myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...

Case Study Questions Class 12 Physics
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE will ask two Case Study Questions in the CBSE class 12 Physics questions paper. Question numbers 15 and 16 are case-based questions where 5 MCQs will be asked based on a paragraph. Each theme will have five questions and students will have a choice to attempt any four of them. You can download CBSE Class 12 Physics case study questions from the myCBSEguide App and our free student dashboard .
You can Score High
CBSE class 12 Physics question paper will carry questions for 70 marks. Certainly, the question paper is a bit easier this year. It is because the syllabus is already reduced and there are more internal choices. Besides this, the case study questions are a plus to winning the game with good marks.
In simple words, all circumstances are in favour of the sincere students who are working hard to score high this year. Although it has been a difficult time for students as they were not getting the personal attention of the teachers. We know that online classes have their own limits, but we still expect better scores, especially from students who are putting extra effort into their studies.
Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions
CBSE class 12 Physics question paper will have case study questions too. These case-based questions will be objective type in nature. So, class 12 Physics students must prepare themselves for such questions. First of all, you should study NCERT Textbooks line by line and then you should practice as many questions as possible.
Case Study Syllabus
We know that CBSE has reduced the syllabus. Hence, practice only relevant questions. don’t waste time on case study questions from deleted portion. It is of no use. You can download the latest class 12 Physics case study questions from the myCBSEguide App.
Physics Case Studies
Class 12 Physics has many chapters but all chapters are not important for case studies. As we know case studies are not exactly given from NCERT books but these may be extracted from some newspaper articles, magazines, journals or other books. So, it is very much important that you are studying only the most relevant case studies. Here, the myCBSEguide app helps you a lot. We have case study questions that are prepared by a team of expert teachers. These experts exactly know what types of questions can come in exams.
Case Study Questions
There are a number of study apps available over the internet. But if you are a CBSE student and willing to get an app for the CBSE curriculum, you have very limited options. And if you want an app that is specifically designed for CBSE students, your search will definitely end on finding myCBSEguide. Case study questions are the latest updates in CBSE syllabus. It is exclusively available in the myCBSEguide app.
Here are some example questions. For more questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App.
Physics Case Study -1
Read the following source and answer any four out of the following questions: Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of charges positive and negative charges. Also, like charges repel each other whereas unlike charges attract each other.
- -3.2 × × 10 -18 C
- 3.2 × × 10 18 C
- -3.2 × × 10 -17 C
- 3.2 × × 10 -17 C
- -1.6 × × 10 -18 C
- 1.6 × × 10 -18 C
- 2.6 × × 10 -18 C
- 1.6 × × 10 -21 C
- 9.1 × × 10 -31 kg
- 9.1 × × 10 -31 g
- 1.6 × × 10 -19 kg
- 1.6 × × 10 -19 g
- there is only a positive charge in the body
- there is positive as well as negative charge in the body but the positive charge is more than the negative charge
- there is equally positive and negative charge in the body but the positive charge lies in the outer regions
- the negative charge is displaced from its position
- valence electrons only
- electrons of inner shells
- both valence electrons and electrons of the inner shell.
- none of the above
Physics Case Study -2
Read the following source and answer any four out of the following questions: Resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit. Resistance is measured in ohms. Also, Resistivity is the electrical resistance of a conductor of unit cross-sectional area, and unit length. … A characteristic property of each material, resistivity is useful in comparing various materials on the basis of their ability to conduct electric currents.
- nature of material
- temperature
- dimensions of material
- cross-sectional area
- length of wire
- wire’s nature
- all of the above
- more resistance
- less resistance
- same resistance
Physics Case Study -3
Read the source given below and answer any four out of the following questions: The Bohr model of the atom was proposed by Neil Bohr in 1915. It came into existence with the modification of Rutherford’s model of an atom. Rutherford’s model introduced the nuclear model of an atom, in which he explained that a nucleus (positively charged) is surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
- The energy of the electrons in the orbit is quantized
- The electron in the orbit nearest the nucleus has the lowest energy
- Electrons revolve in different orbits around the nucleus
- The position and velocity of the electrons in the orbit cannot be determined simultaneously
- Single proton
- Multiple electrons
- emitted only
- absorbed only
- both (a) and (b)
- none of these
- It must emit a continuous spectrum
- It loses its energy
- Gaining its energy
- A discrete spectrum
- dequantized
Physics Case Study & myCBSEguide App
We at myCBSEguide provide the best case study questions for CBSE class 12 Physics. We have Physics case study questions for every chapter in 12th class Physics. Students can access the Physics case study questions with answers on the myCBSEguide App or on the student dashboard . Here are some features that make myCBSEguide the best learning app for CBSE students:
- Updated syllabus
- Up to date question bank
- Model papers and 10-year questions
- NCERT and Exemplar sulutions
- Best quality learning videos
- Detailed revision notes
12 Physics Question Paper Design
Here is the question paper design for CBSE class 12 Physics. It shows the typology of the questions and their weightage in CBSE board exams.
QUESTION PAPER DESIGN Theory (Class: 12)
Maximum Marks: 70 Duration: 3 hrs
| Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas | 27 | 38% | |
| Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way | 22 | 32% | |
| Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, the validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria. Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions. | 21 | 30% | |
| 70 | 100 | ||
| 30 | |||
| 100 |
Note: The above template is only a sample. Suitable internal variations may be made for generating similar templates keeping the overall weightage to different forms of questions and typology of questions the same.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
2 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 12 Physics”
Good question l will check answers sheet
Question 2 answer key ?
