communication among parents and adolescents in addition to parenting styles with respect to game control must be discussed in treatment. However, because only two studies examined the top two ranked combined interventions within this paper, such findings warrant replication.
Limitations and future directions
These authors identified methodological limitations and future directions in the reviewed studies, which include the following. The authors included non-RCTs to capture data on emerging treatments, but a lack of RCT studies contributes to this paper’s identified methodological concerns. Of 17 studies included, seven were RCT studies and 10 were non-RCT studies. The lack of RCT studies has been repeatedly mentioned in previous review studies 17 , 18 . In fact, one of the two identified reviews 17 made the criticism that even CBT (the most widely studied treatment for excessive gaming) was mostly conducted in non-RCT studies, which was commensurate with this paper’s data (only one out of four CBT studies included in this review is a RCT). Including non-RCTs may be likely to increase selection bias by employing easily accessible samples and assigning participants with more willingness (which is an indicator of better treatment outcome) to intervention groups. Selection bias may have increased the effect size of treatments than what is represented in reality and may limit the generalizability of this finding. Thus, more rigorous evaluation through RCTs is necessary in future studies.
While there are concerns surrounding assessment tools, given that all included studies used self-report measures without clinical interviews, this may lead to inaccurate results due to perceived stigma. Additionally, 11 self-reported measurement tools were employed in the included studies—and some of those tools may have poor sensitivity or specificity. A previous narrative review 45 and a recent meta-analytic review 46 suggested that the Game Addiction Scale-7, Assessment of Internet and Computer Addiction Scale-Gaming, Lemmens Internet Gaming Disorder Scale-9, Internet Gaming Disorder Scale 9- Short Form, and Internet Gaming Disorder Test-10 have good internal consistency and test–retest reliability. Thus, there is a need for studies to employ clinical interviews and self-report measures with good psychometric features.
Many studies in this included review did not describe whether participants and experimenters were blinded and there was no information about whether treatments adhered to intervention protocols. Although blinding of participants and personnel may be impossible in most psychotherapy studies, it is crucial to evaluate possible performance biases such as social desirability. Also, a fidelity check by content experts is needed to confirm whether treatments adhered to intervention protocols.
Finally, future studies need to examine treatment efficacy in treating both excessive gaming and its comorbid psychiatric symptoms. Internet/gaming addiction has been reported to have a high comorbidity with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, depression, anxiety, and other substance abuse 47 , 48 . Our results showed that CBT, BT, and BT + Mindfulness may be effective in reducing depression or anxiety symptoms of excessive gamers. However, other psychological and/or pharmacological treatments such as CBT + Bupropion or Bupropion as a standalone treatment have been also reported as potentially effective treatments for excessive gamers with major depressive disorder 49 , 50 . Thus, it would be worthwile to examine efficacy of treatments on excessive gamers with dual diagnoses.
TO the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first pairwise meta-analytic and network meta-analytic study that examined the overall effectiveness of psychological treatments and compared the relative effectiveness of diverse treatment options for excessive gaming. Although the authors intentionally used network meta-analysis because of its usefulness in comparing relative effectiveness of currently existing literature, this finding should be interpreted with caution due to the small number of studies. However, as previously indicated, the global prevalence of excessive gaming highlights the need for greater attention to this topic. Studies focused on the effectiveness of diverse gaming interventions help meet the call for further inquiry and study on this topic placed by the DSM-5 7 , and allow greater advances to be made in treating individuals who may have difficulty controlling excessive gaming habits. As such, this study can provide preliminary support for beneficial treatment interventions for excessive gaming as well as recommendations for more rigorous studies to be directed at helping those who have excessive gaming habits.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
•Indicates studies used in the meta-analysis
Griffiths, M. D., Király, O., Pontes, H. M. & Demetrovics, Z. Mental Health in the Digital Age: Grave Dangers, Great Promise (Oxford University Press, 2015).
Google Scholar
Wong, H. Y. et al. Relationships between severity of internet gaming disorder, severity of problematic social media use, sleep quality and psychological distress. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 17 , 1879 (2020).
Article Google Scholar
Brandtner, A., Wegmann, E. & Brand, M. Desire thinking promotes decisions to game: The mediating role between gaming urges and everyday decision-making in recreational gamers. Addict. Behav. Rep. 12 , 100295 (2020).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ferguson, C. J., Coulson, M. & Barnett, J. A meta-analysis of pathological gaming prevalence and comorbidity with mental health, academic and social problems. J. Psychiatr. Res. 45 , 1573–1578 (2011).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
King, D. L. & Delfabbro, P. H. The concept of “harm” in Internet gaming disorder. J. Behav. Addict. 7 , 562–564 (2018).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 11th edn. (World Health Organization, 2019).
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) (American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013).
Book Google Scholar
Stevens, M. W., Dorstyn, D., Delfabbro, P. H. & King, D. L. Global prevalence of gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 55 , 553–568 (2020).
Chiang, C. L., Zhang, M. W. & Ho, R. C. Prevalence of internet gaming disorder in medical students: A meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 12 , 760911 (2021).
Rumpf, H.-J. et al. Including gaming disorder in the ICD-11: The need to do so from a clinical and public health perspective: Commentary on: A weak scientific basis for gaming disorder: Let us err on the side of caution (van Rooij et al. 2018). J. Behav. Addict. 7 , 556–561 (2018).
Dullur, P. & Hay, P. Problem internet use and internet gaming disorder: A survey of health literacy among psychiatrists from Australia and New Zealand. Australas. Psychiatry. 25 , 140–145 (2017).
Knocks, S., Sager, P. & Perissinotto, C. “Onlinesucht” in der Schweiz [“Online-addiction” in Switzerland] (2018).
Stevens, M. W., King, D. L., Dorstyn, D. & Delfabbro, P. H. Cognitive–behavioral therapy for Internet gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 26 , 191–203 (2019).
Mihara, S. & Higuchi, S. Cross-sectional and longitudinal epidemiological studies of I nternet gaming disorder: A systematic review of the literature. Psychiatry. Clin. Neurosci. 71 , 425–444 (2017).
Rehbein, F. & Baier, D. Family-, media-, and school-related risk factors of video game addiction. J. Media Psychol. 15 , 118–128 (2013).
Yu, C., Li, X. & Zhang, W. Predicting adolescent problematic online game use from teacher autonomy support, basic psychological needs satisfaction, and school engagement: A 2-year longitudinal study. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 18 , 228–233 (2015).
Zajac, K., Ginley, M. K. & Chang, R. Treatments of internet gaming disorder: A systematic review of the evidence. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 20 , 85–93 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
King, D. L. et al. Treatment of Internet gaming disorder: An international systematic review and CONSORT evaluation. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 54 , 123–133 (2017).
•He, J., Pan, T., Nie, Y., Zheng, Y. & Chen, S. Behavioral modification decreases approach bias in young adults with internet gaming disorder. Addict. Behav. 113 , 106686 (2021).
•Wölfling, K. et al. Efficacy of short-term treatment of internet and computer game addiction: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 76 , 1018–1025 (2019).
Mavridis, D., Giannatsi, M., Cipriani, A. & Salanti, G. A primer on network meta-analysis with emphasis on mental health. Evid. Based Ment. Health. 18 , 40–46 (2015).
Benz, F. et al. The efficacy of cognitive and behavior therapies for insomnia on daytime symptoms: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 80 , 101873 (2020).
Cuijpers, P. et al. A network meta-analysis of the effects of psychotherapies, pharmacotherapies and their combination in the treatment of adult depression. World Psychiatry 19 , 92–107 (2020).
Ha, A., Kim, S. J., Shim, S. R., Kim, Y. K. & Jung, J. H. Efficacy and safety of 8 atropine concentrations for myopia control in children: A network meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 129 , 322–333 (2021).
Hutton, B. et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 162 , 777–784 (2015).
Team, R. C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing (2013).
Cheung, M. W. L., Ho, R. C., Lim, Y. & Mak, A. Conducting a meta-analysis: Basics and good practices. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 15 , 129–135 (2012).
Hedges, L. V. & Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-analysis (Academic Press, 1985).
MATH Google Scholar
Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988).
Rosenthal, R. Meta-Analytic Procedures for Social Science Research Vol. 15, 148 (Sage Publications, 1991).
Higgins, J. P. & Thompson, S. G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 21 , 1539–1558 (2002).
Salanti, G., Ades, A. & Ioannidis, J. P. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: An overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 64 , 163–171 (2011).
Nielsen, P. et al. Multidimensional family therapy reduces problematic gaming in adolescents: A randomised controlled trial. J. Behav. Addict. 10 , 234–243 (2021).
Pornnoppadol, C. et al. A comparative study of psychosocial interventions for internet gaming disorder among adolescents aged 13–17 years. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 18 , 932–948 (2020).
Shim, S., Yoon, B.-H., Shin, I.-S. & Bae, J.-M. Network meta-analysis: Application and practice using Stata. Epidemiol. Health 39 , e2017047 (2017).
Dias, S. et al. Evidence synthesis for decision making 4: Inconsistency in networks of evidence based on randomized controlled trials. Med. Decis. Mak. 33 , 641–656 (2013).
Cavicchioli, M., Movalli, M. & Maffei, C. The clinical efficacy of mindfulness-based treatments for alcohol and drugs use disorders: A meta-analytic review of randomized and nonrandomized controlled trials. Eur. Addict. Res. 24 , 137–162 (2018).
Maynard, B. R., Wilson, A. N., Labuzienski, E. & Whiting, S. W. Mindfulness-based approaches in the treatment of disordered gambling: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Res. Soc. Work. Pract. 28 , 348–362 (2018).
•Liu, L. et al. Altered intrinsic connectivity distribution in internet gaming disorder and its associations with psychotherapy treatment outcomes. Addict. Biol. 26 , e12917 (2021).
Bowditch, L., Chapman, J. & Naweed, A. Do coping strategies moderate the relationship between escapism and negative gaming outcomes in World of Warcraft (MMORPG) players? Comput. Hum. Behav. 86 , 69–76 (2018).
Bonnaire, C. & Phan, O. Relationships between parental attitudes, family functioning and Internet gaming disorder in adolescents attending school. Psychiatry Res. 255 , 104–110 (2017).
Schneider, L. A., King, D. L. & Delfabbro, P. H. Family factors in adolescent problematic Internet gaming: A systematic review. J. Behav. Addict. 6 , 321–333 (2017).
Shi, J., Renwick, R., Turner, N. E. & Kirsh, B. Understanding the lives of problem gamers: The meaning, purpose, and influences of video gaming. Comput. Hum. Behav. 97 , 291–303 (2019).
Siste, K. et al. Gaming disorder and parenting style: A case series. Addict. Disord. Their. Treat. 19 , 185–190 (2020).
King, D. L., Haagsma, M. C., Delfabbro, P. H., Gradisar, M. & Griffiths, M. D. Toward a consensus definition of pathological video-gaming: A systematic review of psychometric assessment tools. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 33 , 331–342 (2013).
Yoon, S. et al. Reliability, and convergent and discriminant validity of gaming disorder scales: a meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 12 , 5659 (2021).
Ho, R. C. et al. The association between internet addiction and psychiatric co-morbidity: A meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 14 , 1–10 (2014).
González-Bueso, V. et al. Association between internet gaming disorder or pathological video-game use and comorbid psychopathology: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 15 , 668 (2018).
Kim, S. M., Han, D. H., Lee, Y. S. & Renshaw, P. F. Combined cognitive behavioral therapy and bupropion for the treatment of problematic on-line game play in adolescents with major depressive disorder. Comput. Hum. Behav. 28 , 1954–1959 (2012).
Han, D. H. & Renshaw, P. F. Bupropion in the treatment of problematic online game play in patients with major depressive disorder. J. Psychopharmacol. 26 , 689–696 (2012).
•Kuriala, G. K. & Reyes, M. E. S. Efficacy of the acceptance and cognitive restructuring intervention program (ACRIP) on the internet gaming disorder symptoms of selected Asian adolescents. J. Technol. Behav. Sci. 5 , 238–244 (2020).
•Li, W. et al. Mindfulness-oriented recovery enhancement for internet gaming disorder in US adults: A stage I randomized controlled trial. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 31 , 393 (2017).
•Park, S. Y. et al. The effects of a virtual reality treatment program for online gaming addiction. Comput. Methods. Progr. Biomed. 129 , 99–108 (2016).
•Zheng, Y., He, J., Fan, L. & Qiu, Y. Reduction of symptom after a combined behavioral intervention for reward sensitivity and rash impulsiveness in internet gaming disorder: A comparative study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 153 , 159–166 (2022).
•Choi, O. Y. & Son, C. N. Effects of the self-control training program on relief of online game addiction level, aggression, and impulsivity of college students with online game addiction. Korean J. Clin. Psychol. 30 , 723–745 (2011).
•Torres-Rodriguez, A., Griffiths, M. D., Carbonell, X. & Oberst, U. Treatment efficacy of a specialized psychotherapy program for Internet Gaming Disorder. J. Behav. Addict. 7 , 939–952 (2018).
•Kang, H. Y. & Son, C. N. The effects of self-esteem enhancement cognitive behavioral therapy for adolescents’ internet addiction and game addiction. Korean J. Psychol. Health 15 , 143–159 (2010).
•Lee, H. C. & An, C. Y. A study on the development and effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy for internet addiction. Korean J. Psychol. Health. 7 , 463–486 (2002).
•Lee, J. H. & Son, C. N. The effects of the group cognitive behavioral therapy on game addiction level, depression and self-control of the high school students with internet game addiction. Korean Soc. Stress. Med. 16 , 409–417 (2008).
•Deng, L.-Y. et al. Craving behavior intervention in ameliorating college students’ internet game disorder: A longitudinal study. Front. Psychol. 8 , 526 (2017).
•Zhang, J.-T. et al. Altered resting-state neural activity and changes following a craving behavioral intervention for Internet gaming disorder. Sci. Rep. 6 , 1–8 (2016a).
•Zhang, J.-T. et al. Effects of craving behavioral intervention on neural substrates of cue-induced craving in Internet gaming disorder. NeuroImage Clin. 12 , 591–599 (2016b).
•Ju, H. W., Hyun, M. H. & Park, J. S. Effects of the transtheoretical model-based intervention in game-addicted adolescents. Korean J. Youth. Stud. 18 , 227–246 (2011).
•Pyo, M. H. & Lee, Y. M. The effects of game control program on the mitigation of internet game addiction and self-efficacy. Kor. Elem. Cnslr. Edu. Assoc. 105–118 (2004).
Download references
This research was supported by the project investigating scientific evidence for registering gaming disorder on Korean Standard Classification of Disease and Cause of Death funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare and Korea Creative Content Agency.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, Chungnam National University, W12-1, Daejeon, 34134, South Korea
Jueun Kim, Sunmin Lee & Dojin Lee
Department of Health and Medical Informatics, College of Health Sciences, Kyungnam University, Changwon, South Korea
Sungryul Shim
Department of Counseling Psychology, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA
Daniel Balva
School of Psychology, Korea University, Seoul, South Korea
Kee-Hong Choi
Department of Psychology, Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea
Jeanyung Chey & Woo-Young Ahn
Dr. Shin’s Neuropsychiatric Clinic, Seoul, South Korea
Suk-Ho Shin
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
J.K., K.-H.C., J.C., S.-H.S., and W.-Y.A. contributed to the conception and design of the study. J.K. wrote the draft of the manuscript and D.B. reviewed and edited the draft. D.L., S.L., and S.S. extracted the data and performed the analyses.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jueun Kim .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kim, J., Lee, S., Lee, D. et al. Psychological treatments for excessive gaming: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 12 , 20485 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24523-9
Download citation
Received : 06 October 2022
Accepted : 16 November 2022
Published : 28 November 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24523-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

Video Game Addiction
The argument against video game addiction, many researchers are skeptical that video games are truly "addictive.".
Updated July 3, 2023 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
- What Is Video Game Addiction?
- Find a therapist near me
- Video games have many benefits for gamers.
- Research on gaming disorder—aka video game addiction—is flawed and not sufficiently conclusive.
- Because video games are less socially acceptable, they may be unfairly targeted.
- There are other explanations for many reports of video game addiction, including autism, ADHD, and depression.
This is half of a pair of articles that highlight the evidence for and against the existence of video game addiction . Read the counter-argument here .
For decades, psychologists, parents, and gamers have asserted that video games can be addictive. Although video games seem to influence enthusiasts differently from those of other hobbies, there is insufficient empirical evidence to designate them as an actual addiction . Further, video games are a fun and socially beneficial activity for many, so labeling them as addictive would prevent many from accessing these benefits.
For example, video games connect lonely or introverted people with one another , relieve stress , and even help people explore their own identities . Some therefore argue that, because of video games’ benefits and popularity, gaming addiction should not be considered an official diagnosis until overwhelming evidence supports this assertion.
Flawed Research
Several studies have concluded that gaming disorder qualifies as an addiction. Because addictions share several characteristics, researchers created theoretical criteria that a gamer must meet to have the diagnosis. For example, people with addictions suffer consequences in various aspects of their life and struggle to quit without help. This is true regardless of the substance.
Based on the assumption that people with video game addiction must be affected similarly, researchers have surveyed gamers on similar criteria to determine what percent have an addiction. These include questions such as, “How often do you find it difficult to stop gaming?” and “Have you deceived a family member, significant other, employer, or therapist regarding the amount of time spent engaging in gaming activities?”
Although questions like these may reasonably assess someone’s behavior, researchers use too many different questionnaires to be compared cleanly. Even when researchers use the same survey, they sometimes interpret the results differently.
In other words, someone would need to answer “Yes” to six of the eleven Gaming Addiction Screening questions to be considered addicted. They would need to respond “Sometimes” or “Often” to five or more of the ten questions in the Ten Item Internet Gaming Disorder Test to qualify. If the same person took both surveys, one survey might conclude that they had an addiction and the other might not. Further, some studies only measure how many hours per week a person spends gaming instead of targeting the effect games have on their functioning.
This has resulted in wildly different estimates of gaming addiction’s prevalence. It is difficult to draw meaningful conclusions from these data until researchers use standardized measures.
It is also very difficult to estimate one’s actual screen time each week. One meta-analysis of the research found that in 95 percent of studies, participants did not accurately report how much time they spend on screens . This calls into question all studies which rely on participants’ subjective estimates of how they use their time because they have based their conclusions on a statistic that is likely inaccurate.
Why Not Other Hobbies?
Other critics of the diagnosis point out that gaming has been unfairly targeted and pathologized. A person who plays golf instead of spending time with family is inconsiderate. A person who plays video games instead of spending time with family is addicted.
This demonstrates a clear bias . Society considers video games a waste of time, so an enthusiastic gamer is criticized more harshly than someone with a more acceptable hobby.
What Else Might Account for Excessive Gaming
Many of my clients report that they feel addicted to technology. When I continue the assessment process, many report that they were previously diagnosed with autism or ADHD . This complicates the diagnostic process because many people with these disorders already struggle to stop scrolling through social media or playing video games.
Most of us have looked up from our phones and realized that half an hour or more had suddenly passed. The hypnotic “flow” which we experienced blinded us to the passage of time. Autistic people* and those with ADHD are especially susceptible to this phenomenon. So if, for example, a person with ADHD finds it particularly difficult to turn off a game, does that person have an addiction or is it simply how this kind of stimulus affects those with ADHD?

Some research has found that heavy gamers have reduced gray matter in areas of the brain associated with attention , impulse control. However, these studies do not sufficiently demonstrate that gaming caused the differences, only that they are associated. Correlation is not causation. Some studies even show that brain scans for people with ADHD look remarkably similar to scans of those with gaming disorder , even after treatment.
One researcher pointed out this conundrum by relating it to depression . “We would not diagnose depressed individuals with hypersomnia with a comorbid ‘bed addiction.’” In other words, someone with depression might stay in bed for days, but this does not mean that they are addicted to the bed. In the same way, an autistic person or someone with depression or ADHD might appear to be addicted to video games even when they are not. In short, many diagnosed with gaming disorder may simply be autistic or have ADHD.
It is possible that video games are addictive. However, the current body of research is too flawed to state decisively that the negative consequences outweigh the benefits the games afford players. It is premature to consider gaming disorder to be an official addiction.
*Although many refer to autistic people as “people with autism” or “people with autism spectrum disorders,” almost 90 percent of autistic adults prefer “autistic person.” This language is used here to respect that preference.
Bean, A. M., Nielsen, R. K. L., van Rooij, A. J., & Ferguson, C. J. (2017). Video game addiction: The push to pathologize video games. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 48 (5). Retrieved from http://psycnet.apa.org/record/2017-29288-001
Diament, M. (2022, December 2). 'Autistic' or 'person with autism'? It depends. Disability Scoop. https://www.disabilityscoop.com/2022/12/02/autistic-or-person-with-auti…
Fishman, A. (2019, January 22). Video games are social spaces. Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/video-game-health/201901/video-…
Fishman, A. (2022, November 7). Why it's so hard to walk away from a video game. Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/video-game-health/202211/why-it…
Fishman, A. (2023, February 20). How gamers use video games to explore their gender identity. Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/intl/blog/video-game-health/202302/how-…
Gentile, D. (n.d.) Gaming Addiction Screening. University of California, Santa Cruz. https://caps.ucsc.edu/pdf/gaming-addiction-screening.pdf
Han, D.H., Bae, S., Hong, J., Kim, S.M., Son, Y.D., & Renshaw, P. (2019). Resting-state fMRI study of ADHD and Internet Gaming Disorder. Journal of Attention Disorders, 25 (8). Retrieved from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1087054719883022
Király, O., Bőthe, B., Ramos-Díaz, J., Rahimi-Movaghar, A., Lukavska, K., Hrabec, O., Miovsky, M., Billieux, J., Deleuze, J., Nuyens, F., Karila, L.M., Griffiths, M.D., Nagygyörgy, K., Urbán, R., Potenza, M., King, D.L., Rumpf, H., Carragher, N., Lilly, E., & Demetrovics, Z. (2019). Ten-Item Internet Gaming Disorder Test (IGDT-10): Measurement invariance and cross-cultural validation across seven language-based samples. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 33 (1). Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328615597_Ten-Item_Internet_Ga…
Parry, D.A., Davidson, B.I., Sewall, C.J.R., Fisher, J.T., Mieczkowski, H., & Quintana, D.S. (2021). Nature Human Behavior, 5 . Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41562-021-01117-5
van Rooij, A.J., Ferguson, C., Carras, M.C. Kardefelt-Winther, D., Shi, J., Aarseth, E., Bean, A., Bergmark, K.H., Brus, A., Coulson, M., Deleuze, J., Dullur, P., Dunkels, E., Edman, J., Elson, M., Etchells, P.J., Fiskaali, A., Granic, I., Jansz, J...& Przybylski, A.K. (2018). A weak scientific basis for gaming disorder: Let us err on the side of caution. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 7 (1) Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323542721_A_weak_scientific_ba…
van Rooij, A.J., Schoenmakers, T., van den Eijnden, R.J.J.M., Vermulst, A.A., & van de Mheen, D. (2012). Video Game Addiction Test: Validity and psychometric characteristics. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15 (9). Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/230696095_Video_Game_Addiction…

