AP English Literature and Composition
Review the free-response questions from the 2024 ap exam, new for 2024-25: mcqs will have four answer choices.
Starting in the 2024-25 school year, AP English Literature and Composition multiple-choice questions (MCQs) will have four answer choices instead of five. This change will take effect with the 2025 exam. All resources have been updated to reflect this change.

Exam Overview
Exam questions assess the course concepts and skills outlined in the course framework. For more information, download the AP English Literature and Composition Course and Exam Description (.pdf) (CED).
Encourage your students to visit the AP English Literature and Composition student page for exam information.
Wed, May 7, 2025
AP English Literature and Composition Exam
Exam format.
The AP English Literature and Composition Exam has consistent question types, weighting, and scoring guidelines every year, so you and your students know what to expect on exam day. There will also be a consistent range of difficulty in the reading passages across all versions of the exam from year to year. The free-response questions will be scored using analytic rubrics, rather than the previous holistic rubrics.
Section I: Multiple Choice
55 Questions | 1 Hour | 45% of Exam Score
- Includes 5 sets of questions with 8–13 questions per set.
- Each set is preceded by a passage of prose fiction, drama, or poetry of varying difficulty.
- The multiple-choice section will always include at least 2 prose fiction passages (this may include drama) and at least 2 poetry passages.
Section II: Free Response
3 Questions | 2 Hours | 55% of Exam Score
- A literary analysis of a given poem
- A literary analysis of a given passage of prose fiction (this may include drama)
- An analysis that examines a specific concept, issue, or element in a work selected by the student. In responding to Question 3, students should select a work of fiction that will be appropriate to the question. A general rule is to use a work that is similar in quality to those they have read in their AP class(es).
Scoring Rubrics
One-page ap english literature and composition scoring rubrics.
This is a simplified version of the longer scoring rubric document, with the decision rules and scoring notes taken out. This document features a student-friendly single-page rubric for each free-response question.
AP English Literature and Composition Rubrics with Decision Rules and Scoring Notes
This document features general scoring criteria that apply to each of the three free-response questions, regardless of specific question prompt.
Exam Questions and Scoring Information
Ap english literature and composition exam questions and scoring information.
View free-response questions and scoring information from past exams.
Score Reporting
Online score reports.
Access your score reports.

5 Tips for Writing a Great AP Lit Essay
Nervous about the 'free response prompt' on AP Lit? Don't be. We broke it down into manageable steps!

This year, if you’re taking the AP English Literature exam, you’ll be responsible for responding to three questions, which the College Board calls “free response prompts.” First , you’ll write a literary analysis of a poem. Second, you’ll write a literary analysis of a piece of fiction, which could be an excerpt from a play. Third , you’ll analyze a major literary aspect—a theme or a literary device, for example—of a literary work of your choosing.
The last of these prompts attracts perhaps the most attention and, by extension, produces the most anxiety among students. Anyone would admit that such a capacious (‘open, roomy’) question is challenging, especially when a year of AP Lit has taught you to focus on the details of the book you’re reading. And it certainly doesn’t help that this question comes at the very end of the essay, and you and your fingers are about as tired as they could possibly be!
But if you approach the prompt with enthusiasm, it can be the cherry on top of your exam, not the straw that breaks the camel’s back (getting creative with metaphors is always important in AP Lit!).
Here are five tips to help you write a great essay response to the third prompt on the AP Lit exam.
1. Select the perfect work.
Wait a minute—you can write about anything under the sun, as long as the College Board defines it as “a work of literary merit?” How is that even possible? In truth, your evaluators are using this prompt as a way to gauge your analytical abilities no matter the text. You’re not going to be judged for the work you select, as long as it’s substantial enough to ensure your analysis can be rich and meaningful. A good rule to live by: if a work pops into your head and you don’t immediately have at least a few different ideas for how to answer the prompt with it, toss it out of your brainstorming process. You want to find a work that is challenging and complex in order to show that you’re capable of effectively analyzing such works.
You have two main options for selecting the perfect work, both equally effective. The first is probably the most common: choose a book, play, or other literary work you read in AP Lit. Because you read it in class, you will almost surely be familiar with its themes and literary devices. Your second option is to pick a work you’ve read on your own, which could be anything from a novel you adored over summer break or the Shakespeare play you starred in at school. We recommend creating a short list of works you’d like to write about before you take your AP Lit exam, just to have your options at hand. As you’ve learned to do in class, consider each work’s rhetorical situation. This way, if you’re on the fence about whether a work is really “of literary merit,” you can ask your teacher or someone else in the know for an expert second opinion!
2. Practice really does make perfect.
You don’t know what the third free-response prompt will be, but you know that it will be! The College Board’s AP Lit exam page is only one of a gazillion easily accessible resources online that compile prompts from past years and devise hypothetical ones, too. These are great places to look. In the weeks leading up to the exam, we recommend selecting three to seven prompts—the more diverse in content, the better—and practicing with your list of works of literary merit. We recommend practicing with a work no more than two or three times—it’s great to know a text inside and out, but you don’t want to be a one-trick pony in case the prompt on the exam doesn’t lend itself to an essay about that text.
3. Outline, outline, outline!
Whether for AP exams , the SAT , or the ACT , you’ve heard the dictum a million times—outlines make better essays, even when your time feels extremely limited! When it’s time for the test, this can feel a little bit trite, but we challenge you to find one soul in the grand history of the AP English Literature exam who hasn’t benefited from creating even a rough outline. This is the place where your reasoning and organization come alive. We recommend devoting 5-7 minutes to your outline—the lower end if you’re confident you know the text inside and out and just need to nail down your claims and evidence, and the higher end if you need to jog your memory and give your thesis a bit more time to gestate.
What should your outline include? Keep it clear and concise. You definitely want to write your thesis; plan the topics of your body paragraphs, including potential topic sentences; and—a helpful, oft-forgotten third part—remind yourself why the work you’ve chosen is the best for the prompt. This last part won’t be formally integrated into your essay, but it’s extremely helpful as you try to stay focused and pointed while writing what can feel like an impossible broad essay.

4. Each paragraph is a new opportunity to be creative
The third free-response prompt, and the AP Lit exam in general, is extremely structured. It can feel downright constricting. The little-known truth about the last essay is that it’s the most creative part of the whole exam. You not only get to choose the prompt, but within the roughly five-paragraph structure of the essay you’re penning, you get to be quite creative with what you say in each paragraph. There are so many ways to explain to your readers how, say, a symbol illuminates an important theme in a text. We find this knowledge incredibly liberating; paired wisely with the organization that the outline and the essay require, this creative approach can lead to a top-notch essay.

5. Proofread, but not just for the sake of proofreading.
We’ve all been there—time is nearly up, you’ve put the period at the end of your conclusion, and now it’s time to make sure you haven’t written an incoherent jumble of nothingness. This is the last, crucial step before handing in your AP Lit exam and never reading again (just kidding!)
Because you’re so exhausted from hours of test-taking, proofreading your third free-response essay can feel like a chore—a hurdle you have to jump to reach the finish line. But it can also be an opportunity to make sure your argument, your analysis, and your claims and evidence are coherent . We don’t mean that you should restructure your thesis—there isn’t time for that, and we’re sure it’s great, anyway!—but we encourage you to make sure that every sentence is as clear, concise, and (reasonably) creative as possible. Proofreading is the time to read every sentence with a fundamental question in the back of your head: What is this sentence doing, and what are the words that form it doing? If something feels like it’s not pulling its weight, don’t hesitate—change or delete it. Now that you’ve nailed the bigger picture, you must demand only the best from the details.
WORK WITH ONE OF OUR AP EXAMS TUTORS
Our team of 50+ brilliant and caring tutors have helped thousands of students gain confidence, improve AP test scores, and achieve their academic goals!
Related Blog Posts

Our Services
College Admissions Counseling
UK University Admissions Counseling
EU University Admissions Counseling
College Athletic Recruitment
Crimson Rise: College Prep for Middle Schoolers
Indigo Research: Online Research Opportunities for High Schoolers
Delta Institute: Work Experience Programs For High Schoolers
Graduate School Admissions Counseling
Private Boarding & Day School Admissions
Essay Review
Financial Aid & Merit Scholarships
Our Leaders and Counselors
Our Student Success
Crimson Student Alumni
Our Results
Our Reviews
Our Scholarships
Careers at Crimson
University Profiles
US College Admissions Calculator
GPA Calculator
Practice Standardized Tests
SAT Practice Test
ACT Practice Tests
Personal Essay Topic Generator
eBooks and Infographics
Crimson YouTube Channel
Summer Apply - Best Summer Programs
Top of the Class Podcast
ACCEPTED! Book by Jamie Beaton
Crimson Global Academy
+1 (646) 419-3178
Go back to all articles
Your Complete Guide: AP English Literature and Composition Exam
/f/64062/937x549/f91fc5a817/languages.jpg)
What's on The Exam?
Exam Format
Exam Scoring
Expert Tips
If you're gearing up to take the AP English Literature and Composition exam, your literary prowess, we've got your back.
In this complete guide, we’ll explain what the AP English Lit exam will test you on, shed light on the format and duration, explain how the exam is graded, and most importantly, provide you with expert tips to ace it!
What’s on the AP English Literature and Composition Exam?
You can anticipate what the AP English Literature and Composition exam will test you on by looking at the skills the AP English Literature and Composition course aims to teach you.
Here are the skills you’ll learn on The AP English Literature and Composition course:
- Explain the function of character.
- Explain the function of setting.
- Explain the function of plot and structure.
- Explain the function of the narrator or speaker.
- Explain the function of word choice, imagery, and symbols.
- Explain the function of comparison.
- Develop textually substantiated arguments about interpretations of part or all of a text.
The foundation of the AP English Literature and Composition course rests on a set of big ideas. These ideas aren’t just concepts; they're the pillars that you build your understanding on.
Here are the big ideas of The AP English Literature and Composition course as defined by the College Board :
- Character: Characters in literature allow readers to study and explore a range of values, beliefs, assumptions, biases, and cultural norms represented by those characters.
- Setting: Setting and the details associated with it not only depict a time and place, but also convey values associated with that setting.
- Structure: The arrangement of the parts and sections of a text, the relationship of the parts to each other, and the sequence in which the text reveals information are all structural choices made by a writer that contribute to the reader’s interpretation of a text.
- Narration: Enduring Understanding NAR-1: A narrator’s or speaker’s perspective controls the details and emphases that affect how readers experience and interpret a text.
- Figurative Language: Comparisons, representations, and associations shift meaning from the literal to the figurative and invite readers to interpret a text.
- Literary Argumentation: Enduring Understanding LAN-1: Readers establish and communicate their interpretations of literature through arguments supported by textual evidence.

What’s the Format of the AP English Literature and Composition Exam?
The AP English literature and composition exam is split into sections:
Section 1: Multiple Choice
- Duration: 1 Hour
- Total questions: 55
- 45% of exam score
The multiple choice section is computer-graded, and it makes up 45% of your total exam score.
The 55 questions in this section consist of:
- 5 passages of prose fiction, drama, or poetry of varying difficulty.
- 5 sets of questions for each passage, with 8–13 questions per set.
The multiple-choice section will always include at least 2 prose fiction passages (including drama) and at least 2 poetry passages.
Section 2: Free Response
- Duration: 2 Hours
- Total Questions: 3
- 55% of exam score
In this section, you’ll write three different essays in response to three free-response prompts. These three prompts combined make up more than half your exam weight.
The 3 prompts are from the following categories:
- A literary analysis of a given poem
- A literary analysis of a given passage of prose fiction (this may include drama)
- An analysis that examines a specific concept, issue, or element in a work of your choice.
In responding to the third prompt, you should select a work of fiction that’s appropriate to the question. The College Borad lists a general rule for this: use a work that is similar in quality to those you have read in your AP class.
AP English Literature and Composition Format
| Section | Duration | Structure | Score Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple Choice | 1 hour | - 5 passages of prose fiction, drama, or poetry of varying difficulty. - 5 sets of questions for each passage, with 8–13 questions per set. | 45% |
| Free Response | 2 hours | 3 prompts from the following categories: - A literary analysis of a given poem - A literary analysis of a given passage of prose fiction (this may include drama) - An analysis that examines a specific concept, issue, or element in a work of your choice. | 55% |
How Long Is the AP English Literature and Composition Exam?
The exam is 3 hours long. The first section is 1 hour long, and the second section is 2 hours long.
How is the AP English Literature and Composition Exam Scored?
Your total score is scaled down to be a number from 1 to 5, similar to a letter grade.
To put this into context, let’s compare AP scores to its closet letter grade equivalent:
AP English Literature Exam Scores
| AP CSP Exam Score | Qualification | Closest Equivalent College Grade |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Extremely well qualified | A+ or A |
| 4 | Very well qualified | A-, B+, or B |
| 3 | Qualified | B-, C+, or C |
| 2 | Possibly qualified | - |
| 1 | No recommendation | - |
To increase your chances of getting credit at a top university , you’ll need a score of 4 or 5 - that’s the score most schools accept to grant college credit .
The multiple choice section is graded by a computer, and it’s worth 55 points in total, 1 point per question. These points are then scaled down to equal 45% of your total score.
On the other hand, the free response section is worth 18 points, with 6 points allocated to each of the 3 questions.