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 12th Standard Physics Subject Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Part - II
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
12th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
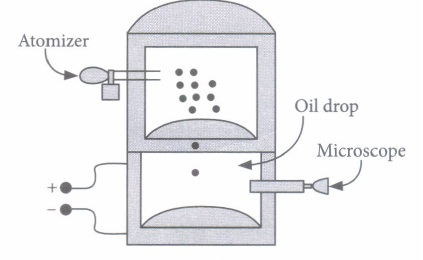
| C | C |
| C | C |
(ii) Extra electrons on this particular oil drop (given the presently known charge of the electron) are
(iii) A negatively charged oil drop is prevented from falling under gravity by applying a vertical electric field 100 V m -1 .If the mass of the drop is 1.6 X 10 -3 g, the number of electrons carried by the drop is (g= 10 m s -2 )
(iv) The important conclusion given by Millikan's experiment about the charge is
(v) If in Millikan's oil drop experiment, charges on drops are found to be \(8 \mu \mathrm{C}, 12 \mu \mathrm{C}, 20 \mu \mathrm{C}\) then quanta of charge is
This energy possessed by a system of charges by virtue of their positions. When two like charges lie infinite distance apart, their potential energy is zero because no work has to be done in moving one charge at infinite distance from the other. In carrying a charge q from point A to point B, work done \(W=q\left(V_{A}-V_{B}\right)\) . This work may appear as change in KE/PE of the charge. The potential energy of two charges q 1 and q 2 at a distance r in air is \(\frac{q_{1} q_{2}}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0} r}\) . It is measured in joule. It may be positive, negative or zero depending on the signs of q l and q 2 . (i) Calculate work done in separating two electrons form a distance of 1m to 2m in air, where e is electric charge and k is electrostatic force constant.
| /2 | /2 |
(ii) Four equal charges q each are placed at four corners of a square of side a each. Work done in carrying a charge -q from its centre to infinity is
(iii) Two points A and B are located in diametrically opposite directions of a point charge of +2 \(\mu \mathrm{C}\) at distances 2 m and 1 m respectively from it. The potential difference between A and B is
| V | V | V | V |
(iv) Two point charges A = +3 nC and B = +1 nC are placed 5 ern apart in air. The work done to move charge B towards A by 1 cm is
| J | J | J | J |
(v) A charge Q is placed at the origin. The electric potential due to this charge at a given point in space is V. The work done by an external force in bringing another charge q from infinity up to the point is
Metals have a large number of free electrons nearly 10 28 per cubic metre. In the absence of electric field, average terminal speed of the electrons in random motion at room temperature is of the order of 10 5 m s -1 When a potential difference V is applied across the two ends of a given conductor, the free electrons in the conductor experiences a force and are accelerated towards the positive end of the conductor. On their way, they suffer frequent collisions with the ions/atoms of the conductor and lose their gained kinetic energy. After each collision, the free electrons are again accelerated due to electric field, towards the positive end of the conductor and lose their gained kinetic energy in the next collision with the ions/atoms of the conductor. The average speed of the free electrons with which they drift towards the positive end of the conductor under the effect of applied electric field is called drift speed of the electrons. (i) Magnitude of drift velocity per unit electric field is
(ii) The drift speed of the electrons depends on
(iii) We are able to obtain fairly large currents in a conductor because
(iv) Drift speed of electrons in a conductor is very small i.e., i = 10 -4 m s -1 . The Electric bulb glows immediately. When the switch is closed because
(v) The number density offree electrons in a copper conductor is 8.5 x 10 28 m -3 . How long does an electron take to drift from one end of a wire 3.0 m long to its other end? The area of cross-section of the wire is 2.0 x 10 -6 m 2 and it is carrying a current of 3.0 A.
| s | s | s | S |
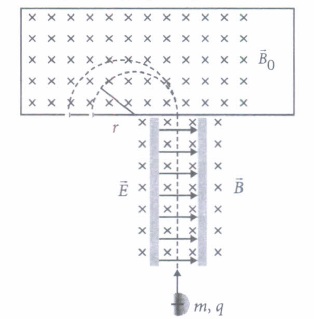
(ii) Radius of particle in second magnetic field B o is
(iii) Which of the following will trace a circular trajectory wit largest radius?
| particle |
(iv) Mass of the particle in terms q, B o, B,r and E is
(v) The particle comes out of velocity selector along a straight line, because
When the atomic dipoles are aligned partially or fully, there is a net magnetic moment in the direction of the field in any small volume of the material. The actual magnetic field inside material placed in magnetic field is the sum of the applied magnetic field and the magnetic field due to magnetisation. This field is called magnetic intensity (H). \(H=\frac{B}{\mu_{0}}-M\) where M is the magnetisation of the material, llo is the permittivity of vacuum and B is the total magnetic field. The measure that tells us how a magnetic material responds to an external field is given by a dimensionless quantity is appropriately called the magnetic susceptibility: for a certain class of magnetic materials, intensity of magnetisation is directly proportional to the magnetic intensity. (i) Magnetization of a sample is
(ii) Identify the wrongly matched quantity and unit pair.
(iii) A bar magnet has length- 3 cm, cross-sectional area 2 cm 2 and magnetic moment 3 A m 2 . The intensity of magnetisation of bar magnet is
(iv) A solenoid has core of a material with relative permeability 500 and its windings carry a current of 1 A. The number of turns of the solenoid is 500 per metre. The magnetization of the material is nearly
(v) The relative permeability of iron is 6000. Its magnetic susceptibility is
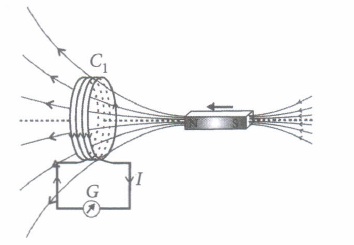
(ii) Two similar circular loops carry equal currents in the same direction. On moving the coils further apart, the electric current will
(iii) A closed iron ring is held horizontally and a bar magnet is dropped through the ring with its length along the axis of the ring. The acceleration of the falling magnet is
(iv) Whenever there is a relative motion between a coil and a magnet, the magnitude of induced emf set up in the coil does not depend upon the
(v) A coil of metal wire is kept stationary in a non-uniform magnetic field
A transformer is essentially an a.c. device. It cannot work on d.c. It changes alternating voltages or currents. It does not affect the frequency of a.c. It is based on the phenomenon of mutual induction. A transformer essentially consists of two coils of insulated copper wire having different number of turns and wound on the same soft iron core. The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of an ideal transformer are 2000 and 50 respectively. The primary coil is connected to a main supply of 120 V and secondary coil is connected to a bulb of resistance \(0.6 \Omega\) (i) The value of voltage across the secondary coil is
(ii) The value of current in the bulb is
(iii) The value of current in primary coil is
(iv) Power in primary coil is
(v) Power in secondary coil is
Electrons oscillating in a circuit give rise to radiowaves. A transmitting antenna radiates most effectively the radiowaves of wavelength equal to the size of the antenna. The infrared waves incident on a substance set into oscillation all its electrons, atoms and molecules. This increases the internal energy and hence the temperature of the substance. (i) If v g , v x and vm are the speeds of gamma rays, X-rays and microwaves respectively in vacuum, then
| > V > V | > V > V | = V = V |
(ii) Which of the following will deflect in electric field?
| -rays |
(iii) \(\Upsilon\) -rays are detected by
(iv) The frequency of electromagnetic wave, which best suited to observe a particle of radius 3 x 10 -4 cm is the order of
| Hz | Hz | Hz | Hz |
(v) We consider the radiation emitted by the human body. Which one of the following statements is true?