Andrew Fishman is a licensed social worker in Chicago, Illinois. He is also a lifelong gamer who works with clients to understand the impact video games have had on their mental health.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
15.9 Cause-and-Effect Essay
Learning objective.
- Read an example of the cause-and-effect rhetorical mode.
Effects of Video Game Addiction
Video game addition is a serious problem in many parts of the world today and deserves more attention. It is no secret that children and adults in many countries throughout the world, including Japan, China, and the United States, play video games every day. Most players are able to limit their usage in ways that do not interfere with their daily lives, but many others have developed an addiction to playing video games and suffer detrimental effects.
An addiction can be described in several ways, but generally speaking, addictions involve unhealthy attractions to substances or activities that ultimately disrupt the ability of a person to keep up with regular daily responsibilities. Video game addiction typically involves playing games uncontrollably for many hours at a time—some people will play only four hours at a time while others cannot stop for over twenty-four hours. Regardless of the severity of the addiction, many of the same effects will be experienced by all.
One common effect of video game addiction is isolation and withdrawal from social experiences. Video game players often hide in their homes or in Internet cafés for days at a time—only reemerging for the most pressing tasks and necessities. The effect of this isolation can lead to a breakdown of communication skills and often a loss in socialization. While it is true that many games, especially massive multiplayer online games, involve a very real form of e-based communication and coordination with others, and these virtual interactions often result in real communities that can be healthy for the players, these communities and forms of communication rarely translate to the types of valuable social interaction that humans need to maintain typical social functioning. As a result, the social networking in these online games often gives the users the impression that they are interacting socially, while their true social lives and personal relations may suffer.
Another unfortunate product of the isolation that often accompanies video game addiction is the disruption of the user’s career. While many players manage to enjoy video games and still hold their jobs without problems, others experience challenges at their workplace. Some may only experience warnings or demerits as a result of poorer performance, or others may end up losing their jobs altogether. Playing video games for extended periods of time often involves sleep deprivation, and this tends to carry over to the workplace, reducing production and causing habitual tardiness.
Video game addiction may result in a decline in overall health and hygiene. Players who interact with video games for such significant amounts of time can go an entire day without eating and even longer without basic hygiene tasks, such as using the restroom or bathing. The effects of this behavior pose significant danger to their overall health.
The causes of video game addiction are complex and can vary greatly, but the effects have the potential to be severe. Playing video games can and should be a fun activity for all to enjoy. But just like everything else, the amount of time one spends playing video games needs to be balanced with personal and social responsibilities.
Online Cause-and-Effective Essay Alternatives
Lawrence Otis Graham examines racism, and whether it has changed since the 1970s, in The “Black Table” Is Still There :
- http://scremeens.googlepages.com/TheBlackTableessay.rtf
Robin Tolmach Lakoff discusses the power of language to dehumanize in From Ancient Greece to Iraq: The Power of Words in Wartime :
- http://www.nytimes.com/2004/05/18/science/essay-from-ancient-greece-to-iraq-the-power-of-words-in-wartime.html
Alan Weisman examines the human impact on the planet and its effects in Earth without People :
- http://discovermagazine.com/2005/feb/earth-without-people
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is Video Game Addiction?
Definition, Symptoms, Effects, Treatment, and Coping
Carol Yepes / Moment / Getty Images
Understanding Video Game Addiction
Video game addiction is the compulsive or uncontrolled use of video games, in a way that causes problems in other areas of the person's life.
Often considered a form of computer addiction or internet addiction , video game addiction has been an increasing concern for parents as video games have become more commonplace and are often targeted at children.
Video games include computer games, console games, arcade machine games, and even cell phone, and advanced calculator games. Games can be embedded in social networking sites, such as Facebook.
Since the 1950s, gaming has grown into a multi-billion dollar industry. Some people are concerned about the long-term effects of video game playing, particularly in children. Concerns center on the following questions:
- “Are video games harmful?”
- “Do violent video games cause aggression?”
- “Are video games addictive?”
While research is inconclusive, there does appear to be evidence that video games can be harmful, can increase aggression, and can be addictive. However, these effects are highly individual and may involve many more factors than simply the amount of time spent playing games.
Signs of Video Game Addiction
Some symptoms of video game addiction can include:
- Neglecting duties at work, home, or school in order to play video games
- Thinking about video games all the time
- Not being able to decrease playing time even when you try
- Continuing to play despite the problems video games cause in your life
- Playing video games to deal with anxiety, bad moods, or negative feelings
- Feeling upset if you are not able to game
- Not doing other things you used to enjoy in order to play video games
- Hiding how much time you spend playing video games or lying about your gaming habits
Playing video games a lot is not necessarily a sign of a video game addiction, however. Some people are simply very enthusiastic about them and that is how they enjoy spending their free time. If gaming creates distress and interferes with a person's ability to function in their life, then it might be a sign that there is a problem.
How Common Is Video Game Addiction?
Research studies show that 1% to 16% of video gamers meet the criteria for addiction. However, the official definition of video game addiction varies across different organizations. Considering this, it is easy to be confused about whether your or someone else’s gaming falls in the average or heavy ranges.
As with all addictions, it is important when considering the possibility of a video game addiction to not simply consider the amount of time spent gaming, but also the function it is serving the individual. Video game playing, as one of a range of recreational activities, may not be harmful or indicate an addiction.
When game playing is addictive, it takes over as the person’s main way of coping with life, with other important areas of life being neglected or disrupted as a result.
Video game addiction or video game overuse is seen most commonly in players of the persistent multiplayer gaming universe, or Massive Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Game—MMORPG games for short. MMORPGs make up 25% of gaming revenue worldwide. These games hold many attractions for gamers—they are interactive, social, competitive, and happen in real-time.
Research indicates that MMORPGs are more addictive in nature. As a result, they tend to have greater negative impacts on physical health, sleep habits and academic performance.
Diagnosis of Video Game Addiction
Like other behavioral addictions , video game addiction is a controversial idea. While video gaming research is showing some disturbing effects, particularly in younger players, there is a lack of long-term research and insufficient evidence to definitively conclude that video game overuse is indeed an addiction.
In addition, cautionary messages from groups, such as the American Medical Association, which believes that video games are potentially harmful, have to compete with the aggressive marketing of the video games industry, whose own research, unsurprisingly, shows no ill effects.
Currently, it is not recognized as a distinct condition in the " Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders " (DSM-5-TR), the "gold standard" reference for mental health conditions. Internet gaming disorder, however, is included as a condition for further study in the DSM.
Although it is not yet recognized fully as a disorder, proposed criteria have been published.
To be diagnosed, gaming behavior must be severe enough that it creates significant problems in different areas of life, including home, work, family, school, and other areas. Symptoms must also be present for a year or longer.
Similarity to Other Addictions
Video game addictions are similar to other addictions in terms of the amount of time spent playing, the strong emotional attachment to the activity, and the patterns of social difficulties experienced by gaming addicts.
As with other addictions, gaming addicts become preoccupied with game-playing, and it disrupts family and other areas of life, such as school.
The younger that children begin playing video games, the more likely they are to develop dependence-like behaviors.
As with other addictive behaviors, there is a range of different responses to the activity. While some gamers feel unable to reduce the time they spend playing, others do not experience cravings if they are unable to play.
Effects of Video Game Addiction
Some studies suggest that violent video games may increase aggressive thoughts and behaviors. However, there is conflicting research on this, and some studies have not found this effect or suggest that it is influenced by other factors such as moral disengagement and disinhibition.
Research on people who are addicted to video games shows that they have poorer mental health and cognitive functioning including poorer impulse control and ADHD symptoms , compared to people who do not have video game addiction.
People who are addicted to video games also have increased emotional difficulties, including increased depression and anxiety, report feeling more socially isolated, and are more likely to have problems with internet pornography use.
Treatment for Video Game Addiction
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that can be helpful in the treatment of behavioral addictions such as video game addiction.
Working with a therapist, people learn to identify the thoughts that contribute to excessive, compulsive video game use. Once people learn to recognize these thoughts, they can then work to replace them with ones that are more helpful and productive.
Therapy can also help people develop different coping strategies to deal with feelings of stress and distract themselves from urges to play video games.
Coping With Video Game Addiction
If you suspect that you have a video game addiction or simply want to reduce your video game use, there are strategies you can use that can help. Some things you can try include:
- Setting limits on your video game use : Decide how much you want to play each day. Set aside a specific block of time and set a timer so you'll know when it is time to quit. Consider enlisting the help of a friend to help keep you accountable.
- Find distractions : Look for other things to hold your interest and fill your time when you feel the urge to play video games. Going for a walk, calling a friend, watching a movie, or reading a book are a few ideas, but trying out new hobbies and interests can also serve as welcome distractions.
- Keep electronics out of your bedroom : Keep gaming systems, phones, and other electronic devices out of your bedroom so you aren't tempted to play games in the evening or before bedtime.
- Practice relaxation techniques : If you are playing games in order to cope with feelings of stress or anxiety, try replacing your gaming habit with other effective coping strategies. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing , mindfulness meditation , and yoga can be a great way to unwind and destress without having to rely on video games.
If you or a loved one are struggling with addiction, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357 for information on support and treatment facilities in your area.
For more mental health resources, see our National Helpline Database .
Li AY, Chau CL, Cheng C. Development and validation of a parent-based program for preventing gaming disorder: The game over intervention . Int J Environ Res Public Health . 2019;16(11). doi:10.3390/ijerph16111984
Jeromin F, Nyenhuis N, Barke A. Attentional bias in excessive internet gamers: Experimental investigations using an addiction Stroop and a visual probe . J Behav Addict . 2016;5(1):32-40. doi:10.1556/2006.5.2016.012
Hong JS, Kim SM, Jung JW, Kim SY, Chung US, Han DH. A comparison of risk and protective factors for excessive internet game play between Koreans in Korea and immigrant Koreans in the United States . J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(23):e162. doi:10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e162
American Psychiatric Association (APA). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . 5th ed, text revision. Washington, D.C.; 2022.
Yao M, Zhou Y, Li J, Gao X. Violent video games exposure and aggression: The role of moral disengagement, anger, hostility, and disinhibition . Aggress Behav . 2019;45(6):662-670. doi:10.1002/ab.21860
Ra CK, Cho J, Stone MD, et al. Association of digital media use with subsequent symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder among adolescents . JAMA . 2018;320(3):255-263. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.8931
Stockdale L, Coyne SM. Video game addiction in emerging adulthood: Cross-sectional evidence of pathology in video game addicts as compared to matched healthy controls . J Affect Disord . 2018;225:265-272. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2017.08.045
By Elizabeth Hartney, BSc, MSc, MA, PhD Elizabeth Hartney, BSc, MSc, MA, PhD is a psychologist, professor, and Director of the Centre for Health Leadership and Research at Royal Roads University, Canada.
- Fact sheets
- Facts in pictures
- Publications
- Questions and answers
- Tools and toolkits
- Endometriosis
- Excessive heat
- Mental disorders
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- All countries
- Eastern Mediterranean
- South-East Asia
- Western Pacific
- Data by country
- Country presence
- Country strengthening
- Country cooperation strategies
- News releases
- Feature stories
- Press conferences
- Commentaries
- Photo library
- Afghanistan
- Cholera
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Greater Horn of Africa
- Israel and occupied Palestinian territory
- Disease Outbreak News
- Situation reports
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- Surveillance
- Health emergency appeal
- International Health Regulations
- Independent Oversight and Advisory Committee
- Classifications
- Data collections
- Global Health Estimates
- Mortality Database
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Health Inequality Monitor
- Global Progress
- World Health Statistics
- Partnerships
- Committees and advisory groups
- Collaborating centres
- Technical teams
- Organizational structure
- Initiatives
- General Programme of Work
- WHO Academy
- Investment in WHO
- WHO Foundation
- External audit
- Financial statements
- Internal audit and investigations
- Programme Budget
- Results reports
- Governing bodies
- World Health Assembly
- Executive Board
- Member States Portal
- Questions and answers /
Addictive behaviours: Gaming disorder
Gaming disorder is defined in the 11th Revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) as a pattern of gaming behavior (“digital-gaming” or “video-gaming”) characterized by impaired control over gaming, increasing priority given to gaming over other activities to the extent that gaming takes precedence over other interests and daily activities, and continuation or escalation of gaming despite the occurrence of negative consequences.
For gaming disorder to be diagnosed, the behaviour pattern must be of sufficient severity to result in significant impairment in personal, family, social, educational, occupational or other important areas of functioning and would normally have been evident for at least 12 months.
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is the basis for identification of health trends and statistics globally and the international standard for reporting diseases and health conditions. It is used by medical practitioners around the world to diagnose conditions and by researchers to categorize conditions.
The inclusion of a disorder in ICD is a consideration which countries take into account when planning public health strategies and monitoring trends of disorders.
WHO released the 11th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) in mid-2018.
A decision on inclusion of gaming disorder in ICD-11 is based on reviews of available evidence and reflects a consensus of experts from different disciplines and geographical regions that were involved in the process of technical consultations undertaken by WHO in the process of ICD-11 development.
The inclusion of gaming disorder in ICD-11 follows the development of treatment programmes for people with health conditions identical to those characteristic of gaming disorder in many parts of the world, and will result in the increased attention of health professionals to the risks of development of this disorder and, accordingly, to relevant prevention and treatment measures.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Essay on Video Games Addiction | Video Games Addiction Essay for Students and Children in English
February 14, 2024 by Prasanna
Essay on Video Games Addiction: In a world where the youth are already struggling with different types of addictions, the emergence of video game addictions is an unwelcome addition. Every day there seems to be a rise in the number of video game addicts. Be it children, teenagers, and even adults. Video games are very entertaining and can hook anyone of any age in. Especially since a person’s emotions are involved in it. It is very easy to get hooked and spend hours and hours playing video games.
There needs to be regulation of the time spent playing video games and intervention from friends and family if they see someone whose life revolves around the video games they play. Addictions do not affect only the person who is addicted. Like any other, this addiction can take over a person’s life and affect their education, work, family life, and the lives of those who love them.
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more.
Long and Short Essays on Video Games Addiction for Students and Kids in English
We provide children and students with essay samples on a long essay of 500 words and a short essay of 150 words on the topic “Video Game Addiction” for reference.
Short Essay on Video Games Addiction 150 Words in English
Short Essay on Video Games Addiction is usually given to classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6.
Video games are a great source of entertainment and a way to fight boredom. They also help people wind down and relax after a stressful day at work. Gaming communities can also often be a safe space for individuals to make friends and interact with peers. However, there are also negative consequences of spending too much time playing video games. Gamer Rage is a well-known thing that can have adverse effects. Individuals that experience this can end up destroying things at home and even hurting family members.
In other words, excessive gaming can cause great harm. People who spend hours and hours on end playing video games can lose their bearings in the real world when they get off the game. They can find themselves disoriented and unable to function normally. This means that there must be some self-control when gaming, not to let it consume a person’s life.
Introduction
Video game addiction is as harmful an addiction as any other. Individuals even suffer from withdrawal syndrome if they are away from their consoles or systems for too long. Those who are addicted end up playing video games for multiple hours at a stretch without taking a break except for something necessary.
Most video games rely on the gamer coming back to beat the next high score or make the next discovery for open-world games. For those who are a part of gaming communities, it is about beating the next team together and gaining more resources or whatever else it is that is required in the game to advance. This is especially true for role-playing games where the player can customize their character and interact with others.
One of the main problems resulting from excessive gaming is gamer rage that comes from frustration and anger when a player cannot beat their opponent. It results in swearing and abusing opponents and family members verbally. They also sometimes end up attacking family members if the game happens to be cut short or if they are asked to leave the game to tend to their other duties for some time.
Physical Consequences
This addiction can result in carpal tunnel syndrome, poor eyesight, migraines, backaches, pain from poor posture, and even obesity and cardiovascular diseases. With a lack of routine in the outside world, it can have significant physical consequences.
Those who play video games need to be mindful of the amount of time that is spent. They also need to be careful that they do not neglect other responsibilities that they may have. Especially for those who have young children at home that cannot be ignored.
Long Essay on Video Games Addiction 500 Words in English
Long Essay on Video Games Addiction is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10.
Video games are a fun and entertaining way to relax. They help people who are isolated to form friends and be a part of a community. There are many stories where children with developmental issues learn how to interact and be a part of society. It helps them with brain development and helps them grow in many ways. However, there is a downside to it, with excessive gaming that can result in addiction. This is an extreme that we cannot go to as it harms everyone involved.
Massive Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games play a huge role in players that get addicted to gaming. In this sort of gaming, the player can create their character and play with others on quests to get better gear. These are games that one pays for, which means that there is a waste of money if a person isn’t playing. That, coupled with how enjoyable the game is, can result in players playing for hours on end. The visuals’ effects and quality are generally very high in these, which makes gameplay all the more captivating. It is difficult for players to reorient themselves when they come back to the real world.
As unique and fun as the games are, this is also a problem that needs to be addressed. Precisely because the games are so enjoyable that players find it difficult to disconnect and be a part of the real world.
Social Consequences
People often find a way to balance their time to either go to work or school, finish what they have to do, come home, and spend all their time playing games. Often they think that this is a good compromise. It is not.
It is not healthy to divide life between the two in that manner. There needs to be a balance where individuals spend time with their family and friends as well. This can result in isolation in social life and regression in learning how to function in society. This can result in behavioral issues as well. When teenagers spend time in this manner, they do not learn the basic skills required to function in society and to hold jobs.
This is an issue that affects individuals that are married as well. There are many stories where the spouse works through the day and comes home and plays, neglecting the house or the children. Resulting in one parent handling all the load of the house, which is extremely stressful and challenging. It can lead to a break in relationships as well.
When a person spends hours gaming, they give no time to walking around or any physical activity. It can lead to poor eyesight, carpal tunnel syndrome, and pain and aches due to bad posture. It can lead to migraines and, in extreme cases, neurological issues. Not walking around can result in obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and posture issues for years. Gamer rage can also result in strokes.
Mental Consequences
Many times, gamers find it difficult to be a part of the real world after gaming for so many hours. They tend to try functioning in the real world as they would in games. In this manner, they can harm themselves and other people. Like the incident of the boy who shot a random person on the street expecting him to become a zombie as people were doing in the game that he was playing. This is an extreme case of disorientation and disconnect from the real world.
Addiction can also result in paranoia and anxiety if excessive time is spent playing intense games. It can also lead to mental regression and a loss of social skills.
Fortunately, rehab centers for this addiction also exist so that people who seek help can go back to having a normal life. Even so, rehabs are not a guarantee of freedom, and therefore people must be careful and practice self-control themselves when it comes to how much time is spent playing video games.
Video Games Addiction Essay Conclusion
While video games are an excellent source for an individual to be able to wind down and relax and entertainment, there still needs to be control and regulation. Excessive gaming can result in the development of an addiction, which can severely hamper a person’s growth and well-being. Video games are a tool that is meant to be used for fun or to connect with other people. But it becomes a significant issue if we let this become a lifestyle. It also disrupts family life. Therefore, this is an issue that we need to deal with so that it doesn’t take over people’s lives and futures.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Video Game Addiction and Emotional States: Possible Confusion Between Pleasure and Happiness?
1 Research Center for Work and Consumer Psychology, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium
2 Department of Psychiatry and Neurosciences, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands
Nicolas Debue
Jonathan lete, cécile van de leemput, associated data.
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/supplementary material.
Internet gaming disorder is characterized by a severely reduced control over gaming, resulting in an increasing gaming time and leading to negative consequences in many aspects of the individual life: personal, family, social, occupational and other relevant areas of functioning (World Health Organization). In the last years, the significant boom in using video games has been raising health issues that remain insufficiently understood. The extent of this phenomenon (the estimated prevalence is between 1.7 and 10% of the general population) has led the mentioned Organization to include gaming disorders in the list of mental health conditions (2018). Several studies show converging findings that highlight the common brain activities between substance use disorders and behavioral addictions (i.e., gaming disorders). Addiction specialists observed that addict subjects tend to confuse pleasure with happiness when linking emotional states to their addictive activities. As far as we know, beyond the mentioned observations, distinguishing the perception of these two emotional states in the frame of an addiction has not been yet the object of formal research. This study aims at examining the possible confusion between pleasure and happiness within the addiction sphere. Video game addiction has been chosen to explore the possible occurrence of this perceptional distortion. A mixed design lab-based study was carried out to compare between video games addicts and non-addicts (between-subjects), and video games-related activities and neutral activities (within-subject). Emotional reactions were gauged by self-reported scales and physiological data acquired through a range of biosensors: Relaxation and Hearth Rate. From a therapeutic standpoint, this research intends to explore alternatives to deal with this sort of disorders. More specifically, at the cognitive level, the idea is elaborating guidelines to develop patients’ insights into these emotional states and thus increasing their ability to handle them. Overall, several indices resulting from this study constitute a bundle of arguments that argue in favor of the confusion between pleasure and happiness made by addict users when associating their affective states to video gaming. Furthermore, this approach illustrates how reappraising emotions may contribute to reducing the perceptional distortion of these emotional states.
Introduction
In the last years, the significant boom in using video games (VG) has been raising health issues that remain insufficiently understood ( Khazaal et al., 2016 ). The World Health Organization [WHO] (2018) has recently included “gaming disorders” in the list of mental health conditions. According to WHO this affliction is a “persistent or recurrent behavior pattern of sufficient severity to result in significant impairment in personal, family, social, educational, occupational or other important areas of functioning.”
The fifth revision of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) considers the ‘Internet Gaming Disorder’ as a potential new diagnosis that requires further research ( Petry et al., 2015 ). The prevalence of problematic gaming is estimated to range from 1.7% to over 10% among general population ( Griffiths et al., 2012 ).
Compared to the core topics of research in neuroscience such as stress, depression, etc., the chronic use of VG is a rather recent field of investigation. Yet, a growing number of studies have been produced in this field in the last two decades ( Andreassen et al., 2016 ). Indeed, several research projects have been exploring VG addiction from a behavioral, emotional, brain circuits and genetic perspectives ( Griffiths et al., 2012 ; Dong et al., 2017 ).
There seems to be converging findings that highlight the common brain activities between VG disorders (belonging to the cluster of behavioral addictions) and substance use disorders (SUD). It has been shown that the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, orbital frontal cortex, para-hippocampal gyrus and thalamus were activated in both disorders ( Han et al., 2011 ). The limbic structures appear to be the key circuits linked with reward and addiction ( Cooper et al., 2017 ). In subjects suffering from these disorders, cues associated with SUD and with behavioral addiction can trigger craving, which is connected with the dopamine reward system ( Ko et al., 2009 ; Han et al., 2011 ). In addition, it has been observed that the level of dopamine released in the ventral striatum when playing a competition like video game is comparable to that provoked by psycho-stimulant drugs ( Koepp et al., 1998 ; Yau et al., 2012 ). Few studies have been carried out on the genetic aspects of this topic. Some of them indicate that there would be genetic background similarities between these two disorders. For example, the homozygous short allelic variant of the 5HTTLPR gene (encoding the serotonin transporter) is more prevalent among the excessive Internet user, which is also linked with increased drug consumption ( Serretti et al., 2006 , as cited in Yau et al., 2012 ; Lee et al., 2008 , as cited in Yau et al., 2012 ).
As described later, studying the confusion between pleasure and happiness in the frame of addiction requires as clear a demarcation as possible between these two emotional states. Although a consensus among scientists on how to define and distinguish pleasure and happiness remains to be reached (see next section Pleasure and Happiness ), in this research we have adopted the following distinctive traits to describe and to work with these two emotional states: pleasure relates to a transient emotional state resulting from the satisfaction of a desire, a craving, and happiness refers to a lasting emotional state of contentment, euthymia ( Pollard, 2003 ; Lustig, 2017 ).
According to Lustig (2017) , addictions together with depression are two rampant afflictions in the last decades and constitute the harmful extremes of pleasure (associated with the dopaminergic system) and happiness (associated with the serotoninergic system) respectively ( Üstün et al., 2004 ; Lepine and Briley, 2011 ; Szalavitz, 2011 ; Whiteford et al., 2013 ; Gowing et al., 2015 ; Keyes et al., 2015 ). Based on his long practice on addiction issues, this author argues that confusing pleasure (in the sense of longing, craving, strongly driven by a short term reward) with happiness is linked with SUD and with behavioral addictions (i.e., gambling, eating disorders, excessive use of technology like for example social media and VG, etc.), which could lead to depression ( Lawrence et al., 2014 ). According to the author, confusing pleasure with happiness is related to the growth rate of this disorder insofar as it would encourage seeking immediate gratifications perceived as sources of happiness, which in turn triggers the reward system with the risk to sink into the vicious circle of addiction ( Pollard, 2003 ). Besides, the significant industrial development, through its commercial campaigns, probably tended to lead individuals to equate consumption with happiness ( Schmidt, 2016 ; Lustig, 2017 ). From a physiological standpoint, the author highlights that an over excited reward system engenders an excess of dopamine (DA) release from the ventral tegmental area, which in return decreases serotonin (5HT) level (associated with depression) ( Pollard, 2003 ; MacNicol, 2016 ).
Moreover, Lustig underlines that DA and 5HT amino acids (needed for the production of DA and 5HT) share the amino acid transporters, which poses a problem in case of DA amino acid over presence: that is to say, the more amino acids for DA, the less amino acids transporters are available for 5HT amino acids. In short, this DA-5HT unbalance illustrates one of the facets of the DA-5HT interaction in which the low 5HT level, associated with depression, prevents the serotoninergic system to exert its inhibitory role to imped the over drive of the dopaminergic system ( Esposito et al., 2008 ).
Chronic stress and anxiety may further aggravate this problem by increasing the cortisol level and thus creating a loop with dopamine activating the sympathetic nerve system and reinforcing the reward seeking behavior while down-regulating 5HT -1a receptor, which decreases the serotonin signaling and increases the depression likelihood ( Lustig, 2017 ). These findings are in line with studies that associate stress, anxiety and depression with Internet gaming disorders ( Wenzel et al., 2009 ; Griffiths et al., 2012 ).
Fundamentally, from a phylogenetic standpoint, it is likely that pleasure has contributed more than happiness ( Pollard, 2003 ; Lustig, 2017 ), which could explain the stronger drive of the short term gratifications over the quest for medium and long term euthymia. In sum, this suggests that identifying the possible confusion between the mentioned emotional states associated with the addictive activities may contribute to deepen the understanding of this sort of disorders and consequently to explore new therapeutic options.
The emotional states (and their consequences) associated with VG as felt and perceived by chronic users led to thorough interrogations of health professionals. Several studies intended to explore this issue by focusing on the individual characteristics of addict players. For instance, the general level of happiness appears to be a firm candidate to predict addiction to VG playing ( Hull et al., 2013 ). In effect, it has been shown that gaming disorders are positively correlated with depression and loneliness and negatively correlated with well-being ( Lemmens et al., 2011 ; Sarda et al., 2016 ). These two studies relied on a eudaimonic notion of well-being (i.e., life satisfaction, a life well lived). Thus, based on the mentioned definitions of pleasure and happiness, on the semantic net (see Annex ) and on the analysis made in the next section (Pleasure and Happiness), in this research well-being is assimilated to happiness due to the considerable common ground shared between these two concepts. In line with these findings, another study highlights the association between high frequency of online gaming with depression and social phobia ( Wei et al., 2012 ). Similar results were found in a study in which, compared with no addict Internet user, Internet addict subjects used to play online games reported significantly more depressive symptoms ( Geisel et al., 2015 ).
From a psychological symptoms standpoint, it has also been observed that when playing VG, addict gamers have a sense of well being or euphoria while playing VG, inability to stop the activity, craving more time at playing VG, feeling empty, depressed, irritable when not playing VG, with all the pernicious consequences these symptoms have on the private, social and professional life ( Griffiths, 2008 ). At glance, the coexistence of well being and craving might come across as paradoxical, although the mentioned work ( Lustig, 2017 ) on this issue provides some elements of answer to this finding.
Using a video game clip as a stimulation trial, it has been studied ( Kim et al., 2018 ) the craving state of chronic users when playing VG through measures resulting from addiction questionnaires and several bio signals such as eye blinking, eye saccadic movements, skin conductance and respiratory rate. The results of this work showed that during the stimulation trial video game there was a decrease of eye blinking rate, eye saccadic movement rate and mean amplitude of the skin conductance response whereas there was a significant increase of the mean respiratory rate.
Another study ( Lu et al., 2010 ; as cited in Kim et al., 2018 ) focused on a group of individuals with high risks of developing Internet gaming disorders (IGD) and their sympathetic nervous system responses. When using Internet in this experiment, increases were observed in blood volume, body temperature and respiratory rate. Heart rate (HR) has also been used as a reliable indicator of craving in subjects with SUD ( Kennedy et al., 2015 ).
Pleasure and Happiness
The psychophysiological and brain mechanisms of pleasure and happiness are quite complex and probably more research is required to better discerning these processes. Some studies have underlined that the hedonic system includes wanting and liking and each of these two emotional states may operate in a conscious and unconscious mode ( Berridge and Kringelbach, 2011 ). Studies indicate that unconscious wanting would function as a conditioned desire involving the nucleus accumbens, ventral tegmental area, hypothalamus and dopamine; on the other hand the unconscious liking would relate to a sensory hedonic dimension associated with the nucleus accumbens, ventral pallidum, periaqueductal gray, amygdala, opioids and cannabinoids ( Kringelbach and Berridge, 2009 ; Berridge and Kringelbach, 2013 ). The same studies show that conscious wanting would relate to cognitive incentives, subjective desires and dopamine whereas conscious liking would be linked with subjective pleasures, opioids and cannabinoids; both would involve the orbitofrontal cortex, anterior cingulate and insular.
It has been shown that the level of activation of some of the mentioned areas would be altered in subjects with Internet gaming disorders: sensing craving for gaming is associated with an increased activation of the left orbitofrontal cortex (correlated with desire for VG play) and with a decreased activation in the anterior cingulate cortex (probably linked with the reduced capacity to inhibit craving for gaming) ( Wang et al., 2017 ).
There might be a relation between the complexity of these brain circuits linked to these emotional states and the polysemy of these two terms, happiness and pleasure , which may contribute to the possible confusion between them. Indeed, the intense interrelation between them finds expression in subtle distinctive features and in some connotations with vague borders, to the extent that these words might be regarded as almost synonyms. The semantic analysis of these two terms produced in this research intends to show their core meanings, their nuances and the possible intersections between them ( Procter, 1985 ). Trying to unravel and to understand these two emotional states is not a recent endeavor. For instance, Greek thinkers approached the notion of happiness as a state constituted by two components: Hedonia (pleasure) and Eudaimonia (a life well lived) ( Kringelbach and Berridge, 2009 ).
Due to its nature, defining and studying happiness is a quite uneasy task. Although progress has been made on this rather recent area of study, there is still a lack of consensus when it comes to defining this concept. Some authors distinguish fluctuating happiness (self centered) from durable, authentic happiness (self-transcendent) ( Dambrun et al., 2012 ). Another study uses the value-arousal model on emotions to define it, according to which happiness results from a positive valence, high arousal and engaged and satisfied in life ( Cipresso et al., 2014 ). Lustig (2017) emphasizes the time perspective as one of the distinguishing traits between these two emotional states by opposing the short-term logic of pleasure to the longer-term characteristics of happiness .
These last two studies are quite illustrative of the differences with regard to defining happiness , in particular when it comes to including or not pleasure in it. Whilst there seems to be a consensus on “life satisfaction,” “connecting with others” and “contentment” as the main traits of happiness , it is less clear whether pleasure is part of it. Usually, in the literature there are two understandings to articulate these emotional states: either both ( happiness and pleasure) are seen as inseparable concepts or happiness is regarded as a state free from distress (‘liking’ without ‘wanting’) ( Kringelbach and Berridge, 2010 ; Berridge and Kringelbach, 2011 ; Loonen and Ivanova, 2016 ; Lustig, 2017 ). Whether or not pleasure is included in the definition of happiness , to the best of our knowledge there is no study that includes craving (intense desire, longing) as a trait of happiness .
Thus, based on the mentioned definitions and on the association between craving and arousal ( Kennedy et al., 2015 ), craving for playing VG may subscribe itself within the realm of pleasure , but stands outside of the happiness’ sphere.
Within the frame of this research, Pleasure refers to the hedonic reward processes driven by a desire to obtain a gratification that can lead to craving in certain circumstances ( Berridge and Kringelbach, 2011 ). Pleasure has been associated with the dopaminergic circuit which can, in certain circumstances, function in an addictive mode and can affect also habits, conditioning, motivation and executives functions such as decision making, inhibitory control, etc. ( Volkow et al., 2011 ).
Happiness is understood as contentment and euthymic state, in line with a happy emotional state defined by a positive valence and low arousal ( Jatupaiboon et al., 2013 ). Physiologically, this state implies a reposed mind; akin to the relaxation state measured through the brain electrical activity ( Teplan and Krakovskà, 2009 ). In the literature this mood is related to the serotoninergic circuit ( Lustig, 2017 ).
To the best of our knowledge, there is no existing questionnaire focusing on the association between VG and pleasure/happiness. Thus, our study required a preliminary phase to design such self-report tool whose aim is to explore the perceived emotional states (pleasure/happiness) associated with VG play.
As far as we know, distinguishing the perception of these two emotional states in the frame of an addiction has not been yet the object of formal research, hence the reduced literature on this specific issue, in particular the experimental one.
Consequently this research may be seen as a preliminary study, which aims at examining the possible confusion between pleasure and happiness within the addiction sphere. VG addiction has been chosen to explore the possible occurrence of this perceptional distortion. Emotional reactions of VG addicts and VG non-addicts were gauged via self-report scales and physiological data (Heart rate and Relaxation state) acquired by a range of biosensors.
Resulting from the mentioned background, it is hypothesized that addict VG users:
Are likely to confuse the notions of pleasure with that of happiness when associating their emotional states to VG play.
The results of this study are expected to show that addict VG users associate happiness with VG activities while feeling craving for playing accompanied by an increased HR and a low relaxation level. Given the shortage of previous researches on the specific issue related to the confusion between pleasure and happiness in VG addiction, the outcome of this study is approached in an exploratory manner.
From a therapy standpoint, this project intends to explore alternatives to deal with this kind of scenarios. More specifically, at the cognitive level, the idea is finding means to develop patients’ insights into these emotional states and thus increasing their ability to handle them.
Materials and Methods
Preliminary phase: design of the “pleasure and/or happiness and vg” questionnaire, participants.
In total 105 VG players participated in this survey, out of which 61 filled all the questionnaires required for the design of the “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” questionnaire. The mean age of these 61 participants was 24.28 and the standard deviation 5.48. There were 33 males (54.1%) and 28 females (45.9%). The mean of playtime during working days was 4.49 h and the standard deviation 6.82, and during holidays and weekends 4.68 h and the standard deviation 3.13.
An online survey was run via video game forum and Reddit site (network of communities with common interests). The purpose of this survey was to evaluate the internal coherence of our self-report tool (Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG) relative to two validated questionnaires (on Hedonic tone and Happiness). Thus the survey consisted in filling the three questionnaires. Participants completed anonymously and voluntarily the questionnaires through their online gamers groups.
Two validated and known questionnaires were used to construct the ‘ Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG’ questionnaire through which the emotional states associated with VG activities were evaluated: the Snaith-Hamilton Pleasure Scale (SHAPS) ( Snaith et al., 1995 ), an assessment tool of hedonic tone, and the Oxford Happiness Questionnaire (OHQ) ( Hills and Argyle, 2002 ). The French version of these two questionnaires was used ( Loas et al., 1997 ; Bruchon-Schweitzer and Boujut, 2014 ).
The abbreviated SHAPS is composed of 14 items to assess the hedonic tone and the absence of it. The answer scale for each item offers four possible options ranging from ‘Definitely agree’ to ‘Strongly disagree.’ The OHQ is extensively used to evaluate the individual level of happiness. For each of its 29 items, the answer scale has 6 options going from ‘Strongly disagree’ to ‘Strongly agree.’
Several items of the SHAPS and the OHQ are quite adapted to the VG paradigm and lend themselves to be contextualized. For example, the first item of the SHAPS questionnaire is formulated as: “I would enjoy my favorite television or radio program.” In this case “television or radio program” is replaced by “video game.” An example of OHQ concerns the item “I am very happy,” which became “I am very happy when playing VG.” So, these kinds of items constitute the questionnaire whose aim is identifying the emotional states that users associate with VG. Initially, eight items were adapted to VG from these two questionnaires: four items from SHAPS and four items from OHQ. The answer scale provides with six possible options ranging from ‘fully disagree’ to ‘fully agree.’
Statistical Analysis
In order to ensure the usefulness of the designed self-report tool, an Alpha Cronbach test was run on the results of this survey to measure the internal coherence between the ‘VG and Pleasure/Happiness’ and the two other questionnaires (SHAPS and OHQ). Moreover, it has been examined whether there is a correlation between VG play frequency and the two areas explored in this survey: the general happiness level (OHQ) and the emotional states associated with VG (‘Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG’).
The Experiment
The study was announced through the Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB) scientific social media as well as via leaflets available in public cyber games centers in Brussels. Gamers interested to participate in this study had to answer an on-line survey ( N = 163), in which the following data was gathered: age, play frequency, name of VG played and a validated test to assess the gaming addiction level (Gaming Addiction Scale, Lemmens et al., 2009 ). The French version of this scale was used ( Gaetan et al., 2014 ). Being used to play to at least one of these five popular VG (Fornite, Overwatch, League of Legends, Counter-Strike or Rocket League) and an age ranging from 18 to 70 years old were the inclusion criteria. Competing against another team and playing in groups are the common characteristics of these VG. The exclusion criteria were having vision impairments and neurological problems.
Two groups of gamers were invited to participate in this study: addict users (AU) and non-addict users (NAU). None of the invitees met the exclusion criteria. The selection and recruitment were based on the score obtained in the test on gaming addiction, resulting in: AU ( N = 12) and NAU ( N = 17) (7 females and 22 males, ranging from 19 to 29 years old). They were all French speakers Belgian residents. The mean age was 23 and the standard deviation of 3. The difference between sexes in terms of VG addiction is not statistically significant (3/7 AU females and 9/22 AU males, U 45.5, p = 0.130).
This experiment took place within the frame in the usability laboratory of the Research Centre of Work and Consumer Psychology, Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB).
Before the experiment all the procedures were explained to participants and their consent was asked on formal basis. They were informed that:
- – This experiment aims at better understanding the video game phenomenon (without mentioning the issue relative to the emotional states and VG).
- – They have to fill several questionnaires (in French).
- – Some non-invasive artifacts are set to gather measurements on physiological signals while they watch video clips.
- – The Ethical Committee of ULB approved this study in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
The participants were welcome into the testing room of the laboratory by the examiner. They were seated and given an informed consent form. Once the form was read and signed, the study procedure was explained. Then, the Electroencephalogram (EEG) headset was placed onto the participant’s head and an impedance check was run.
Before the beginning of the experiment, each participant chose his/her favorite VG he/she uses to play among the five initially proposed. During the experiment, the examiner observed the participant through a one-way-glass, avoiding interference.
Finally, participants were thanked for their participation, compensated and given information on obtaining the results of the study. The whole experimental run took around 1 h.
Prior to starting the operational phases of the experiment, all devices are set to initiate the baseline recording of all the physiological signals.
Six phases compose this experiment ( Figure 1 ). In each phase of the experiment the emotional states associated with VG were examined either through self-report questionnaires or via physiological measures. The physiological measures were recorded during the visioning of two sorts of video clips: VG clips whose aim was to induce craving and neutral video clips (documentaries on nature) intending to reduce craving.