Expert Tips and Material to Prepare For the AP English Literature Exam
1. understand the scoring rubrics and guidelines.
Before diving into preparation, we recommend you familiarize yourself with the scoring rubrics and guidelines provided by the College Board.
Understanding how your essays will be evaluated can significantly impact your approach to studying and writing.
Take the time to dissect these guidelines, paying close attention to what examiners are looking for in your responses.
You can read the rubrics and guidelines from the College Board here:
- Scoring Guidelines Set 1
- Scoring Guidelines Set 2
2. Review the Chief Reader Report
The Chief Reader Report from previous years can be a goldmine of insights. This report offers valuable feedback from experienced AP Literature teachers who have evaluated student responses.
By reviewing these reports, you can gain a deeper understanding of common mistakes, successful strategies , and areas where students often struggle. Learning from others' experiences can help you refine your own exam-taking skills.
You can read the Chief Reader Reports here:
3. Study past exams
Practice makes perfect, and there's no better way to prepare for the AP English Literature Exam than by tackling past exam questions.
Dive into previous years' exams and familiarize yourself with the format, types of questions, and the literary works covered. Pay attention to the themes, characters, and literary devices commonly examined in these questions.
Practice dissecting passages, analyzing poetry, and crafting insightful essays under timed conditions to build your confidence and proficiency.
- You can view all past exams here .
4. Take practice exams
In addition to studying past exams, we recommend you simulate the exam experience as closely as possible by taking practice exams. Set aside dedicated time to complete full-length practice tests under timed conditions.
This will not only help you gauge your readiness but also improve your time management skills and endurance for the actual exam day.
- You can find practice exams from the College Board here .
5. Interact with the text
When preparing for the exam, don't just passively read through texts. Engage with them actively by circling, underlining, and highlighting key passages, literary devices, and themes.
Resist the temptation to rely solely on your memory when answering questions. Instead, return to the text and examine it closely for evidence to support your interpretations.
By developing a habit of close reading and textual analysis, you'll be better equipped to tackle any question that comes your way on exam day.
6. Read books and poems, more than once
To excel in the student-choice essay section of the exam, it's essential to have a deep understanding of a variety of literary works.
Read books and poems multiple times, each time focusing on different aspects such as characterization, imagery, symbolism, and themes.
By revisiting texts and gaining new insights with each reading, you'll be better prepared to write a strong, well-supported essay that demonstrates your literary analysis skills.
7. Work with a tutor
If you're feeling overwhelmed or struggling to grasp certain concepts, consider working with one of our expert tutors who specialize in AP English Literature.
A qualified tutor can provide personalized guidance, targeted practice, and valuable feedback to help you improve your skills and confidence, and we have some of the best teachers in the world tutoring at Crimson!
What Makes Crimson Different
Similar Guides:
- AP Computer Science Principles
- AP Computer Science A
- AP English Language and Composition
- AP Physics 1
- AP Chemistry
- AP Statistics
More Articles
Ranking the easiest and hardest ap classes based on exam scores.
/f/64062/1200x630/bb8c1f55db/easiest-and-hardest-ap-classes.jpg)
AP Exams Going Digital: What's New in 2024?
/f/64062/1920x800/c76568bb29/student-writing-with-laptop.png)
The AP Macroeconomics Exam: A Comprehensive Guide
/f/64062/800x450/40c0ce36c9/what-can-you-do-with-an-economics-degree.jpg)
How to Crush It on the AP® English Literature Exam Essays
by Heather Garcia
Many students are far too familiar with multiple-choice tests and they know, relatively, what to expect when they sit down to take one. Even though the AP ® English Literature Exam has multiple-choice questions that are a little more intense than other tests, it is still, at its core, a multiple-choice test. For many kids, that isn’t too scary. (But seriously, all literature and no non-fiction can be a bit daunting, especially when you hit those sonnets. Phew!)
When taking the AP ® English Literature exam, the part that intimidates many students is the Free-Response section. In other terms, the essay section. The AP ® English Literature exam has an essay section where you get the opportunity to show the readers, AP ® English Literature teachers and college professors from around the nation, what you can do. The readers are looking to see how well you read, how well you think, and how well you write in a timed setting. This is your chance to prove to the world (or to the readers) that you have thoughtfully prepared for this exam and you are ready for college-level literary analysis.
The AP ® readers are not expecting perfection in the essays you write. You are writing under a time constraint and the readers are completely aware of this. However, they do expect you to write three essays in two hours, spending approximately 40 minutes on each essay. The three essays are quite different, so it helps to start preparing early for each type of essay. Timed essay writing can certainly improve, but only with repeated practice and constructive feedback (or intense analysis of previously-scores samples).
The three essay types that you will be asked to write are: poetry analysis , prose analysis , and a literary argument .
For each essay that you write, it is my suggestion that you annotate the prompt. Read the prompt once. Then read it again and annotate how many separate tasks the prompt is asking you to perform. Sometimes you only need to identify the purpose and the devices being used. Sometimes there are four components of the prompt you need to address. Either way, number them so you can be certain when you are writing that you aren’t leaving anything important out.
Beyond that, each of the three essays requires a slightly different approach during the testing period. Below you will find specific suggestions for each one:
Poetry Analysis:
In this essay, you will be given a poem that you most likely have never read. I am surprised every year by which poem the test writers choose. They work diligently to ensure that they find poems that are rich in interpretive opportunities and that are not frequently included in textbook anthologies. They want students to have an interpretation that isn’t filtered through a textbook company or a teacher. They want thought and analysis from you, the student.
When you approach this essay, it is best to read and annotate the prompt, but also to give the poem a solid first read before you try to do any interpretation. On the first read-through, check to see if you can determine the tone, the purpose, and a general gist of what the poem is about. Then go back and re-read the prompt and poem again. In this read-through, you should start underlining and circling, making quick notes about what you notice so that you have fodder to write about. This should take you about 7-8 minutes.
The next step is to complete a quick, and I mean quick , outline. I use the word outline loosely. This could be a scribbled list of topics you want to cover with arrows pointing to the textual evidence you plan to use. It could be a brain map with lines and bubbles and arrows. It could be just placing numbers beside your annotations so you know what order you want to tackle them in. Regardless of the method you choose, it is important that you choose one. So many students think they are beyond pre-planning for an essay, and sadly, it shows. The essays lack the finesse that they could have had if they had taken the three or four minutes to jot down a map of where the essay was headed.
The final step is to write the essay. This part should take about 30 minutes. It may seem like an impossible task, but with a specific direction to head and with the poem already analyzed, the essay should flow smoothly. You aren’t writing a 200 page dissertation. You are writing a 2 to 4 page essay. In pen. In your best handwriting. Saving a few minutes at the end for proofreading. No problem. Right?
This is just the first essay. There are two more. (See why I said preparing early is key?)
Prose Analysis:
This essay is similar to the poetry essay in many respects. You will be given a passage that you most likely have never seen before, and you must respond to a prompt asking you about it. The main difference is that this excerpt will not be a poem. It will be an excerpt from a novel, a short story, or a play. Again, most likely one you haven’t read or even heard of, but that is half the fun.
Similar to the poetry essay, you will begin by reading the prompt and annotating it, but for this essay, you most likely won’t have time to read the passage in its entirety twice.
You will want to annotate and respond to the prompt as you go. Speed is as essential as analysis. You don’t want to spend more than 10 minutes reading and making notes. You need to save 3 or 4 minutes for a pre-write, just like you did with the poetry prompt. Then, you will spend about 25 minutes writing. Quickly. I like that this essay is in the middle of the Free Response section of the test because even though you can write the essays in any order you choose, if you keep this one in the middle, your brain is already in analysis mode, your hands are warmed up, but not yet beyond achy, and this essay can run smoothly.
Literary Argument:
This, by far, is my favorite essay. This essay asks you to respond to an open prompt about a novel you read and analyzed deeply. College Board asks that you write about books that are worthy of college-level analysis and that you only write about a single book, but other than that, the options are open. College Board will provide you a list of book titles that would fit the prompt, but you are certainly not limited to that list.
Even though this essay appears last in the test packet, I always encourage my students to write this essay first. My students usually spend the last couple of weeks prior to the exam reviewing specific scenes from their favorite novels, refreshing themselves on the themes, symbols, and how to spell the characters’ names (you think I am kidding, but some of those names are tricky). When they get to the essay section, they feel like their brains are going to explode with all of the information, so they write this essay first. They get it out of the way before the other passages fill them up with more themes and symbols to contend with.
When writing this essay, it is still important to annotate the prompt and to make a pre-writing plan, but there is no text to cite from. You only have your brain. When you choose the book to write about, ensure that you include the full title and the author’s name in the introductory paragraph. Without that the reader is just guessing at your book. And don’t worry if you choose an obscure book. Your reader will most likely have read it. And if not, they will pass the essay on to someone who has read the book.
DO NOT spend time summarizing the plot of the book you choose. It is a waste of time and space and does nothing to influence your score positively. Instead, assume the reader has read your chosen book, and use a phrase to ground them in the plot before jumping into analysis. Instead of giving three sentences to describe a scene, just say, “in the part where Jane and Rochester kiss under the chestnut tree” or “in the section of the play where King Lear cuts Cordelia out of her inheritance.” Nothing more is needed that that. The readers will jump right into the plot with you.
You have to remember that the readers are there to reward what you do well, not bash you on the moments where you might mess up. On test day, it is important to remember to have fun with each of the essays. If you are enjoying the process of writing them, the readers will enjoy the process of reading them. Find interesting perspectives, make cogent observations, and dazzle the readers with your insight and thought-provoking arguments. But leading up to test day…PRACTICE!
While the AP ® English Literature free-response questions can be challenging, practicing will ease your stress on test day!

Heather Garcia is an English teacher at Charlotte High School, Florida, where she teaches AP English Literature and AP ® English Language. She is a professional development leader in her district, running annual new-teacher trainings and is now the Curriculum and Instructional Specialist for her district for grades 6-12. After 16 years of hands-on experience, Heather has developed a series of strategies to help her students navigate challenging texts. Her favorite book is the Steinbeck classic, East of Eden .