An astronomical telescope is an optical instrument which is used for observing distinct images of heavenly bodies libe stars, planets etc. It consists of two lenses. In normal adjustment of telescope, the final image is formed at infinity. Magnifying power of an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended at the eye by the angle subtended at the eye by the final image to the angle subtended at the eye, by the object directly, when the final image and the object both lie at infinite distance from the eye. It is given by, \(m=\frac{f_{0}}{f_{e}}\) To increase magnifying power of an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment, focal length of objective lens should be large and focal length of eye lens should be small. (i) An astronomical telescope of magnifying power 7 consists of the two thin lenses 40 cm apart, in normal adjustment. The focal lengths of the lenses are
(ii) An astronomical telescope has a magnifying power of 10. In normal adjustment, distance between the objective and eye piece is 22 cm. The focal length of objective lens is
(iii) In astronomical telescope compare to eye piece, objective lens has
(iv) To see stars, use
(v) For large magnifying power of astronomical telescope
| \((a) f_{v}< | \((b) f_{v}=f_{\mathrm{e}}\) | \((c) f_{o}>>f_{\mathrm{e}}\) |
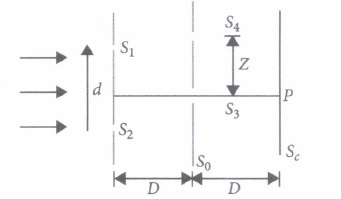
| \((a) \lambda\) | \((b) \lambda / 2\) | \((c) 3 / 2 \lambda\) | \((d) 2 \lambda\) |
(ii) Find the ratio of the maximum to minimum intensity observed on \(S_{c} \text { if } z=\frac{\lambda D}{d}\)
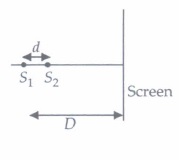
(iv) In the case of light waves from two coherent sources S 1 and S 2 . there will be constructive interference at an arbitrary point P, if the path difference S 1 P - S 2 P is
| \(\text { (a) }\left(n+\frac{1}{2}\right) \lambda \) | \( \text { (b) } n \lambda\) | \( \text { (c) }\left(n-\frac{1}{2}\right) \lambda\) | \( \text { (d) } \frac{\lambda}{2}\) |
(v) Two monochromatic light waves of amplitudes 3A and 2A interfering at a point have a phase difference of 60°. The intensity at that point will be proportional to
If we allow radiations of a fixed frequency to fall on plate and the accelerating potential difference between the two electrodes is kept fixed, then the photoelectric current is found to increase linearly with the intensity of incident radiation. Here, radiation pressure is P = \(\left(\frac{1+e}{C}\right) I\) . As, atmosphere pressure at sea level is 10 5 Pa. If the intensity of light of a given wavelength, is increased, there is an increase in the number of photons incident on a given area in a given time. But the energy of each photon remain the same. (i) The number of photons hitting the cone second
(ii) A radiation of energy E falls normally on a perfect reflecting surface. The momentum transferred to the surface is
(iii) Which one is correct?
(iv) The incident intensity on a horizontal surface at sea level from the Sun is about 1 k W m -2 . Assuming that 50% of this intensity is reflected and 50% is absorbed, determine the radiation pressure on this horizontal surface.
| Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa |
(v) Find the ratio of radiation pressure to atmospheric pressure P 0 about 1 x 10 5 Pa at sea level.
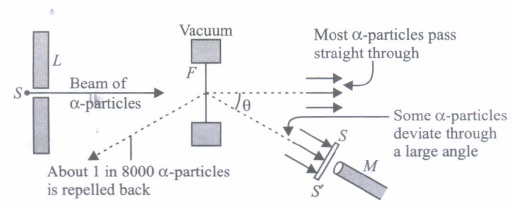
(ii) Gold foil used in Geiger-Marsden experiment is about 10 -8 m thick. This ensures
(iii) In Geiger-Marsden scattering experiment, the trajectory traced by an a-particle depends on
(iv) In the Geiger-Marsden scatteririg experiment, in case of head-on collision, the impact parameter should be
(v) The fact only a small fraction of the number of incident particles rebound back in Rutherford scattering indicates that
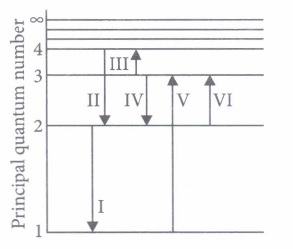
(ii) The wavelength of the radiation involved in transition II is
(iii) Which transition will occur when a hydrogen atom is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 103 nm?
(iv) The electron in a hydrogen atom makes a transition from n = n 1 to n = n 2 state. The time period of the electron in the initial state is eight times that in the final state. The possible values of n 1 and n 2 are
| = 4, n = 2 | = 8, n = 2 | = 8, n = 3 | = 6, n = 2 |
(v) The Balmer series for the H-atom can be observed
Neutrons and protons are identical particle in the sense that their masses are nearly the same and the force, called nuclear force, does into distinguish them. Nuclear force is the strongest force. Stability of nucleus is determined by the neutron proton ratio or mass defect or packing fraction. Shape of nucleus is calculated by quadrupole moment and spin of nucleus depends on even or odd mass number. Volume of nucleus depends on the mass number. Whole mass of the atom (nearly 99%) is centred at the nucleus. (i) The correct statements about the nuclear force is/are
(ii) The range of nuclear force is the order of
| m | m | m | m |
(iii) A force between two protons is same as the force between proton and neutron. The nature of the force is
(iv) Two protons are kept at a separation of 40 \(\dot A\) . Fn is the nuclear force and F e is the electrostatic force between them. Then
| << F | = F | >> F | \(\approx \) F |
(v) All the nucleons in an atom are held by
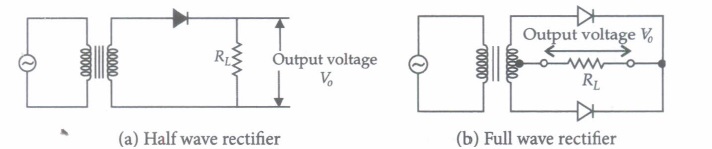
(v) With an ac input from 50 Hz power line, the ripple frequency is
*****************************************
Cbse 12th standard physics subject case study questions with solution 2021 part - ii answer keys.