Synthetic view of the experimental phases.
The six experimental phases:
- (1) “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” (six items): Participants were invited to fill the self-report questionnaire designed in the preliminary phase.
- (2) Watching a neutral clip during 2 min while recording physiological signals related the mentioned two emotional states. This phase intends to decrease craving in participants.
- (3) Craving score: Participants were asked to express their craving state to play their favorite VG via a one item self-report questionnaire.
- (4) Watching a VG clip during 2 min while recording the same physiological signals as in phase two related to the mentioned emotional states. The objective of this phase is to increase craving in participants.
- (5) Craving score: the same procedure and self-report tool as in phase 3 were applied.
- (6.1) “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” (Three bipolar items).
- (6.2) “Key words and VG”: participants were invited to associate a list of words to VG activities.
- (6.3) “Pleasure and VG or Happiness and VG” (one bipolar item): participants were asked to associate one of the two emotional states to VG play.
The cycle from the 2nd phase to the 5th phase was repeated five times for each participant. In each of these five cycles, different episodes of video clips (the chosen VG and the neutral clip) were shown randomly so as to avoid the habituation phenomenon and minimize the influence that the order of the sequence of episodes could have on participants’ responses.
- – Experimental groups: AU and NAU
The Gaming Addiction Scale (GAS) ( Lemmens et al., 2009 ; Gaetan et al., 2014 ) was used to constitute these groups. As a tool to measure game addiction, GAS possesses significant assets. Lemmens et al. (2009) showed the validity of this scale from a cross population point of view and its one-dimensional characteristic resulting from the factorial analysis. In addition, in the same study it has been shown the concurrent validity of GAS insofar as this scale is associated with play frequency as well as with psychological features related with game addiction, namely decreased level of social competence and of well being, and high level of aggression and of loneliness. Moreover, high scores in GAS are also linked with attentional deficiencies in response inhibition when perceiving game cues ( van Holst et al., 2012 ; in Khazaal et al., 2016 ), which converges with results produced by other researches associating impulsivity and cue reactivity with other addictive behaviors ( Billieux et al., 2011 ; Khazaal et al., 2012 ; Torres et al., 2013 ). Relative to other game addiction measurements, GAS has the most complete covering of the Internet gaming disorder criteria of the DSM-5 ( Petry et al., 2014 ). Although it was initially designed for adolescents, there are substantial evidences to state that GAS is applicable for young adults too ( Khazaal et al., 2016 ).
Each of the seven items of this scale starts with the question “How often in the last 6 months…?” to explore the impact of video gaming on different aspects of the subject’s life. The possible answers are: never, rarely, sometimes, often and very often. The first two answers score 0, the last three answers score 1. If the total sum of these scores is 4 or higher, the subject is considered an AU according to this scale.
- – The experiment
In the first phase, participants were asked to fill the “ Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” questionnaire composed by six items: three items that tie Pleasure (P) and VG, three items that tie Happiness (H) and VG (six-items in total).
The answer scale for each item was composed of six options ranging from ‘Fully disagree’ to ‘fully agree.’ Each of these six items is answered separately, thus the overall possible results of this questionnaire can be: (1) P and VG > H and VG or (2) H and VG < P and VG or, (3) P and VG = H and VG.
In the second phase (Neutral video clip), two physiological signals related to Pleasure and Happiness were recorded. Based on the correlates found between HR and craving, this physiological signal is used as an indicator of arousal ( Kennedy et al., 2015 ).
Despite the difficulty in defining and in measuring happiness , the brain electrical activity is recorded (Electroencephalogram, EEG) mainly to detect the relaxation state. This state appears close to the notion of happiness; in the literature it is accepted that the increase of alpha waves is correlated with mental and physical rest ( Teplan and Krakovskà, 2009 ).
In the third phase, participants were asked to express their craving state to play his/her favorite VG. The statement employed in this self-report tool was: “State your present craving for gaming.” Participants have to choose the answer that best fitted their self-assessment among six possible answers offered by the scale ranging from “I do not feel any craving for gaming” to “I feel a very strong craving for gaming.”
In the fourth phase (VG clip), the same physiological signals as in the second phase were measured.
In the fifth phase, the same procedure to assess craving for gaming as in the third phase was employed.
In the sixth phase, three other self-report questionnaires were submitted to participants and used to evaluate the association between the mentioned emotional states and VG:
- – “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” (three bipolar items). The same six items of the “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” questionnaire used in phase 1 were presented in a bipolar structure: three items opposing “Pleasure and VG” vs. “Happiness and VG.” For example, if in the six items questionnaire the items “I would enjoy my favorite VG” (Pleasure/VG) and “I am happy when playing VG” (Happiness/VG) are presented separately, in this questionnaire they are part of the same item: “I would enjoy my favorite VG” vs. “I am happy when playing VG.” By doing so, participants are encouraged to choose which of their emotional states (Pleasure, Happiness) is associated with VG playing. That said, the scale has an uneven number of options (five) between the two extremes, the central option representing the equal association of Pleasure and Happiness with VG play. Thus, the overall possible results are identical as in phase 1.
- – “Key words and VG”. Participants were asked to choose three words (out of ten) that they associate most with their VG activities. These 10 key words come from the semantic mapping elaborated in this research of the terms used in the formal statements defining pleasure and happiness in this study. For example, some words from the happiness sphere are contentment and well being , whereas desire and joy relate to pleasure . Besides, they are in line with both definitions Lustig’s (2017) . Only the ten words (French version) were shown to participants. Although the possible results are similar to those of six-item “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” questionnaire and three-bipolar item “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” questionnaire, this time the same association (emotional states and VG) is tackled via key words directly linked to the two studied emotional states ( Pleasure, Happiness ) but without mentioning them. This self-report format intends to gain accuracy in the identification of gamers’ emotional states associated with VG.
- – “Pleasure and VG or Happiness and VG”. The written definitions of both pleasure and happiness , based on work Lustig’s (2017) , were shown to participants. Then they were asked to read carefully these definitions and to take them into account when answering one bi-polar item that opposes “Pleasure and VG” vs. “Happiness and VG.” Unlike in the three-bipolar items questionnaire, the answer scale between these this bipolar item has an even number of options (six). This time is an “either/or” choice they are faced with, therefore the possible results are: P and VG < H and VG or P and VG > H and VG. Basically this questionnaire intends to strengthen consistency in participants’ insights into this issue by inviting them to confront their perception of their emotional states associated with VG play with the mentioned formal definitions, comparable to an emotions reappraisal process ( Seay and Kraut, 2007 ).
In short, four self-report questionnaires (see Annex ) aim at exploring this dependent variable (association between these two emotional states and VG play) by looking at the consistency of participants’ answers to the different formats of questions. The questions’ formats are:
- – Pleasure and/or happiness can be associated with VG (six independent items);
- – Pleasure and/or happiness can be associated to VG (three bipolar items);
- – Pleasure and/or happiness can be associated to VG through key words defining the two emotional states (without mentioning the words pleasure and happiness );
- – Pleasure or happiness can be associated to VG (written explicit definitions of pleasure and happiness are given to participants).
This approach aims at exploring the coherence between the self-reported answers and the physiological signals, as a means to objectivize the perceived emotional states associated with VG play by the two mentioned groups of participants (addict gamers and non-addict gamers).
The previously mentioned theoretical framework indicates that the notion of craving relates to an arousal state that could lead to an addictive pattern and consequently stands out of the realm of happiness.
Expected Results
Based on the analysis made on this issue previously as well as on the hypothesis of this study, the expected results could be synthesized as shown in Table 1 .
Summary of the expected results.
| Addict Users (AU | Happiness and VG > Pleasure and VG | – VG clip increasing effect on craving – VG clip increasing effect on HR – VG clip decreasing effect on relaxation | Happiness and VG > Pleasure and VG | Happiness and VG > Pleasure and VG | Pleasure and VG > Happiness and VG |
| Non Addict Users (NAU) | Pleasure and VG > Happiness and VG | Pleasure and VG > Happiness and VG | Pleasure and VG > Happiness and VG | Pleasure and VG > Happiness and VG |
- – Self-Report Questionnaires
For the self-report questionnaires, it is expected that, compared to NAU, the AU group:
- – In “Pleasure and/or happiness associated with VG” (six independent items) associates more happiness than pleasure with VG play.
- – Reports more craving for playing after watching VG clip.
- – In “ Pleasure and/or happiness associated to VG” (three bipolar items) associates more happiness than pleasure with VG play.
- – Associates VG play with key words more related to happiness category than to those of pleasure .
- – In “ Pleasure or happiness associated to VG” associates VG play with pleasure (like NAU).
- – Physiological Signals
It is expected to observe an interaction between the groups (AU, NAU) and the conditions (VG clip, Neutral clip). Namely, it is assumed that visioning the VG clips has an effect on AU increasing HR while decreasing Relaxation.
After verifying the normality of distributions (Kolmogorov–Smirnov), the means comparison between the two groups (NAU, AU) was calculated for self-report questionnaires measuring the association between VG and Pleasure/Happiness (Mann–Whitney U ) for the six-items “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG,” the three-bipolar items “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” and the one-bipolar item “Pleasure and VG or Happiness and VG.” The Chi square was used for “Key words and VG.” In order to determine whether there are differences between independent groups over time and to identify possible interactions between the two independent variables on the dependent variables, a two-way mixed ANOVA (within and between subjects) was used for the craving scores and the physiological signals recorded ( Table 2 ).
Synthetic view of independent and dependent variables.
| – Addict Users (AU) – Non-Addict Users (NAU) | – Happiness and/or Pleasure associated to VG (6-items) | – Heart Rate and Relaxation – Craving score | – Happiness and/or Pleasure associated to VG (3-bipolar items) – Key words associated to VG – Happiness or Pleasure associated to VG (1 bipolar item) |
The experiment was run on a desktop computer with an Intel Core i7 quad processor and 8 GB RAM, running Windows 10. Stimuli were displayed on a 22-inch monitor and resolution was set to 1680 × 1050. Participants used standard mouse and keyboard as input devices. EEG measurement includes detecting the fluctuation of voltage potential generated by large group of neurons in the brain. The EEG signal was obtained through the use of EPOC headset. This device allows to remotely getting data of brain activity using a wireless set of fourteen electrodes (AF3, AF4, F3, F4, F7, F8, FC5, FC6, T7, T8, P7, P8, O1, O2) sampled at 128 hertz.
The relaxation state was measured by one of the composite metrics of the Emotiv software. HR was measured by using Schimer 3 (Photoplethysmography). The I. Motions software version 7.1 (Imotions Inc. 2018) was used to recording the mentioned data and presenting stimuli to participants. The statistical analysis was conducted with IBM SPSS statistics v.25.
Design of the “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” Questionnaire
The Cronbach’s alpha (0.859) showed a high internal coherence between the SHAPS and three items (out of four) of the “Pleasure and VG” within the “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” questionnaire. The fourth item has been disregarded; its presence would have dropped the Cronbach’s alpha to 0.685. The internal coherence obtained between the OHQ and the “Happiness and VG” items within the “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” questionnaire was quite high for the four items concerned (alpha 0.901). However, the internal coherence between these four items was too weak due to one item (alpha 0.407). The exclusion of this item raised the alpha significantly (0.836). Consequently, only the consistent items have been kept (six out of the initial eight items: three on “Pleasure and VG,” and three on “Happiness and VG,” see Annex ).
Moreover, it has been examined whether there is an association between VG play frequency and the two areas explored in this survey: the general happiness level (OHQ) and the emotional states associated with VG via the “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” questionnaire. The constitution of the group of frequent gamers and that of non-frequent gamers was determined by calculated median (18 h per week). In line with several studies linking problematic gaming and well-being and life satisfaction, a moderate negative correlation ( R = −0.249; p = 0.056) was found between VG high play frequency and the OHQ scores ( Griffiths, 2008 ; Lemmens et al., 2011 ). In addition, there is a marginal significant difference [ T (58) = 1.923; p = 0.059] between frequent VG users and non-frequent VG users relative to the OHQ scores.
The “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” Six-Items Questionnaire
The Kolmogorov–Smirnov outcome indicates the need for using a non-parametric test to compare the two groups. The Mann–Whitney test shows that there was no significant difference observed between the AU and NAU relative to association between VG play and pleasure (item 1. U = 78, p = 0.30; item 3. U = 75, p = 0.24 and item 5 U = 86, p = 0.49) ( Table 3 ).
Descriptive statistics of “Pleasure and/or Happiness associated with VG” (6-items): [Pleasure (P), Happiness (H) associated with VG].
| Item 1 P/VG | NAU | 17 | 13.69 | 231.00 |
| AU | 12 | 17.00 | 294.00 | |
| Item 2 H/VG | NAU | 17 | 11.35 | 193.00 |
| AU | 12 | 20.17 | 242.00 | |
| Item 3 P/VG | NAU | 17 | 13.41 | 228.00 |
| AU | 12 | 17.25 | 207.00 | |
| Item 4 H/VG | NAU | 17 | 12.18 | 207.00 |
| AU | 12 | 19.00 | 228.00 | |
| Item 5 P/VG | NAU | 17 | 14.06 | 239.00 |
| AU | 12 | 16.33 | 196.00 | |
| Item 6 H/VG | NAU | 17 | 11.03 | 187.50 |
| AU | 12 | 20.63 | 247.50 | |
| Mean P/VG | NAU | 17 | 12.88 | 219.00 |
| AU | 12 | 18.00 | 216.00 | |
| Mean H/VG | NAU | 17 | 10.59 | 180.00 |
| AU | 12 | 21.25 | 255.00 |
In contrast, there is a significant statistical difference in the three items where AU associate VG play with happiness (item 2. U = 40, p = 0.005; item 4. U = 54, p = 0.034 and item 6. U = 34, p = 0.002) more than NAU.
Craving Scores
Results in craving ( Table 4 and Figure 2 ) show a statistically significant interaction F (1,25) = 4.78 ( p = 0.038). Indeed, relative to the neutral clip, the VG clip condition has significantly amplified the reported craving difference between the two groups (AU craving score > NAU craving scores).
Descriptive statistics for self-report Craving.
| Neutral clips | NAU | 2.27 | 1.09 | 0.222 | –0.954 | 17 |
| AU | 2.02 | 0.98 | 1.617 | 2.567 | 10 | |
| Total | 2.17 | 1.03 | 1.062 | 1.248 | 27 | |
| VG clips | NAU | 4.11 | 0.82 | –0.169 | 0.135 | 17 |
| AU | 4.96 | 0.52 | –2.523 | 7.414 | 10 | |
| Total | 4.42 | 0.82 | –1.271 | 2.528 | 27 |