Please read Marco Learning’s Terms and Conditions, click to agree, and submit to continue to your content.
Please read Marco Learning’s Terms and Conditions, click to agree, and submit at the bottom of the window.
MARCO LEARNING TERMS OF USE
Last Modified: 1/24/2023
Acceptance of the Terms of Use
These terms of use are entered into by and between You and Marco Learning LLC (“ Company “, “ we “, or “ us “). The following terms and conditions (these “ Terms of Use “), govern your access to and use of Marco Learning , including any content, functionality, and services offered on or through Marco Learning (the “ Website “), whether as a guest or a registered user.
Please read the Terms of Use carefully before you start to use the Website. By using the Website or by clicking to accept or agree to the Terms of Use when this option is made available to you, you accept and agree to be bound and abide by these Terms of Use. You may not order or obtain products or services from this website if you (i) do not agree to these Terms of Use, or (ii) are prohibited from accessing or using this Website or any of this Website’s contents, goods or services by applicable law . If you do not want to agree to these Terms of Use, you must not access or use the Website.
This Website is offered and available to users who are 13 years of age or older, and reside in the United States or any of its territories or possessions. Any user under the age of 18 must (a) review the Terms of Use with a parent or legal guardian to ensure the parent or legal guardian acknowledges and agrees to these Terms of Use, and (b) not access the Website if his or her parent or legal guardian does not agree to these Terms of Use. By using this Website, you represent and warrant that you meet all of the foregoing eligibility requirements. If you do not meet all of these requirements, you must not access or use the Website.
Changes to the Terms of Use
We may revise and update these Terms of Use from time to time in our sole discretion. All changes are effective immediately when we post them, and apply to all access to and use of the Website thereafter.
These Terms of Use are an integral part of the Website Terms of Use that apply generally to the use of our Website. Your continued use of the Website following the posting of revised Terms of Use means that you accept and agree to the changes. You are expected to check this page each time you access this Website so you are aware of any changes, as they are binding on you.
Accessing the Website and Account Security
We reserve the right to withdraw or amend this Website, and any service or material we provide on the Website, in our sole discretion without notice. We will not be liable if for any reason all or any part of the Website is unavailable at any time or for any period. From time to time, we may restrict access to some parts of the Website, or the entire Website, to users, including registered users.
You are responsible for (i) making all arrangements necessary for you to have access to the Website, and (ii) ensuring that all persons who access the Website through your internet connection are aware of these Terms of Use and comply with them.
To access the Website or some of the resources it offers, you may be asked to provide certain registration details or other information. It is a condition of your use of the Website that all the information you provide on the Website is correct, current, and complete. You agree that all information you provide to register with this Website or otherwise, including but not limited to through the use of any interactive features on the Website, is governed by our Marco Learning Privacy Policy , and you consent to all actions we take with respect to your information consistent with our Privacy Policy.
If you choose, or are provided with, a user name, password, or any other piece of information as part of our security procedures, you must treat such information as confidential, and you must not disclose it to any other person or entity. You also acknowledge that your account is personal to you and agree not to provide any other person with access to this Website or portions of it using your user name, password, or other security information. You agree to notify us immediately of any unauthorized access to or use of your user name or password or any other breach of security. You also agree to ensure that you exit from your account at the end of each session. You should use particular caution when accessing your account from a public or shared computer so that others are not able to view or record your password or other personal information.
We have the right to disable any user name, password, or other identifier, whether chosen by you or provided by us, at any time in our sole discretion for any or no reason, including if, in our opinion, you have violated any provision of these Terms of Use.
Intellectual Property Rights
The Website and its entire contents, features, and functionality (including but not limited to all information, software, text, displays, images, graphics, video, other visuals, and audio, and the design, selection, and arrangement thereof) are owned by the Company, its licensors, or other providers of such material and are protected by United States and international copyright, trademark, patent, trade secret, and other intellectual property or proprietary rights laws. Your use of the Website does not grant to you ownership of any content, software, code, date or materials you may access on the Website.
These Terms of Use permit you to use the Website for your personal, non-commercial use only. You must not reproduce, distribute, modify, create derivative works of, publicly display, publicly perform, republish, download, store, or transmit any of the material on our Website, except as follows:
- Your computer may temporarily store copies of such materials in RAM incidental to your accessing and viewing those materials.
- You may store files that are automatically cached by your Web browser for display enhancement purposes.
- You may print or download one copy of a reasonable number of pages of the Website for your own personal, non-commercial use and not for further reproduction, publication, or distribution.
- If we provide desktop, mobile, or other applications for download, you may download a single copy to your computer or mobile device solely for your own personal, non-commercial use, provided you agree to be bound by our end user license agreement for such applications.
- If we provide social media features with certain content, you may take such actions as are enabled by such features.
You must not:
- Modify copies of any materials from this site.
- Use any illustrations, photographs, video or audio sequences, or any graphics separately from the accompanying text.
- Delete or alter any copyright, trademark, or other proprietary rights notices from copies of materials from this site.
You must not access or use for any commercial purposes any part of the Website or any services or materials available through the Website.
If you wish to make any use of material on the Website other than that set out in this section, please contact us
If you print, copy, modify, download, or otherwise use or provide any other person with access to any part of the Website in breach of the Terms of Use, your right to use the Website will stop immediately and you must, at our option, return or destroy any copies of the materials you have made. No right, title, or interest in or to the Website or any content on the Website is transferred to you, and all rights not expressly granted are reserved by the Company. Any use of the Website not expressly permitted by these Terms of Use is a breach of these Terms of Use and may violate copyright, trademark, and other laws.
Trademarks, logos, service marks, trade names, and all related names, logos, product and service names, designs, and slogans are trademarks of the Company or its affiliates or licensors (collectively, the “ Trademarks ”). You must not use such Trademarks without the prior written permission of the Company. All other names, logos, product and service names, designs, and slogans on this Website are the trademarks of their respective owners.
Prohibited Uses
You may use the Website only for lawful purposes and in accordance with these Terms of Use. You agree not to use the Website:
- In any way that violates any applicable federal, state, local, or international law or regulation (including, without limitation, any laws regarding the export of data or software to and from the US or other countries).
- For the purpose of exploiting, harming, or attempting to exploit or harm minors in any way by exposing them to inappropriate content, asking for personally identifiable information, or otherwise.
- To send, knowingly receive, upload, download, use, or re-use any material that does not comply with the Content Standards set out in these Terms of Use.
- To transmit, or procure the sending of, any advertising or promotional material, including any “junk mail”, “chain letter”, “spam”, or any other similar solicitation.
- To impersonate or attempt to impersonate the Company, a Company employee, another user, or any other person or entity (including, without limitation, by using email addresses or screen names associated with any of the foregoing).
- To engage in any other conduct that restricts or inhibits anyone’s use or enjoyment of the Website, or which, as determined by us, may harm the Company or users of the Website or expose them to liability.
Additionally, you agree not to:
- Use the Website in any manner that could disable, overburden, damage, or impair the site or interfere with any other party’s use of the Website, including their ability to engage in real time activities through the Website.
- Use any robot, spider, or other automatic device, process, or means to access the Website for any purpose, including monitoring or copying any of the material on the Website.
- Use any manual process to monitor or copy any of the material on the Website or for any other unauthorized purpose without our prior written consent.
- Use any device, software, or routine that interferes with the proper working of the Website.
- Introduce any viruses, Trojan horses, worms, logic bombs, or other material that is malicious or technologically harmful.
- Attempt to gain unauthorized access to, interfere with, damage, or disrupt any parts of the Website, the server on which the Website is stored, or any server, computer, or database connected to the Website.
- Attack the Website via a denial-of-service attack or a distributed denial-of-service attack.
- Otherwise attempt to interfere with the proper working of the Website.
If you use, or assist another person in using the Website in any unauthorized way, you agree that you will pay us an additional $50 per hour for any time we spend to investigate and correct such use, plus any third party costs of investigation we incur (with a minimum $300 charge). You agree that we may charge any credit card number provided for your account for such amounts. You further agree that you will not dispute such a charge and that we retain the right to collect any additional actual costs.
User Contributions
The Website may contain message boards, chat rooms, personal web pages or profiles, forums, bulletin boards, and other interactive features (collectively, “ Interactive Services “) that allow users to post, submit, publish, display, or transmit to other users or other persons (hereinafter, “ post “) content or materials (collectively, “ User Contributions “) on or through the Website.
All User Contributions must comply with the Content Standards set out in these Terms of Use.
Any User Contribution you post to the site will be considered non-confidential and non-proprietary. By providing any User Contribution on the Website, you grant us and our affiliates and service providers, and each of their and our respective licensees, successors, and assigns the right to use, reproduce, modify, perform, display, distribute, and otherwise disclose to third parties any such material for any purpose.
You represent and warrant that:
- You own or control all rights in and to the User Contributions and have the right to grant the license granted above to us and our affiliates and service providers, and each of their and our respective licensees, successors, and assigns.
- All of your User Contributions do and will comply with these Terms of Use.
You understand and acknowledge that you are responsible for any User Contributions you submit or contribute, and you, not the Company, have full responsibility for such content, including its legality, reliability, accuracy, and appropriateness.
For any academic source materials such as textbooks and workbooks which you submit to us in connection with our online tutoring services, you represent and warrant that you are entitled to upload such materials under the “fair use” doctrine of copyright law. In addition, if you request that our system display a representation of a page or problem from a textbook or workbook, you represent and warrant that you are in proper legal possession of such textbook or workbook and that your instruction to our system to display a page or problem from your textbook or workbook is made for the sole purpose of facilitating your tutoring session, as “fair use” under copyright law.
You agree that we may record all or any part of any live online classes and tutoring sessions (including voice chat communications) for quality control and other purposes. You agree that we own all transcripts and recordings of such sessions and that these Terms of Use will be deemed an irrevocable assignment of rights in all such transcripts and recordings to us.
We are not responsible or liable to any third party for the content or accuracy of any User Contributions posted by you or any other user of the Website.
Monitoring and Enforcement: Termination
We have the right to:
- Remove or refuse to post any User Contributions for any or no reason in our sole discretion.
- Take any action with respect to any User Contribution that we deem necessary or appropriate in our sole discretion, including if we believe that such User Contribution violates the Terms of Use, including the Content Standards, infringes any intellectual property right or other right of any person or entity, threatens the personal safety of users of the Website or the public, or could create liability for the Company.
- Disclose your identity or other information about you to any third party who claims that material posted by you violates their rights, including their intellectual property rights or their right to privacy.
- Take appropriate legal action, including without limitation, referral to law enforcement, for any illegal or unauthorized use of the Website.
- Terminate or suspend your access to all or part of the Website for any or no reason, including without limitation, any violation of these Terms of Use.
Without limiting the foregoing, we have the right to cooperate fully with any law enforcement authorities or court order requesting or directing us to disclose the identity or other information of anyone posting any materials on or through the Website. YOU WAIVE AND HOLD HARMLESS THE COMPANY AND ITS AFFILIATES, LICENSEES, AND SERVICE PROVIDERS FROM ANY CLAIMS RESULTING FROM ANY ACTION TAKEN BY ANY OF THE FOREGOING PARTIES DURING, OR TAKEN AS A CONSEQUENCE OF, INVESTIGATIONS BY EITHER SUCH PARTIES OR LAW ENFORCEMENT AUTHORITIES.
However, we do not undertake to review material before it is posted on the Website, and cannot ensure prompt removal of objectionable material after it has been posted. Accordingly, we assume no liability for any action or inaction regarding transmissions, communications, or content provided by any user or third party. We have no liability or responsibility to anyone for performance or nonperformance of the activities described in this section.
Content Standards
These content standards apply to any and all User Contributions and use of Interactive Services. User Contributions must in their entirety comply with all applicable federal, state, local, and international laws and regulations. Without limiting the foregoing, User Contributions must not:
- Contain any material that is defamatory, obscene, indecent, abusive, offensive, harassing, violent, hateful, inflammatory, or otherwise objectionable.
- Promote sexually explicit or pornographic material, violence, or discrimination based on race, sex, religion, nationality, disability, sexual orientation, or age.
- Infringe any patent, trademark, trade secret, copyright, or other intellectual property or other rights of any other person.
- Violate the legal rights (including the rights of publicity and privacy) of others or contain any material that could give rise to any civil or criminal liability under applicable laws or regulations or that otherwise may be in conflict with these Terms of Use and our Privacy Policy .
- Be likely to deceive any person.
- Promote any illegal activity, or advocate, promote, or assist any unlawful act.
- Cause annoyance, inconvenience, or needless anxiety or be likely to upset, embarrass, alarm, or annoy any other person.
- Impersonate any person, or misrepresent your identity or affiliation with any person or organization.
- Involve commercial activities or sales, such as contests, sweepstakes, and other sales promotions, barter, or advertising.
- Give the impression that they emanate from or are endorsed by us or any other person or entity, if this is not the case.
(collectively, the “ Content Standards ”)
Copyright Infringement
If you believe that any User Contributions violate your copyright, please contact us and provide the following information:
- An electronic or physical signature of the person authorized to act on behalf of the owner of the copyright interest;
- A description of the copyrighted work that you claim has been infringed;
- A description of where the material you claim is infringing is located on the website (and such description must reasonably sufficient to enable us to find the alleged infringing material);
- Your address, telephone number and email address;
- A written statement by you that you have a good faith belief that the disputed use is not authorized by the copyright owner, its agent, or the law; and
- A statement by you, made under the penalty of perjury, that the above information in your notice is accurate and that you are the copyright owner or authorized to act on the copyright owner’s behalf.
We may terminate the accounts of any infringers.
Reliance on Information Posted
From time to time, we may make third party opinions, advice, statements, offers, or other third party information or content available on the Website or from tutors under tutoring services (collectively, “Third Party Content”). All Third Party Content is the responsibility of the respective authors thereof and should not necessarily be relied upon. Such third party authors are solely responsible for such content. WE DO NOT (I) GUARANTEE THE ACCURACY, COMPLETENESS OR USEFULNESS OF ANY THIRD PARTY CONTENT ON THE SITE OR ANY VERIFICATION SERVICES DONE ON OUR TUTORS OR INSTRUCTORS, OR (II) ADOPT, ENDORSE OR ACCEPT RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE ACCURACY OR RELIABILITY OF ANY OPINION, ADVICE, OR STATEMENT MADE BY ANY TUTOR OR INSTRUCTOR OR ANY PARTY THAT APPEARS ON THE WEBSITE. UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES WILL WE BE RESPONSBILE OR LIABLE FOR ANY LOSS OR DAMAGE RESULTING FROM YOUR RELIANCE ON INFORMATION OR OTHER CONENT POSTED ON OR AVAILBLE FROM THE WEBSITE.
Changes to the Website
We may update the content on this Website from time to time, but its content is not necessarily complete or up-to-date. Any of the material on the Website may be out of date at any given time, and we are under no obligation to update such material.
Information About You and Your Visits to the Website
All information we collect on this Website is subject to our Privacy Policy . By using the Website, you consent to all actions taken by us with respect to your information in compliance with the Privacy Policy.
Online Purchases and Other Terms and Conditions
All purchases through our site or other transactions for the sale of services and information formed through the Website or resulting from visits made by you are governed by our Terms of Sale, which are hereby incorporated into these Terms of Use.
Additional terms and conditions may also apply to specific portions, services, or features of the Website. All such additional terms and conditions are hereby incorporated by this reference into these Terms of Use.
Linking to the Website and Social Media Features
You may link to our homepage, provided you do so in a way that is fair and legal and does not damage our reputation or take advantage of it, but you must not establish a link in such a way as to suggest any form of association, approval, or endorsement on our part without our express written consent.
This Website may provide certain social media features that enable you to:
- Link from your own or certain third-party websites to certain content on this Website.
- Send emails or other communications with certain content, or links to certain content, on this Website.
- Cause limited portions of content on this Website to be displayed or appear to be displayed on your own or certain third-party websites.
You may use these features solely as they are provided by us, and solely with respect to the content they are displayed with and otherwise in accordance with any additional terms and conditions we provide with respect to such features. Subject to the foregoing, you must not:
- Establish a link from any website that is not owned by you.
- Cause the Website or portions of it to be displayed on, or appear to be displayed by, any other site, for example, framing, deep linking, or in-line linking.
- Link to any part of the Website other than the homepage.
- Otherwise take any action with respect to the materials on this Website that is inconsistent with any other provision of these Terms of Use.
The website from which you are linking, or on which you make certain content accessible, must comply in all respects with the Content Standards set out in these Terms of Use.
You agree to cooperate with us in causing any unauthorized framing or linking immediately to stop. We reserve the right to withdraw linking permission without notice.
We may disable all or any social media features and any links at any time without notice in our discretion.
Links from the Website
If the Website contains links to other sites and resources provided by third parties (“ Linked Sites ”), these links are provided for your convenience only. This includes links contained in advertisements, including banner advertisements and sponsored links. You acknowledge and agree that we have no control over the contents, products, services, advertising or other materials which may be provided by or through those Linked sites or resources, and accept no responsibility for them or for any loss or damage that may arise from your use of them. If you decide to access any of the third-party websites linked to this Website, you do so entirely at your own risk and subject to the terms and conditions of use for such websites.
You agree that if you include a link from any other website to the Website, such link will open in a new browser window and will link to the full version of an HTML formatted page of this Website. You are not permitted to link directly to any image hosted on the Website or our products or services, such as using an “in-line” linking method to cause the image hosted by us to be displayed on another website. You agree not to download or use images hosted on this Website or another website, for any purpose, including, without limitation, posting such images on another website. You agree not to link from any other website to this Website in any manner such that the Website, or any page of the Website, is “framed,” surrounded or obfuscated by any third party content, materials or branding. We reserve all of our rights under the law to insist that any link to the Website be discontinued, and to revoke your right to link to the Website from any other website at any time upon written notice to you.
Geographic Restrictions
The owner of the Website is based in the state of New Jersey in the United States. We provide this Website for use only by persons located in the United States. We make no claims that the Website or any of its content is accessible or appropriate outside of the United States. Access to the Website may not be legal by certain persons or in certain countries. If you access the Website from outside the United States, you do so on your own initiative and are responsible for compliance with local laws.
Disclaimer of Warranties
You understand that we cannot and do not guarantee or warrant that files available for downloading from the internet or the Website will be free of viruses or other destructive code. You are responsible for implementing sufficient procedures and checkpoints to satisfy your particular requirements for anti-virus protection and accuracy of data input and output, and for maintaining a means external to our site for any reconstruction of any lost data. TO THE FULLEST EXTENT PROVIDED BY LAW, WE WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOSS OR DAMAGE CAUSED BY A DISTRIBUTED DENIAL-OF-SERVICE ATTACK, VIRUSES, OR OTHER TECHNOLOGICALLY HARMFUL MATERIAL THAT MAY INFECT YOUR COMPUTER EQUIPMENT, COMPUTER PROGRAMS, DATA, OR OTHER PROPRIETARY MATERIAL DUE TO YOUR USE OF THE WEBSITE OR ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE OR TO YOUR DOWNLOADING OF ANY MATERIAL POSTED ON IT, OR ON ANY WEBSITE LINKED TO IT.
YOUR USE OF THE WEBSITE, ITS CONTENT, AND ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE IS AT YOUR OWN RISK. THE WEBSITE, ITS CONTENT, AND ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE ARE PROVIDED ON AN “AS IS” AND “AS AVAILABLE” BASIS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. NEITHER THE COMPANY NOR ANY PERSON ASSOCIATED WITH THE COMPANY MAKES ANY WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION WITH RESPECT TO THE COMPLETENESS, SECURITY, RELIABILITY, QUALITY, ACCURACY, OR AVAILABILITY OF THE WEBSITE. WITHOUT LIMITING THE FOREGOING, NEITHER THE COMPANY NOR ANYONE ASSOCIATED WITH THE COMPANY REPRESENTS OR WARRANTS THAT THE WEBSITE, ITS CONTENT, OR ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE WILL BE ACCURATE, RELIABLE, ERROR-FREE, OR UNINTERRUPTED, THAT DEFECTS WILL BE CORRECTED, THAT OUR SITE OR THE SERVER THAT MAKES IT AVAILABLE ARE FREE OF VIRUSES OR OTHER HARMFUL COMPONENTS, OR THAT THE WEBSITE OR ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE WILL OTHERWISE MEET YOUR NEEDS OR EXPECTATIONS.
TO THE FULLEST EXTENT PROVIDED BY LAW, THE COMPANY HEREBY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, NON-INFRINGEMENT, AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
THE FOREGOING DOES NOT AFFECT ANY WARRANTIES THAT CANNOT BE EXCLUDED OR LIMITED UNDER APPLICABLE LAW.
Limitation on Liability
TO THE FULLEST EXTENT PROVIDED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL THE COMPANY, ITS AFFILIATES, OR THEIR LICENSORS, SERVICE PROVIDERS, EMPLOYEES, AGENTS, OFFICERS, OR DIRECTORS BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, UNDER ANY LEGAL THEORY, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH YOUR USE, OR INABILITY TO USE, THE WEBSITE, ANY WEBSITES LINKED TO IT, ANY CONTENT ON THE WEBSITE OR SUCH OTHER WEBSITES, INCLUDING ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PERSONAL INJURY, PAIN AND SUFFERING, EMOTIONAL DISTRESS, LOSS OF REVENUE, LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS OR ANTICIPATED SAVINGS, LOSS OF USE, LOSS OF GOODWILL, LOSS OF DATA, AND WHETHER CAUSED BY TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), BREACH OF CONTRACT, OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF FORESEEABLE.
THE FOREGOING DOES NOT AFFECT ANY LIABILITY THAT CANNOT BE EXCLUDED OR LIMITED UNDER APPLICABLE LAW.
Indemnification
You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold harmless the Company, its affiliates, licensors, and service providers, and its and their respective officers, directors, employees, contractors, agents, licensors, suppliers, successors, and assigns from and against any claims, liabilities, damages, judgments, awards, losses, costs, expenses, or fees (including reasonable attorneys’ fees) arising out of or relating to your violation of these Terms of Use or your use of the Website, including, but not limited to, your User Contributions, any use of the Website’s content, services, and products other than as expressly authorized in these Terms of Use or your use of any information obtained from the Website.
Governing Law and Jurisdiction
All matters relating to the Website and these Terms of Use and any dispute or claim arising therefrom or related thereto (in each case, including non-contractual disputes or claims), shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the internal laws of the State of New Jersey without giving effect to any choice or conflict of law provision or rule (whether of the State of New Jersey or any other jurisdiction).
Any legal suit, action, or proceeding arising out of, or related to, these Terms of Use or the Website shall be instituted exclusively in the federal courts of the United States or the courts of the State of New Jersey in each case located in the County of Monmouth although we retain the right to bring any suit, action, or proceeding against you for breach of these Terms of Use in your country of residence or any other relevant country. You waive any and all objections to the exercise of jurisdiction over you by such courts and to venue in such courts. You may not under any circumstances commence or maintain against us any class action, class arbitration, or other representative action or proceeding.
Arbitration
By using this Website, you agree, at Company’s sole discretion, that it may require you to submit any disputes arising from the use of these Terms of Use or the Website, including disputes arising from or concerning their interpretation, violation, invalidity, non-performance, or termination, to final and binding arbitration under the Rules of Arbitration of the American Arbitration Association applying New Jersey law. In doing so, YOU GIVE UP YOUR RIGHT TO GO TO COURT to assert or defend any claims between you and us. YOU ALSO GIVE UP YOUR RIGHT TO PARTICIPATE IN A CLASS ACTION OR OTHER CLASS PROCEEDING. Your rights may be determined by a NEUTRAL ARBITRATOR, NOT A JUDGE OR JURY. You are entitled to a fair hearing before the arbitrator. The arbitrator can grant any relief that a court can, but you should note that arbitration proceedings are usually simpler and more streamlined than trials and other judicial proceedings. Decisions by the arbitrator are enforceable in court and may be overturned by a court only for very limited reasons.
Any proceeding to enforce this arbitration provision, including any proceeding to confirm, modify, or vacate an arbitration award, may be commenced in any court of competent jurisdiction. In the event that this arbitration provision is for any reason held to be unenforceable, any litigation against Company must be commenced only in the federal or state courts located in Monmouth County, New Jersey. You hereby irrevocably consent to the jurisdiction of those courts for such purposes.
Limitation on Time to File Claims
ANY CAUSE OF ACTION OR CLAIM YOU MAY HAVE ARISING OUT OF OR RELATING TO THESE TERMS OF USE OR THE WEBSITE MUST BE COMMENCED WITHIN ONE (1) YEAR AFTER THE CAUSE OF ACTION ACCRUES, OTHERWISE, SUCH CAUSE OF ACTION OR CLAIM IS PERMANENTLY BARRED.
Waiver and Severability
No waiver by the Company of any term or condition set out in these Terms of Use shall be deemed a further or continuing waiver of such term or condition or a waiver of any other term or condition, and any failure of the Company to assert a right or provision under these Terms of Use shall not constitute a waiver of such right or provision.
If any provision of these Terms of Use is held by a court or other tribunal of competent jurisdiction to be invalid, illegal, or unenforceable for any reason, such provision shall be eliminated or limited to the minimum extent such that the remaining provisions of the Terms of Use will continue in full force and effect.
Entire Agreement
The Terms of Use, our Privacy Policy, and Terms of Sale constitute the sole and entire agreement between you and Marco Learning LLC regarding the Website and supersede all prior and contemporaneous understandings, agreements, representations, and warranties, both written and oral, regarding the Website.
Communications and Miscellaneous
If you provide us your email address, you agree and consent to receive email messages from us. These emails may be transaction or relationship communications relating to the products or services we offer, such as administrative notices and service announcements or changes, or emails containing commercial offers, promotions or special offers from us.
Your Comments and Concerns
This website is operated by Marco Learning LLC, a New Jersey limited liability company with an address of 113 Monmouth Road, Suite 1, Wrightstown, New Jersey 08562.
Please contact us for all other feedback, comments, requests for technical support, and other communications relating to the Website.
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
How to Write the AP Lang Argument Essay (With Example)
December 14, 2023
We’d like to let you in on a little secret: no one, including us, enjoys writing timed essays. But a little practice goes a long way. If you want to head into your AP English Exam with a cool head, you’ll want to know what you’re getting into ahead of time. We can’t promise the AP Lang Argument Essay will ever feel like an island vacation, but we do have tons of hand tips and tricks (plus a sample essay!) below to help you do your best. This article will cover: 1) What is the AP Lang Argumentative Essay? 2) AP Lang Argument Rubric 3) AP Lang Argument Sample Prompt 4) AP Lang Argument Essay Example 5) AP Lang Argument Essay Example: Answer Breakdown.
What is the AP Lang Argument Essay?
The AP Lang Argument Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you to synthesize, analyze, and interpret texts and develop well-reasoned arguments. The three essays include:
Synthesis essay: You’ll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write-up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here.
Argumentative essay: You’ll take a stance on a specific topic and argue your case.
Rhetorical essay: You’ll read a provided passage, then analyze the author’s rhetorical choices and develop an argument that explains why the author made those rhetorical choices. Read our write-up on How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Essay here.
AP Lang Argument Essay Rubric
The AP Lang Argument Essay is graded on 3 rubric categories : Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . How can you make sure you cover all three bases in your essay? We’ll break down each rubric category with dos and don’ts below:
- Thesis (0-1 point)
When it comes to grading your thesis, AP Exam graders are checking off a box: you either have a clear thesis or you don’t. So, what crucial components of a thesis will get you your check mark?
- Make sure your thesis argues something . To satisfy your graders, your thesis needs to take a clear stance on the issue at hand.
- Include your thesis statement in your intro paragraph. The AP Lang Argumentative essay is just that: an essay that makes an argument, so make sure you present your argument right away at the end of your first paragraph.
- A good test to see if you have a thesis that makes an argument for your AP Lang Argumentative Essay: In your head, add the phrase “I agree/disagree that…” to the beginning of your thesis. If what follows doesn’t logically flow after that phrase (aka if what follows isn’t an agreement or disagreement), it’s likely you’re not making an argument.
- In your thesis, outline the evidence you’ll cover in your body paragraphs.
AP Lang Argument Essay Rubric (Continued)
- Avoid a thesis that merely restates the prompt.
- Avoid a thesis that summarizes the text but does not make an argument.
- Avoid a thesis that weighs the pros and cons of an issue. Your job in your thesis is to pick a side and stick with it.
- Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points)
This rubric category is graded on a scale of 0-4 where 4 is the highest grade. Unlike the rhetorical and synthesis essays, the evidence you need to write your AP Lang Argument Essay is not provided to you. Rather, you’ll need to generate your own evidence and comment upon it.
What counts as evidence?
Typically, the AP Lang Argument Essay prompt asks you to reflect on a broad cultural, moral, or social issue that is open to debate. For evidence, you won’t be asked to memorize and cite statistics or facts. Rather, you’ll want to bring in real-world examples of:
- Historical events
- Current-day events from the news
- Personal anecdotes
For this essay, your graders know that you’re not able to do research to find the perfect evidence. What’s most important is that you find evidence that logically supports your argument.
What is commentary?
In this essay, it’s important to do more than just provide examples relevant evidence. After each piece of evidence you include, you’ll need to explain why it’s significant and how it connects to your main argument. The analysis you include after your evidence is commentary .
- Take a minute to brainstorm evidence that logically supports your argument. If you have to go out of your way to find the connection, it’s better to think of different evidence.
- Include multiple pieces of evidence. There is no magic number, but do make sure you incorporate more than a couple pieces of evidence that support your argument.
- Make sure you include more than one example of evidence, too. Let’s say you’re working on an essay that argues that people are always stronger together than apart. You’ve already included an example from history: during the civil rights era, protestors staged group sit-ins as a powerful form of peaceful protest. That’s just one example, and it’s hard to make a credible argument with just one piece of evidence. To fix that issue, think of additional examples from history, current events, or personal experience that are not related to the civil rights era.
- After you include each piece of evidence, explain why it’s significant and how it connects to your main argument.
- Don’t summarize or speak generally about the topic. Everything you write must be backed up with specific and relevant evidence and examples.
- Don’t let quotes speak for themselves. After every piece of evidence you include, make sure to explain and connect the evidence to your overarching argument.
AP Lang Argument Essay (Continued)
- Sophistication (0-1 point)
According to the College Board , one point can be awarded to AP Lang Argument essays that achieve a high level of sophistication. You can accomplish that in four ways:
- Crafting a nuanced argument by consistently identifying and exploring complexities or tensions.
- Articulating the implications or limitations of an argument by situating it within a broader context.
- Making effective rhetorical choices that consistently strengthen the force and impact of the student’s argument.
- Employing a style that is consistently vivid and persuasive.
In sum, this means you can earn an additional point for going above and beyond in depth, complexity of thought, or by writing an especially persuasive, clear, and well-structured essay. In order to earn this point, you’ll first need to do a good job with the fundamentals: your thesis, evidence, and commentary. Then, to earn your sophistication point, follow these tips:
- Outline your essay before you begin to ensure it flows in a clear and cohesive way.
- Include well-rounded evidence. Don’t rely entirely on personal anecdotes, for example. Incorporate examples from current events or history, as well.
- Thoroughly explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis in order to fully develop your argument.
- Explore broader implications. If what you’re arguing is true, what does that mean to us today? Who is impacted by this issue? What real-world issues are relevant to this core issue?
- Briefly explore the other side of the issue. Are the instances where your argument might not be true? Acknowledge the other side, then return to proving your original argument.
- Steer clear of generalizations (avoid words like “always” and “everyone”).
- Don’t choose an argument you can’t back up with relevant examples.
- Avoid complex sentences and fancy vocabulary words unless you use them often. Long, clunky sentences with imprecisely used words are hard to follow.
AP Lang Argument Sample Prompt
The sample prompt below is published online by the College Board and is a real example from the 2021 AP English Exam. The prompt provides background context, essay instructions, and the text you need to analyze.
Suggested time—40 minutes.
Many people spend long hours trying to achieve perfection in their personal or professional lives. Similarly, people often demand perfection from others, creating expectations that may be challenging to live up to. In contrast, some people think perfection is not attainable or desirable.
Write an essay that argues your position on the value of striving for perfection.
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that presents a defensible position.
- Provide evidence to support your line of reasoning.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
AP Lang Argument Essay Example
As the old phrase says, “Practice makes perfect.” But is perfection something that is actually attainable? Sometimes, pushing for perfection helps us achieve great things, but most often, perfectionism puts too much pressure on us and prevents us from knowing when we have done the best we can. Striving for perfection can only lead us to shortchange ourselves. Instead, we should value learning, growth, and creativity and not worry whether we are first or fifth best.
Students often feel the need to be perfect in their classes, and this can cause students to struggle or stop making an effort in class. In elementary and middle school, for example, I was very nervous about public speaking. When I had to give a speech, my voice would shake, and I would turn very red. My teachers always told me “relax!” and I got Bs on Cs on my speeches. As a result, I put more pressure on myself to do well, spending extra time making my speeches perfect and rehearsing late at night at home. But this pressure only made me more nervous, and I started getting stomach aches before speaking in public.
Once I got to high school, however, I started doing YouTube make-up tutorials with a friend. We made videos just for fun, and laughed when we made mistakes or said something silly. Only then, when I wasn’t striving to be perfect, did I get more comfortable with public speaking.
AP Lang Argumentative Essay Example (Continued)
In the world of art and business and science, perfectionism can also limit what we are able to achieve. Artists, for example, have to take risks and leave room for creativity. If artists strive for perfection, then they won’t be willing to fail at new experiments and their work will be less innovative and interesting. In business and science, many products, like penicillin for example, were discovered by accident. If the scientist who discovered penicillin mold growing on his petri dishes had gotten angry at his mistake and thrown the dishes away, he would never have discovered a medicine that is vital to us today.
Some fields do need to value perfection. We wouldn’t like it, for example, if our surgeon wasn’t striving for perfection during our operation. However, for most of us, perfectionism can limit our potential for learning and growth. Instead of trying to be perfect, we should strive to learn, innovate, and do our personal best.
AP Lang Argument Essay Example: Answer Breakdown
The sample AP Lang Argumentative Essay above has some strengths and some weaknesses. Overall, we would give this essay a 3 or a 4. Let’s break down what’s working and what could be improved:
- The essay offers a thesis that makes a clear argument that is relevant to the prompt: “Striving for perfection can only lead us to shortchange ourselves. Instead, we should value learning, growth, and creativity and not worry whether we are first or fifth best.”
- The first body paragraph provides evidence that supports the essay’s thesis. This student’s personal anecdote offers an example of a time when perfectionism led them to shortchange themselves.
- The second body paragraph provides additional evidence that supports the essay’s thesis. The example describing the discovery of penicillin offers another example of a situation in which perfectionism might have limited scientific progress.
- The writer offers commentary explaining how her examples of public speaking and penicillin illustrate that we should “value learning, growth, and creativity” over perfectionism.
- The essay follows one line of reasoning and does not stray into tangents.
- The essay is organized well with intro, body, and concluding paragraphs. Overall, it is easy to read and is free of grammar errors.
What could be improved:
- Although the second body paragraph provides one good specific example about the discovery of penicillin, the other examples it offers about art and business are only discussed generally and aren’t backed up with evidence. This paragraph would be stronger if it provided more examples. Or, if this writer couldn’t think of examples, they could have left out mentions of art and business altogether and included alternate evidence instead.
- This writer would more thoroughly support their argument if they were able to offer one more example of evidence. They could provide another personal anecdote, an example from history, or an example from current events.
- The writer briefly mentions the other side of the argument in their concluding paragraph: “Some fields do need to value perfection. We wouldn’t like it, for example, if our surgeon wasn’t striving for perfection during our operation.” Since it’s so brief a mention of the other side, it undermines the writer’s overall argument. This writer should either dedicate more time to reflecting on why even surgeons should “value learning, growth, and creativity” over perfectionism, or they should leave these sentences out.
AP Lang Argument Essay Example—More Resources
Looking for more tips to help you master your AP Lang Argumentative Essay? Brush up on 20 Rhetorical Devices High School Students Should Know and read our Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension .
If you’re ready to start studying for another part of the AP English Exam, find more expert tips in our How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis and How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Essay blog posts.
- High School Success
Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- ADHD/LD/Autism/Executive Functioning
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
AP English Literature and Composition
Learn all about the course and exam. Already enrolled? Join your class in My AP.
Not a Student?
Go to AP Central for resources for teachers, administrators, and coordinators.
About the Course
What makes a work of literature great? In AP English Literature and Composition, you’ll examine how authors and poets create meaning through their rich, purposeful use of language. As you write and refine essays about literature, you’ll develop the skills of analysis and composition that will allow you to communicate your interpretation effectively.
New for 2024-25: MCQs Will Have Four Answer Choices
Starting in the 2024-25 school year, AP English Literature and Composition multiple-choice questions (MCQs) will have four answer choices instead of five. This change will take effect with the 2025 exam. All resources have been updated to reflect this change.
Skills You'll Learn
Read a text closely and draw conclusions from details
Identify the techniques used by an author and their effects
Develop an interpretation of a text
Present your interpretation and make an argument for it in writing
Equivalency and Prerequisites
College course equivalent.
An introductory college-level literature course
Recommended Prerequisites
Wed, May 7, 2025
AP English Literature and Composition Exam
This is the regularly scheduled date for the AP English Literature and Composition Exam.
About the Units
The course content outlined below is organized into commonly taught units of study that provide one possible sequence for the course. Your teacher may choose to organize the course content differently based on local priorities and preferences.
Course Content
Unit 1: short fiction i.
You’ll learn critical reading skills to help you critically read, interpret, and analyze prose.
Topics may include:
- Interpreting the role of character in fiction
- Identifying and interpreting setting
- Understanding how a story’s structure affects interpretations
- Understanding and interpreting a narrator’s perspective
- Reading texts literally and figuratively
- The basics of literary analysis
Unit 2: Poetry I
You’ll continue your critical reading exploration in poetry and learn to analyze similar elements within a wide variety of poems.
- Identifying characters in poetry
- Understanding and interpreting meaning in poetic structure
- Analyzing word choice to find meaning
- Identifying techniques like contrast, simile, metaphor, and alliteration
Unit 3: Longer Fiction or Drama I
You’ll observe how the literary techniques you’ve explored in prior units unfold over the course of longer works and analyze how characters develop and interact over the course of a narrative.
- Interpreting character description and perspective
- Character evolution throughout a narrative
- Conflict and plot development
- Interpreting symbolism
- Identifying evidence and supporting literary arguments
Unit 4: Short Fiction II
You’ll delve deeper into the roles of character and conflict in fiction and explore how a narrator’s perspective can color storytelling.
- Protagonists, antagonists, character relationships, and conflict
- Character interactions with setting and its significance
- Archetypes in literature
- Types of narration like stream of consciousness
- Narrative distance, tone, and perspective
Unit 5: Poetry II
You’ll study different forms of poetry and examine how structure and figurative language can create and impact meaning.
- Traits of closed and open structures in poetry
- Use of techniques like imagery and hyperbole
- Types of comparisons in poetry including personification and allusion
- Identifying and interpreting extended metaphors
Unit 6: Longer Fiction or Drama II
You’ll analyze how various literary techniques play out and shift over the course of longer works, charting how characters change (or don’t) as they’re affected by developments in the plot.
- Interpreting foil characters
- Understanding and interpreting character motives
- Understanding nonlinear narrative structures like flashbacks and foreshadowing
- The effect of narrative tone and bias on reading
- Characters as symbols, metaphors, and archetypes
- Developing literary arguments within a broader context of works
Unit 7: Short Fiction III
You’ll examine how works of fiction interact with and comment on the world around them and the society their authors live or lived in.
- Sudden and more gradual change in characters
- Epiphany as a driver of plot
- Relationships between characters and groups
- Character interactions with settings
- The significance of the pacing of a narrative
- Setting as a symbol
- Interpreting texts in their historical and societal contexts
Unit 8: Poetry III
You’ll develop your interpretation of poetry further by examining how contrasts, ambiguous language, and various other techniques can add layers of meaning to a poetic work.
- Looking at punctuation and structural patterns
- Interpreting juxtaposition, paradox, and irony
- How ambiguity can allow for various interpretations
- Identifying symbols, conceits, and allusions
- Learning proper attribution and citation in literary analysis
Unit 9: Longer Fiction or Drama III
You’ll consider longer narratives in the context of the various techniques and interpretations you’ve learned in prior units and build a nuanced analysis of each complex work as a whole.
- Looking at a character’s response to the resolution of a narrative
- Suspense, resolution, and plot development
- Narrative inconsistencies and contrasting perspectives
Credit and Placement