(i) (a): As, \(q E=m g \Rightarrow q=\frac{1.08 \times 10^{-14} \times 9.8}{1.68 \times 10^{5}}\) \(=6.4 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}\) (ii) (a): \(q=n e \text { or } \Rightarrow n=\frac{6.4 \times 10^{-19}}{1.6 \times 10^{-19}}=4\) (iii) (c) : For the drop to be stationary, Force on the drop due to electric field = Weight of the drop qE=mg \(q=\frac{m g}{E}=\frac{1.6 \times 10^{-6} \times 10}{100}=1.6 \times 10^{-7} \mathrm{C}\) Number of electrons carried by the drop is \(n=\frac{q}{e}=\frac{1.6 \times 10^{-7} \mathrm{C}}{1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}}=10^{12}\) (iv) (c) (v) (d): Millikan's experiment confirmed that the charges are quantized, i.e., charges are small integer multiples of the base value which is charge on electron. The charges on the drops are found to be multiple of 4. Hence, the quanta of charge is 4 \(\mu \) C.
(i) (c): \(W=(\text { P.E. })_{\text {final }}-(\text { P.E. })_{\text {initial }}\) \(=\frac{k e^{2}}{2}-\frac{k e^{2}}{1}=\frac{-k e^{2}}{2}\) (ii) (b) : Potential at the centre of the square due to four equal charges q at four corners \(V=\frac{4 q}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}(a \sqrt{2}) / 2}=\frac{\sqrt{2} q}{\pi \varepsilon_{0} a}\) \(W_{0 \rightarrow \infty}=-W_{\infty \rightarrow 0}=-(-q) V=\frac{\sqrt{2} q^{2}}{\pi \varepsilon_{0} a}\) (iii) (c): Here, \(q=2 \mu \mathrm{C}=2 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{C}, r_{A}=2 \mathrm{~m}, r_{B}=1 \mathrm{~m}\) \(\therefore \ V_{A}-V_{B}=\frac{q}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}}\left[\frac{1}{r_{A}}-\frac{1}{r_{B}}\right]\) \(=2 \times 10^{-6} \times 9 \times 10^{9}\left[\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{1}\right] \mathrm{V}=-9 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~V}\) (iv)(b) : Required work done = Change in potential energy of the system \(W=U_{f}-U_{i}=k \frac{q_{1} q_{2}}{r_{f}}-k \frac{q_{1} q_{2}}{r_{i}}=k q_{1} q_{2}\left[\frac{1}{r_{f}}-\frac{1}{r_{i}}\right]\) \(\therefore \ W=\left(9 \times 10^{9}\right)\left(3 \times 10^{-9} \times 1 \times 10^{-9}\right)\) \(\times\left[\frac{1}{4 \times 10^{-2}}-\frac{1}{5 \times 10^{-2}}\right]\) \(=27 \times 10^{-7} \times(0.05)=1.35 \times 10^{-7} \mathrm{~J}\) (v) (b)
(i) (d): Mobility is defined as the magnitude of drift velocity per unit electric field Mobility, \(\mu=\frac{\left|v_{d}\right|}{E}\) (ii) (c): Drift velocity \(v_{d}=\frac{I}{n e A}\) where the symbols have their usual meanings (iii) (b): I = neAv d v d is of order offew m S -I , e = 1.6 x 10 -19 C, A is of the order of mm 2 , so a large I is due to a large value of n in conductors. (iv) (c): When we close the circuit, an electric field is established instantly with the speed of electromagnetic wave which causes electrons to drift at every portion of the circuit, due to which the current is set up in the entire circuit instantly. The current which is set up does not wait for electrons to flow from one end of the conductor to another. Thus, the electric bulb glows immediately when switch is closed. (v) (b): Here, Number density of free electrons, n = 8.5 x 10 28 m -3 Area of cross-section of a wire, A = 2.0 x 10 -6 m 2 Length of the wire, 1= 3.0 m Current, I = 3.0 A The drift velocity of an electron is \(v_{d}=\frac{I}{n e A}\) ...(i) The time taken by the electron to drift from one end to other end of the wire is \(t=\frac{l}{v_{d}}=\frac{\ln e A}{I}\) \(=\frac{(3.0 \mathrm{~m})\left(8.5 \times 10^{28} \mathrm{~m}^{-3}\right)\left(1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}\right)\left(2.0 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~m}^{2}\right)}{(3.0 \mathrm{~A})}\) = 2.7 x 10 4 s
(i) (c): In mass spectrometer, the ions are sorted out by accelerating them through electric and magnetic field. (ii) (c): As \(\frac{m v^{2}}{r}=q v B_{0} \therefore r=\frac{m v}{q B_{0}}\) (iii) (b): As radius \(r \propto \frac{m}{q}\) \(\therefore\) r will be maximum for \(\alpha\) - particle. (iv) (b) : Here, \(r=\frac{m v}{q B_{0}} \text { or } m=\frac{r q B_{0}}{v}\) As \(v=\frac{E}{B}, \therefore m=\frac{q B_{0} B r}{E}\) (v) (c): From the relation v = E/B, it is clear electric and magnetic force balance each other.