Self-report craving (groups: AU, NAU; conditions: Neutral clips, VG clips).
Physiological Signals Measurements
The AU’s relaxation is significantly lower [ F (1,24) = 8.616; p = 0.007] than NAU’s in both conditions (Between-Subjects Effects). The relaxation level decreases in both groups during the VG clip. On the other hand, conditions do not influence the relaxation difference between the two groups [ F (1,24) = 0.001; p = 0.98] ( Table 5 and Figure 3 ). Furthermore, there is a significant statistical gender difference in both conditions (Neutral clip: Male 17.36, Female 7.57. U = 25, p = 0.008 – VG clip: Male 17.09, Female 8.43. U = 31, p = 0.019).
Descriptive statistics: Relaxation index (EEG EPOC, Emotiv software).
| Neutral clips | NAU | 0.33 | 0.07 | –0.873 | 1.095 | 15 |
| AU | 0.24 | 0.09 | 1.256 | 3.303 | 11 | |
| Total | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.292 | 0.460 | 26 | |
| VG clips | NAU | 0.31 | 0.05 | –1.380 | 1.390 | 15 |
| AU | 0.23 | 0.07 | 1.633 | 4.688 | 11 | |
| Total | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0.292 | 2.630 | 26 |

Relaxation [groups: AU, NAU; Conditions: (1) Neutral clips, (2) VG clips].
Concerning the other physiological variable (HR) ( Table 6 and Figure 4 ), there is an effect of VG clips on both groups [ F (1,15) = 20.802; p < 0.001]. Nevertheless, there was no statistically significant interaction [ F (1,15) = 0.028; p = 0.86], nor an effect of addiction on VG clip condition [ F (1,15) = 0.083; p = 0.777]. It is important noting that due to corrupted data the number of valid subjects taken into account was 17 (8 AU and 9 NAU).
Descriptive statistics: Heart Rate (HR).
| Neutral clips | NAU | 78.36 | 7.94 | 0.054 | –0.292 | 9 |
| AU | 79.51 | 8.36 | 2.130 | 5.013 | 8 | |
| Total | 78.90 | 7.90 | 0.972 | 1.530 | 17 | |
| VG clips | NAU | 80.29 | 9.20 | –0.502 | 0.219 | 9 |
| AU | 81.58 | 9.34 | 2.037 | 4.661 | 8 | |
| Total | 80.89 | 8.99 | 0.614 | 1.535 | 17 |

Heart Rate [groups: AU, NAU; Conditions: Neutral clips (1), VG clips (2)].
The “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” Three-Bipolar Items Questionnaire
The descriptive statistics of this three-bipolar items questionnaire ( Table 7 ), indicate that the AU group linked VG activities more with happiness than the NAU group. The Mann–Whitney test shows a significant difference between these two associations ( U = 47; p = 0.013).
Descriptive Statistics: Pleasure/VG vs. Happiness/VG (3 bipolar items).
| Mean | NAU | 17 | 11.76 | 200.00 |
| AU | 12 | 19.58 | 235.00 | |
| Bipolar item 1 | NAU | 17 | 13.29 | 226.00 |
| AU | 12 | 17.42 | 209.00 | |
| Bipolar item 2 | NAU | 17 | 13.91 | 236.50 |
| AU | 12 | 16.54 | 198.50 | |
| Bipolar item 3 | NAU | 17 | 13.3 | 221.50 |
| AU | 12 | 17.79 | 213.50 |
Key Words and VG
Results state the absence of significant difference between AU and NAU in associating the key words from the Pleasure cluster with VG play, and words from the Happiness cluster with VG (Chi square, p = 0.942) ( Table 8 ). When taking words separately, the biggest gap between the two groups relates to the word well-being (belonging to the happiness cluster) associated to VG play (AU: 25%, NAU: 0%).
Descriptive statistics: number of words per category (Pleasure, Happiness) associated to VG play chosen by NAU and AU.
| % | NAU (N17) | 17 × 3 words = 51 | 19.60 | 47.05 | 33.33 | 100 |
| % | AU (12) | 12 × 3 words = 36 | 22.22 | 47.22 | 30.55 | 100 |

“Pleasure and VG or Happiness and VG” (One Bipolar Item Questionnaire With Written Definitions)
The outcome of this questionnaire indicates that there is no significant difference between AU and NAU ( U = 102, p = 1). Both groups have clearly associated VG play with pleasure ( Table 9 ).
Descriptive statistics: Happiness/VG or Pleasure/VG (1 bipolar item, with Definitions of Pleasure and Happiness shown to subjects).
| NAU | 4.82 | 0.636 | 17 | |
| AU | 4.58 | 1.379 | 12 |
The following scheme summarizes the outcomes of the self-report tools used to evaluate the association between the emotional states (Pleasure and Happiness) with VG play ( Table 10 ).
Synthetic view of self-report results (Emotional states associated with VG play).
| Results | AU associated more Happiness to VG than NAU (Significant difference) | AU associated more Happiness to VG than NAU (Significant difference) | Both groups associated Pleasure and Happiness to VG (No significant difference) | Both groups associated Pleasure to VG (No significant difference) |
The following table indicates the mean, standard deviation and Skewness and Kurtosis values of the self-report craving, the HR and the relaxation level for both groups in the two conditions ( Table 11 ).
Descriptive statistics for self-report Craving, Relaxation, Heart Rate.
| Neutral clips | NAU | 2.27 | 1.09 | 0.222 | –0.954 | 17 |
| AU | 2.02 | 0.98 | 1.617 | 2.567 | 10 | |
| Total | 2.17 | 1.03 | 1.062 | 1.248 | 27 | |
| VG clips | NAU | 4.11 | 0.82 | –0.169 | 0.135 | 17 |
| AU | 4.96 | 0.52 | –2.523 | 7.414 | 10 | |
| Total | 4.42 | 0.82 | –1.271 | 2.528 | 27 | |
| Neutral clips | NAU | 0.33 | 0.07 | –0.873 | 1.095 | 15 |
| AU | 0.24 | 0.09 | 1.256 | 3.303 | 11 | |
| Total | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.292 | 0.460 | 26 | |
| VG clips | NAU | 0.31 | 0.05 | –1.380 | 1.390 | 15 |
| AU | 0.23 | 0.07 | 1.633 | 4.688 | 11 | |
| Total | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0.292 | 2.630 | 26 | |
| Neutral clips | NAU | 78.36 | 7.94 | 0.054 | –0.292 | 9 |
| AU | 79.51 | 8.36 | 2.130 | 5.013 | 8 | |
| Total | 78.90 | 7.90 | 0.972 | 1.530 | 17 | |
| VG clips | NAU | 80.29 | 9.20 | –0.502 | 0.219 | 9 |
| AU | 81.58 | 9.34 | 2.037 | 4.661 | 8 | |
| Total | 80.89 | 8.99 | 0.614 | 1.535 | 17 |
Overall, the results of this study show that AU associate happiness to VG while reporting craving for VG play and having a low relaxation level. These outcomes observed in this experiment constitute a bundle of arguments that argue in favor of the hypothesis of this study ( Lustig, 2017 ). Indeed, in AU, the high self-report craving score and low Relaxation level during VG clips visioning do contrast with their association of VG more with happiness than with pleasure in the mentioned “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” questionnaires (six-items and three-bipolar-items) relative to NAU. Consistent with previous findings in this area, these four measurements highlight the coexistence of the perception of happiness linked with VG play combined with elements related to pleasure such as craving ( strong desire, wanting ) ( Pollard, 2003 ; Griffiths, 2008 ; Waterman et al., 2008 ). Since craving and low Relaxation are rather incompatible with the mentioned notion of happiness ( Pollard, 2003 ; Waterman et al., 2008 ; Lustig, 2017 ), these indices may raise the question as to how accurate are AU’s insights into their emotional states associated to VG play and may support the idea that AU’s perception of their emotional states is somewhat distorted. In the literature, VG addiction would be linked with impairment in the self-regulation process, this finding may be linked with the difficulties AU have to observe and evaluate their own behavior ( Seay and Kraut, 2007 ). Besides, the mentioned results suggest that VG clip effect on self-report craving would depend on the addiction level.
Considering that sensing happiness and craving are probably experienced as positive emotions by AU, and that usually negative and positive emotional events are reported to last longer and shorter respectively ( Gil and Droit-Volet, 2012 ; Tian et al., 2018 ), the arousal triggered by motivating stimuli, may modify the time perception and could mediate the effect of emotions on behavior ( Gil and Droit-Volet, 2012 ). In other words, the level of excitement produced by VG play could make AU underestimate the time spent at this activity, which may be perceived as an alleviating evasion free from stressors and possibly assimilated with the notion of happiness . This hypothetic mechanism would match one of the possible motives for online gaming ( Demetrovics et al., 2011 ). In this sort of precognitive process, several studies mentioned the involvement of the amygdala in interaction with the thalamus together with the dopaminergic system and a poor inhibitory control ( Gil and Droit-Volet, 2012 ; Petry et al., 2015 ).
It is noteworthy underlining that the bipolar structure of the three-items questionnaire increases the relevance of this outcome. In effect, although participants were incited to choose between the two emotional states opposing each other (VG and pleasure vs. VG and happiness), like in the six-items questionnaire, AU again did choose happiness as the main emotional state linked with VG play. This outcome would further state the difference between these two groups when it comes to associating the two emotional states to VG play. Besides, this would reveal to an important extent that the possibility whereby pleasure and happiness were regarded as synonyms could be overcome. In other words, this outcome shows that the similarity of meanings of these two concepts did not prevent these groups to make a clear choice. Finally, the similar scores obtained in the two questionnaires (six-items and three-bipolar items “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG”), in spite of the different disposition of the same items in these two instances, strengthen the value of the designed scale (“Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG play”).
The absence of interaction between the two independent variables on HR may be explained by the fact that a higher arousal would take place in AU when playing VG rather than when watching at VG clips. Moreover, the reduced number of valid subjects when measuring this physiological parameter (due to technical recording problems) could have contributed to this outcome too. The fact that the independent variables did not produce the expected different HR effects on AU and NAU could also be linked with one of the limitations of this study: the difficulty in integrating in this research the interaction between HR and depression (as mentioned, VG addiction is positively correlated with depression) ( Griffiths et al., 2012 ) that may lead to HR index modifications ( Cipresso et al., 2014 ). In sum, this issue illustrates that the difficulty to circumscribe the notion of happiness is also reflected in the complexity to establish physiological correlates so as to objectify this emotional state ( Cipresso et al., 2014 ).
Associating the clusters of key words with VG did not produce the expected results. Since AU linked VG with both pleasure and happiness , may be these words played a clarification role and facilitated Au’s insights into their emotional states when playing VG. It could also suggest the inadequacy of this self-report tool. However, it is probably worthwhile mentioning an index related our hypothesis: when taking words separately, the word “well-being” associated with VG play was chosen by 25% of AU and by 0% of NAU.
The outcome of the binary question in the “Pleasure and VG or Happiness and VG” one-item questionnaire with the definitions of pleasure and happiness ( Pollard, 2003 ; Deci and Ryan, 2008 ; Waterman et al., 2008 ; Kashdan et al., 2008 ; Lustig, 2017 ) shows that AU ceased associating happiness to VG play and instead, like NAU, clearly linked pleasure to their cyber activity. Caution is required in the analysis of these results because the validity of this questionnaire remains to be demonstrated. Having instructed participants to answer the bipolar question by taking into account the written definitions of the two measured emotional states, did modify the result of AU group relative to both questionnaires (“Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” six-items and three bipolar items). Within the framework of this careful approach, it could be hypothesized that explicit definitions of the two emotional states induced AU to adopting an introspection mode through a more pronounced involvement of cortical brain structures, akin to a therapeutic process in which the appropriate verbalization of pleasure and happiness facilitates the clarification of one own feeling as a prerequisite to elaborate more adaptive behavior in spite of the constraining psychological characteristics usually associated with VG addicts ( Kim et al., 2007 ; Kashdan et al., 2008 ; Wenzel et al., 2009 ).
This may be regarded as an example of emotions reappraisal which would increase accuracy of insights into one-self, reduce distorted perception of emotions and assess the adequacy of the behavioral response to a given stimulus ( Compare et al., 2014 ). In other words, it could be posited that the mentioned explicit definitions have somewhat constrained AU to use a cognitive approach to examine their emotional states related to VG play rather than merely relying on the sensory information as it tends to occur when sensing craving for video gaming ( Wang et al., 2017 ).
Moreover, the result of this one-item binary questionnaire would further support the hypothesis. In effect, the studied interrelation between hedonia and eudaimonia suggests that a highly rated hedonic activity (VG play in this case) is usually related with low rating in eudaimonia ( Waterman et al., 2008 ). This interpretation would fit with the resounding association between depression and gaming disorders ( Lemmens et al., 2011 ; Hull et al., 2013 ; Sarda et al., 2016 ; Bonnaire and Baptista, 2019 ) together with the confusion between pleasure and happiness occurring in addictive activities (AU associated VG with happiness in the first two self-report questionnaires and ended linking pleasure with VG in the last one-item questionnaire) ( Pollard, 2003 ; Lustig, 2017 ).
Overall, the more explicit the definition of pleasure and happiness and the narrower the choice offered by the self-report questionnaires, the less confusion of emotional states associated with VG occurred in AU group members whereas NAU invariably associated pleasure to VG as illustrated in Figure 5 .