Search AP Credit Policies
Find colleges that grant credit and/or placement for AP Exam scores in this and other AP courses.
Course Resources
Ap classroom resources.
Once you join your AP class section online, you’ll be able to access AP Daily videos, any assignments from your teacher, and your assignment results in AP Classroom. Sign in to access them.
- Go to AP Classroom
AP English Literature and Composition Reading Study Skills
Advice to keep up with the reading workload in your AP class.
AP English Literature and Composition Writing Study Skills
Learn to craft your writing process.
AP English Literature and Composition Course and Exam Description
This is the core document for the course. It clearly lays out the course content and describes the exam and AP Program in general.
The Difference Between AP English Language and Composition and AP English Literature and Composition
Learn the similarities and differences between these two courses and exams.
- Go to College Board Blog
See Where AP Can Take You
AP English Literature and Composition can lead to a wide range of careers and college majors
Additional Information
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write the AP Lit Poetry Essay
What’s covered:.
- How to Write the AP Literature Poetry Essay
- Tips for Writing The AP Lit Poetry Essay
To strengthen your AP Literature Poetry Essay essay, make sure you prepare ahead of time by knowing how the test is structured, and how to prepare. In this post, we’ll cover the structure of the test and show you how you can write a great AP Literature Poetry Essay.
What is the AP Lit Poetry Essay?
The AP Literature exam has two sections. Section I contains 55 multiple choice questions, with 1 hour time allotted. This includes at least two prose fiction passages and two poetry passages.
Section II, on the other hand, is a free response section. Here, students write essays to 3 prompts. These prompts include a literary analysis of a poem, prose fiction, or in a work selected by the student. Because the AP Literature Exam is structured in a specific, predictable manner, it’s helpful to prepare yourself for the types of questions you’ll encounter on test day.
The Poetry Essay counts for one-third of the total essay section score, so it’s important to know how to approach this section. You’ll want to plan for about 40 minutes on this question, which is plenty of time to read and dissect the prompt, read and markup the poem, write a brief outline, and write a concise, well-thought out essay with a compelling analysis.
Tips for Writing the AP Lit Poetry Essay
1. focus on the process.
Writing is a process, and so is literary analysis. Think less about finding the right answer, or uncovering the correct meaning of the poem (there isn’t one, most of the time). Read the prompt over at least twice, asking yourself carefully what you need to look for as you read. Then, read the poem three times. Once, to get an overall sense of the poem. Second, start to get at nuance; circle anything that’s recurring, underline important language and diction , and note important images or metaphors. In your annotations, you want to think about figurative language , and poetic structure and form . Third, pay attention to subtle shifts in the poem: does the form break, is there an interruption of some sort? When analyzing poetry, it’s important to get a sense of the big picture first, and then zoom in on the details.
2. Craft a Compelling Thesis
No matter the prompt, you will always need to respond with a substantive thesis. A meaty thesis contains complexity rather than broad generalizations , and points to specifics in the poem.
By examining the colloquial language in Gwendolyn Brooks’s poem, “We Real Cool”, we can see the tension of choosing to be “cool”. This raises important ideas about education, structure, and routine, and the consequences of living to be “real cool”.
Notice how the thesis provides a roadmap of what is to follow in the essay , and identifies key ideas that the essay will explore. It is specific, and not vague. The thesis provides a bigger picture of the text, while zooming in the colloquial language the speaker uses.
A good thesis points out the why as much as the what . Notice how in the above example, the thesis discusses language in the poem as it connects to a bigger message about the poem. For example, it’s not enough to discuss Emily Dickinson’s enjambment and hyphens. A good thesis will make a compelling argument about why those infamous Dickinson hyphens are so widely questioned and examined. Perhaps a good thesis might suggest that this unique literary device is more about self-examination and the lapse in our own judgement.
3. Use Textual Evidence
To support your thesis, always use textual evidence . When you are creating an outline, choose a handful of lines in the poem that will help illuminate your argument. Make sure each claim in your essay is followed by textual evidence, either in the form of a paraphrase, or direct quote . Then, explain exactly how the textual evidence supports your argument . Using this structure will help keep you on track as you write, so that your argument follows a clear narrative that a reader will be able to follow.
Your essay will need to contain both description of the poem, and analysis . Remember that your job isn’t to describe or paraphrase every aspect of the poem. You also need lots of rich analysis, so be sure to balance your writing by moving from explicit description to deeper analysis.
4. Strong Organization and Grammar
A great essay for the AP Literature Exam will contain an introduction with a thesis (not necessarily always the last sentence of the paragraph), body paragraphs that contain clear topic sentences, and a conclusion . Be sure to spend time thinking about your organization before you write the paper. Once you start writing, you only want to think about content. It’s helpful to write a quick outline before writing your essay.
There’s nothing worse than a strong argument with awkward sentences, grammatical errors and spelling mistakes. Make sure to proofread your work before submitting it. Carefully edit your work, paying attention to any run-on sentences, subject-verb agreement, commas, and spelling. You’d be surprised how many mistakes you’ll catch just by rereading your work.
Common Mistakes on the AP Literature Poetry Essay
It can be helpful to know what not to do when it comes time to prepare for the AP Literature Poetry Essay. Here are some common mistakes students make on the AP Literature Poetry Essay:
1. Thesis is not arguable and is too general
Your thesis should be arguable, and indicate the central ideas you will discuss in your essay. Read the prompt carefully and craft your thesis in light of what the prompt asks you to do. If the prompt mentions specific literary devices, find a way to tie those into your thesis. In your thesis, you want to connect to the meaning of the poem itself and what you feel the poet intended when using those particular literary devices.
2. Using vague, general statements rather than focusing on analysis of the poem
Always stay close to the text when writing the AP Literature Poetry Essay. Remember that your job is not to paraphrase but to analyze. Keep explicit descriptions of the poem concise, and spend the majority of your time writing strong analysis backed up by textual evidence.
3. Not using transitions to connect between paragraphs
Make sure it’s not jarring to the reader when you switch to a new idea in a new paragraph. Use transitions and strong topic sentences to seamlessly blend your ideas together into a cohesive essay that flows well and is easy to follow.
4. Textual evidence is lacking or not fully explained
Always include quotes from the text and reference specifics whenever you can. Introduce your quote briefly, and then explain how the quote connects back to the topic sentence after. Think about why the quotes connect back to the poet’s central ideas.
5. Not writing an outline
Of course, to write a fully developed essay you’ll need to spend a few minutes planning out your essay. Write a quick outline with a thesis, paragraph topics and a list of quotes that support your central ideas before getting started.
To improve your writing, take a look at these essay samples from the College Board, with scoring guidelines and commentary.
How Will AP Scores Affect My College Chances?
While you can self-report AP scores, they don’t really affect your admissions chances . Schools are more interested in how you performed in the actual class, as your grades impact your GPA. To understand how your GPA impacts your college chances, use our free chancing engine . We’ll let you know your personal chance of acceptance at over 1500 schools, plus give you tips for improving your profile.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
Expert Guide to the AP Language and Composition Exam
Advanced Placement (AP)