(i) (b) (ii) (d): Magnetic permeability - Henry m -1 (iii) (d): Given, L= 3 cm, A = 2 cm 2 , M = 3 A m 2 .Intensity of magnetisation \(=\frac{M}{l A}=\frac{3}{3 \times 10^{-2} \times 2 \times 10^{-4}}\) \(=\frac{1}{2 \times 10^{-6}}=0.5 \times 10^{6}=5 \times 10^{5} \mathrm{~A} / \mathrm{m}\) (iv) (b) : Here, n = 500 turns/m \(I=1 \mathrm{~A}, \mu_{-}=500\) Magnetic intensity \(H=n I=500 \mathrm{~m}^{-1} \times 1 \mathrm{~A}=500 \mathrm{~A} \mathrm{~m}^{-1}\) As \(\mu_{r}=1+\chi \quad \text { or } \chi=\left(\mu_{r}-1\right)\) Magnetisation, M = XH \(=\left(\mu_{r}-1\right) H=(500-1) \times 500 \mathrm{~A} \mathrm{~m}^{-1}\) \(=2.495 \times 10^{5} \mathrm{~A} \mathrm{~m}^{-1} \approx 2.5 \times 10^{5} \mathrm{~A} \mathrm{~m}^{-1}\) (v) (a) : Relative permeability of iron \(\mu_{r}=6000\) Magnetic susceptibility \(\chi_{m}=\mu_{r}-1=5999\)
(i) (d) : More rapid is the movement of bar magnet, more is the deflection observed in the galvanometer (ii) (c) : Two circular loops carrying current in the same direction will attract each other. If they are now separated, induced currents will try to keep status quo, by increasing the current in both the coils. (iii) (b): Acceleration of the magnet will not be equal to g. It will be less than g. This is because, as the magnet falls, amount of magnetic flux linked with the ring changes. An induced emf is developed in the ring which opposes the downward motion of the magnet. (iv) (c) : The magnitude of induced emf set up in the coil does not depend upon the resistance of the coil whereas induced current set up in the coil depend upon the resistance of the coil. (v) (d) : As long as a coil of metal is kept stationary in a magnetic field, even if it is non-uniform, unless it is changing with respect to time, there will be no induced emf or current in the coil.
(i) (c) : As \(\frac{E_{s}}{E_{p}}=\frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \Rightarrow E_{s}=E_{p} \cdot \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}}\) \(=\frac{120 \times 50}{2000}=3 \mathrm{~V}\) (ii) (d) : \(I_{s}=\frac{E_{s}}{R} \Rightarrow I_{s}=\frac{3}{0.6}=5 \mathrm{~A}\) (iii) (a) : As \(\frac{I_{p}}{I_{s}}=\frac{E_{s}}{E_{p}}\) \(\Rightarrow I_{p}=\frac{E_{s}}{E_{p}} \times I_{s}=\frac{\ 3}{120} \times 5=0.125 \mathrm{~A}\) (iv) (d) : Power in primary \(P_{p}=E_{p} \times I_{p}=120 \times 0.125\) = I5W (v) (a) : Power in secondary coil \(P_{s}=E_{s} \times I_{s}=3 \times 5\) = 15W
(i) (d) : All electromagnetic waves travel in vacuum with the same speed. (ii) (c) : Cathode rays (beam of electrons) get deflected in an electric field. (iii) (c) : \(\Upsilon\) -rays are detected by ionization chamber. (iv) (b) : Size of particle \(=\lambda=\frac{c}{v}\) \(v=\frac{c}{\lambda}=\frac{3 \times 10^{10} \mathrm{~cm} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}}{3 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~cm}}=3 \times 10^{14} \mathrm{~Hz}\) (v) (a) : Every body at a temperature T > 0 K emits radiation in the infrared region.
(i) (a) : \(m=\frac{f_{o}}{f_{e}}=7\) \(f_{o}=7 f_{e}\) In normal adjustment, distance between the lenses \(f_{o}+f_{e}=40 \) \(7 f_{0}+f_{e}=40 \Rightarrow f_{e}=\frac{40}{8}=5 \mathrm{~cm} \) \(f_{o}=7 f_{e}=7 \times 5=35 \mathrm{~cm}\) (ii) (d) : \(m=-10 ; L=22 \mathrm{~cm}\) \(\text { As } m=\frac{-f_{o}}{f_{e}} \Rightarrow-10=-\frac{f_{o}}{f_{e}}\) \(f_{o}=10 f_{\mathrm{e}} \) \(\text { As } L=f_{o}+f_{e} \) \(22=10 f_{e}+f_{e}=11 f_{e} \) \(\text { or } f_{e}=\frac{22}{11}=2 \mathrm{~cm}\) \(f_{o}=10 f_{e}=20 \mathrm{~cm}\) (iii) (d) : Objective lens has larger focal length than eye-piece. (iv) (d): Astronomial telescope is used to see stars, sun etc. (v) (c) :f 0 >>f e
(i) (b) : \(\text { As } z=\frac{\lambda D}{2 d}\) \(\text { At } S_{4}: \frac{\Delta x}{d}=\frac{z}{D}\) \(\Rightarrow \Delta x=\frac{\lambda D}{2 d} \frac{d}{d}=\frac{\lambda}{2}\) (ii) (c) : \(z=\frac{\lambda D}{d}\) \(\Delta x \text { at } S_{4}: \Delta x=\frac{\lambda D}{d} \frac{d}{d}=\lambda\) Hence, maxima at S 4 as well as S 3 ' Resultant intensity at S 4 I = 4I 0 \(\therefore \quad \frac{I_{\max }}{I_{\min }}=\frac{\left[\left(4 I_{0}\right)^{1 / 2}+4\left(4 I_{0}\right)^{1 / 2}\right]^{2}}{\left[\left(4 I_{0}\right)^{1 / 2}-\left(4 I_{0}\right)^{1 / 2}\right]^{2}}=\infty\) (iii) (a) : When the screen is placed perpendicular to the line joining the 'sources, the fringes will be concentric circles. (iv) (b) : Constructive interference occurs when the path difference (S 1 P - S 2 P) is an integral multiple of \(\lambda\) .or S 1 P - S 2 P = n \(\lambda\) , where n = 0,1,2,3, ..... (v) (d) : Here, A 1 = 3A, A 2 = 2A and \(\varphi\) = 60° The resultant amplitude at a point is \(R =\sqrt{A_{1}^{2}+A_{2}^{2}+2 A_{1} A_{2} \cos \phi} \) \(=\sqrt{(3 A)^{2}+(2 A)^{2}+2 \times 3 A \times 2 A \times \cos 60^{\circ}} \) \(=\sqrt{9 A^{2}+4 A^{2}+6 A^{2}}=A \sqrt{19}\) As, Intensity \(\infty\) (Amplituder) 2 Therefore, intensity at the same point is \(I \propto 19 A^{2}\)
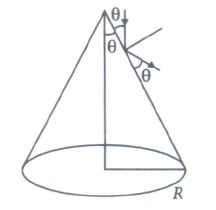
(i) (d) : Rutherford's atom had a positively charged centre and electrons were revolving outside it.It is also called the planetary model of the atom as in option (d). (ii) (d) : As the gold foil is very thin, it can be assumed that a-particles will suffer not more than one scattering during their passage through it. Therefore, computation of the trajectory of an a-particle scattered by a single nucleus is enough. (iii) (c) : Trajectory of a-particles depends on impact parameter which is the perpendicular distance of the initial velocity vector of the a particles from the centre of the nucleus. For small impact parameter a particle close to the nucleus suffers larger scattering. (iv) (b) : At minimum impact parameter, a particles rebound back ( \(\theta\) = \(\pi\) ) and suffers large scattering. (v) (d) : In case of head-on-collision, the impact parameter is minimum and the a-particle rebounds back. So, the fact that only a small fraction of the number of incident particles rebound back indicates that the number of a-particles undergoing head-on collision is small. This in turn implies that the mass of the atom is concentrated in a small volume. Hence, option (a) and (b) are correct.