Shift of AU perception of their emotional states associated with VG according to the self-report tools.
Based on these results, it could be postulated that the tendency of AU to perceive happiness when feeling craving and pleasure linked to VG play, might be moderated by a clarifying cognitive process on the meaning of these studied emotional sates, which would interfere with the behavioral habits linked to the urge of gaming ( Ko et al., 2009 ).
The findings resulting from “Pleasure and/or Happiness and VG” six-items questionnaire could be regarded as an illustration of the confusion that AU might have when linking the studied emotional states with VG play. Unlike NAU, the significantly higher association between VG play and happiness expressed by AU matches the perceived level of well being reported by individuals with Internet gaming disorders ( Griffiths, 2008 ). On the other hand, apart from well-being , the same author cites euphoria as the other main emotional state that addict gamers may report when playing VG. Whilst happiness and well-being rely on each other to define themselves, euphoria would convey the notion of intense excitement, which would rather stand in the pleasure sphere. Moreover, in medical terms, euphoria refers to a feeling of great elation, not necessarily founded (especially when resulting from substances consumption). Since AU also associated VG with pleasure although they did it to a lesser extent than with happiness, it could hypothesized that the feeling of intense excitement derives, at least partially, from satisfying the craving for VG play, which in turn could engender relieve experienced as a sense of well-being ( Loonen and Ivanova, 2016 ).
The impact of VG clips on AU craving and relaxation scores underlines relevant aspects of this study, which support the hypothesis of this research. First of all, it highlights the incongruent perception of AU’s emotional states whereby both craving and happiness coexist as emotional states associated with VG play. Thus, this finding constitutes a relevant component of the confusion that consists in placing a short-term pleasure (VG play) within the sphere of happiness. Besides, the low relaxation state of AU would correspond with their self-reported craving and, therefore, further highlights the contrast between the perceived happiness associated with VG play and the indicators measured during the VG clip visioning (high craving level and low relaxation state level). Finally, it is noteworthy mentioning that relaxation was the only measure in this study where gender differences were observed. The lower relaxation level in female gamers in both conditions might be related to the gender expectation about playing VG in society at large and in the gamers’ community in particular ( Shen et al., 2016 ). Indeed, since female gamers are a minority in these sorts of VG ( Shen et al., 2016 ) (in line with our sample: 7 females, 22 males), it could be posited that they feel under scrutiny in an activity regarded as male oriented.
Putative Reasons of Distorted Perceptions of Emotional States Associated With VG Addiction
The social dimension of popular VG has been identified as one of the factors that may explain the addiction pattern ( Hull et al., 2013 ). In this kind of competitive games, improving the required abilities and obtaining better results would be part of the key motives for VG play ( Demetrovics et al., 2011 ), that usually generates the appreciation and the acceptance of the other group players. Getting this sort of feedback from others can be motivating indeed, especially when taking into account the correlation between IGD and social isolation, low self-esteem, traumatic experiences, depression and low life satisfaction ( Petry et al., 2015 ; Schimmenti et al., 2017 ; Bonnaire and Baptista, 2019 ). In turn, these psychosocial characteristics are probably related also with the high impulsivity level in VG addicts ( Billieux et al., 2011 ), which has been found to be associated with difficulties in interpersonal relationships ( Ryu et al., 2018 ). Thus, it would seem that VG activities are, at least partially, sating the mentioned social and psychological deficiencies. This suggests that AU’s emotional states related to VG play may be quite contrasting, in which components of happiness (i.e., interacting with others, fellowship and belonging to a group) are intertwined with those of short-term pleasure (i.e., craving for getting quick results, praise from others, etc.) ( Loonen and Ivanova, 2016 ). Now, craving for undertaking these cyber activities to respond to the mentioned social isolation issues places this emotional state much closer to the ‘pleasure governed by desire’ than to ‘atmosphere of good fellowship’ (Happiness) ( Lawrence et al., 2014 ; Lustig, 2017 ).
The flow, defined as the emotional state embracing perception distortion and enjoyment produced by VG activities, is another element that can create confusion in gamers’ insights into their emotional states ( Chou and Ting, 2003 ; Hull et al., 2013 ). As described in the mentioned study, experiencing flow implies not only losing the notion of time but also merging oneself with the VG actions. In these conditions, the gamer’s senses and attention are in the here and now , with little or no awareness about sources of stress relative to past, present or future events. In this line, the motivation to experience immersion has been associated with problematic gaming ( Billieux et al., 2011 ). Considering the fact that loneliness and depression have been identified as predictors of VG addiction and of Internet Gaming Disorders ( Hull et al., 2013 ; Sarda et al., 2016 ), it is understandable why in gamers’ mind experiencing flow could equate this feeling with a relieving emotional state ( Loonen and Ivanova, 2016 ). This sense of alleviation could match the notion of happiness as free from distress ( Kringelbach and Berridge, 2010 ; Loonen and Ivanova, 2016 ) if it resulted from the quality of real life being lived. Instead, in AU, this relieving and enjoyable emotional state would be engendered by a virtual activity (VG), possibly used as a means to escape from stress and to forget tensions ( Demetrovics et al., 2011 ; Bonnaire and Baptista, 2019 ). In the literature, the escaping strategy is a way to find relieve from stressors through the engagement in a pleasant activity, which may end up representing a space of happiness ( Seay and Kraut, 2007 ).
In sum, the incongruence lies in the coexistence of regarding VG as a space of happiness while using VG to get quick pleasures and relief. Individuals suffering from this disorder tend to pursuit short-term pleasures rather than long-term gains ( Dong and Potenza, 2015 ). Being driven by short-term gratifications rather belongs to the reward-seeking realm ( Waterman et al., 2008 ; Lustig, 2017 ). Thus, this pleasant emotional state could be associated with the arousal linked to a reward seeking behavior through which quick and positive results are obtained, which in turn reinforce the mentioned behavior. Probably, this intense arousal situates itself within the sphere of pleasure as a dysfunction in the rewarding system ( Pollard, 2003 ; Berridge and Kringelbach, 2013 ; Lustig, 2017 ) and not in that of happiness in spite of the relieving benefits it provides.
Another possible reading on why the emotional states generated by these cyber activities are linked with happiness may be related to the way in interpreting the experienced sensations. This representation is probably shaped by the individual background, experiences, culture, etc. From a brain mechanism stand point, conscious liking does not limit it self to a sensory outcome, it is also translated into a subjective liking through the recruitment of cognitive processes ( Berridge and Kringelbach, 2013 ). Indeed, these authors state that conscious pleasure rating is sometimes detached from affective reactions as people can elaborate reasons to themselves for how they should feel. Therefore, associating VG with happiness may be the result of a rationalization process to reduce the cognitive dissonance. In other words, the unwished consequences of the VG addiction pattern (increased stress, problems at working, studying, socializing, etc.) ( Griffiths et al., 2012 ) probably produce an increasing amount of pressure (due to the difficulty to reduce gaming time, guilt, etc.) that can become overwhelming if it lasts too long. Consequently, if the affected individuals are unable to master the yearning for VG, perceiving VG activities as a source of well being may reduce the mentioned pressures insofar as the notion of happiness usually suggests a socially acceptable mood, a legitimate aim and a safe emotional state. In this perspective, equating happiness with satisfying craving and with short-term pleasure might contribute to feed the addictive pattern ( Lustig, 2017 ).
In a broader perspective, the rationalization process described in the previous paragraph may be also related with coping strategies to deal with adversity. For instance, it has been observed that problematic gamers may use VG play as a means to cope with stressors and to enhance mood ( Demetrovics et al., 2011 ). An association has been found between stressful life events and addiction to Internet activities ( Schimmenti et al., 2017 ), with the mediating role of psychological needs satisfaction and the moderating role of coping styles ( Dongping et al., 2016 ). Several theories and studies support this approach that strives for a more holistic understanding of this issue. The self-determination theory postulates that humans share three universal psychological needs ( Deci and Ryan, 2000 ; in Dongping et al., 2016 ): autonomy (i.e., feeling of being self-determining in one’s behavior), relatedness (i.e., the feeling of connectedness to others) and competence (i.e., the feeling of dealing with issues in a competent manner). Besides, individuals can adopt different strategies to cope with adversity ( Lazarus and Folkman, 1984 ; in Dongping et al., 2016 ). According to Zheng et al. (2012 ; in Dongping et al., 2016 ), the positive coping approach is the set of strategies aiming at problem solving, support seeking and cognitive restructuring to address the stressors. On the other hand, according to the same authors, the negative coping consists in strategies such as blaming, social withdrawing, denial and disengagement so as to avoid the stressful situations. Now, a parallel can be established between these two coping styles and the brain activities involved in the goal-directed learning and the habit learning.
The goal-directed learning would correspond to the positive coping style insofar as it focuses on the relationship between an action and the motivational value of the outcome, and is associated with the activation of the prefrontal cortex, the dorsomedial striatum and the dorsomedial thalamus ( Ballaine and Dickinson, 1998 ; in Schwabe et al., 2012 ). On the other hand, habit learning, would be linked with the avoidant coping style. This learning process encodes the relationship between a response and preceding stimuli without taking into account the outcome caused by the response and is related to the activation of the dorsolateral striatum ( Yin et al., 2004 ; Tricomi et al., 2009 ; in Schwabe et al., 2012 ). According to Schwabe et al. (2012) , stressful situations may modulate the processes involved in instrumental learning in a way that may produce the shift from goal-directed learning to habitual learning.
In line with these findings, it has been observed that, like cocaine cues, psychological stress induction can generate the same craving response in a cocaine abusers population ( Bradley et al., 1989 ; Wallace, 1989 ; in Sinha et al., 2000 ). The relevance of these observations lies in the fact that both SUD and behavioral addictions (including gaming disorders, Han et al., 2011 ) recruit to an important extent common brain regions and produce similar physiological patterns, as quoted in the introduction of this document.
Considering the association between unhappiness and VG disorders mentioned earlier, it could be posited that the gamers concerned could not overcome the causes of their unhappiness. Indeed, studies suggest that subjects with Internet gaming disorders embark in VG play more to deal with negative affect than to achieve a good performance in the game ( Schimmenti and Caretti, 2010 ; Billieux et al., 2013 ; both in Bonnaire and Baptista, 2019 ). In this scenario, based on the mentioned studies, a low level of happiness would imply that psychological needs are somewhat unmet and associated with the avoidant coping style together with the habit learning. Furthermore, this pattern is supported by compensatory Internet use theory, which postulates that adversity can operate as a stimulus to seek psychological comfort (i.e., satisfying the psychological needs via the cyberspace) ( Kardefelt-Winther, 2014 ; in Dongping et al., 2016 ).
In other words, the psychological comfort engendered by the VG activities in this population of gamers, combined with the characteristics of the avoidant coping style (denial, social withdrawal, avoiding stressful situation, etc.) and with the traits of the habitual learning (actions’ outcomes are disregarded, with little or no awareness of actions’ consequences), might explain, at least partially, the biased perception of the emotional states in AU ( happiness associated to VG) and of their causes of craving for VG. This assumption suggests that online gaming might not be the cause of VG addiction, but rather that VG excessive use could be a compensatory strategy to deal with pre-existing psychological characteristics and deleterious social context ( Kowert et al., 2015 ). For instance, some studies suggest that traumatic experiences, poor emotions regulation, elements of impulsivity and the motivation to experience immersion in a virtual world would increase the likelihood of IGD and Internet addiction ( Billieux et al., 2011 ; Schimmenti et al., 2017 ).
In sum, it would seem as if for AU the mentioned behavioral pattern is a manner to mitigate the difficulties to deal with stressors. This interpretation would be in line with the motives for play in problematic gaming ( Demetrovics et al., 2011 ). Through a massive survey these authors observed seven dimensions that would cover the entire spectrum of motives for VG play in all sort of on line games: escape (from reality), cope (with stressors, playing as a way to improve mood), fantasy (trying new identities/things in a virtual world), skills development (improving concentration, coordination, new skills) recreation (relaxing aspects of gaming), competing (sense of achievement), and social (knowing/being/playing with others). This study suggests that there would be positive and beneficial motives for playing (entertaining gaming) as well as harmful ones (problematic gaming). The correlations between these factors appear to shed light on the positive and negative aspects of gaming. Whilst the weakest correlation is between escape and recreation (also low correlation was found between escape and both, skills development and competition), the strongest correlations were observed between escape and cope and fantasy. These results would indicate that escape and coping are motives associated with problematic gaming, however, the authors argue that escapism would facilitate the coping efforts to deal with stressors and negative moods. Moreover, it is noteworthy underlining that escapism had the lowest mean score in this study among the seven dimensions, which would match with the prevalence level of problematic gaming mentioned previously ( Griffiths et al., 2012 ).
Probably, regarding AU, the accuracy in perceiving emotional states, the ability to deal with stressors and the quality of insights into oneself are dimensions that deserve much attention in the therapeutic processes.
Therapeutic Implications
A cognitive-behavioral approach may contribute to the recovery process by enabling problematic gamers to explore the motives that lead them to abuse of VG play ( Orzack et al., 2006 ; in Griffiths, 2008 ). Developing strategies to tackle stressors appears to be a therapeutic priority for treating this disorder. Consequently, this axis of work includes the understanding of the environmental demands that are perceived as exceeding the individual abilities to handle them. In this line, ensuring the accuracy of the individual’s insights into the emotional states linked to the sources of stress as well as to the game habit could increase the awareness of the underlying issues to be addressed. In particular, deciphering the conditioned desires (unconscious wanting) and the hedonic dimension (unconscious liking) ( Kringelbach and Berridge, 2009 ; Berridge and Kringelbach, 2013 ) linked to VG play may produce added value information for understanding and overcoming the problematic gaming pattern. Within this frame, it could be hypothesized that distinguishing between happiness and feeling alleviated could be beneficial to the therapeutic process, although it remains to be demonstrated.
Overall, this sort of therapeutic approach may contribute to reduce the alexithymia, usually associated with this kind of disorders ( Kandri et al., 2014 ).
In problematic internet/gaming several studies have explored and highlighted to role of alexithymia and its links with other therapeutic issues. For instance, it has been shown that alexithymic individuals are more associated with Internet addiction than non-alexthymic ones ( Baysan-Arslan et al., 2016 ). In this research, the authors consider that the difficulty in identifying and differentiating emotions that characterizes alexithymia may lead individuals with this affliction to regulate their emotional states via their addictive activities.
Another study showed that IGD would be related with alexithymia, anxiety and depression ( Bonnaire and Baptista, 2019 ).
Schimmenti et al. (2017) observed that traumatic experiences (mainly in males) and traits of alexithymia (mainly in females) were associated with Internet addiction symptoms, which may enable a tailored prevention and treatment approach. Besides, Internet addiction (including online role-playing) would be correlated with alexithymia, dissociation (protecting one-self in a more pleasant created reality as a means to deal with traumatic experiences) and insecure attachment ( Craparo, 2011 ).
However, the causal link in the association between alexithymia and Internet addiction would still need to be verified, as indicated by Mahapatra and Sharma (2018) . Moreover, discerning the nature of alexithymia remains an uneasy task: this emotional identification and differentiation disorder might be regarded as a stable personality trait that could increase risks of mental disorder development, and also may be seen as a defense mechanism to cope with psychological stressors ( Mikolajczak and Luminet, 2006 ; in Mahapatra and Sharma, 2018 ).
Apart from alexithymia and traumatic memories, high urgency (a dimension of impulsivity defined by the proneness to have strong reactions usually tied with negative affect) and being motivated to experience immersion in a virtual world would be psychological predictors of problematic multiplayer online games ( Billieux et al., 2011 ). These findings led the authors to posit that individuals with the two mentioned traits are more likely to use the immersion in the virtual world as a means to avoiding facing real life adverse issues. According to the authors, this behavior will lead to a deleterious outcome (culpability and embarrassment as a result of feeling unable to deal with problems), which in turn is experienced as a pernicious condition likely to activate behaviors related to high urgency and immersion.
Like the previously mentioned clinical issues, this vicious loop reinforcing escapism also appears to be a therapeutic target.
Considering the possible association between alexithymia and problematic gaming as a manner to regulate emotions ( Baysan-Arslan et al., 2016 ; Bonnaire and Baptista, 2019 ), the Emotion Regulation Therapy (ERT) might strengthen the therapeutic process. The aim being that the observed difficulties in Internet (including VG) addicts to identifying emotions and regulating affects ( Caretti et al., 2010 ; in Craparo, 2011 ) could be, at least partially, overcome through the ERT process. In effect, Compare et al. (2014) , show that ERT operates as a means to reappraise emotions that trigger actions leading to negative consequences. Reappraising emotions is associated with the involvement of the medial prefrontal cortex, which attenuates the amygdala activation and, thus, reduces the intensity of negative affect; these two areas being coordinated by the orbitofrontal cortex ( Compare et al., 2014 ). Since AU would be prone to associate happiness with VG play, ERT might facilitate the perceptional change enabling to link VG play with pleasure [ Caretti and Craparo, 2009 ; in Craparo (2011) consider Internet addiction (including VG) “as a syndromic condition characterized by a recurrent and reiterated search for pleasure derived from dependence behavior, associated with abuse, craving , clinically significant stress, and compulsive dependence actions despite the possible negative consequences”]. Within this approach, it may be postulated that enabling problematic gamers to familiarize with and to see the self-transcendent notion of happiness could favor the distinction between pleasure and happiness and would render them less vulnerable from impulses and from environmental circumstances ( Dambrun et al., 2012 ). The idea is to facilitate the shift from wanting more than liking (or even without liking) toward liking with little or without wanting ( Berridge and Kringelbach, 2011 ). Furthermore, regarding motives for playing, it could be posited that helping problematic gamers to identify and distinguish the emotions tied to escaping/coping from those related to recreational gaming ( Demetrovics et al., 2011 ), would be a necessary condition to orient effectively the ERT toward the escaping issues and targeted emotional states requiring therapeutic input. In this line, based on the previously mentioned studies in this section, it might be useful exploring the possible link that the excessive time spent in cyber activity could have with past traumatic experiences, insecure attachment, impulsivity, anxiety and depression.
In conclusion, this study suggests that the mentioned confusion of emotional states (pleasure and happiness) associated with addiction ( Lustig, 2017 ), could take place in subjects with VG addiction, and potentially in the entire spectrum of addictions. Moreover, from a cognitive therapeutic perspective, it shows the potential benefits of reappraising emotions as a means to contribute to the emotional distortion reduction.
Limitations
The small sample of this study demands cautiousness when making generalizations from its results. Besides, watching VG clips rather than actually playing VG might be less stimulating for chronic gamers and could have influenced the physiological values recorded during the clip visioning phases. That said, many gamers do attend to public competitions to watch other gamers playing VG. Although, to the best of our knowledge, there is no information available to affirm that there are VG addicts in these audiences.
We also faced the usual paradox when assessing craving via self-report tools. Indeed, participants were asked to judge their craving intensity for VG play whereas sensing craving often may imply a compromised self-awareness level and thus a self-assessment whose value needs to be interpreted carefully.
Although the GAS is a validated tool, which has shown its usefulness in screening addict gamers, having complemented this measurement with thorough diagnostic-driven interviews run by specialists when choosing participants to form the AU and the NAU groups would have strengthened the selection process.
The participants’ selection was centered on the gamer status (gaming addiction/non-addiction and names of games usually played) rather than on the cultural and/or educational background of the persons. Future researches could complete this approach by assessing the possible cultural and educational bias in perceiving the studied emotional states.
Moreover, including more physiological parameters related to pleasure and happiness could further complete the self-reported information and may enable reaching more robust results.
Prospective Research
Further research is required to better understand the relationship between the studied emotional states and this addiction. For instance, since VG addiction decreases with age ( Wittek et al., 2016 ) a longitudinal study could reveal the factors (psychophysiological, environmental, etc.) that operate that change. Moreover, VG addiction is only one area of the spectrum of addictions. Undertaking similar researches on other addictions and with larger samples could also contribute to deepening the comprehension of this issue. Finally, keep enhancing the scales that measure pleasure and happiness may provide with more accurate information about the range of nuances intrinsic to these two emotional states.
Data Availability Statement
Ethics statement.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Université Libre de Bruxelles Ethical Committee. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
LG developed the proposal and the conception of the original project research, searched and articulated the theoretical background, participated in the study and protocol design, elaborated the results interpretation, assembled all the chapters of the study, and in charge of the manuscript writing. ND was involved in the scientific and publication management, participated – as the Research Center Manager – in the study and protocol design, and in charge of the configuration and writing of the physiological measures. JL, as a member of the Research Center, was involved in the study and protocol design, also involved in the configuration of physiological measures, managed the experimental phases in the laboratory, and elaborated the data analysis. CL, as a full Professor at the Faculty of Psychology and Director of the Research Center for Work and Consumer Psychology, assured the scientific and publication management, participated in the study and protocol design, in charge of making the critical reviews of the manuscript along the process, and involved in the manuscript writing.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Maastricht University (Department of Psychiatry and Neuropsychology) as well as Université Libre de Bruxelles (Faculty of Psychological Sciences and of Education – Research Center for Work and Consumer Psychology). This work was performed as a partial fulfillment toward the International Master in Affective Neuroscience of Maastricht University and the University of Florence.
Abbreviations
| AU | addict users |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| ETR | Emotions Regulation Therapy |
| GAS | Gaming Addiction Scale |
| H | happiness |
| HR | heart rate |
| I.G.D. | Internet Gaming Disorders |
| NAU | non-addict users |
| OHQ | Oxford Happiness Questionnaire |
| P | pleasure |
| SHAPS | Snaith-Hamilton Pleasure Scale |
| VG | video games. |
Self-Report Questionnaires
– Six items Questionnaire: Pleasure and/or Happiness associated with VG play (Items 7 and 8 were suppressed after the preliminary phase)
- (1) I enjoy playing video games.
- (2) I am happy when I play video games.
- (3) I would find pleasure in my video game activities.
- (4) I find video games amusing.
- (5) I enjoy playing my favorite video game.
- (6) I often experience joy and exaltation when playing video games.
- (7) I would feel pleasure when I receive praise from other people on my capacity to play video games.
- (8) I don’t have fun when playing video games with other people.
fully disagree disagree slightly disagree slightly agree agree fully agree
<———I——————I——————I————————I——————I—————I———>
– Questionnaire on Craving for playing VG
– After having watched this clip I feel craving for playing video games.
– Three bipolar items Questionnaire: Pleasure and/or Happiness associated with VG play
Bipolar items.
(1) I enjoy playing video games I am happy when I play video games
I——————I——————I——————I—————I
(2) I would find pleasure in I find video games amusing my video game activities
(3) I enjoy playing my favorite I often experience joy and exaltation video game when playing video games
– Ten key words [resulting from the semantic mapping of pleasure (P) and happiness (H)]: 3/10 words to be associated with VG play
- – Joy
- – Craving
- – Well-being
- – Impulsivity
- – Fellowship
- – Desire
- – Fun
- – Contentment
- – Gratification
- – Serenity
Pleasure cluster: joy, craving, impulsivity, desire, fun, gratification.
Happiness cluster: well-being, fellowship, contentment, serenity.
– One bipolar item Questionnaire: Pleasure or Happiness associated with VG play (with explicit definitions)
Happiness : emotional state of lasting contentment.
Pleasure : transient emotional state when satisfying a desire, a craving.
A bipolar item