With the 2023 AP English Language and Composition exam happening on Tuesday, May 9, it's time to make sure that you're familiar with all aspects of the exam. In this article, I'll give a brief overview of the test, do a deeper dive on each of the sections, discuss how the exam is scored, offer some strategies for studying, and finally wrap up with some essential exam day tips.
Exam Overview
The AP Language and Composition exam tests your rhetorical and composition skills. Essentially, how do authors construct effective arguments in their writing? What tools do they use? How can you use those tools to craft effective writing yourself? That is the essence of rhetorical analysis.
The exam has two parts: the first section is an hour-long, 45 question multiple-choice section. It includes five sets of questions, each based on a passage or passages. In this section, there will be 23-25 rhetorical analysis questions which test your rhetorical skills. There will also be 20-22 writing questions which require you to consider revisions to the texts you're shown.
The second section is free response. It starts with a 15-minute reading period, and then you'll have 120 minutes to write three analytical essays:
- One essay where you synthesize several provided texts to create an argument
- One essay where you analyze a nonfiction passage for its rhetorical construction
- One essay where you create an original argument in response to a prompt.
You will have about 40 minutes to write each essay, but no one will prompt you to move from essay to essay—you can structure the 120 minutes as you wish.
In the next sections I'll go over each section of the exam more closely—first multiple choice, and then free response.
The AP English Language and Composition Multiple-Choice
The multiple-choice section tests you on two main areas. The first is how well you can read and understand nonfiction passages for their use of rhetorical devices and tools. The second is how well you can "think like a writer" and make revisions to texts in composition questions.
You will be presented with five passages, about which you will receive a small amount of orienting information, e.g. "This passage is excerpted from a collection of essays on boating" or "This passage is excerpted from an essay written in 19th-century Haiti." Each passage will be followed by a set of questions.
There are, in general, eight question types you can expect to encounter on the multiple-choice section of the exam. I've taken my examples from the sample questions in the " Course and Exam Description ."

Magic eight-ball says there are eight types of multiple-choice questions!
Type 1: Reading Comprehension
These questions are focused on verifying that you understood what a certain part of the passage was saying on a concrete, literal level. You can identify these questions from phrases like "according to" "refers," etc. The best way to succeed on these questions is to go back and re-read the part of the passage referred to very carefully.

Type 2: Implication
These questions take reading comprehension one step further—they are primarily focused on what the author is implying without directly coming out and saying it. These questions will have a correct answer, though, based on evidence from the passage. Which interpretation offered in the answers does the passage most support? You can identify questions like these from words like "best supported," ‘"implies," "suggests," "inferred," and so on.

Type 3: Overall Passage and Author Questions
These questions ask about overall elements of the passage or the author, such as the author's attitude on the issue discussed, the purpose of the passage, the passage's overarching style, the audience for the passage, and so on.
You can identify these questions because they won't refer back to a specific moment in the text. For these questions, you'll need to think of the passage from a "bird's-eye view" and consider what all of the small details together are combining to say.

Type 4: Relationships Between Parts of the Text
Some questions will ask you to describe the relationship between two parts of the text, whether they are paragraphs or specific lines. You can identify these because they will usually explicitly ask about the relationship between two identified parts of the text, although sometimes they will instead ask about a relationship implicitly, by saying something like "compared to the rest of the passage."

Type 5: Interpretation of Imagery/Figurative Language
These questions will ask you about the deeper meaning or implication of figurative language or imagery that is used in the text. Essentially, why did the author choose to use this simile or this metaphor? What is s/he trying to accomplish?
You can generally identify questions like this because the question will specifically reference a moment of figurative language in the text. However, it might not be immediately apparent that the phrase being referenced is figurative, so you may need to go back and look at it in the passage to be sure of what kind of question you are facing.

Type 6: Purpose of Part of the Text
Still other questions will ask you to identify what purpose a particular part of the text serves in the author's larger argument. What is the author trying to accomplish with the particular moment in the text identified in the question?
You can identify these questions because they will generally explicitly ask what purpose a certain part of the text serves. You may also see words or phrases like "serves to" or "function."

Type 7: Rhetorical Strategy
These questions will ask you to identify a rhetorical strategy used by the author. They will often specifically use the phrase "rhetorical strategy," although sometimes you will be able to identify them instead through the answer choices, which offer different rhetorical strategies as possibilities.

Type 8: Composition
This is the newest question type, first seen in the 2019/2020 school year. For these questions, the student will need to act as though they are the writer and think through different choices writers need to make when writing or revising text.
These questions can involve changing the order of sentences or paragraphs, adding or omitting information to strengthen an argument or improve clarity, making changes to draw reader attention, and other composition-based choices.