(i) (d) : For Balmer series, n 1 = 2; n 2 = 3, 4, ... (lower) (higher) Therefore, in transition (VI), photon of Balmer series is absorbed. (ii) (c) : In transition II \(E_{2}=-3.4 \mathrm{eV}, E_{4}=-0.85 \mathrm{eV}\) \(\Delta E=2.55 \mathrm{eV} \Rightarrow \Delta E=\frac{h c}{\lambda} \Rightarrow \lambda=\frac{h c}{\Delta E}=487 \mathrm{nm}\) (iii) (d) : Wavelength of radiation = 1030 \(\dot A\) \(\Delta E=\frac{12400}{1030 \dot A}=12.0 \mathrm{eV}\) So, difference of energy should be 12.0 eV (approx.) Hence for n 1 = 1 to n 2 = 3. \(E_{n_{3}}-E_{n_{1}}=-1.51 \mathrm{eV}-(-13.6 \mathrm{eV}) \approx 12 \mathrm{eV}\) Therefore, transition V will occur. (iv) (a) : \(T^{2} \propto r^{3} \text { and } r \propto n^{2} \Rightarrow T^{2} \propto n^{6} \Rightarrow T \propto n^{3}\) \(\frac{T_{1}}{T_{2}}=\left(\frac{n_{1}}{n_{2}}\right)^{3} \Rightarrow 8=\left(\frac{n_{1}}{n_{2}}\right)^{3} \text { or } \frac{n_{1}}{n_{2}}=2\) (v) (b)
(i) (d) : All options are basic properties of nuclear forces. So, all options are correct. (ii) (d) : The nuclear force is of short range and the range of nuclear force is the order of 1.4 x 10 -15 m Now, volume \(\propto R^{3} \propto A\) (iii) (d) (iv) (a) : Nuclear force is much stronger than the electrostatic force inside the nucleus i.e., at distances of the order of fermi. At 40 \(\dot A\) , nuclear force is ineffective and only electrostatic force of repulsion is present.This is very high at this distance because nuclear force is not acting now and the gravitational force is very feeble.F nuclear << F electrostatiinc this case. (v) (a).
(i) (a) :The rms value of the output voltage at the load resistance \(V_{\mathrm{rms}}=\frac{V_{0}}{\sqrt{2}}\) (ii) (d) (iii) (a) (iv) (c) : The given circuit works as a half wave rectifier. In this circuit, we will get current through R when p-n junction is forward biased and no current when p-n junction is reverse biased. Thus the current (I) through resistor (R) will be shown in option (c). (v) (c)

Related 12th Standard CBSE Physics Materials
12th standard cbse syllabus & materials, 12th maths vector algebra chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths three dimensional geometry chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths probability chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths linear programming chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths differential equations chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths continuity and differentiability chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths application of integrals chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry the d and f block elements chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry haloalkanes and haloarenes chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry coordination compounds chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry chemical kinetics chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry biomolecules chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry amines chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th aldehydes ketones and carboxylic acids chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry alcohols phenols and ethers chapter case study question with answers cbse.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

12th Standard CBSE Study Materials

12th Standard CBSE Subjects


Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: Class 12 / 12 board
- Post comments: 0 Comments
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions Electromagnetic Induction to know their preparation level.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 12 Physics Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Electromagnetic Induction Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: Currents can be induced not only in conducting coils but also in conducting sheets or blocks. Current is induced in solid metallic masses when the magnetic flux threading through them changes. Such currents flow in the form of irregularly shaped loops throughout the body of the metal. These currents look like eddies or whirlpools in water so they are known as eddy currents. Eddy currents have both undesirable effects and practically useful applications. For example, it causes unnecessary heating and wastage of power in electric motors, dynamos, and in the cores of transformers. (I) The working of speedometers of trains is based on
| (a) wattless currents | (b) eddy currents |
| (c) alternating currents | (d) pulsating currents |
Answer: (b) eddy currents
(ii) Identify the wrong statement
| (a) Eddy currents are produced in a steady magnetic field |
| (b) Induction furnace uses eddy currents to produce heat. |
| (c) Eddy currents can be used to produce braking force in moving trains |
| (d) Power meters work on the principle of eddy currents. |
Answer: (a) Eddy currents are produced in a steady magnetic field
(iii) Which of the following is the best method to reduce eddy currents?
| (a) Laminating core | (b) Using thick wires |
| (c) By reducing hysteresis loss | (d) None of these |
Answer: (a) Laminating core
(iv) The direction of eddy currents is given by
| (a) Fleming’s left-hand rule | (b) Biot-Savart law |
| (c) Lenz’s law | (d) Ampere-circuital law |
Answer: (c) Lenz’s law
(v) Eddy currents can be used to heat localized tissues of the human body. This branch of medical therapy is called
| (a) Hyperthermia | (b) Diathermy |
| (c) Inductothermy | (d) none of these |
Answer: (c) Inductothermy
Case Study 2: Self Induction. When a current I flows through a coil, the flux linked with it is φ = LI, where L is a constant known as the self-inductance of the coil.