- Andreassen C. S., Billieux J., Griffiths M. D., Kuss D. J., Demetrovics Z., Mazzoni E., et al. (2016). The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol. Behav. 30 252–262. 10.1037/adb0000160 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ballaine B. W., Dickinson A. (1998). Goal-directed instrumental action: contingency and incentive learning and their cortical substrates. Neuropharmacology 37 407–419. 10.1016/s0028-3908(98)00033-1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baysan-Arslan S., Cebeci S., Kaya M., Canbal M. (2016). Relationship between Internet addiction and alexithymia among university students. Clin. Invest. Med. 39 S111–S115. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berridge K., Kringelbach M. (2011). Building a neuroscience of pleasure and well being. Psychol. Well Being 1 1–3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berridge K. C., Kringelbach M. L. (2013). Neuroscience of affect: brain mechanisms of pleasure and displeasure. Current Opin. Neurobiol. 23 294–303. 10.1016/j.conb.2013.01.017 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Billieux J., Chanal J., Khazaal Y., Rochat L., Gay P., Zullino D., et al. (2011). Psychological predictors of problematic involvement in massively multiplayer online role-playing games: illustration in a sample of male cybercafé players. Psychopathology 44 165–171. 10.1159/000322525 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Billieux J., Van der Linden M., Achab S., Khazaal Y., Paraskevopoulos L., Zullino D., et al. (2013). Why do you play Warcraft? An in-depth exploration of self-reported motivation to play online and in the game behaviors in the virtual world of Azeroth. Compt. Hum. Behav. 29 103–109. 10.1016/j.chb.2012.07.021 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bonnaire C., Baptista D. (2019). Internet gaming disorder in male and female young adults: the role of alexithymia, depression, anxiety and gaming type. Psychiatry Res. 272 521–530. 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.158 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bradley B. P., Phillips G., Green L., Gossop M. (1989). Circumstances surrounding the initial lapse to opiate use following detoxification. Br. J. Psychiatry 154 354–359. 10.1192/bjp.154.3.354 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bruchon-Schweitzer M., Boujut E. (2014). Psychologie de la Santé: Concepts, Methods et Modèles. Paris: Dunod, 10.3917/dunod.bruch.2014.01 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Caretti V., Craparo G. (2009). “ Psychological issues of technological addiction. New diagnostic criteria for addiction ,” in Annual Review of Cybertherapy and Telemedicine 2009. Advanced Technologies in the Behavioural, Social and Neurosciences , eds Wiederhold B. K., Riva G. (Amsterdam: IOS Press; ), 227–280. [ Google Scholar ]
- Caretti V., Craparo G., Schimmenti A. (2010). “ Alcune evidenze empireche sul construtto di trance dissi-ociativa da videoterminale ,” in Addiction , eds Caretti V., La Barbera D. (Milano: Rafaelo Cortina; ), 167–182. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chou T., Ting C. H. (2003). The role of flow experience in cyber-game addiction. Cyber Psychol. Behav. 6 663–675. 10.1089/109493103322725469 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cipresso P., Serino S., Riva G. (2014). The pursuit of happiness measurement: a psychometric model based on psychological correlates. Sci. World J. 2014 : 139128 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Compare A., Zarbo C., Shonin E., van Gordon W., Marconi C. (2014). Emotional regulation and depression: a potential mediator between heart and mind. Cardiovasc. Psychiatry Neurol. 2014 : 324374 . 10.1155/2014/324374 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper S., Robinson A. J., Mazei-Robinson M. (2017). Reward circuitry in addiction. Neurotherapeutics 14 687–697. 10.1007/s13311-017-0525-z [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Craparo G. (2011). Internet addiction, dissociation and alexithymia. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 30 1051–1056. 10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.10.205 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dambrun M., Ricard M., Després G., Drelon E., Gibelin E., Gibelin M., et al. (2012). Measuring happiness: from fluctuating happiness to authentic, durable happiness. Front. Psychol. 3 : 16 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00016 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deci E. L., Ryan R. M. (2000). The “what” and “why” of goal pursuits: human needs and the self-determination of behaviour. Psychol. Inq. 11 227–668. [ Google Scholar ]
- Deci E. L., Ryan R. M. (2008). Hedonia, eudamonia, and well-being: an introduction. J. Happiness Stud. 9 1–11. 10.1007/s10902-006-9018-1 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Demetrovics Z., Urbán R., Nagygyörgy K., Farkas J., Zilahy D., Mervó B., et al. (2011). Why do you play? The development of the motives for online gaming questionnaire (MOGQ). Behav. Res. Methods 43 814–825. 10.3758/s13428-011-0091-y [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dong G., Li H., Potenza M. (2017). Cognitive control and reward/loss processing in Internet gaming disorders: results from a comparison with recreational Internet game users. Eur. Psychiatry 44 : 3038 . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dong G., Potenza M. (2015). A cognitive-behavioural model of Internet gaming disorders: theoretical underpinnings and clinical implications. J. Psychiatry Res. 58 7–11. 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.07.005 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dongping L., Wenhau Z., Xian L., Yueyue Z., Liyan Z., Yanhui W. (2016). Stressful life events and adolescent Internet addiction: the mediating role of psychological needs satisfaction and the moderating role of coping style. Comp. Hum. Behav. 63 408–415. 10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.070 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Esposito E., Di Matteo V., Di Giovanni G. (2008). Serotonin-dopamine interaction: an overview. Prog. Brain Res. 172 3–6. 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00901-1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gaetan S., Bonnet A., Brejard V., Cury F. (2014). French validation of the 7-item Game Addiction Scale for adolescents. Rev. Eur. Psychol. Appl. 64 161–168. 10.1016/j.erap.2014.04.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Geisel O., Panneck P., Stickel A., Schneider M., Müller C. A. (2015). Characteristics of social network gamers: results of an online survey. Front. Psychiatry 6 : 69 . 10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00069 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gil S., Droit-Volet S. (2012). Emotion time distortions: the fundamental role of arousal. Cogn. Emot. 26 847–862. 10.1080/02699931.2011.625401 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gowing L., Ali R. L., Allsop S., Marsden J., Turf E. E., West R., et al. (2015). Global statistics on addictive behaviours: 2014 status report. Society for the study of addiction. Addiction 110 904–919. 10.1111/add.12899 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Griffiths M. (2008). Diagnosis and management of video game addiction. New Direct. Addict. Treat. Prevent. 12 27–41. [ Google Scholar ]
- Griffiths M., Kuss D., King D. (2012). Video game addiction: past. Present and future. Curr. Psychiatry Rev. 8 308–318. 10.2174/157340012803520414 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Han D. H., Bolo N., Daniels M. A., Arenella L., Lyoo I. K., Renshaw P. F. (2011). Brain activity and desire for Internet video game play. Comprehen. Psychiatry 52 88–95. 10.1016/j.comppsych.2010.04.004 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hills P., Argyle M. (2002). The oxford happiness questionnaire: a compact scale for the measurement of psychological well-being. Pers. Individ. Differ. 33 1073–1082. 10.1016/s0191-8869(01)00213-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hull D., William G. A., Griffiths M. D. (2013). Video game characteristics, happiness and flow as predictors of addiction among video game players: a pilot study. J. Behav. Addict. 2 145–152. 10.1556/JBA.2.2013.005 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jatupaiboon N., Pan-ngum S., Israsena P. (2013). Real-time EEG-based happiness detection system. Sci. World J. 2013 : 618649 . 10.1155/2013/618649 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kandri T. A., Bonotis K. S., Floros G. D., Zafiropoulou M. M. (2014). Alexithymia components in excessive internet users: a multi-factorial analysis. Psychiatry Res. 220 348–355. 10.1016/j.psychres.2014.07.066 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kardefelt-Winther D. (2014). A conceptual and methodological critique of Internet addiction research: towards a model of compensatory Internet use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 31 351–354. 10.1016/j.chb.2013.10.059 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kashdan T., Bsiwas-Diener R., King L. (2008). “Reconsidering Happiness: the cost of distinguishing between hedonics and eudemonia”. .J. Posit. Psychol. 3 219–233. 10.1080/17439760802303044 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kennedy A., Epstein D. H., Jobes M. L., Agage D., Tyburski M., Phillips K. A., et al. (2015). Continuous in-the-field measurement of heart rate: correlates of drug use, craving, stress and mood in polydrug users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 151 159–166. 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.03.024 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Keyes K. M., Jager J., Hamilton A., O’Malley P. M., Miech R., Schulenberg J. (2015). National multi-cohort time trends in adolescent risk preference and relation with substance use and problem behavior from 1976 to 2011. Drug Alcohol Depend. 155 267–274. 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.06.031 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Khazaal Y., Chatton A., Rothen S., Achab S., Thorens G., Zullino D., et al. (2016). Psychometric properties of the 7-item game addiction scale among French and German adults. BMC Psychiatry 16 : 132 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Khazaal Y., Zullino D., Billieux J. (2012). The Geneva smoking pictures: development and preliminary validation. Eur. Addict. Res. 18 103–109. 10.1159/000335083 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim E. J., Namkoong K., Ku T., Kim S. J. (2007). The relationship between online game addiction and aggression, self, control and narcissistic personality traits. Eur. Psychiatry 23 212–218. 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.10.010 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim H., Ha J., Chang W. D., Park W., Kim L., Im C. H. (2018). Detection of craving for gaming in adolescents with internet gaming disorders using multimodal bio signals. Sensors 18 : 102 . 10.3390/s18010102 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ko C.-H., Gin-Chung L., Sigmund H., Ju-Yu Y., Ming-Jen Y., Wei-Chen L., et al. (2009). Brain activities associated with gaming urge of online gaming addiction. J. Psychiatry Res. 43 739–747. 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.09.012 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Koepp M. J., Gunn R. N., Lawrence A. D., Cunningham V. J., Dagher A., Jones T., et al. (1998). Evidence for striatal dopamine release during a video game. Nature 393 266–268. 10.1038/30498 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kowert R., Vogelgesang J., Festl R., Quandt T. (2015). Psychological causes and consequences of online video game play. Comput. Hum. Behav. 45 51–58. 10.1016/j.chb.2014.11.074 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kringelbach M., Berridge K. (2009). Towards a functional neuro-anatomy of pleasure and happiness. Trends Cogn. Sci. 13 479–487. 10.1016/j.tics.2009.08.006 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kringelbach M., Berridge M. (2010). The neuroscience of happiness and pleasure. Soc. Res. 77 659–678. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lawrence L. M., Ciorciari J., Kyrios M. (2014). “Relationships that compulsive buying has with addiction, obsessive-compulsiveness, hoarding and depression”. Compr. Psychiatry 55 1137–1145. 10.1016/j.comppsych.2014.03.005 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lazarus R. S., Folkman S. (1984). Stress, Appraisal and Coping. New York, NY: Springer. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee Y., Han D., Yang K. C., Daniels M. A., Na C., Kee B. S., et al. (2008). Depression like characteristics of 5HTTLPR polymorphism and temperament in excessive Internet users. J. Affect. Disord. 2 165–169. 10.1016/j.jad.2007.10.020 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lemmens J., Valkenburg P., Peter J. (2011). Psychological causes and consequences of pathological gaming. Comput. Hum. Behav. 27 144–152. 10.1016/j.chb.2010.07.015 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lemmens J. S., Valkenburg P. M., Peter J. (2009). Development and validation of game addiction scale for adolescents. Media Psychol. 12 77–95. 10.1080/15213260802669458 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lepine J.-P., Briley M. (2011). The increasing burden of depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 7 ( Suppl. 1 ), 3–7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Loas G., Dubal S., Perot P., Tirel F., Nowaczkowski P., Pierson A. (1997). Etude de validation de la version française de l’échelle de plaisir de Snaith et Hamilton. L’Encephale 23 454–458. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Loonen A., Ivanova S. (2016). Circuits regulating pleasure and happiness – mechanisms of depression. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 10 : 571 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lu D., Wang J. W., Huang A. C. (2010). Differentiation of internet addiction risk level based on autonomic nervous responses: the internet-addiction hypothesis of autonomic activity. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 13 371–378. 10.1089/cyber.2009.0254 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lustig R. (2017). The Hacking of the American Mind. New York, NY: Avery. [ Google Scholar ]
- MacNicol B. (2016). The biology of addiction. Can. J. Anesthesia 64 141–148. 10.1097/YPG.0000000000000095 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mahapatra A., Sharma P. (2018). Association of internet addiction and alexithymia – A scoping review. Addict. Behav. 81 175–182. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.02.004 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mikolajczak M., Luminet O. (2006). Is alexithymia affected by situational stress or is it a stable trat related to emotion regulation? Pers. Individ. Differ. 40 1399–1408. 10.1016/j.paid.2005.10.020 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Orzack M. H., Vouse A. C., Wolf D., Hennen J. (2006). An on-going study of group treatment for men involved in problematic Internet enabled sexual behaviour. CyberPsychol. Behav. 9 348–360. 10.1089/cpb.2006.9.348 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Petry N. M., Rehbein F., Gentile D. A., Lemmens J. S., Rumpf H. J., Mößle T., et al. (2014). An international consensus for assessing Internet gaming disorder using new DSM-5 approach. Addiction 109 1399–1406. 10.1111/add.12457 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Petry N. M., Rehbein F., Ko C. H., O’Brien C. H. (2015). Internet gaming disorders in the DSM-5. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 17 : 19 . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pollard I. (2003). From Happiness to Depression”. Today’s Life Science. Available at: www.biotechnews.com.au (accessed August, 2019). [ Google Scholar ]
- Procter P. (1985). Longman Concise English Dictionary. England: Longman Group Limited. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryu H., Lee J., Choi A., Park S., Kim D., Choi J. (2018). The relationship between impulsivity and internet gaming disorders in young adults: mediating effects of interpersonal relationships and depression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15 : 458 . 10.3390/ijerph15030458 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sarda E., Bègue L., Bry C., Gentile D. (2016). Internet gaming disorders and well-being: a scale validation. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 19 674–679. 10.1089/cyber.2016.0286 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schimmenti A., Caretti V. (2010). Psychic retreats or psychic pits? Unbearable states of mind ad technological addiction. Psychoanalogy 27 115–132. 10.1037/a0019414 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schimmenti A., Passanisi A., Caretti V., La Marca L., Granieri A., Iacolino C., et al. (2017). Traumatic experiences, alexithymia and Internet addiction symptoms among late adolescents: a moderated mediation analysis. Addict. Behav. 64 314–320. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2015.11.002 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schmidt L. A. (2016). “ What are addictive substances and behaviours and how far do they extend? ,” in Impact of Addictive Substances and Behaviours on Individual and Societal Well-Being , eds Anderson P., Rehm J., Room R. (London: Oxford Unversity Press; ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwabe L., Tegenhoff M., Höffken O., Wolf O. (2012). Simultaneous glucocorticoid and noradrenergic activity disrupts the neural basis of goal-directed action in the human brain. J. Neurosci. 32 10146–10155. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1304-12.2012 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seay A. F., Kraut R. E. (2007). “ Project massive: self-regulation and problematic use of on-line gambling ,” in Proceedings of the ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems , San Jose, CA. [ Google Scholar ]
- Serretti A., Calati R., Mandelli L., Ronchi D. D. (2006). Serotonin transporter gene variant and behaviour: a comprehensive review. Curr. Drug Targets 7 1659–1669. 10.2174/138945006779025419 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shen C., Ratan C., Dora Y., Leavitt A. (2016). Do men advance faster than women? Debunking the gender performance gap in two massively multiplayer online games. J. Comput. Med Commun. 21 312–329. 10.1111/jcc4.12159 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sinha R., Fuse T., Aubin L. R., O’Malley S. S. (2000). Psychological stress drug-related cues and cocaine craving. Psychopharmacology 152 140–148. 10.1007/s002130000499 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Snaith R. P., Hamilton M., Morley S., Humayan A. (1995). A scale for the assessment of the hedonic tone: the Snaith-Hamilton Pleasure Scale. Br. J. Psychiatry 167 99–103. 10.1192/bjp.167.1.99 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Szalavitz M. (2011). What does a 400% increase in antidepressant use really mean?. Patna: Time. [ Google Scholar ]
- Teplan M., Krakovskà A. (2009). “ EEG features of psycho-physiological relaxation ,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Applied Sciences in Biomedical and Communication Technologies ISABEL 2009 , (Bratislava: Institute of Measurement Science SAS; ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Tian Y., Liu P., Huang X. (2018). The role of emotion regulation in reducing emotional distortions of duration perception. Front. Psychol. 9 : 347 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00347 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Torres A., Catena A., Megias A., Maldonado A., Candido A., Verdejo-Garcia A., et al. (2013). Emotional and non-emotional pathways to impulsive behavior and addiction. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 7 : 43 . 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00043 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tricomi E., Ballaine B. W., O’Doherty J. P. (2009). A specific role for posterior dorsolateral striatum in human habit learning. Eur. J. Neurosci. 29 2225–2232. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06796.x [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Üstün T. B., Ayuso-Mateos J. L., Chatterji S., Mathers C., Murray C. J. (2004). Global burden of depressive disorders in the year 2000. Br. J. Psychiatry 184 386–392. 10.1192/bjp.184.5.386 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Holst R. J., Lemmens J. S., Valkenburg P. M., Peter J., Veltman D. J., Goudriaan A. E. (2012). Attentional bias and disinhibition toward gaming cues are related to problem gaming in male adolescents. J. Adolescent. Health 50 541–546. 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2011.07.006 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Volkow N., Wang G., Fowler J., Tomasi D., Telang F. (2011). Addiction: beyond dopamine reward circuitry. PNAS 108 15037–15042. 10.1073/pnas.1010654108 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wallace B. C. (1989). Psychological and environmental determinants of relapse in crack cocaine smokers. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 6 95–106. 10.1016/0740-5472(89)90036-6 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang L., Wu L., Wang Y., Li H., Liu X., Du X., et al. (2017). Altered brain activities associated with craving and cue reactivity in people with Internet gaming disorders: evidence from the comparison with recreational Internet game users. Front. Psychol. 8 : 1150 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01150 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Waterman A., Schwartz S., Conti R. (2008). The implication of the two conceptions of happiness (Hedonic. (enjoyment)and Eudamonia) for the understanding of intrinsic motivation. J. Happiness Stud. 9 41–79. 10.1007/s10902-006-9020-7 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wei H.-T., Chen M. H., Huang P. C., Bai Y. M. (2012). The association between online gaming, social phobia and depression: an internet survey. BMC Psychiatry 12 : 92 . 10.1186/1471-244X-12-92 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wenzel H. G., Bakken I. J., Johansson A., Götestam K. G., Øren A. (2009). Excessive computer game playing among Norwegian adults: self-reported consequences of playing and association with mental health problems. Psychol. Rep. 105 1237–1247. 10.2466/pr0.105.f.1237-1247 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whiteford H., Degenhardt L., Rehm J., Baxter A. J., Ferrari A. J., Erskine H. E., et al. (2013). “Global burden of attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the global burden of disease study 2010”. Lancet 382 1575–1586. 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61611-6 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wittek C. T., Reiten Finseras T., Pallesen S., Mentzoni A., Hanss D., Griffiths M., et al. (2016). Prevalence and predictors of video game addiction: a study based on a national and representative sample gamers. Int. J. Mental Health Addict. 14 672–686. 10.1007/s11469-015-9592-8 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization [WHO] (2018). Available at: https://www.who.int/features/qa/gaming-disorder/en/ (accessed December, 2018). [ Google Scholar ]
- Yau Y., Crowley M., Mayes L., Potenza M. (2012). Are Internet use and video game play addictive behaviours? Biological, clinical and public health implications for youths and adults. Minerva Psichiatrica 53 153–170. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin H. H., Knowlton B. J., Ballaine B. W. (2004). Lesions of dorsolateral striatum preserve outcome expectancy but disrupt habit formation in instrumental learning. Eur. J. Neurosci. 19 181–189. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03095.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zheng Y., Fan F., Liu X., Mo L. (2012). Life events, coping and posttraumatic stress symptoms among Chinese adolescents exposed to 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake. China. PLoS One 7 : e29404 . 10.1371/journal.pone.0029404 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

Video Game Addiction: Causes, Effects & Treatment Options
- AddictionExperts
- Reviewed By Dr. John Elgin Wilkaitis
- November 20, 2015
How to Recognize & Treat Video Game Addiction

Video Game Addiction Statistics
Researchers and social scientists have been troubled by video game addictions since the phenomenon first presented itself with the advent of video games in the 1970s and 1980s. Today, “gaming” has become a popular term used by people of all ages, not just teens. Ironically, video game addiction isn’t just for kids, either. Adults can have just as much trouble turning away from video games as children do.
Some of the more recent statistics involving video game addiction are pretty startling and are indicators that it’s time to start taking this type of addiction as seriously as other addictions:
- In a survey, 41 percent of respondents said they play video games to escape from real life. These gamers were considered dependent on video games to avoid real-life situations.
- Multiplayer and role-playing games online appear to be the most addictive types of video games, perhaps because of the illusion of community they create.
- Intense ADHD symptoms are linked to video game addiction severity.
- Boys are more likely to become video game addicts than girls. Girls who are addicted tend to prefer games that involve puzzles and other interactive activities rather than violence and aggression.
- Studies have shown that the regions of the brain (the pleasure centers) that are activated in drug addicts and alcohol addicts are also activated in the regions of the brain of video game addicts.
- 13.9 percent of male students in Hong Kong report spending over 21 hours per week playing video games.
- As of 2019, the global prevalence of video game disorder was 3.05 percent.
With information like this, everyone needs to realize that video game addiction is not to be taken lightly.
Risk Factors for Video Game Addiction
Why do some people become video game addicts while others seem to have no problem turning away from the games? The answer might lie in risk factors such as the following:
- The video game addict has been sexually or emotionally abused and is trying to escape the situation.
- The video game addict has been bullied by their peer group and is seeking acceptance in an alternative community.
- The video game addict is socially awkward and uncomfortable interacting with people in a natural environment.
- The video game addict’s parents or siblings are also addicted to playing video games, making it a family pastime.
- The video game addict seeks out gaming to show their aggression toward the world or deal with anger.
- The video game addict has little control in their own life, so they turn to gaming to feel confident.
- The video game addict has lowered self-esteem and constantly uses video games to elevate feelings of self-worth.
- The video game addict is left alone for long periods and turns to gaming — primarily multi-player gaming — as a source of community and comfort.
- The video game addict suffers from untreated depression and uses video games to get a “high” to combat their moods.
- The video game addict is spontaneous and rash by nature and cannot control their impulsivity.
- The video game addict has a history of addiction (i.e., to work, love, drugs, nicotine).
If you notice you have one or more of these risk factors and causes of video game addiction, and you regularly game, you may already be addicted to video games. It’s important not to try to go it alone if you want to overcome this problem. Always seek treatment from a trained expert who can guide you through recovery, including proven solutions to video game addiction.
How to Know If You’re Addicted to Video Games
Are you worried you, or someone you know, is a video game addict? Answer this brief assessment to help you find out:
- Do you play video games for hours and hours, sometimes not eating or sleeping so you can stay in the game?
- Is gaming more important to you than hanging out with people in “real life?”
- When you finish playing a video game, do you feel a sense of pleasure and want to get that “high” again?
- Do you have trouble stepping away from video games or stopping play?
- Can you leave a video game in the middle of play for an emergency?
- Have you ever hidden your gaming because you were embarrassed by how often you play?
- Have people told you that you play too many video games or that you’re addicted to video games?
- Do you become moody or angry when you can’t play video games?
- Have you ever played video games when you should be working?
- Have you ever lost a job because you were playing video games or missed work because of gaming?
- Has gaming hurt your relationships with your loved ones?
- Have you spent money on gaming you should have spent on bills or paying down debt?
The more “yes” answers you have, the greater your chances are that you may be addicted to video games. In that case, you deserve to get help immediately. Call a treatment center or therapist who has experience in video game addiction. You’ll be glad you took the first step toward recovery.
How Parents Can Help Their Kids Avoid Video Game Addiction
Because video game addiction so often happens in childhood, parents need to recognize that they play a huge role in stopping video game addiction in children . Moms and dads should be ready to address this subject, and they can take several proactive steps to help their kids avoid becoming video game addicts.
If you’re a parent of a child who enjoys playing video games or who hasn’t yet started playing video games, the following suggestions may prevent a future issue:
- Talk to your child about the risks of video games . Make sure they understand (at an age-appropriate level) that gaming is meant to be fun, but it should not be all-consuming.
- Know which video games your child is playing . Most video games are rated, but don’t assume the ratings are up to your standards. Check each game thoroughly, and you may even want to play a game with your child.
- Limit the time your child is allowed to play video games . Some parents make video gaming only available on the weekend. This eliminates worries about gaming interfering with schoolwork or grades.
- Make video game playing a seldom-offered reward for a job well done . For instance, if your son comes home with all “A”s on a report card, you may allow him to play a favorite video game for an extra hour or two.
- Monitor all computer and device activity . Children who want to play video games will often sneak around. Make it a practice to check your child’s technology equipment regularly for signs of video game usage.
- Watch for signs of video game addiction violence . If you tell your child to stop playing a game, do they suddenly lash out? When they can’t play, do they withdraw from you? This signals that you need help from a therapist or treatment center.
- Make your child aware of things to do other than video games . Redirect their attention to more positive activities, such as playing outside or helping older neighbors with chores.
- Deal with your own video game addiction and recovery . If you’re addicted to video games, it will be impossible to tell your child not to play.
By being aware of what’s happening with your son or daughter, you’ll be in a much better position to stave off long-term problems associated with video game addiction.
The Effects of Video Game Addiction
Left untreated, video game addiction is unlikely to go away on its own. Like all other addictions, intervention and treatment is the key to ending any cycle of abusive behavior. And make no mistake — video game addiction abuses not only the gamer but also those around them.
The effects of video game addiction have been documented around the world:
- Video game addicts are less likely to succeed in life.
- Video game addicts may suffer from lifelong low self-confidence.
- Video game addicts may never have a fulfilling career or relationships.
- Video game addicts are at risk of depression and potentially suicide.
- Video game addicts are at risk of developing headaches.
- Video game addicts are at risk of insomnia.
- Video game addicts may become obese, leading to other problems, such as diabetes and hypertension.
Learn more about the adverse effects of video game addiction here . Society doesn’t need more video game addicts. It needs more productive people.
How Video Game Addiction is Treated
The treatment plans typically used for video game addicts will vary according to the person being treated. However, there are some steps habitually used by therapists who are focused on working with this type of addiction:
- The behavior is stopped . In some circles, this is called going “cold turkey” and can cause significant withdrawal symptoms. When accompanied by therapy, the withdrawal can be controlled.
- A plan of action is created . This plan includes a listing of the triggers associated with video game addiction. For instance, an addict may find they play video games when they are stressed out. Thus, the next time the person is under severe anxiety, they can recognize this as a trigger and do something different and healthier, such as going for a walk, calling a friend, or journaling.
- Daily schedules and routines are developed . A daily routine can be an asset to video game addicts because their days are mapped out. When they are just beginning treatment, this can be a powerful ally in keeping them focused on getting better and not turning to gaming.
- Ongoing therapy sessions are scheduled . Therapy is essential to overcoming addictions, including video game addictions. Therapy sessions will help restore self-confidence and allow the addict to move past whatever was holding them back.
- Group sessions may be prescribed. These sessions are similar to AA meetings, where each group member expresses support for the others dealing with an addiction.
Other forms of treatment that may be utilized or suggested could be rewards for not playing video games, art therapy, and music therapy. Depending upon the video game addiction level, inpatient treatment centers may be a better fit for the addict, even if the addict is a teenager.
What to Do After a Video Game Addiction Relapse
Relapsing is a commonplace phenomenon in the treatment of video game addiction. A relapse can be considered part of recovery, however, and not an end to it. As soon as the relapse has occurred, the video game addict must return to their treatment center or therapist. The faster a relapse is evaluated, the sooner the addict can continue toward complete recovery.
If you’re the parent of a child or teen who has undergone treatment for video game addiction and suspects a relapse has occurred, do not hesitate to take action . You may feel uncomfortable confronting your child with your suspicions, but it’s better to have an awkward conversation than to enable them to experience a full-blown video game addiction again.
Can a Video Game Addict Ever Play Video Games Again?
There’s an old saying: “Once an addict, always an addict.” If this statement is to be taken conclusively, it means someone diagnosed as a video game addict should avoid video games in the future. Even one video game session could lead to a relapse.
The good news is that, unlike food addicts who need to eat , video game addicts do not have to play video games. Of course, for kids addicted to video games, not gaming may mean not attending social events like parties and other celebrations where gaming will be available. This is similar to the practice of alcoholics not going to functions where alcoholic beverages are likely to be served.
In general, it’s best if the video game addict never returns to gaming. That way, they have a much better chance of beating the addiction completely.
Sponsored Treatment Center:

Reviewed By:

Dr. John Elgin Wilkaitis
Dr. John Elgin Wilkaitis completed medical school at The University of Mississippi Medical Center and residency in general psychiatry in 2003. He completed a fellowship in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital in 2005. Following this, he served as Chief Medical Officer for 10 years of Brentwood Behavioral Healthcare a private health system including a 105-bed hospital, residential treatment, and intensive outpatient services.
Addiction Experts is a group of addiction and behavioral health specialists dedicated to providing helpful, and free, addiction treatment guides. Millions of people have utilized our resources and suggestions for substance use disorders, mental health treatment, and process addiction treatment. Don’t hesitate to reach out to us with any questions you may have!
Recent Posts:
Can a meth addict donate organs, can methadone treat meth addiction, when was crystal meth first invented, is buprenorphine safer than other opioids, the curious case of shoplifting vs. kleptomania, what are the symptoms of a drug overdose, get started on the road to recovery, resources by state.

Addiction Experts is a group of addiction and behavioral health specialists dedicated to providing helpful, and free, addiction treatment guides.
Drug Addiction
- Benzodiazepines
- Sleeping Pills
- All Other Drugs
Process Addiction
- Eating Disorders
- Exercise Addiction
- Food Addiction
- Gambling Addiction
- Kleptomania
- Love Addiction
- Porn Addiction
- Sex Addiction
- Shopping Addiction
- Tanning Addiction
- Technology Addiction
- Work Addiction
Treatment Programs
- Medical Detox
- Inpatient Rehab
- Outpatient Rehab
- Interventions
- Dual Diagnosis
- Medication Assisted Treatment
- Sex Addiction Hotline
- Porn Addiction Hotline
- Gambling Addiction Hotline
- Eating Disorder Hotline
- Food Addiction Helpline
- Video Game Addiction Helpline
- Shopping Addiction Helpline
When You're Ready, We're Here to Talk
Addiction to Online Gaming: A Review of Literature Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
The problem of interest, the qualitative research method to be used, the review of literature.
The rapid development of technologies has led not only to numerous breakthroughs in various spheres of people’s lives but also to significant issues related to the inability of some individuals to limit their time spent on gadget use. Whereas the Internet has presented ample opportunity for communication and research, it has also become the reason why too many users have become dependent on it. The selected topic of research is the addiction to online gaming among adults. This specific kind of addiction does not produce such a devastating effect on one’s health as the excessive consumption of alcohol or drugs. However, online gaming addiction poses other threats, which are no less severe both for the addicts and their close ones.
Researchers have presented evidence on the severity of online gaming addiction (Marino & Spada, 2017). Still, too many people continue to neglect the issue’s potential adverse outcomes. Therefore, more research is needed to investigate the problem from different angles, which will suggest viable solutions to it. The present paper is an overview of scholarly sources on online gaming addiction and the analysis of narrative inquiry as the most suitable qualitative research method to use for the investigation of this problem.
Despite the constant development and enhancement of community resources and entertainment opportunities, the number of individuals addicted to online gaming is growing annually. What previously used to be viewed merely as a leisure activity has now come to be considered as a serious threat due to its potential to provoke addiction in users. Online gaming is related to social and psychological problems by facilitating self-regulation deficiency (Gong et al., 2019). Furthermore, the age of gamers has increased considerably, and the activity is no longer regarded as a teenage male hobby (Pietersen et al., 2018). Whereas, in the past, playing video games online, was considered as a useless pastime, at present, it has become an important part of many people’s lifeworlds. The increasing popularity of online gaming is associated with the idea that video games are “richly expressive and creative,” and they grant people much more immersive experience than other media forms do (Pietersen et al., 2018, p. 123). Therefore, one of the core aims in performing current research is to enhance the understanding of people’s likelihood to become addicted to online gaming.
Another rationale for selecting the problem is the need to analyze the possible ways of mitigating a growing issue of online game addiction among the population. Typically, game addicts are male individuals who report unique experiences related to their gaming activity and a high rate of engagement as the triggers of addiction (Tang et al., 2017). However, it is evident that the problem affects not only those directly involved in it but also anyone they interact with within their personal, professional, social, and family lives. Specifically, as Tang et al. (2017) mention, addiction to online gaming can cause a range of social and family problems that present a significant public health concern.
With the increasing interest of researchers in the question of problematic use of the Internet by gamers, a new clinical definition has been suggested to characterize the issue: Internet gaming disorder (Marino & Spada, 2017). Other terms utilized to denote the problem include ‘online gaming addiction,’ ‘problematic online gaming,’ ‘pathological gaming,’ and ‘video gaming dependence’ (Marino & Spada, 2017). The prevalence of Internet gaming disorder is reported to vary from 1.6 to 8.5% among Western youths. Furthermore, the disorder is frequently accompanied by other psychological problems, such as depression, anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and social phobia (Marino & Spada, 2017). Thus, it is crucial to analyze the available research in order to synthesize what has already been found and single out questions for further detailed research.
The main focus of the study will be the development of online gaming addiction and individuals’ feelings about it. According to Monacis et al. (2017), excessive use of technology has become an emerging issue of concern in the past few decades. The most common symptoms of online gaming addiction are unpleasant feelings when there is no access to the Internet (emptiness and depression), excessive investment of time spent on playing online games, and the refusal to admit a problem (Monacis et al., 2017). One of the major motives for engaging in online gaming is seeking sensation (Hu et al., 2017).
Other common reasons for developing online gaming addiction are concerned with coping, escape, competition, fantasy, and social motives (Šporčić & Glavak-Tkalić, 2018). Hence, it is crucial to investigate why individuals develop an addiction to online gaming and how they feel about it at the stage when they are only starting to engage in excessive Internet use and at the point when online games begin to take up too much time and initiate psychological problems. Personal stories of online gamers will serve as a solid ground for identifying the principal problems and suggesting solutions to them.
Taking into consideration the nature of the problem under investigation, the most suitable qualitative research method to employ in the study is narrative inquiry. This method involves the process of collecting data from respondents through storytelling. The study of the narrative becomes the means of understanding the ways people perceive the world and various situations in their lives. The self-narrative construction is manifested both in the content and form of narratives (Androutsopoulou & Stefanoua, 2018). According to Lieblich et al., there are two core dimensions for interpreting and scrutinizing narratives: “holistic versus categorical” and “content versus form” (as cited in Androutsopoulou & Stefanoua, 2018, p. 130).
According to Androutsopoulou and Stefanoua (2018), the most beneficial approach to employing a narrative inquiry analysis is a holistic one. The holistic-content dimension implies that the researcher should use the whole life story of an individual, which allows focusing on emerging topics. Meanwhile, the holistic-content mode presupposes that researchers look inside the structure of a respondent’s life story (Androutsopoulou & Stefanoua, 2018). As a result, the use of narrative inquiry helps to understand people’s attitudes toward the events happening in their lives and the ways they feel about them.
The selected research method enables scholars to focus on respondents’ thoughts about their lives rather than on events happening. By using this holistic approach, an individual is able to construct a coherent story of their life with the past, present, and future (James, 2018; McAlpine, 2016). When one tells a researcher about their experiences, the latter becomes “narratives as part of inquiry” and makes the audience “vicarious” participants of these experiences (Chen, 2019, p. 382). Narrative inquiry is composed of three dimensions: temporality, sociality, and space (Kovinthan, 2016). These presuppose a transitional movement of people and places in the story, the revelation of the person’s emotions and feelings, and the possibility of the physical space of inquiry to change (Kovinthan, 2016). Overall, narrative inquiry allows for receiving valuable and reliable first-hand information about the researched issues and problems.
Benefits and Limitations of the Selected Research Design
As a research design, a narrative inquiry has a number of advantages and disadvantages that should be considered before utilizing it. The major benefit is undoubtedly the possibility to receive information from the respondent openly, honestly, and without bias. Narrative inquiry is considered to be the most suitable way of uncovering and understanding people’s complex problems (James, 2018). The next advantage of the selected research design is placing the respondent’s self in the central part of the story (Gordon et al., 2015). As a result, the narrator is able to present and construct events, identities, and realities in close synergy with others (Gordon et al., 2015). With the help of narrative research, individuals find it easier to story and re-story their lives in various problematic contexts (Sheilds et al., 2015). Another strength of the narrative inquiry is the likelihood of improving people’s well-being by allowing them to express their thoughts and apprehensions (Ho et al., 2020). When an individual receives an opportunity to express their problems out loud, the chances of coping with these issues increase.
What is more, narrating personal experience equals making sense of it (Ho et al., 2020). In the case of online gamers, the use of narrative inquiry enables researchers to understand “what it means to be a gamer” (Pietersen et al., 2018, p. 123). With this information available, scholars can understand the mechanisms of addiction better since unique personal data allows for a thorough analysis of how people develop an addiction to online gaming and how they feel about it. The next benefit of the selected research design is that it incorporates not only inward but also outward analysis. According to Law and Chan (2015), narrative inquirers consider both the participants’ and researchers’ identities, feelings, hopes, moral tendencies, the environment, conditions, and people affecting the forces and factors from respondents’ contexts. Kovinthan (2016) reports that narrative inquiry helps researchers to cross the boundary between themselves and participants. Additionally, the selected research design enables scholars to investigate the issues faced by respondents and draw out the implicit beliefs and values of researchers (Kovinthan, 2016).
One more advantage of narrative inquiry is the possibility of this approach to unite not only participants and researchers but also the readers of results obtained. As Martinie et al. (2016) note, the audience is likely to reevaluate their own experiences and views on the problem investigated in a study. According to Clandinin and Murphy, narrative inquiry gives knowledge about the experiences of people “composing lives within complex storied landscapes” (as cited in Martinie et al., 2016, p. 659). Finally, as McAlpine (2016) notes, narrative research is a beneficial research design due to creating the opportunity to value different ways of learning about people’s problems and experiences. Therefore, narrative inquiry offers numerous advantages to researchers and, consequently, to research participants.
Disadvantages
What concerns the research design’s limitations is that it must be acknowledged that personal narratives cannot be void of subjectivity without the opportunity to check the information given by respondents (Bruce et al., 2016). Another problem is that the selected research design is not suitable for investigations involving a large number of participants. As James (2018) remarks, since narrative inquiry requires an in-depth and holistic approach to each participant, this method is not appropriate for the studies covering large samples. A limitation closely related to this one is the lack of the possibility to generalize findings due to the uniqueness of each participant’s story (Sheilds et al., 2015). One more difficulty is the fact that narrative inquiry is interpreted and implemented differently by various scholars (James, 2018). Due to this aspect, some researchers argue for the need to draw a firmer line between what narrative inquiry is and what it is not (James, 2018). A disadvantage is also presented by the potentially lacking understanding and trust between participants and researchers or researchers and ethics review boards (Bruce et al., 2016).
The next limitation is concerned with the fact that identity construction that is described in the narrative constitutes only one of the features presented by identity-in-action (McAlpine, 2016). Also, according to Taylor, the narratives’ innate structure frequently leads to the problem of overlooking the “overarching sense of indeterminacy, partiality, and complexity” (as cited in McAlpine, 2016, p. 46). Hence, researchers should be cautious of the information that is left out from respondents’ stories and mind the inconsistencies in narrations. Along with this difficulty, there is a challenge of the researcher’s wrong interpretation of the data given by respondents. Finally, there is a limitation concerned with narrowing the focus of research and ignoring the broader structural problems (McAlpine, 2016). Thus, despite the variety of benefits presented by narrative inquiry, researchers utilizing this approach should be highly attentive to avoid possible mistakes in the process of collecting and analyzing data.
The Evaluation of the Selected Software Analysis Program
Electronic analysis of research data has been commonly associated with quantitative methods. However, one must admit the presence of a sufficient amount of software for qualitative data analysis. Still, despite their availability, these tools are not favored by qualitative research specialists, and the most probable reason for it is the difficulty mastering the software (Zamawe, 2015). In the present study, the software analysis program to be utilized is NVivo. This program is aimed not so much at analyzing the collected data but at aiding the process of analysis (Zamawe, 2015). NVivo is a popular data management program that has such features as multimedia functions, rich text capabilities, and character-based coding. Furthermore, the program incorporates built-in facilities enabling individuals from different geographical areas to operate the same information files simultaneously via a network.
Another benefit of NVivo is in its high level of compatibility of the program with research designs. Since NVivo is not “methodological-specific,” it can be utilized with a variety of qualitative research designs and data analysis methods, including ethnography, grounded theory, literature reviews, discourse analysis, phenomenology, conversation analysis, and mixed methods (Zamawe, 2015, p. 13). NVivo has been available since the 1980s, but only a small amount of researchers have utilized it. Zamawe (2015) notes that despite some limitations, the program is rather useful, and, hence, underestimated. For instance, an evident advantage of NVivo is “easy, effective and efficient coding,” making the retrieval process easier (Zamawe, 2015, p. 14). The program also enables scholars to gather information across sources to group the material that is related (Dollah et al., 2017). Apart from easy data management, NVivo offers such advantages as simplicity in finding topics, the opportunity to save time, and the simplification of data classification.
At the same time, it is necessary to admit some drawbacks of the system. For instance, researchers admit that NVivo may present difficulty processing audio files (Zamawe, 2015). What is more, the program requires much time to master (Dollah et al., 2017). Also, NVivo may be expensive for researchers, as well as it may present complications when attempting to interpret data (Dollah et al., 2017). Still, taking into consideration all advantages and disadvantages of NVivo and bearing in mind the purpose of the present research, it is relevant to use the selected software for the simplification of data analysis in the process of work on the research problem.
Validity Threats in the Selected Qualitative Design
As with any qualitative research design, narrative inquiry meets threats to validity. There are two major dimensions in which the selected method’s validity may be undermined. Firstly, there may arise the problem of a disparity between individuals’ experiences and the stories they tell about these experiences (Wang & Geale, 2015). Secondly, there may emerge wrong connections between the stories told and the interpretations of these stories. In case any of these two issues appear, the validity of research will inevitably suffer. To avoid these common problems, the researcher has to make sure that participants understand the purpose of the study and are aware of the need to be precise and objective about their narratives. On the other hand, the researcher also should do their best to remain impartial and help respondents to uncover their stories in a logical and untwisted way.
Validity in qualitative research is established through such qualities as confirmability, credibility, trustworthiness, and dependability. Apart from that, rigorous data collection and analysis are required, as is member checking (Byrne, 2015). There may also emerge some validity threats of narrative inquiry as a research design in connection with these issues. Confirmability is related to the establishment of trustworthiness and the level of confidence that the study is based on respondents’ narratives rather than on the researcher’s biased opinions (Abkhezr et al., 2020; Heilmann, 2018). In order to make sure that the study focuses on participants’ narratives solely, the researcher has to reflect on their choice of the topic and the attitudes toward data collection and interpretation.
Another important aspect that can pose a threat to validity is credibility. According to Haydon et al. (2018), researchers have to consider whether narrative inquiry has the potential to answer the research question. One of the ways of overcoming this threat is long-term communication between the researcher and the participant, which allows for the confirmation of data collection, thus leading to a higher level of rigor and credibility (Haydon et al., 2018; Nolan et al., 2017).
To mitigate threats to dependability and trustworthiness, narrative inquirers need to be highly attentive when listening to individuals’ stories. Furthermore, as Nolan et al. (2017) mention, it is of utmost importance to respond to critics’ notes. Without a sober reaction to criticism, a researcher risks making the study biased, which can lead to a lack of trustworthiness and dependability. It is a good idea to let participants check the final interpretation of their narratives to evaluate whether it coincides with the experience they described in their stories (Nolan et al., 2017). Harfitt (2015) also emphasizes the significance of validating the field notes with participants as a crucial prerequisite of maintaining trustworthiness. The process of data analysis is no less essential than that of data collection when it comes to maintaining the study’s validity. As Wang and Geale (2015) remark, it is necessary to perform validation checks throughout collecting and analyzing data. Furthermore, the researcher should maintain a close connection with the participants at all stages of the study to ensure its dependability and trustworthiness.
Potential Ethical Issues
When considering narrative inquiry as a research design, ethical issues are probably the most significant ones to be addressed. The main problem that may arise is that sharing one’s experiences may turn into something more personal than mere information exchange (Caine et al., 2019). As a result, by the end of the study, investigators may develop too friendly relationship with their respondents. Another potential ethical issue is that researchers place the narratives of the participants within a larger narrative, which means that scholars are imposing meaning on respondents’ experiences. Consequently, there may arise the problem of the misinterpretation of data.
The next ambiguous issue is the subjectivity of the study on the part of a researcher (Caine et al., 2019). Because some of the personal narratives are ambiguous, it is impossible to rule out researchers’ personal assessment of the situations, through the prism of which respondents’ narrations may be altered from what they were meant to uncover initially. Narrative inquirers should also bear in mind that their relationships with the participants can affect the final result of the study (Law & Chan, 2015). Therefore, researchers should be cautious of their own interpretations of the respondents’ narratives, as well as they should make sure that their interactions do not influence the final result.
In order to minimize the risk of the mentioned ethical issues in the current research, the following steps will be taken. Firstly, the researchers will make it a rule not to become too close or friendly with the participants in order to remain as objective as possible throughout the whole process of the study. Secondly, the researcher will listen to the narratives attentively and ask clarifying questions if needed, which will enable avoiding misinterpretations. Finally, at all stages of the research project, the researcher will refrain from offering a personal assessment of situations described by participants. By following these steps, it will become possible to avoid the most viable ethical concerns.
Summary of Research
Research on the topic of online gaming addiction available so far is rich in directions of investigation. Scholars have analyzed individuals’ disposition toward engaging in online gaming (Balakrishnan & Griffiths, 2018; Pietersen et al., 2018; Tang et al., 2017), the desire for online group gaming (Gong et al., 2019), and dysfunctional cognitions associated with Internet gaming disorder (Marino & Spada, 2017). These and other topics of research allowed for an in-depth understanding of the research question, but they have not answered all the questions related to online gaming addiction.
A connection between individuals’ loyalty toward online gaming and developing online gaming addiction has been found. Research findings reveal that addiction to online mobile games is associated with game loyalty (Balakrishnan & Griffiths, 2018). Furthermore, scholars report a positive relationship between online gaming addiction and the tendency to purchase mobile in-game applications. Finally, researchers have investigated that online gaming loyalty boosts players’ desire to buy online game applications. However, researchers failed to provide a discussion of how these processes evolve.
A study by Gong et al. (2019) has resulted in finding a positive correlation between the desire for playing online games and addiction to this activity. Additionally, the authors have found that the desire for group gaming is connected with people’s social identities, expected enjoyment, and specific attitudes. However, the research lacks generalizability since Gong et al. (2019) have analyzed only one type of social game played online. Meanwhile, each online game has its own unique features aimed at supporting specific social ties, which can have different effects on players’ predisposition toward becoming addicted to playing.
Marino and Spada (2017) have examined the peculiarities of the gaming disorder with the help of a narrative review, which makes this study especially valuable in light of the selected topic and research design. Scholars report that online gaming-associated dysfunctional conditions are numerous, and their quantity increases with the growth of the industry. Marino and Spada (2017) remark that it is crucial to differentiate between dysfunctional cognitions and metacognitions in Internet gaming disorder. Implications for future research based on these findings include the comparison between dysfunctional cognitions and metacognitions with the aim of finding effective evidence-based treatment for online gaming addictive individuals.
Findings of Tang et al.’s (2017) research suggest that males are usually more addicted to online games than women, whereas females are more predisposed to online social networking addiction. Pietersen et al.’s (2018) study has resulted in valuable insights into what it is to be a gamer based on online gaming addicts’ personal narratives. Whereas these studies have addressed some of the aspects of online gaming and the development of addiction to it, more thorough research is needed in various dimensions of the research topic. Specifically, it is important to focus research on understanding the development of online gaming addiction and people’s feelings about it.
Abkhezr, P., McMahon, M., Campbell, M., & Glasheen, K. (2020). Exploring the boundary between narrative research and narrative intervention: Implications of participating in narrative inquiry for young people with refugee backgrounds. Narrative Inquiry, 30 (2), 316-342. Web.
Androutsopoulou, A., & Stefanoua, M. M. (2018). Seeking “home”: Personal narratives and turning points in the lives of adult homeless. The European Journal of Counselling Psychology , 7 (1), 126-147. Web.
Balakrishnan, J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2018). Loyalty towards online games, gaming addiction, and purchase intention toward online mobile in-game features. Computers in Human Behavior , 87 , 238-246. Web.
Bruce, A., Beuthin, R., Sheilds, L., Molzahn, A., & Schick-Makaroff, K. (2016). Narrative research evolving: Evolving through narrative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 15 (1), 1-6. Web.
Byrne, G. (2015). Narrative inquiry and the problem of representation: “Giving voice”, making meaning. International Journal of Research & Method in Education, 40 (1), 36-52. Web.
Caine, V., Chung, S., Steeves, P., & Clandinin, D. J. (2019). The necessity of a relational ethics alongside Noddings’ ethics of care in narrative inquiry. Qualitative Research, 20 (3), 265-276. Web.
Chen, J. C. (2019). Restorying a “newbie” teacher’s 3d virtual teaching trajectory, resilience, and professional development through action research: A narrative case study. TESOL Quarterly, 54 (2), 375-403. Web.
Dollah, S., Abduh, A., & Rosmaladewi. (2017). Benefits and drawbacks of NVivo QSR application. Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research, 149 , 61-63. Web.
Gong, X., Zhang, K. Z. K., Cheung, C. M., Chen, C., & Lee, M. K. O. (2019). Alone or together? Exploring the role of desire for online group gaming in players’ social game addiction. Information & Management , 56 (6). Web.
Gordon, L. J., Rees, C. E., Ker, J. S., & Cleland, J. (2015). Leadership and followership in the healthcare workplace: Exploring medical trainees’ experiences through narrative inquiry. BMJ Open, 5 , e008898. Web.
Harfitt, G. J. (2015). From attrition to retention: A narrative inquiry of why beginning teachers leave and then rejoin the profession. Asia-Pacific Journal of Teacher Education, 43 (1), 22-35. Web.
Haydon, G., Browne, G., & van der Riet, P. (2018). Narrative inquiry as a research methodology exploring person centred care in nursing. Collegian, 25 (1), 125-129. Web.
Heilmann, S. (2018). A scaffolding approach using interviews and narrative inquiry networks. An Online Journal for Teacher Research, 20 (2). Web.
Ho, I. K., Newton, T. L., & McCabe, A. (2020). The narrative structure of stressful interpersonal events. Narrative Inquiry , 30 (1), 1-17. Web.
Hu, J., Zhen, S., Yu, C., Zhang, Q., & Zhang, W. (2017). Sensation seeking and online gaming addiction in adolescents: A moderated mediation model of positive affective associations and impulsivity. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 . Web.
James, G. (2018). A narrative inquiry perspective into coping mechanisms of international postgraduate students’ transition experiences. American Journal of Qualitative Research , 2 (1), 41-56.
Kovinthan, T. (2016). Learning and teaching with loss: Meeting the needs of refugee children through narrative inquiry. Diaspora, Indigenous, and Minority Education, 19 (3), 141-155. Web.
Law, B. Y.-S., & Chan, E. A. (2015). The experience of learning to speak up: A narrative inquiry on newly graduated registered nurses. Journal of Clinical Nurses, 24 , 1837-1848. Web.
Marino, C., & Spada, M. M. (2017). Dysfunctional cognitions in online gaming and internet gaming disorder: A narrative review and a new classification. Current Addiction Reports , 4 (3), 308-316. Web.
Martinie, S. L., Kim, J.-H., & Abernathy, D. (2016). “Better to be a pessimist”: A narrative inquiry into mathematics teachers’ experience of the transition to the Common Core. The Journal of Educational Research, 109 (6), 658-665. Web.
McAlpine, L. (2016). Why might you use narrative methodology? A story about narrative. Eesti Haridusteaduste Ajakiri, 4 (1), 32-57. Web.
Monacis, L., de Palo, V., Griffiths, M. D., & Sinatra, M. (2017). Exploring individual differences in online addictions: The role of identity and attachment. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 15 , 853-868. Web.
Nolan, S., Hendricks, J., Williamson, M., & Ferguson, S. (2017). Using narrative inquiry to listen to the voices of adolescent mothers in relation to their use of social networking sites (SNS). Journal of Advanced Nursing, 74 (3), 743-751. Web.
Pietersen, A. J., Coetzee, J. K., Byczkowska-Owczarek, D., Elliker, F., & Ackermann, L. (2018). Online gamers, lived experiences, and sense of belonging: Students at the University of the Free State, Bloemfontein. Qualitative Sociology Review , 14 (4), 122-137. Web.
Sheilds, L., Molzahn, A., Bruce, A., Schick Makaroff, K., Stajduhar, K., Beuthin, R., & Shermak, S. (2015). Contrasting stories of life-threatening illness: A narrative inquiry. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 52 (1), 207–215. Web.
Šporčić, B., & Glavak-Tkalić, R. (2018). The relationship between online gaming motivation, self-concept clarity and tendency toward problematic gaming. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 12 (1). Web.
Tang, C. S. K., Koh, Y. W., & Gan, Y. (2017). Addiction to Internet use, online gaming, and online social networking among young adults in China, Singapore, and the United States. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health , 29 (8), 673-682. Web.
Wang, C. C., & Geale, S. K. (2015). The power of story: Narrative inquiry as a methodology in nursing research. International Journal of Nursing Sciences, 2 (2), 195-198. Web.
Zamawe, F. C. (2015). The implication of using NVivo software in qualitative data analysis: Evidence-based reflections. Malawi Medical Journal, 27 (1), 13-15. Web.
- Impact of Video Games on Children and Adolescents
- “Dishonored” Game: Plot and Players
- Online gaming and behavior
- The Gaming Industry in the USA
- Macau's and Singapore's Gaming & Casino Industry
- Playing Video Games Can Help to Control Dreams
- Does Video Game Violence Lead to Aggression in Children?
- Video Games as a Way to Fix Reality
- The Impact of Video Games on the Human Psyche
- Natural Law and Video Games
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, September 27). Addiction to Online Gaming: A Review of Literature. https://ivypanda.com/essays/addiction-to-online-gaming-a-review-of-literature/
"Addiction to Online Gaming: A Review of Literature." IvyPanda , 27 Sept. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/addiction-to-online-gaming-a-review-of-literature/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Addiction to Online Gaming: A Review of Literature'. 27 September.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Addiction to Online Gaming: A Review of Literature." September 27, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/addiction-to-online-gaming-a-review-of-literature/.
1. IvyPanda . "Addiction to Online Gaming: A Review of Literature." September 27, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/addiction-to-online-gaming-a-review-of-literature/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Addiction to Online Gaming: A Review of Literature." September 27, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/addiction-to-online-gaming-a-review-of-literature/.