Some very important stylish effects going on here.
The AP English Language and Composition Free Response
The free response section has a 15-minute reading period. After that time, you will have 120 minutes to write three essays that address three distinct tasks.
Because the first essay involves reading sources, it is suggested that you use the entire 15-minute reading period to read the sources and plan the first essay. However, you may want to glance at the other questions during the reading period so that ideas can percolate in the back of your mind as you work on the first essay.
Essay One: Synthesis
For this essay, you will be briefly oriented on an issue and then given anywhere from six to seven sources that provide various perspectives and information on the issue. You will then need to write an argumentative essay with support from the documents.
If this sounds a lot like a DBQ , as on the history AP exams, that's because it is! However, this essay is much more argumentative in nature—your goal is to persuade, not merely interpret the documents.
Example (documents not included, see 2022 free response questions ):

Essay Two: Rhetorical Analysis
In the second essay, you'll be presented with an excerpt from a nonfiction piece that advances an argument and asked to write an essay analyzing the rhetorical strategies used to construct the passage's argument. You will also be given some orienting information—where the passage was excerpted from, who wrote it, its approximate date, where it was published (if at all), and to whom it was directed.
Example (excerpt not included, see 2022 free response questions ):

Essay Three: Argument
In the third essay, you will be presented with an issue and asked to write a persuasive essay taking a position on the issue. You will need to support your position with evidence from your "reading, experience, and observations."

This doesn't look like a very well-constructed argument.
How The AP Language and Composition Exam Is Scored
The multiple-choice section of the exam is worth 45% of your score, and the free-response section is worth the other 55%. So each of the three free-response essays is worth about 18% of your score.
As on other APs, your raw score will be converted to a scaled score of 1-5. This exam has a relatively low 5 rate. Only 10% of test takers received a 5 in 2022 , although 56% of students received a score of 3 or higher.
In terms of how the raw score is obtained, the multiple-choice section is similar to other AP multiple-choice sections: you receive a point for every question you answer correctly, and there is no penalty for guessing.
The grading rubrics for the free-response questions were revamped in 2019. They are scored using analytic rubrics instead of holistic rubrics. For each free-response question, you will be given a score from 0-6. The rubrics assess three major areas:
#1: Thesis (0 to 1 points): Is there a thesis, and does it properly respond to the prompt?
#2: Evidence and Commentary (0 to 4 points): Does the essay include supporting evidence and analysis that is relevant, specific, well organized, and supports the thesis?
#3: Sophistication (0 to 1 points): Is the essay well-crafted and does it show a sufficiently nuanced understanding of the prompt?
Each scoring rubric broadly assesses these three factors. However, each task is also different in nature, so the rubrics do have some differences. I'll go over each rubric—and what it really means—for you here.
Synthesis Essay Rubrics
| 0 | For any of the following: | |
| 1 |
EVIDENCE AND COMMENTARY
| 0 | ||
| 1 | AND | |
| 2 | AND | |
| 3 | AND | |
| 4 | AND |
SOPHISTICATION
| 0 | ||
| 1 | Responses that earn this point may demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation by doing any of the following: |

Time to synthesize this dough into some cookies.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Rubrics
| 0 | ||
| 1 | AND | |
| 2 | AND | |
| 3 | AND AND | |
| 4 | AND AND |

Examine your texts closely!
Argumentative Essay Rubrics

The best kind of frenzy is a puppy frenzy!
AP English Language Prep Tips
Unlike its cousin, the AP English Literature and Composition exam, the AP Language and Composition exam (and course) have very little to do with fiction or poetry. So some students used to more traditional English classes may be somewhat at a loss as to what to do to prepare.
Luckily for you, I have a whole slate of preparation tips for you!
Read Nonfiction—In a Smart Way
A major thing you can do to prepare for the AP Lang and Comp exam is to read nonfiction— particularly nonfiction that argues a position , whether explicitly (like an op-ed) or implicitly (like many memoirs and personal essays). Read a variety of non-fiction genres and topics, and pay attention to the following:
- What is the author's argument?
- What evidence do they use to support their position?
- What rhetorical techniques and strategies do they use to build their argument?
- Are they persuasive? What counterarguments can you identify? Do they address them?
Thinking about these questions with all the reading you do will help you hone your rhetorical analysis skills.
Learn Rhetorical Terms and Strategies
Of course, if you're going to be analyzing the nonfiction works you read for their rhetorical techniques and strategies, you need to know what those are! You should learn a robust stable of rhetorical terms from your teacher, but here's my guide to the most important AP Language and Composition terms .
- We've compiled a list of 20 rhetorical devices you should know.
- A heroic individual from Riverside schools in Ohio uploaded this aggressively comprehensive list of rhetorical terms with examples. It's 27 pages long, and you definitely shouldn't expect to know all of these for the exam, but it's a useful resource for learning some new terms.
- Another great resource for learning about rhetorical analysis and how rhetorical devices are actually used is the YouTube Channel Teach Argument , which has videos rhetorically analyzing everything from Taylor Swift music videos to Super Bowl commercials. It's a fun way to think about rhetorical devices and get familiar with argumentative structures.
- Finally, a great book—which you might already use in your class—is " They Say, I Say. " This book provides an overview of rhetoric specifically for academic purposes, which will serve you well for AP preparation and beyond.
You also need to practice argumentative and persuasive writing. In particular, you should practice the writing styles that will be tested on the exam: synthesizing your own argument based on multiple outside sources, rhetorically analyzing another piece of writing in-depth, and creating a completely original argument based on your own evidence and experience.
You should be doing lots of writing assignments in your AP class to prepare, but thoughtful, additional writing will help. You don't necessarily need to turn all of the practice writing you do into polished pieces, either—just writing for yourself, while trying to address some of these tasks, will give you a low-pressure way to try out different rhetorical structures and argumentative moves, as well as practicing things like organization and developing your own writing style.

Not the most auspicious start to an argumentative essay.
Practice for the Exam
Finally, you'll need to practice specifically for the exam format. There are sample multiple-choice questions in the " AP Course and Exam Description ," and old free-response questions on the College Board website.
Unfortunately, the College Board hasn't officially released any complete exams from previous years for the AP English Language and Composition exam, but you might be able to find some that teachers have uploaded to school websites and so on by Googling "AP Language complete released exams." I also have a guide to AP Language and Composition practice tests .
Once you're prepped and ready to go, how can you do your best on the test?

AP Language and Composition Test Day Tips
Here are four key tips for test-day success.

You are one hundred percent success!
Interact With the Text
When you are reading passages, both on the multiple-choice section and for the first two free-response questions, interact with the text! Mark it up for things that seem important, devices you notice, the author's argument, and anything else that seems important to the rhetorical construction of the text. This will help you engage with the text and make it easier to answer questions or write an essay about the passage.
Think About Every Text's Overarching Purpose and Argument
Similarly, with every passage you read, consider the author's overarching purpose and argument. If you can confidently figure out what the author's primary assertion is, it will be easier to trace how all of the other aspects of the text play into the author's main point.
Plan Your Essays
The single most important thing you can do for yourself on the free-response section of the AP English Language exam is to spend a few minutes planning and outlining your essays before you start to write them.
Unlike on some other exams, where the content is the most important aspect of the essay, on the AP Language Exam, organization, a well-developed argument, and strong evidence are all critical to strong essay scores. An outline will help you with all of these things. You'll be able to make sure each part of your argument is logical, has sufficient evidence, and that your paragraphs are arranged in a way that is clear and flows well.
Anticipate and Address Counterarguments
Another thing you can do to give your free responses an extra boost is to identify counterarguments to your position and address them within your essay. This not only helps shore up your own position, but it's also a fairly sophisticated move in a timed essay that will win you kudos with AP graders.

Address counterarguments properly or they might get returned to sender!
Key Takeaways
The AP Language and Composition exam tests your rhetorical skills. The exam has two sections.
The first section is an hour-long, 45 question multiple-choice test based on the rhetorical techniques and composition choices.
The second section is a two-hour free-response section (with a 15-minute initial reading period) with three essay questions: one where you must synthesize given sources to make an original argument, one where you must rhetorically analyze a given passage, and one where you must create a wholly original argument about an issue with no outside sources given.
You'll receive one point for every correct answer on the multiple-choice section of the exam, which is worth 45% of your score. The free-response section is worth 55% of your score. For each free-response question, you'll get a score based on a rubric from 0-6. Your total raw score will be converted to a scaled score from 1-5.
Here are some test prep strategies for AP Lang:
#1 : Read nonfiction with an eye for rhetoric #2 : Learn rhetorical strategies and techniques #3 : Practice writing to deploy rhetorical skills #4 : Practice for the exam!
Here are some test-day success tips:
#1 : Interact with each passage you encounter! #2 : Consider every text's overarching purpose and argument. #3 : Keep track of time #4 : Plan your essays #5 : Identify and address counterarguments in your essays.
With all of this knowledge, you're ready to slay the AP English Language and Composition beast!

Noble knight, prepare to slay the AP dragon!
What's Next?
Want more AP Lang review? We have a complete collection of released AP Language practice tests , as well as a list of the AP Lang terms you need to know and a guide to the multiple choice section .
Taking the AP Literature exam? Check out our ultimate guide to the AP English Literature test and our list of AP Literature practice tests .
Taking other AP exams? See our Ultimate Guides to AP World History , AP US History , AP Chemistry , AP Biology , AP World History , and AP Human Geography .
Need more AP prep guidance? Check out how to study for AP exams and how to find AP practice tests .
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ellen has extensive education mentorship experience and is deeply committed to helping students succeed in all areas of life. She received a BA from Harvard in Folklore and Mythology and is currently pursuing graduate studies at Columbia University.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
We are experiencing sporadically slow performance in our online tools, which you may notice when working in your dashboard. Our team is fully engaged and actively working to improve your online experience. If you are experiencing a connectivity issue, we recommend you try again in 10-15 minutes. We will update this space when the issue is resolved.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., guide to the ap english literature and composition exam.

Do you know how to conduct a close reading of prose and poetry? Can you write effectively under time constraints? The AP ® English Literature and Composition exam tests topics and skills discussed in your AP English Literature course. If you score high enough, your AP English score could earn you college credit!
Check out our AP English Literature Guide for what you need to know about the exam:
- Exam Overview
- Structure & Question Types
- How to Prepare
What’s on the AP English Literature & Composition Exam?
The College Board lists 6 Skill Categories that should be covered in your AP English Literature and Composition course, or as you prepare for the test:
- Character—Characters in literature show a wide range of values, beliefs, assumptions, biases, and cultural norms, and provide an opportunity to study and explore what the characters represent.
- Setting—A setting and the details associated with it represent a time and place, but also convey values associated with the setting.
- Structure—Structure refers to the arrangements of sections and parts of a text, the relationship of the parts to each other, and the sequence in which the text reveals information. These are all choices made by a writer that allow you to interpret a text.
- Narration—Any narrator’s or speaker’s perspective controls the details and emphases that readers encounter; therefore, narration affects how readers experience and interpret a text.
- Figurative language—Comparisons, representations, and associations shift meaning from the literal to the figurative. Figurative language can include word choice, imagery, and symbols. Simile, metaphor, personification, and allusions are all examples of figurative language.
- Literary argumentation—How do you write about literature yourself? You develop your interpretation (using the first five of the Big Six!) and then communicate it. You need to develop a thesis—a defensible claim—and support it with textual evidence.
The multiple-choice section of the AP English Literature and Composition exam will be testing your knowledge of the Big Six. Each one is weighted a certain amount in the multiple-choice questions.
AP English Literature & Composition Book List
There is no required reading or book list for the AP English Literature exam, but the College Board provides a list of authors and poets with whom you should be familiar and whose work is of the caliber and density that you are expected to understand. These lists include:
- Poetry: W.H. Auden, Elizabeth Bishop, William Blake, Anne Bradstreet, Edward Kamau Brathwaite, Gwendolyn Brooks, Robert Browning, George Gordon/Lord Byron, Lorna Dee Cervantes, Geoffrey Chaucer, Lucille Clifton, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Billy Collins, H.D. (Hilda Doolittle), Emily Dickinson, John Donne, Rita Dove, Paul Laurence Dunbar, T.S. Eliot, Robert Frost, Joy Harjo, Seamus Heaney, George Herbert, Garrett Hongo, Gerard Manley Hopkins, Langston Hughes, Ben Jonson, John Keats, Philip Larkin, Robert Lowell, Andrew Marvell, John Milton, Marianne Moore, Sylvia Plath, Edgar Allan Poe, Alexander Pope, Adrienne Rich, Anne Sexton, William Shakespeare, Percy Bysshe Shelley, Leslie Marmon Silko, Cathy Song, Wallace Stevens, Alfred, Lord Tennyson, Derek Walcott, Walt Whitman, Richard Wilbur, William Carlos Williams, William Wordsworth, William Butler Yeats
- Drama: Aeschylus, Edward Albee, Amiri Baraka, Samuel Beckett, Anton Chekhov, Caryl Churchill, William Congreve, Athol Fugard, Lorraine Hansberry, Lillian Hellman, David Henry Hwang, Henrik Ibsen, Ben Jonson, David Mamet, Arthur Miller, Molière, Marsha Norman, Sean O’Casey, Eugene O’Neill, Suzan-Lori Parks, Harold Pinter, Luigi Pirandello, William Shakespeare, George Bernard Shaw, Sam Shepard, Sophocles, Tom Stoppard, Luis Valdez, Oscar Wilde, Tennessee Williams, August Wilson
- Fiction (Novel and Short Story): Chinua Achebe, Sherman Alexie, Isabel Allende, Rudolfo Anaya, Margaret Atwood, Jane Austen, James Baldwin, Saul Bellow, Charlotte Bronte, Emily Bronte, Raymond Carver, Willa Cather, John Cheever, Kate Chopin, Sandra Cisneros, Joseph Conrad, Edwidge Danticat, Daniel Defoe, Anita Desai, Charles Dickens, Fyodor Dostoevsky, George Eliot, Ralph Ellison, Louise Erdrich, William Faulkner, Henry Fielding, F. Scott Fitzgerald, E.M. Forster, Thomas Hardy, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Ernest Hemingway, Zora Neale Hurston, Kazuo Ishiguro, Henry James, Ha Jin, Edward P. Jones, James Joyce, Maxine Hong Kingston, Joy Kogawa, Jhumpa Lahiri, Margaret Laurence, D.H. Lawrence, Chang-rae Lee, Bernard Malamud, Gabriel García Márquez, Cormac McCarthy, Ian McEwan, Herman Melville, Toni Morrison, Bharati Mukherjee, Vladimir Nabokov, Flannery O’Connor, Orhan Pamuk, Katherine Anne Porter, Marilynne Robinson, Jonathan Swift, Mark Twain, John Updike, Alice Walker, Evelyn Waugh, Eudora Welty, Edith Wharton, John Edgar Wideman, Virginia Woolf, Richard Wright
- Expository Prose: Joseph Addison, Gloria Anzaldua, Matthew Arnold, James Baldwin, James Boswell, Joan Didion, Frederick Douglass, W.E.B. Du Bois, Ralph Waldo Emerson, William Hazlitt, bell hooks, Samuel Johnson, Charles Lamb, Thomas Macaulay, Mary McCarthy, John Stuart Mill, George Orwell, Michael Pollan, Richard Rodriguez, Edward Said, Lewis Thomas, Henry David Thoreau, E.B. White, Virginia Woolf
Read More: Review for the exam with our AP English Literature Cram Courses
AP English Literature Structure & Question Types
The AP English Literature & Composition exam takes 3 hours to complete and consists of two sections: a multiple-choice section and a free response section.
|
|
|
| |
| Section 1 | 60 minutes | 55 multiple-choice questions | 45% |
| Section 2 | 120 minutes | 3 free response questions | 55% |
Multiple-Choice
AP English Literature multiple-choice questions are grouped in sets. You will be given 5 passages or poems to read, with 8-13 multiple-choice questions to assess your reading comprehension. Each multiple-choice question has 5 answer choices (A through E). That’s a lot of reading then recalling, understanding, and interpreting. Use your time effectively and wisely!
Free Response
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that presents an interpretation and may establish a line of reasoning.
- Select and use evidence to develop and support your line of reasoning.
- Explain the relationship between the evidence and your thesis.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
How to Interpret AP English Literature Scores
AP scores are reported from 1 to 5. Colleges are generally looking for a 4 or 5 on the AP English Literature exam, but some may grant credit for a 3. (Here's a quick overview of AP credit policy .) Each test is curved so scores vary from year to year. Here’s how AP English Lit students scored on the May 2022 test:
|
|
|
|
| 5 | Extremely qualified | 16.9% |
| 4 | Well qualified | 27.3% |
| 3 | Qualified | 33.7% |
| 2 | Possibly qualified | 14.1% |
| 1 | No recommendation | 7.9% |
Source: College Board
How can I prepare?
AP classes are great, but for many students they’re not enough! For a thorough review of AP English Literature content and strategy, pick the AP prep option that works best for your goals and learning style.
- AP Exams