Any change in current sets up an induced emf in the coil. Thus, the self-inductance of a coil is the induced emf set up in it when the current passing through it changes at the unit rate. It is a measure of the opposition to the growth of the decay of current flowing through the coil. Also, the value of self-inductance depends on the number of turns in the solenoid, its area of cross-section, and the permeability of its core material.
(i) The inductance in a coil plays the same role as (a) inertia in mechanics (b) energy in mechanics (c) momentum in mechanics (d) force in mechanics
Answer: (a) inertia in mechanics
(ii) A current of 2.5 A flows through a coil of inductance 5 H. The magnetic flux linked with the coil is (a) 0.5 Wb (b) 12.5 Wb (c) zero (d) 2 Wb
Answer: (b) 12.5 Wb
The inductance L of a solenoid depends upon its radius R as (a) L ∝ R (b) L ∝ 1/R (c) L ∝ R 2 (d) L ∝ R 3
Answer: (c) L ∝ R2
(iv) The unit of self-inductance is
(a) Weber ampere (b) Weber -1 ampere (c) Ohm second (d) Farad
Answer: (c) Ohm second
(v) The induced emf in a coil of 10 henry inductance in which current varies from 9 A to 4 A in 0.2 second is (a) 200 V (b) 250 V (c) 300 V (d) 350 V
Answer: (b) 250 V
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 13 Physics Electromagnetic Induction Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate

You Might Also Like
Mcq class 12 english the enemy questions with answers english chapter 4, poets and pancakes summary class 12 english pdf, class 12 maths: case study of chapter 11 three dimensional geometry pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

The Topper Combo Flashcards
- Contains the Latest NCERT in just 350 flashcards.
- Colourful and Interactive
- Summarised Important reactions according to the latest PYQs of NEET(UG) and JEE
No thanks, I’m not interested!
CBSE Expert
Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Case Study Question Nuclei PDF Download
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Nuclei to know their preparation level.

In CBSE Class 12 Physics Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Nuclei Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
The nucleus was first discovered in 1911 by Lord Rutherford and his associates by experiments on the scattering of a-particles by atoms. He found that the scattering results could be explained if atoms consist of a small, central, massive, and positive core surrounded by orbiting electrons. The experimental results indicated that the size of the nucleus is of the order of 10–14 m and is thus 10000 times smaller than the size of an atom.
The ratio of the mass of the nucleus with a mass of an atom is approximately (a) 1 (b) 10 (c) 10 3 (d) 10 10
Answer: (a) 1
Masses of nuclei of hydrogen, deuterium and tritium are in ratio (a) 1 : 2 : 3 (b) 1 : 1 : 1 (c) 1 : 1 : 2 (d) 1 : 2 : 4
Answer: (a) 1 : 2 : 3
Nuclides with the same neutron number but different atomic numbers is (a) isobars (b) isotopes (c) isotones (d) none of these
Answer: (c) isotones
If R is the radius and A is the mass number, then log R versus log A graph will be (a) a straight line (b) a parabola (c) an ellipse (d) None of these
Answer: (a) a straight line
The ratio of the nuclear radii of the mercury isotope 198 80 Hg and silver isotope 107 47 Ag is (a) 1.23 (b) 0.216 (c) 2.13 (d) 3.46
Answer: (a) 1.23
In the year 1939, German scientist Otto Hahn and Strassmann discovered that when an uranium isotope was bombarded with a neutron, it breaks into two intermediate mass fragments. It was observed that, the sum of the masses of new fragments formed were less than the mass of the original nuclei. This difference in the mass appeared as the energy released in the process. Thus, the phenomenon of splitting of a heavy nucleus (usually A > 230) into two or more lighter nuclei by the bombardment of proton, neutron, a-particle, etc with liberation of energy is called nuclear fission.
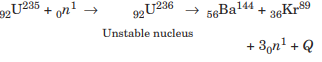
Nuclear fission can be explained on the basis of (a) Millikan’s oil drop method (b) Liquid drop model (c) Shell model (d) Bohr’s model
Answer: (b) Liquid drop model
For sustaining the nuclear fission chain reaction in a sample (of small size) of 235 92 U, it is desirable to slow down fast neutrons by (a) friction (b) elastic damping/scattering (c) absorption (d) cooling
Answer: (b) elastic damping/scattering
On average, the number of neutrons and the energy of a neutron released per fission of a uranium atom are respectively (a) 2.5 and 2 keV (b) 3 and 1 keV (c) 2.5 and 2 MeV (d) 2 and 2 keV
Answer: (c) 2.5 and 2 MeV
In any fission process, the ratio of the mass of the daughter nucleus to the mass of the parent nucleus is (a) less than 1 (b) greater than 1 (c) equal to 1 (d) depends on the mass of parent nucleus
Answer: (a) less than 1
Neutrons and protons are identical particles in the sense that their masses are nearly the same and the force, called nuclear force, does distinguish them. The nuclear force is the strongest force. The stability of the nucleus is determined by the neutron proton ratio mass defect or packing fraction. The shape of the nucleus is calculated by quadrupole moment and the spin of the nucleus depends on even or odd mass numbers. The volume of the nucleus depends on the mass number. The whole mass of the atom (nearly 99%) is centered at the nucleus
The correct statements about the nuclear force is/are (a) charge independent (b) short range force (c) non-conservative force (d) all of these
Answer: (d) all of these
A force between two protons is the same as the force between proton and neutron. The nature of the force is
(a) electrical force (b) weak nuclear force (c) gravitational force (d) strong nuclear force
Answer: (d) strong nuclear force
All the nucleons in an atom are held by (a) nuclear forces (b) Van der Waal’s forces (c) tensor forces (d) coulomb forces
Answer: (a) nuclear forces
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 13 Physics Nuclei Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
CBSE Class 12th - PHYSICS : Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
CBSE will ask two Case Study Questions in the CBSE class 12 Physics questions paper. Question numbers 15 and 16 are cased-based questions where 5 MCQs will be asked based on a paragraph. Each theme will have five questions and students will have a choice to attempt any four of them.