How to Prevent a Gaming Addiction

Written by Steve Rose
Addiction and recovery, 0 comments(s).
On the go? Listen to the audio version of the article here:
In 2018, the World Health Organization classified Gaming disorder as an official form of addictive behavior. It consists of three components:
- The loss of control over one’s gaming
- Gaming taking priority over other areas of life
- Continued use despite harmful consequences and impaired functioning in other areas of one’s life.
In my work with persons addicted to gaming, I’ve noticed a few common factors contributing to this issue.
By considering the reasons why people become addicted to games, we can gain insight into how to prevent gaming addiction before it starts.
So how do you prevent a gaming addiction?
Develop a sense of self-esteem, social belonging, and purpose. Gaming addiction develops as a way to meet these basic needs. Meeting these needs outside of a gaming environment will reduce your risk of developing a dependency.
Let’s look at what the research says about each of these basic needs and how you can reduce your risk of a gaming addiction by strengthening each of these areas.
Table of Contents
Develop a Healthy Sense of Self Esteem
According to a 2005 study , online games provide an environment for persons with low self-esteem to escape, allowing them to feel more confident. A more recent 2018 study finds the same correlation, focusing on the link between low self-esteem and risk of internet addiction.
Developing a healthy sense of self-esteem may sound like a cliché baby-boomer parenting strategy, marked by participation robbins and positive affirmations about how great we all are, but this is not what I mean by self-esteem boosting.
A 2003 study already debunked the idea that boosting self-esteem improves performance and life satisfaction. The point is not to boost self-esteem by cheerleading ourselves and our children. Instead, self-esteem begins to rise as we take action toward meaningful goals, improving our skills and abilities.
In a gaming environment, success is a quick fix. Like any form of addiction, it is a short-term solution to a long-term problem.
If experiencing low self-esteem, games can offer a temporary experience of leveling up and gaining skills. Unfortunately, these experiences are limited to the gaming world. Once outside the game, your self-esteem remains the same, going down slightly over time as you begin to neglect your offline life.
To prevent a gaming addiction, it is important to consider small ways to gain success in the offline world. Here are a few potential areas of development:
- Maintain a clean and organized personal environment.
- Pick up a new skill or hobby.
- Read books (I like audiobooks, personally).
- Consider advancing your formal education.
- Take small steps to advance your career.
Anything that gives you a sense of growth allows you to build self-esteem, lowering the risk of needing to seek it in a gaming environment.
Self-esteem comes from seeing the result of your actions, not from falsely telling yourself how great you are. This requires changing your relationship with yourself, considering the ways your thoughts or anxieties may be blocking further growth.
If you want to learn more about how to have a productive relationship with yourself, I highly recommend checking out The Confidence Gap: A Guide to Overcoming Fear and Self-Doubt by Russ Harris.
Develop Strong Social Connections
The power of social connection is a key theme throughout all of my work. Social isolation is just as detrimental to your health as smoking, according to research .
Human beings are social creatures, so if we feel isolated or are isolating ourselves due to shame or anxiety, we may find creative ways to meet this social need. Online gaming may be one way to meet our social need for a sense of belonging and connection with others.
It can be healthy to connect with others in gaming environments if it is balanced with offline social activities. When gaming begins to negatively affect offline relationships, it might be time to reconsider ways to repair and maintain our offline relationships to prevent further harm.
A 2011 study on the psychosocial causes and consequences of pathological gaming found that “lower psychosocial well-being is more likely to be a cause than a consequence of pathological gaming.” This confirms the fact that maintaining healthy relationships is a preventative factor for gaming addiction.
So how can you maintain healthy offline relationships?
- Consider joining a local club or meetup group (Check out the Meetup App )
- Dedicate at least one day a week to meaningfully connect with parents, relatives, or close friends, in person.
- Regularly engage coworkers or acquaintances in small-talk about their own interests or recent events.
My article on How to Spend Less Time on Social Media may also be helpful if you want specific strategies tailored to a social media environment.
By fostering and maintaining strong offline social relationships, online gaming can serve as a supplemental form of entertainment and connection rather than a way to cope with isolation in an all-consuming way.
Online relationships in gaming environments can be beneficial and deeply rewarding, sometimes even turning into in-person relationships. The power of these relationships should not be discounted.
The goal of preventing a gaming addiction is to consider its impact on your life. If gaming is balanced and adding to your offline life, then it may be healthy. If it is taking away from your offline life, it may be helpful to reconsider the balance.
Working to develop offline social connections is one way to help meet our social needs, reducing the risk of a gaming addiction.
If social anxiety is preventing you from reaching out and connecting with others, I again recommend The Confidence Gap: A Guide to Overcoming Fear and Self-Doubt by Russ Harris (…no, I am not getting paid for this recommendation. I just love the book!).
Develop a Sense of Purpose
Without a sense of purpose, life can become unbearable. Floating around in a directionless haze is its own unique form of torture.
As human beings, we are built to pursue goals. The dopamine systems in our brains are made for this purpose. In the absence of meaningful goals, gaming can fill this void, offering a sense of purpose through elaborate missions or storylines.
Although it can be entertaining to play games, for this reason, we need to recognize when the online world is becoming a substitute for a sense of purpose in our offline world.
So what is the antidote to offline purposelessness?
Make yourself useful!
In theory, it sounds easy. It’s not too hard to find someone needing help. The problem is that you can’t be useful to anyone else if you’re not useful to yourself first.
The key is that your way of contributing fits your unique personal strengths.
Misalignment between your strengths, values, and interests can hinder your level of usefulness and the resulting level of purpose you feel toward the role. Finding alignment between your abilities and your role requires first knowing your strengths and cultivating them.
If you want to delve way more in-depth into this topic, you can check out my comprehensive article: What Does It Mean to Have a Purpose?
Developing a sense of purpose in our offline worlds can help reduce the risk of a gaming addiction by filling this basic human need to strive for something beyond ourselves.
Conclusion
Gaming is not necessarily the problem. It is often used as a solution to an underlying problem. When our needs are not being met in our offline world, gaming is one way to meet these needs.
When gaming becomes an addiction, things outside the gaming environment begin not to matter. Self-esteem goes down, relationships suffer, and our non-gaming lives lose a sense of purpose.
Although games are used to cope with the lack of these needs being met, a gaming addiction takes a person further away from being able to meet these needs outside of gaming. The unmet needs lead to more gaming, and more gaming leads to further unmet needs.
To prevent a gaming addiction, it is important to develop a sense of self-esteem, social belonging, and purpose.
If you or a loved one is struggling with a gaming addiction, you may find it helpful to check out Game Quitters . It is a comprehensive resource designed to support gamers and loved ones.
You can also check out my recent article on How to Help Someone With an Addiction for general insights on how to maintain a productive helping relationship with the person you are supporting.
Fascinated by ideas? Check out my podcast:
Struggling with an addiction.
If you’re struggling with an addiction, it can be difficult to stop. Gaining short-term relief, at a long-term cost, you may start to wonder if it’s even worth it anymore. If you’re looking to make some changes, feel free to reach out. I offer individual addiction counselling to clients in the US and Canada. If you’re interested in learning more, you can send me a message here .
Other Mental Health Resources
If you are struggling with other mental health issues or are looking for a specialist near you, use the Psychology Today therapist directory here to find a practitioner who specializes in your area of concern.
If you require a lower-cost option, you can check out BetterHelp.com . It is one of the most flexible forms of online counseling. Their main benefit is lower costs, high accessibility through their mobile app, and the ability to switch counselors quickly and easily, until you find the right fit.
*As an affiliate partner with Better Help, I receive a referral fee if you purchase products or services through the links provided.
As always, it is important to be critical when seeking help, since the quality of counselors are not consistent. If you are not feeling supported, it may be helpful to seek out another practitioner. I wrote an article on things to consider here .
You May Also Like…

What Causes Gambling Addiction?
Jul 5, 2024
https://open.spotify.com/episode/1MdAw2KLcbYQ1pk3v7pT02?si=95ec586806b74982 It's a question you might be wondering as...

The Truth About Alcohol
Jun 8, 2024
On the go? Listen to the article on Spotify here:...

How to Stop Smartphone Addiction
May 29, 2024
On the go? Listen to the audio version of the article here: You wake up, and the first thing you reach for is your...
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Essay on Online Games Addiction
Students are often asked to write an essay on Online Games Addiction in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Online Games Addiction
Understanding online games addiction.
Online games addiction means playing games on the internet too much. This happens when someone spends more time playing games than doing other important things. This can cause problems like poor grades in school, less time with friends and family, and even health issues.
Reasons for Addiction
There are many reasons why people get addicted to online games. Some people play to escape from real-world problems. Others find the games exciting and challenging. Some people even play to feel a sense of achievement.
Effects of Addiction
Playing games too much can cause many problems. It can lead to poor performance in school or at work. It can also cause health problems like eye strain and lack of sleep. It can even hurt relationships with friends and family.
Overcoming Addiction
Overcoming online games addiction can be tough, but it’s possible. It’s important to set limits on how much time you spend playing games. It can also help to find other hobbies or activities to do instead of playing games. It might also be helpful to talk to a counselor or therapist.
Also check:
250 Words Essay on Online Games Addiction
What is online games addiction.
Online games addiction is when a person cannot stop playing games on the internet. They spend too much time playing these games and ignore other important things in life. This can harm their studies, health, and relationships.
Why Do People Get Addicted?
People get addicted to online games for many reasons. Some find these games fun and exciting. They enjoy the challenges and rewards that these games offer. Others use these games to escape from stress or problems in real life.
Effects of Online Games Addiction
Online games addiction can have many bad effects. It can cause poor grades in school because students spend too much time playing games instead of studying. It can also lead to health problems like eye strain and lack of sleep. Moreover, it can harm relationships with family and friends because the person is always busy with the games.
How to Overcome Online Games Addiction
Overcoming online games addiction is not easy, but it is possible. One way is to set a limit on how much time you can spend on games each day. Another way is to find other fun activities to do, like playing sports or reading books. It can also help to talk to a trusted adult about the problem.
500 Words Essay on Online Games Addiction
Online games addiction is when a person spends too much time playing games on the internet and finds it hard to stop. This can lead to problems in other parts of life like school, work, or relationships. It’s a bit like when someone can’t stop eating sweets, even though they know it’s bad for them. They might want to stop, but they find it very hard to do so.
There are many reasons why people get addicted to online games. Some people play games to escape from real-life problems or to feel good about themselves. Games can make people feel like they’re winning or achieving something, which can be very satisfying. Other people might get addicted because the games are so much fun and they lose track of time. Sometimes, people get addicted because they’re trying to be the best at the game and can’t stop until they are.
The Impact of Online Games Addiction
Secondly, addiction can harm relationships. If a person spends too much time playing games, they might not spend enough time with their friends and family. This can make people feel lonely and isolated.
Lastly, spending too much time playing games can also be bad for health. It can lead to problems like poor posture, eye strain, and lack of physical activity.
How to Prevent and Overcome Online Games Addiction
If someone is already addicted to online games, it might be hard for them to stop on their own. In this case, it can be helpful to seek help from a professional, like a counselor or a psychologist. They can provide guidance and support to help the person overcome their addiction.
In conclusion, online games addiction is a serious problem that can affect a person’s school, work, relationships, and health. It’s important to balance time spent on gaming with other activities and seek professional help if needed. Remember, games are meant to be fun, not something that takes over your life.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay on Video Game Addiction - 1 (200 Words) Video game addiction is also known by the term gaming disorder. It is known as an irresistible use of video games that promotes significant imbalance in the various life realms over a long period of time. Too much indulgence into anything or work leads to addiction.
In the review papers authored by Schneider et al. (2017) and Stevens et al. (2019) ... This is because they did not report on video game addiction or were of a study design or methodology stated in the exclusion criteria. The remaining 118 articles were then read fully. It was found that only 27 of them ultimately agreed with the inclusion ...
obsessive thinking about video or internet games. loss of interest in other hobbies or activities. poor work performance and strained relationships. poor concentration or motivation. lack of ...
Treat Game Addiction • 7 years ago. Yes and no. The game addicts are addicted to online video games. Thats a fact. However, the real reason anyone gets addicted to games is to satisfy one or several of the 6 human needs. certainty. uncertainty/variety, significance, growth, contribution and love/connection.
Gaming addiction: context. Research on gaming addiction has paid little attention to the context of online gaming. However, a few studies have now shed some light on the embedding of Internet gaming addiction in the context of the individual, 71 the game and gaming environment, 6, 72 and the broader framework of culture. 73 Each of these will be addressed in turn.
Introduction and background. Video game addiction falls into the category of Internet gaming disorders (IGDs), which have been strongly correlated with motivational control issues and are regularly compared with gambling [].Many studies have suggested that behavioral addiction can result from compulsive use of the internet [2-4].Although the spectrum of internet addiction includes video gaming ...
INTRODUCTION. Game addiction is a form of behavioral addiction that shows impulsiveness, indifference to interpersonal relationships, association with other addictions, and psychological and physical symptoms when the game is stopped [].As most modern games are based on the Internet due to the development and dissemination of the Internet, the term "Internet gaming disorder" has been ...
The search used the keywords "online game addiction", "mental health", and "youth". The inclusive criteria for the included literature in this study were as follow; the literature had to be ...
The effects of self-esteem enhancement cognitive behavioral therapy for adolescents' internet addiction and game addiction. Korean J. Psychol. Health 15 , 143-159 (2010). Article Google Scholar
Video games have many benefits for gamers. Research on gaming disorder—aka video game addiction—is flawed and not sufficiently conclusive. Because video games are less socially acceptable ...
Video game addiction may result in a decline in overall health and hygiene. Players who interact with video games for such significant amounts of time can go an entire day without eating and even longer without basic hygiene tasks, such as using the restroom or bathing. The effects of this behavior pose significant danger to their overall health.
Diagnosis of Video Game Addiction . Like other behavioral addictions, video game addiction is a controversial idea. While video gaming research is showing some disturbing effects, particularly in younger players, there is a lack of long-term research and insufficient evidence to definitively conclude that video game overuse is indeed an addiction.
Gaming disorder is defined in the 11th Revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) as a pattern of gaming behavior ("digital-gaming" or "video-gaming") characterized by impaired control over gaming, increasing priority given to gaming over other activities to the extent that gaming takes precedence over other ...
Video game addiction (VGA), also known as gaming disorder or internet gaming disorder, is generally defined as a psychological addiction that is problematic, compulsive use of video games that results in significant impairment to an individual's ability to function in various life domains over a prolonged period of time. This and associated concepts have been the subject of considerable ...
Long Essay on Video Games Addiction 500 Words in English. Long Essay on Video Games Addiction is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. Introduction. Video games are a fun and entertaining way to relax. They help people who are isolated to form friends and be a part of a community. There are many stories where children with developmental ...
Thesis: Regardless of the severity of the addiction, many suffer detrimental effects. II. Supporting Topic Sentence 1: One common effect of video game addiction is isolation and withdrawal from social experiences. A. Hiding at home or an internet cafe. B. some interaction in gaming communities but.
Video game addiction has been chosen to explore the possible occurrence of this perceptional distortion. A mixed design lab-based study was carried out to compare between video games addicts and non-addicts (between-subjects), and video games-related activities and neutral activities (within-subject). Emotional reactions were gauged by self ...
Depending upon the video game addiction level, inpatient treatment centers may be a better fit for the addict, even if the addict is a teenager. What to Do After a Video Game Addiction Relapse. Relapsing is a commonplace phenomenon in the treatment of video game addiction. A relapse can be considered part of recovery, however, and not an end to it.
The most common symptoms of online gaming addiction are unpleasant feelings when there is no access to the Internet (emptiness and depression), excessive investment of time spent on playing online games, and the refusal to admit a problem (Monacis et al., 2017). One of the major motives for engaging in online gaming is seeking sensation (Hu et ...
Develop a Healthy Sense of Self Esteem. According to a 2005 study, online games provide an environment for persons with low self-esteem to escape, allowing them to feel more confident.A more recent 2018 study finds the same correlation, focusing on the link between low self-esteem and risk of internet addiction.. Developing a healthy sense of self-esteem may sound like a cliché baby-boomer ...
100 Words Essay on Online Games Addiction Understanding Online Games Addiction. Online games addiction means playing games on the internet too much. This happens when someone spends more time playing games than doing other important things. This can cause problems like poor grades in school, less time with friends and family, and even health ...