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
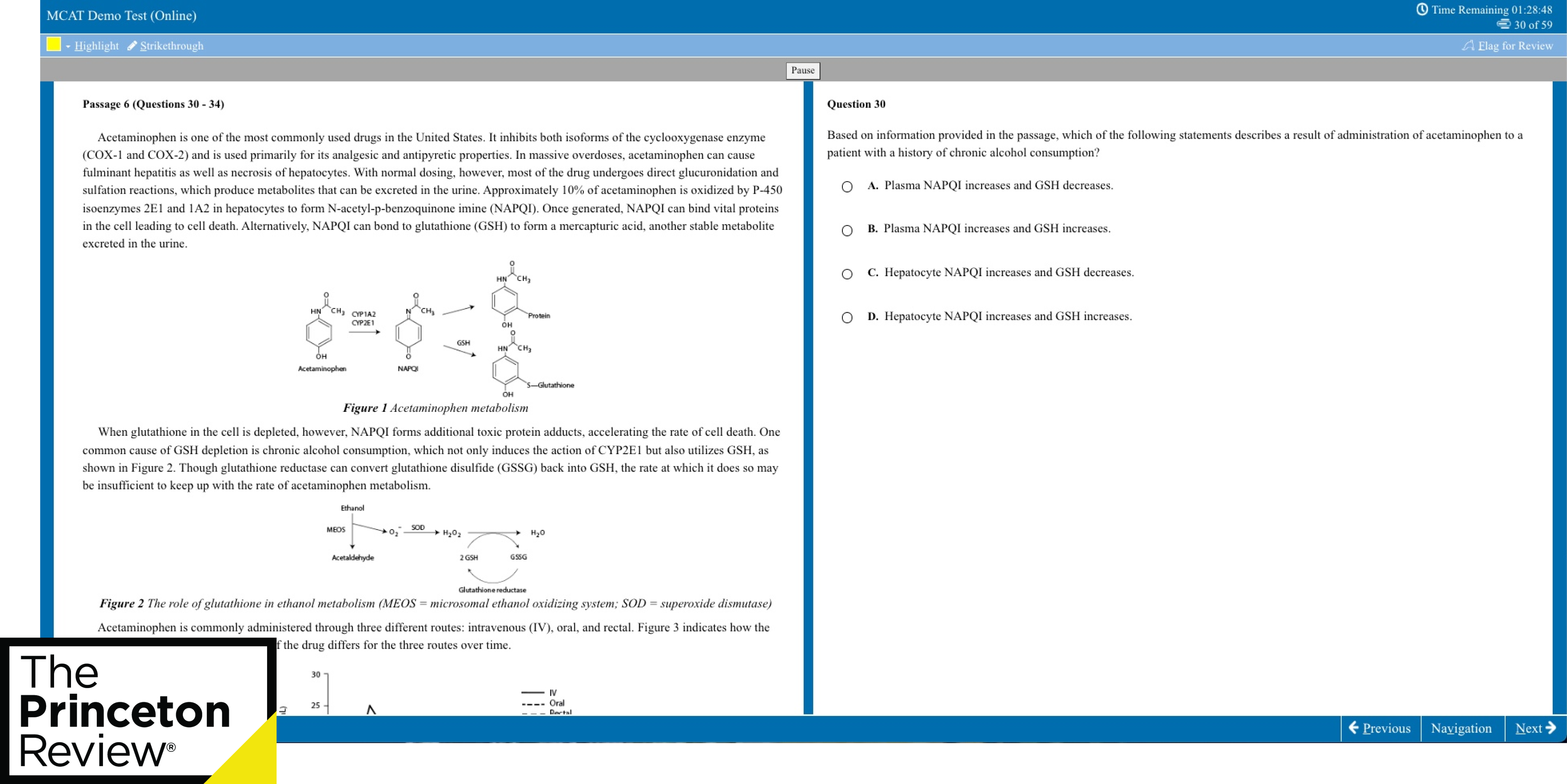
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
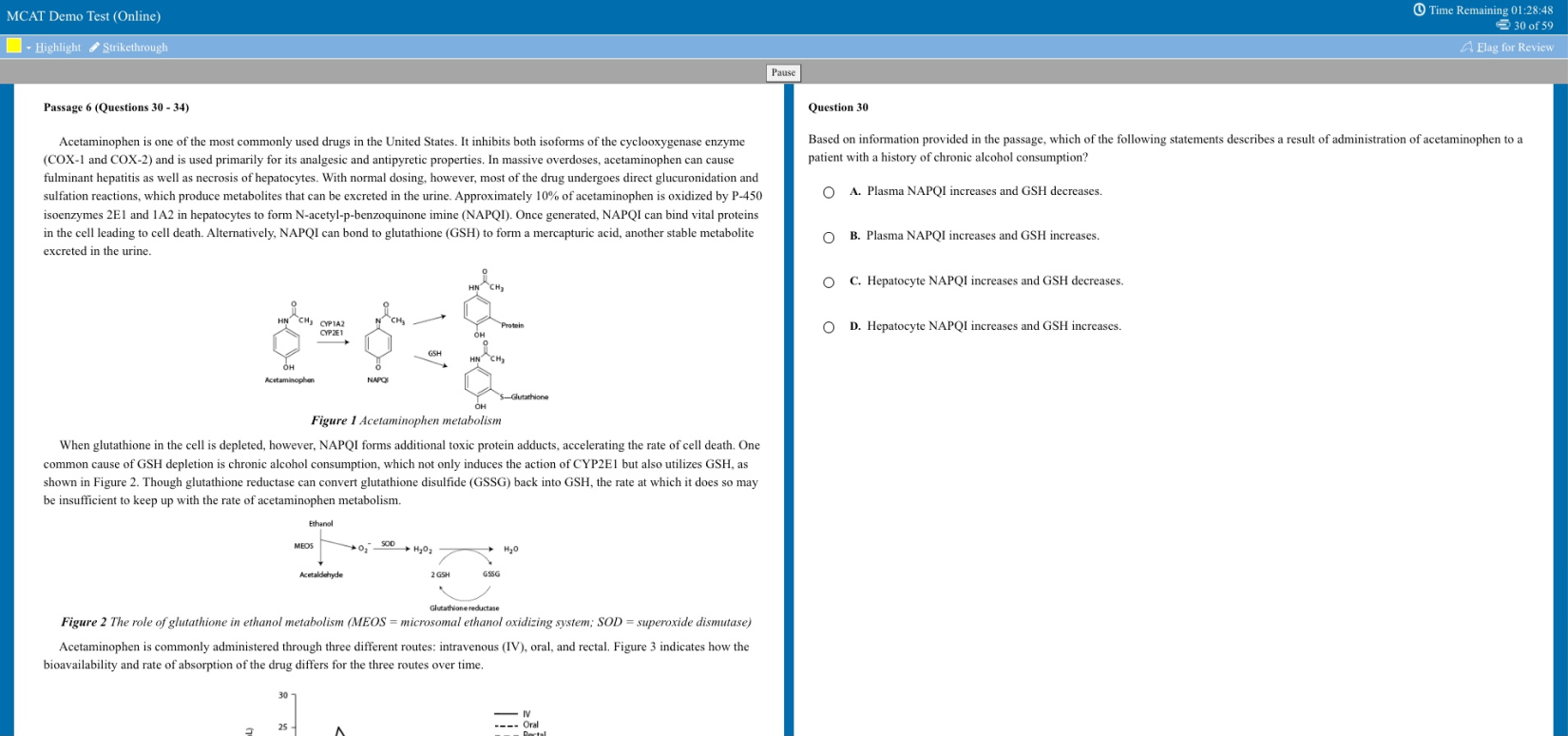
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.

AP® English Literature
Ap® english literature exam faq: everything you need to know for 2024.
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: January 29, 2024

Are you hoping to find answers to the most commonly asked questions about the 2024 AP® English Literature exam? You’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ll cover how difficult the AP® English Literature exam is, how the exam is scored, strategies for passing the exam, and much more. Let’s get started!
What We Review
Is AP® English Literature Easy? What Can Make It Hard?
The AP® English Literature exam is not considered easy. A review of passing rates over the last few years has shown it to be one of the more difficult tests to pass. That level of difficulty will be increased if reading, writing, and analyzing texts are not academic strengths for you or if you cannot succeed in a class designed to teach at a college level.
In 2021, the AP® English Literature exam had a passing rate of 43.9% and a mean score of 2.47 . Both of these statistics showed that, in 2021, the AP® English Literature exam was harder than the average AP® exam for students to pass.
However, the 2022 AP® English Literature exam results showed a major jump in passing rate!
In 2022, the AP® English Literature and Composition exam had a passing rate of 77.9% and a mean score of 3.31 . These are both significant improvements over previous years! This growth likely results from hard work from students and improved instructional focus from teachers.
The passing rate percentages for the 2022 AP® English Literature exam are based on an average total of 339,401 test takers. That number makes the AP® English Literature exam the third most popular AP® exam, behind AP® US History and AP® English Language. The high number of test takers provides a higher level of reliability to the passing percentages for this exam.
In order to do your best on the AP® English Literature exam, you will want to know how the content units are weighted in the exam. For the AP® English Literature exam, the units are divided into three categories: short fiction, poetry, and longer fiction or drama.
Of these sections, short fiction makes up 42-49% of the exam. Poetry accounts for 36-45%, and longer fiction or drama makes up 15-18% of the exam questions. Understanding these weightings can help you create a study plan to prepare for the AP® English Literature exam.
You can increase your chances of passing by knowing how many questions you need to answer correctly on the exam in order to pass. This can help you to know if you need to devote valuable time to tough questions or if it is safe to skip them.
Albert provides an AP® English Literature score calculator that can provide information on how many questions you need to get right to achieve the score you want. For example, if you want to score a 3, you need something like the score breakdown shown below:
Return to the Table of Contents
Is AP® English Literature Worth It?
The AP® English Literature exam is worth taking for a variety of reasons, from academic to financial. When you successfully complete an AP® course, you can know that you are prepared for the increased pace and academic rigor that is required of college-level courses. This knowledge will increase your confidence as you move into this new phase of academic life.
Passing the AP® English Literature exam can also help you with the college admissions process. AP® courses send a signal to admissions counselors that you are prepared for college and that you approached your high school education with ambition and determination.
Perhaps the most important benefit of AP® courses is in their ability to save you money. Graduating from high school with college credits means that those are classes you won’t need to pay for in college. You can either bank those savings or use the freed-up credit hours to explore earning a minor or other classes outside your major.
This chart shows just a few of the colleges that will allow you to use your passing AP® English Literature score for college credit and the estimated savings you could see from that decision.
| American University | 4 | 6 | |
| University of CA- Berkeley | 4 | 5.3 | |
| Syracuse University | 4 | 6 | |
| Texas A & M | 3 | 3 | |
| San Diego State University | 3 | 6 | |
| Auburn University | 4 | 3 | |
| University of WI: Madison | 4 | 3 | |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 5 | 9 |
As you can see from the chart, there is a real financial savings opportunity when you take and pass AP® English Literature. These savings, combined with the academic benefits of AP® exams, show that taking AP® English Literature is worth it.
When is the 2024 AP® English Literature Exam?
The 2024 AP® English Literature exam will be given in person using paper-and-pencil tests. The AP® English Literature and Composition exam will take place on:
Wednesday, May 8, 2024, at 8am local time
Curious about when other AP® exams are happening in 202 4? View or download the complete AP® exam schedule here .
Is the 2024 AP® English Literature test a digital exam?
Schools can take the 2024 AP® English Literature exam as a traditional paper-and-pencil test or as an in-school digital exam on computers. More information on the digital option is available here .
You should check with your teacher and AP® Coordinator to know if you’ll take a paper-and-pencil or digital version.
When do AP® English Literature scores typically come out?
According to the latest update from the College Board exam season timeline , students will receive their AP® scores in July 2024. Historically, the College Board typically releases AP® scores early in the month of July.
You’ll be able to access your AP® scores online with your College Board account username and password.
How is AP® English Literature Scored? What’s the Weighting of Different Questions?
The chart below outlines the scoring breakdown for the AP® English Literature exam:
| 1: Multiple Choice | 55 questions | 1 hour | 45% |
| 2: Free Response | 3 questions | 2 hours | 55% |
This breakdown is somewhat unusual among AP® courses. Most AP® courses put at least half, and often over half, of the scoring percentage in the multiple choice question. Over half of the points in the AP® English Literature course will come from the free response questions .
- The multiple-choice portion of the AP® English Literature exam consists of 55 questions that will need to be answered within 60 minutes.
- The questions will be grouped in 5 sets with 8 – 13 questions per set. Each of the sets will relate to a supplied passage of prose fiction, drama or poetry. There will be a minimum of 2 prose fiction and two poetry passages.
- The free-response section consists of three questions. You will have 2 hours to answer these questions. Two of the questions will cover the literary analysis of a poem and a passage from prose fiction (both supplied). The third question will require an analysis of a concept, issue, or element in a literary work.
Pro tip: Don’t be afraid to let your own belief system show in your essays. These can add weight and personality to your argument.
You can view the chart below to see how the individual units from the course are reflected in the exam questions. You can see how these weightings translate to the overall exam score with Albert’s free AP® English Literature score calculator .
| Short Fiction (Units 1, 4, 7) | 42-49% |
| Poetry (Units 2, 5, 8) | 36-45% |
| Longer Fiction or Drama (Units 3, 6, 9) | 15-18% |
What Happens If You Fail AP® English Literature Exam?