| 1. Electric Charges and Fields | |
| 2. Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance | |
| 3. Current Electricity | |
| 4. Moving Charges And Magnetism | |
| 5. Magnetism And Matter | |
| 6. Electromagnetic Induction | |
| 7. Alternating Current | |
| 8. Electromagnetic Waves | |
| 9. Ray Optics & Optical Instruments | |
| 10. Wave Optics | |
| 11. Dual Nature Radiation & Matter | |
| 12. Atoms | |
| 13. Nuclei | |
| 14. Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices & Simple Circuits |

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- CBSE Class 12 Compartment Results 2024 Released, Pass Percentage at 29.78% - Direct Link Here 2 August, 2024, 5:40 pm
- CBSE 12th Exam 2024-25 : Mathematics (Volume-2) Official Competency Focused Practice Questions released by CBSE 1 August, 2024, 5:46 pm
- CBSE 12th Exam 2024-25 : English (Volume-2) Official Competency Focused Practice Questions released by CBSE 1 August, 2024, 5:22 pm
- Education Budget 2024 : Major Education, Jobs, Women's Schemes and Upskilling Budget Highlights 24 July, 2024, 1:50 pm
- CBSE Class 12 Second Board Exam Set for June; Under Government Consideration 17 July, 2024, 11:21 am
- NIOS Class 12 Result 2024 Declared at results.nios.ac.in: Check Passing Marks and Details 22 June, 2024, 11:02 am
- Unlock Success After Class 12: Learn These 10 Essential Skills 15 June, 2024, 5:54 pm
- CBSE 12th 2024-25 : Physics Official Competency Focused Practice Questions released by CBSE 28 May, 2024, 4:12 pm
- CBSE 12th 2024-25 : Chemistry Official Competency Focused Practice Questions released by CBSE 28 May, 2024, 4:12 pm

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei
- Last modified on: 2 years ago
- Reading Time: 4 Minutes

Case Study Question 1:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Neutrons and protons are identical particle in the sense that their masses are nearly the same and the force, called nuclear force, does into distinguish them. Nuclear force is the strongest force. Stability of nucleus is determined by the neutron proton ratio or mass defect or packing fraction. Shape of nucleus is calculated by quadrupole moment and spin of nucleus depends on even and odd mass number. Volume of nucleus depends on the mass number. Whole mass of the atom (nearly 99%) is centred at the nucleus.
(i) The correct statements about the nuclear force is/are (a) charge independent (b) short range force (c) non-conservative force (d) all of these.
(ii) The range of nuclear force is the order of (a) 2 x 10 -10 m (b) 1.5 x 10 -20 m (c) 1.2 x 10 -4 m (d) 1.4 x 10 -15 m
(iii) A force between two protons is same as the force between proton and neutron. The nature of the force is (a) electrical force (b) weak nuclear force (c) gravitational force (d) strong nuclear force
(iv) two protons are kept at a separation of 40 A 0 . F n is the nuclear force and F e is the electrostatic force between them. Then (a) F n <<F e (b) F n = F e (c) F n >> F e (d) F n ≈ F e
(v) All the nucleons in an atom are held by (a) nuclear forces (b) vander waal’s forces (c) tensor forces (d) coulomb forces
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
3 thoughts on “ Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei ”
plz give ANSWER THIS QUESTIONS
Answers uploaded.
could you send me class xi case study based questions and answers
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

COMMENTS
Physics Case Study for Class 12: Here, you will get class 12 case study questions and answers for Physics pdf at free of cost. Along with you can also download Physics case study questions for class 12 chapter wise for getting higher marks in board exams.
CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) is a renowned educational board in India that designs the curriculum for Class 12 Physics with the goal of promoting a scientific temperament and nurturing critical thinking among students. As part of their Physics examination, CBSE includes case study questions to assess students' ability to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios ...
CBSE Class 12 Physics Case Study Download PDF CBSE Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions will help students this year to score good marks. Because such types of problems are a bit easier compared to other types of questions. Also, Class 12th Physics is a bit complex so having case-based problems, assertion and reason and Multiple Choice Questions will give a huge relief to the students ...
Physics is more than just formulas and equations, right? It's a way to interpret the natural world, and case studies provide a perfect opportunity for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations. So, what's the importance of case studies in class 12 Physics?
Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physics. Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields. Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance. Chapter 3: Current Electricity. Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism. Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter. Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction. Chapter 7: Alternating Current. Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves.
CBSE will ask two Case Study Questions in CBSE class 12 Physics questions paper. The question number 15 and 16 are cased based questions.
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 ...
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern.
Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 8 Electromagnetic Waves. December 24, 2021 Physics Gurukul 1 Comment.
CBSE 12th Standard Physics Subject Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Part - II. QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams.
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 ...
Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Semiconductor Alternating Current Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Case Study Question Alternating Current to know their preparation level. Download Books for Boards.
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern.
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern.
Case Study Question for Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 Current Electricity Case Study Question 1: Whenever an electric current is passed through a conductor, it becomes hot after some time. The phenomenon of the production of heat in a resistor by the flow of an electric current through it is called heating effect of current or Joule heating.
The PDF file of the Electric Charges and Fields Case Study for Class 12 Physics with Solutions is a very important study resource that can help students better prepare for the exam and boost conceptual learning. The solutions are in the hint manner as well as contain full examples too, refer to the link to access the Case Study on Electric ...
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern.
Case Study Question for Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields There is Case Study Questions in class 12 Physics in session 2020-21. The first two questions in the board exam question paper will be based on Case Study and Assertion & Reason. Case Study Questions will have 5 MCQs out of which students will have to attempt any 4 questions. Here are the questions based on case study.
Case Study Question for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current. Question 1: Read the para given below and answer the questions that follow: Resonant Series LCR Circuit. When the frequency of ac supply is such that the inductive reactance and capacitive reactance become equal, the impedance of the series LCR circuit is equal to the ohmic ...
CBSE Case Study Class 12: Here, you will get class 12 case study questions and answers for maths, physics, chemistry and biology pdf at free of cost. Along with you can also download case study questions for class 12 chapter wise for getting higher marks in board exams.
CBSE Class 12th - PHYSICS : Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution CBSE will ask two Case Study Questions in the CBSE class 12 Physics questions paper. Question numbers 15 and 16 are cased-based questions where 5 MCQs will be asked based on a paragraph. Each theme will have five questions and students will have a choice to attempt any four of them.
Case Study Question 1: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Neutrons and protons are identical particle in the sense that their masses are nearly the same and the force, called nuclear force, does into distinguish them. Nuclear force is the strongest force. Stability of nucleus is determined by the neutron proton … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class ...