If you happen to fail the AP® English Literature exam, don’t panic! It’s not the end of the world, and you can minimize the impact on your academic future in several ways.
As far as your high school grades go, failing the AP® English Literature exam won’t have any impact on your GPA. Your school will use your academic year coursework to determine your grade in AP® English Literature. Your AP® exam grade is separate and not factored into your course grade.
If you want to use the AP® English Literature exam for college credit, you will need to retake the exam. Most colleges won’t award credit for any score lower than 3. Some schools require a 4 or even a 5 for college credit.
Luckily, you can retake the AP® English Literature exam as often as you want. You can retake it to achieve a passing score or reach a higher score. You will need to pay the exam fee each time you take the exam, but there are no penalties for retaking it.
You also get to choose who sees your AP® exam scores. If you scored lower than you want on the AP® English Literature exam, you could choose not to share that score with colleges. If you send in a score and then score higher at a retake, you can also ask the college to substitute your higher score for the earlier lower score.
When Do Students Typically Take AP® English Literature? When is Best?
AP® English Literature is typically taken during your junior or senior year in high school. Technically, the course has no prerequisites, so you could theoretically take it earlier.
However, this course is considered one of the more time-consuming AP® courses, so students typically wait until they have more time management experience before taking it.
AP® English Literature is an extremely reading and writing-intensive course. You should wait to take this course until you feel confident you can spend long periods of time reading complex texts.
You should also have enough writing experience to feel comfortable crafting a written argument about the assigned texts and meeting the page requirements.
If you want to take AP® English Literature, you should consider all of these factors and decide when it feels right for you to take it. You will want to be sure to balance AP® English Literature with any other AP® courses you may want to take.
As with all academic decisions, you may want to consult your guidance counselor and get advice from some of the AP® teachers before deciding when to take AP® English Literature.
Where Can I find Past AP® English Literature Exams?
Reviewing past AP® exam questions can be a very useful study strategy. The College Board has made the FRQs from the last 20 years of AP® English Literature exams available to you via the AP® Central website .
While this year’s test won’t be likely to reuse questions from past exams, the questions will likely cover the same general concepts and require the same skills to answer. You should review the past free-response exam questions from the last 5 years to get an idea of the types of questions they will ask to test your knowledge of the material covered in the course.
You can access those past free-response questions using the links below:
- 2023 AP® English Literature Free-Response Questions
- 2022 AP® English Literature Free-Response Questions
- 2021 AP® English Literature Free-Response Questions
- 2019 AP® English Literature Free-Response Questions
- 2018 AP® English Literature Free-Response Questions
- 2017 AP® English Literature Free-Response Questions
- 2016 AP® English Literature Free-Response Questions
- 2015 AP® English Literature Free-Response Questions
You’ll also want to spend some time studying for the multiple-choice portion of the exam. The College Board has also provided a few sample multiple choice questions on the AP® English Literature Course and Exam Description. The number of questions is pretty limited, so you’ll want to add in more practice questions.
You can find additional multiple-choice practice questions on Albert’s AP® English Literature website . Albert’s team has designed these questions to ensure that they cover the units as they are weighted on the exam.
The College Board’s AP® English Literature website offers some really useful information from past exams. You should really take the time to look over the resources they have provided. Reviewing the links below will make you more prepared and confident going into this year’s exam.
- AP® English Literature Scoring Guidelines 2023 / 2022 / 2021 / 2019
- AP® English Literature Chief Reader Reports 2023 / 2022 / 2021 / 2019
- AP® English Literature Scoring Reports 2023 / 2022 / 2021 / 2019
The Scoring Guidelines report lets you view previous free-response questions along with a detailed breakdown of the rubric used to determine the points awarded for each question. Your questions might be different, but you may find some common elements in past questions that would be useful for this year’s exam.
The Chief Reader report is one you should not ignore when preparing for this year’s AP® English Literature exam. Chief Readers are experts in the field of the AP® exam and provide their expert analysis of past exam answers. These reports detail what elements were included in a strong answer and where weak answers went wrong.
Understanding the weaknesses and strengths of past answers can ensure that you focus your study in those areas and are prepared to address often overlooked concepts and arguments.
For example, in the 2019 Chief Reader report, the reader noted that some of the best essays incorporated the student’s beliefs about concepts such as “idealism” and allowed those beliefs to permeate their discussion of the work and the concept.
The sample responses can also provide useful information from past exams. The College Board provides three sample responses for each past exam question: a strong answer, an average answer, and a weak answer. Each response is graded, and an explanation of that grade is included.
While the free-response portion takes most of the exam time and accounts for over half of your score, don’t forget to prepare for the multiple-choice section. It makes up 45% of your score and can’t be your downfall if you aren’t prepared. Check out Albert’s AP® English Literature practice page for multiple-choice practice before the exam.
Who Should Take AP® English Literature? What Sort of Students May Like It More Than Others?

Not everyone will excel at AP® English Literature, so you should consider how the course aligns with your academic strengths before deciding to take it. The decision should also be based on your academic goals after high school.
If you plan to major in English in college, taking AP® English Literature is an easy choice. If you enjoy reading, AP® English Literature could be a good choice, as long as you are equally comfortable with analyzing what you read and writing a cohesive essay about that analysis.
Unlike AP® English Language, AP® English Literature focuses primarily on poetry and fiction. There is a significant amount of reading, so you will also need to possess the ability to read for large stretches of time. The course overview can shed more light on what to expect from the course.
Non-English majors can also benefit from taking AP® English Literature. The course teaches how to read texts critically, which can be useful for various disciplines. It also relies heavily on classroom discussion, which can benefit future college classes.
The passing rate for the AP® English Literature exam is fairly low, at 49.7% for 2019. This factor should be considered if you plan to use the course for college credit. If your goal is to score a 4 or 5 on this exam, you’ll want to devote extra study time to accomplish that goal. In 2019, only 21.9% of students scored a 4 or 5 on the AP® English Literature exam.
Taking AP® English Literature is a personal decision only you can make. You’ll want to review the course overview and decide if this course is a good fit for your academic talents and if it is a course that would interest you. You might also want to consult with your guidance counselor and your parents before making this decision.
How Do Students Typically Score On AP® English Literature? What’s the Score Distribution?
The AP® English Literature exam is one that has a wide variety in score distribution. As one of the most popular AP® exams, past scores reflect a variety of factors, such as how well students studied for the exam, their writing aptitude and their ability to do well at the advanced placement level. The score distributions for the AP® English Literature exam for the last three years are below.
| 2023 | 14.9% | 27.8% | 34.5% | 29.5% | 14.4% | 77.2% |
| 2022 | 16.9% | 27.3% | 33.7 | 14.1% | 7.9% | 77.9% |
| 2021 | 4.9% | 12.0% | 26.9% | 37.3% | 18.8% | 43.9% |
| 2019 | 6.2% | 15.7% | 27.8% | 34.3% | 16.0% | 49.2% |
| 2018 | 5.6% | 14.5% | 27.2% | 36.0% | 16.7% | 47.3% |
| 2017 | 6.8% | 16.1% | 29.7% | 33.9% | 13.5% | 52.6% |
Until the 2022 exam cycle, the AP® English Literature exam had averaged a passing rate of slightly below 50%. In 2022, there was a significant jump in the pass rate for the exam — nearly 78% passing!
The exam typically attracts around 400,000 exam takers each year.
In 2023, the mean score among all 356,043 AP® English Literature exam test takers was 3.26 .
Need Help Preparing For Your AP® English Literature Exam?
Albert has hundreds of AP® English Literature multiple-choice practice questions, free-response questions, and full-length practice tests to try out.
Interested in a school license?
Popular posts.

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, creating a thesis for ap lit.
This year, I'm taking AP Lit and I'm struggling with writing thesis statements for my essays. Does anyone have any tips or insight on how to write a solid thesis statement for AP Lit essays?
I can definitely give you some advice on how to create a solid thesis statement for your AP Lit essays. In AP Lit, your thesis statement should provide a clear, original, and specific claim about your chosen literary work, which your essay will then analyze and support with textual evidence.
Here are a few steps you can follow to create a strong thesis statement:
1. Read the prompt carefully: Make sure you understand what the prompt is asking you to do, whether it's analyzing a specific aspect of the text, exploring a theme, or discussing a particular character.
2. Choose a clear and specific focus: Decide what aspect of the work you want to explore, such as characterization, theme, symbolism, or structure. Your thesis statement should be specific enough that your analysis doesn't become too broad or unfocused.
3. Make an original claim: Your thesis statement should present an original argument or interpretation, rather than merely stating an obvious fact or restating the prompt. Make sure your claim is one that can be both supported by evidence from the text and challenged by other interpretations.
4. Include some direction for your essay: A strong thesis statement not only makes a claim but also gives some indication of how your essay will support that claim. This helps guide your reader and sets up the organization of your essay.
For example: In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald uses the contrasting settings of East Egg, West Egg, and the Valley of Ashes to illustrate the corrupting influence of wealth and social class on the characters and their ultimate disillusionment with the American Dream.
In this thesis statement, the focus is on the contrasting settings and their impact on the characters, making a specific claim about the author's intent. It provides direction for the essay, indicating that the writer will explore how Fitzgerald uses these settings to convey his message.
Remember, writing a strong thesis statement takes practice, so keep working at it and tweaking it until you feel confident in your ability to craft a well-argued and coherent claim about the text. Good luck in your AP Lit class!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The AP Literature Exam is a three-hour exam that contains two sections in this order: An hour-long, 55-question multiple-choice section. A two-hour, three-question free-response section. The exam tests your ability to analyze works and excerpts of literature and cogently communicate that analysis in essay form.
Hey there! In AP Lit, the essay length ultimately depends on the depth and quality of your analysis and how effectively you can communicate your points. However, as a general guideline, most high-scoring AP Lit essays tend to be around 2-3 pages double-spaced (approximately 600-900 words). This allows you to provide a thorough analysis while being concise enough to stay focused on the main points.
Fifth: Give each literary device its own body paragraph. In this essay, the writer examines the use of two literary devices that are supported by multiple pieces of evidence. The first is "romantic imagery" and the second is "hyperbolic imagery.". The writer dedicates one paragraph to each idea. You should do this, too.
A prose passage of approximately 500 to 700 words and a prompt will be given to guide your analytical essay. Worth about 18% of your total grade, the essay will be graded out of six points depending on the quality of your thesis (0-1 points), evidence and commentary (0-4 points), and sophistication (0-1 points).
Starting in the 2024-25 school year, AP English Literature and Composition multiple-choice questions (MCQs) will have four answer choices instead of five. This change will take effect with the 2025 exam. ... Students write essays that respond to 3 free-response prompts from the following categories: A literary analysis of a given poem;
The first section of the AP Literature exam is one hour long and consists of 45 multiple-choice questions—23-25 Reading questions and 20-22 Writing questions. The multiple-choice questions are grouped in five sets of questions, with each set linked to a passage of prose fiction or poetry that contains between 8 and 13 questions.
2. Pick one side of the argument, but acknowledge the other side. When you write the essay, it's best if you pick one side of the debate and stick with it for the entire essay. All your evidence should be in support of that one side. However, in your introductory paragraph, as you introduce the debate, be sure to mention any merit the ...
Here are five tips to help you write a great essay response to the third prompt on the AP Lit exam. 1. Select the perfect work. Wait a minute—you can write about anything under the sun, as long as the College Board defines it as "a work of literary merit?".
1. Introduction: Start with a hook to engage the reader. Introduce the work you'll be discussing (including the title and author). Provide any necessary context or background info. 2. Thesis statement: In a clear, concise sentence, state your overall argument or claim. This should appear towards the end of your introduction.
Total questions: 55. 45% of exam score. The multiple choice section is computer-graded, and it makes up 45% of your total exam score. The 55 questions in this section consist of: 5 passages of prose fiction, drama, or poetry of varying difficulty. 5 sets of questions for each passage, with 8-13 questions per set.
The final step is to write the essay. This part should take about 30 minutes. It may seem like an impossible task, but with a specific direction to head and with the poem already analyzed, the essay should flow smoothly. You aren't writing a 200 page dissertation. You are writing a 2 to 4 page essay.
Write an essay that argues your position on the value of striving for perfection. In your response you should do the following: Respond to the prompt with a thesis that presents a defensible position. Provide evidence to support your line of reasoning. Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
The Best AP® English Literature Review Guide for 2024. Scoring a 5 on the AP® English Literature and Composition exam is no easy task. In 2019, for example, only 6.2% of students earned a 5 on the test. While this statistic may be discouraging at first glance, it does indicate that a perfect score is possible for those willing to do extra ...
Each body paragraph should focus on one main idea, which supports your thesis in a coherent way. 7. Keep track of time: Time management is crucial during the AP Lit Exam. Allocate enough time for each essay, and make sure you're aware of how much time you have left while writing. Try to allocate time for planning, writing, and proofreading. 8.
Starting in the 2024-25 school year, AP English Literature and Composition multiple-choice questions (MCQs) will have four answer choices instead of five. This change will take effect with the 2025 exam. All resources have been updated to reflect this change.
The AP® English Literature and Composition exam is designed to test your ability to think critically and analyze literary excerpts. The test is three hours long and consists of a multiple-choice portion (worth 45% of your grade) and a free response portion (worth 55% of your grade). The best way to score a 5 on the AP® English Literature exam ...
For AP lit, I think I wrote ~700-800 words in 40 mins 3x for 3 essays. 600 definitely isn't bad, but try to get it to at least 700 just to ensure your analysis is strong. 1000 definitely isn't necessary, imo. Reply.
The exam takes 3 hours. It is comprised of three free-response essays and 55 multiple-choice questions. The free-response section accounts to 55% of your score. You will be given two hours to complete three free-response essays. The first will correspond to a given poem.
The AP Literature exam has two sections. Section I contains 55 multiple choice questions, with 1 hour time allotted. This includes at least two prose fiction passages and two poetry passages. Section II, on the other hand, is a free response section. Here, students write essays to 3 prompts.
So each of the three free-response essays is worth about 18% of your score. As on other APs, your raw score will be converted to a scaled score of 1-5. This exam has a relatively low 5 rate. Only 10% of test takers received a 5 in 2022, although 56% of students received a score of 3 or higher.
The AP English Literature & Composition exam takes 3 hours to complete and consists of two sections: a multiple-choice section and a free response section. Timing. Number of questions. % of Exam Score. Section 1. 60 minutes. 55 multiple-choice questions. 45%. Section 2.
The passing rate for the AP® English Literature exam is fairly low, at 49.7% for 2019. This factor should be considered if you plan to use the course for college credit. If your goal is to score a 4 or 5 on this exam, you'll want to devote extra study time to accomplish that goal.
In AP Lit, your thesis statement should provide a clear, original, and specific claim about your chosen literary work, which your essay will then analyze and support with textual evidence. Here are a few steps you can follow to create a strong thesis statement: 1. Read the prompt carefully: Make sure you understand what the prompt is asking you ...